Genome-Wide Analysis of Callose Synthase (CALS) Genes in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.): Identification and Expression Profiling During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterization of BoCALS Family Genes in B. oleracea
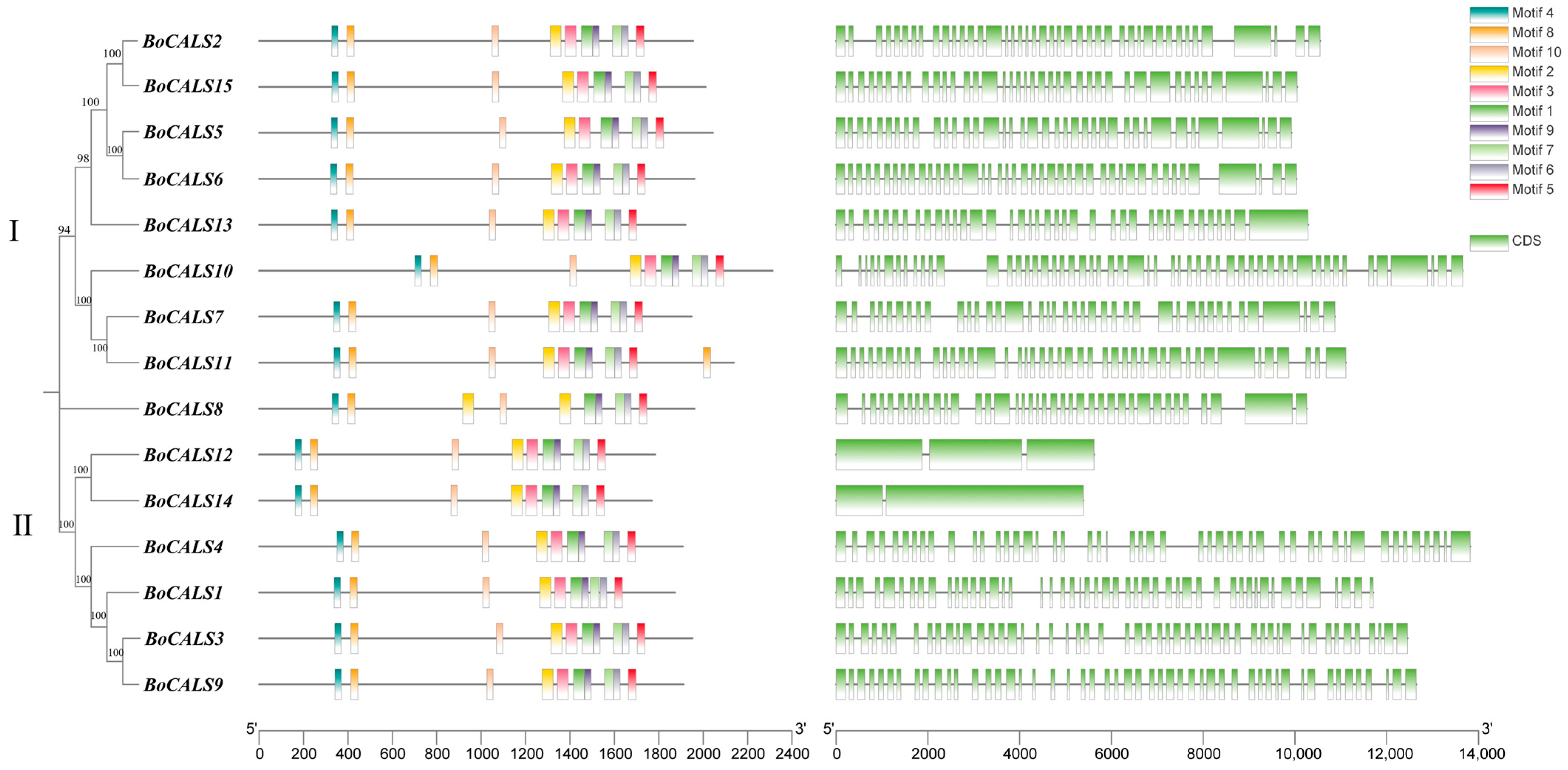
2.2. Phylogenetic and Gene Structural Analysis of BoCALS Genes
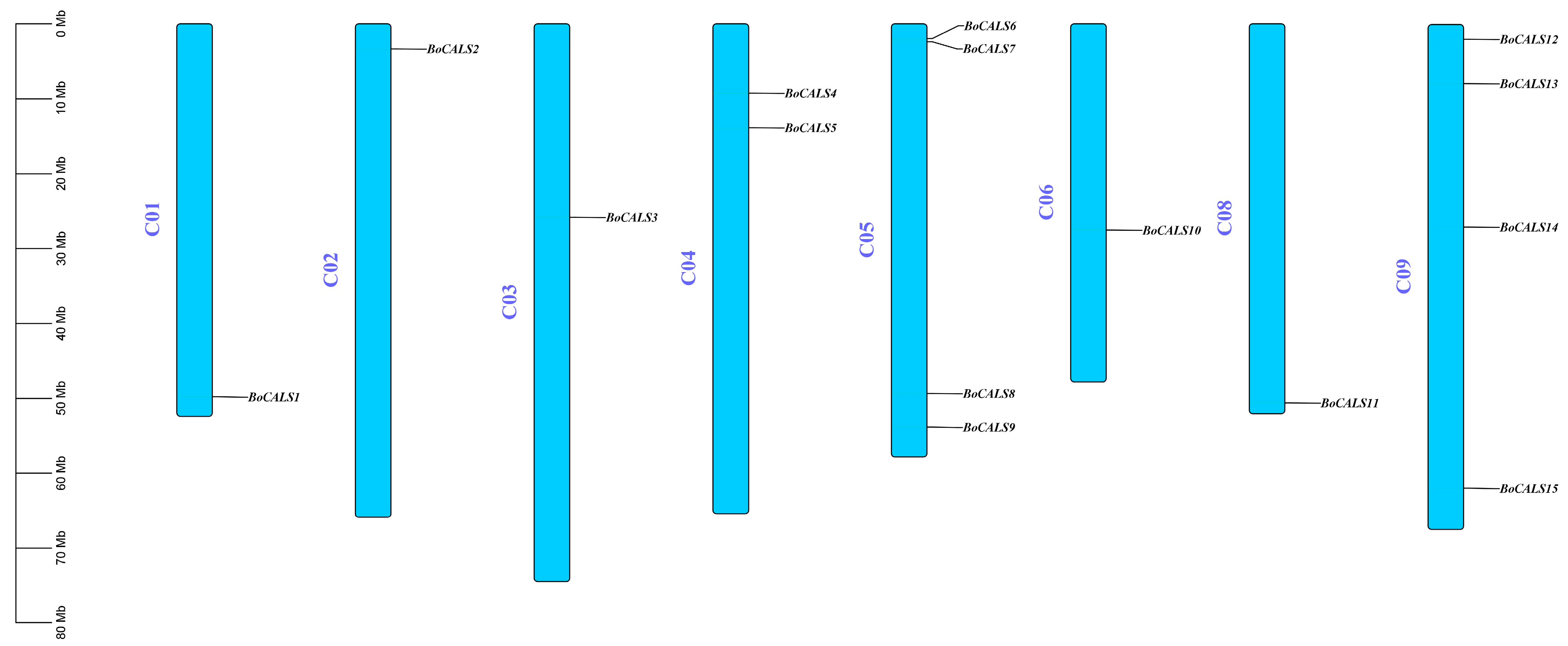
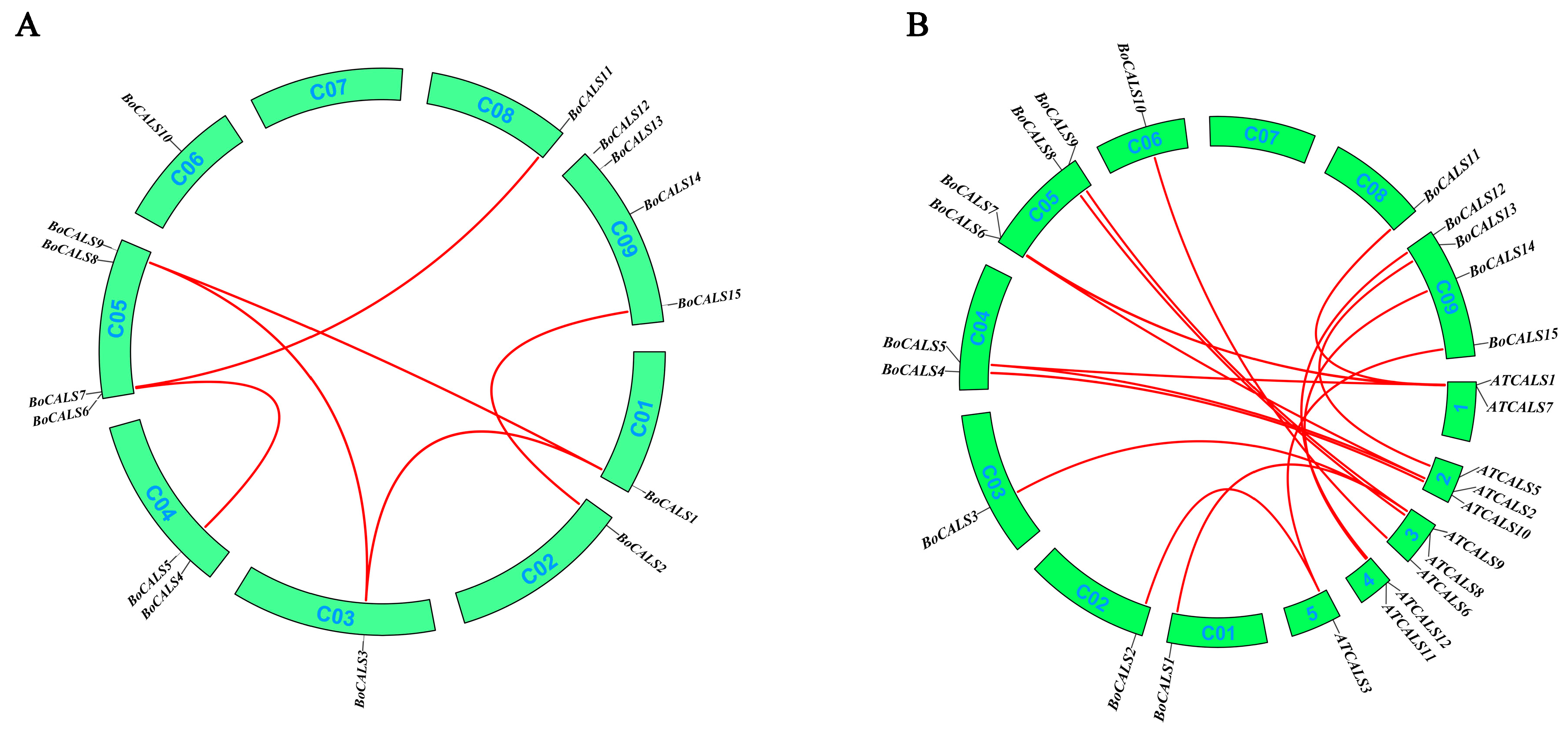
2.3. Chromosomal Localization and Collinearity Analysis of BoCALS Genes
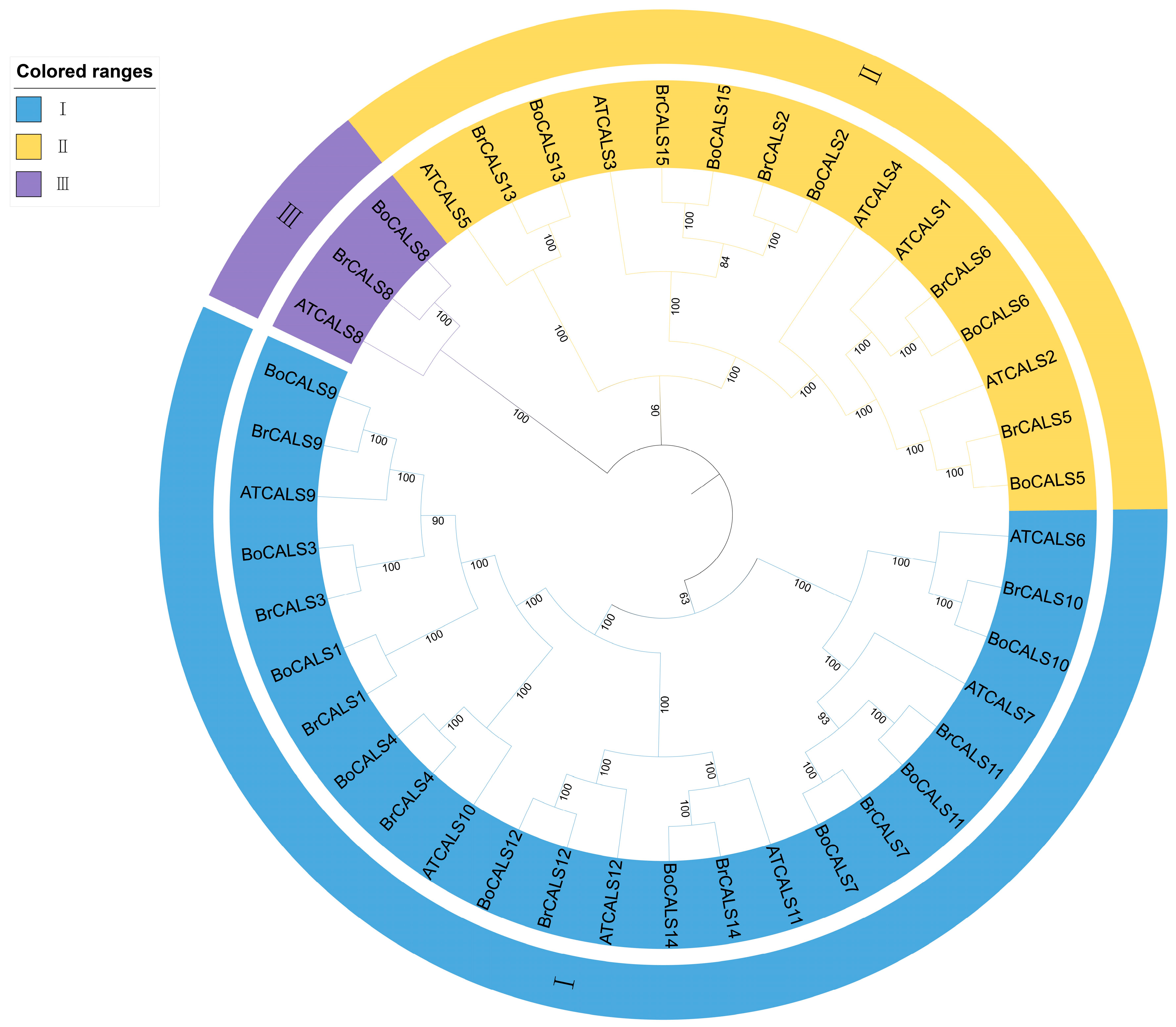
2.4. Analysis of Phylogenetic Tree of CALS Genes Across B. oleracea, B. rapa and A. thaliana
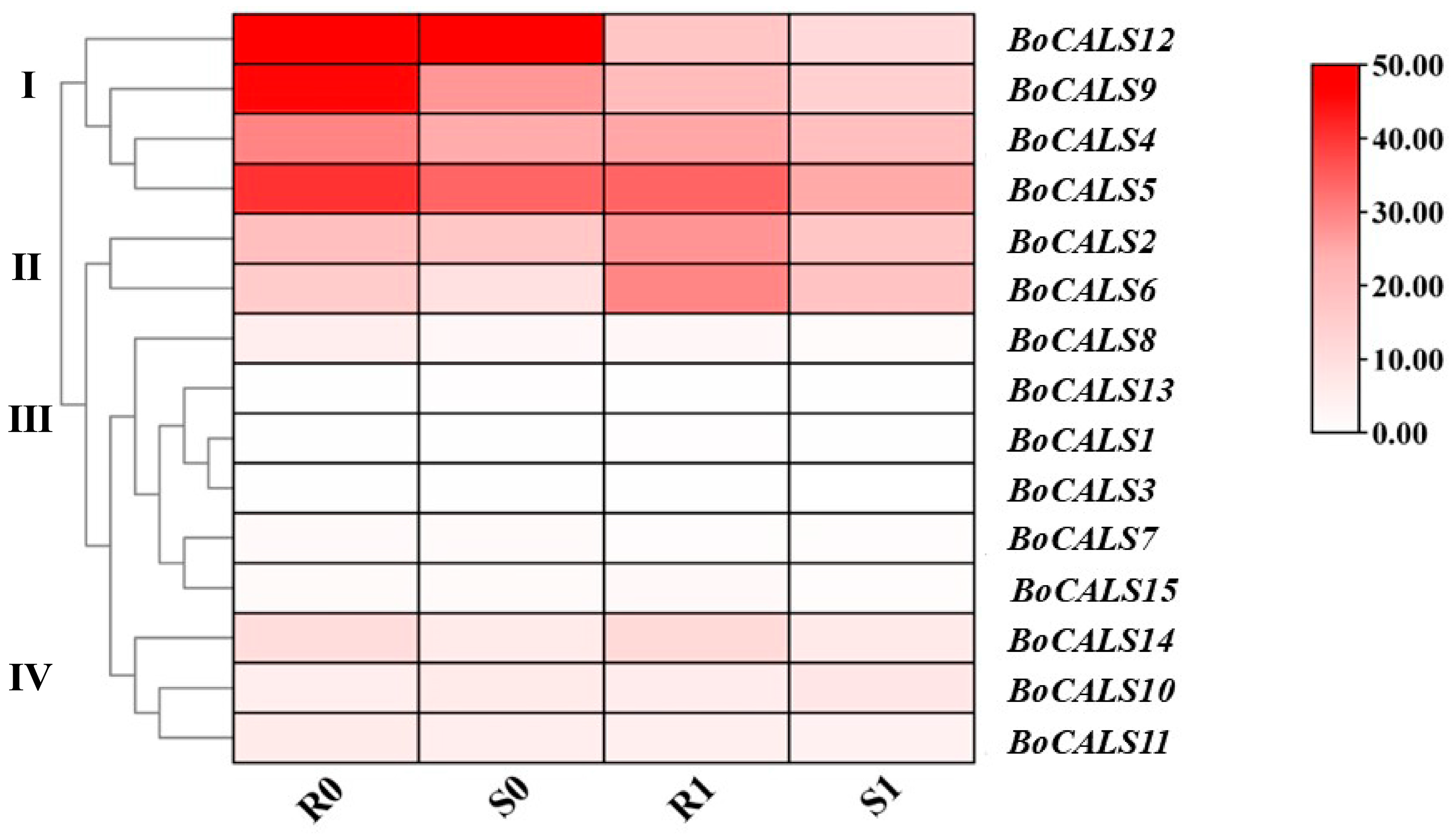
2.5. Expression Profiles of BoCALS Genes in Different Tissues of B. oleracea
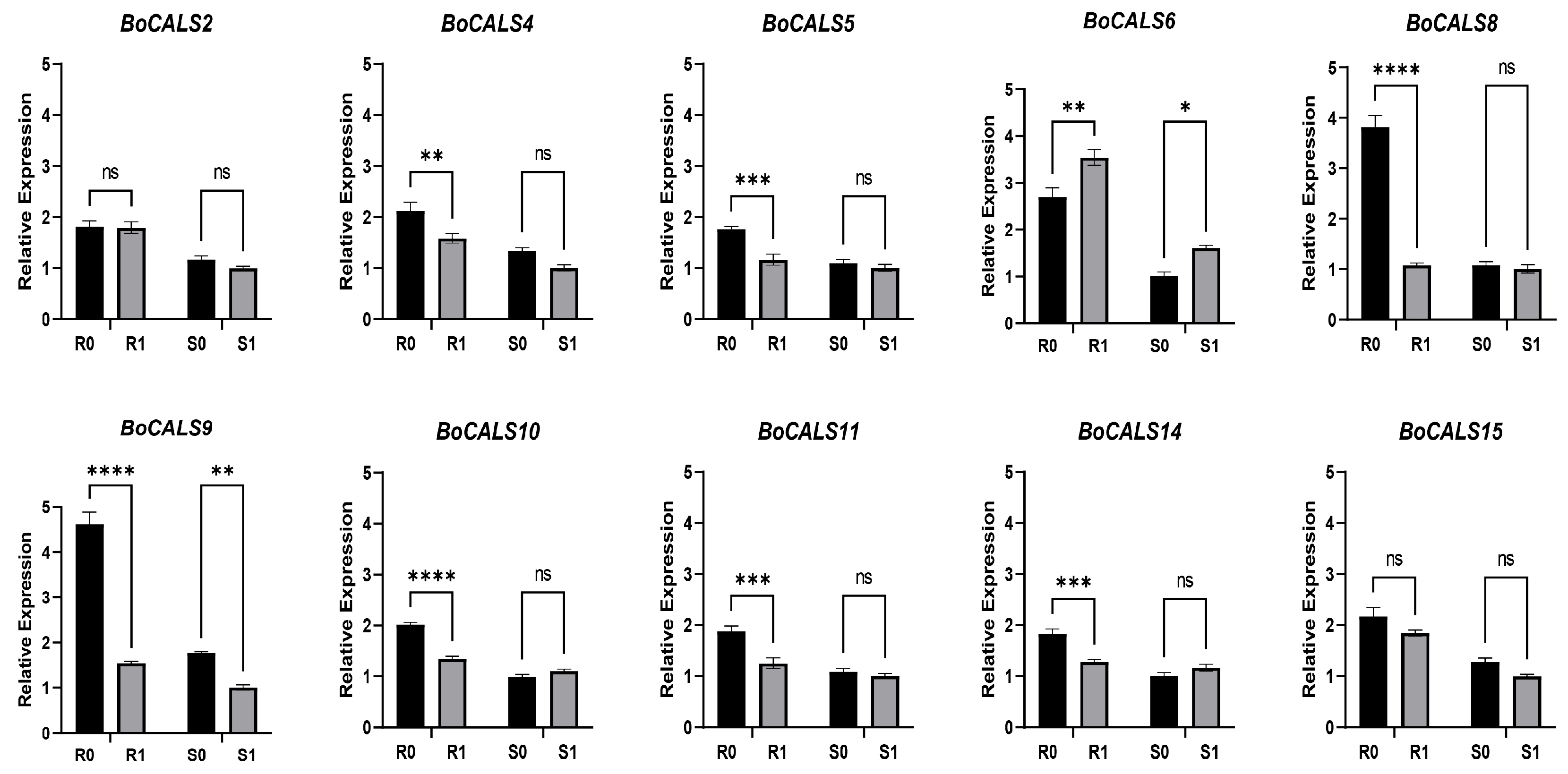
2.6. Relative Expression Analysis of BoCALS Genes Under H. parasitica Challenge
2.7. Cis-Acting Element Analysis of BoCALS6
3. Discussion
3.1. Characterization of BoCALS Family Genes in B. oleracea
3.2. Multiple Functional Roles of the CALS Gene Family in Plant Development
3.3. The Multiple Roles and Mechanisms of the CALS Gene Family in Stress Responses in Higher Plants
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genome-Wide Identification of the BoCALS Genes in B. oleracea
4.2. Gene Structure, Physicochemical Characterization, and Subcellular Localization Prediction and Cis-Acting Element Analysis of the BoCALS Proteins
4.3. Chromosomal Localization and Collinearity Analysis
4.4. Protein Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.5. Expression Analysis of BoCALS Genes Using Published RNA-Seq Data
4.6. Plant Materials and Treatment
4.7. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, X.; Han, X.; Lu, T. Callose Synthesis during Reproductive Development in Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous Plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 11, e1062196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y. Callose Synthesis in Higher Plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, B.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Z. Regulation and Function of Defense-Related Callose Deposition in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicek, C.P.; Starr, T.L.; Glass, N.L. Plant Cell Wall–Degrading Enzymes and Their Secretion in Plant-Pathogenic Fungi. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-W.; Kumar, R.; Iswanto, A.B.B.; Kim, J.-Y. Callose Balancing at Plasmodesmata. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 5325–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillaud, M.-C.; Wirthmueller, L.; Sklenar, J.; Findlay, K.; Piquerez, S.J.M.; Jones, A.M.E.; Robatzek, S.; Jones, J.D.G.; Faulkner, C. The Plasmodesmal Protein PDLP1 Localises to Haustoria-Associated Membranes during Downy Mildew Infection and Regulates Callose Deposition. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Yao, G.; Wu, S.; Hou, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D. Callose Deposition at Plasmodesmata Is a Critical Factor in Restricting the Cell-to-Cell Movement of Soybean Mosaic Virus. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, D.P.S.; Hong, Z. Plant Callose Synthase Complexes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 47, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Lin, Z.; Yu, P.; Zeng, Y.; Du, S.; Huang, L.-J. The Multifarious Role of Callose and Callose Synthase in Plant Development and Environment Interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1183402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, T.A.; Somerville, C.R. The Cellulose Synthase Superfamily. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Hayashi, T.; Nakayama, K.; Koike, S. Expression Analysis of Genes for Callose Synthases and Rho-Type Small GTP-Binding Proteins That Are Related to Callose Synthesis in Rice Anther. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkar-Purushothama, C.R.; Brosseau, C.; Giguère, T.; Sano, T.; Moffett, P.; Perreault, J.-P. Small RNA Derived from the Virulence Modulating Region of the Potato spindle tuber viroid Silences Callose synthase Genes of Tomato Plants. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2178–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zou, Z.; Fernando, W.G.D. Characterization of Callose Deposition and Analysis of the Callose Synthase Gene Family of Brassica napus in Response to Leptosphaeria maculans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Hou, L.; Guo, Y.; Ullah, I.; Yang, Y.; Yue, Y. Genome-wide Analysis of the Callose Enzyme Families of Fertile and Sterile Flower Buds of the Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 1432–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Xia, X.; Zhang, R. Classification and Expression Analysis of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Callose Synthase (CalS) Family Genes and Localization of CsCalS4, a Protein Involved in Pollen Development. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 1992–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Su, S.; Jiang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Yu, T.; Yi, H.; Tang, J.; Cao, M. Characterization and Expression Analyses of Callose Synthase Enzyme (Cals) Family Genes in Maize (Zea mays L.). Biochem. Genet. 2022, 60, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Guan, M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, D.; Du, J. Genomic Identification of Callose Synthase (CalS) Gene Family in Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and Comparative In Silico Expression Analysis under Aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) Infestation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, I.A.; Salomon, S.; Schäfer, W.; Becker, D. Downregulation of Glucan Synthase-Like (TaGSL) Genes in Wheat Leads to Inhibition of Transgenic Plant Regeneration. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. -Plant 2014, 50, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatian, B.; Kohalmi, S.E.; Cui, Y. Localization of Arabidopsis Glucan Synthase-Like 5, 8, and 12 to Plasmodesmata and the GSL8-Dependent Role of PDLP5 in Regulating Plasmodesmal Permeability. Plant Signal. Behav. 2023, 18, 2164670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Yachi, K.; Nguyen, T.A.N.; Kanno, S.; Yasuda, S.; Tadai, H.; Tateda, C.; Lee, T.; Nguyen, U.; Inoue, K.; et al. Defense-related Callose Synthase PMR4 Promotes Root Hair Callose Deposition and Adaptation to Phosphate Deficiency in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2024, 120, 2639–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümke, A.; Somerville, S.C.; Voigt, C.A. Transient Expression of the Arabidopsis thaliana Callose Synthase PMR4 Increases Penetration Resistance to Powdery Mildew in Barley. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, J.; Schober, M.S.; Shirley, N.J.; Singh, R.R.; Jacobs, A.K.; Douchkov, D.; Schweizer, P.; Fincher, G.B.; Burton, R.A.; Little, A. Down-regulation of the Glucan Synthase-like 6 Gene (HvGsl6) in Barley Leads to Decreased Callose Accumulation and Increased Cell Wall Penetration by Blumeria graminis f. Sp. Hordei. New Phytol. 2016, 212, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, L.M.; Galdeano, D.M.; D’Alessandre, N.D.R.; Breton, M.C.; Machado, M.A. Callose Synthase Family Genes Plays an Important Role in the Citrus Defense Response to Candidatus Liberibacter Asiaticus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 155, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, W.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Whole-Genome Assembly for Hyaloperonospora parasitica, A Pathogen Causing Downy Mildew in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). J. Fungi 2023, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yang, P.; Chai, C.; Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Yu, H. Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Fungal β-1,3-Glucan Synthase FKS1. Nature 2023, 616, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiflett, S.L.; Ward, D.M.; Huynh, D.; Vaughn, M.B.; Simmons, J.C.; Kaplan, J. Characterization of Vta1p, a Class E Vps Protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 10982–10990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Záveská Drábková, L.; Honys, D. Evolutionary History of Callose Synthases in Terrestrial Plants with Emphasis on Proteins Involved in Male Gametophyte Development. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yao, X.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y. Genome-Wide Characterization of CaM/CML Gene Family in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata): Expression Profiling and Functional Implications during Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, S.B.; Takewakt, N.; Takasuka, T.; Mio, T.; Adachi, M.; Fujii, Y.; Miyamoto, C.; Arisawa, M.; Furuichi, Y.; Watanabe, T. Characterization and Gene Cloning of 1,3-Beta-D-Glucan Synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 231, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffares, D.C.; Penkett, C.J.; Bähler, J. Rapidly Regulated Genes Are Intron Poor. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulombe-Huntington, J.; Majewski, J. Characterization of Intron Loss Events in Mammals. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M. Intron Evolution as a Population-Genetic Process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6118–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.Y.; Shi, X.; Cao, P.P.; Chu, Y.; Guan, W.; Yang, N.; Cheng, H.; Sun, Y.J. The NOXA Promoter Could Function as an Active Enhancer to Regulate the Expression of BCL2 in the Apoptosis Response. Yi Chuan Hered. 2020, 42, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Zhu, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Y. Identification and Transcriptional Analysis of Zinc Finger-Homeodomain (ZF-HD) Family Genes in Cucumber. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 884–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Lee, J.-Y. Arabidopsis Callose Synthases CalS1/8 Regulate Plasmodesmal Permeability during Stress. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.R.; Yan, D.; Sevilem, I.; Helariutta, Y. Plasmodesmata-Mediated Intercellular Signaling during Plant Growth and Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmbach, L.; Bourdon, M.; Belevich, I.; Safran, J.; Lemaire, A.; Heo, J.; Otero, S.; Blob, B.; Pelloux, J.; Jokitalo, E.; et al. Putative pectate lyase PLL12 and callose deposition through polar CALS7 are necessary for long-distance phloem transport in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 926–939.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Mi, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Tang, N.; et al. APP1/NTL9-CalS8 Module Ensures Proper Phloem Differentiation by Stabilizing Callose Accumulation and Symplastic Communication. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Cui, Y.; Yan, D. Heat Stress Reduces Root Meristem Size via Induction of Plasmodesmal Callose Accumulation Inhibiting Phloem Unloading in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatian, B.; Austin, R.S.; Tian, G.; Chen, C.; Nguyen, V.; Kohalmi, S.E.; Geelen, D.; Cui, Y. Analysis of a Novel Mutant Allele of GSL8 Reveals Its Key Roles in Cytokinesis and Symplastic Trafficking in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaoka, M.M.; Shimizu, K.K.; Xie, B.; Urban, S.; Freeman, M.; Hong, Z.; Okada, K. KOMPEITO, an Atypical Arabidopsis Rhomboid-Related Gene, Is Required for Callose Accumulation and Pollen Wall Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Niu, J.; Sun, M.-X.; Zhu, J.; Gao, J.-F.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Z.-N. CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE G1 Is Associated with the Spliceosome to Regulate CALLOSE SYNTHASE5 Splicing and Pollen Wall Formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Wang, X.; Hong, Z. Precocious Pollen Germination in Arabidopsis Plants with Altered Callose Deposition during Microsporogenesis. Planta 2010, 231, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, X.-Y.; Rim, Y.; Han, X.; Cho, W.K.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, J.-Y. Arabidopsis Glucan Synthase-like 10 Functions in Male Gametogenesis. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 166, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töller, A.; Brownfield, L.; Neu, C.; Twell, D.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Dual Function of Arabidopsis Glucan Synthase-like Genes GSL8 and GSL10 in Male Gametophyte Development and Plant Growth. Plant J. 2008, 54, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Storme, N.; De Schrijver, J.; Van Criekinge, W.; Wewer, V.; Dörmann, P.; Geelen, D. GLUCAN SYNTHASE-LIKE8 and STEROL METHYLTRANSFERASE2 Are Required for Ploidy Consistency of the Sexual Reproduction System in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enns, L.C.; Kanaoka, M.M.; Torii, K.U.; Comai, L.; Okada, K.; Cleland, R.E. Two Callose Synthases, GSL1 and GSL5, Play an Essential and Redundant Role in Plant and Pollen Development and in Fertility. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 58, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Han, L.; Wu, J.; Lu, T. GLUCAN SYNTHASE-LIKE 5 (GSL5) Plays an Essential Role in Male Fertility by Regulating Callose Metabolism During Microsporogenesis in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Q.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, P.; Su, S.; Jiang, B.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Li, C.; et al. ZmMS39 Encodes a Callose Synthase Essential for Male Fertility in Maize (Zea mays L.). Crop J. 2023, 11, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, E.; Pastor, V.; Robert, J.; Flors, V.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Ton, J. Callose Deposition: A Multifaceted Plant Defense Response. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cheng, W.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C. Genome-Wide Identification of Callose Synthase Family Genes and Their Expression Analysis in Floral Bud Development and Hormonal Responses in Prunus Mume. Plants 2023, 12, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Voorrips, R.E.; Steenhuis-Broers, G.; van’t Westende, W.; Vosman, B. Reduced Phloem Uptake of Myzus Persicae on an Aphid Resistant Pepper Accession. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbiza, N.I.T.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; et al. GhCalS5 Is Involved in Cotton Response to Aphid Attack through Mediating Callose Formation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 892630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gui, F.; Chen, F. Elevated CO2 Enhances the Host Resistance against the Western Flower Thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis, through Increased Callose Deposition. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, W.; Sager, R.; Modla, S.; Czymmek, K.; Zybaliov, B.; van Wijk, K.; Zhang, C.; Lu, H.; et al. A Plasmodesmata-Localized Protein Mediates Crosstalk between Cell-to-Cell Communication and Innate Immunity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3353–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Guo, X.; Su, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lian, M.; Xue, H.; Li, Q.; He, Y.; Zou, X.; Song, Z.; et al. ABA-CsABI5-CsCalS11 Module Upregulates Callose Deposition of Citrus Infected with Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhad276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tör, M.; Wood, T.; Webb, A.; Göl, D.; McDowell, J.M. Recent Developments in Plant-Downy Mildew Interactions. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 148–149, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y. Fine Mapping and Identification of the Downy Mildew Resistance Gene BoDMR2 in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczynska, I.; Stumpe, M.; Doan, T.G.; Mauch, F. A Phytophthora Effector Protein Promotes Symplastic Cell-to-cell Trafficking by Physical Interaction with Plasmodesmata-localised Callose Synthases. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 1467–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Hong, Z.; Chatterjee, J.; Kim, S.; Verma, D.P.S. Expression of Callose Synthase Genes and Its Connection with Npr1 Signaling Pathway during Pathogen Infection. Planta 2008, 229, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, G.; Wei, M. Functional mechanisms of WRKY transcription factors in regulating plant response to abiotic stresses. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, A.; Su, N.; Li, Z.; Landau, U.; Chakraborty, J.; Gerbi, N.; Liu, J.; Qin, Y.; Yuan, B.; Wei, W.; et al. Construction of Multi-Targeted CRISPR Libraries in Tomato to Overcome Functional Redundancy at Genome-Scale Level. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamesch, P.; Berardini, T.Z.; Li, D.; Swarbreck, D.; Wilks, C.; Sasidharan, R.; Muller, R.; Dreher, K.; Alexander, D.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): Improved Gene Annotation and New Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1202–D1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, T.; He, X.; Cai, X.; Lin, R.; Liang, J.; Wu, J.; King, G.; Wang, X. BRAD V3.0: An Upgraded Brassicaceae Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D1432–D1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The Protein Families Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.; Andreeva, A.; Florentino, L.C.; Chuguransky, S.R.; Grego, T.; Hobbs, E.; Pinto, B.L.; Orr, A.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Ponamareva, I.; et al. InterPro: The Protein Sequence Classification Resource in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 53, D444–D456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bo, Y.; Han, L.; He, J.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: Functional Classification of Proteins via Subfamily Domain Architectures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D200–D203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A.; et al. The Conserved Domain Database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D384–D388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 Years of the SMART Protein Domain Annotation Resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent Updates, New Developments and Status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools in the ExPASy Server. In 2-D Proteome Analysis Protocols; Link, A.J., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 531–552. ISBN 978-1-59259-584-6. [Google Scholar]
- Savojardo, C.; Martelli, P.L.; Fariselli, P.; Profiti, G.; Casadio, R. BUSCA: An Integrative Web Server to Predict Subcellular Localization of Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W459–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “One for All, All for One” Bioinformatics Platform for Biological Big-Data Mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a Database of Plant Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements and a Portal to Tools for in Silico Analysis of Promoter Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Higgins, D.G. Multiple Sequence Alignment Using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2003, 2.3.1–2.3.22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis Version 12 for Adaptive and Green Computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Protein ID | Simplified ID | Peptide Length (Amino Acid Residues) | MW (kDa) | Isoelectric Points (pl) | Subcellular Localization (BUSCA) | Grand Average of Hydropathicity (GRAVY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BolC01g053890.2J | BoCALS1 | 1872 | 214.95 | 8.45 | plasma membrane | −0.046 |
| BolC02g005380.2J | BoCALS2 | 1954 | 225.84 | 9.09 | plasma membrane | −0.122 |
| BolC03g038840.2J | BoCALS3 | 1951 | 223.85 | 8.78 | plasma membrane | 0.019 |
| BolC04g011790.2J | BoCALS4 | 1908 | 218.90 | 8.73 | plasma membrane | 0.021 |
| BolC04g017120.2J | BoCALS5 | 2043 | 236.67 | 9.20 | plasma membrane | −0.046 |
| BolC05g003830.2J | BoCALS6 | 1960 | 226.98 | 9.16 | plasma membrane | −0.069 |
| BolC05g004600.2J | BoCALS7 | 1947 | 226.58 | 8.85 | plasma membrane | −0.169 |
| BolC05g051770.2J | BoCALS8 | 1960 | 227.86 | 8.59 | plasma membrane | −0.124 |
| BolC05g058550.2J | BoCALS9 | 1911 | 219.20 | 8.41 | plasma membrane | −0.052 |
| BolC06g024740.2J | BoCALS10 | 2312 | 267.09 | 8.85 | plasma membrane | −0.076 |
| BolC08g058150.2J | BoCALS11 | 2137 | 247.27 | 8.98 | plasma membrane | −0.219 |
| BolC09g002840.2J | BoCALS12 | 1783 | 207.22 | 9.21 | plasma membrane | −0.032 |
| BolC09g011540.2J | BoCALS13 | 1920 | 220.22 | 9.05 | plasma membrane | −0.072 |
| BolC09g029770.2J | BoCALS14 | 1768 | 204.90 | 9.15 | plasma membrane | 0.069 |
| BolC09g060050.2J | BoCALS15 | 2010 | 232.54 | 9.13 | plasma membrane | −0.078 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Yao, X.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhang, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of Callose Synthase (CALS) Genes in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.): Identification and Expression Profiling During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110304
Li J, Wu Y, Yao X, Yang L, Zhuang M, Lv H, Wang Y, Ji J, Zhang Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of Callose Synthase (CALS) Genes in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.): Identification and Expression Profiling During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110304
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiamin, Yuankang Wu, Xuehui Yao, Limei Yang, Mu Zhuang, Honghao Lv, Yong Wang, Jialei Ji, and Yangyong Zhang. 2025. "Genome-Wide Analysis of Callose Synthase (CALS) Genes in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.): Identification and Expression Profiling During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110304
APA StyleLi, J., Wu, Y., Yao, X., Yang, L., Zhuang, M., Lv, H., Wang, Y., Ji, J., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Genome-Wide Analysis of Callose Synthase (CALS) Genes in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.): Identification and Expression Profiling During Hyaloperonospora parasitica Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110304









