The Length of Lactation and Model of Weaning Modulate Key Regulatory Nodes of Murine Mammary Gland Involution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
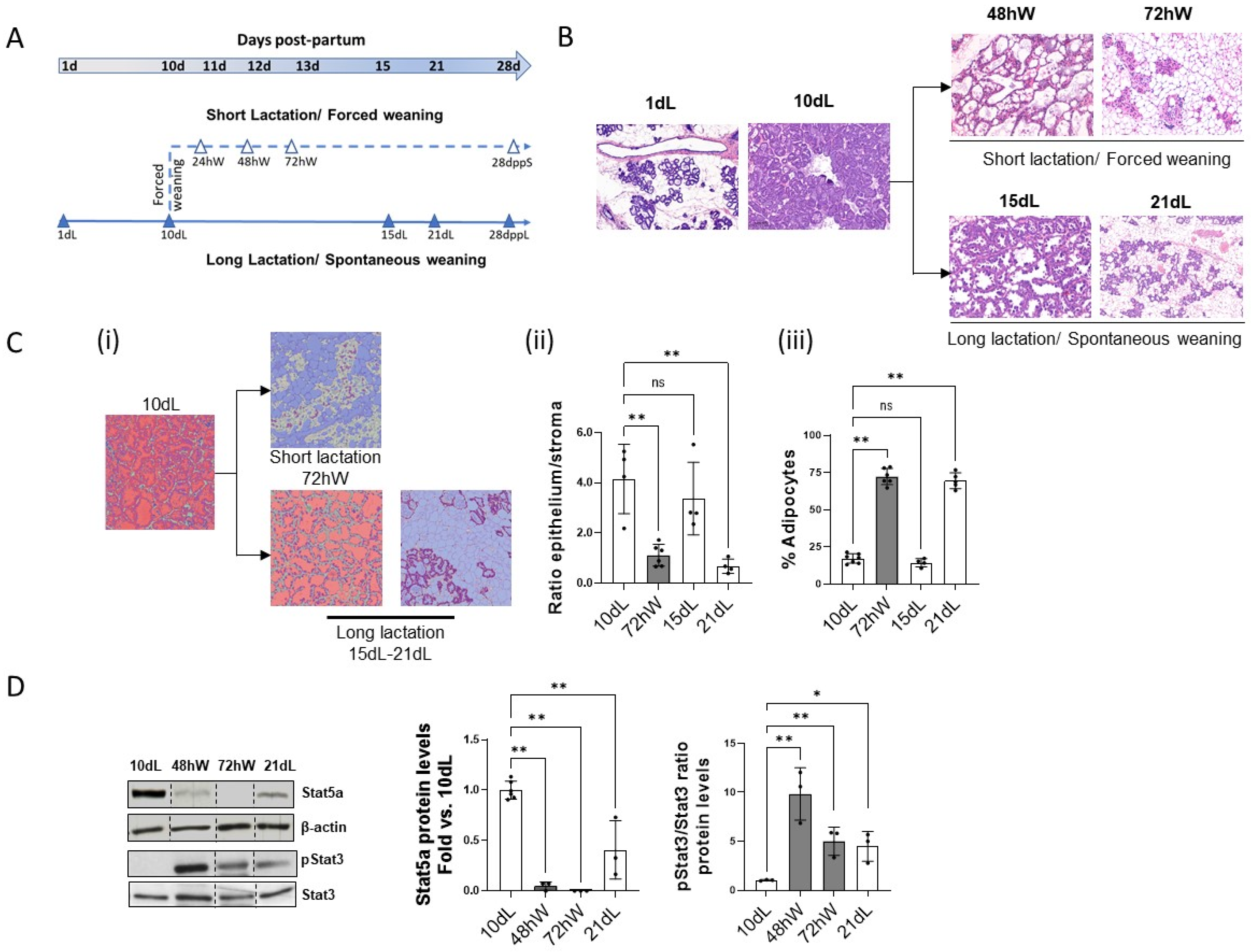
2.1. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of the Second Phase of Mammary Gland Involution in Forced and Spontaneous Weaning
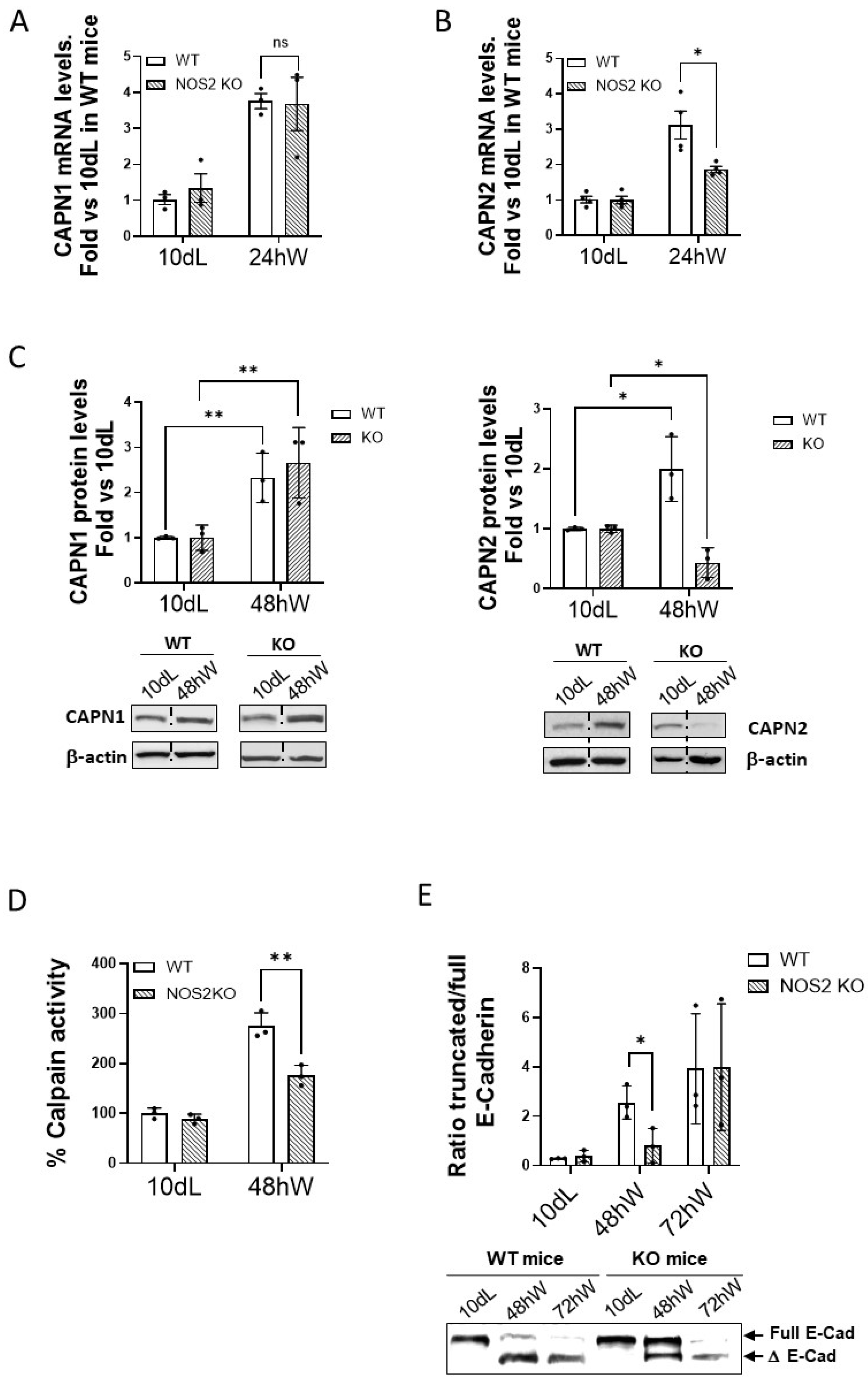
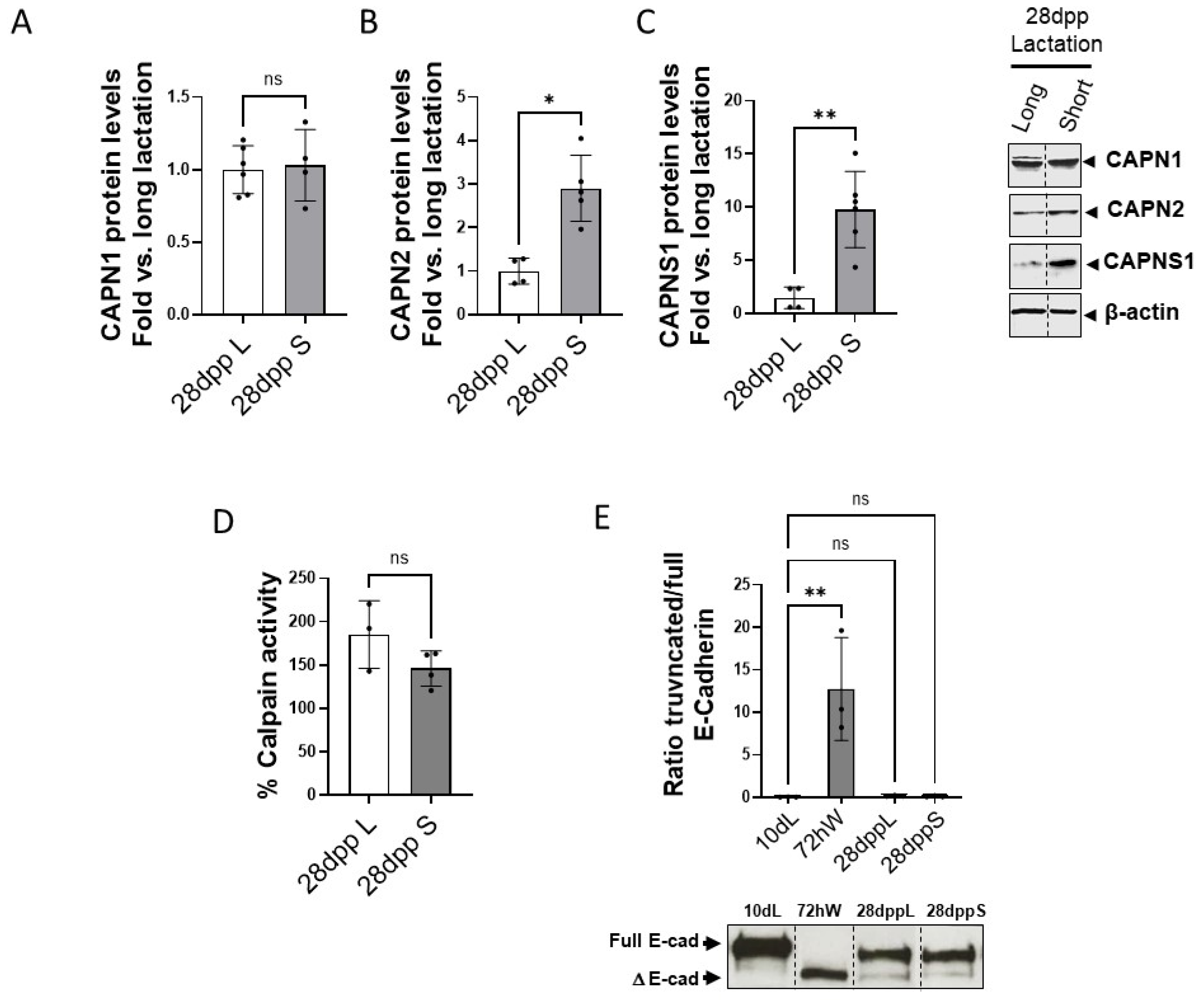
2.2. Effect of the Duration of Lactation on Calpain Expression and Activity During Mammary Gland Involution
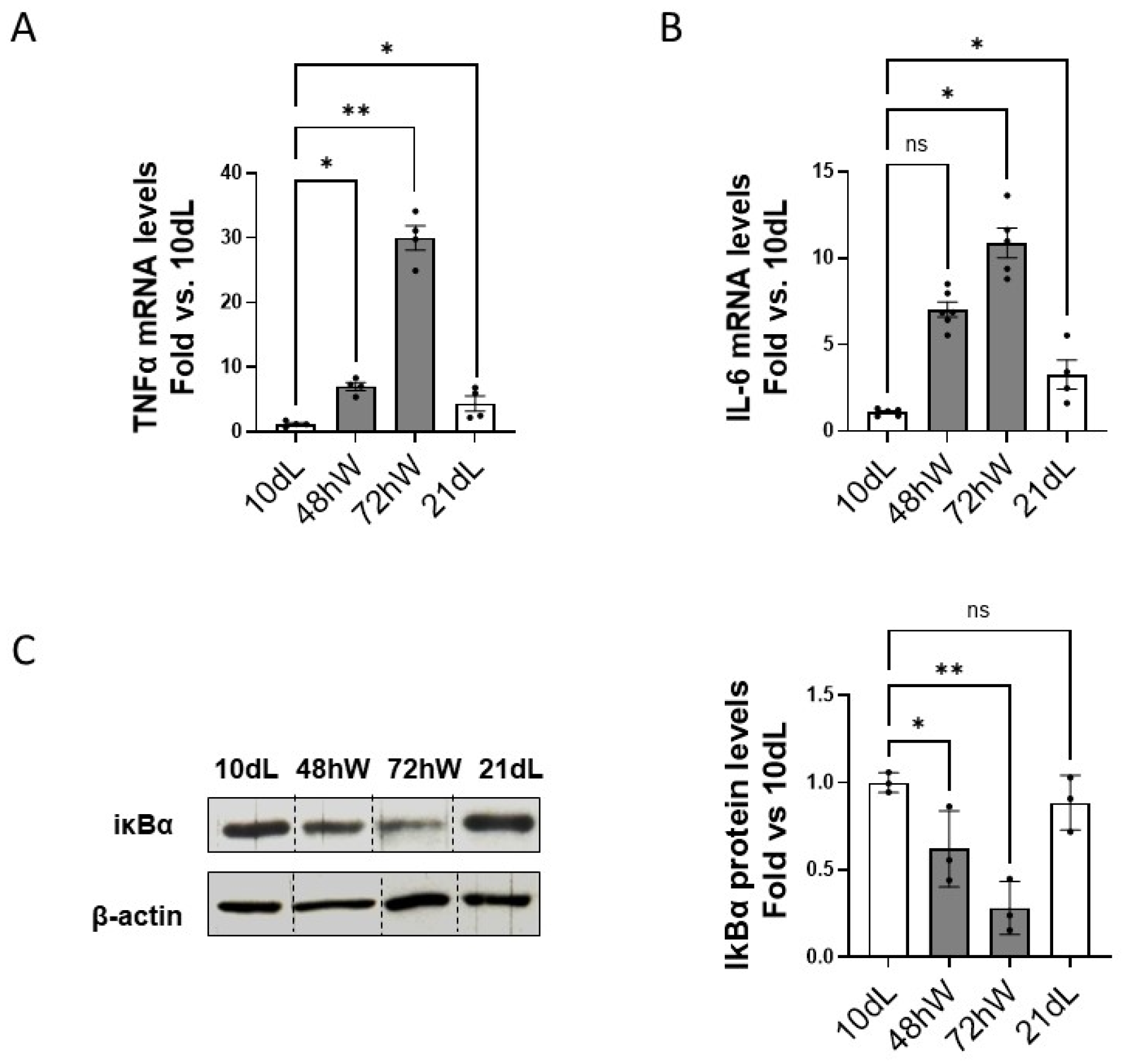
2.3. Role of the Inflammatory Response on the Modulation of Calpains During Mammary Gland Involution
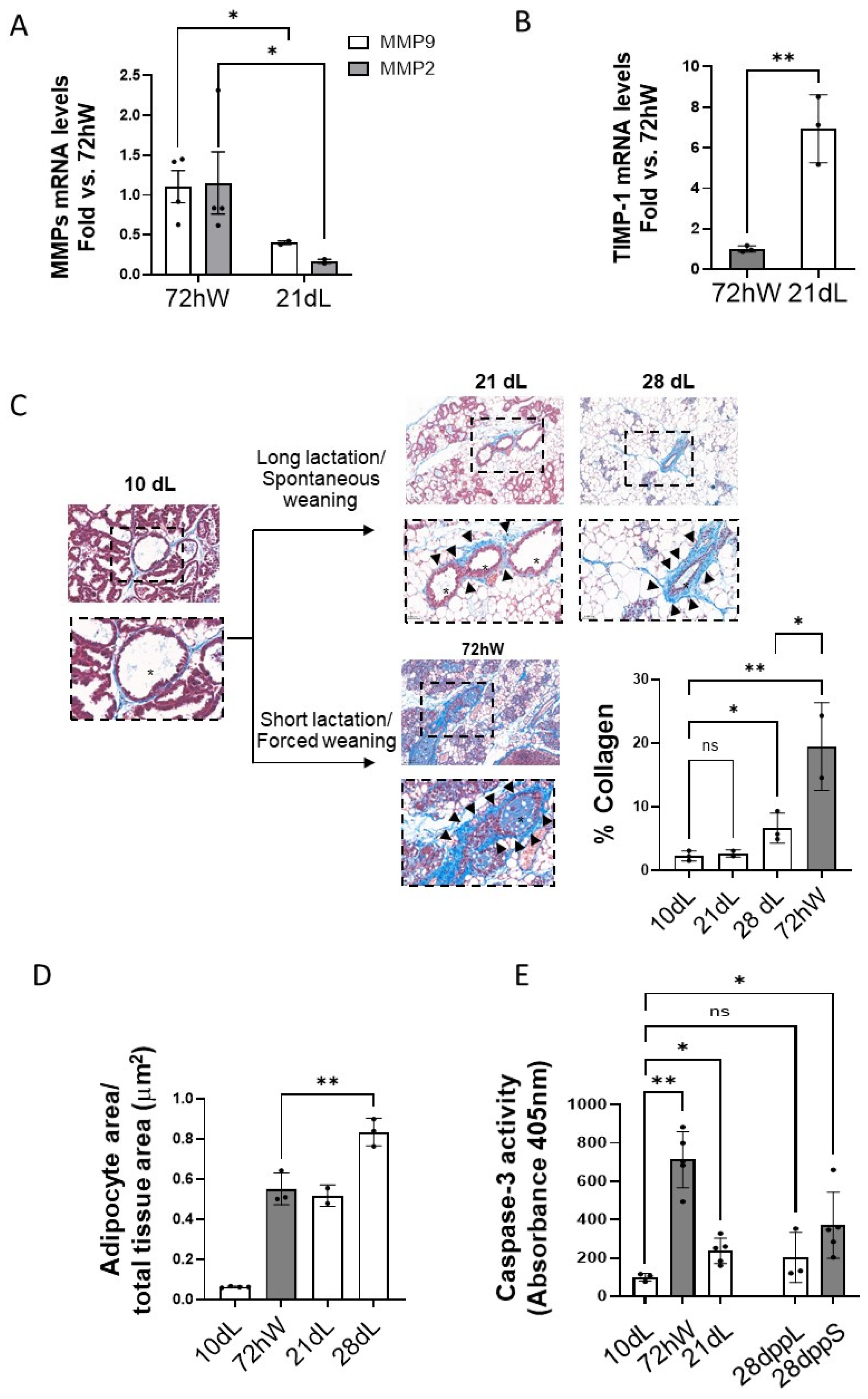
2.4. Effect of the Duration of Lactation on Mammary Tissue Remodeling
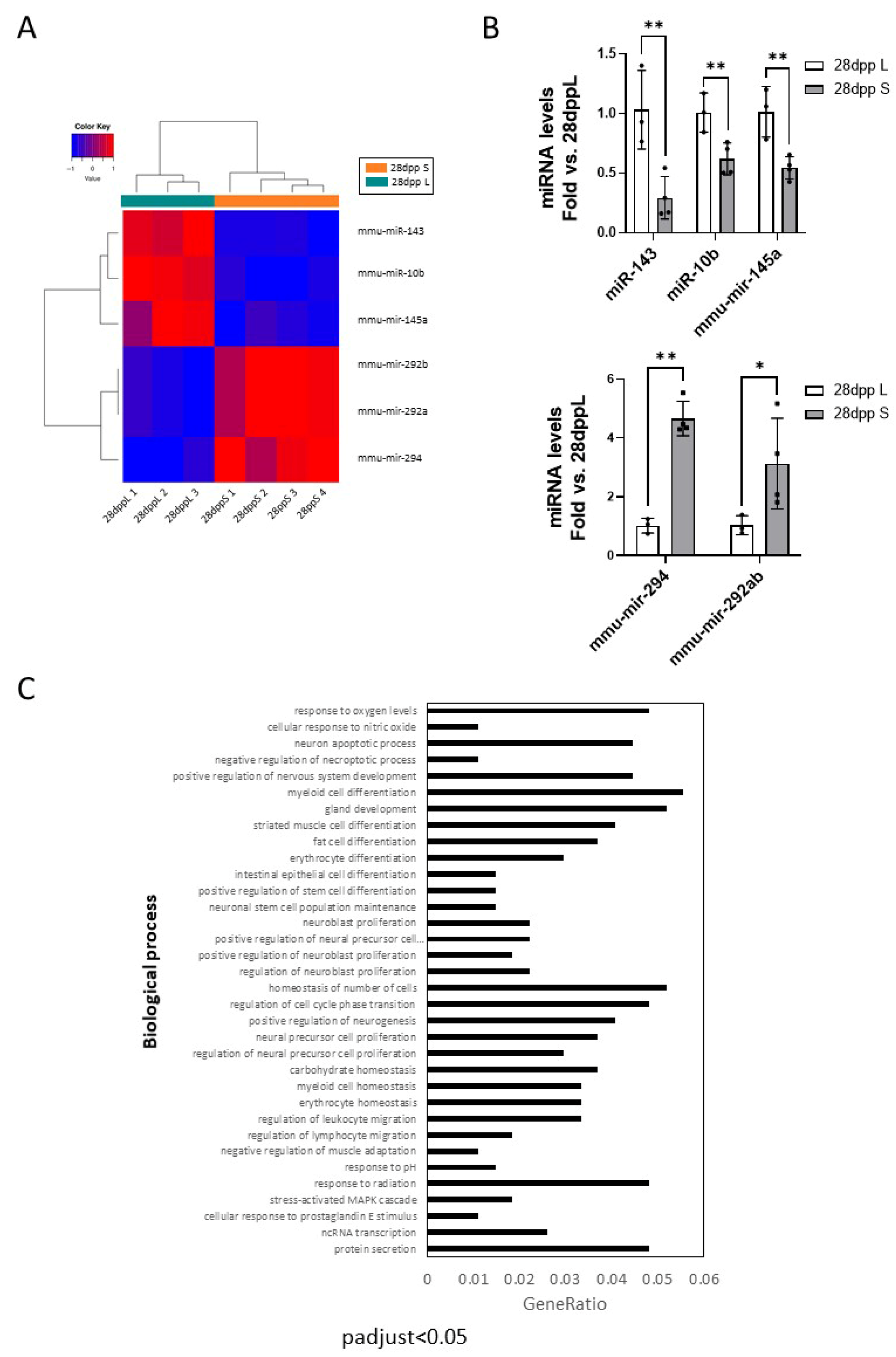
2.5. Effect of the Lactation Model on Regulatory Nodes upon Full Regression of Mammary Gland
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Histological Analysis
4.4. Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR
4.5. Total Protein Extraction and Immunoblotting
4.6. CAPN Activity Assay
4.7. Caspase-3 Activity Assay
4.8. miRnome Analysis
4.9. qPCR Validation of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAPN | Calpain |
| dL | Days of lactation |
| dpp | Days post-partum |
| hW | Hours after forced weaning |
| IκBα | Inhibitor of kappa B |
| L/S | Long or Short model of lactation |
| MMP | Metalloproteinase |
| NFκB | Nuclear Factor kappa B |
| NOS-2 | Nitric oxide synthase-2 |
| PPBC | Post-partum breast cancer |
| TIMP-1 | Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- García-Trevijano, E.R.; Ortiz-Zapater, E.; Gimeno, A.; Viña, J.R.; Zaragozá, R. Calpains, the proteases of two faces controlling the epithelial homeostasis in mammary gland. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1249317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauner, G.; Kuperwasser, C. Microenvironmental control of cell fate decisions in mammary gland development and cancer. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, H.; Ma, B. Calpain–calpastatin system and cancer progression. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basree, M.M.; Shinde, N.; Koivisto, C.; Cuitino, M.; Kladney, R.; Zhang, J.; Stephens, J.; Palettas, M.; Zhang, A.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Abrupt involution induces inflammation, estrogenic signaling, and hyperplasia linking lack of breastfeeding with increased risk of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Mishra, S.; Shinde, N.; Cuitino, M.C.; Bauer, M.; Ahirwar, D.; Basree, M.M.; Bharti, V.; Ormiston, K.; Mawalkar, R.; et al. Divergent paths of mammary gland involution: Unveiling the cellular dynamics in abruptly and gradually involuted mouse models. Breast Cancer Res. 2025, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.J.; Khaled, W.T. Mammary development in the embryo and adult: New insights into the journey of morphogenesis and commitment. Development 2020, 147, dev169862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.J.; Khaled, W.T. Mammary development in the embryo and adult: A journey of morphogenesis and commitment. Development 2008, 135, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Banerjee, S.; Baker, G.W.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Chowdhury, I. The Mammary Gland: Basic Structure and Molecular Signaling during Development. IJMS 2022, 23, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.; Serna, E.; Bosch, A.; Zaragozá, R.; García, C.; Miralles, V.J.; Sandoval, J.; Viña, J.R.; García-Trevijano, E.R. NF-ĸB as Node for Signal Amplification During Weaning. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 28, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragozá, R.; García-Trevijano, E.R.; Lluch, A.; Ribas, G.; Viña, J.R. Involvement of Different networks in mammary gland involution after the pregnancy/lactation cycle: Implications in breast cancer. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnandis, T.; Ferrer-Vicens, I.; García-Trevijano, E.R.; Miralles, V.J.; García, C.; Torres, L.; Viña, J.R.; Zaragozá, R. Calpains mediate epithelial-cell death during mammary gland involution: Mitochondria and lysosomal destabilization. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnandis, T.; Ferrer-Vicens, I.; Torres, L.; García, C.; Garcia-Trevijano, E.R.; Zaragoza, R.; Viña, J.R. Differential functions of calpain 1 during epithelial cell death and adipocyte differentiation in mammary gland involution. Biochem. J. 2014, 459, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, L.; Ferrer-Vicens, I.; García, C.; Oltra, S.S.; Zaragozá, R.; Viña, J.R.; García-Trevijano, E.R. Isoform-specific function of calpains in cell adhesion disruption: Studies in postlactational mammary gland and breast cancer. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2893–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, L.; Company, S.; Zaragozá, R.; Viña, J.R.; García-Trevijano, E.R. Cleavage and activation of LIM kinase 1 as a novel mechanism for calpain 2-mediated regulation of nuclear dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y.; Sorimachi, H. Calpains—An elaborate proteolytic system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorimachi, H.; Mamitsuka, H.; Ono, Y. Understanding the substrate specificity of conventional calpains. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 853–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Hu, X. Evidence for calpains in cancer metastasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8233–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapovalov, I.; Harper, D.; Greer, P.A. Calpain as a therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2022, 26, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragozá, R.; Bosch, A.; García, C.; Sandoval, J.; Serna, E.; Torres, L.; García-Trevijano, E.R.; Viña, J.R. Nitric oxide triggers mammary gland involution after weaning: Remodelling is delayed but not impaired in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Biochem. J. 2010, 428, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Tian, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, H.; Lu, M.; Wang, H. Calpain-1 mediates vascular remodelling and fibrosis via HIF-1α in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniappan, L.; Okuyama, M.; Javidan, A.; Thiagarajan, D.; Jiang, W.; Moorleghen, J.J.; Yang, L.; Balakrishnan, A.; Howatt, D.A.; Uchida, H.A.; et al. Inducible Depletion of Calpain-2 Mitigates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in Mice. ATVB 2021, 41, 1694–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhouk, R.S.; Bissell, M.J.; Werb, Z. Coordinated expression of extracellular matrix-degrading proteinases and their inhibitors regulates mammary epithelial function during involution. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 118, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedin, P. Pregnancy-associated breast cancer and metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrère, H.; Lenaerts, L.; Borges, V.F.; Schedin, P.; Neven, P.; Amant, F. Postpartum breast cancer: Mechanisms underlying its worse prognosis, treatment implications, and fertility preservation. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2021, 31, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Smyth, G.K. Moderated statistical tests for assessing differences in tag abundance. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2881–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Smyth, G.K. Small-sample estimation of negative binomial dispersion, with applications to SAGE data. Biostatistics 2007, 9, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasch, C.; Plummer, P.N.; Jovanovic, L.; McInnes, L.M.; Wescott, D.; Saunders, C.M.; Schneeweiss, A.; Wallwiener, M.; Nelson, C.; Spring, K.J.; et al. Heterogeneity of miR-10b expression in circulating tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, H.E.; Camps, C.; Buffa, F.M.; Colella, S.; Sheldon, H.; Gleadle, J.M.; Ragoussis, J.; Harris, A.L. MicroRNA-10b and breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2008, 455, E8–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Liu, C.-G.; Veronese, A.; Spizzo, R.; Sabbioni, S.; Magri, E.; Pedriali, M.; Fabbri, M.; Campiglio, M.; et al. MicroRNA Gene Expression Deregulation in Human Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, C.; Moi, L.; Kiselev, Y.; Pedersen, M.I.; Dalen, S.M.; Braaten, T.; Busund, L.-T. Expression and function of the miR-143/145 cluster in vitro and in vivo in human breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerson, A.; Eliraz, Y.; Yehuda, H.; Knight, B.; Crundwell, M.; Ferguson, D.; Lee, B.P.; Harries, L.W. Obesity impacts the regulation of miR-10b and its targets in primary breast tumors. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Pochampally, R.; Watabe, K.; Lu, Z.; Mo, Y.-Y. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-10b promotes cell invasion in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Role of miR-10b-5p in the prognosis of breast cancer. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, D.; Cong, Q.; Bai, C. Biological functions and potential mechanisms of miR-143-3p in cancers (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2024, 52, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wu, N.; Leong, M.C.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Z.; Li, R.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Yao, X.; et al. miR-145 improves metabolic inflammatory disease through multiple pathways. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, E.T.; Bassale, S.; Schedin, T.; Jindal, S.; Johnston, J.; Cabral, E.; Latour, E.; Lyons, T.R.; Mori, M.; Schedin, P.J.; et al. Association Between Postpartum Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Metastasis and the Clinical Features Underlying Risk. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e186997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrère, H.; Floris, G.; Schmidt, M.K.; Neven, P.; Warner, E.; Cardonick, E.; Peccatori, F.A.; Loibl, S.; Maggen, C.; De Mulder, H.; et al. Data describing the poor outcome associated with a breast cancer diagnosis in the post-weaning period. Data Brief 2021, 38, 107354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Breast cancer and breastfeeding: Collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 47 epidemiological studies in 30 countries, including 50,302 women with breast cancer and 96,973 women without the disease. Lancet 2002, 360, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storr, S.J.; Zhang, S.; Perren, T.; Lansdown, M.; Fatayer, H.; Sharma, N.; Gahlaut, R.; Shaaban, A.; Martin, S.G. The calpain system is associated with survival of breast cancer patients with large but operable inflammatory and non-inflammatory tumours treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47927–47937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, T.; Salomonis, N.; Nuyten, D.S.A.; van de Vijver, M.J.; Gusterson, B.A. A Mouse Mammary Gland Involution mRNA Signature Identifies Biological Pathways Potentially Associated with Breast Cancer Metastasis. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2009, 14, 99–116, Erratum in: J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia. 2009, 14, 117–119.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Su, L.; Liu, Z. Critical role of calpain in inflammation. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, T.R.; O’Brien, J.; Borges, V.F.; Conklin, M.W.; Keely, P.J.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Marusyk, A.; Tan, A.-C.; Schedin, P. Postpartum mammary gland involution drives progression of ductal carcinoma in situ through collagen and COX-2. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, N.F.; Martin, L.J.; Yaffe, M.J.; Minkin, S. Mammographic density and breast cancer risk: Current understanding and future prospects. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniappan, L.; Javidan, A.; Jiang, W.; Mohammadmoradi, S.; Moorleghen, J.J.; Katz, W.S.; Balakrishnan, A.; Howatt, D.A.; Subramanian, V. Calpain Inhibition Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Fibrosis in Diet-induced Obese Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuda, D.; Randriamboavonjy, V.; Fleming, I. Regulation of calpain 2 expression by miR-223 and miR-145. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieckmann, K.; Winnerling, N.; Huebecker, M.; Leyendecker, P.; Ribeiro, D.J.S.; Gnad, T.; Pfeifer, A.; Wachten, D.; Hansen, J.N. AdipoQ-a simple, open-source software to quantify adipocyte morphology and function in tissues and in vitro. Mol. Biol. Cell 2022, 33, br22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puebla, S.; Gimeno, A.; Ortíz-Zapater, E.; Zaragozá, R.; Viña, J.R.; García-Trevijano, E.R. The Length of Lactation and Model of Weaning Modulate Key Regulatory Nodes of Murine Mammary Gland Involution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110501
Puebla S, Gimeno A, Ortíz-Zapater E, Zaragozá R, Viña JR, García-Trevijano ER. The Length of Lactation and Model of Weaning Modulate Key Regulatory Nodes of Murine Mammary Gland Involution. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110501
Chicago/Turabian StylePuebla, Sara, Amparo Gimeno, Elena Ortíz-Zapater, Rosa Zaragozá, Juan R. Viña, and Elena R. García-Trevijano. 2025. "The Length of Lactation and Model of Weaning Modulate Key Regulatory Nodes of Murine Mammary Gland Involution" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110501
APA StylePuebla, S., Gimeno, A., Ortíz-Zapater, E., Zaragozá, R., Viña, J. R., & García-Trevijano, E. R. (2025). The Length of Lactation and Model of Weaning Modulate Key Regulatory Nodes of Murine Mammary Gland Involution. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110501







