The Tumor Suppressor p53 Downregulates p107 (RBL1) Through p21–RB/E2F Signaling and Tandem E2F Sites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
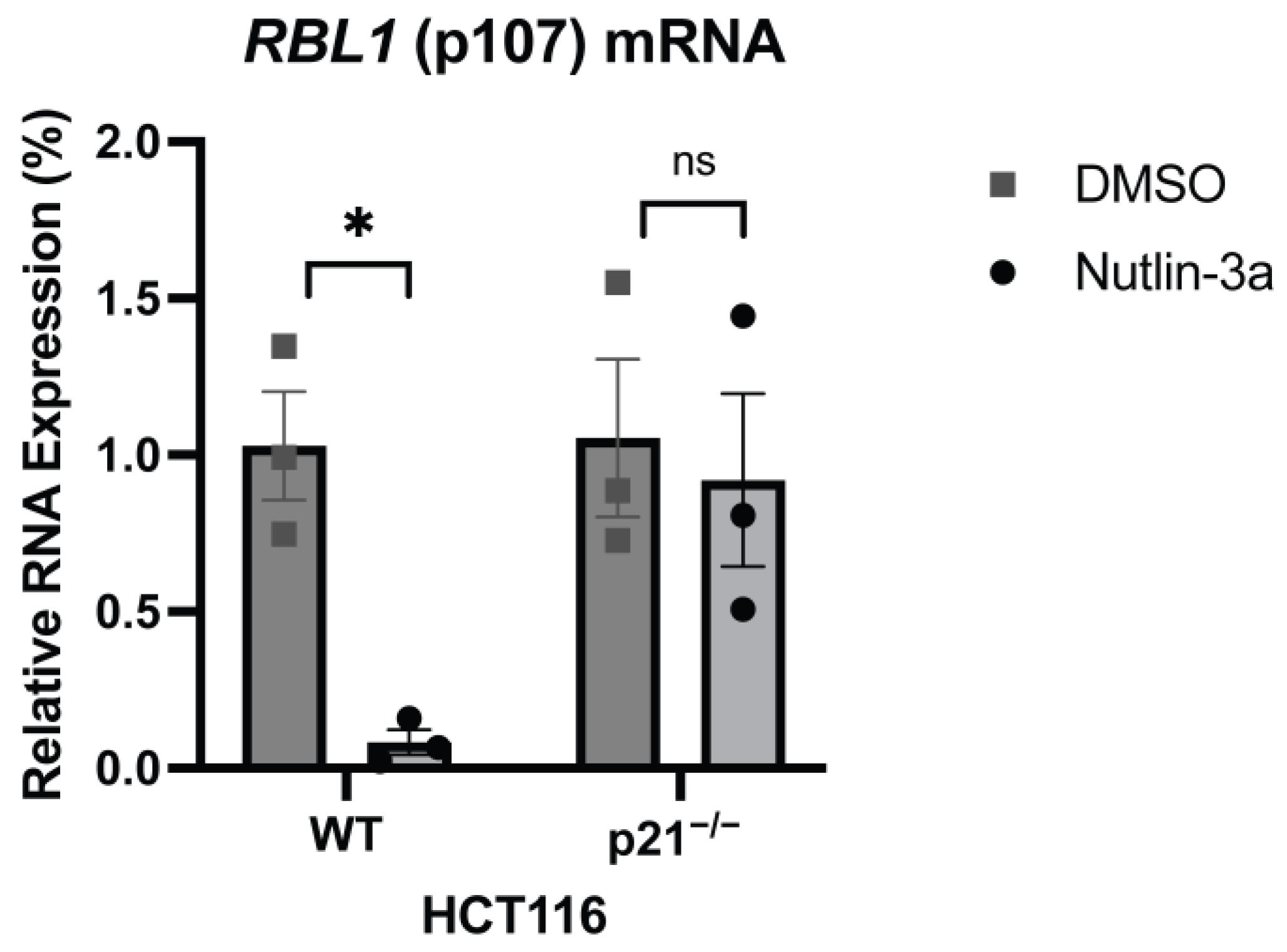
2.1. p53 Represses RBL1 Expression in a p21-Dependent Manner
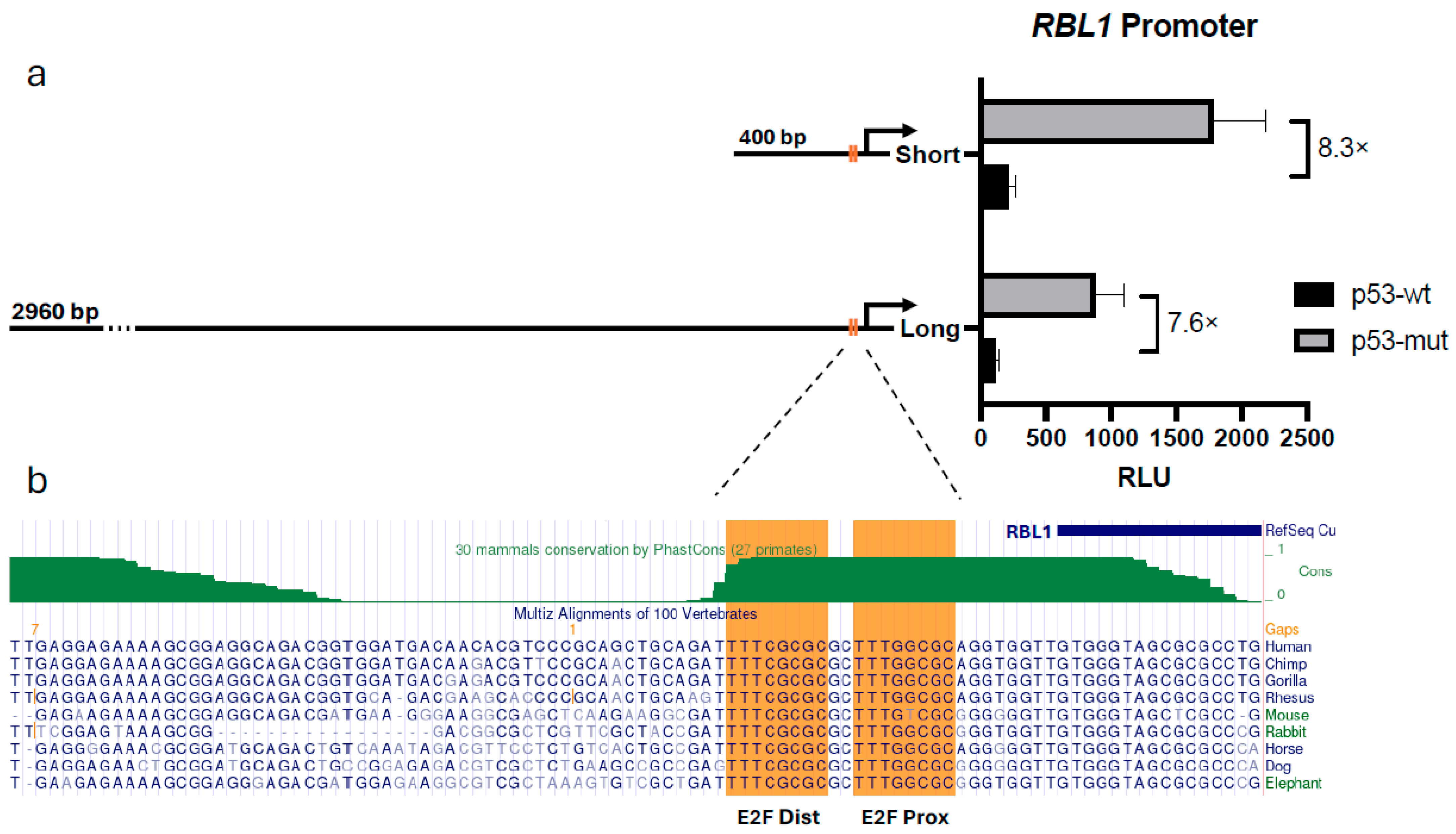
2.2. p53-Mediated Regulation of RBL1 Is Retained in a Short Promoter Fragment Containing Conserved E2F Sites
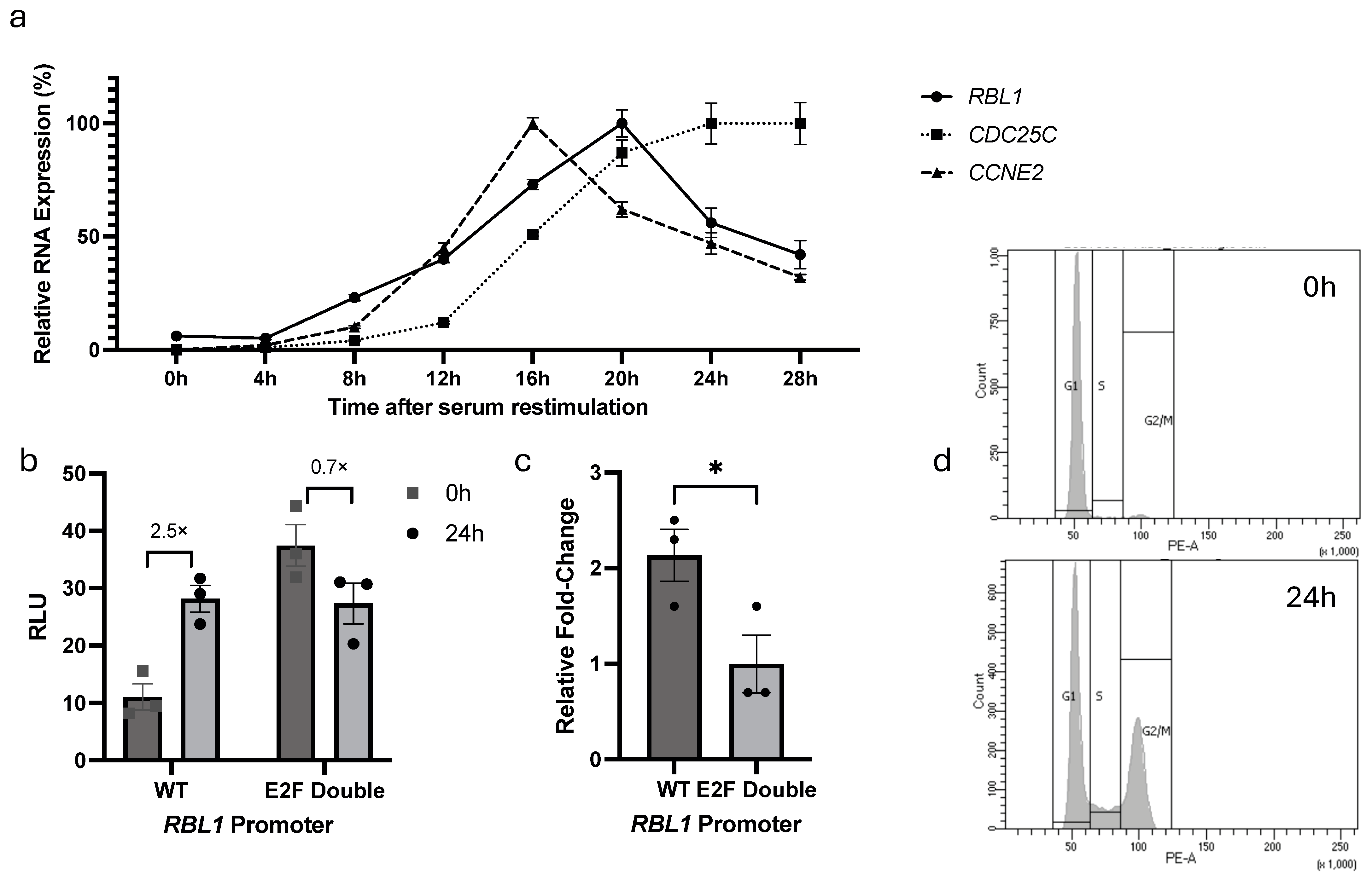
2.3. E2F Binding Sites Are Essential for Cell Cycle–Dependent Regulation of RBL1
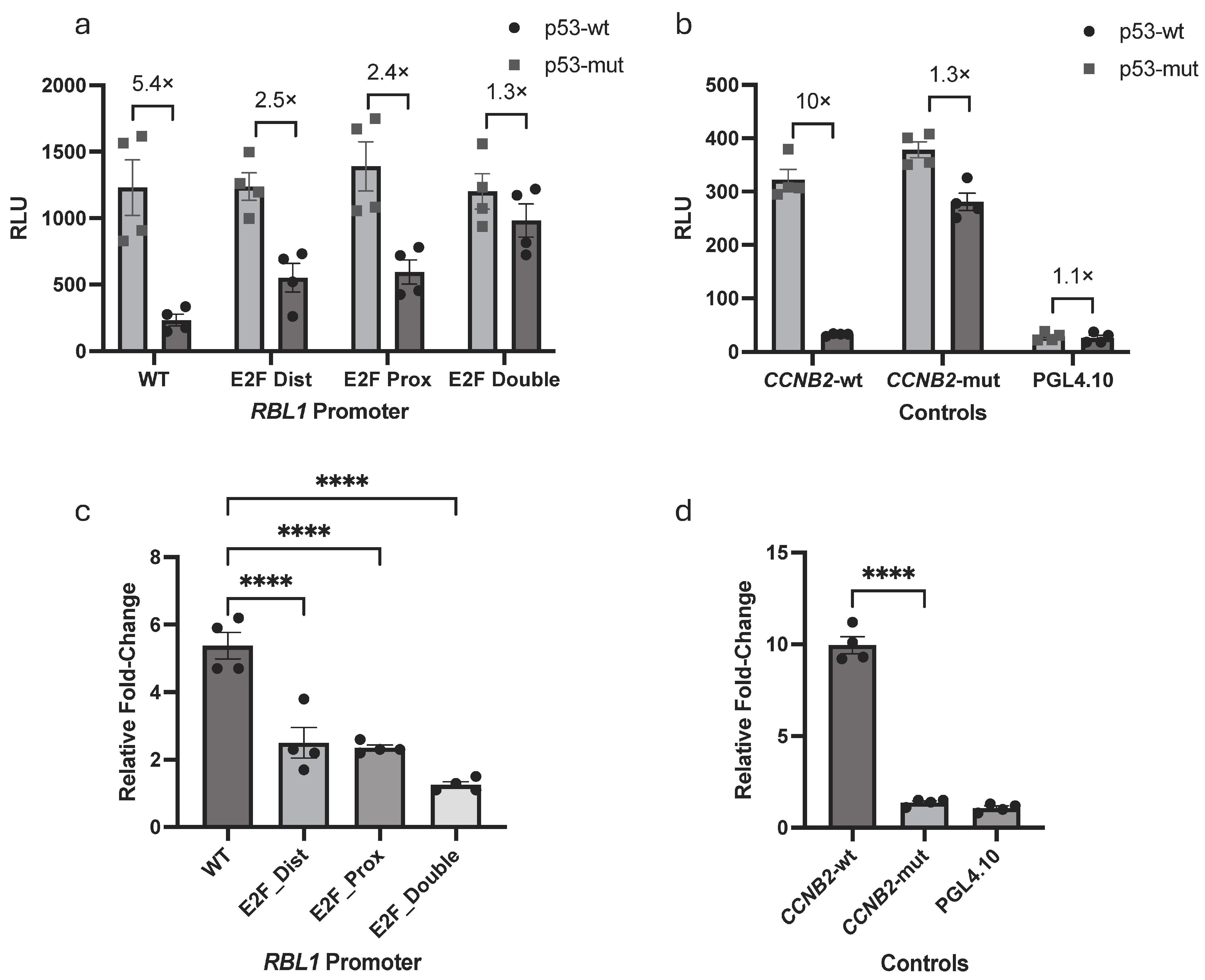
2.4. p53-Dependent Repression of RBL1 Requires Both Tandem E2F Binding Sites
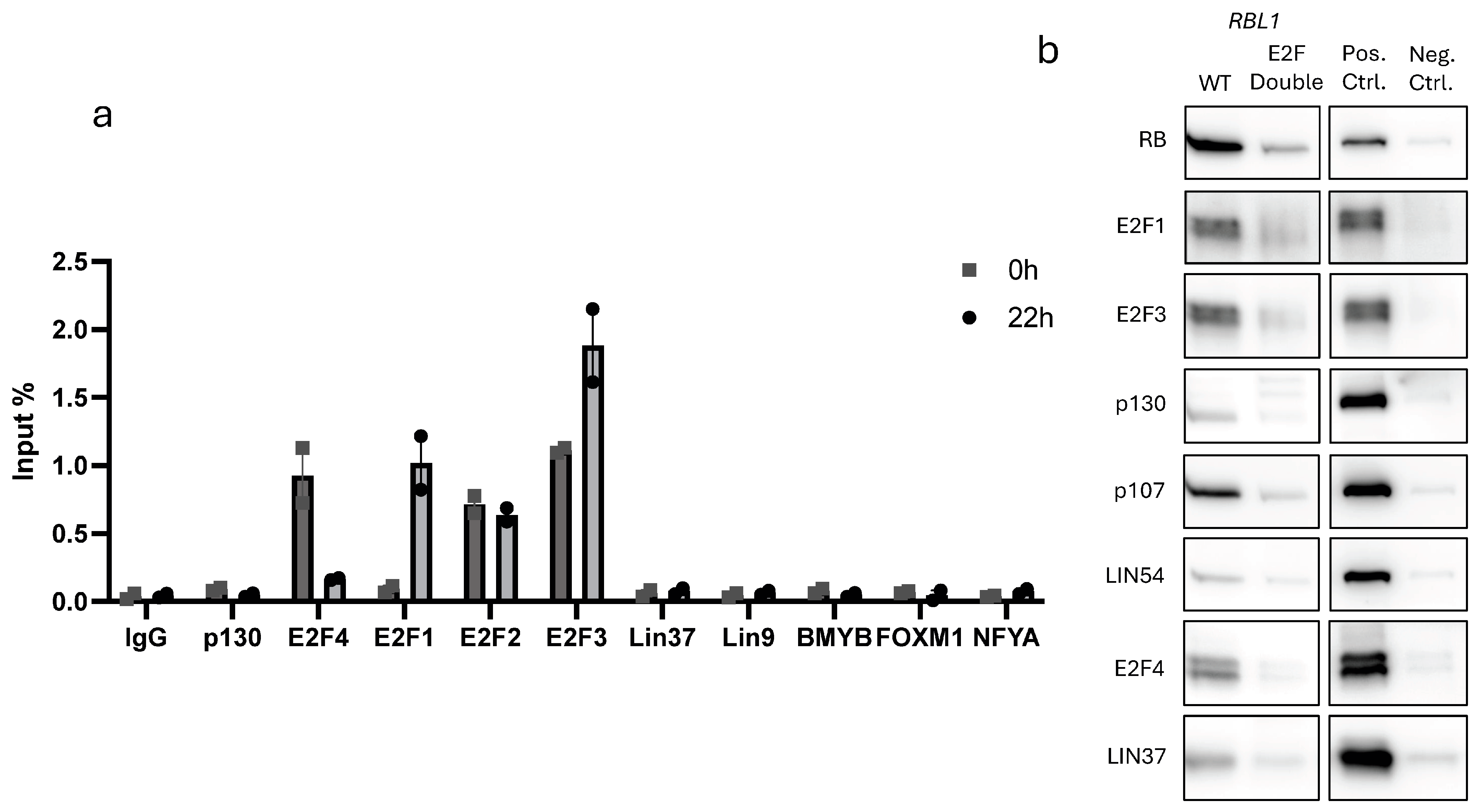
2.5. E2F1–4, RB, and p107 Bind to the RBL1 Promoter Through the Two E2F Binding Sites
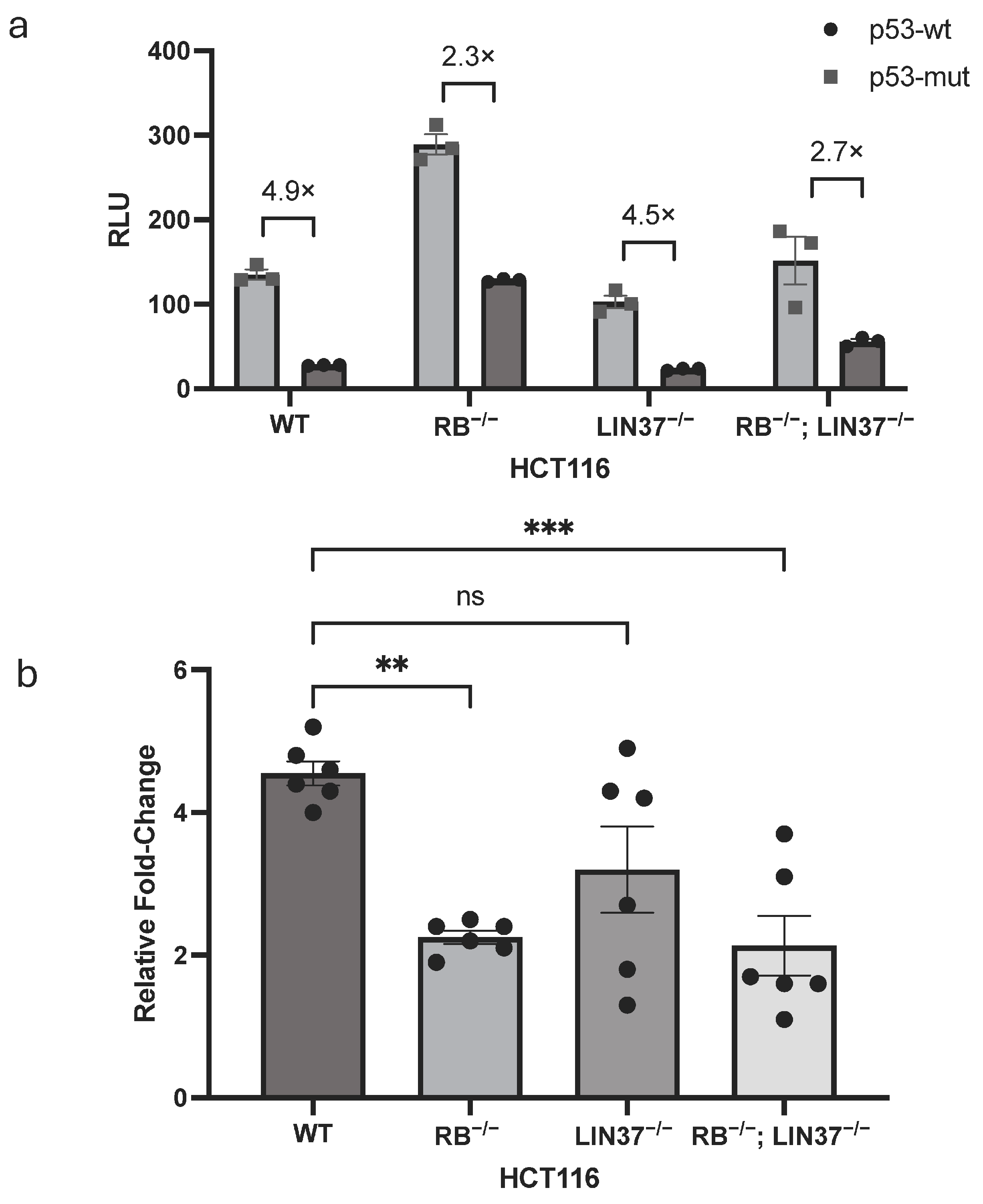
2.6. p53-Dependent Repression of RBL1 Is Mediated by RB with Partial Support from DREAM
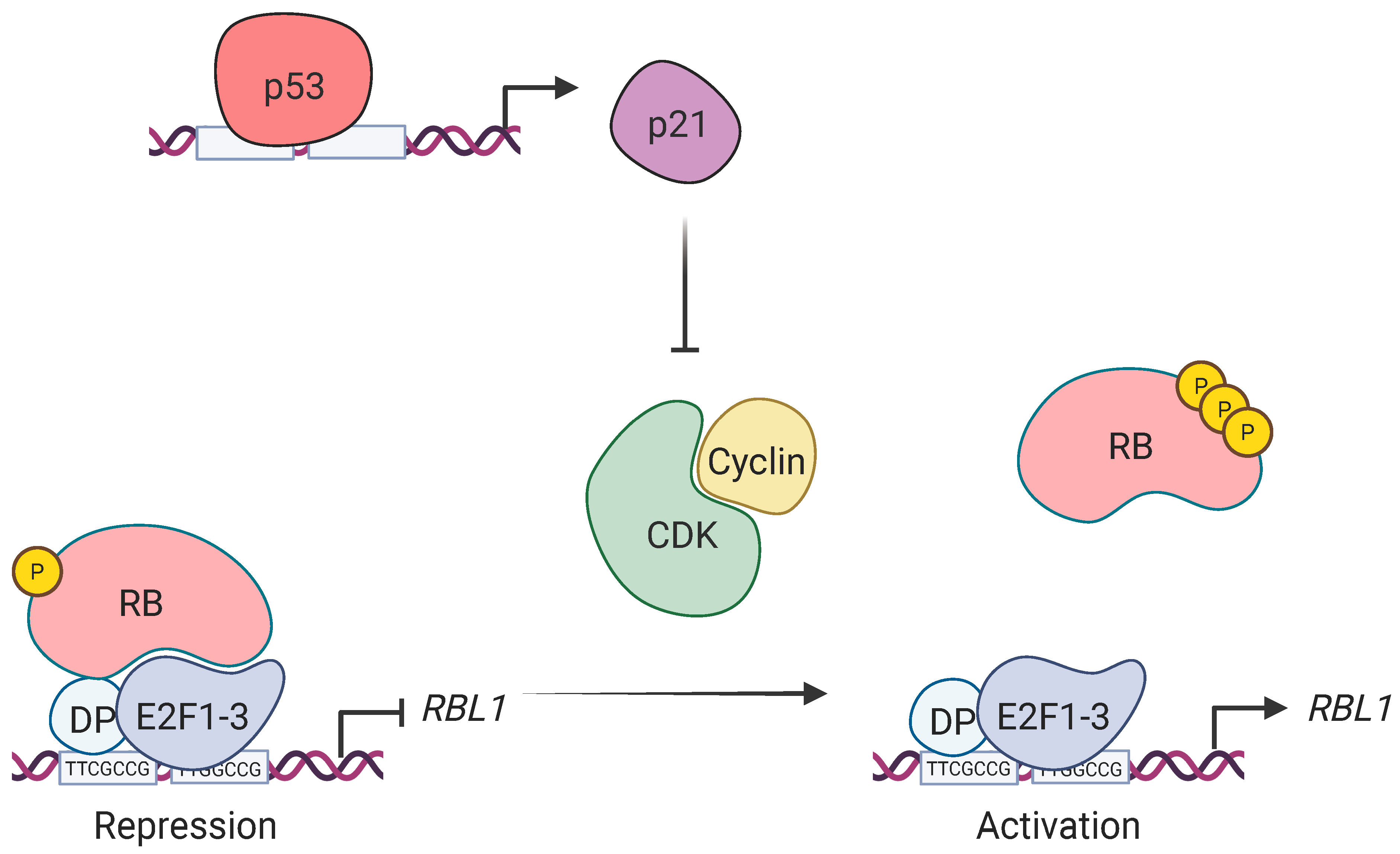
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Knockouts
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.3. Flow Cytometry
4.4. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.5. Cloning and Mutagenesis
4.6. Luciferase Promoter Reporter Assays
4.7. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
4.8. DNA Affinity Purification
4.9. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.10. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMYB | B-Myb transcription factor |
| β-Actin | Beta-actin |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21) |
| CDC25C | Cell division cycle 25C phosphatase |
| ChIP | Chromatin immunoprecipitation |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DREAM | Dimerization partner, RB-like, E2F, and MuvB complex |
| E2F | E2 promoter-binding factor |
| FACS | Fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| FCS | Fetal calf serum |
| FOXM1 | Forkhead box M1 transcription factor |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| LIN37 | Lin-37 cell cycle regulatory protein |
| LIN54 | Lin-54 cell cycle regulatory protein |
| LIN9 | Lin-9 cell cycle regulatory protein |
| MDM2 | Mouse double minute 2 homolog |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| MuvB | Multi-vulva class B core complex |
| NFYA | Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit alpha |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene difluoride |
| RB | Retinoblastoma protein |
| RBL1 | Retinoblastoma-like protein 1 (p107) |
| RLU | Relative light unit |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| TBS-T | Tris-buffered saline with Tween 20 |
| U6 | U6 small nuclear RNA |
| WT | Wild-type |
References
- Lane, D.P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature 1992, 358, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Lu, X. Live or let die: The cell’s response to p53. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.P.; Levine, A.J. p53 Research: The Past Thirty Years and the Next Thirty Years. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J.; Oren, M. The first 30 years of p53: Growing ever more complex. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deiry, W.S.; Tokino, T.; Velculescu, V.E.; Levy, D.B.; Parsons, R.; Trent, J.M.; Vogelstein, B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 1993, 75, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, C.J.; Roberts, J.M. CDK inhibitors: Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, R.A. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 1995, 81, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, N. The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2245–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helin, K.; Lees, J.A.; Vidal, M.; Dyson, N.; Harlow, E.; Fattaey, A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell 1992, 70, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, J.A.; Saito, M.; Vidal, M.; Valentine, M.; Look, T.; Harlow, E.; Dyson, N.; Helin, K. The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 7813–7825. [Google Scholar]
- Harbour, J.W.; Luo, R.X.; Santi, A.D.; Postigo, A.; Dean, D.C. Cdk phosphorylation triggers sequential intramolecular interactions that progressively block Rb functions as cells move through G1. Cell 1999, 98, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Müller, G. Cell cycle transcription control: DREAM/MuvB and RB-E2F complexes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 52, 638–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmit, F.; Korenjak, M.; Mannefeld, M.; Schmitt, K.; Franke, C.; von Eyss, B.; Gagrica, S.; Hänel, F.; Brehm, A.; Gaubatz, S. LINC, a human complex that is related to pRB-containing complexes in invertebrates, regulates the expression of G2/M genes. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litovchick, L.; Sadasivam, S.; Florens, L.; Zhu, X.; Swanson, S.K.; Velmurugan, S.; Chen, R.; Washburn, M.P.; Liu, X.S.; DeCaprio, J.A. Evolutionarily conserved multisubunit RBL2/p130 and E2F4 protein complex represses human cell cycle-dependent genes in quiescence. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeland, K. Cell cycle arrest through indirect transcriptional repression by p53: I have a DREAM. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Steiner, L.; Engeland, K. The transcription factor p53: Not a repressor, solely an activator. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3037–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeland, K. Cell cycle regulation: p53-p21-RB signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriga, J.; Limón, A.; Mayol, X.; Rane, S.G.; Albrecht, J.H.; Reddy, E.P.; Andrés, V.; Graña, X. Differential regulation of the retinoblastoma family of proteins during cell proliferation and differentiation. Biochem. J. 1998, 333, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.J.; Leone, G.; Nevins, J.R. Distinct mechanisms control the accumulation of the Rb-related p107 and p130 proteins during cell growth. Cell Growth Differ. 1998, 9, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhart, D.L.; Viatour, P.; Ho, V.M.; Sage, J. GFP reporter mice for the retinoblastoma-related cell cycle regulator p107. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2544–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zini, N.; Trimarchi, C.; Claudio, P.P.; Stiegler, P.; Marinelli, F.; Maltarello, M.C.; La Sala, D.; De Falco, G.; Russo, G.; Ammirati, G.; et al. pRb2/p130 and p107 control cell growth by multiple strategies and in association with different compartments within the nucleus. J. Cell. Physiol. 2001, 189, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zhu, L.; Xie, E.; Chang, L.S. Differential roles of two tandem E2F sites in repression of the human p107 promoter by retinoblastoma and p107 proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 3552–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Livne-bar, I.; Vanderluit, J.L.; Slack, R.S.; Agochiya, M.; Bremner, R. Cell-specific effects of RB or RB/p107 loss on retinal development implicate an intrinsically death-resistant cell-of-origin in retinoblastoma. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dannenberg, J.H.; Schuijff, L.; Dekker, M.; van der Valk, M.; te Riele, H. Tissue-specific tumor suppressor activity of retinoblastoma gene homologs p107 and p130. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2952–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, D.; Sage, J.; Kim, T.; Ho, D.; McLaughlin, M.E.; Jacks, T. Cell type-specific effects of Rb deletion in the murine retina. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robanus-Maandag, E.; Dekker, M.; van der Valk, M.; Carrozza, M.L.; Jeanny, J.C.; Dannenberg, J.H.; Berns, A.; te Riele, H. p107 is a suppressor of retinoblastoma development in pRb-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, J.; Miller, A.L.; Pérez-Mancera, P.A.; Wysocki, J.M.; Jacks, T. Acute mutation of retinoblastoma gene function is sufficient for cell cycle re-entry. Nature 2003, 424, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.W.; Gu, W.; Zhu, L.; Mahdavi, V.; Nadal-Ginard, B. Reversal of terminal differentiation mediated by p107 in Rb−/− muscle cells. Science 1994, 264, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gray, J.; Wu, L.; Leone, G.; Rowan, S.; Cepko, C.L.; Zhu, X.; Craft, C.M.; Dyer, M.A. Rb regulates proliferation and rod photoreceptor development in the mouse retina. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, S.D.; West, J.C.; Danielian, P.S.; Caron, A.M.; Stone, J.R.; Lees, J.A. Mutation of p107 exacerbates the consequences of Rb loss in embryonic tissues and causes cardiac and blood vessel defects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14932–14936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.S.; Mason-Richie, N.A.; Gettler, C.A.; Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K.A. Retinoblastoma family proteins have distinct functions in pulmonary epithelial cells in vivo critical for suppressing cell growth and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8733–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Santos, M.; Segrelles, C.; Leis, H.; Jorcano, J.L.; Berns, A.; Paramio, J.M.; Vooijs, M. Unique and overlapping functions of pRb and p107 in the control of proliferation and differentiation in epidermis. Development 2004, 131, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, D.A.; Dong, L.; Callaghan, S.M.; Hou, Y.X.; Dagnino, L.; Slack, R.S. Neural precursor cells differentiating in the absence of Rb exhibit delayed terminal mitosis and deregulated E2F 1 and 3 activity. Dev. Biol. 1999, 207, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurford, R.K., Jr.; Cobrinik, D.; Lee, M.H.; Dyson, N. pRB and p107/p130 are required for the regulated expression of different sets of E2F responsive genes. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirt, S.E.; Sage, J. p107 in the public eye: An Rb understudy and more. Cell Div. 2010, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Grossmann, P.; Padi, M.; DeCaprio, J.A. Integration of TP53, DREAM, MMB–FOXM1 and RB–E2F target gene analyses identifies cell cycle gene regulatory networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6070–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Schwarz, R.; Riege, K.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Hoffmann, S. TargetGeneReg 2.0: A comprehensive web-atlas for p53, p63, and cell cycle–dependent gene regulation. NAR Cancer 2022, 4, zcac009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, L.T.; Vu, B.T.; Graves, B.; Carvajal, D.; Podlaski, F.; Filipovic, Z.; Kong, N.; Kammlott, U.; Lukacs, C.; Klein, C.; et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004, 303, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, W.J.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, D. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Rayman, J.B.; Dynlacht, B.D. Analysis of promoter binding by the E2F and pRB families in vivo: Distinct E2F proteins mediate activation and repression. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M. p21 governs p53’s repressive side. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 2852–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, A.E.; Fischer, M.; DeCaprio, J.A. RB, p130 and p107 differentially repress G1/S and G2/M genes after p53 activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 11197–11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobrinik, D.; Lee, M.H.; Hannon, G.; Mulligan, G.; Bronson, R.T.; Dyson, N.; Harlow, E.; Beach, D.; Weinberg, R.A.; Jacks, T. Shared role of the pRB-related p130 and p107 proteins in limb development. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Williams, B.O.; Mulligan, G.; Mukai, S.; Bronson, R.T.; Dyson, N.; Harlow, E.; Jacks, T. Targeted disruption of p107: Functional overlap between p107 and Rb. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, N.; Miller, J.P.; Gaur, T.; Capellini, T.D.; Nikolich-Zugich, J.; De La Hoz, C.; Selleri, L.; Bromage, T.G.; Van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, G.S.; et al. Cooperation between p27 and p107 during Endochondral Ossification Suggests a Genetic Pathway Controlled by p27 and p130. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 5161–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cam, H.; Balciunaite, E.; Blais, A.; Spektor, A.; Scarpulla, R.C.; Young, R.; Kluger, Y.; Dynlacht, B.D. A common set of gene regulatory networks links metabolism and growth inhibition. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunz, F.; Dutriaux, A.; Lengauer, C.; Waldman, T.; Zhou, S.; Brown, J.P.; Sedivy, J.M.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science 1998, 282, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mages, C.F.; Wintsche, A.; Bernhart, S.H.; Müller, G.A. The DREAM complex through its subunit Lin37 cooperates with Rb to initiate quiescence. eLife 2017, 6, e26876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uxa, S.; Castillo-Binder, P.; Kohler, R.; Stangner, K.; Müller, G.A.; Engeland, K. Ki-67 gene expression. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 3357–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.T.; Chien, Y.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Wu, H.H.; Lee, D.F.; Yu, Y.L. The function of the mutant p53-R175H in cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasner, M.; Tschöp, K.; Spiesbach, K.; Haugwitz, U.; Johne, C.; Mössner, J.; Mantovani, R.; Engeland, K. Cyclin B1 transcription is enhanced by the p300 coactivator and regulated during the cell cycle by a CHR-dependent repression mechanism. FEBS Lett. 2003, 536, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasner, M.; Haugwitz, U.; Reinhard, W.; Tschöp, K.; Spiesbach, K.; Lorenz, J.; Mössner, J.; Engeland, K. Three CCAAT-boxes and a single cell cycle genes homology region (CHR) are the major regulating sites for transcription from the human cyclin B2 promoter. Gene 2003, 312, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, M.; Böhlig, L.; Kirschner, R.D.; Engeland, K.; Hauschildt, S. Identification of two regulatory binding sites which confer myotube-specific expression of the mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase ART1 gene. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Quaas, M.; Wintsche, A.; Müller, G.A.; Engeland, K. Polo-like kinase 4 transcription is activated via CRE and NRF1 elements, repressed by DREAM through CDE/CHR sites and deregulated by HPV E7 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.A.; Engeland, K. DNA Affinity Purification: A Pulldown Assay for Identifying and Analyzing Proteins Binding to Nucleic Acids. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2267, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Promoter | −27 E2F Dist | E2F Prox −9 | TSS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human RBL1 WT | 5′-CAGCTGCAGA | TTTTCGCGCG | CTTTGGCGCA | GGTGGTTGTG-3′ |
| Human RBL1 E2F Proximal | 5′-CAGCTGCAGA | TTTTCGCGCG | CAGCTCACCA | GGTGGTTGTG-3′ |
| Human RBL1 E2F Distal | 5′-CAGCTGCAGA | TCACTCGACG | CTTTGGCGCA | GGTGGTTGTG-3′ |
| Human RBL1 E2F Double | 5′-CAGCTGCAGA | TCACTCGACG | CAGCTCACCA | GGTGGTTGTG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azzahrani, K.; Alqahtani, F. The Tumor Suppressor p53 Downregulates p107 (RBL1) Through p21–RB/E2F Signaling and Tandem E2F Sites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209903
Azzahrani K, Alqahtani F. The Tumor Suppressor p53 Downregulates p107 (RBL1) Through p21–RB/E2F Signaling and Tandem E2F Sites. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209903
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzzahrani, Khaled, and Faleh Alqahtani. 2025. "The Tumor Suppressor p53 Downregulates p107 (RBL1) Through p21–RB/E2F Signaling and Tandem E2F Sites" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209903
APA StyleAzzahrani, K., & Alqahtani, F. (2025). The Tumor Suppressor p53 Downregulates p107 (RBL1) Through p21–RB/E2F Signaling and Tandem E2F Sites. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209903






