Crustacean Protein Kinases A and C: Bioinformatic Characterization in Decapods and Other Non-Model Organisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
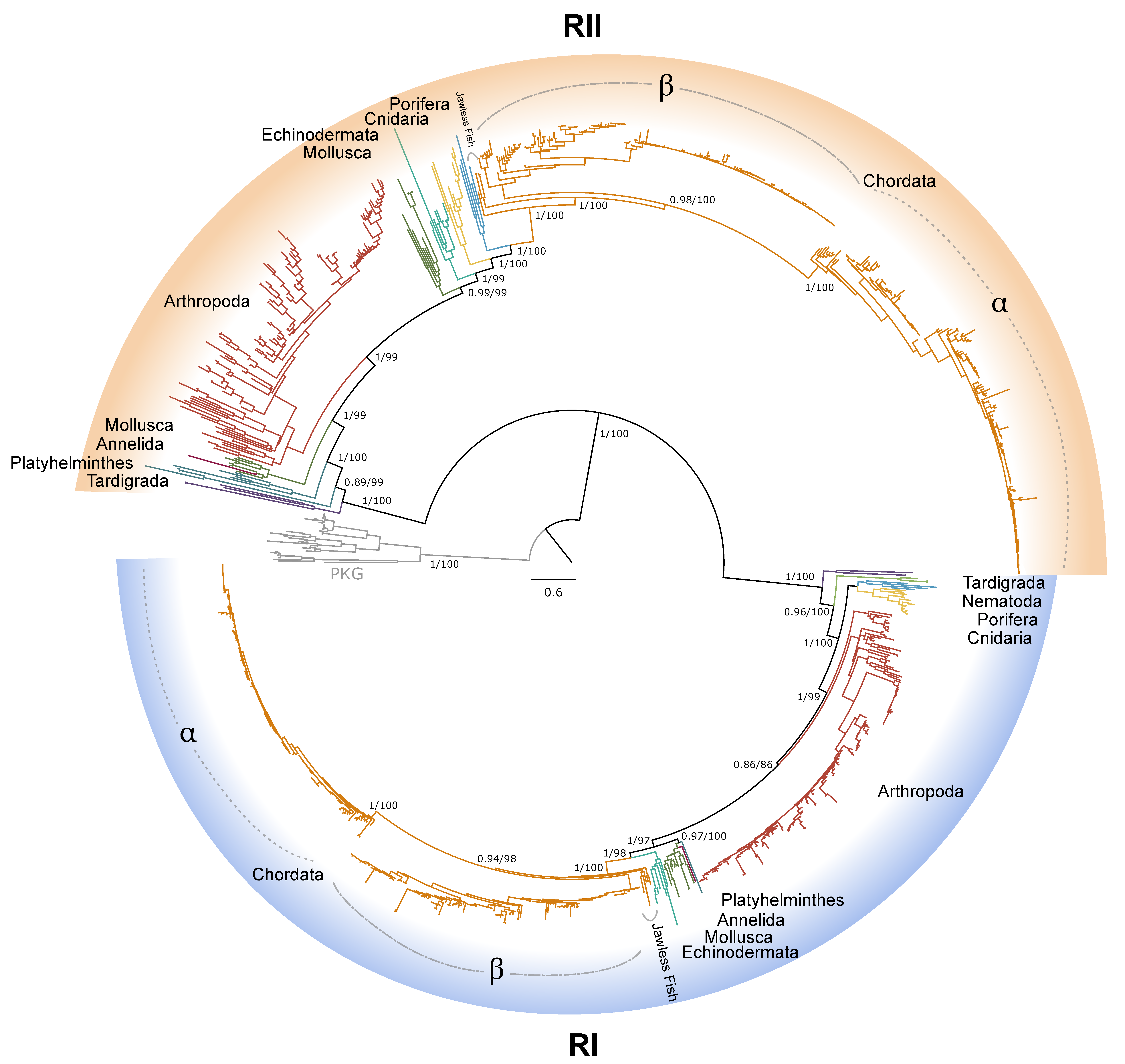
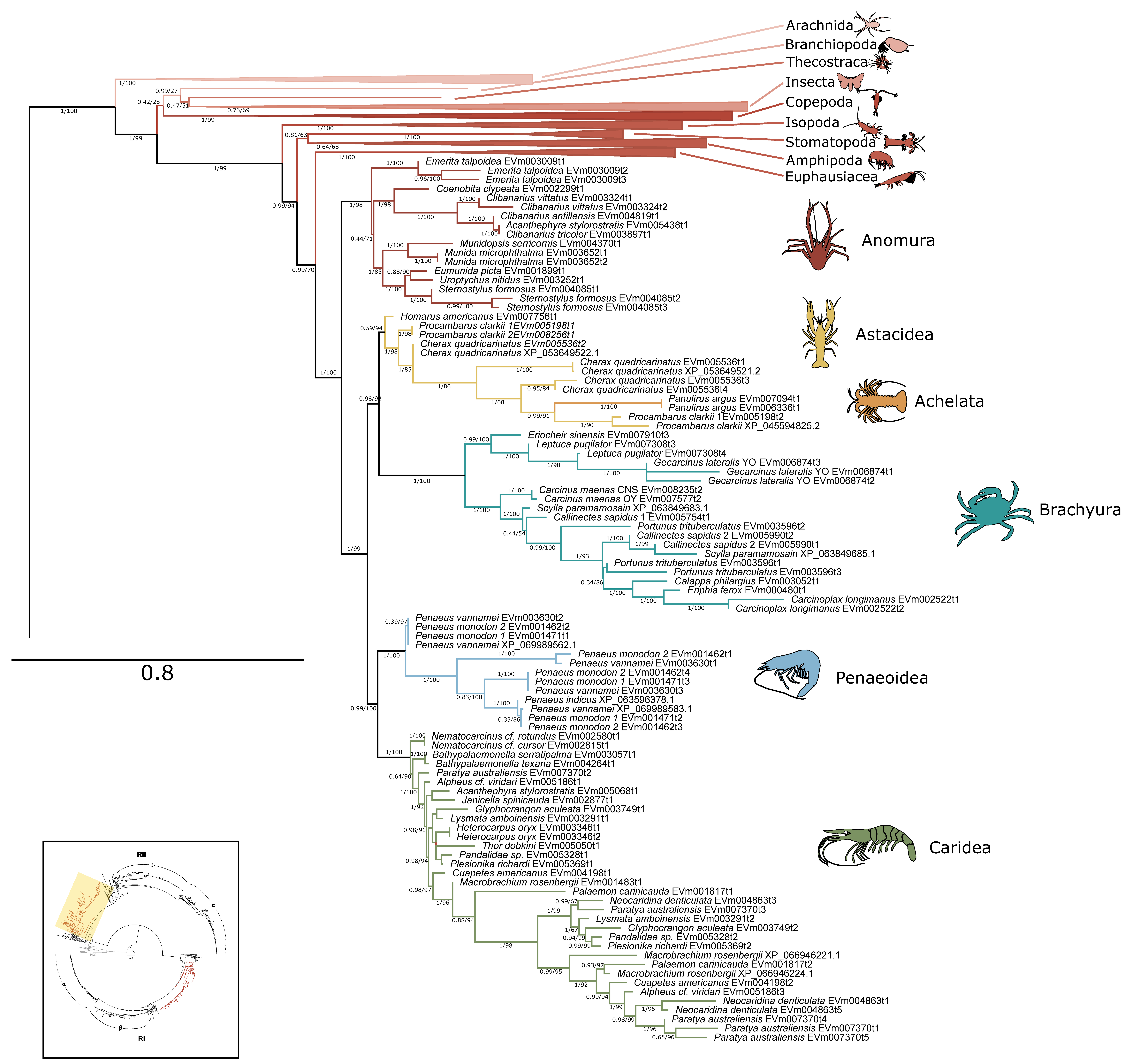
2. Results
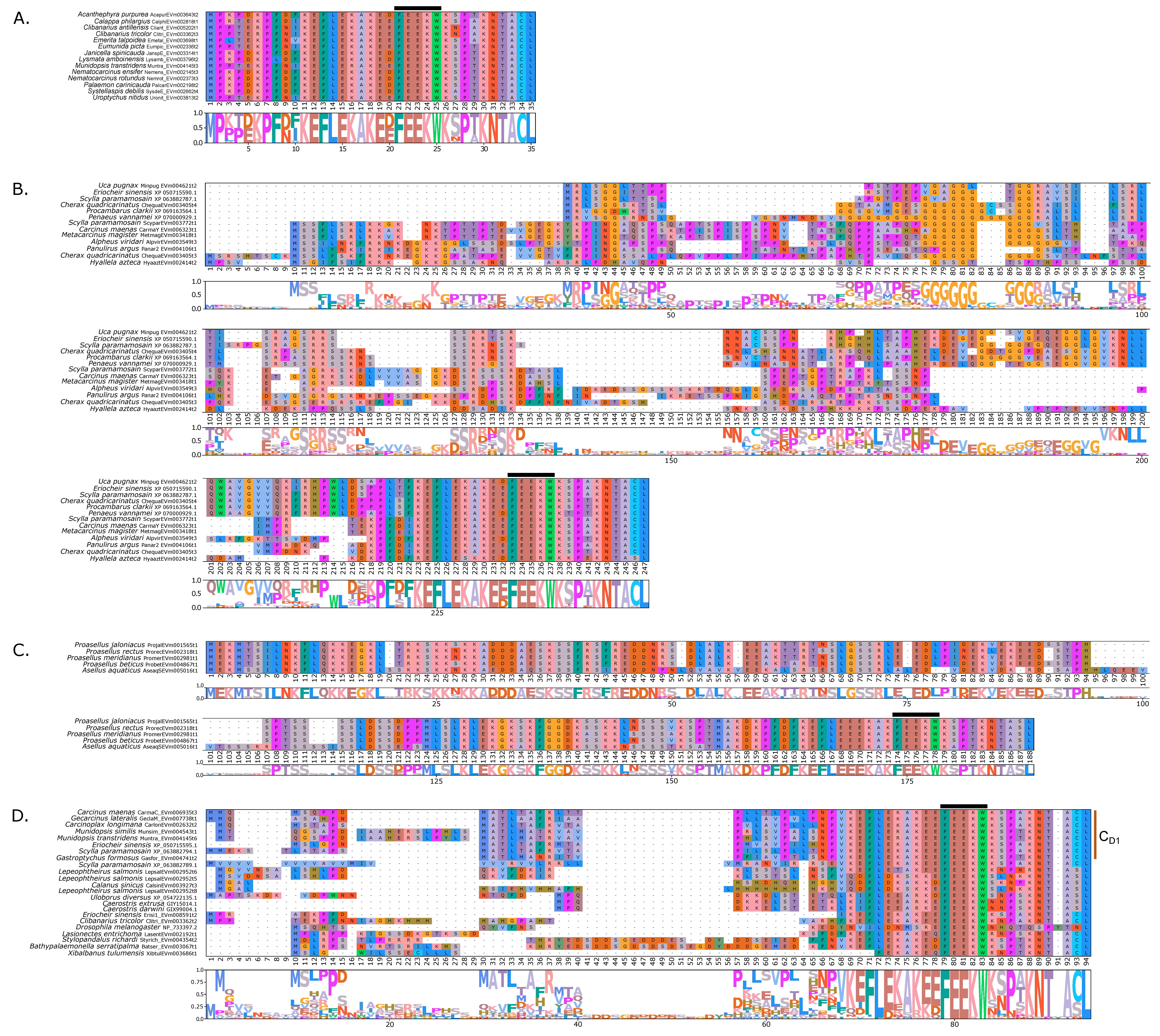
2.1. PKA Catalytic Subunit
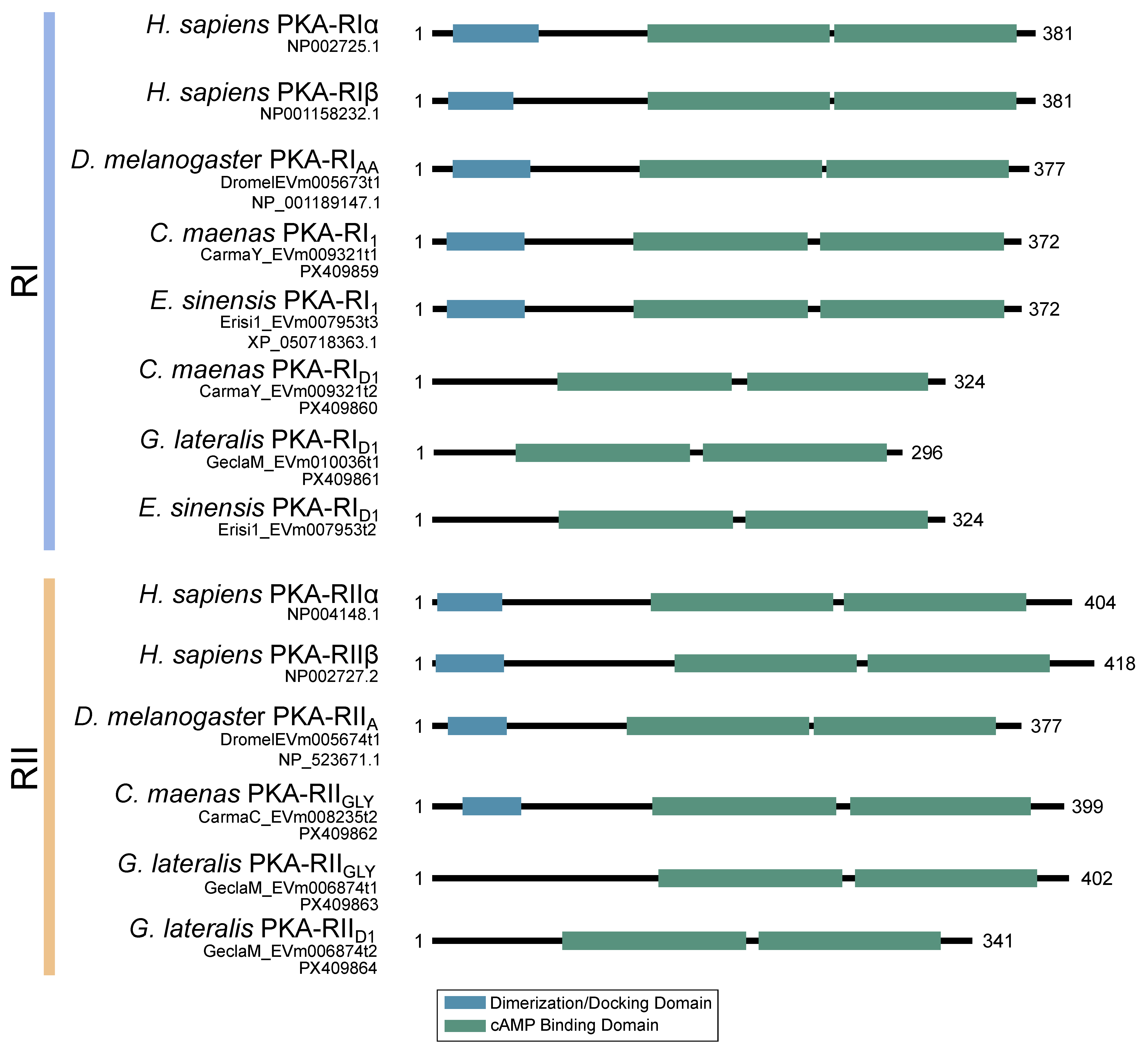
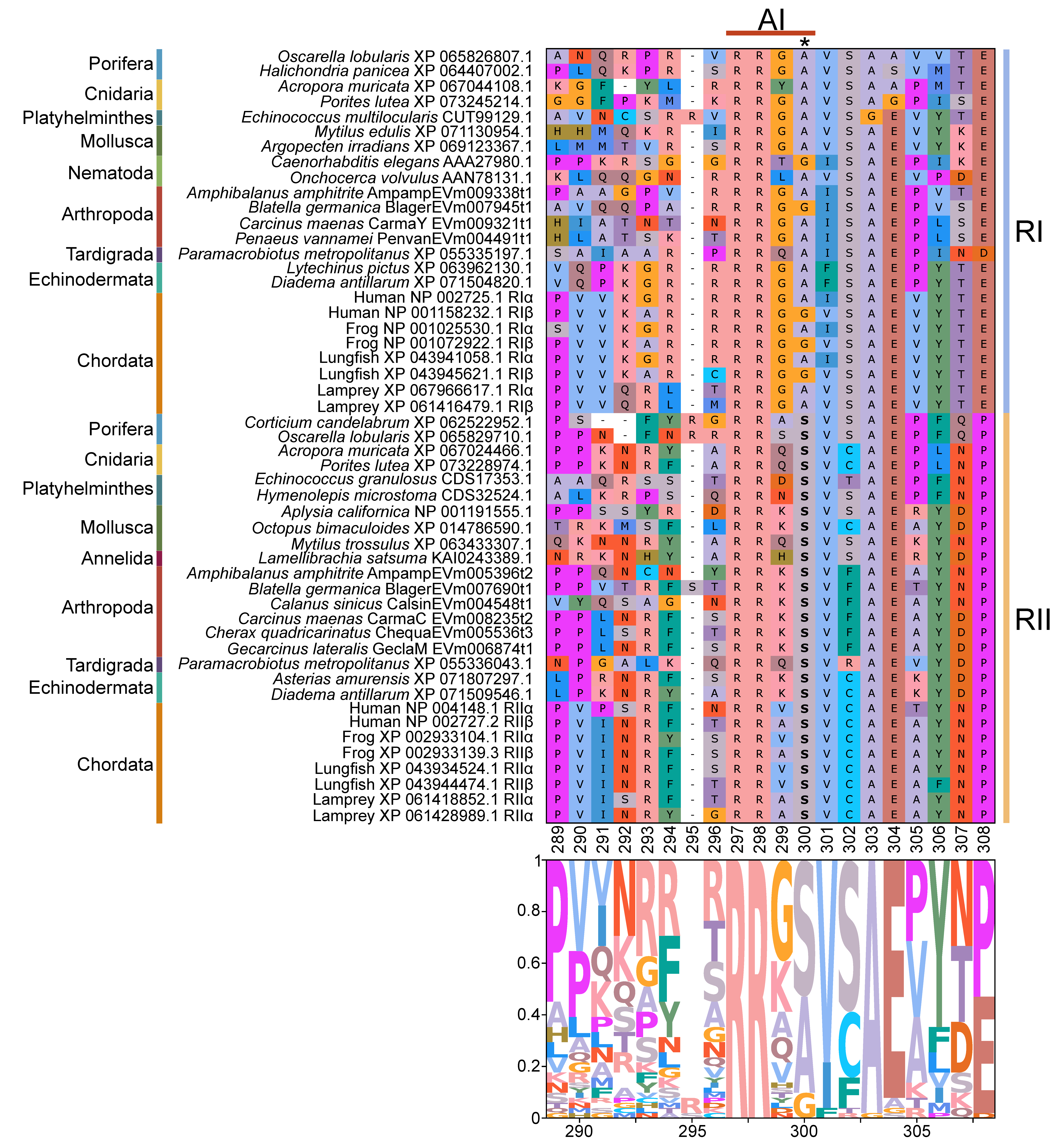
2.2. PKA Regulatory Subunit
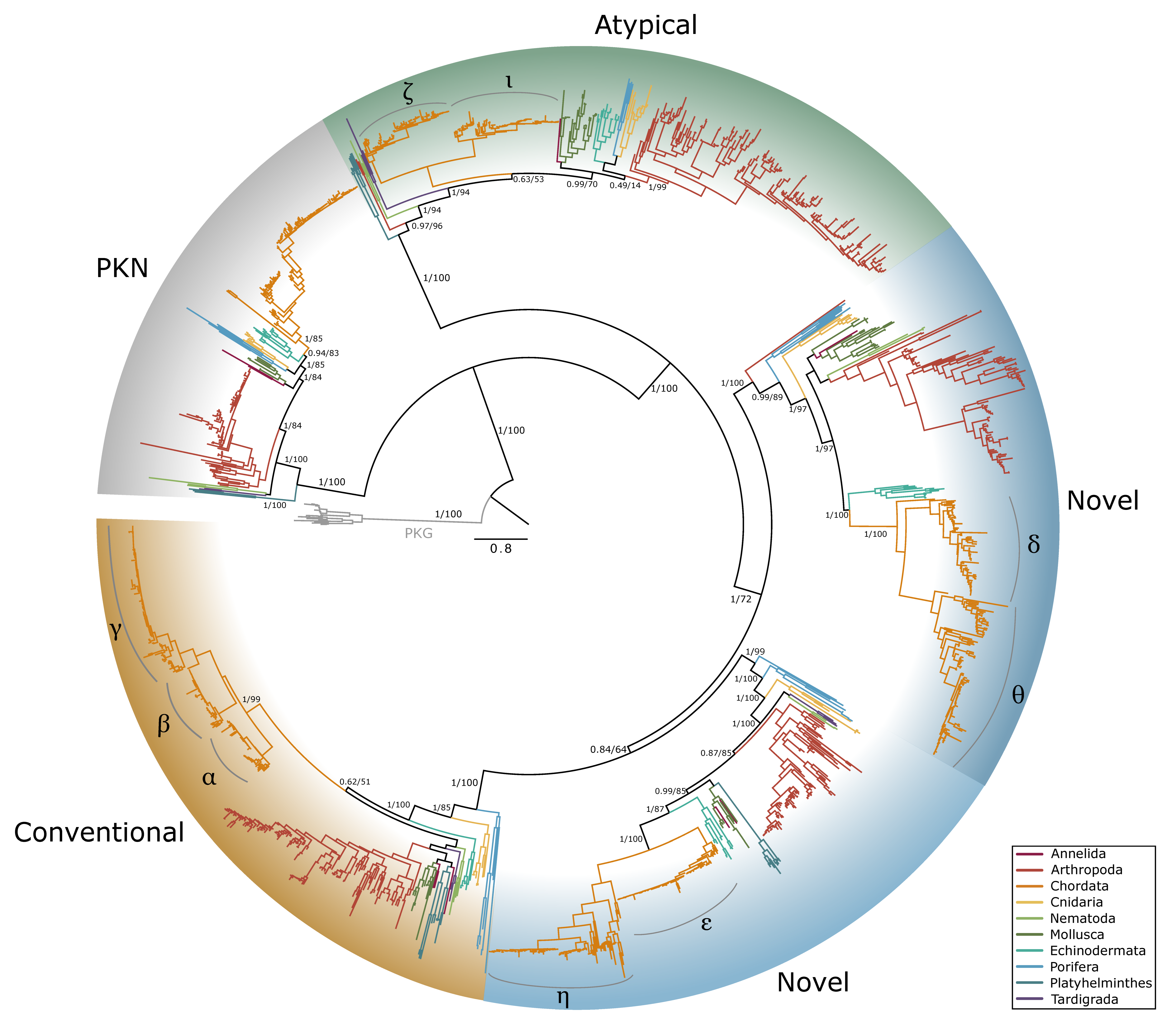
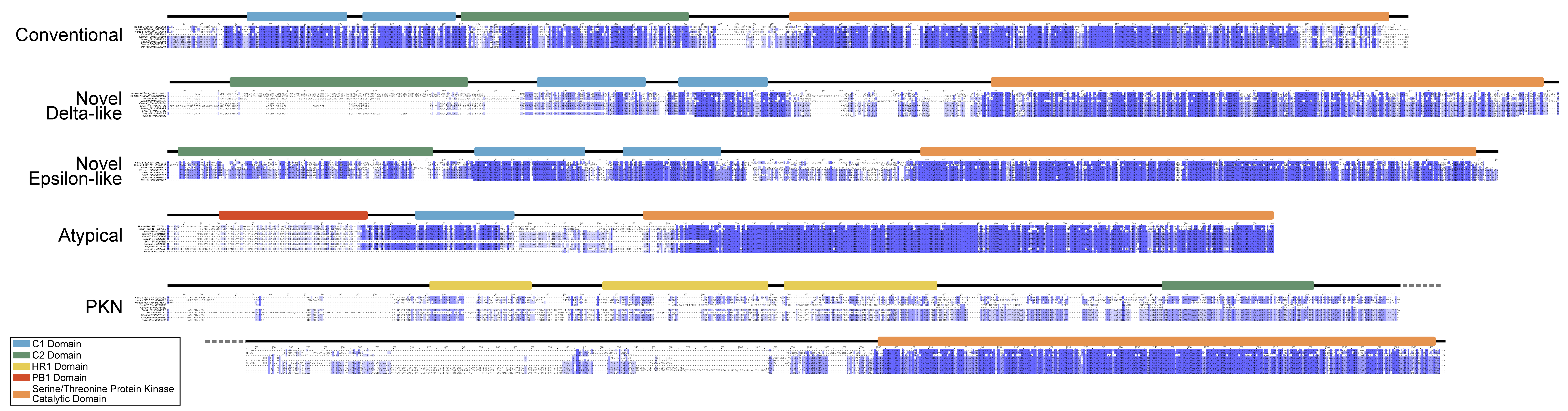
2.3. PKC Sequences
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.2. Multiple Sequence Alignments
4.3. Identity and Similarity Calculations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pearce, L.R.; Komander, D.; Alessi, D.R. The nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, A.E.; Schulze, J.O.; Biondi, R.M. AGC Kinases, mechanisms of regulation and innovative drug development. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 48, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenegger, D.; Parvez, K.; Lukowiak, K. Enhancing memory formation by altering protein phosphorylation balance. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2008, 90, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.S.; Søberg, K.; Kobori, E.; Wu, J.; Pautz, S.; Herberg, F.; Skålhegg, B. The tails of PKA. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 101, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.H.; Corbin, J.D. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. In Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Lennarz, W.J., Lane, M.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 574–579. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.S.; Buechler, J.A.; Yonemoto, W. cAMP-dependent protein kinase: Framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1990, 59, 971–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knighton, D.R.; Zheng, J.H.; Ten Eyck, L.F.; Ashford, V.A.; Xuong, N.H.; Taylor, S.S.; Sowadski, J.M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science 1991, 253, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedioune, I.; Gandon-Renard, M.; Dessillons, M.; Barthou, A.; Varin, A.; Mika, D.; Bichali, S.; Cellier, J.; Lechène, P.; Karam, S.; et al. Essential Role of the RIα Subunit of cAMP-Dependent Protein Kinase in Regulating Cardiac Contractility and Heart Failure Development. Circulation 2024, 150, 2031–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, J.I.; Cleveland, K.H.; Kang, M.; Odle, B.J.; Forbush, K.A.; Scott, J.D. The evolution of AKAPs and emergence of PKA isotype selective anchoring determinants. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskén, K.; Aandahl, E.M. Localized effects of cAMP mediated by distinct routes of protein kinase A. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 137–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.S.; Wu, J.; Bruystens, J.G.H.; Del Rio, J.C.; Lu, T.-W.; Kornev, A.P.; Ten Eyck, L.F. From structure to the dynamic regulation of a molecular switch: A journey over 3 decades. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.S.; Zhang, P.; Steichen, J.M.; Keshwani, M.M.; Kornev, A.P. PKA: Lessons learned after twenty years. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baro Graf, C.; Ritagliati, C.; Stival, C.; Luque, G.M.; Gentile, I.; Buffone, M.G.; Krapf, D. Everything you ever wanted to know about PKA regulation and its involvement in mammalian sperm capacitation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 518, 110992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Aye, T.T.; Snel, B.; van Breukelen, B.; Scholten, A.; Heck, A.J.R. Spatial organization in protein kinase A signaling emerged at the base of animal evolution. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2976–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccolo, M.; Zerio, A.; Lobo, M.J. Subcellular organization of the cAMP signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 278–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isensee, J.; Kaufholz, M.; Knape, M.J.; Hasenauer, J.; Hammerich, H.; Gonczarowska-Jorge, H.; Zahedi, R.P.; Schwede, F.; Herberg, F.W.; Hucho, T. PKA-RII subunit phosphorylation precedes activation by cAMP and regulates activity termination. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2167–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Concejo, A.; Larhammar, D. Protein kinase C family evolution in jawed vertebrates. Dev. Biol. 2021, 479, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.M.; Burns, D.J. Lipid activation of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 4661–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Kazanietz, M.G.; Blumberg, P.M.; Hurley, J.H. Crystal structure of the cys2 activator-binding domain of protein kinase C delta in complex with phorbol ester. Cell 1995, 81, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.C. Protein kinase C: Structure, function, and regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28495–28498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyland, M.E. Protein kinase C isoforms: Multi-functional regulators of cell life and death. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 2386–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, S.F. Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1341–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, Y.; Yoshinaga, S.; Takeya, R.; Suzuki, N.N.; Horiuchi, M.; Kohjima, M.; Sumimoto, H.; Inagaki, F. Structure of a cell polarityregulator, a complex between atypical PKC and Par6 PB1 domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9653–9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.G.; Tan, B.J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Armstrong, J.S.; Li, Q.T.; Dong, Q.; Chan, E.; Smith, D.; Verma, C.; et al. The very C-terminus of PRK1/PKN is essential for its activation by RhoA and downstream signaling. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maesaki, R.; Ihara, K.; Shimizu, T.; Kuroda, S.; Kaibuchi, K.; Hakoshima, T. The structural basis of Rho effector recognition revealed by the crystal structure of human RhoA complexed with the effector domain of PKN/PRK1. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.H.; Ridden, J.; Parker, P.J. Cloning and expression patterns of two members of a novel protein-kinase-C-related kinase family. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 227, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehsenfeld, S. Endocrinology. In Ecophysiology of the European Crab Crab (Carcinus maenas) and Related Species: Mechanisms Behind the Success of a Global Invader; Weihrauch, D., Mcgaw, I.J., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2024; pp. 159–179. [Google Scholar]
- Mykles, D.L.; Musgrove, L.; Ventura, T. Crustacean endocrinology. In Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science, 2nd ed.; Atkinson, P.W., Yamanaka, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Mykles, D.L. Signaling pathways that regulate the crustacean molting gland. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 113658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, S.G. Endocrinology of metabolism and water balance: Crustacean hyperglycemic hormone. In The Natural History of the Crustacea: Physiology; Chang, E.S., Thiel, M., Eds.; Oxford Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; Volume 4, pp. 36–67. [Google Scholar]
- Head, T.B.; Pérez-Moreno, J.L.; Ventura, T.; Durica, D.S.; Mykles, D.L. Two cGMP-dependent protein kinases have opposing effects on molt-inhibiting hormone regulation of Y-organ ecdysteroidogenesis. J. Exp. Biol. 2025, 228, JEB249739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaziani, E.; Mattson, M.P.; Wang, W.N.L.; McDougall, H.E. Signaling pathways for ecdysteroid hormone synthesis in crustacean Y-organs. Am. Zool. 1999, 39, 496–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Li, J.; Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Qin, C.; Li, E.; Qin, J.; Chen, L. The regulatory effects of arginine on ovary development in the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Aquacult. Rep. 2024, 37, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Toullec, J.-Y.; Lee, C.-Y. The crustacean hyperglycemic hormone superfamily: Progress made in the past decade. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 578958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.S.; Zmora, N.; Katayama, H.; Tsutsui, N. Crustacean hyperglycemic hormone (CHH) neuropeptidesfamily: Functions, titer, and binding to target tissues. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 166, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasankar, V.; Tomy, S.; Wilder, M.N. Insights on molecular mechanisms of ovarian development in decapod crustacea: Focus on vitellogenesis-stimulating factors and pathways. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 577925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.; Plowman, G.D.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. Evolution of protein kinase signaling from yeast to man. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Moreno, J.L.; Kozma, M.T.; DeLeo, D.M.; Bracken-Grisson, H.D.; Durica, D.S.; Mykles, D.L. CrusTome: A transcriptome database resource for large-scale analyses across Crustacea. G3-Genes Genomes Genet. 2023, 13, jkad098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søberg, K.; Jahnsen, T.; Rognes, T.; Skålhegg, B.S.; Laerdahl, J.K. Evolutionary paths of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) catalytic subunits. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søberg, K.; Moen, L.; Skålhegg, B.; Laerdahl, J. Evolution of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) catalytic subunit isoforms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.F.K.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature Meth. 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, H.R.; Zheng, N.; Scott, J.D. Beyond PKA: Evolutionary and structural insights that define a docking and dimerization domain superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, T.; Nguyen, P.V. Regulation of hippocampus-dependent memory by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. In Progress in Brain Research; Sossin, W.S., Lacaille, J.-C., Castellucci, V.F., Belleville, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 169, pp. 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- Uhler, M.D.; Chrivia, J.C.; McKnight, G.S. Evidence for a second isoform of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 15360–15363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigil, D.; Blumenthal, D.K.; Heller, W.T.; Brown, S.; Canaves, J.M.; Taylor, S.S.; Trewhella, J. Conformational differences among solution structures of the type Iα, IIα and IIβ protein kinase A regulatory subunit homodimers: Role of the linker regions. J. Molec. Biol. 2004, 337, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beushausen, S.; Bayley, H. A relative of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in Aplysia spermatozoa. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 6775–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beushausen, S.; Lee, E.; Walker, B.; Bayley, H. Catalytic subunits of Aplysia neuronal cAMP-dependent protein kinase with two different N termini. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1641–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L.; Cherry, J.; Dauwalder, B.; Han, P.L.; Skoulakis, E. The cyclic AMP system and Drosophila learning. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1995, 149, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, E.; Capuzzo, A. Cyclic AMP signaling in bivalve molluscs: An overview. J. Exp. Zool. 2010, 313A, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, S.F.; Del Vecchio, M.; Velinzon, K.; Hogel, C.; Russell, S.R.; Tully, T.; Kaiser, K. Defective learning in mutants of the Drosophila gene for a regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 8817–8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalderon, D.; Rubin, G.M. Isolation and characterization of Drosophila cAMP-dependent protein kinase genes. Genes Dev. 1988, 2, 1539–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaves, J.M.; Taylor, S.S. Classification and Phylogenetic Analysis of the cAMP-Dependent Protein Kinase Regulatory Subunit Family. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, B.D.; Sahley, C.L. Learning in simple systems. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradham, C.A.; Foltz, K.R.; Beane, W.S.; Arnone, M.I.; Rizzo, F.; Coffman, J.A.; Mushegian, A.; Goel, M.; Morales, J.; Geneviere, A.-M.; et al. The sea urchin kinome: A first look. Dev. Biol. 2006, 300, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhardt, D.; Kühn, C.; Leboulle, G. The PKA-CREB system encoded by the honeybee genome. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; LaFourcade, C.; Maldonado, H.; Romano, A. Characterisation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase isoforms in the brain of the crab Chasmagnathus. J. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 171, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Souvorov, A.; Murphy, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Kitts, P. Eukaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline. In The NCBI Handbook; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, W.H.; Qin, M.; Zhong, H. Myristoylation alone is sufficient for PKA catalytic subunits to associate with the plasma membrane to regulate neuronal functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021658118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veron, M.; Radzio-Andzelm, E.; Tsigelny, I.; Ten Eyck, L.F.; Taylor, S.S. A conserved helix motif complements the protein kinase core. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10618–10622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, T.; Cameron, S.; Sass, P.; Zoller, M.; Scott, J.D.; McMullen, B.; Hurwitz, M.; Krebs, E.G.; Wigler, M. Cloning and characterization of BCY1, a locus encoding a regulatory subunit of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1987, 7, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeberg, L.K.; Scott, J.D. Signalling scaffolds and local organization of cellular behaviour. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søberg, K.; Skålhegg, B.S. Themolecular basis for specificity at the level of the protein kinase A catalytic subunit. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.R.; Nicodemus-Johnson, J.; Carnegie, G.K.; Danziger, R.S. Molecular evolution of a-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP)-7: Implications in comparative PKA compartmentalization. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steichen, J.M.; Kuchinskas, M.; Keshwani, M.M.; Yang, J.; Adams, J.A.; Taylor, S.S. Structural basis for the regulation of protein kinase A by activation loop phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 14672–14680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Knape, M.J.; Ahuja, L.G.; Keshwani, M.M.; King, C.C.; Sastri, M.; Herberg, F.W.; Taylor, S.S. Single turnover autophosphorylation cycle of the PKA RIIβ holoenzyme. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Molec. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A.; et al. The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D384–D388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, K.A.; Pérez-Moreno, J.L.; Durica, D.S.; Mykles, D.L. Phylogenetic and transcriptomic characterization of insulin and growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases in crustaceans. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1379231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozewicki, J.; Li, S.L.; Amada, K.M.; Standley, D.M.; Katoh, K. MAFFT-DASH: Integrated protein sequence and structural alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W5–W10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenwyk, J.L.; Buida III, T.J.; Li, Y.; Shen, X.; Rokas, A. ClipKIT: A multiple sequence alignment trimming software for accurate phylogenomic inference. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3001007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximations for phylogenetic bootstrap. Molec. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeslee, A.M.H.; Keogh, C.L.; Fowler, A.E.; Griffen, B.D. Assessing the effects of trematode Infection on invasive green crabs in eastern North America. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Plaksina, M.P.; Dvoretsky, V.G. First record of nematode larvae in the amphipod Ischyrocerus commensalis colonizing red king crabs in the Barents Sea. Diversity 2023, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, J.D. Parasites of crustaceans. In Invertebrate Pathology; Rowley, A.F., Coates, C.J., Whitten, M.M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 458–502. [Google Scholar]
- Anisimova, M.; Gil, M.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Dessimoz, C.; Gascuel, O. Survey of branch support methods demonstrates accuracy, power, and robustness of fast likelihood-based approximation schemes. Syst. Biol. 2011, 60, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, M.T.; Pérez-Moreno, J.L.; Gandhi, N.S.; Hernandez Jeppesen, L.; Durica, D.S.; Ventura, T.; Mykles, D.L. In silico analysis of crustacean hyperglycemic hormone family G protein-coupled receptor candidates. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1322800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P. The sequence manipulation suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. Biotechniques 2000, 28, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalefski, E.A.; Falke, J.J. The C2 domain calcium-binding motif: Structural and functional diversity. J. Prot. Sci. 1996, 5, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, K.J.; Storey, K.B. Protein kinase and phosphatase responses to anoxia in crayfish, Orconectes virilis: Purification and characterization of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2001, 130B, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covi, J.A.; Chang, E.S.; Mykles, D.L. Conserved role of cyclic nucleotides in the regulation of ecdysteroidogenesis by the crustacean molting gland. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 152A, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Spaziani, E. Cyclic AMP mediates the negative regulation of Y-organ ecdysteroid production. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1985, 42, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Spaziani, E. Regulation of Y-organ ecdysteroidogenesis by molt-inhibiting hormone in crabs: Involvement of cyclic AMP-mediated protein synthesis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1986, 63, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Spaziani, E. Regulation of crab Y-organ steroidogenesis in vitro: Evidence that ecdysteroid production increases through activation of cAMP-phosphodiesterase by calcium-calmodulin. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1986, 48, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Sonobe, H.; Watson, R.D. Molt-inhibiting hormone-mediated regulation of ecdysteroid synthesis in Y-organs of the crayfish (Procambarus clarkii): Involvement of cyclic GMP and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 253, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaziani, E.; Jegla, T.C.; Wang, W.L.; Booth, J.A.; Connolly, S.M.; Conrad, C.C.; Dewall, M.J.; Sarno, C.M.; Stone, D.K.; Montgomery, R. Further studies on signaling pathways for ecdysteroidogenesis in crustacean Y-organs. Am. Zool. 2001, 41, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lin, W.; Zhang, J.-F.; Newton, A.C.; Mehta, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Sensitive fluorescent biosensor reveals differential subcellular regulation of PKC. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2025, 21, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Spaziani, E. Demonstration of protein kinase C activity in crustacean Y-organs, and partial definition of its role in regulation of ecdysteroidogenesis. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 1987, 49, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Vraspir, L.; Zhou, W.; Durica, D.S.; Mykles, D.L. Transcriptomic analysis of differentially expressed genes in the molting gland (Y-organ) of the blackback land crab, Gecarcinus lateralis, during molt-cycle stage transitions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 28, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, A.; Alexander, J.L.; Swain, M.T.; Webster, S.G.; Wilcockson, D.C. Transcriptomic analysis of crustacean neuropeptide signaling during the moult cycle in the green shore crab, Carcinus maenas. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyamal, S.; Das, S.; Guruacharya, A.; Mykles, D.L.; Durica, D.S. Transcriptomic analysis of crustacean molting gland (Y-organ) regulation via the mTOR signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
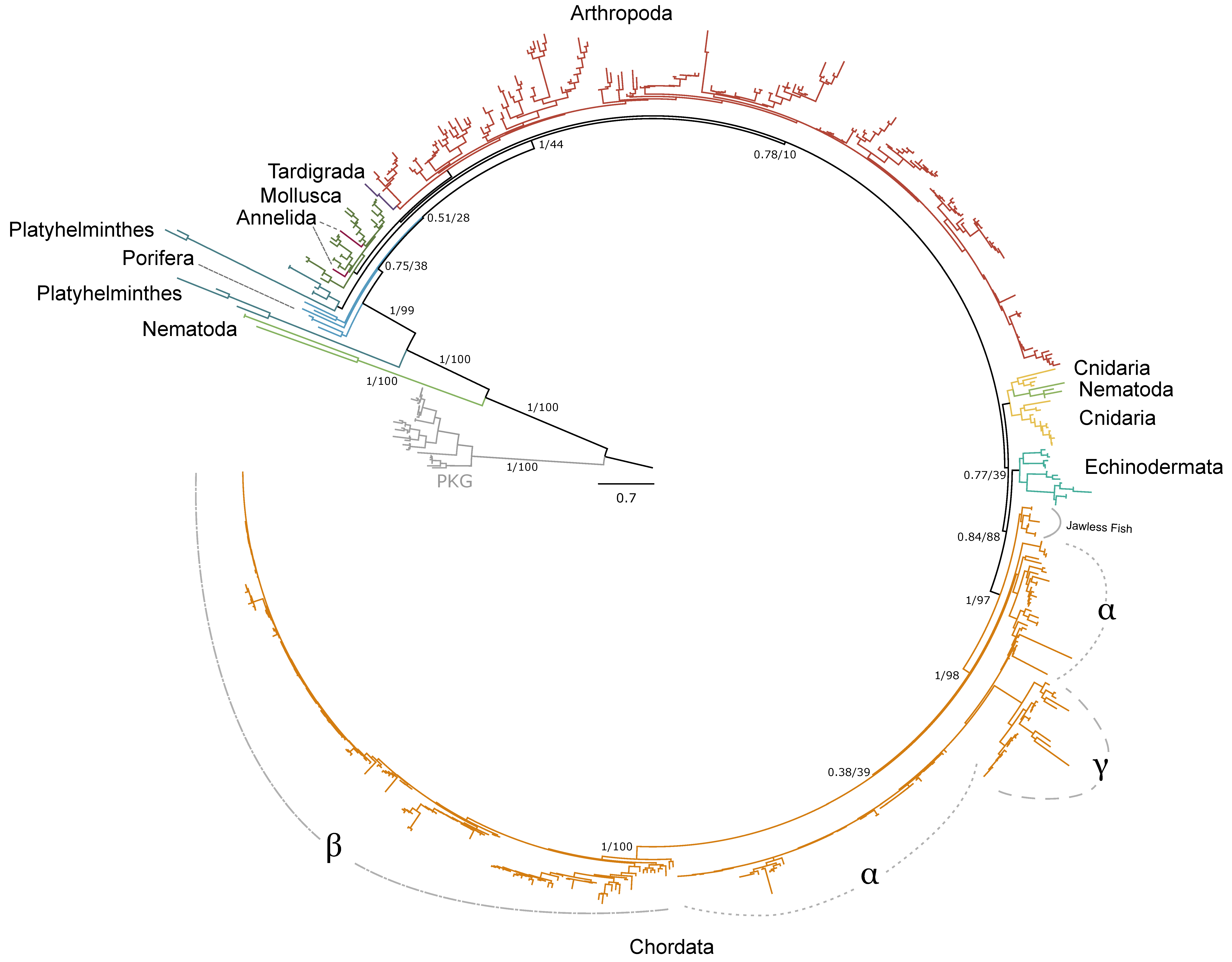
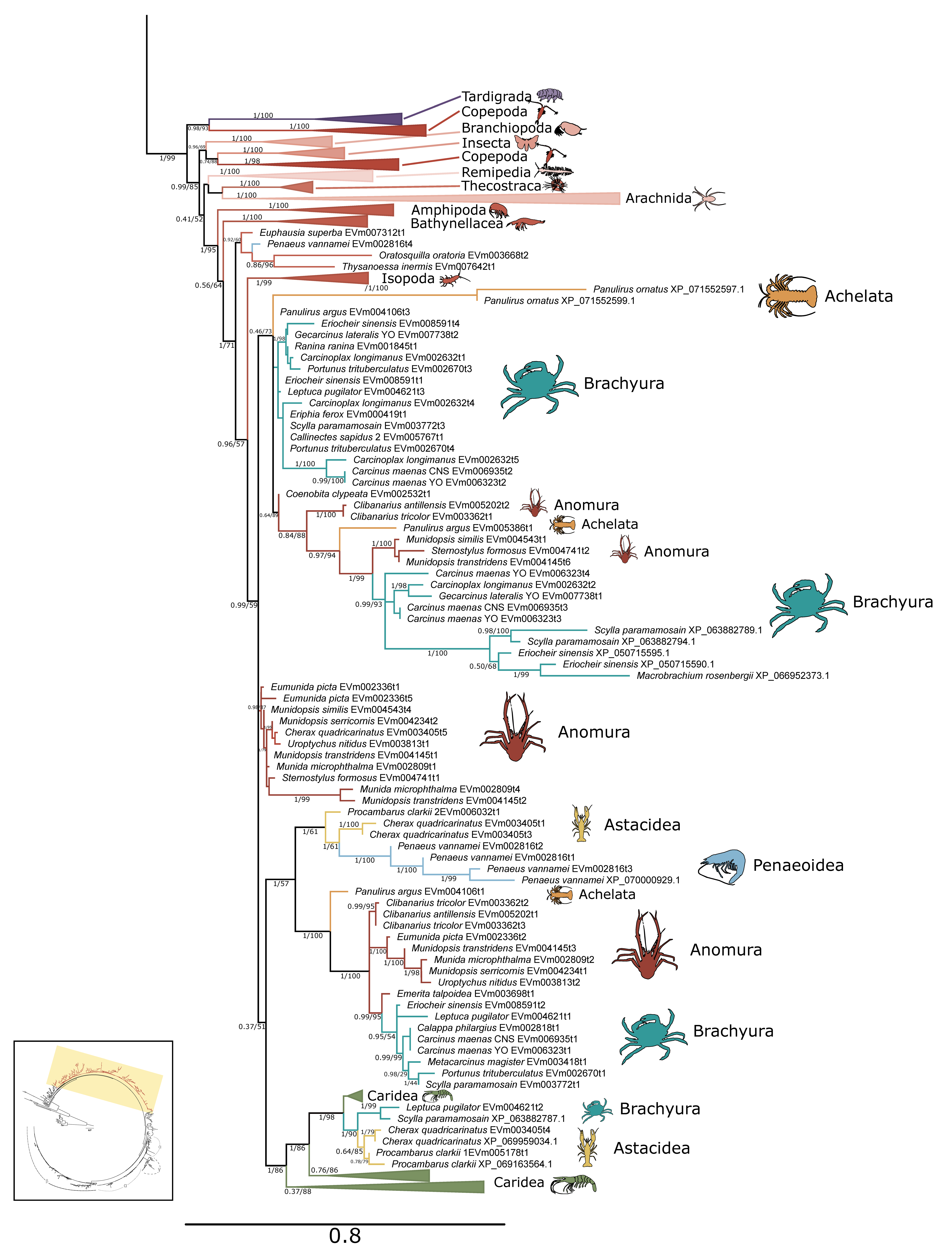
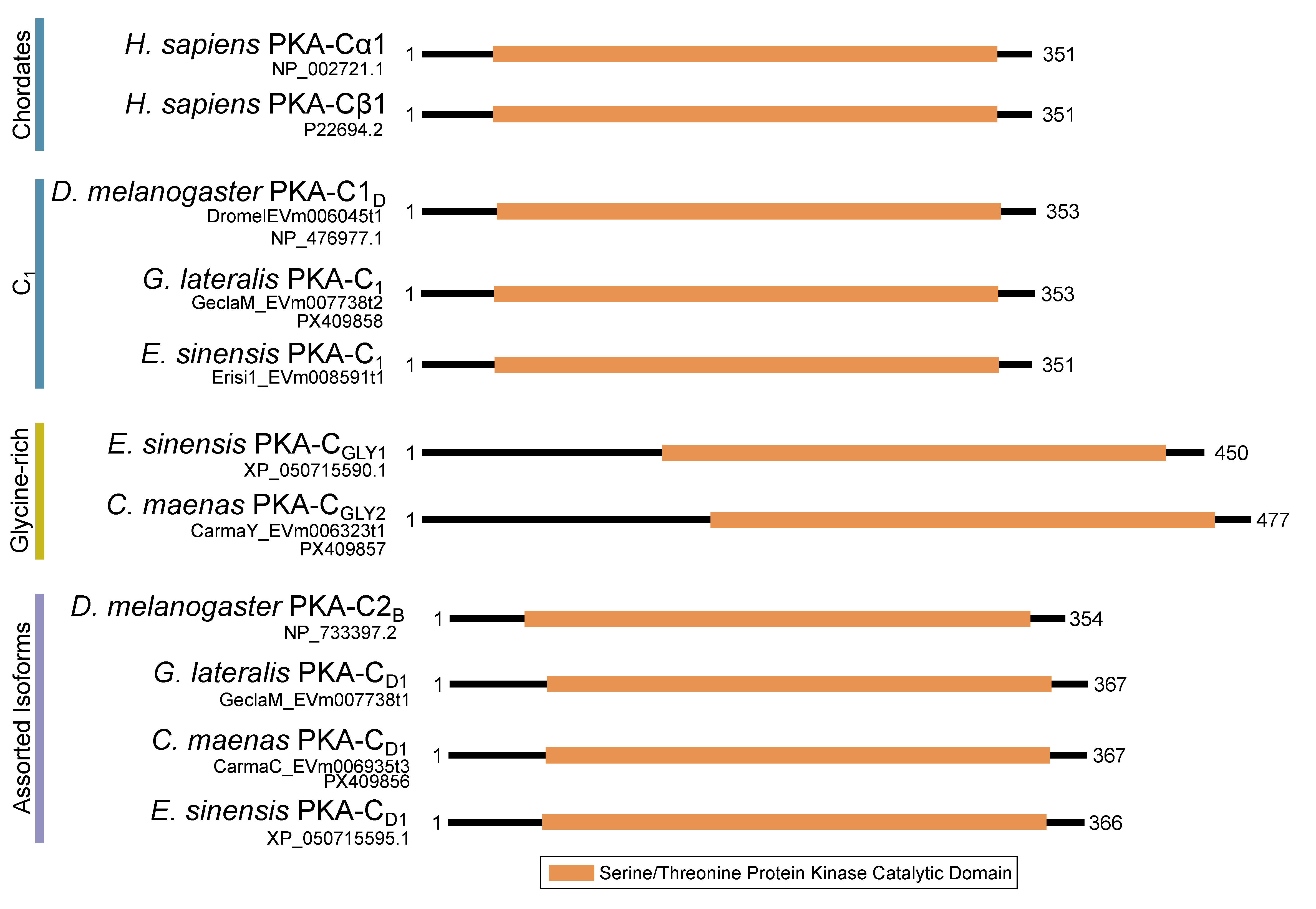
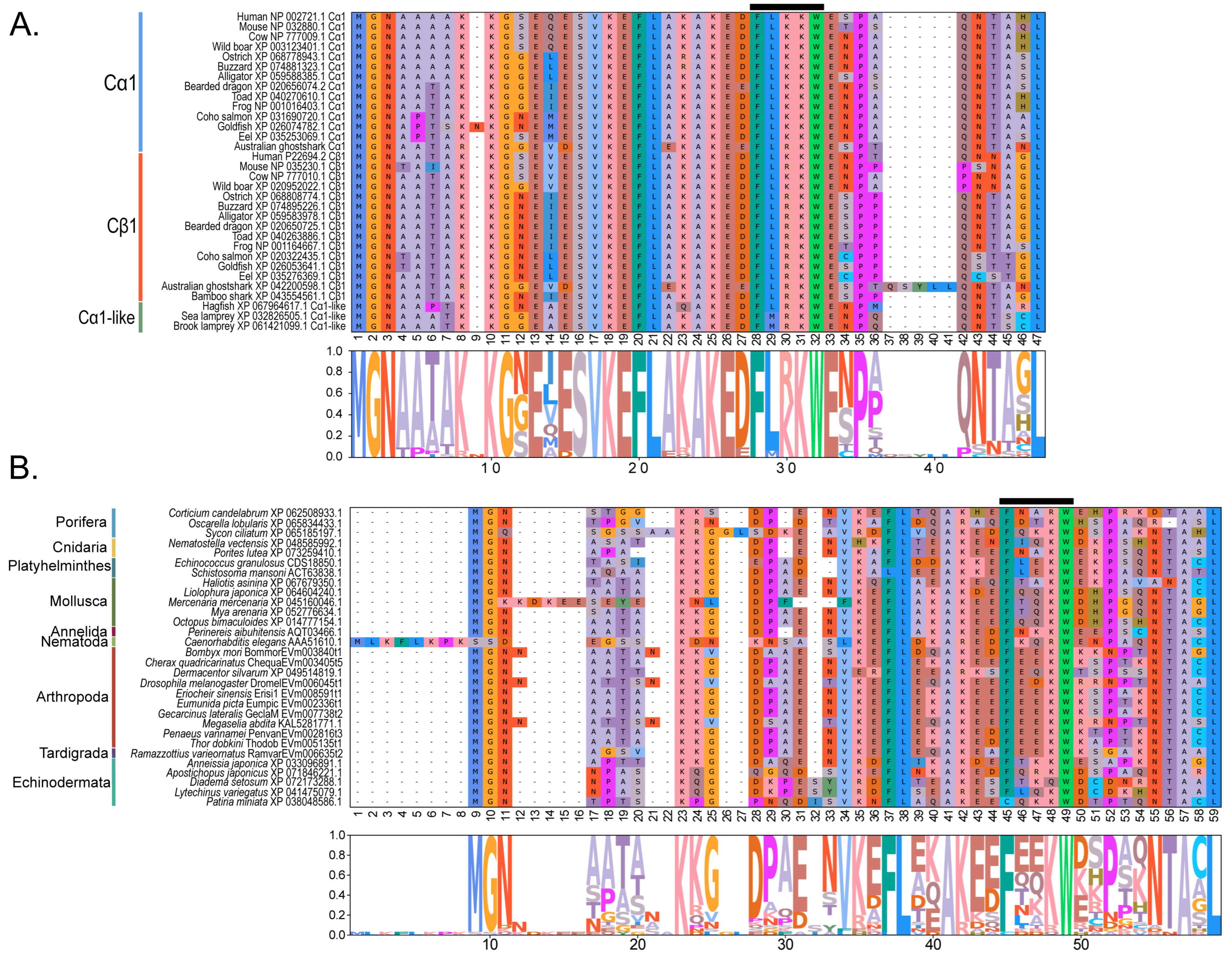



| Phylum | Number of Species | PKA Catalytic | PKA Regulatory | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | Type II | ||||
| Annelida | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| Arthropoda | 150 | 227 | 191 | 148 | 566 |
| Order Decapoda | 59 | 131 | 105 | 97 | 333 |
| Chordata | 286 | 327 | 334 | 341 | 1002 |
| Cnidaria | 16 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 42 |
| Echinodermata | 14 | 16 | 9 | 11 | 36 |
| Mollusca | 17 | 26 | 14 | 17 | 57 |
| Nematoda | 6 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| Platyhelminthes | 6 | 10 | 1 | 8 | 19 |
| Porifera | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 15 |
| Tardigrada | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 |
| Chordate | Arthropod | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decapod | |||||||||||||
| H. sapiens PKACα NP_002721.1 | H. sapiens PKACβ P22694.2 | D. melanogaster PKA-C1 DromelEVm006045t1/NP_476977.1 | G. lateralis PKA-C1 GeclaM_EVm007738t2 | E. sinensis PKA-C1 Erisi1_EVm008591t1 | C. maenas PKA-CD1 CarmaC_EVm006935t3 | C. maenas PKA-CGLY2 CarmaY_Evm006323t1 | C. quadricarinatus PKA-C1 ChequaEVm003405t5 | P. vannamei PKA-C1 PenvanEVm002816t3 | P. vannamei PKA-CGLY1 XP_070000929.1 | ||||
| Chordate | H. sapiens PKACα NP_002721.1 | 100 | 92.9 | 82.4 | 86.9 | 87.2 | 81.7 | 62.1 | 86.3 | 81.3 | 59.2 | Percent Identity | |
| H. sapiens PKACβ P22694.2 | 95.2 | 100 | 82.2 | 86.0 | 86.3 | 80.4 | 61.2 | 86.0 | 80.2 | 58.1 | |||
| D. melanogaster PKA-C1 DromelEVm006045t1/NP_476977.1 | 89.0 | 89.2 | 100 | 90.4 | 90.9 | 84.6 | 64.7 | 90.1 | 83.1 | 60.2 | |||
| Arthropod | Decapod | G. lateralis PKA-C1 GeclaM_EVm007738t2 | 91.2 | 90.9 | 94.3 | 100 | 99.2 | 91.3 | 69.4 | 99.2 | 89.8 | 64.1 | |
| E. sinensis PKA-C1 Erisi1_EVm008591t1 | 91.5 | 91.2 | 94.6 | 99.7 | 100 | 92.1 | 70.0 | 98.6 | 89.2 | 63.6 | |||
| C. maenas PKA-CD1 CarmaC_EVm006935t3 | 86.7 | 85.6 | 88.6 | 92.9 | 93.2 | 100 | 71.3 | 90.7 | 81.8 | 62.0 | |||
| C. maenas PKA-CGLY2 CarmaY_Evm006323t1 | 65.6 | 64.8 | 68.1 | 70.9 | 71.1 | 72.0 | 100 | 62.2 | 62.2 | 63.2 | |||
| C. quadricarinatus PKA-C1 ChequaEVm003405t5 | 91.2 | 91.5 | 94.6 | 99.4 | 99.7 | 92.9 | 66.4 | 100 | 90.6 | 64.7 | |||
| P. vannamei PKA-C1 PenvanEVm002816t3 | 87.5 | 86.7 | 88.7 | 93.2 | 93.5 | 87.0 | 66.4 | 93.8 | 100 | 71.7 | |||
| P. vannamei PKA-CGLY1 XP_070000929.1 | 64.3 | 63.2 | 65.1 | 67.0 | 67.2 | 65.6 | 68.5 | 67.4 | 72.1 | 100 | |||
| Percent Similarity | |||||||||||||
| Chordate | Arthropod | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decapod | |||||||||||||||
| H. sapiens PKA-RIα NP_002725.1 | H. sapiens PKA-RIβ NP_001158232.1 | D. melanogaster PKA-RIAA DromelEVm005673t1/NP_001189147.1 | C. maenas PKA-RI1 CarmaY_EVm009321t1 | C. maenas PKA-RID1 CarmaY_EVm009321t2 | E. sinensis PKA-RI1 Erisi1_EVm007953t3/XP_050718363.1 | E. sinensis PKA-RID1 Erisi1_EVm007953t2 | G. lateralis PKA-RID1 GeclaM_EVm010036t1 | C. quadricarinatus PKA-RI1 ChequaEVm006131t1 | C. quadricarinatus PKA-RID1 XP_053629376.1 | P. vannamei PKA-RI1 PenvanEVm004491t1/ XP_069981575.1 | P. vannamei PKA-RID1 XP_069981583.1 | ||||
| Chordate | H. sapiens PKA-RIα NP_002725.1 | 100 | 81.4 | 70.4 | 67.5 | 58.5 | 68.0 | 59.3 | 58.3 | 67.5 | 58.8 | 66.8 | 59.8 | Percent Identity | |
| H. sapiens PKA-RIβ NP_001158232.1 | 89.5 | 100 | 71.5 | 69.0 | 59.8 | 70.1 | 60.6 | 59.8 | 69.0 | 60.1 | 67.6 | 61.2 | |||
| D. melanogaster PKA-RIAA DromelEVm005673t1/NP_001189147.1 | 80.1 | 80.4 | 100 | 73.7 | 63.7 | 74.8 | 64.7 | 61.8 | 73.7 | 63.9 | 71.1 | 64.5 | |||
| Arthropod | Decapod | C. maenas PKA-RI1 CarmaY_EVm009321t1 | 79.8 | 80.3 | 83.6 | 100 | 85.2 | 96.5 | 82.3 | 76.6 | 93.8 | 79.3 | 90.7 | 80.1 | |
| C. maenas PKA-RID1 CarmaY_EVm009321t2 | 68.8 | 69.3 | 72.7 | 85.5 | 100 | 82.3 | 96.6 | 88.0 | 79.3 | 93.2 | 77.0 | 94.1 | |||
| E. sinensis PKA-RI1 Erisi1_EVm007953t3/XP_050718363.1 | 79.0 | 80.6 | 84.1 | 98.1 | 84.1 | 100 | 85.2 | 79.0 | 95.2 | 81.2 | 91.0 | 80.9 | |||
| E. sinensis PKA-RID1 Erisi1_EVm007953t2 | 68.2 | 69.3 | 73.2 | 84.1 | 98.5 | 85.5 | 100 | 90.7 | 81.2 | 95.4 | 77.8 | 95.1 | |||
| G. lateralis PKA-RID1 GeclaM_EVm010036t1 | 66.1 | 66.7 | 68.7 | 78.5 | 90.1 | 79.3 | 91.1 | 100 | 76.3 | 87.7 | 72.4 | 86.4 | |||
| C. quadricarinatus PKA-RI1 ChequaEVm006131t1 | 79.3 | 80.3 | 84.1 | 96.5 | 82.0 | 96.8 | 82.8 | 77.2 | 100 | 85.2 | 91.5 | 80.7 | |||
| C. quadricarinatus PKA-RID1 XP_053629376.1 | 68.2 | 69.3 | 73.2 | 82 | 96.0 | 82.8 | 96.9 | 88.6 | 85.5 | 100 | 80.7 | 94.8 | |||
| P. vannamei PKA-RI1 PenvanEVm004491t1/ XP_069981575.1 | 77.8 | 79.1 | 81.1 | 93.5 | 79.6 | 93.0 | 79.6 | 74.2 | 94.1 | 83.3 | 100 | 81.9 | |||
| P. vannamei PKA-RID1 XP_069981583.1 | 69.3 | 70.3 | 73.5 | 82.8 | 96.9 | 82.8 | 96.9 | 88.6 | 83.3 | 97.5 | 82.2 | 100 | |||
| Percent Similarity | |||||||||||||||
| Chordate | Arthropod | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decapod | |||||||||||||
| H. sapiens PKA-RIIα NP_004148.1 | H. sapiens PKA-RIIβ NP_002727.2 | D. melanogaster PKA-RIIA DromelEVm005674t1/NP_523671.1 | C. maenas PKA-RIIGLY CarmaC_EVm008235t2 | G. lateralis PKA-RIIGLY GeclaM_EVm006874t1 | G. lateralis PKA-RIID1 GeclaM_EVm006874t3 | C. quadricarinatus PKA-RIIGLY ChequaEVm005536t2 | C. quadricarinatus PKA-RIID1 ChequaEVm005536t4 | P. vannamei PKA-RIIGLY XP_069989562.1 | P. vannamei PKA-RIID1 XP_069989583.1 | ||||
| Chordate | H. sapiens PKA-RIIα NP_004148.1 | 100 | 65.5 | 46.5 | 48.5 | 45.8 | 45.5 | 49.4 | 45.3 | 48.8 | 46.3 | Percent Identity | |
| H. sapiens PKA-RIIβ NP_002727.2 | 76.4 | 100 | 41.3 | 46.7 | 43.5 | 43.6 | 49.3 | 44.8 | 51.1 | 46.7 | |||
| D. melanogaster PKA-RIIA DromelEVm005674t1/NP_523671.1 | 60.5 | 58.9 | 100 | 55.6 | 52.9 | 54.4 | 58.7 | 55.2 | 58.8 | 56.0 | |||
| Arthropod | Decapod | C. maenas PKA-RIIGLY CarmaC_EVm008235t2 | 63.2 | 61.8 | 70.8 | 100 | 70.3 | 72.4 | 79.7 | 67.8 | 79.2 | 69.0 | |
| G. lateralis PKA-RIIGLY GeclaM_EVm006874t1 | 57.6 | 59.9 | 66.8 | 79.0 | 100 | 77.9 | 70.7 | 67.2 | 71.2 | 67.2 | |||
| G. lateralis PKA-RIID1 GeclaM_EVm006874t3 | 57.3 | 57.9 | 66.2 | 76.2 | 78.6 | 100 | 71.5 | 83.0 | 72.0 | 82.9 | |||
| C. quadricarinatus PKA-RIIGLY ChequaEVm005536t2 | 64.2 | 62.9 | 72.2 | 86.7 | 79.2 | 77.2 | 100 | 81.6 | 89.9 | 74.9 | |||
| C. quadricarinatus PKA-RIID1 ChequaEVm005536t4 | 57.6 | 58.1 | 67.2 | 74.3 | 73.2 | 90.2 | 82.4 | 100 | 74.6 | 86.2 | |||
| P. vannamei PKA-RIIGLY XP_069989562.1 | 62.6 | 63.2 | 72.9 | 85.7 | 78.5 | 76.9 | 93 | 77.7 | 100 | 82.3 | |||
| P. vannamei PKA-RIID1 XP_069989583.1 | 58.4 | 58.6 | 69.3 | 74.3 | 72.3 | 89.7 | 78.2 | 90.6 | 83.1 | 100 | |||
| Percent Similarity | |||||||||||||
| Phylum | Number of Species | PKN | Conventional | Novel δ/θ | Novel ε/η | Atypical | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annelida | 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 9 |
| Arthropoda | 173 | 115 | 153 | 106 | 100 | 204 | 678 |
| Order Decapoda | 52 | 77 | 62 | 34 | 44 | 98 | 315 |
| Chordata | 231 | 132 | 223 | 173 | 185 | 147 | 860 |
| Cnidaria | 16 | 8 | 11 | 10 | 7 | 13 | 49 |
| Echinodermata | 17 | 17 | 8 | 12 | 12 | 16 | 65 |
| Mollusca | 23 | 11 | 14 | 26 | 12 | 26 | 89 |
| Nematoda | 10 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 17 |
| Platyhelminthes | 12 | 3 | 11 | 0 | 9 | 7 | 30 |
| Porifera | 7 | 6 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 4 | 35 |
| Tardigrada | 3 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 11 |
| Conventional | Novel δ/θ | Novel ε/η | Atypical | PKN | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human: | PKCα | PKCβ | PKCδ | PKCθ | PKCε | PKCη | PKCι | PKCζ | PKN1 | PKN2 | PKN3 |
| Drosophila melanogaster | DromelEVm002580t1 PKC53EF | DromelEVm001975t2 | DromelEVm001975t1 D1 | DromelEVm002874t2 | NP_788290.1 | ||||||
| 66.1 | 66.2 | 34.5 | 34.8 | 57.1 | 51.5 | 58.3 | 55.7 | 43.4 | 46.8 | 37.6 | |
| DromelEVm002394t1 | DromelEVm002874t1 PKCAC | ||||||||||
| 45.8 | 40.3 | 65.1 | 61.0 | ||||||||
| Carcinus maenas | CarmaY_EVm003058t1 cPKCD1 | CarmaC_EVm004306t1 nPKCD1δ | CarmaY_EVm002701t1 nPKCD1ε | CarmaY_EVm004113t1 aPKCD1 | CarmaY_EVm003480t1 * PNKD1 | ||||||
| 64.6 | 63.2 | 40.0 | 41.5 | 57.7 | 52.8 | 66.2 | 61.9 | 33.5 | 32.5 | 31.2 | |
| CarmaY_EVm004113t2 aPKCD2 | |||||||||||
| 58.3 | 56.6 | ||||||||||
| Gecarcinus lateralis | GeclaM_EVm002835t1 cPKCD1 | GeclaM_EVm003046t1 nPKCD1δ | GeclaM_EVm002409t1 nPKCD1ε | GeclaM_EVm003606t1 aPKCD1 | GeclaM_EVm004548t1 * PNKD1 | ||||||
| 66.0 | 64.7 | 42.6 | 42.9 | 57.8 | 52.6 | 65.7 | 61.8 | 31.2 | 27.4 | 27.4 | |
| GeclaM_EVm003046t2 nPKCD1δ | |||||||||||
| 40.4 | 41.0 | ||||||||||
| Eriocheir sinensis | Erisi1_EVm005209t1 * cPKCD1 | Erisi1_EVm001544t1 * nPKCD1δ | Erisi1_EVm002283t1 nPKCD1ε | Erisi1_EVm009429t2 * aPKCD1 | Erisi1_EVm001069t3 PKND1 | ||||||
| 49.1 | 49.2 | 35.9 | 36.2 | 57.9 | 52.5 | 43.0 | 41.6 | 47.2 | 51.4 | 42.6 | |
| Cherax quadricarinatus | ChequaEVm002328t1 cPKCD1 | ChequaEVm001435t3 nPKCD1δ | ChequaEVm001960t1 nPKCD1ε | ChequaEVm002958t1 aPKCD1 | ChequaEVm000705t3 PKND1 | ||||||
| 58.0 | 51.7 | 42.7 | 40.0 | 58.0 | 51.3 | 66.4 | 61.8 | 44.4 | 47.9 | 39.7 | |
| ChequaEVm000705t1 PKND2 | |||||||||||
| ChequaEVm002328t2 cPKCD1 Δ | ChequaEVm002958t2 aPKCD3 | 42.3 | 46.4 | 37.7 | |||||||
| 66.4 | 67.1 | 65.2 | 55.9 | XP_053646711.1 PKND3 | |||||||
| 38.2 | 40.1 | 33.7 | |||||||||
| Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei | PenvanEVm004159t1 cPKCD1 | PenvanEVm003492t1 * nPKCD1δ | PenvanEVm001947t1 * nPKCD1ε | PenvanEVm001352t1 * aPKCD1 | PenvanEVm000367t1 PKND1 | ||||||
| 47.0 | 65.1 | 31.7 | 30.1 | 50.0 | 43.8 | 66.1 | 45.2 | 45.1 | 48.3 | 40.5 | |
| C. maenas | G. lateralis | E. sinensis | C. quadricarinatus | P. vannamei | Proposed Classification | Motif | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKA | Catalytic | GeclaM_EVm007738t2 (PX409858) | Erisi1_EVm008591t1 | ChequaEVm003405t5 | PenvanEVm002816t3 | PKA-C1 | 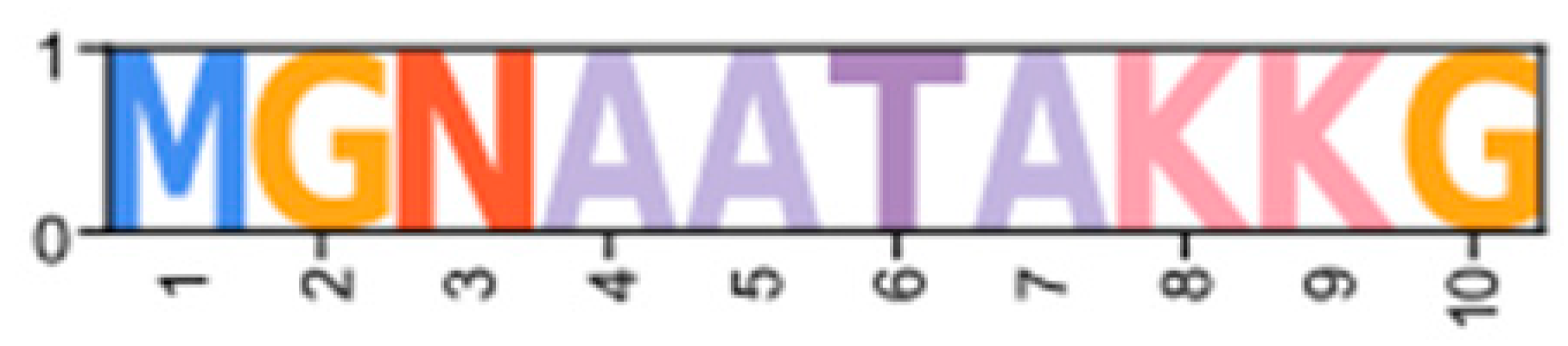 | |
| XP_050715590.1 | ChequaEVm003405t4 | XP_070000929.1 | PKA-CGLY1 | 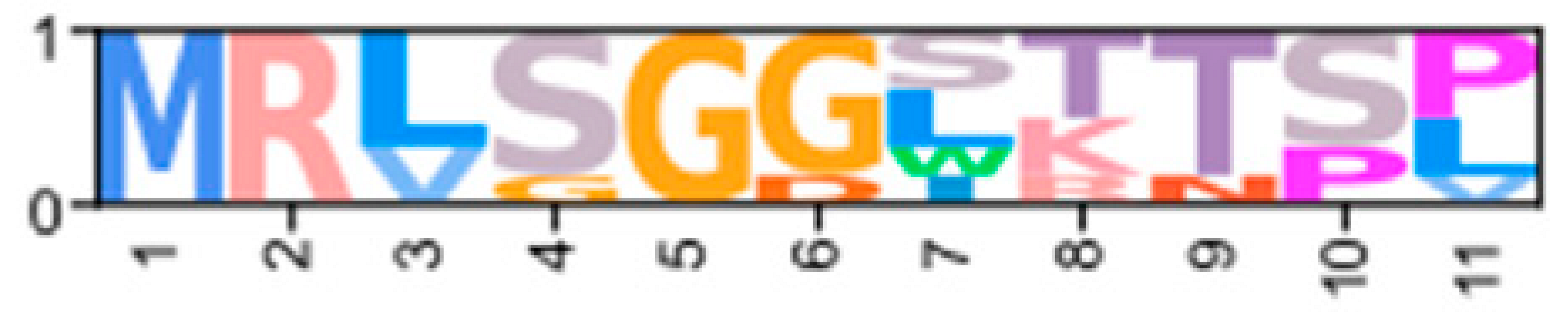 | ||||
| CarmaY_Evm006323t1 (PX409857) | ChequaEVm003405t3 | PKA-CGLY2 |  | |||||
| CarmaC_EVm006935t3 | GeclaM_EVm007738t1 | XP_050715595.1 | PKA-CD1 | 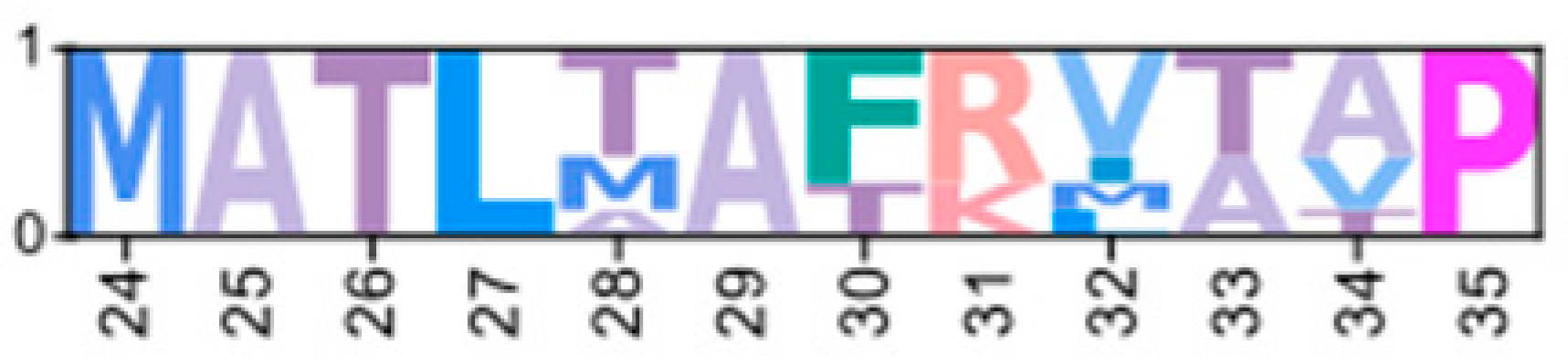 | ||||
| Regulatory I | CarmaY_EVm009321t1 (PX409859) | Erisi1_EVm007953t3 (XP_050718363.1) | ChequaEVm006131t1 | PenvanEVm004491t1 (XP_069981575.1) | PKA-RI1 | 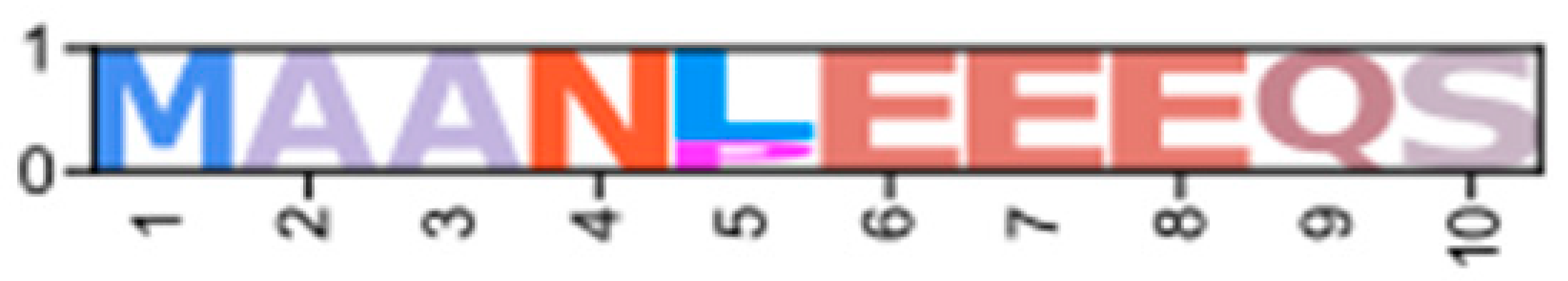 | ||
| CarmaY_EVm009321t2 (PX409860) | GeclaM_EVm010036t1 (PX409861) | Erisi1_EVm007953t2 | XP_053629376.1 | XP_069981583.1 | PKA-RID1 |  | ||
| Regulatory II | CarmaC_EVm008235t2 (PX409862) | GeclaM_EVm006874t1 (PX409863) | ChequaEVm005536t2 | XP_069989562.1 | PKA-RIIGLY |  | ||
| GeclaM_EVm006874t3 | ChequaEVm005536t4 | XP_069989583.1 | PKA-RIID1 | 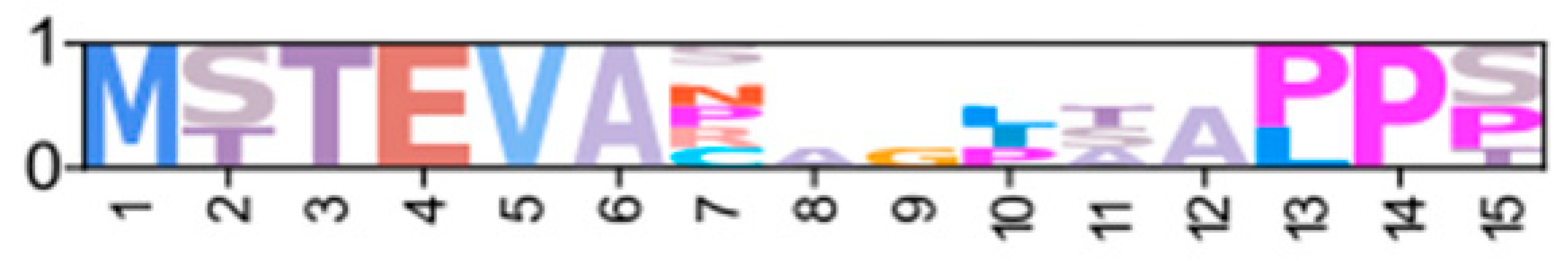 | ||||
| PKC | PKN | CarmaY_EVm003480t1 * | GeclaM_EVm004548t1 * | Erisi1_EVm001069t3 (XP_050729390.1 *) | ChequaEVm000705t3 | PenvanEVm000367t1 | PKND1 | 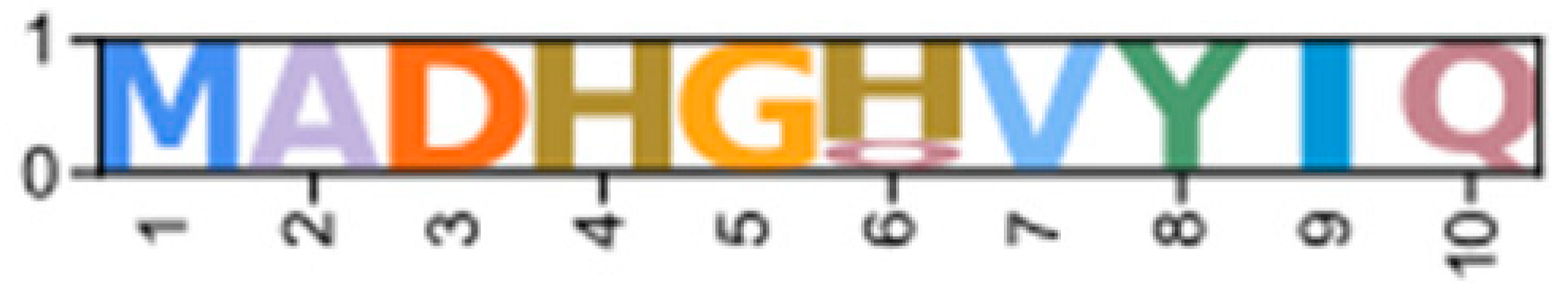 |
| Conventional | CarmaY_EVm003058t1 (PX409868) | GeclaM_EVm002835t1 (PX409871) | Erisi1_EVm005209t1 * | ChequaEVm002328t1 | PenvanEVm001352t1 | cPKCD1 |  | |
| Novel δ | CarmaC_EVm004306t1 (PX409866) | GeclaM_EVm003046t2 (PX409874) | Erisi1_EVm001544t1 * | ChequaEVm001435t3 | PenvanEVm003492t1 * | nPKCD1δ | 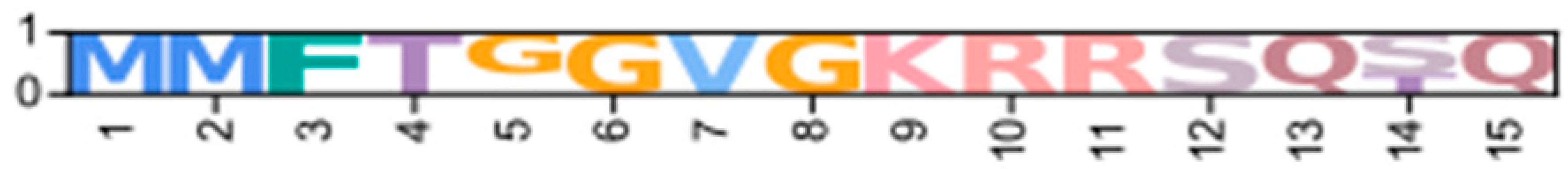 | |
| Novel ε | CarmaY_EVm002701t1 (PX409865) | GeclaM_EVm002409t1 (PX409873) | Erisi1_EVm002283t1 | ChequaEVm001960t1 | PenvanEVm001947t1 * | nPKCD1ε | 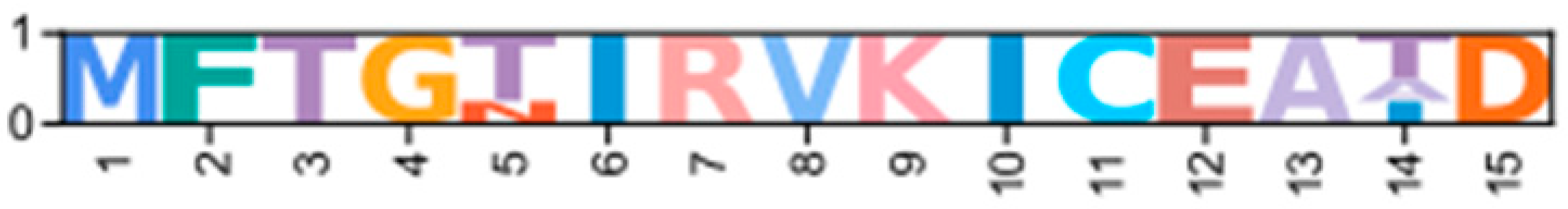 | |
| Atypical | CarmaY_EVm004113t1 (PX409869) | GeclaM_EVm003606t1 (PX409872) | Erisi1_EVm009429t2 * | ChequaEVm002958t1 (XP_069952440.1) | PenvanEVm004159t1 * | aPKCD1 |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Head, T.B.; Pérez-Moreno, J.L.; Antizzo, L.E.; Durica, D.S.; Mykles, D.L. Crustacean Protein Kinases A and C: Bioinformatic Characterization in Decapods and Other Non-Model Organisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110585
Head TB, Pérez-Moreno JL, Antizzo LE, Durica DS, Mykles DL. Crustacean Protein Kinases A and C: Bioinformatic Characterization in Decapods and Other Non-Model Organisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110585
Chicago/Turabian StyleHead, Talia B., Jorge L. Pérez-Moreno, Laura E. Antizzo, David S. Durica, and Donald L. Mykles. 2025. "Crustacean Protein Kinases A and C: Bioinformatic Characterization in Decapods and Other Non-Model Organisms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110585
APA StyleHead, T. B., Pérez-Moreno, J. L., Antizzo, L. E., Durica, D. S., & Mykles, D. L. (2025). Crustacean Protein Kinases A and C: Bioinformatic Characterization in Decapods and Other Non-Model Organisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110585





