Molecular Targets for Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
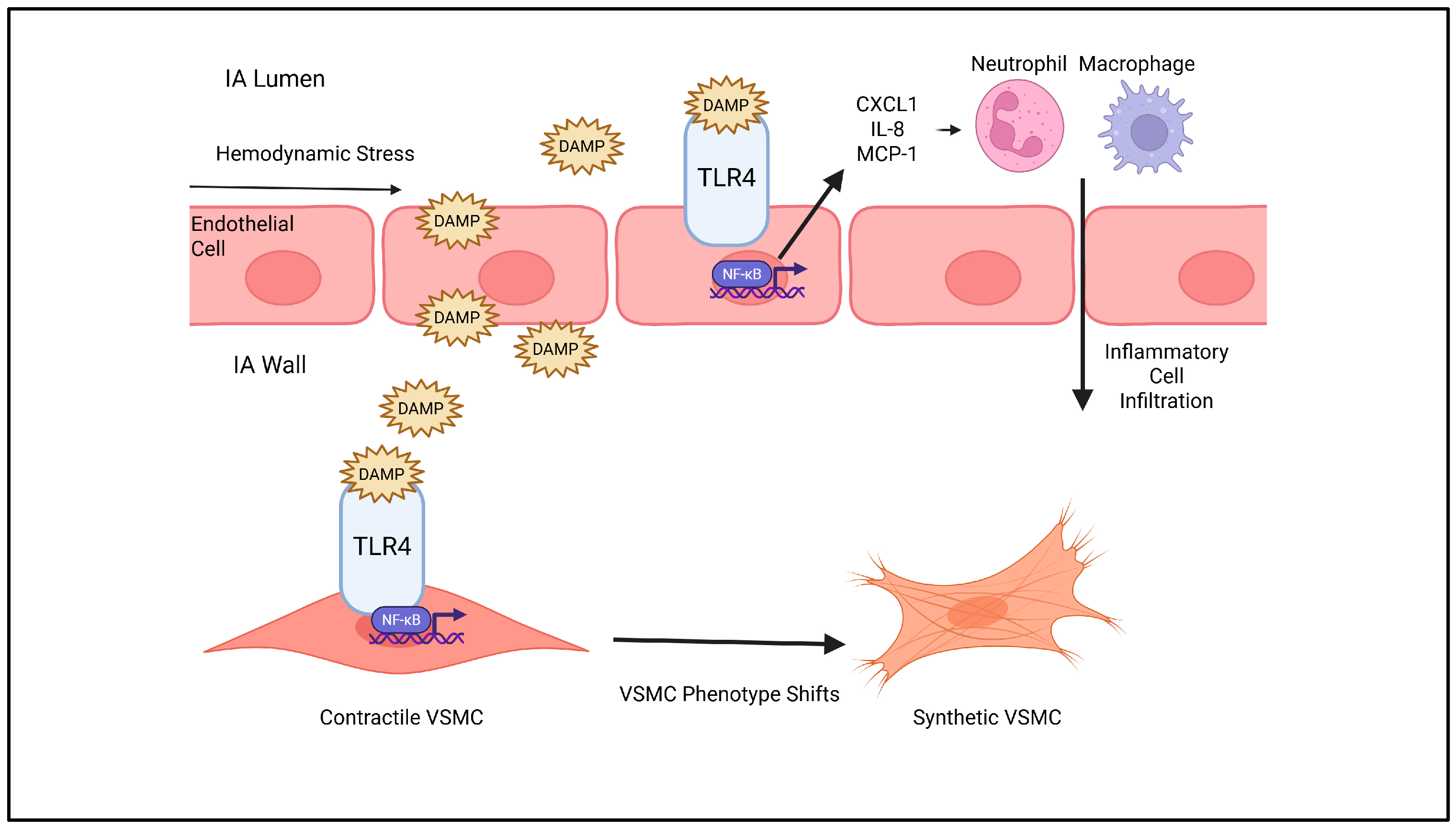
2. Inflammatory Pathways
3. VSMC Phenotypic Shift and ECM Remodeling
4. Endothelial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Cell Death
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IA | Intracranial Aneurysm |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| SAH | Subarachnoid Hemorrhage |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor κB |
| VSMC | Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor-4 |
| DAMP | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| IL | Interleukin |
| CXCL | Chemokine receptor ligand |
| SDF-1α | Stromal-Cell-Derived Factor-1α |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| TNFR1 | Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 |
| NET | Neutrophil Extracellular Trap |
| TAAD | Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection |
| TIMP | Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases |
| TGF-ß | Transforming Growth Factor-ß |
| eNOS | Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| iNOS | Intrinsic Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| NOX | NADPH Oxidase |
References
- Bos, D.; Poels, M.M.F.; Adams, H.H.H.; Akoudad, S.; Cremers, L.G.M.; Zonneveld, H.I.; Hoogendam, Y.Y.; Verhaaren, B.F.J.; Verlinden, V.J.A.; Verbruggen, J.G.J.; et al. Prevalence, Clinical Management, and Natural Course of Incidental Findings on Brain MR Images: The Population-Based Rotterdam Scan Study. Radiology 2016, 281, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlak, M.H.; Algra, A.; Brandenburg, R.; Rinkel, G.J. Prevalence of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms, with Emphasis on Sex, Age, Comorbidity, Country, and Time Period: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.G.; Brown, R.D.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Broderick, J.P.; Cockroft, K.M.; Connolly, E.S.; Duckwiler, G.R.; Harris, C.C.; Howard, V.J.; Johnston, S.C.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Stroke 2015, 46, 2368–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.A.; Halpin, B.; Olson, V.; Putzler, D.; Ghoche, M.; Pachón-Londoño, M.J.; Turcotte, E.L.; Maroufi, S.F.; Segovia, D.; Patra, D.P.; et al. Risk Factors for Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms in Asymptomatic Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Who Needs Screening? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2025, 143, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alg, V.S.; Sofat, R.; Houlden, H.; Werring, D.J. Genetic Risk Factors for Intracranial Aneurysms: A Meta-Analysis in More than 116,000 Individuals. Neurology 2013, 80, 2154–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, M.T.; Vates, G.E. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinkel, G.J.; Djibuti, M.; Algra, A.; van Gijn, J. Prevalence and Risk of Rupture of Intracranial Aneurysms: A Systematic Review. Stroke 1998, 29, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Sohn, M.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Shin, Y.-I.; Oh, G.-J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Joo, M.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Song, M.-K.; et al. Five-Year Functional Outcomes Among Patients Surviving Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e251678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooij, W.J.; Sluzewski, M.; Beute, G.N. Endovascular Treatment of Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Florez-Perdomo, W.A.; Reyes Bello, J.S.; García-Ballestas, E.; Moscote-Salazar, L.R.; Barthélemy, E.J.; Janjua, T.; Maurya, V.P.; Agrawal, A. Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Cocaine Consumption: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis. World Neurosurg. 2024, 184, 241–252.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expert Panel on Neurological Imaging; Ledbetter, L.N.; Burns, J.; Shih, R.Y.; Ajam, A.A.; Brown, M.D.; Chakraborty, S.; Davis, M.A.; Ducruet, A.F.; Hunt, C.H.; et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Cerebrovascular Diseases-Aneurysm, Vascular Malformation, and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2021, 18, S283–S304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, H.; Summers, R.; Yang, M.; Cousins, B.G.; Tsui, J. Current Treatment Strategies for Intracranial Aneurysms: An Overview. Angiology 2018, 69, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darsaut, T.E.; Findlay, J.M.; Bojanowski, M.W.; Chalaala, C.; Iancu, D.; Roy, D.; Weill, A.; Boisseau, W.; Diouf, A.; Magro, E.; et al. A Pragmatic Randomized Trial Comparing Surgical Clipping and Endovascular Treatment of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2023, 44, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, K. Risk Factors of Angiographic Recurrence After Endovascular Coil Embolization of Intracranial Saccular Aneurysms: A Retrospective Study Using a Multicenter Database. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbacher, S.; Grüter, B.E.; Wanderer, S.; Andereggen, L.; Cattaneo, M.; Trost, P.; Gruber, P.; Diepers, M.; Remonda, L.; Steiger, H.-J. Risk of Intracranial Aneurysm Recurrence after Microsurgical Clipping Based on 3D Digital Subtraction Angiography. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 138, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turjman, A.S.; Turjman, F.; Edelman, E.R. Role of Fluid Dynamics and Inflammation in Intracranial Aneurysm Formation. Circulation 2014, 129, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimny, M.; Kawlewska, E.; Hebda, A.; Wolański, W.; Ładziński, P.; Kaspera, W. Wall Shear Stress Gradient Is Independently Associated with Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm Development: A Case-Control CFD Patient-Specific Study Based on 77 Patients. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisman, J.L.; Song, J.K.; Newell, D.W. Cerebral Aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, W.C. Phenotypic Heterogeneity of the Endothelium: I. Structure, Function, and Mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalouhi, N.; Ali, M.S.; Jabbour, P.M.; Tjoumakaris, S.I.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Rosenwasser, R.H.; Koch, W.J.; Dumont, A.S. Biology of Intracranial Aneurysms: Role of Inflammation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1659–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnal, J.F.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Pueyo, M.; Darblade, B.; Rami, J. Endothelium-Derived Nitric Oxide and Vascular Physiology and Pathology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 55, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frösen, J.; Piippo, A.; Paetau, A.; Kangasniemi, M.; Niemelä, M.; Hernesniemi, J.; Jääskeläinen, J. Remodeling of Saccular Cerebral Artery Aneurysm Wall Is Associated with Rupture: Histological Analysis of 24 Unruptured and 42 Ruptured Cases. Stroke 2004, 35, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix Metalloproteinases and the Regulation of Tissue Remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, A.W.; Hastings, N.E.; Blackman, B.R.; Wamhoff, B.R. Complex Regulation and Function of the Inflammatory Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype in Atherosclerosis. J. Vasc. Res. 2010, 47, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolega, J.; Gao, L.; Mandelbaum, M.; Mocco, J.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Natarajan, S.K.; Meng, H. Cellular and Molecular Responses of the Basilar Terminus to Hemodynamics during Intracranial Aneurysm Initiation in a Rabbit Model. J. Vasc. Res. 2011, 48, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Cornelius, J.F.; Muhammad, S. The Role of NF-κB in Intracranial Aneurysm Pathogenesis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Nishimura, M.; Ishibashi, R.; Kataoka, H.; Takagi, Y.; Hashimoto, N. Toll-like Receptor 4 Expression during Cerebral Aneurysm Formation. Laboratory Investigation. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 851–858, Erratum in J. Neurosurg. 2010, 119, 825–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Hao, Z.; Xing, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M. Impinging Flow Induces Expression of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in Endothelial Cells Through Activation of the c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase/c-Jun/P38/c-Fos Pathway. World Neurosurg. 2022, 164, e681–e693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoh, B.L.; Hosaka, K.; Downes, D.P.; Nowicki, K.W.; Wilmer, E.N.; Velat, G.J.; Scott, E.W. Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 Promoted Angiogenesis and Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in Aneurysm Walls. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, K.W.; Hosaka, K.; He, Y.; McFetridge, P.S.; Scott, E.W.; Hoh, B.L. Novel High-Throughput in Vitro Model for Identifying Hemodynamic-Induced Inflammatory Mediators of Cerebral Aneurysm Formation. Hypertension 2014, 64, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, K.; Ikedo, T.; Kamio, Y.; Furukawa, H.; Lawton, M.T.; Hashimoto, T. TLR4 (Toll-Like Receptor 4) Mediates the Development of Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture. Hypertension 2020, 75, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalouhi, N.; Points, L.; Pierce, G.L.; Ballas, Z.; Jabbour, P.; Hasan, D. Localized Increase of Chemokines in the Lumen of Human Cerebral Aneurysms. Stroke 2013, 44, 2594–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zhao, Q.; He, Z.; Tang, S.; Duan, J.; Xing, W. Current Understanding of Macrophages in Intracranial Aneurysm: Relevant Etiological Manifestations, Signaling Modulation and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1320098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, L.; Lu, H.; Zhu, Y. Roles of Inflammation in the Natural History of Intracranial Saccular Aneurysms. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 424, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Fukuda, M.; Nishimura, M.; Nozaki, K.; Narumiya, S. Critical Role of TNF-Alpha-TNFR1 Signaling in Intracranial Aneurysm Formation. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starke, R.M.; Raper, D.M.S.; Ding, D.; Chalouhi, N.; Owens, G.K.; Hasan, D.M.; Medel, R.; Dumont, A.S. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Modulates Cerebral Aneurysm Formation and Rupture. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Starke, R.M.; Jabbour, P.M.; Tjoumakaris, S.I.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Rosenwasser, R.H.; Owens, G.K.; Koch, W.J.; Greig, N.H.; Dumont, A.S. TNF-α Induces Phenotypic Modulation in Cerebral Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: Implications for Cerebral Aneurysm Pathology. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Ishibashi, R.; Nozaki, K.; Egashira, K.; Hashimoto, N. Impact of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Deficiency on Cerebral Aneurysm Formation. Stroke 2009, 40, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoh, B.L.; Hosaka, K.; Downes, D.P.; Nowicki, K.W.; Fernandez, C.E.; Batich, C.D.; Scott, E.W. Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 Promotes Inflammatory Vascular Repair of Murine Carotid Aneurysms via a Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1α and Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-2-Dependent Pathway. Circulation 2011, 124, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavinzski, G.; Talazoglu, V.; Killer, M.; Richling, B.; Gruber, A.; Gross, C.E.; Plenk, H. Gross and Microscopic Histopathological Findings in Aneurysms of the Human Brain Treated with Guglielmi Detachable Coils. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 91, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, J.; Lyson, T.; Chrzanowski, R.; Sawicki, K.; Milewska, A.J.; Tylicka, M.; Zińczuk, J.; Matowicka-Karna, J.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Mariak, Z.; et al. Ratio of IL-8 in CSF versus Serum Is Elevated in Patients with Unruptured Brain Aneurysm. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houard, X.; Touat, Z.; Ollivier, V.; Louedec, L.; Philippe, M.; Sebbag, U.; Meilhac, O.; Rossignol, P.; Michel, J.-B. Mediators of Neutrophil Recruitment in Human Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushamae, M.; Miyata, H.; Shirai, M.; Shimizu, K.; Oka, M.; Koseki, H.; Abekura, Y.; Ono, I.; Nozaki, K.; Mizutani, T.; et al. Involvement of Neutrophils in Machineries Underlying the Rupture of Intracranial Aneurysms in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Dodd, W.S.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Chowdhury, M.A.B.; Hosaka, K.; Hoh, B.L. Neutrophils: Novel Contributors to Estrogen-Dependent Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Via Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e029917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Rhee, M.H.; Kim, E.; Cho, J.Y. BAY 11-7082 Is a Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor with Anti-Inflammatory Activity against Multiple Targets. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 416036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, A.; Shanahan, R.M.; Hudson, J.S.; Nowicki, K.W.; Gersey, Z.C.; Agarwal, P.; Jacobs, R.C.; Lang, M.J.; Gross, B. Pharmaceutical Modulation of Intracranial Aneurysm Development and Rupture. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Chaudhry, S.R.; Dobreva, G.; Lawton, M.T.; Niemelä, M.; Hänggi, D. Vascular Macrophages as Therapeutic Targets to Treat Intracranial Aneurysms. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 630381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bosscher, K.; Schmitz, M.L.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Plaisance, S.; Fiers, W.; Haegeman, G. Glucocorticoid-Mediated Repression of Nuclear Factor-kappaB-Dependent Transcription Involves Direct Interference with Transactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13504–13509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, T.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X. Dexamethasone Reduces the Formation of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection in a Murine Model. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 405, 112703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Tutino, V.M.; Xiang, J.; Siddiqui, A. High WSS or Low WSS? Complex Interactions of Hemodynamics with Intracranial Aneurysm Initiation, Growth, and Rupture: Toward a Unifying Hypothesis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, T.; Paget, A.; Shin, Y.S.; Li, X.; Mayer, J.; Chaudhry, H.; Niimi, Y.; Silane, M.; Berenstein, A. TNF-Alpha-Mediated Inflammation in Cerebral Aneurysms: A Potential Link to Growth and Rupture. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, T.; Berenstein, V.; Li, X.; Mayer, J.; Silane, M.; Shin, Y.S.; Niimi, Y.; Kiliç, T.; Gunel, M.; Berenstein, A. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Is a Key Modulator of Inflammation in Cerebral Aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, 558–564, discussion 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbaum, M.; Kolega, J.; Dolan, J.M.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H. A Critical Role for Proinflammatory Behavior of Smooth Muscle Cells in Hemodynamic Initiation of Intracranial Aneurysm. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, N.; Nagahiro, S.; Sano, T.; Satomi, J.; Satoh, K. Phenotypic Modulation of Smooth Muscle Cells in Human Cerebral Aneurysmal Walls. Acta Neuropathol. 2000, 100, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Morimoto, M.; Nozaki, K.; Hashimoto, N. Macrophage-Derived Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and -9 Promote the Progression of Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats. Stroke 2007, 38, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, G.; Todor, R.; Lewis, I.; Chyatte, D. Vascular Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Cerebral Aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, H.; Tada, Y.; Wada, K.; Liang, E.I.; Chang, M.; Mobashery, S.; Kanematsu, Y.; Kurihara, C.; Palova, E.; Kanematsu, M.; et al. Pharmacological Stabilization of Intracranial Aneurysms in Mice: A Feasibility Study. Stroke 2012, 43, 2450–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Moriwaki, T.; Nozaki, K.; Hashimoto, N. Role of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in the Progression of Cerebral Aneurysms. Stroke 2007, 38, 2337–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Dietmann, A.; Beer, R.; Broessner, G.; Helbok, R.; Pfausler, B.; Schmutzhard, E.; Lackner, P. Differential Regulation of Matrix-Metalloproteinases and Their Tissue Inhibitors in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golombek, S.; Doll, I.; Kaufmann, L.; Lescan, M.; Schlensak, C.; Avci-Adali, M. A Novel Strategy for the Treatment of Aneurysms: Inhibition of MMP-9 Activity through the Delivery of TIMP-1 Encoding Synthetic mRNA into Arteries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Heng, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xia, T.; Ji, C.; Zhang, L.-J. Dermal Extracellular Matrix Molecules in Skin Development, Homeostasis, Wound Regeneration and Diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 128, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staarmann, B.; Smith, M.; Prestigiacomo, C.J. Shear Stress and Aneurysms: A Review. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, S.; Higgs, E.A. Nitric Oxide and the Vascular Endothelium. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 213–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Ing, M.H.; Salazar, A.; Lassègue, B.; Griendling, K.; Navab, M.; Sevanian, A.; Hsiai, T.K. Pulsatile versus Oscillatory Shear Stress Regulates NADPH Oxidase Subunit Expression: Implication for Native LDL Oxidation. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usategui-Martín, R.; Jiménez-Arribas, P.; Sakas-Gandullo, C.; González-Sarmiento, R.; Rodríguez-Arias, C.A. Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Rs1799983 Gene Polymorphism Is Associated with the Risk of Developing Intracranial Aneurysm. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, N.; Fox, J.M.D.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H.; Kolega, J. Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase and Superoxide Mediate Hemodynamic Initiation of Intracranial Aneurysms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiber, A.; Xia, N.; Steven, S.; Oelze, M.; Hanf, A.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Münzel, T.; Li, H. New Therapeutic Implications of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) Function/Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheinberg, D.L.; McCarthy, D.J.; Elwardany, O.; Bryant, J.-P.; Luther, E.; Chen, S.H.; Thompson, J.W.; Starke, R.M. Endothelial Dysfunction in Cerebral Aneurysms. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Naritomi, H.; Nagata, I.; Nozaki, K.; Kondo, S.; Kurino, M.; Kikuchi, H. Prevention of Rat Cerebral Aneurysm Formation by Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Synthase. Circulation 2000, 101, 2532–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, H.; Roebuck, K.A. Oxidant Stress and Endothelial Cell Dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, C719–C741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke, R.M.; Chalouhi, N.; Ali, M.S.; Jabbour, P.M.; Tjoumakaris, S.I.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Rosenwasser, R.H.; Koch, W.J.; Dumont, A.S. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Cerebral Aneurysm Formation and Rupture. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2013, 10, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadamasa, N.; Nozaki, K.; Hashimoto, N. Disruption of Gene for Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Reduces Progression of Cerebral Aneurysms. Stroke 2003, 34, 2980–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, A.M.; Hippelheuser, J.E.; Lauric, A. Vortex Formation and Associated Aneurysmogenic Transverse Rotational Shear Stress near the Apex of Wide-Angle Cerebral Bifurcations. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 136, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Sheng, R.; Qin, Z.-H. NADPH Oxidases in the Central Nervous System: Regional and Cellular Localization and the Possible Link to Brain Diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2021, 35, 951–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šćepanović, V.; Tasić, G.; Repac, N.; Nikolić, I.; Janićijević, A.; Todorović, D.; Stojanović, M.; Šćepanović, R.; Mitrović, D.; Šćepanović, T.; et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress as a Risk Factor for Rupture of Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Aneurysms. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.-C.; Chen, C.-M.; Hamdin, C.D.; Orekhov, A.N.; Sobenin, I.A.; Layne, M.D.; Yet, S.-F. Therapeutic Potential of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Aneurysmal Diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrissobolis, S.; Faraci, F.M. The Role of Oxidative Stress and NADPH Oxidase in Cerebrovascular Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Liang, D.; Song, B.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhao, P.; Wu, W.; Zhang, N.; et al. Neurofilament Light Protein Predicts Disease Progression in Idiopathic REM Sleep Behavior Disorder. J. Park. Dis. 2023, 13, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Mactaggart, J.; Knispel, R.; Worth, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Baxter, B.T.; Johanning, J. Inhibition of Reactive Oxygen Species Attenuates Aneurysm Formation in a Murine Model. Atherosclerosis 2009, 202, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorce, S.; Krause, K.-H.; Jaquet, V. Targeting NOX Enzymes in the Central Nervous System: Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 2387–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yoshioka, H.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Okami, N.; Sakata, H.; Maier, C.M.; Narasimhan, P.; Goeders, C.E.; Chan, P.H. Oxidative Stress in Ischemic Brain Damage: Mechanisms of Cell Death and Potential Molecular Targets for Neuroprotection. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2011, 14, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Dhandapani, K.M.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Brann, D.W. NADPH Oxidase in Brain Injury and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.N.P.; Kamio, Y.; Kawakatsu, T.; Makino, H.; Hokamura, K.; Imai, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Hiramatsu, H.; Zhitong, L.; Umemura, K.; et al. Protective Effect of Resveratrol Against Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture in Mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2025, 103, e70059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; An, Q.; Qin, X.; Qin, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhou, B.; Leng, B. Resveratrol Inhibits Cerebral Aneurysms in Mice via Downregulating the NF-κB Pathway. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2022, 69, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, C.-N.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms of Resveratrol: A Narrative Review. Foods 2020, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekelis, K.; Kerley-Hamilton, J.S.; Teegarden, A.; Tomlinson, C.R.; Kuintzle, R.; Simmons, N.; Singer, R.J.; Roberts, D.W.; Kellis, M.; Hendrix, D.A. MicroRNA and Gene Expression Changes in Unruptured Human Cerebral Aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Pavlov, V.; Gareev, I.; Xu, S. Identification of Key Genes and miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Networks Associated with Intracranial Aneurysm Progression by Integrative Bioinformatics Analysis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Gu, C.; Zhao, X.; Gong, X.; Yang, X.; Pan, J.; Xi, Y. Neutrophil-like Cell Membrane-Coated Metal-Organic Frameworks for siRNA Delivery Targeting NOX4 to Alleviate Oxidative Stress in Acute Ischemic Injury. Acta Biomater. 2025, 196, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvy, C.S. Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 2357–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Sun, J.; Nie, S.; Gao, X.; Huang, Y. A Comprehensive Proteomic Analysis Reveals Novel Inflammatory Biomarkers in Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Proteom. 2025, 313, 105374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Datta, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Dey, G.; Khan, A.A.; Mangalaparthi, K.K.; Saharan, P.; Chinnapparaj, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Singla, N.; et al. Intracranial Aneurysm Biomarker Candidates Identified by a Proteome-Wide Study. OMICS 2020, 24, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.; Kundu, M.; Begum, J. Artificial Intelligence in Cancer Diagnosis: A Game-Changer in Healthcare. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2025, 26, 1314–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Barbarite, E.; Chaudhry, N.S.; Gupta, K.; Dellarole, A.; Peterson, E.C.; Elhammady, M.S. Search for Biomarkers of Intracranial Aneurysms: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ferronato, G.A.; Cerezetti, M.B.; Bridi, A.; Prado, C.M.; Dos Santos, G.; Bastos, N.M.; da Rosa, P.M.S.; Ferst, J.G.; da Silveira, J.C. MicroRNA Profiling Using a PCR-Based Method. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2595, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ning, K.; Liu, D.; Wu, D.; Wan, R.; Ge, J. MiR-140 Promotes the Progression of Intracranial Aneurysms by Targeting BCL2L2. Neuroreport 2023, 34, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wu, J.; Yuan, K.; Song, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, W. Upregulation of microRNA-205 Is a Potential Biomarker for Intracranial Aneurysms. Neuroreport 2019, 30, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, F. Circulating microRNAs Serve as Novel Biological Markers for Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuno, K.; Bilguvar, K.; Bijlenga, P.; Low, S.-K.; Krischek, B.; Auburger, G.; Simon, M.; Krex, D.; Arlier, Z.; Nayak, N.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Intracranial Aneurysm Identifies Three New Risk Loci. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuno, K.; Bakırcıoğlu, M.; Low, S.-K.; Bilgüvar, K.; Gaál, E.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; Niemelä, M.; Hata, A.; Bijlenga, P.; Kasuya, H.; et al. Common Variant near the Endothelin Receptor Type A (EDNRA) Gene Is Associated with Intracranial Aneurysm Risk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19707–19712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeuwsen, J.A.L.; van’ t Hof, F.N.G.; van Rheenen, W.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Veldink, J.H.; Ruigrok, Y.M. Circulating microRNAs in Patients with Intracranial Aneurysms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Im, S.-K.; Fang, S. Mouse Cre-LoxP System: General Principles to Determine Tissue-Specific Roles of Target Genes. Lab. Anim. Res. 2018, 34, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanaty, M.; Roa, J.A.; Nakagawa, D.; Chalouhi, N.; Allan, L.; Al Kasab, S.; Limaye, K.; Ishii, D.; Samaniego, E.A.; Jabbour, P.; et al. Aspirin Associated with Decreased Rate of Intracranial Aneurysm Growth. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 133, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.-C.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Jiao, Y.-M.; Fu, W.-L.; Huo, R.; Yan, Z.-H.; Xu, H.-Y.; Zhan, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Aspirin and Growth of Small Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm: Results of a Prospective Cohort Study. Stroke 2020, 51, 3045–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, S.; Ditto, M.C.; Ghellere, F.; Panaro, S.; Piccione, F.; Borrelli, R.; Fusaro, E. Update on Tocilizumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Narrative Review. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1470488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, C.A.; Hur, C.; Korzenik, J.R.; Gazelle, G.S.; Sands, B.E. Risks and Benefits of Infliximab for the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1017–1024, quiz 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-L.; Wei, J.C.-C.; Wu, Y.-T.; Ku, Y.-H.; Lu, K.-L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chiou, J.-Y. The Association Between Usage of Colchicine and Pneumonia: A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors as Investigational and Therapeutic Tools in Unrestrained Tissue Remodeling and Pathological Disorders. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 148, 355–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoh, B.L.; Ko, N.U.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Chou, S.H.-Y.; Cruz-Flores, S.; Dangayach, N.S.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Du, R.; Hänggi, D.; Hetts, S.W.; et al. 2023 Guideline for the Management of Patients With Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2023, 54, e314–e370, Erratum in Stroke 2023, 54, e516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossen, L.V.; Weiss, M.; Albanna, W.; Conzen-Dilger, C.; Schulze-Steinen, H.; Rossmann, T.; Schmidt, T.P.; Höllig, A.; Wiesmann, M.; Clusmann, H.; et al. Intra-Arterial Nimodipine for the Treatment of Refractory Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2024, 17, e31–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskey, C.J.; Meyers, P.M.; Nguyen, T.N.; Ansari, S.A.; Jayaraman, M.; McDougall, C.G.; DeMarco, J.K.; Gray, W.A.; Hess, D.C.; Higashida, R.T.; et al. Indications for the Performance of Intracranial Endovascular Neurointerventional Procedures: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e661–e689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAvoy, M.; Ratner, B.; Ferreira, M.J.; Levitt, M.R. Gene Therapy for Intracranial Aneurysms: Systemic Review. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2025, 17, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, D.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Dodd, W.S.; Martinez, M.; Chowdhury, M.A.B.; Hosaka, K.; Motwani, K.; Hoh, B. Combination Release of Chemokines from Coated Coils to Target Aneurysm Healing. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023, 15, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.R.; Frerichs, K.; Spetzler, R. Natural History and General Management of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Neurosurg. Focus 2004, 17, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hutchinson, H.; Rezk, R.; Farag, M.; Hanna, A.; Lucke-Wold, B. Molecular Targets for Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010053
Hutchinson H, Rezk R, Farag M, Hanna A, Lucke-Wold B. Molecular Targets for Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleHutchinson, Hunter, Rogina Rezk, Mariam Farag, Abanob Hanna, and Brandon Lucke-Wold. 2025. "Molecular Targets for Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010053
APA StyleHutchinson, H., Rezk, R., Farag, M., Hanna, A., & Lucke-Wold, B. (2025). Molecular Targets for Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010053






