Abstract
Periodontitis (PD) is a multifactorial, progressive inflammatory disease affecting the teeth-supporting tissues, characterized by an imbalance of the oral microbiota and the presence of bacterial biofilms leading to host response. Nowadays, reliable biochemical markers for early and objective diagnosis, and for predicting disease progression, are still lacking. Our previous proteomic investigations revealed the significant overexpression of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in periodontal pocket tissue, gingival crevicular fluid (GCF), and tooth-surface-collected material (TSCM) from PD patients in comparison to periodontally healthy controls, proposing it as a possible biomarker of PD. This study aimed to evaluate the expression of GAPDH in saliva, a more accessible, non-invasive, and clinically relevant oral sample. The whole saliva was analyzed by a preliminary mass spectrometry-based proteomic approach, identifying significantly increased levels of GAPDH also in salivary samples from periodontal-affected subjects. These data were further validated by enzyme-linked-immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Additionally, protein–protein interaction networks were generated through the Human Protein Atlas database, using different datasets (OpenCell, IntAct, and BioGRID). Bioinformatic analysis provided noteworthy GAPDH-associated networks potentially relevant to periodontal pathology. The scientific significance of this study lies in the detection of salivary GAPDH as a novel strategy to advance periodontal clinical diagnostics from the perspective of a non-invasive screening test. In correlation with other protein markers, salivary GAPDH could constitute a promising set of distinctive and predictive targets to enhance early diagnosis of PD, disease monitoring, and treatment planning in periodontology.
1. Introduction
The first findings relating to the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) enzyme date back to the first half of the last century [1]. In normal cellular conditions, the human cytoplasmic form of GAPDH exists principally as a tetramer of four equal 37 kDa subunits, arranged in a quaternary assembly [2,3]. The homotetramer is also defined as a dimer of dimers, with three 2-fold-symmetry axes [4,5,6]. The crystal structure was determined by X-ray diffraction, and high-resolution ribbon drawing of the GAPDH tetramer highlights the tridimensional configuration of the four subunits, each of which comprises two conserved functional domains [3]. Specifically, human GAPDH contains 335 amino acids and constitutes an N-terminal domain, comprising the NAD+-binding site (residues 1–150 and 317–335), and a highly conserved catalytic domain, containing the substrate-binding site (amino acids 151–316), corresponding to the C-terminal domain [5]. GAPDH is ubiquitously expressed in nature, is abundant in cells, and is found in all domains of life. For a long time, it was considered just a housekeeping glycolytic enzyme, mainly present in the cytoplasm, with a key role in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis [1]. Effectively, GAPDH is a highly conserved, NAD+-dependent, catalytic enzyme within the glycolytic pathway. It reversibly catalyzes an essential energy-yielding reaction in carbohydrate metabolism, that is, the 6th step of the aerobic glycolytic pathway, namely the reversible oxidative phosphorylation of D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-diphospho-glycerate, in the presence of NAD+ (as co-factor, in oxidized form) and inorganic phosphate (as co-substrate), with the production of NADH + 2H+ (NAD in reduced form and two hydrogen ions, respectively) (InterPro database). The discovery of GAPDH in other cellular compartments besides the cytoplasm, including the nucleus, plasma membrane, and mitochondria, has motivated an in-depth exploration of its function and meaning in both human health and disease conditions [7]. It has been defined as a multifaceted protein, or a “moonlighting protein” [8,9], since, in addition to its primary well-outlined role in glycolysis, it was found involved also in several non-metabolic processes, depending on its subcellular localization, such as apoptosis [10,11], intracellular signaling and transduction, abiotic stress [7,12], endocytosis [13], control of gene expression [14], DNA replication and repair [15], modulation of mRNA stability [16], regulation of energy metabolism [17], oxidative stress response [18], and membrane trafficking [19]. These activities are essentially regulated by biomolecular interactions, protein oligomerization, changes in cellular location, and posttranslational modifications, such as phosphorylation, nitrosylation, acetylation, and N-acetylglucosamine modification [20]. Other studies also provide evidence that GAPDH is implicated in various diseases, including cancer [21,22,23,24], neurodegenerative disorders [25,26,27,28], and those of pathogenic origin [4]. Therefore, human GAPDH is directly considered a useful molecular target for the treatment of numerous diseases [29].
Periodontitis (PD) is a chronic inflammation and a serious infection that affects and damages the tooth-supporting components, such as the periodontal ligament, alveolar bone, and gingival tissue around teeth [30]. In severe and aggressive forms, this condition can be worsened by the formation of a deep periodontal pocket, leading to tooth loss. Usually, the development of periodontal disease begins with the formation of bacterial plaque by microbial pathogens, and, if left untreated, can evolve over time into PD [31]. Despite advances in technology and growing awareness of good oral hygiene practices, PD still represents a public health problem today. Particularly severe PD is estimated as the sixth most prevalent disease worldwide [32]. Unfortunately, although progress has been made in various research areas, such as microbiology and genetics, to date, the periodontal diagnosis is still based on clinical examination and radiological imaging; a hopeful future perspective is molecular diagnostics [33]. From this point of view, the highly interdisciplinary research field of oral proteomics can be applied in dentistry [34] to deepen the knowledge of PD, as it enables the identification of proteins in cells, tissues, and body fluids, allowing us to gain a comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying pathologies and to discover novel biomarkers [35,36]. In the proteomic era, several oral samples were analyzed in an attempt to characterize oral biomarkers for PD, such as periodontal gingival tissue and gingival crevicular fluid (GCF), tooth pulp, dentin, root canal content, secretion from salivary glands, periodontal ligament, dental stem cells, and saliva [37]. Undoubtedly, the latter is the most advantageous and attractive sample among those mentioned above, since it is easily and abundantly accessible, and its collection is totally safe and non-invasive for patients, with a good cost–benefit ratio [38]. Moreover, whole saliva contains proteins from salivary glands, epithelial cells, and microorganisms, thus providing an overall assessment of periodontal status. In addition, it contains most of the serum constituents, so it can provide valuable information, not only regarding the oral cavity status (for example, dental caries, periodontal diseases, oral cancer) but also about the systemic disease status [39]. However, the proteomic analysis of human saliva is challenging due to the wide dynamic range of protein abundances, spanning several orders of magnitude [40]. To overcome this drawback, different depletion and fractionation techniques have been developed to maximize the coverage of the salivary proteome, enriching the detection of the low-abundance fraction. Nevertheless, depletion methods may lead to the concomitant removal of non-targeted molecules, as previously demonstrated [41].
Currently, salivary diagnostics is applied in numerous conditions, such as autoimmune diseases (Sjogren’s syndrome, multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis), genetic disorders (e.g., cystic fibrosis), bacterial, viral, and fungal infections, cardiovascular diseases, malignancy, metabolic bone disorder, and renal diseases, as well as for drug-level monitoring, occupational and environmental medicine, psychological stress research, and forensic evidence [42,43]. Recently, inflammatory mediators present in the oral fluids and blood samples of type 1 diabetes mellitus adult patients diagnosed with periodontal disease have been proposed as novel diabetes biomarkers, and as indicators of the patient’s degree of susceptibility to worsening of the periodontal state [44].
In our previous proteomic works conducted on different oral samples obtained from patients with PD, namely, periodontal pocket gingival tissue [37,45], GCF [46], and tooth-surface-collected material (TSCM) [47], we reported the overexpression of a common protein, that is, GAPDH.
The aim of the present preliminary study was to search for GAPDH in saliva samples from periodontopathic subjects compared to periodontally healthy controls, to assess the presence of this molecule in a more advantageous oral sample. The analyses were performed by electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) coupled to liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), and through enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA test) as an orthogonal validation and quantification method. Additionally, GAPDH-associated protein interaction networks were searched and created from the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) database.
2. Results
2.1. Protein Band Analysis and GAPDH Identification by LC-MS/MS
After salivary proteins’ separation by SDS-PAGE, the densitometric analysis of the protein bands by the QuantityOne 1D image analysis software revealed a significantly different band at 37 kDa between healthy and pathological samples (the original, uncropped, and unprocessed gel image is reported in Supplementary Figure S1). Specifically, the band intensity level (expressed as OD × volume) was found to be significantly higher in periodontal patients (0.149 ± 0.036, mean ± SD) in comparison to healthy control subjects (0.095 ± 0.023, mean ± SD), resulting in a p-value of 0.018.
The protein mixture extracted from the 37 kDa band was subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis, thus leading to the identification of GAPDH in the salivary proteome of PD patients and controls. The identification was achieved by LC-ESI-QO-MS/MS mass spectrometer, through the analysis of raw data by a Mascot MS/MS ion search, with the SwissProt database. GAPDH results were identified with the entry name G3P_HUMAN, P04406 as the primary accession number, and with an experimental monoisotopic mass (Mr) of 36201 Da. The exponentially modified protein abundance index (emPAI), which estimates the absolute content of a given protein in a complex mixture, was 94.87 in healthy controls and 140.76 in periodontopathic patients, respectively, with a 1.5-fold increase (Table 1). The number of significant matching peptides, as well as the number of significant sequences, are reported in the following columns.

Table 1.
GAPDH identification by LC-MS/MS analysis in saliva samples of controls and periodontal patients.
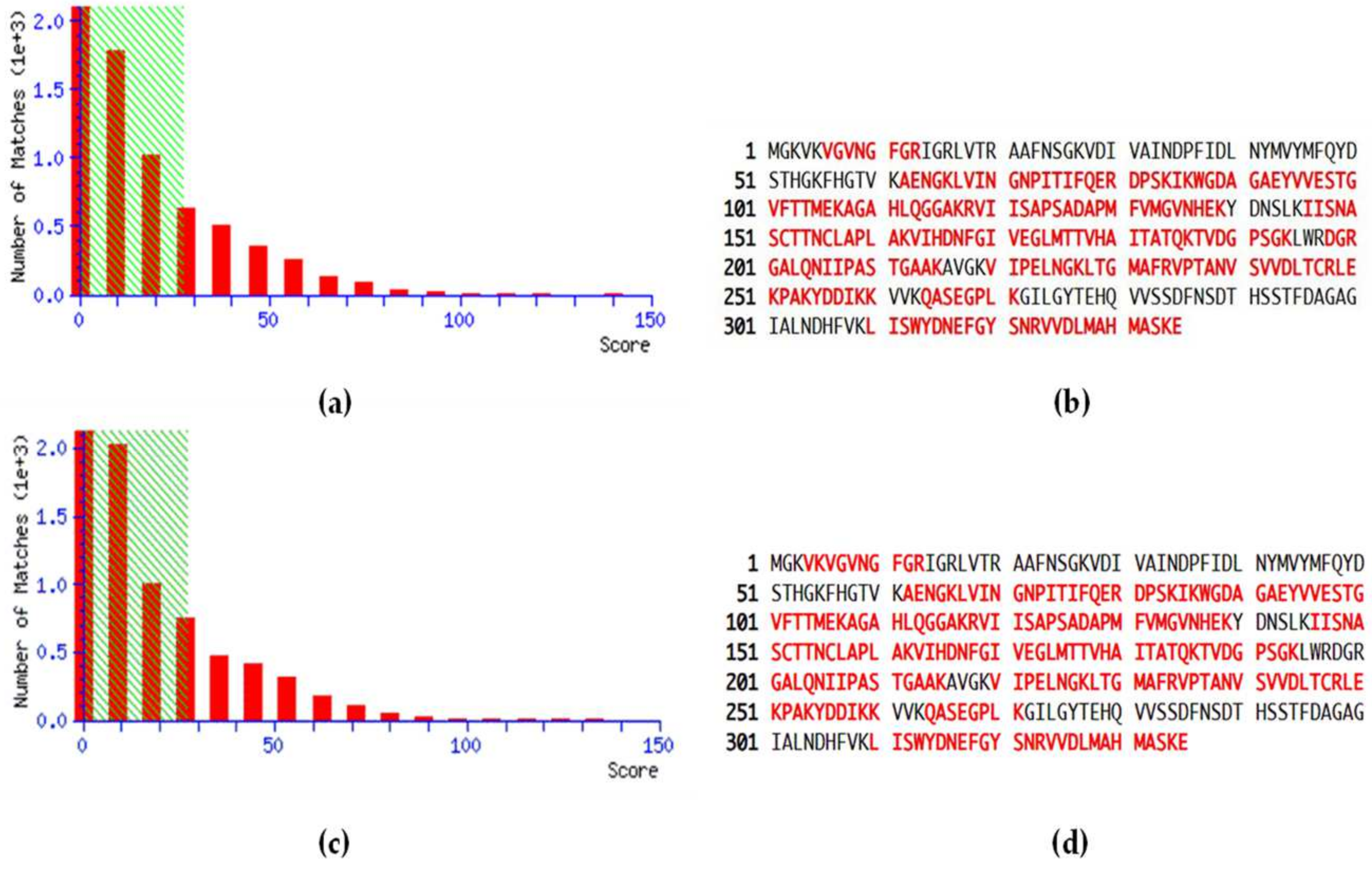
MS data related to the peptide score distributions are shown in Figure 1, for healthy (Figure 1a) and pathological samples (Figure 1c). The peptide score distribution is represented by the ion score, where ion score is −10log(P), and P is the probability that the observed match is a random event. On average, individual ion scores greater than 27 (beyond green shading) indicate identity or extensive homology (p < 0.05). Moreover, a high percentage of peptide sequence coverage was achieved for both healthy controls (Figure 1b) and pathological patients (Figure 1d), corresponding to 68% and 67%, respectively.
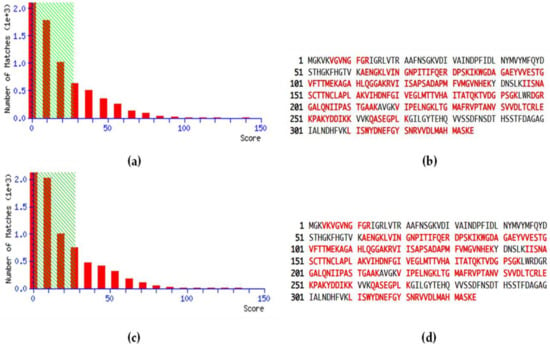
Figure 1.
Peptide score distribution resulting from the search in the SwissProt database for GAPDH in healthy samples (a) and periodontopathic samples (c). The x-axis indicates the probability-based mowse score, and the y-axis the numbers of hits. Protein sequence coverage: the matching peptides are shown in bold red, corresponding to 68% in healthy controls (b) and 67% in PD patients (d).
Some representative MS/MS fragmentation spectra of matching prototypic peptides, used for the identification of GAPDH, are reported in Supplementary Figure S2.
2.2. Salivary GAPDH Quantification and Validation
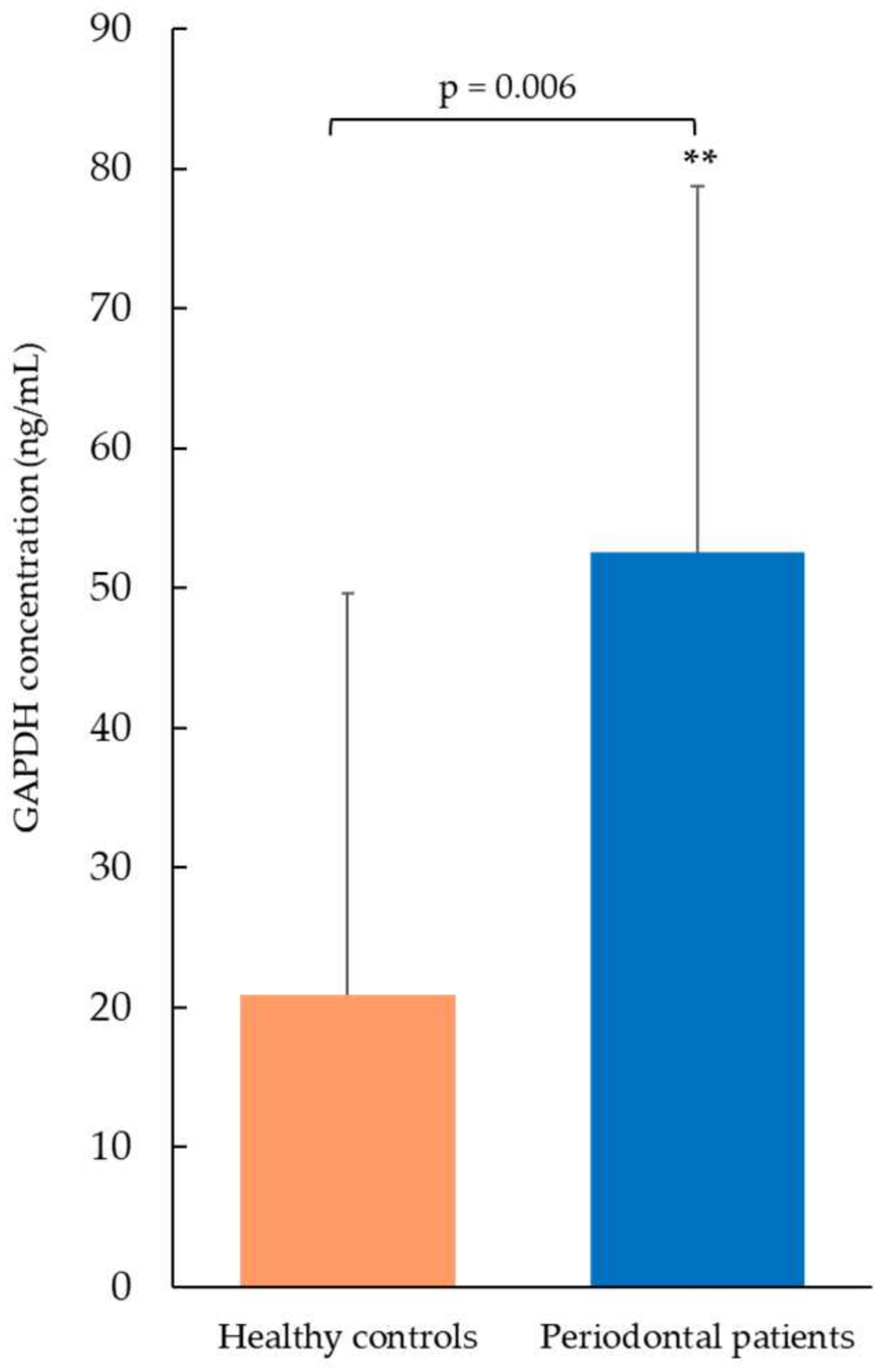
The GAPDH concentration was measured in saliva samples by ELISA (Figure 2). Periodontal patients showed significantly higher levels of GAPDH (52.6 ng/mL ± 26.1, mean ± SD) compared to the healthy control group (20.9 ng/mL ± 28.7, mean ± SD, p-value = 0.006). These findings were consistent with those obtained by proteomic analysis. A 7-point standard calibration curve, ranging from 1.56 to 100 ng/mL, was applied to calculate sample concentrations. All salivary values, both from healthy controls and pathological patients, fell within the limits of the calibration curve, and therefore no sample needed to be diluted and re-tested.
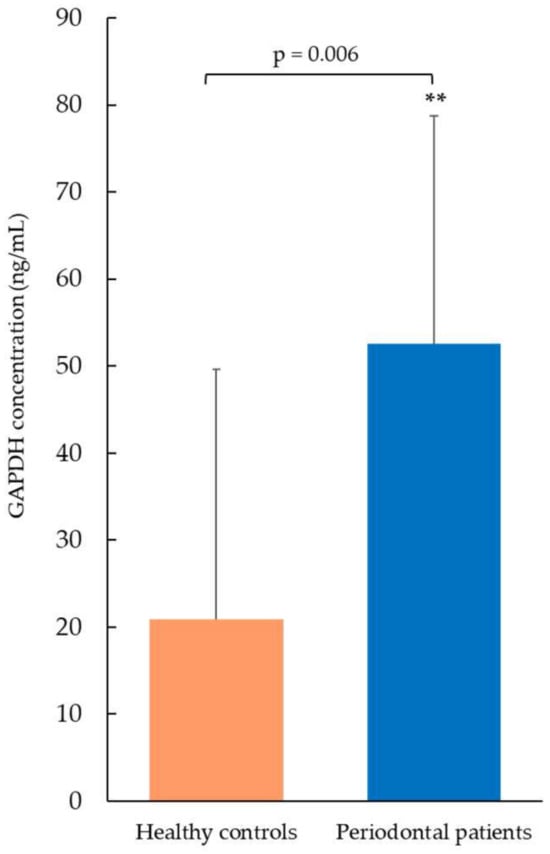
Figure 2.
GAPDH concentration measured by ELISA test. Periodontal patients showed significantly increased salivary GAPDH levels compared to healthy controls (** p < 0.01). Data are expressed as mean ± SD, and statistical differences were obtained by Student’s t-test.
2.3. GAPDH Identification in Our Previous Proteomic Studies
GAPDH was previously identified in our proteomic studies performed in different oral samples (Table 2). It was identified in periodontal pocket gingival tissue by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) coupled to Nano LC-ESI-Q-ToF, using the UniProt database [45], and confirmed through SDS-PAGE in association with LC-ESI-QO-MS/MS analysis, using the neXtProt database for identification results [37]. Moreover, GAPDH was detected in GCF samples of patients with severe PD, with a +2.00-fold change in expression in diseased sites compared to periodontally healthy ones [46]. Additionally, LC-MS/MS analysis of both protein bands and spots, obtained from TSCM samples of patients diagnosed with PD and candidates for resective bone therapy, revealed different isoforms of GAPDH [47].

Table 2.
Previous identification of GAPDH in different periodontal oral samples by proteomics.
2.4. Interaction Networks
The network plots showing the GAPDH-related genes, achieved via the HPA database according to three different datasets, are displayed in Figure 3.
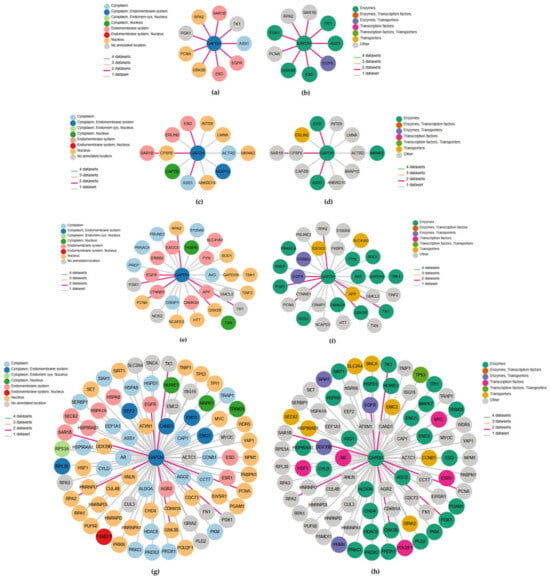
Figure 3.
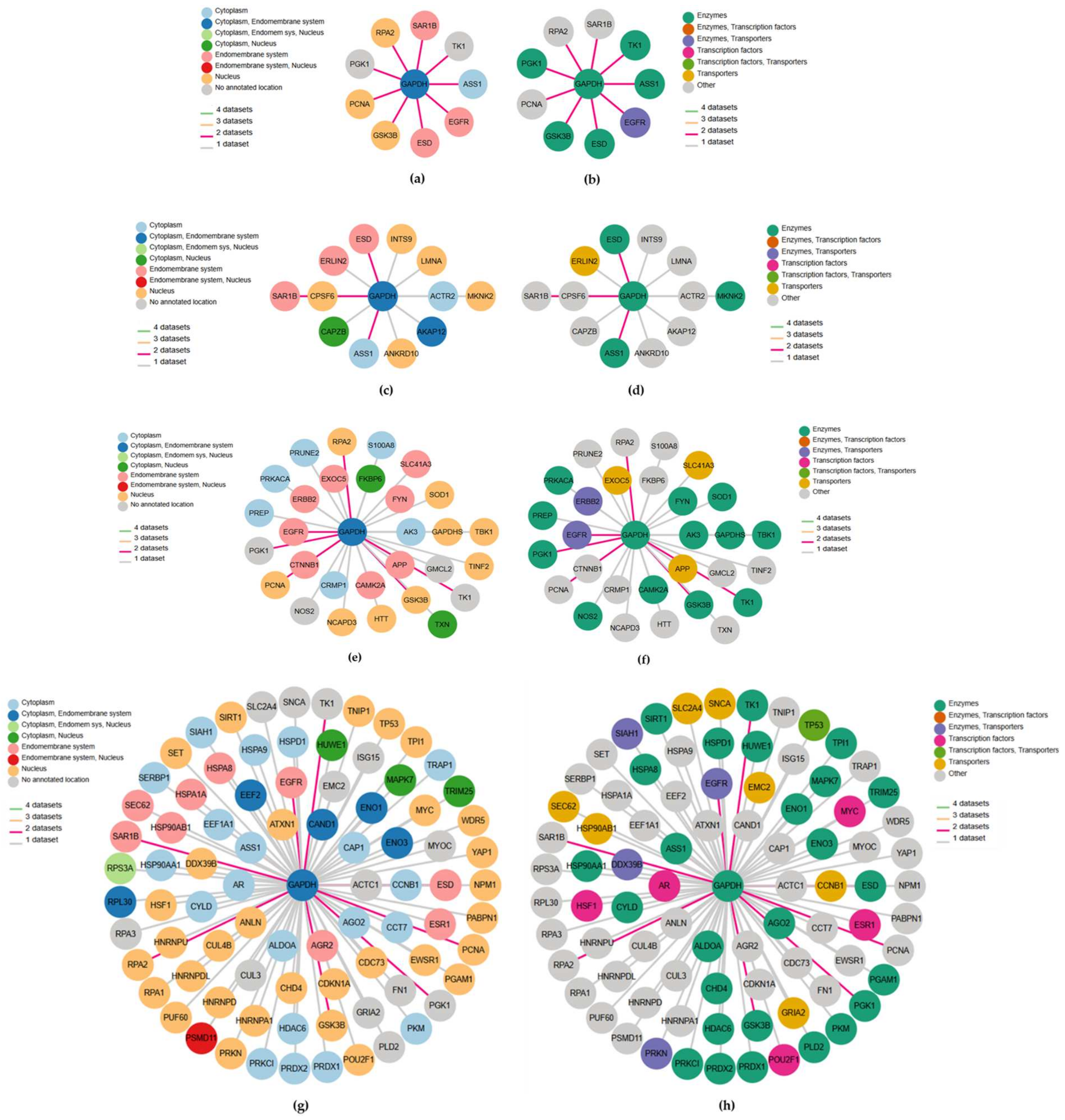
GAPDH interaction networks from different databases colored according to subcellular location and protein class, respectively, for the first-level consensus (a,b), OpenCell (c,d), IntAct (e,f) and BioGRID (g,h). In each network plot, the nodes correspond to genes and edge color refers to the number of datasets to which the interaction belongs.
A first-level consensus network chart was also included. In each network plot, the nodes represent genes and are colored according to their subcellular location (Figure 3a,c,e,g) and protein class (Figure 3b,d,f,h), respectively, while edge colors refer to the number of datasets for the interacting pair. The first-level consensus network showed nine interactions (ASS1, EGFR, ESD, GSK3B, PCNA, PGK1, RPA2, SAR1B, TK1) present in at least two of the queried datasets (Figure 3a,b). With OpenCell, 12 significant GAPDH interaction partners were found (Figure 3c,d), while the molecular interaction database IntAct recognized 29 direct correlations and physical associations with high and medium confidence (Figure 3e,f). Finally, a total of 83 physical multi-validated connections were provided by BioGRID (Figure 3g,h). All the identified GAPDH-interacting key-player genes derived from each dataset, comprising the first-level consensus, are shown in Table 3. The first column refers to the gene symbols (corresponding to those reported in Figure 3), here listed in alphabetical order, followed by the full gene names. The last column shows the main function provided by the HPA database according to gene expression across single cell types or tissue expression cluster. Overall, considering the three queried datasets, a total of 124 key genes interacting with GAPDH were identified (repeated ones are evidenced in italics and are compliant with those of the first-level consensus). Genes previously identified in our PD studies, or those potentially relevant to periodontal disease, are highlighted in bold.

Table 3.
List of genes correlated to GAPDH based on different interaction databases.
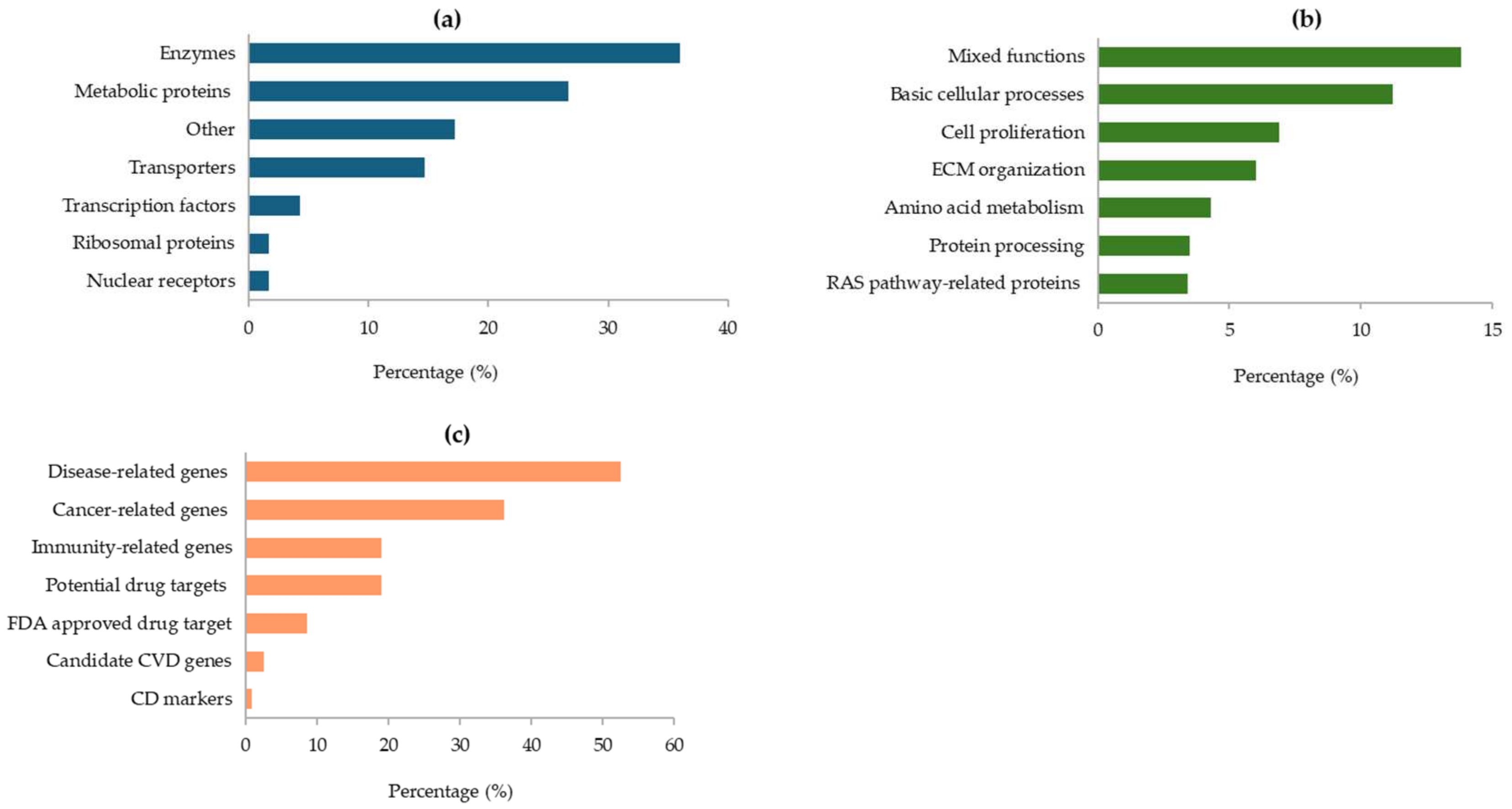
As illustrated in Figure 4, most of the proteins encoded by the GAPDH-related genes are enzymes (36%), other metabolic proteins (27%), or transporters and transcription factors (Figure 4a). At cellular level, their main functions are essentially linked to basic cellular processes, cell proliferation, and organization of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in the connective tissue. Furthermore, some proteins are involved in amino acids metabolism and protein processing, while others are related to the RAS pathway (Figure 4b). In addition, many of the GAPDH-associated genes were found to be correlated with various diseases (53%) and the immune response (19%). Notably, several genes are potential drug targets, and some of them have already been approved by the FDA (Figure 4c).
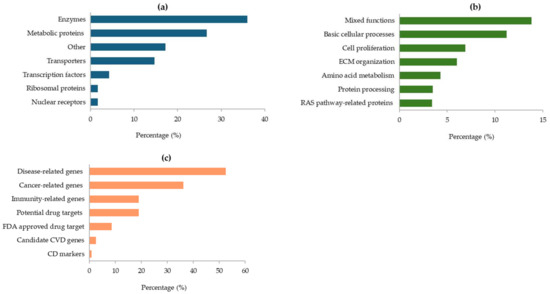
Figure 4.
Protein classes assigned by the HPA database for proteins encoded by GAPDH-related genes (a); main cellular functions of the identified proteins (b); roles of GAPDH-related genes in human diseases (c). All data are derived from the HPA database.
Interestingly, proteins involved in immunity, ECM organization, amino acid metabolism, and protein processing were previously reported in our proteomic studies on PD [37], as further discussed below.
3. Discussion
Recent advances in mass spectrometry-based proteomics methodologies have opened new avenues to acquiring relevant information in the dental field [34]. In this regard, saliva is the chief oral biofluid in terms of importance and interest in clinical diagnostics, and Salivaomics is emerging as a new tool able to offer substantial advantages to deepen the study of oral diseases [48,49]. Over the past few years, salivary proteomic research applied to PD has encompassed different applications, including the understanding of the disease mechanisms, as well as the discovery of periodontal-specific biomarkers [39,50]. Currently, the use of salivary biomarkers in routine clinical settings is still evolving, and there is growing interest in their potential, mainly due to the non-invasive nature of saliva collection, ease of repeating sampling, and relatively low cost [51].
The purpose of the present proteomic work was to investigate GAPDH as a possible PD-related biomarker. Detection, quantification, and validation data were obtained by SDS-PAGE (Supplementary Figure S1) and LC-MS/MS analysis (Figure 1, Table 1) and through the ELISA test (Figure 2), respectively, demonstrating a significant overexpression of salivary GAPDH in PD patients compared to periodontally healthy control subjects. In addition to its primary activity in glycolysis, the eukaryotic form of GAPDH has multiple known functions. For example, it has been demonstrated that its accumulation within the nucleus induces cellular apoptosis, as it takes part in the gene expression program and transcriptional activation [7,11,52]. The finding of high GAPDH levels in oral samples from patients with PD may be associated with the destruction of the periodontal gingival tissue caused by intensified cell death. In support of this hypothesis, increased apoptosis events and apoptotic pathways were previously observed by other authors in periodontal gingival tissue, even if the exact mechanisms related to these processes remain unclear [53,54]. The occurrence of apoptotic cells, principally neutrophils, in the gingival tissue of adult subjects with chronic PD in comparison with healthy donors, was demonstrated by Gamonal et al., suggesting that apoptosis is implicated in the pathogenesis of the disease, and that apoptotic processes are involved in the inflammatory response associated with periodontal tissue destruction [55]. The presence of GAPDH could also be combined with the synthesis of pro-apoptotic proteins, like BAX, c-JUN, and GAPDH itself (InterPro database), inducing danger signals and the consequent stimulation of proinflammatory processes, typical of PD. Moreover, GAPDH aggregation mediates cell death under oxidative stress [56]. It has been proven that GAPDH is a key mediator of many oxidative stress responses, involving its nuclear translocation and induction of apoptosis [12]. Cytosolic GAPDH may work as a sensor for redox signals and an information center, with the aim of transducing these signals into appropriate reactions [57]. GAPDH is also involved in other nuclear events, such as DNA replication or repair, RNA export/transport, membrane fusion, and microtubule clustering (HPA database). In this regard, GAPDH binding to actin and tropomyosin may have a role in cytoskeleton assembly (InterPro database). Elevated amounts of actin [45,58] and GAPDH [45] were previously detected in our proteomic studies conducted in periodontal pocket tissue, probably indicating an attempt to restore the damaged gingival tissue. An actin-related protein was also found in the present study by the HPA database (Figure 3, Table 3).
Several oral bacteria exhibit GAPDH on their surface, where it acts as an adhesin. Surface GAPDH binds host ECM proteins (e.g., fibronectin, laminin) and plasminogen, which can promote initial colonization and tissue invasion. Oral streptococci (early colonizers) use GAPDH in co-aggregation and matrix binding, which may facilitate later colonizers associated with PD [59]. Long fimbriae of Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis) bind human GAPDH and interact with streptococcal surface GAPDH (e.g., S. oralis), promoting the formation of mixed biofilms and epithelial invasion, key early events in periodontal pathogenesis [60]. Moreover, bacterial surface moonlighters (including GAPDH in multiple species) act as plasminogen receptors; once converted to plasmin, this promotes fibrin/ECM degradation and pathogen tissue penetration, mechanisms also observed in organisms relevant to periodontal ecology [61]. In addition, GAPDH plays a role in microbial virulence, as it is involved in evading host immune surveillance. Because of this property, GAPDH has been suggested as an eligible target for a vaccine to limit diseases caused by various pathogens [62]. This assumption could be applied to PD as well, since it is triggered by bacterial microorganisms, or groups of specific microorganisms. On the other hand, GAPDH also exhibits antimicrobial functions during epithelial infection, protecting tissue through antifungal strategies and immunomodulation [63]. Furthermore, it participates in innate immunity, by promoting TNF-induced NF-kB activation and type I interferon production [64]. In accordance with these activities, the up-regulation of salivary GAPDH detected in PD-affected patients might enhance immune stimulation for defensive and/or reparative purposes against the ongoing disease, thus becoming a new potential therapeutic factor. An active involvement of the immune system was also confirmed by the interaction networks, since a considerable number of GAPDH-associated genes were linked to the innate or adaptive immune response (Table 3). Based on these assumptions, the high amount of salivary GAPDH found in PD could originate from host cell secretion or cell dead release (e.g., neutrophils, gingival cells), active secretion, or bacterial production (e.g., S. oralis, P. gingivalis).
Additionally, the implication of GAPDH in different diseases has been widely documented, comprising those of cardiovascular, diabetic, degenerative, and pathogenic origins [4]. Accordingly, GAPDH may have a possible role in PD due to the microbial pathogenic origin of this disease. The involvement of GAPDH has also been proved in some neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Machado–Joseph, and Huntington’s diseases, in association with abnormal neuronal apoptosis. GAPDH can bind the gene products of these diseases through the interaction with RNA and other proteins, thus improving neuronal survival by reducing the synthesis of pro-apoptotic proteins (InterPro database). From this perspective, GAPDH could also be considered a potential therapeutic target in PD.
In this work, the interaction networks between GAPDH and other proteins/genes were widely investigated. Protein–protein interactions are crucial for several cellular mechanisms, such as gene expression and control, antibody–antigen binding, and cell signaling. Frequently, the alteration or blockage of these ways can lead to diseases, so knowledge of the interaction networks can contribute to the understanding of pathological processes. The HPA is the largest and most comprehensive database for protein spatial distribution in cells and tissues, generating spatial maps of human protein-coding genes [65]. The interaction networks for GAPDH were based on data from OpenCell, IntAct, and BioGRID datasets, integrated with data related to protein function and classification (Figure 3, Table 3). Notably, some proteins encoded by these genes were previously detected in our proteomic studies conducted on various oral samples from PD patients. Peroxiredoxin 1 (PRDX1), peroxiredoxin 2 (PRDX2), and triosephosphate isomerase (TPI1), together with some related protein forms (like protein S100-A9, alpha enolase, ENOA, and the beta-1 form of heat shock protein, HSPB1) were found up-regulated in the first preliminary proteomic analysis performed directly on periodontal pocket tissue [45]. Then, the eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha 1 (EEF1A1), the enzyme pyruvate kinase (PKM2), as well as other protein partners, such as Hsp60 and Hsp70, were detected in TSCM proteome of periodontopathic patients by 2-DE coupled to LC-MS/MS analysis [47]. In addition, EEF1A1 was also identified in pocket-associated gingival tissue from patients with severe PD, concurrently with fibronectin 1 (FN1) [37]. Recently, in our latest proteomic work carried out on saliva samples, PRDX1, TPI1, thioredoxin (TXN), phosphoglycerate mutase 1 (PGAM1), and correlated forms of superoxide dismutase (SOD2), peroxiredoxin-6 (PRDX6), protein S100-A9, heat shock proteins (HSPB1, Hsp90-beta), and proteasome (subunits alpha and beta), were revealed to be overexpressed in patients with advanced PD when compared to periodontally healthy subjects [66]. Therefore, the present study contributed to further supporting their biological and diagnostic relevance, validating the arguments in favor of using these key players as focal targets for the treatment of PD. Likewise, the crucial mediators interacting with GAPDH mainly included enzymes, as also reported in saliva [66], proteins involved in ECM organization in connective tissue, as found in damaged periodontal pocket gingival tissue [37], and several immunity-related proteins (Figure 4). Various forms of immunoglobulins were found early on, especially in GCF [46] and periodontal tissue [37]. It is remarkable to note that certain GAPDH-related genes reported in Table 3 are recognized as potential drug targets (e.g., ERLIN2, implicated in salivary secretion, SOD1, ENO3, HSPD1, TPI1), and some of these are already approved by the FDA (e.g., EEF2 and FN1) (data inferred from the HPA database).
A comprehensive understanding of the molecular determinants and signaling pathways involving GAPDH might allow its potential rational targeting as a modulation/regulation point or selective biomarker for predictive and therapeutic applications in pathological conditions, such as PD. Advances in proteomic-based technologies promise to constantly help in understanding what is still unexplored in oral health and disease, gradually leading to the transition from laboratory research to clinical practice, through the discovery and validation of potential biochemical markers for use in daily saliva-based testing, in addition to clinical scores [67].
At present, PD is diagnosed after periodontal damage has already occurred. Moreover, the diagnosis is subjective and must be performed by trained and experienced operators to be validated. The best periodontal diagnosis of the future should be, above all, an early diagnosis, made before such damage occurs, and should combine radiological, clinical, and laboratory assays [33]. Accordingly, the unbiased protein biomarkers identified in our studies could support the feasibility of translating proteomic findings into practical high-throughput screening tests, such as saliva-based protein microarrays, for an objective early diagnosis and desirable routine periodontal monitoring.
3.1. Final Remarks
GAPDH is more than just a glycolytic enzyme in the periodontal niche. In PD, it may contribute to colonization by P. gingivalis and other pathogens, immune evasion, and proinflammatory signaling. This is a classic example of a bacterial housekeeping enzyme, which acquires moonlighting roles in pathogenesis, helping bacteria survive in the hostile periodontal pocket while amplifying the destruction of host tissue.
GAPDH was found to be overexpressed in all types of oral samples previously analyzed (Table 2), namely, periodontal pocket gingival tissue [37,45], GCF [46], and TSCM [47], and now that is also confirmed in saliva of patients with severe PD. Furthermore, several important GAPDH-interacting proteins, such as PRDX1, PRDX2, TPI1, EEF1A1, FN1, PKM2, TXN, and PGAM1, earlier detected in other proteomic studies, were confirmed by data from the HPA database analysis, together with some partner proteins (i.e., ENO1, ENO3, protein S100-A8, SOD1, HSPD1, other forms of Hsp60, Hsp70, and proteasome). These are key findings, as the use of multiple biomarkers, representing different components and mechanisms of complex disease pathways, can provide a broader evaluation of the disease itself [68]. A good biomarker is not conceived as a single gold standard, but rather as a cluster of multiple molecules.
3.2. Limitations and Future Directions
Further validations are needed to assess disease specificity, comparing the expression profiles in other oral inflammatory conditions, such as gingivitis or mucositis in longitudinal studies, to better define the discriminatory potential of these candidate biomarkers. Subsequent confirmation of the current preliminary results in a larger, independent cohort will be planned. This could allow for the calculation of diagnostic performance metrics, such as sensitivity, specificity, and ROC curve/AUC, to perform a diagnostic efficacy evaluation. Moreover, additional key objectives will be to define the source of elevated salivary GAPDH concentrations found in PD, as well as to experimentally validate the specific mechanisms in which it is involved.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
Dithiothreitol (DTT), iodoacetamide, 2X Laemmli sample buffer, ampholyte pH 3–10, Protein assay Dye Reagent, Precision Plus Protein Standard - All Blue, and Coomassie Blue G-250 were purchased from Bio-Rad Laboratories (Milan, Italy). Trichloroacetic acid, urea, thiourea, trifluoroacetic acid, 3-[(3-Cholamidopropyl)-dimethylammonium]-propane-sulfonate (CHAPS), bovine serum albumin, and 2-mercaptoethanol were from Merck KGaA (Milan, Italy). Precast gel Bolt™ 4–12% Bis-Tris Plus and MES SDS-PAGE BoltTM Running Buffer were from Life Technologies Italia (Monza, Italy). Trypsin Gold Mass Spectrometry grade was furnished from Promega Corporation (Milan, Italy). The solvents, acetone, acetonitrile, and glacial acetic acid, all of mass spectrometry purity, were from Carlo Erba Reagents (Milan, Italy). Versylene sterile water (Fresenius Kabi, Isola della Scala, Italy) was used for all dilutions, electrophoresis, and MS protocols.
4.2. Enrollment of Study Participants
The participants in this study were enrolled at the Periodontology Unit of Dentistry and Oral-Maxillofacial Surgery of the University Hospital of Modena, Italy, after approval of the local Health Service Ethic Committee, Emilia-Romagna region (protocol code n. 3968/2017, registration C.E. n. 315/17, date of approval 24 October 2017, and supplementary amendment protocol AOU n. 0026796/22, date of approval 21 September 2022). All the enrolled individuals, selected from January 2023 to February 2024, were fully informed about the procedures, before signing an informed consent to participate, according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
A total of 30 subjects in good general health were recruited, divided into a control group composed of 20 periodontally healthy individuals (9 males/11 females), with a mean age of 24.7 ± 4.0 years (range 18–32), found free of gingivitis and PD after a dental examination, and a pathological group, consisting of 10 patients with grade III/IV PD [69], (4 males/6 females) with a mean age of 52.9 ± 8.3 years (range 43–65 years), referred to dental and periodontal therapy. The stringent screening criteria included systemically healthy subjects aged between 18 and 65 years, who were non-smokers, not pregnant or lactating, and not undergoing pharmacological treatments (comprising anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics), without history of alcohol abuse and in the absence of diabetes, bone diseases, inflammatory conditions, and recent infections [70]. All dental–periodontal procedures and clinical measurements were previously reported in detail [37,46,66].
4.3. Saliva Collection and Salivary Protein Extraction and Quantification
To reduce variability due to the circadian rhythm and external factors (such as food, beverages, and oral hygiene products), saliva samples were collected in the morning from subjects who had not eaten, drunk, brushed their teeth, or used mouthwash for at least 30 min prior to collection. This protocol aimed to control for variables in salivary composition between individuals, thus ensuring more accurate data comparability.
Whole saliva samples were harvested using oral salivary swabs SalivaBio (Salimetrics, State College, PA, USA), that were centrifuged at 1500× g for 15 min at +4 °C. Then, the concentrated samples were aliquoted in sterile Eppendorf tubes and stored at −80 °C until further analysis.
Subsequently, proteins were extracted from saliva as described by Jessie et al. [71]. In the first step, saliva samples were precipitated overnight at –20 °C, with a precipitation solution composed of 90% acetone/20% trichloroacetic acid (TCA)/20 mM DTT. The protein precipitate, obtained by centrifugation at 15.000× g, for 30 min, at +4 °C (Centrisart® A-14C, Sartorius) was first washed with 90% acetone/20 mM DTT, and subsequently with 80% acetone/10 mM DTT. Finally, the protein pellet was resuspended in 30 μL of rehydration buffer, composed of 6 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 4% CHAPS, and 25 mM DTT, 0.2% ampholyte pH range 3–10.
The total protein content of each sample was quantified by the spectrophotometric Bradford method, using the protein assay dye reagent (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA), and bovine serum albumin was the standard for the calibration curve. Measurements were performed in a microplate reader (MultiskanTM FC, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), at a wavelength of 595 nm.
4.4. Protein Separation by SDS-PAGE and LC-MS/MS Analysis
Salivary protein separation was carried out by SDS-PAGE under denaturing conditions. The equivalent of 20 µg of protein from each extract was denatured with 2X Laemmli sample buffer (Bio-Rad), supplemented with 0.5% of 2-mercaptoethanol, by incubation at +95 °C in Thermomixer Comfort (Eppendorf, Milan, Italy). Separation was performed on precast gradient gel BoltTM 4–12% Bis-Tris Plus (Life Technologies, Monza, MD, Italy) in MES SDS-PAGE BoltTM Running Buffer (Life Technologies, Monza, MD, Italy) at a voltage of 200 V. The gels were stained overnight with Coomassie Blue G-250, and de-stained with 5% glacial acetic acid. Subsequently, gel images were acquired by a calibrated densitometer (model GS-800, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and then analyzed by QuantityOne 1D image analysis software (version 4.6.7, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), which detects protein bands based on their stain intensity. The band density derives from the sum of the intensities of all the pixels that make the band. By eliminating the background noise and correcting for the variability that can result from gel staining, the software allows the detection of differentially expressed protein bands between different samples.
The differentially expressed bands between periodontal healthy controls and patients with PD were removed from the gel and subjected to the “in-gel digestion” protocol, as previously reported [41]. First, bands were de-stained using acetonitrile (ACN), and then proteins were reduced and alkylated with DTT at +56 °C and with 55 mM iodoacetamide, respectively. Digestion was obtained with Trypsin Gold Mass Spectrometry grade (Promega Corporation, Milan, Italy). Finally, peptides were extracted using trifluoroacetic acid and ACN. Mass spectrometry analysis was performed using a Nano UHPLC-MS Exploris 480 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Reinach, Switzerland), consisting of a nano UHPLC Ultimate 3000 System coupled with an Exploris™ 480 Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap™ Mass Spectrometer, as previously described [72]. MS data processing was performed with the Mascot search engine (www.matrixscience.com, accessed on 15 September 2023), through an MS/MS ion search for protein identification, based on raw MS/MS data from one or more peptides.
4.5. Salivary GAPDH Quantification by ELISA
The salivary level of GAPDH was quantified through the Human Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH) ELISA Kit (Invitrogen, provided by Life Technologies Italia, Milan, Italy), following the manufacturer’s guidelines. This is a solid-phase sandwich immunoenzymatic assay, designed to detect and quantify the level of human GAPDH in serum, plasma, and other biological fluids, such as saliva. Briefly, after centrifugation at 1.000× g for 20 min at +4 °C, 100 μL of saliva samples and standards were deposited into the plate wells containing the pre-coated specific antibody for GAPDH. The plate was then incubated for 90 min in a stove set at +37 °C, to allow antigen binding. Afterwards, 100 μL of biotinylated detection antibody was dispensed into each well and incubated for further 60 min. The solution was then aspirated, and the wells were washed with the supplied wash buffer, before adding the HRP conjugate solution. After 30 min incubation, the wash process was repeated 5 times with 300 μL of 1X wash buffer before adding 90 μL of substrate reagent to each well, for the last 15 min incubation at +37 °C, protecting the plate from light. Finally, the reaction was blocked by adding 50 μL of stop solution, turning the color from blue to yellow. A microplate reader (Multiscan FC, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), preheated before the measurements, was employed to read the absorbances at a wavelength of 450 nm, within 10 min after adding the stop solution. The background (blank) OD was subtracted from all data points, and a standard calibration curve was used to read sample concentrations.
4.6. GAPDH Interaction Networks
The HPA database (www.proteinatlas.org, accessed on 27 November 2024), a useful tool for protein localization and expression in cells and tissues [65], was used to create GAPDH-related interaction networks according to the following datasets: OpenCell, a proteome-scale measurement of human protein localization and interactions, IntAct, a molecular interaction database that allows us to generate direct correlations and physical associations with high and medium confidence, and BioGRID, a database of protein, genetic, and chemical connections. A consensus network, showing only interactions present in more than one of the datasets, was also included. The nodes were colored based on subcellular location (according to the data present in the subcellular section of the database) and protein class.
4.7. Statistics and Data Processing
Data were statistically analyzed by an independent parametric Student’s t-test, considering a p-value < 0.05 as significant. All reported data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Mascot parameters for protein identification from primary sequence databases using MS data were set as follows: type of search, MS/MS ion search; preferred taxonomy, Homo sapiens (Human); proteolytic enzyme, trypsin; fixed modification, carbamidomethylation (Cysteines); variable modification, deamidation (Asparagine, Glutamine) and oxidation (Methionine); mass values, monoisotopic; protein mass, unrestricted; peptide mass tolerance, ± 10 ppm; fragment mass tolerance, ± 0.02 Da; max trypsin missed cleavages, one; min. number of significant unique sequences, two; significant threshold, p < 0.05; databases for detection/exclusion of any contaminants, cRAP, and for peptide sequences, SwissProt, respectively (accessed on 14 September 2023).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, oral clinical proteomics has proved to be a promising tool to explore PD-related changes in the proteome composition of oral samples, such as saliva, thus pointing towards the discovery of selective and reliable markers associated with the disease. These results suggest that, in addition to its numerous well-defined functions, GAPDH may also play a role as a predictive biomarker of PD, as well as for the assessment and monitoring of disease progression and periodontal therapy outcomes. In a non-invasive and rapid salivary screening test, GAPDH could be included in a damage-associated molecular pattern, which could find clinical applications to recognize individuals early on who are at risk of active PD, thus improving the clinical management and treatment of periodontal patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms262110441/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.B., S.B. and C.B.; methodology, E.B., S.B. and R.S.; software, E.B. and S.B.; validation, E.B. and S.B.; formal analysis, E.B., S.B. and R.S.; investigation, E.B., S.B. and R.S.; data curation, E.B., S.B.; R.S. and C.B.; writing—original draft preparation, E.B. and S.B.; writing—review and editing, E.B., S.B., R.S. and C.B.; visualization, E.B., S.B., R.S. and C.B.; supervision, E.B., S.B. and C.B.; project administration, E.B., S.B. and C.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Health Service of the Emilia-Romagna region (protocol code n. 3968/2017, registration C.E. n. 315/17, date of approval 24 October 2017, and supplementary amendment protocol AOU n. 0026796/22, date of approval 21 September 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article and in the Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the specialist technicians for their assistance during the analysis with the LC-ESI-QO-MS/MS mass spectrometer (C.I.G.S., University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Modena, Italy).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| 2-DE | Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EEF1A1 | Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha 1 |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| emPAI | Exponentially modified protein abundance index |
| ENOA | Alpha enolase |
| FN1 | Fibronectin 1 |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GCF | Gingival crevicular fluid |
| HPA | Human Protein Atlas database |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| PD | Periodontitis |
| PGAM1 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate kinase |
| PRDX1 | Peroxiredoxin 1 |
| PRDX2 | Peroxiredoxin 2 |
| SOD2 | Superoxide dismutase, mitochondrial |
| TPI1 | Triosephosphate isomerase |
| TSCM | Tooth-surface-collected material |
| TXN | Thioredoxin |
References
- Martin, W.F.; Rüdiger, C. Physiology, phylogeny, early evolution, and GAPDH. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.R.; Khan, M.M.; Deredge, D.; Ross, C.R.; Quintyn, R.; Zucconi, B.E.; Wysocki, V.H.; Wintrode, P.L.; Wilson, G.M.; Garcin, E.D. A dimer interface mutation in glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase regulates its binding to AU-rich RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1770–1785, Erratum in J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcin, E.D. GAPDH as a model non-canonical AU-rich RNA binding protein. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 86, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.R.; Garcin, E.D. D-Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate dehydrogenase structure and function. Subcell. Biochem. 2017, 83, 413–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.L.; Tanner, J.J. High-resolution structure of human D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Acta Cryst. 2006, D62, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-da-Silva, F.; Pereira, P.J.B.; Gales, L.; Roessle, M.; Svewrgun, D.I.; Moradas-Ferreira, P.; Damas, A.M. The crystal and solution structures of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase reveal different quaternary structures. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 33433–33440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristan, C.; Shahani, N.; Sedlak, T.W.; Sawa, A. The diverse functions of GAPDH: Views from different subcellular compartments. Cell Signal. 2011, 23, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Dang, C.V. Multifaceted roles of glycolytic enzymes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirover, M.A. On the functional diversity of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: Biochemical mechanisms and regulatory control. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, D.M.; Ishitani, R. A role for GAPDH in apoptosis and neurodegeneration. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 609–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.D.; Boulton, A.A. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and apoptosis. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 60, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, C.; Li, H.; Liu, J.P. GAPDH: A common enzyme with uncommon functions. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2012, 39, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, A.; Talukdar, S.; Chaubey, G.K.; Dilawari, R.; Modanwal, R.; Chaudhary, S.; Patidar, A.; Boradia, V.M.; Kumbhar, P.; Raje, C.I.; et al. Regulation of macrophage cell surface GAPDH alters LL-37 internalization and downstream effects in the cell. J. Innate Immun. 2023, 15, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirover, M.A. New nuclear functions of the glycolytic protein, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, in mammalian cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 95, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosova, A.A.; Khodyreva, S.N.; Lavrik, O.I. Role of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in DNA repair. Biochemistry 2017, 82, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirover, M.A. Structural analysis of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase functional diversity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 57, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Knuesting, J.; Birkholz, O.; Heinisch, J.J.; Scheibe, R. Cytosolic GAPDH as a redox-dependent regulator of energy metabolism. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.R.; Cascio, M.B.; Sawa, A. GAPDH as a sensor of NO stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1762, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirover, M.A. Subcellular dynamics of multifunctional protein regulation: Mechanisms of GAPDH intracellular translocation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirover, M.A. The role of posttranslational modification in moonlighting glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase structure and function. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colell, A.; Green, D.R.; Ricci, J.E. Novel roles for GAPDH in cell death and carcinogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Yuan, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, W.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, J.; Yun, J.; Xu, R.; Huang, P. Over-expression of GAPDH in human colorectal carcinoma as a preferred target of 3-Bromopyruvate Propyl Ester. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2012, 44, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, F.; Hong, C.Q.; Giuliano, A.E.; Cui, X.J.; Zhou, G.J.; Zhang, G.J.; Cui, Y.K. Critical protein GAPDH and its regulatory mechanisms in cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandic, R.; Agaimy, A.; Pinto-Quintero, D.; Roth, K.; Teymoortash, A.; Schwarzbach, H.; Stoehr, C.G.; Rodepeter, F.R.; Stuck, B.A.; Bette, M. Aberrant expression of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in warthin tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.D. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a target for small-molecule disease-modifying therapies in human neurodegenerative disorders. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004, 29, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gerszon, J.; Rodacka, A. Oxidatively modified glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in neurodegenerative processes and the role of low molecular weight compounds in counteracting its aggregation and nuclear translocation. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 48, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, G.; Mullappilly, N.; Masetto, F.; Palmieri, M.; Scupoli, M.T.; Pacchiana, R.; Donadelli, M. Regulation of autophagy by nuclear GAPDH and its aggregates in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalhausen, E.V.; Medvedeva, M.V.; Muronetz, V.I. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 758, 110065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarev, V.F.; Guzhova, I.V.; Margulis, B.A. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a multifaceted therapeutic target. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Afzali, H.; Graves, D.T. An update on periodontal inflammation and bone loss. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1385436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugasundaram, S.; Nayak, N.; Karmakar, S.; Chopra, A.; Arangaraju, R. Evolutionary history of periodontitis and the oral microbiota—Lessons for the future. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2024, 11, 117, Erratum in Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2024, 11, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, D.; Carvalho, R.; Machado, V.; Chambrone, L.; Mendes, J.J.; Botelho, J. Prevalence of periodontitis in dentate people between 2011 and 2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2023, 50, 604–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolinska, E.; Wisniewski, P.; Pietruska, M. Periodontal molecular diagnostics: State of knowledge and future prospects for clinical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallianta, M.; Pappa, E.; Vastardis, H.; Rahiotis, C. Applications of mass spectrometry in dentistry. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Govila, V.; Saini, A. Proteomics—The research frontier in periodontics. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2015, 5, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurshid, Z.; Zohaib, S.; Najeeb, S.; Zafar, M.S.; Rehman, R.; Rehman, I.R. Advances of proteomic sciences in dentistry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellei, E.; Monari, E.; Bertoldi, C.; Bergamini, S. Proteomic comparison between periodontal pocket tissue and other oral samples in severe periodontitis: The meeting of prospective biomarkers. Science 2024, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnola, M.; Scarano, E.; Passali, G.C.; Messana, I.; Cabras, T.; Iavarone, F.; Di Cintio, G.; Fiorita, A.; De Corso, E.; Paludetti, G. Salivary biomarkers and proteomics: Future diagnostic and clinical utilities. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Shin, Y.J.; Ko, B.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.D. Deep sequencing salivary proteins for periodontitis using proteomics. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 3571–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, E.; Fiorita, A.; Picciotti, P.M.; Passali, G.C.; Calò, L.; Cabras, T.; Inzitari, R.; Fanali, C.; Messana, I.; Castagnola, M.; et al. Proteomics of saliva: Personal experience. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2010, 30, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bellei, E.; Bergamini, S.; Monari, E.; Fantoni, L.I.; Cuoghi, A.; Ozben, T.; Tomasi, A. High-abundance proteins depletion for serum proteomic analysis: Concomitant removal of non-targeted proteins. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malathi, N.; Mythili, S.; Vasanthi, H.R. Salivary diagnostics: A brief review. ISRN Dent. 2014, 2014, 158786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Z.; Wang, S.; Liao, Z.; Liu, W. Developments in diagnostic applications of saliva in human organ diseases. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2022, 13, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Meder, Á.; Costa, R.; López-Jarana, P.; Ríos-Carrasco, B.; Relvas, M.; Salazar, F. Inflammatory mediators in the oral fluids and blood samples of type 1 diabetic patients, according to periodontal status—A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monari, E.; Cuoghi, A.; Bellei, E.; Bergamini, S.; Lucchi, A.; Tomasi, A.; Cortellini, P.; Zaffe, D.; Bertoldi, C. Analysis of protein expression in periodontal pocket tissue: A preliminary study. Proteome Sci. 2015, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellei, E.; Bertoldi, C.; Monari, E.; Bergamini, S. Proteomics disclose the potential of gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) as source of biomarkers for severe periodontitis. Materials 2022, 15, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamini, S.; Bellei, E.; Generali, L.; Tomasi, A.; Bertoldi, C. A proteomic analysis of discolored tooth surfaces after the use of 0.12% Chlorhexidine (CHX) mouthwash and CHX provided with an anti-discoloration system (ADS). Materials 2021, 14, 4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, F.; Santonocito, S.; Polizzi, A.; Lo Giudice, A.; Capodiferro, S.; Favia, G.; Isola, G. The new era of salivaomics in dentistry: Frontiers and facts in the early diagnosis and prevention of oral diseases and cancer. Metabolites 2022, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Saliva diagnostics. Salivaomics, saliva exosomics, and saliva liquid biopsy. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2023, 154, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Henson, B.S.; Camargo, P.M.; Wong, D.T. The clinical value of salivary biomarkers for periodontal disease. Periodontol. 2000 2009, 51, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Martina, E.; Diotallevi, F.; Radi, G.; Marani, A.; Sartini, D.; Emanuelli, M.; Kontochristopoulos, G.; Rigopoulos, D.; Gregoriou, S.; et al. Saliva proteomics as fluid signature of inflammatory and immune-mediated skin diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, C.; Ruvantha Pinto, A.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Simpson, R.; Liu, J.P. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) induces cancer cell senescence by interacting with telomerase RNA component. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13308–13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Zhou, T.; Yang, W.L.; Liu, J.; Shao, L.Q. Programmed cell death in periodontitis: Recent advances and future perspectives. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listyarifah, D.; Al-Samadi, A.; Salem, A.; Syaify, A.; Salo, T.; Tervahartiala, T.; Grenier, D.; Nordström, D.C.; Sorsa, T.; Ainola, M. Infection and apoptosis associated with inflammation in periodontitis: An immunohistologic study. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamonal, J.; Bascones, A.; Acevedo, A.; Blanco, E.; Silva, A. Apoptosis in chronic adult periodontitis analyzed by in situ DNA breaks, electron microscopy, and immunohistochemistry. J. Periodontol. 2001, 72, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Itakura, M.; Kubo, T.; Kaneshlge, A.; Harada, N.; Izawa, T.; Azuma, Y.T.; Kuwaamura, M.; Yamajl, R.; Takeuchi, T. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) aggregation causes mitochondrial dysfunction during oxidative stress-induced cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4727–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, T.; Knuesting, J.; Berndt, C.; Morgan, B.; Scheibe, R. Cytosolic thiol switches regulating basic cellular functions: GAPDH as an information hub? Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldi, C.; Bellei, E.; Pellacani, C.; Ferrari, D.; Lucchi, A.; Cuoghi, A.; Bergamini, S.; Cortellini, P.; Tomasi, A.; Zaffe, D.; et al. Non-bacterial protein expression in periodontal pockets by proteome analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainulainen, V.; Korhonen, T.K. Dancing to another tune-adhesive moonlighting proteins in bacteria. Biology 2014, 3, 178–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Nagano, K. Porphyromonas gingivalis FimA and Mfa1 fimbriae: Current insights on localization, function, biogenesis, and genotype. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2021, 57, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satala, D.; Bednarek, A.; Kozik, A.; Rapala-Kozik, M.; Karkowska-Kuleta, J. The recruitment and activation of plasminogen by bacteria—The involvement in chronic infection development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Casal, J.; Potter, A.A. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a suitable vaccine candidate for protection against bacterial and parasitic diseases. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagener, J.; Schneider, J.J.; Baxmann, S.; Kalbacher, H.; Borelli, C.; Nuding, S.; Küchler, R.; Wehkamp, J.; Kaeser, M.D.; Mailänder-Sanchez, D.; et al. A peptide derived from the highly conserved protein GAPDH is involved in tissue protection by different antifungal strategies and epithelial immunomodulation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Pham, T.H.; Feuerbacher, L.A.; Lubos, M.L.; Huang, M.; Olsen, R.; Mushegian, A.; Slawson, C.; Hardwidge, P.R. NleB, a bacterial effector with glycosyltransferase activity, targets GAPDH function to inhibit NF-κB activation. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thul, P.J.; Lindskog, C. The human protein atlas: A spatial map of the human proteome. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamini, S.; Bellei, E.; Selleri, V.; Salvatori, R.; Micheloni, G.; Nasi, M.; Pinti, M.; Bertoldi, C. The impact of non-surgical periodontal therapy on the salivary proteome: A pilot study. Int. J. Dent. 2025, 2025, 6655743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, T.M.B.; Lima, S.M.F.; Petriz, B.A.; Silva, O.N.; Freire, M.S.; Franco, O.L. Dentistry proteomics: From laboratory development to clinical practice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 2271–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biomarkers Definitions Working Group. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S159–S172, Erratum in J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldi, C.; Monari, E.; Cortellini, P.; Generali, L.; Lucchi, A.; Spinato, S.; Zaffe, D. Clinical and histological reaction of periodontal tissues to subgingival resin composite restorations. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessie, K.; Hashim, O.H.; Rahim, Z.H.A. Protein precipitation method for salivary proteins and rehydration buffer for two-dimensional electrophoresis. Biotechnology 2008, 7, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellei, E.; Rustichelli, C.; Bergamini, S.; Monari, E.; Baraldi, C.; Lo Castro, F.; Tomasi, A.; Ferrari, A. Proteomic serum profile in menstrual-related and post menopause migraine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 184, 113165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).