Genotypic Variation and Genetic Control of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Shanlan Upland Rice Landrace
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
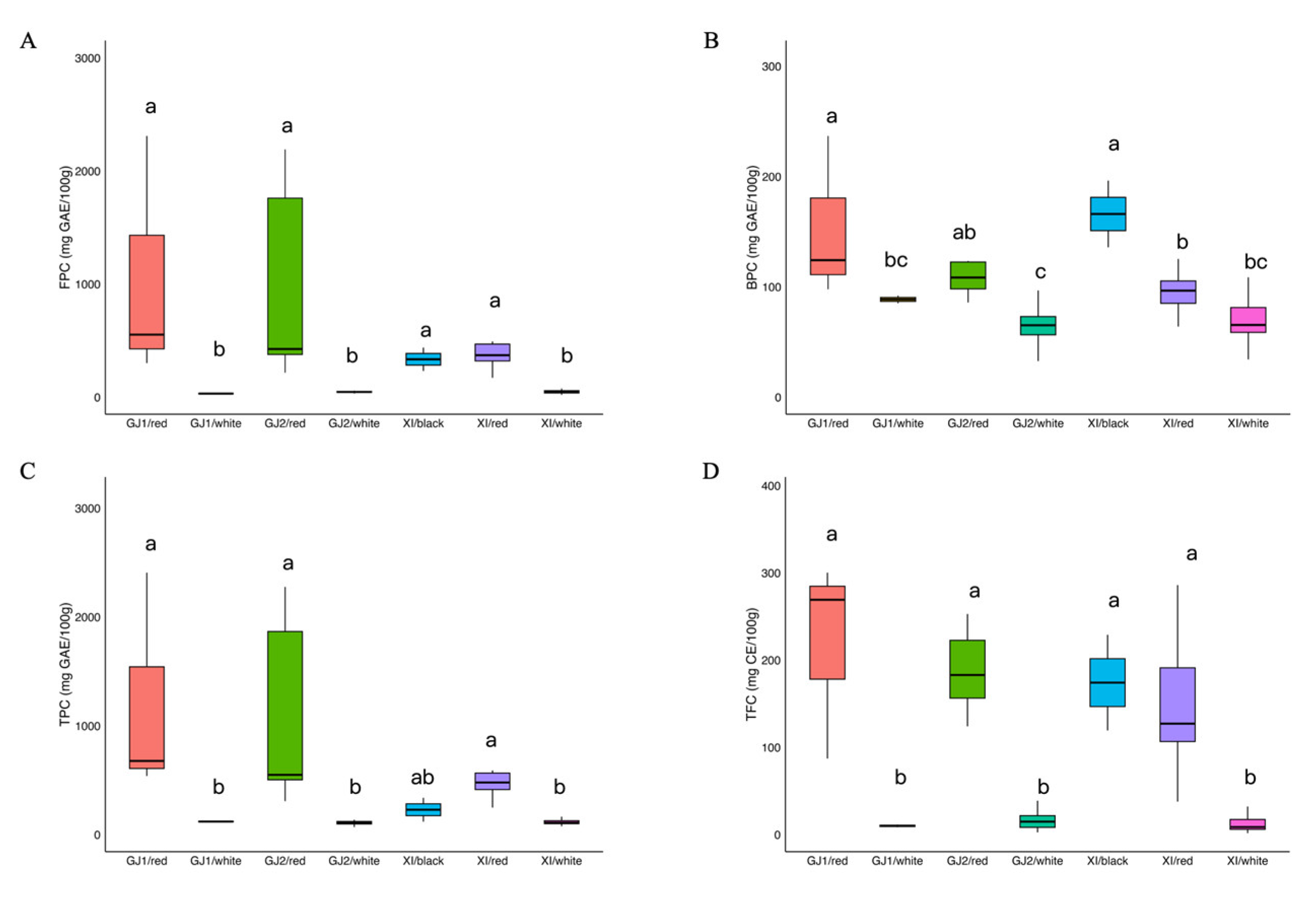
2.1. Analysis of Phenolics and Flavonoids Content
2.2. Antioxidant Properties
2.3. Correlation Analysis
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of Bound Phenolic Acids Compositions
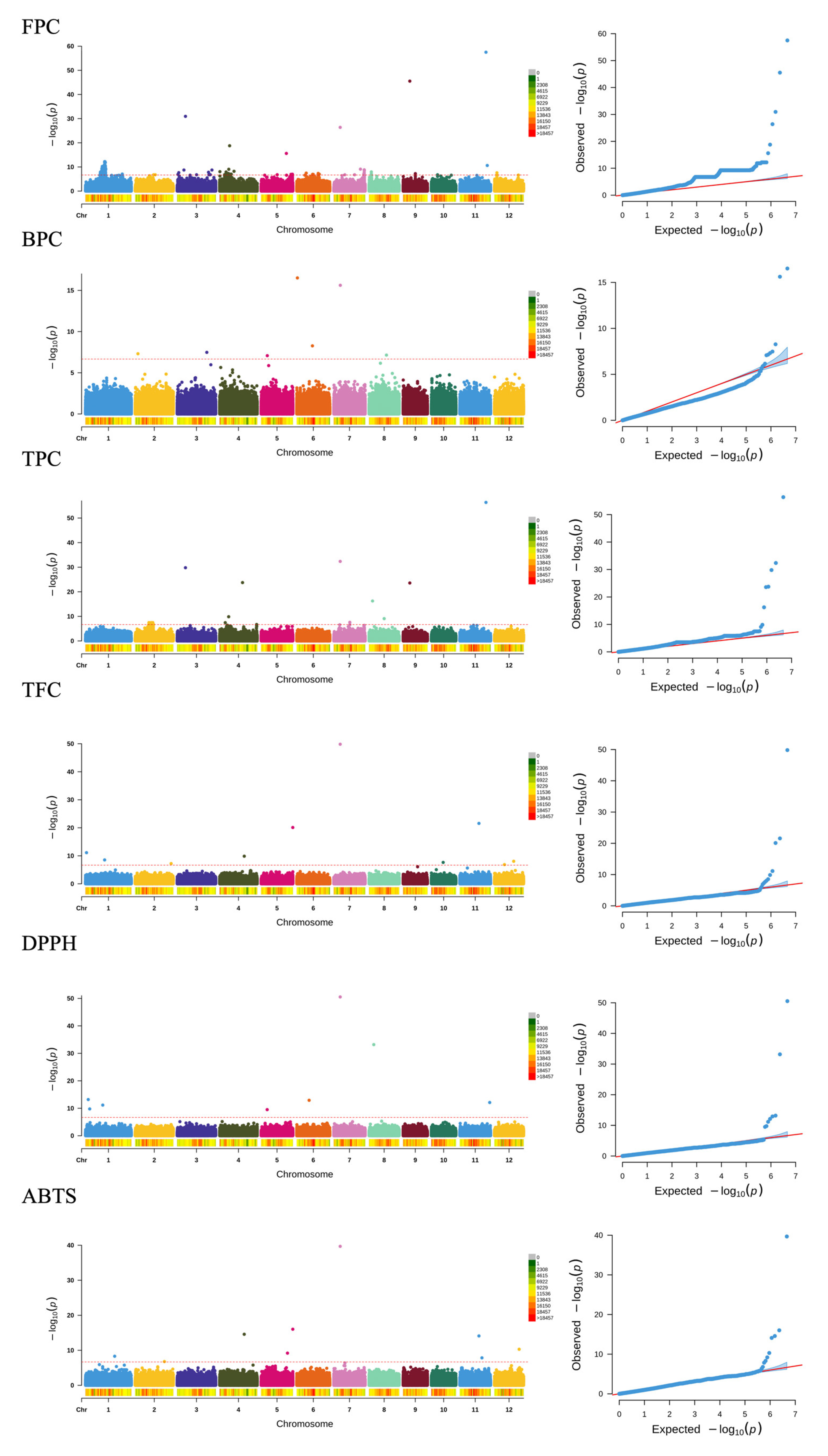
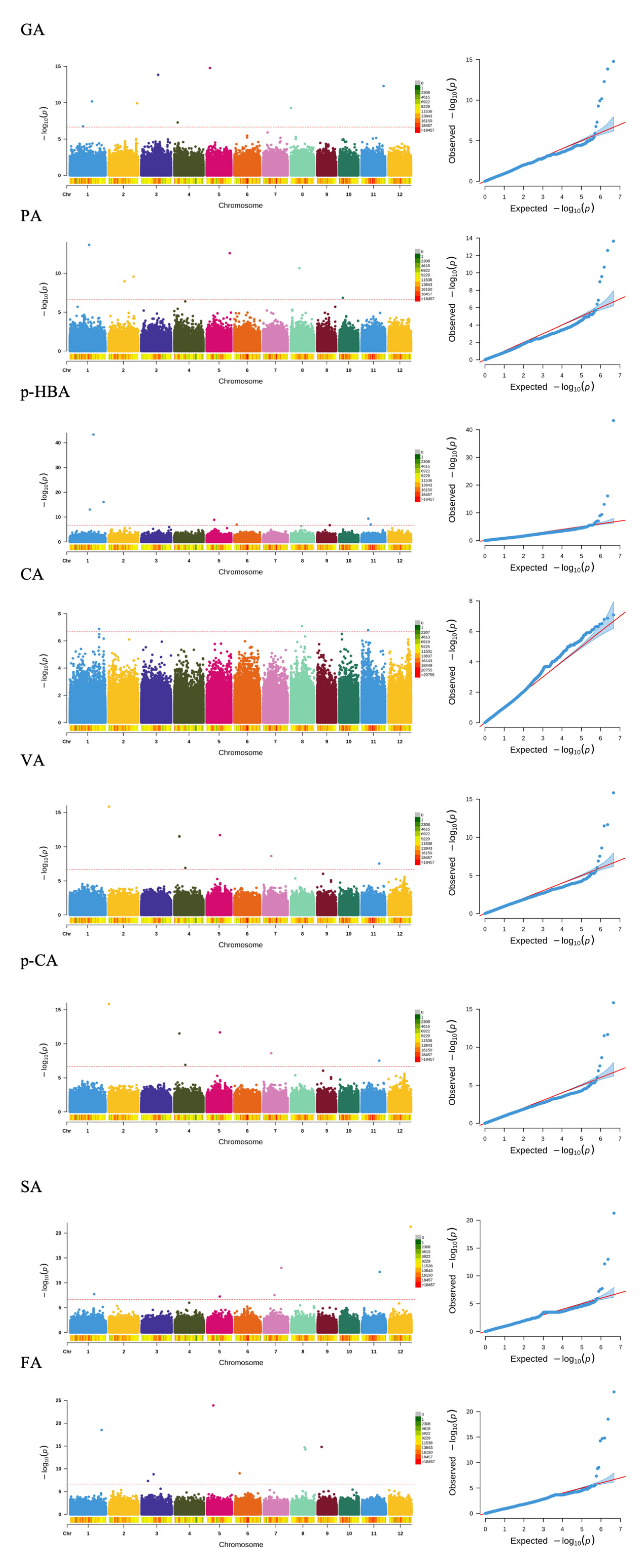
2.5. GWAS Analysis
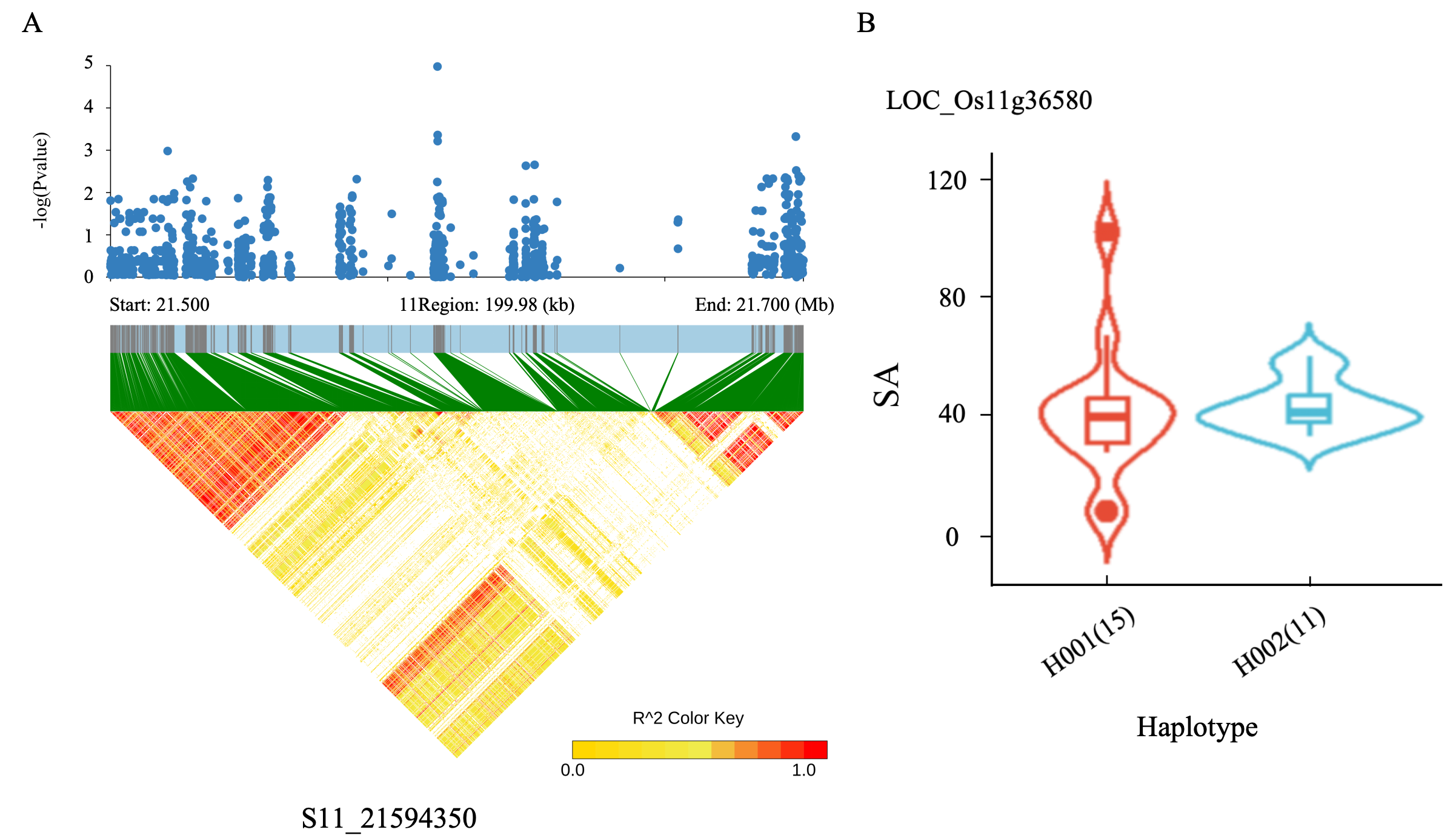
2.6. Identification of Candidate Gene and Haplotype Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Extensive Diversity in Phenolics of Shanlan Rice
3.2. Genetic Basis of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Rice
3.3. Potential Application in Molecular Breeding
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Extraction of Free Phenolic Acids and Insoluble Bound Phenolic Acids
4.4. Determination of Phenolic Acid Content and Flavonoid Content
4.5. Antioxidant Activity Determination
4.6. HPLC Analysis
4.7. Genome-Wide Association Study
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, M.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H. Improving nutritional quality of rice for human health. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 1397–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Ruesten, A.; Feller, S.; Bergmann, M.M.; Boeing, H. Diet and risk of chronic diseases: Results from the first 8 years of follow-up in the EPIC-Potsdam study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardet, A.; Boirie, Y. Associations between food and beverage groups and major diet-related chronic diseases: An exhaustive review of pooled/meta-analyses and systematic reviews. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 741–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, C.J.; Greenway, F.L.; Finley, J.W. Whole grains and pulses: A comparison of the nutritional and health benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7029–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, E.Q.; Chacko, S.A.; Chou, E.L.; Kugizaki, M.; Liu, S. Greater whole-grain intake is associated with lower risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and weight gain. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Rahaman, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, F.; Mithi, F.M.; Alqahtani, T.; Almikhlafi, M.A.; Alghamdi, S.Q.; Alruwaili, A.S.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Role of phenolic compounds in human disease: Current knowledge and future prospects. Molecules 2021, 27, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.Q.; Lin, H.X. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant-environment interactions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avinash, G.; Sharma, N.; Prasad, K.R.; Kaur, R.; Singh, G.; Pagidipala, N.; Thulasinathan, T. Unveiling the distribution of free and bound phenolic acids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, and proanthocyanidins in pigmented and non-pigmented rice genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1324825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Beta, T. Phenolic acid composition and antioxidant potential of insoluble and soluble dietary fibre extracts derived from select whole-grain cereals. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Robards, K.; Helliwell, S.; Blanchard, C. The distribution of phenolic acids in rice. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratne, A.; Wu, K.; Li, D.; Bentota, A.; Corke, H.; Cai, Y.Z. Antioxidant activity and nutritional quality of traditional red-grained rice varieties containing proanthocyanidins. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, T.; Qi, Q.; Du, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, N. Comparison of the contents of phenolic compounds including flavonoids and antioxidant activity of rice (Oryza sativa) and Chinese wild rice (Zizania latifolia). Food chem. 2021, 344, 128600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, S.; Dutta, H.; Saikia, D.; Mahanta, C. Quality characterisation and estimation of phytochemicals content and antioxidant capacity of aromatic pigmented and non-pigmented rice varieties. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Xu, F.; Sun, X.; Bao, J.; Beta, T. Phenolic acids, anthocyanins, and antioxidant capacity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grains at four stages of development after flowering. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Mou, R.; Zhu, Z.; Beta, T. Phenolic acids, anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, antioxidant activity, minerals and their correlations in non-pigmented, red, and black rice. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanjo, E.G.N.; Pasion, E.A.; Jones, H.; Carandang, S.; Misra, G.; Ignacio, J.C.; Kretzschmar, T.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Boyd, L.A. Unravelling marker trait associations linking nutritional value with pigmentation in rice seed. Plant Genome 2023, 16, e20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Qiu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xie, T.; Sun, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, F.; Yu, S. Deciphering the genetic architecture of color variation in whole grain rice by genome-wide association. Plants 2023, 12, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Bao, J. Association mapping of grain color, phenolic content, flavonoid content and antioxidant capacity in dehulled rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Bao, J.; Kim, T.S.; Park, Y.J. Genome-wide association mapping of polyphenol contents and antioxidant capacity in whole-grain rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4695–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, K. Genetic variation and association mapping of phenolic, flavonoid content and antioxidant capacity in USDA rice mini-core collection. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2022, 69, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunya, N.; Geetha, S.; Rajeswari, S.; Anandhi, K.; Mathankumar, P.; Jayakanthan, M.; Santosh, G.P.; Raveendran, M.; Manonmani, S.; Uma, D. Uncovering genomic regions for flavonoid and polyphenol content in whole rice grain through multi-environment GWAS. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 23, 102167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Zhai, N.; Yang, X.; Su, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Qu, P.; Liu, W.; Yuan, Q.; Pei, X. Identification of drought-resistant genes in Shanlan upland rice. Agriculture 2022, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Niu, X.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Q.; Pei, X. Understanding the molecular mechanism of drought resistance in Shanlan upland rice by transcriptome and phenotype analyses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Deng, B.; Peng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Bao, J. Population structure and genetic diversity of shanlan landrace rice for GWAS of cooking and eating quality traits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.Y.; Foley, M.E.; Horvath, D.P.; Anderson, J.V.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L.; Mowry, C.R.; Ye, H.; Suttle, J.C.; Kadowaki, K.; et al. Association between seed dormancy and pericarp color is controlled by a pleiotropic gene that regulates abscisic acid and flavonoid synthesis in weedy red rice. Genetics 2011, 189, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Gu, L.; McClung, A.M.; Bergman, C.J.; Chen, M.H. Free and bound total phenolic concentrations, antioxidant capacities, and profiles of proanthocyanidins and anthocyanins in whole grain rice (Oryza sativa L.) of different bran colours. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumczynski, D.; Kotásková, E.; Družbíková, H.; Mlček, J. Determination of contents and antioxidant activity of free and bound phenolics compounds and in vitro digestibility of commercial black and red rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shao, Y.; Bao, J.; Beta, T. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of breeding lines between the white and black rice. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Ahmed, S.; Xu, Y.; Beta, T.; Zhu, Z.; Shao, Y.; Bao, J. Bound phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of whole grain and bran of white, red and black rice. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.H.; Ferreira, C.D.; Vivian, P.G.; Monks, J.L.; Elias, M.C.; Vanier, N.L.; de Oliveira, M. The revisited levels of free and bound phenolics in rice: Effects of the extraction procedure. Food chem. 2016, 208, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.; Mandal, S.; Das, P.; Ashraf, G.J.; Dua, T.K.; Paul, P.; Nandi, G.; Khanra, R. The bioavailability, health advantages, extraction method, and distribution of free and bound phenolics of rice, wheat, and maize: A review. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Ge, S.; Lin, S. Review of distribution, extraction methods, and health benefits of bound phenolics in food plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3330–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Călinoiu, L.F.; Vodnar, D.C. Whole grains and phenolic acids: A review on bioactivity, functionality, health benefits and bioavailability. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Lim, M.J.; Kim, N.H.; Barathikannan, K.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Elahi, F.; Ham, H.J.; Oh, D.H. Quantification of Amino Acids, Phenolic Compounds Profiling from Nine Rice Varieties and Their Antioxidant Potential. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ti, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M.; Deng, Y.; Wei, Z.; Chi, J.; Zhang, Y. Free and bound phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity of milled fractions of different indica rice varieties cultivated in southern China. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, R.; Wei, Z.; Deng, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, M. Effect of degree of milling on phenolic profiles and cellular antioxidant activity of whole brown rice. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaupa, M.; Calani, L.; Del Rio, D.; Brighenti, F.; Pellegrini, N. Characterization of total antioxidant capacity and (poly) phenolic compounds of differently pigmented rice varieties and their changes during domestic cooking. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; Maekawa, M.; Oki, T.; Suda, I.; Iida, S.; Shimada, H.; Takamure, I.; Kadowaki, K. The Rc and Rd genes are involved in proanthocyanidin synthesis in rice pericarp. Plant J. 2007, 49, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnama, P.R.; Suwanchaikasem, P.; Junbuathong, S.; Chotechuen, S.; Moung-Ngam, P.; Kasettranan, W.; Paliyavuth, C.; Pongpanich, M.; Roytrakul, S.; Comai, L.; et al. Uncovering genetic determinants of antioxidant properties in Thai landrace rice through genome-wide association analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Pu, X.; Zhu, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Diao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Genome-Wide association study reveals the genetic basis of total flavonoid content in brown rice. Genes 2023, 14, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, B.; Cen, W.; Lu, S.; Jia, P.; Wang, X.; Qin, B.; Cai, Z.; Luo, J. The rice pds1 locus genetically interacts with partner to cause panicle exsertion defects and ectopic tillers in spikelets. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shen, S.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Y.; An, L.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, W.; et al. Rice metabolic regulatory network spanning the entire life cycle. Mol. Plant. 2022, 15, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; Sakaguchi, N.; Shimada, H. Two OsGASR genes, rice GAST homologue genes that are abundant in proliferating tissues, show different expression patterns in developing panicles. Genes. Genet. Syst. 2006, 81, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, C.; Fini, A.; Sebastiani, F.; Gori, A.; Tattini, M. Modulation of phytohormone signaling: A primary function of flavonoids in plant-environment interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, W.; Qin, X.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Ma, H.; et al. Two VQ proteins are substrates of the OsMPKK6-OsMPK4 cascade in rice defense against bacterial blight. Rice 2021, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.A.; Saleem, M.H.; Afzal, S.; Hussain, I.; Ameen, F.; Fahad, S. Ferulic acid: Therapeutic potential due to its antioxidant properties, role in plant growth, and stress tolerance. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 104, 1329–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiang, L.; Sheng, J.; Shen, L. Ferulic acid enhances chilling tolerance in tomato fruit by up-regulating the gene expression of CBF transcriptional pathway in MAPK3-dependent manner. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 185, 111775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumurugan, T.; Ito, Y.; Kubo, T.; Serizawa, A.; Kurata, N. Identification, characterization and interaction of HAP family genes in rice. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 279, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yan, W.; Chen, H.; Tan, C.; Han, Z.; Yao, W.; Li, G.; Yuan, M.; Xing, Y. Duplication of OsHAP family genes and their association with heading date in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, K.; Ito, Y.; Serizawa, A.; Kurata, N. OsHAP3 genes regulate chloroplast biogenesis in rice. Plant J. 2003, 36, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Thirumurugan, T.; Serizawa, A.; Hiratsu, K.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Kurata, N. Aberrant vegetative and reproductive development by overexpression and lethality by silencing of OsHAP3E in rice. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.H.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.X.; Zhou, H.J.; Li, Q.P.; Wang, C.R.; Ding, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yu, S.B.; Xing, Y.Z.; et al. A major QTL, Ghd8, plays pleiotropic roles in regulating grain productivity, plant height, and heading date in rice. Mol. Plant. 2011, 4, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ling, S.; Lu, Z.; Ouyang, Y.D.; Liu, S.; Yao, J. OsNF-YB1, a rice endosperm-specific gene, is essential for cell proliferation in endosperm development. Gene 2014, 551, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Tanaka, T.; Nakamura, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Yaeno, T.; Yamaoka, N.; Shimomoto, K.; Takayama, K.; Nishina, H.; et al. Overexpression of a rice heme activator protein gene (OsHAP2E) confers resistance to pathogens, salinity and drought, and increases photosynthesis and tiller number. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zhu, S.; Wu, M.; Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, T.; Cui, S.; Zhou, S.; Li, C.; et al. DHD4, a CONSTANS-like family transcription factor, delays heading date by affecting the formation of the FAC complex in rice. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiosi, R.; dos Santos, W.D.; Constantin, R.P.; de Lima, R.B.; Soares, A.R.; Finger-Teixeira, A.; Mota, T.R.; de Oliveira, D.M.; de Paiva Foletto-Felipe, M.; Abrahão, J.; et al. Biosynthesis and metabolic actions of simple phenolic acids in plants. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 865–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Li, Q.F.; Cai, X.L.; Wang, H.M.; Tang, S.Z.; Yu, H.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Gu, M.H. Molecular marker-assisted selection for improved cooking and eating quality of two elite parents of hybrid rice. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 2354–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Lu, Y.; Shao, Y.F.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, P.; Shen, S.Q.; Corke, H.; Bao, J.S. Molecular marker assisted selection for improvement of the eating, cooking and sensory quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 51, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Xi, J.Z.; Xu, D.; Jin, Y.M.; Wu, F.F.; Tong, Q.Y.; Yin, Y.; Xu, X.M. A comparative HS-SPME/GC-MS-based metabolomics approach for discrimination selected japonica rice varieties from different regions of China in raw and cooked form. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhang, T.; Matsunaga, R. Direct extraction of volatiles of rice during cooking using solid-phase microextraction. Cereal Chem. 2007, 84, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugita, T.; Ohta, T.; Kato, H. Cooking flavor and texture of rice stored under different conditions. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1983, 47, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Traits | White | Red | Black | Total | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | |
| FPC 1 | 55.71 b | 20.99 | 351.83 | 727.66 a | 171.75 | 2310.45 | 340.24 ab | 232.73 | 447.75 | 270.47 | 20.99 | 2310.45 |
| BPC 1 | 66.41 c | 22.00 | 108.75 | 106.03 b | 64.00 | 236.88 | 165.38 a | 105.88 | 224.88 | 81.03 | 22.00 | 236.88 |
| TPC 1 | 122.12 b | 60.93 | 430.20 | 833.70 a | 249.00 | 2408.33 | 505.61 ab | 338.60 | 672.63 | 351.50 | 60.93 | 2408.33 |
| TFC 2 | 19.47 b | 1.76 | 147.12 | 167.86 a | 37.88 | 300.32 | 162.52 a | 119.44 | 205.60 | 68.80 | 1.76 | 300.32 |
| DPPH 3 | 341.61 b | 56.67 | 801.15 | 795.62 a | 680.39 | 809.63 | 780.50 a | 772.84 | 788.16 | 492.59 | 56.67 | 809.63 |
| ABTS 3 | 274.96 b | 31.95 | 1217.84 | 1262.58 a | 529.93 | 1917.77 | 957.00 a | 544.81 | 1369.20 | 596.89 | 31.95 | 1917.77 |
| GA 4 | 0.29 a | 0.06 | 1.88 | 0.25 a | 0.06 | 0.63 | 0.51 a | 0.10 | 0.92 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 1.88 |
| PA 4 | 0.44 a | 0.04 | 2.88 | 0.34 a | 0.12 | 1.06 | 0.51 a | 0.13 | 0.90 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 2.88 |
| p-HBA 4 | 0.33 a | 0.03 | 1.02 | 0.39 a | 0.06 | 3.29 | 0.59 a | 0.20 | 0.98 | 0.35 | 0.03 | 3.29 |
| CA 4 | 0.32 a | 0.07 | 6.22 | 0.30 a | 0.08 | 1.96 | 0.36 a | 0.22 | 0.51 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 6.22 |
| VA 4 | 12.41 a | 0.26 | 53.60 | 9.94 a | 1.83 | 17.37 | 15.46 a | 7.84 | 23.08 | 11.72 | 0.26 | 53.60 |
| p-CA 4 | 4.35 a | 0.30 | 18.08 | 3.52 a | 0.82 | 6.00 | 5.36 a | 2.82 | 7.90 | 4.12 | 0.30 | 18.08 |
| SA 4 | 59.57 a | 0.99 | 237.46 | 44.33 a | 27.03 | 63.24 | 69.29 a | 36.43 | 102.14 | 55.08 | 0.99 | 237.46 |
| FA 4 | 1.45 a | 0.10 | 4.94 | 1.26 a | 0.10 | 2.40 | 1.32 a | 1.25 | 1.38 | 1.39 | 0.10 | 4.94 |
| FPC | BPC | TPC | TFC | DPPH | ABTS | GA | PA | p-HBA | CA | VA | p-CA | SA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPC | 0.293 ** | ||||||||||||
| TPC | 0.998 ** | 0.354 ** | |||||||||||
| TFC | 0.719 ** | 0.570 ** | 0.742 ** | ||||||||||
| DPPH | 0.591 ** | 0.624 ** | 0.620 ** | 0.843 ** | |||||||||
| ABTS | 0.774 ** | 0.530 ** | 0.793 ** | 0.959 ** | 0.837 ** | ||||||||
| GA | −0.065 | −0.014 | −0.064 | 0.006 | 0.038 | −0.051 | |||||||
| PA | −0.159 | −0.123 | −0.164 | −0.131 | −0.093 | −0.172 | 0.555 ** | ||||||
| p-HBA | −0.051 | 0.124 | −0.041 | 0.091 | 0.119 | 0.052 | 0.394 ** | 0.340 ** | |||||
| CA | −0.049 | 0.065 | −0.044 | 0.027 | 0.035 | −0.015 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.116 | ||||
| VA | −0.046 | −0.024 | −0.047 | −0.135 | −0.224 * | −0.123 | 0.067 | 0.14 | 0.034 | 0.125 | |||
| p-CA | −0.046 | −0.024 | −0.047 | −0.135 | −0.224 * | −0.123 | 0.067 | 0.14 | 0.034 | 0.125 | 1.000 ** | ||
| SA | −0.089 | −0.029 | −0.089 | −0.14 | −0.243 * | −0.151 | 0.161 | 0.144 | 0.049 | 0.276 * | 0.941 ** | 0.941 ** | |
| FA | −0.015 | 0.077 | −0.009 | −0.092 | −0.129 | −0.076 | 0.021 | 0 | 0.075 | 0.411 ** | 0.712 ** | 0.712 ** | 0.757 ** |
| Trait | Position 1 | Polymorphism | p-Value | Effect | Candidate Locus | Region | Known Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPC | S4_8608872 | T/C | 9.28 × 10−10 | −231.75 | LOC_Os04g15870 | exonic | |
| S5_27501155 | G/A | 1.20 × 10−11 | 206.42 | LOC_Os05g47960 (dist = 1569) | upstream | ||
| S6_9901517 | C/G | 1.21 × 10−7 | −103.99 | LOC_Os06g17070 (dist = 6349) LOC_Os06g17080 (dist = 2583) | intergenic | ||
| S7_6068071 | A/AACGCGAAAAGTCGG | 4.13 × 10−27 | 159.47 | LOC_Os07g11020 | exonic | Rc | |
| S7_16138785 | A/G | 6.91 × 10−14 | 151.12 | LOC_Os07g27630 (dist = 3320) LOC_Os07g27650 (dist = 6394) | intergenic | ||
| S8_15935332 | G/A | 7.28 × 10−8 | 139.96 | LOC_Os08g26200 (dist = 1553) LOC_Os08g26190 (dist = 1105) | upstream downstream | ||
| S12_6284651 | G/A | 2.82 × 10−14 | 217.92 | LOC_Os12g11590 | exonic | ||
| BPC | S2_2531849 | G/A | 4.88 × 10−8 | −5.49 | LOC_Os02g05260 | exonic | |
| S3_27983323 | T/C | 3.33 × 10−8 | 14.99 | LOC_Os03g49126 (dist = 526) LOC_Os03g49120 (dist = 1360) | upstream downstream | ||
| S5_5790070 | ACAGGTCCTC/A | 8.40 × 10−8 | −13.37 | LOC_Os05g10620, LOC_Os05g10625 (dist = 138) LOC_Os05g10630 (dist = 138) | upstream downstream | ||
| S6_574213 | T/C | 3.08 × 10−17 | −96.32 | LOC_Os06g02010 | exonic | ||
| S6_14781772 | G/A | 5.39 × 10−9 | 11.80 | LOC_Os06g25270 | exonic | ||
| S7_6170573 | G/A | 2.41 × 10−16 | −11.67 | LOC_Os07g11200 | exonic | ||
| S8_16402811 | C/T | 7.12 × 10−8 | 7.81 | LOC_Os08g26890 (dist = 12845) LOC_Os08g26900 (dist = 2170) | intergenic | ||
| TPC | S3_7796717 | T/C | 1.61 × 10−30 | 734.65 | LOC_Os03g14320 | exonic | |
| S4_5262699 | ATTGCAAGGAGTCG/A | 3.66 × 10−8 | −125.76 | LOC_Os04g09810 (dist = 957) | downstream | ||
| S4_8505441 | G/C | 1.41 × 10−10 | 120.20 | LOC_Os04g15640 | exonic | ||
| S4_21608571 | C/T | 1.81 × 10−24 | 300.67 | LOC_Os04g35510 (dist = 802) | downstream | ||
| S7_6068071 | A/AACGCGAAAAGTCGG | 4.29 × 10−33 | 187.80 | LOC_Os07g11020 | exonic | Rc | |
| S8_3232230 | A/G | 5.86 × 10−17 | 556.67 | LOC_Os08g05940 (dist = 4005) LOC_Os08g05950 (dist = 7398) | intergenic | pds1 | |
| S8_14227902 | G/A | 8.32 × 10−10 | −149.50 | LOC_Os08g23500 (dist = 1942) | upstream | ||
| S9_6298533 | C/T | 2.64 × 10−24 | 400.40 | LOC_Os09g11330 (dist = 2581) LOC_Os09g11350 (dist = 2388) | intergenic | ||
| S11_24663643 | T/G | 4.35 × 10−57 | 892.65 | LOC_Os11g41160 (dist = 4315) LOC_Os11g41170 (dist = 7324) | intergenic | ||
| TFC | S1_890709 | A/G | 7.51 × 10−12 | −18.73 | LOC_Os01g02650 (dist = 1386) | upstream | |
| S1_18037853 | G/T | 2.95 × 10−9 | 17.76 | LOC_Os01g32864 (dist = 1287) | upstream | ||
| S2_33906691 | G/A | 5.83 × 10−8 | −12.47 | LOC_Os02g55350 | intronic | ||
| S4_23251954 | T/C | 1.38 × 10−10 | −19.71 | LOC_Os04g39110 (dist = 8752) LOC_Os04g39120 (dist = 17585) | intergenic | OsGASR2 | |
| S5_29897937 | G/A | 7.87 × 10−21 | 46.76 | LOC_Os05g52070 | exonic | ||
| S7_6068071 | A/AACGCGAAAAGTCGG | 1.51 × 10−50 | 66.24 | LOC_Os07g11020 | exonic | Rc | |
| S10_11143309 | T/A | 2.28 × 10−8 | 12.83 | LOC_Os10g21700 (dist = 14656) LOC_Os10g21720 (dist = 3752) | intergenic | ||
| S11_18026280 | T/C | 2.69 × 10−22 | 40.23 | LOC_Os11g30990 | exonic | ||
| S12_9386926 | T/G | 1.38 × 10−7 | −16.13 | LOC_Os12g16400 | intronic | ||
| S12_18137641 | G/A | 9.03 × 10−9 | 20.53 | LOC_Os12g30214 | exonic | ||
| DPPH | S1_2542760 | C/T | 6.65 × 10−14 | −114.38 | LOC_Os01g05370 LOC_Os01g05380 (dist = 28) | upstream | |
| S1_3917148 | C/A | 1.73 × 10−10 | 50.52 | LOC_Os01g08090 (dist = 770) | upstream | ||
| S1_16259756 | G/C | 6.99 × 10−12 | −48.66 | LOC_Os01g29040 LOC_Os01g29050 (dist = 485) | upstream | ||
| S5_5680332 | C/T | 3.12 × 10−10 | −66.34 | LOC_Os05g10430 | intronic | ||
| S6_11653435 | C/T | 1.24 × 10−13 | −87.88 | LOC_Os06g20290 (dist = 387) | downstream | ||
| S7_6068071 | A/AACGCGAAAAGTCGG | 2.95 × 10−51 | 222.93 | LOC_Os07g11020 | exonic | Rc | |
| S8_4407898 | C/A,G | 6.67 × 10−34 | 215.49 | LOC_Os08g07850 | intronic | ||
| S11_28201425 | C/G | 7.93 × 10−13 | −67.71 | LOC_Os11g46920 | exonic | ||
| ABTS | S1_27531822 | T/C | 4.96 × 10−9 | 159.97 | LOC_Os01g49920 | exonic | |
| S2_27557707 | C/T | 1.64 × 10−7 | 117.95 | LOC_Os02g45344 (dist = 1496) | upstream | ||
| S4_23223209 | A/G | 2.63 × 10−15 | −161.85 | LOC_Os04g39070 (dist = 1291) | upstream | ||
| S5_24882400 | AGAGG/A | 6.41 × 10−10 | −120.26 | LOC_Os05g42428 (dist = 4750) LOC_Os05g42436 (dist = 26926) | intergenic | ||
| S5_29897937 | G/A | 9.58 × 10−17 | 290.46 | LOC_Os05g52070 | exonic | ||
| S7_6068071 | A/AACGCGAAAAGTCGG | 2.07 × 10−40 | 444.09 | LOC_Os07g11020 | exonic | Rc | |
| S11_18026280 | T/C | 7.95 × 10−15 | 183.84 | LOC_Os11g30990 | exonic | ||
| S11_20846878 | G/A | 1.41 × 10−8 | 143.26 | LOC_Os11g35560 | intronic | ||
| S12_23293153 | G/A | 5.02 × 10−11 | 121.36 | LOC_Os12g37900 (dist = 309) LOC_Os12g37890 LOC_Os12g37910 (dist = 309) | upstream downstream | ||
| GA | S1_26909462 | A/AC | 6.68 × 10−11 | −0.14 | LOC_Os01g47090 (dist = 7818) LOC_Os01g47100 (dist = 3135) | intergenic | |
| S2_34727049 | A/G | 1.20 × 10−10 | 0.14 | LOC_Os02g56640 | exonic | ||
| S3_20453194 | A/T | 1.46 × 10−14 | 0.26 | LOC_Os03g36860 | exonic | ||
| S4_4113997 | A/G | 5.07 × 10−8 | 0.14 | LOC_Os04g07730 | exonic | ||
| S5_3991938 | A/C | 1.69 × 10−15 | 0.45 | LOC_Os05g07470 (dist = 8338) LOC_Os05g07480 (dist = 6747) | intergenic | ||
| S8_166588 | A/G | 5.41 × 10−10 | −0.14 | LOC_Os08g01260 (dist = 1372) | upstream | OsVQ32 | |
| S11_26976494 | C/T | 4.98 × 10−13 | 0.22 | LOC_Os11g44600 | exonic | ||
| PA | S1_23469338 | A/C | 2.26 × 10−14 | 0.36 | LOC_Os01g41450 (dist = 4153) LOC_Os01g41460 (dist = 2881) | intergenic | |
| S2_19213738 | A/C | 1.06 × 10−9 | −0.23 | LOC_Os02g32480 (dist = 916) | downstream | ||
| S2_30352381 | GC/G | 2.70 × 10−10 | −0.40 | LOC_Os02g49670 (dist = 317) | downstream | ||
| S5_27988411 | T/C | 2.60 × 10−13 | −1.15 | LOC_Os05g48830 | exonic | ||
| S8_10428981 | C/T | 2.21 × 10−11 | −0.25 | LOC_Os08g17030 | exonic | ||
| S10_4396593 | A/T | 1.38 × 10−7 | 0.14 | LOC_Os10g08140 | intronic | ||
| p-HBA | S1_24264360 | T/C | 8.87 × 10−14 | −0.59 | LOC_Os01g42660(dist = 156) | upstream | |
| S1_28671305 | A/C,T | 5.15 × 10−44 | 1.48 | LOC_Os01g49920 | exonic | ||
| S1_41031628 | C/T | 8.14 × 10−17 | 0.34 | LOC_Os01g70890 LOC_Os01g70900 (dist = 147) | upstream | OsNF- YB6 OsHAP3G | |
| S5_9091371 | C/T | 1.32 × 10−9 | 0.16 | LOC_Os05g16080 (dist = 5811) LOC_Os05g16090 (dist = 2759) | intergenic | ||
| S6_2827762 | T/C | 1.13 × 10−7 | −0.07 | LOC_Os06g06115 (dist = 681) | upstream | ||
| S9_15098602 | TTCGTC/N,TGTCGTC | 1.92 × 10−7 | −0.07 | LOC_Os09g25200 (dist = 758) | downstream | ||
| S11_8262262 | G/A | 4.46 × 10−10 | 0.15 | LOC_Os11g14650 | intronic | ||
| S11_11150178 | G/A | 9.82 × 10−8 | 0.13 | LOC_Os11g19380 (dist = 551) | upstream | ||
| p-CA /VA | S2_551933 | G/A | 1.43 × 10−16 | 2.81 | LOC_Os02g01990 (dist = 751) | upstream | DHD4 |
| S4_6167066 | C/T | 3.15 × 10−12 | 1.25 | LOC_Os04g11290 | exonic | ||
| S4_13289104 | C/T | 1.29 × 10−7 | −1.18 | LOC_Os04g23280 | intronic | ||
| S5_16026627 | G/A | 2.18 × 10−12 | 2.29 | LOC_Os05g27540 | exonic | ||
| S7_9790670 | ACGATGGTAAATCG/A | 2.39 × 10−9 | 1.70 | LOC_Os07g16690 (dist = 215) | upstream | ||
| S11_21594350 | C/T | 3.02 × 10−8 | 1.72 | LOC_Os11g36580 (dist = 704) | upstream | ||
| SA | S1_29034197 | C/T | 1.80 × 10−8 | 13.55 | LOC_Os01g50550 (dist = 784) LOC_Os01g50560 (dist = 1076) | upstream downstream | |
| S5_15307396 | T/C | 5.67 × 10−8 | −10.21 | LOC_Os05g26310 LOC_Os05g26320 (dist = 1876) | downstream | ||
| S7_13188853 | G/A | 2.75 × 10−8 | −22.77 | LOC_Os07g23400 | exonic | ||
| S7_21496930 | G/A | 1.01 × 10−13 | 32.74 | LOC_Os07g35920 | intronic | ||
| S11_21594350 | C/T | 6.84 × 10−13 | 32.01 | LOC_Os11g36580 (dist = 704) | upstream | ||
| S12_26390982 | A/G | 5.30 × 10−22 | 40.70 | LOC_Os12g42480 (dist = 626) | upstream | ||
| FA | S1_38008134 | C/CTATTT | 3.08 × 10−19 | −0.72 | LOC_Os01g65480 (dist = 1492) LOC_Os01g65470 (dist = 1494) | upstream downstream | |
| S3_7652662 | C/A | 4.54 × 10−8 | 0.19 | LOC_Os03g14080 (dist = 2103) LOC_Os03g14090 (dist = 3520) | intergenic | OsAUX2 | |
| S3_14331413 | A/G | 1.57 × 10−9 | 0.26 | LOC_Os03g25100 | exonic | ||
| S5_7616250 | A/T | 1.33 × 10−24 | 1.30 | LOC_Os05g13740 (dist = 89) | downstream | ||
| S6_5891020 | T/G | 9.46 × 10−10 | −0.42 | LOC_Os06g11220 LOC_Os06g11230 (dist = 51) | downstream | ||
| S8_16274914 | A/G | 1.98 × 10−15 | −0.40 | LOC_Os08g26770 (dist = 44) LOC_Os08g26760 (dist = 325) | upstream downstream | ||
| S8_17348215 | G/A | 5.60 × 10−15 | 0.59 | LOC_Os08g28410 | intronic | ||
| S9_4720926 | A/AT | 1.55 × 10−15 | −0.57 | LOC_Os09g08900 (dist = 66) | downstream |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Deng, B.; Peng, Y.; Shao, Y.; Bao, J. Genotypic Variation and Genetic Control of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Shanlan Upland Rice Landrace. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199800
Zhang L, Yu J, Deng B, Peng Y, Shao Y, Bao J. Genotypic Variation and Genetic Control of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Shanlan Upland Rice Landrace. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199800
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lin, Jing Yu, Bowen Deng, Yi Peng, Yafang Shao, and Jinsong Bao. 2025. "Genotypic Variation and Genetic Control of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Shanlan Upland Rice Landrace" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199800
APA StyleZhang, L., Yu, J., Deng, B., Peng, Y., Shao, Y., & Bao, J. (2025). Genotypic Variation and Genetic Control of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Shanlan Upland Rice Landrace. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199800







