A Further Case for Targeting PRMT5 and the ERK1/2 and PI3K Pathways in CRC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
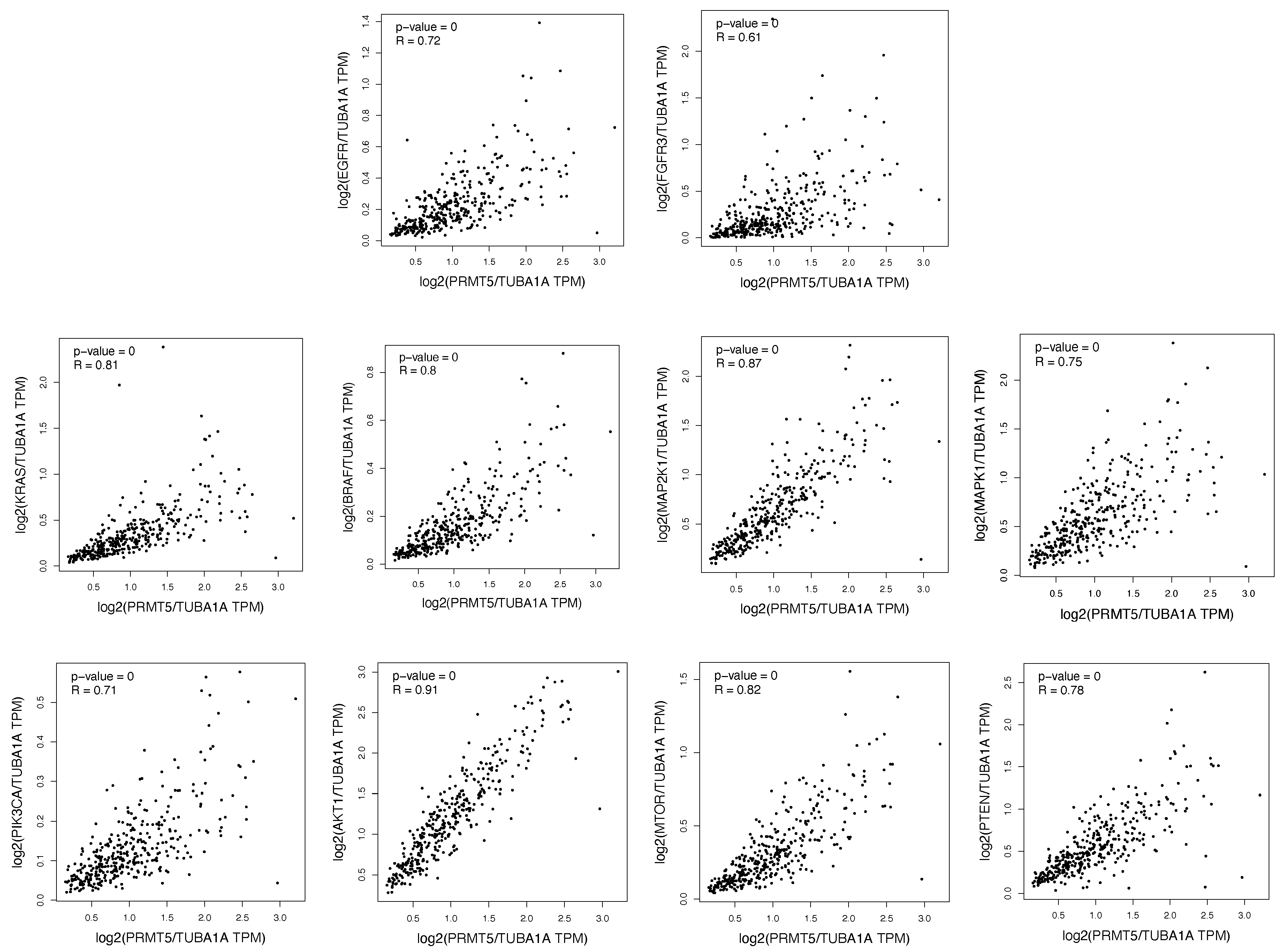
2.1. The ERK1/2 and PI3K Pathway Proteins Are Positively Correlated with PRMT5 in Colon and Rectum Patient Tumor Samples
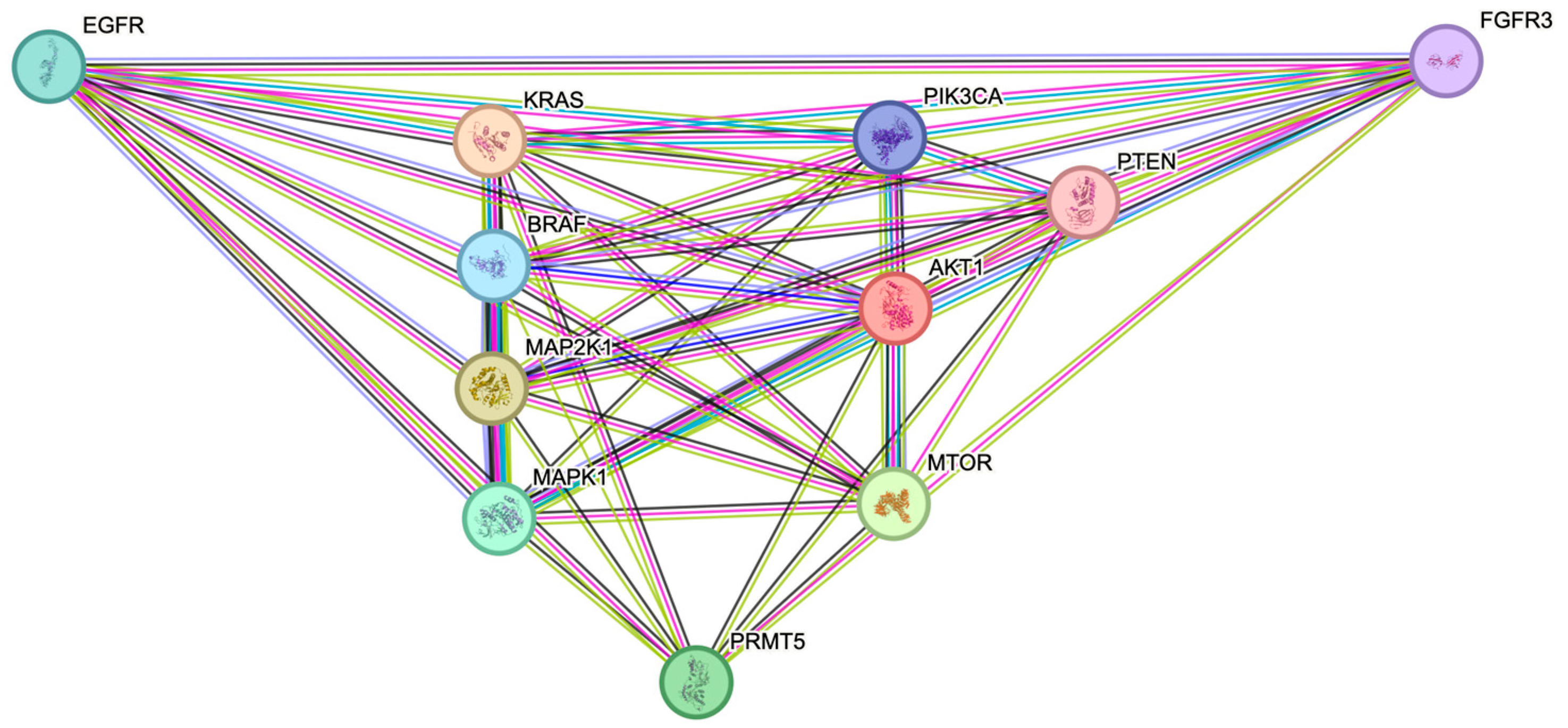
2.2. The ERK1/2 and PI3K Pathway Proteins Have Demonstrated Interactations with PRMT5 in the STRING Protein–Protein Interaction Network
2.3. Protein Network Map and Tabular Model Illustrates the Proteins in the ERK1/2 and PI3K Pathways That Both Positively Correlate with, as Well as Interact with, PRMT5
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA)
4.2. STRING Protein–Protein Interaction Network
4.3. Biorender: Scientific Image and Illustration Software
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PRMT5 | Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| GEPIA | Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, L.H.; Schrag, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.N. Genetic and epigenetic alterations of colorectal cancer. Intest. Res. 2018, 16, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu-Perez, P.; Esteve-Puig, R.; de Torre-Minguela, C.; Lopez-Fauqued, M.; Bech-Serra, J.J.; Tenbaum, S.; Garcia-Trevijano, E.R.; Canals, F.; Merlino, G.; Avila, M.A.; et al. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 regulates ERK1/2 signal transduction amplitude and cell fate through CRAF. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temraz, S.; Mukherji, D.; Shamseddine, A. Dual Inhibition of MEK and PI3K Pathway in KRAS and BRAF Mutated Colorectal Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 22976–22988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezapour, S.; Hosseinzadeh, E.; Marofi, F.; Hassanzadeh, A. Epigenetic-based therapy for colorectal cancer: Prospect and involved mechanisms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19366–19383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Deng, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, E. Epigenetic Alteration in Colorectal Cancer: Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, C. Epigenetic Regulation and Promising Therapies in Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 838–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okugawa, Y.; Grady, W.M.; Goel, A. Epigenetic Alterations in Colorectal Cancer: Emerging Biomarkers. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1204–1225 e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapir, T.; Shifteh, D.; Pahmer, M.; Goel, S.; Maitra, R. Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) and the ERK1/2 & PI3K Pathways: A Case for PRMT5 Inhibition and Combination Therapies in Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.K.; Marzese, D.M.; Hsu, S.C.; Kawas, N.P.; Chong, K.K.; Long, G.V.; Menzies, A.M.; Scolyer, R.A.; Izraely, S.; et al. Epigenetic changes of EGFR have an important role in BRAF inhibitor-resistant cutaneous melanomas. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ma, D.W.; Cao, Y.P.; Li, D.Z.; Zhou, X.; Feng, J.F.; Bao, J. PRMT5 functionally associates with EZH2 to promote colorectal cancer progression through epigenetically repressing CDKN2B expression. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3742–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, R.; Hu, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wong, J. Activated MEK/ERK Pathway Drives Widespread and Coordinated Overexpression of UHRF1 and DNMT1 in Cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papon, N.; Copp, B.R.; Courdavault, V. Marine drugs: Biology, pipelines, current and future prospects for production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 54, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Xiao, K.; Ye, Y.; Liang, H.; Chen, M.; Luo, J.; Qin, Z. High PRMT5 expression is associated with poor overall survival and tumor progression in bladder cancer. Aging 2020, 12, 8728–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shailesh, H.; Zakaria, Z.Z.; Baiocchi, R.; Sif, S. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) dysregulation in cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36705–36718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.C.; Grimmond, S.M.; McArthur, G.A.; Sheppard, K.E. PRMT5: An Emerging Target for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Jain, S.; Coulter, D.W.; Joshi, S.S.; Chaturvedi, N.K. PRMT5 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in MYC-Amplified Medulloblastoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, X.O.; Rozen, E.J.; Sun, X.; Sallis, B.; Verdejo-Torres, O.; Wigglesworth, K.; Moon, D.; Huang, T.; Cavaretta, J.P.; et al. PRMT5 activates AKT via methylation to promote tumor metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Liu, L.; Brobbey, C.; Palanisamy, V.; Ball, L.E.; Olsen, S.K.; Ostrowski, M.C.; Gan, W. PRMT5-mediated arginine methylation activates AKT kinase to govern tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Lu, J.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Gao, X.; Zhou, J. PRMT5/FGFR3/AKT Signaling Axis Facilitates Lung Cancer Cell Metastasis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231161139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, M.; Castano, O.; Zorzano, A. Stochastic modulation evidences a transitory EGF-Ras-ERK MAPK activity induced by PRMT5. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifteh, D.; Sapir, T.; Pahmer, M.; Haimowitz, A.; Goel, S.; Maitra, R. Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 as a Therapeutic Target for KRAS Mutated Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.L.; Jain, R.; Natalio, F.; Hamer, B.; Thakur, A.N.; Muller, W.E. Marine molecular biology: An emerging field of biological sciences. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Pei, L.; Xia, H.; Tang, Q.; Bi, F. Role of oncogenic KRAS in the prognosis, diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taieb, J.; Le Malicot, K.; Shi, Q.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Bouche, O.; Tabernero, J.; Mini, E.; Goldberg, R.M.; Folprecht, G.; Luc Van Laethem, J.; et al. Prognostic Value of BRAF and KRAS Mutations in MSI and MSS Stage III Colon Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; He, F.; Liu, Q.; Gong, J.; Yang, Z.; Gong, Y.; Tang, F.; Wang, Z.; et al. Protein Arginine Methylation: An Emerging Modification in Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 865964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, Y. Role of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 in human cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopa, N.; Krebs, J.E.; Shechter, D. The PRMT5 arginine methyltransferase: Many roles in development, cancer and beyond. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2041–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Feng, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, Q. Protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs): Orchestrators of cancer pathogenesis, immunotherapy dynamics, and drug resistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 221, 116048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abizadeh, E.; Berglas, E.; Abizadeh, A.; Glatman, J.; Lavi, A.B.; Spivak, M.; Sapir, T.; Shifteh, D. Current and Emerging Therapies for Targeting the ERK1/2 & PI3K Pathways in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spivak, M.; Pahmer, M.; Delrahimnia, D.; Sapir, T.; Shifteh, D. PRMT5 Inhibition as a Potential Strategy for KRAS Mutant CRC: Downstream Mediators of the PRMT5-KRAS Crosstalk. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaganovski, A.; Smith-Salzberg, B.; Shimshon, H.K.; Draheim, A.; Spivak, M.; Sapir, T.; Shifteh, D. Current and Emerging Therapies for Targeting Protein Arginine Methyltransferases (PRMTs) in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Dong, S.; Zhu, R.; Hu, C.; Hou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Shao, X.; Bu, Q.; Li, H.; et al. Targeting protein arginine methyltransferase 5 inhibits colorectal cancer growth by decreasing arginine methylation of eIF4E and FGFR3. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22799–22811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasova, V.S.; Riedl, A.; Strobl, M.; Flandorfer, J.; Unterleuthner, D.; Weindorfer, C.; Neuhold, P.; Stang, S.; Hengstschlager, M.; Bergmann, M.; et al. Selective Eradication of Colon Cancer Cells Harboring PI3K and/or MAPK Pathway Mutations in 3D Culture by Combined PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and MEK Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, T.M.; Newton, T.P.; Bradshaw-Pierce, E.L.; Addison, R.; Arcaroli, J.J.; Klauck, P.J.; Bagby, S.M.; Hyatt, S.L.; Purkey, A.; Tentler, J.J.; et al. Dual pharmacological targeting of the MAP kinase and PI3K/mTOR pathway in preclinical models of colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulpia, F.; Schepens, W.; Lepri, S.; Nicolai, J.; Jiang, Z.; Boj, S.F.; Bush, T.L.; Carvalho, M.A.; Chen, F.; Chu, G.; et al. Discovery of Gut-Restricted PRMT5 Inhibitors to Intercept Colorectal Cancer in Patients with Genetic Loss of Tumor Suppressor Adenomatous Polyposis Coli. J. Med. Chem. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Fu, S.; Zou, X.; Zeng, H.; Cui, G.; Peng, Y.; Tang, D.; Zhang, F.; Shen, H.; Zeng, S.; et al. PRMT5 Inhibitor Synergizes with Chemotherapy to Induce Resembling Mismatch Repair Deficiency and Enhance Anti-TIGIT Therapy in Microsatellite-Stable Colorectal Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2500271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spivak, M.; Pahmer, M.; Delrahimnia, D.; Sapir, T.; Shifteh, D. A Further Case for Targeting PRMT5 and the ERK1/2 and PI3K Pathways in CRC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110416
Spivak M, Pahmer M, Delrahimnia D, Sapir T, Shifteh D. A Further Case for Targeting PRMT5 and the ERK1/2 and PI3K Pathways in CRC. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110416
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpivak, Mark, Moshe Pahmer, Dorna Delrahimnia, Tzuriel Sapir, and David Shifteh. 2025. "A Further Case for Targeting PRMT5 and the ERK1/2 and PI3K Pathways in CRC" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110416
APA StyleSpivak, M., Pahmer, M., Delrahimnia, D., Sapir, T., & Shifteh, D. (2025). A Further Case for Targeting PRMT5 and the ERK1/2 and PI3K Pathways in CRC. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110416






