Transcriptomics Data Mining to Identify Novel Regulatory Genes of Iron Uptake in Drought-Stressed Wheat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
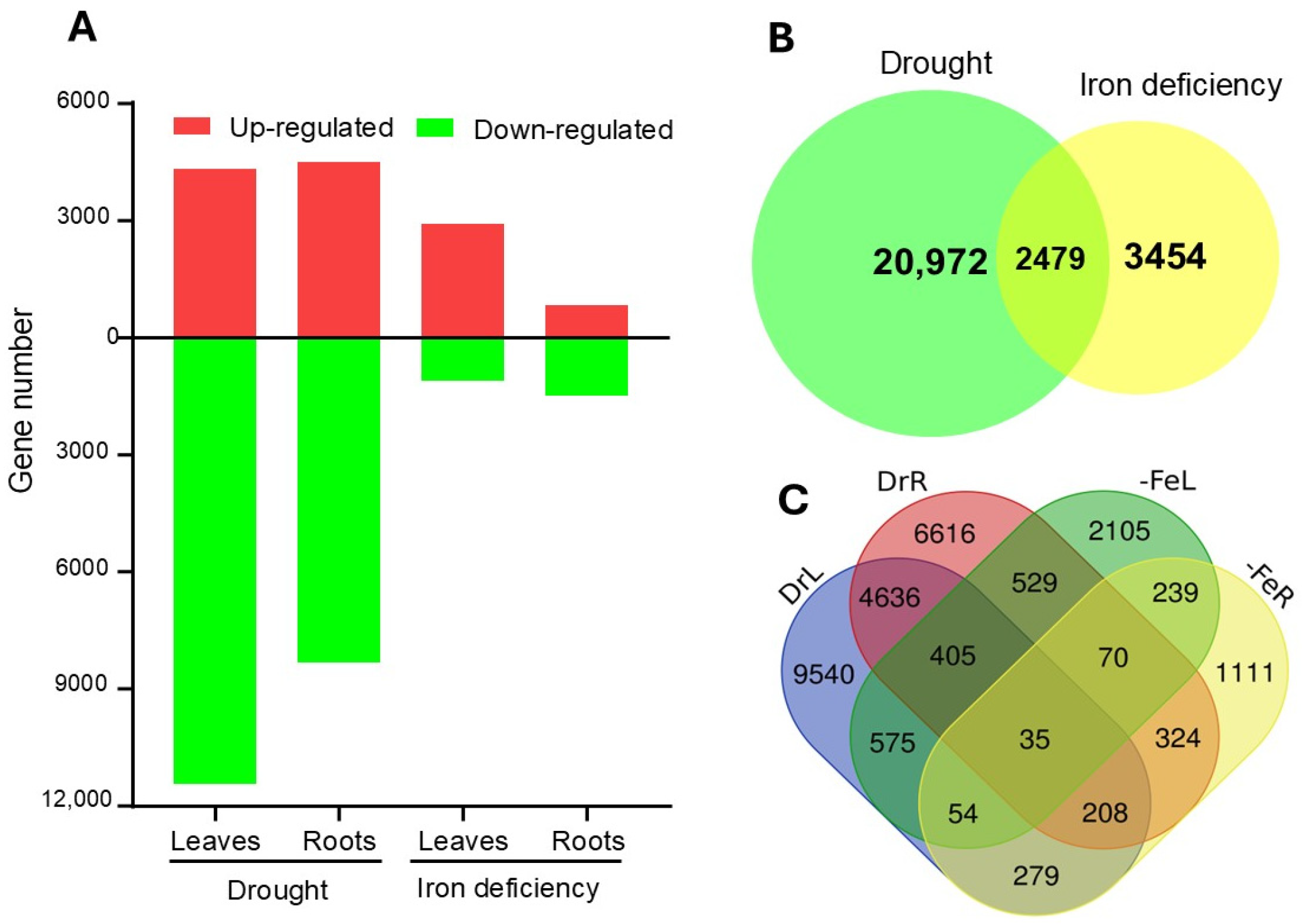
2.1. Identification of DEGs Under Drought and Fe Deficiency
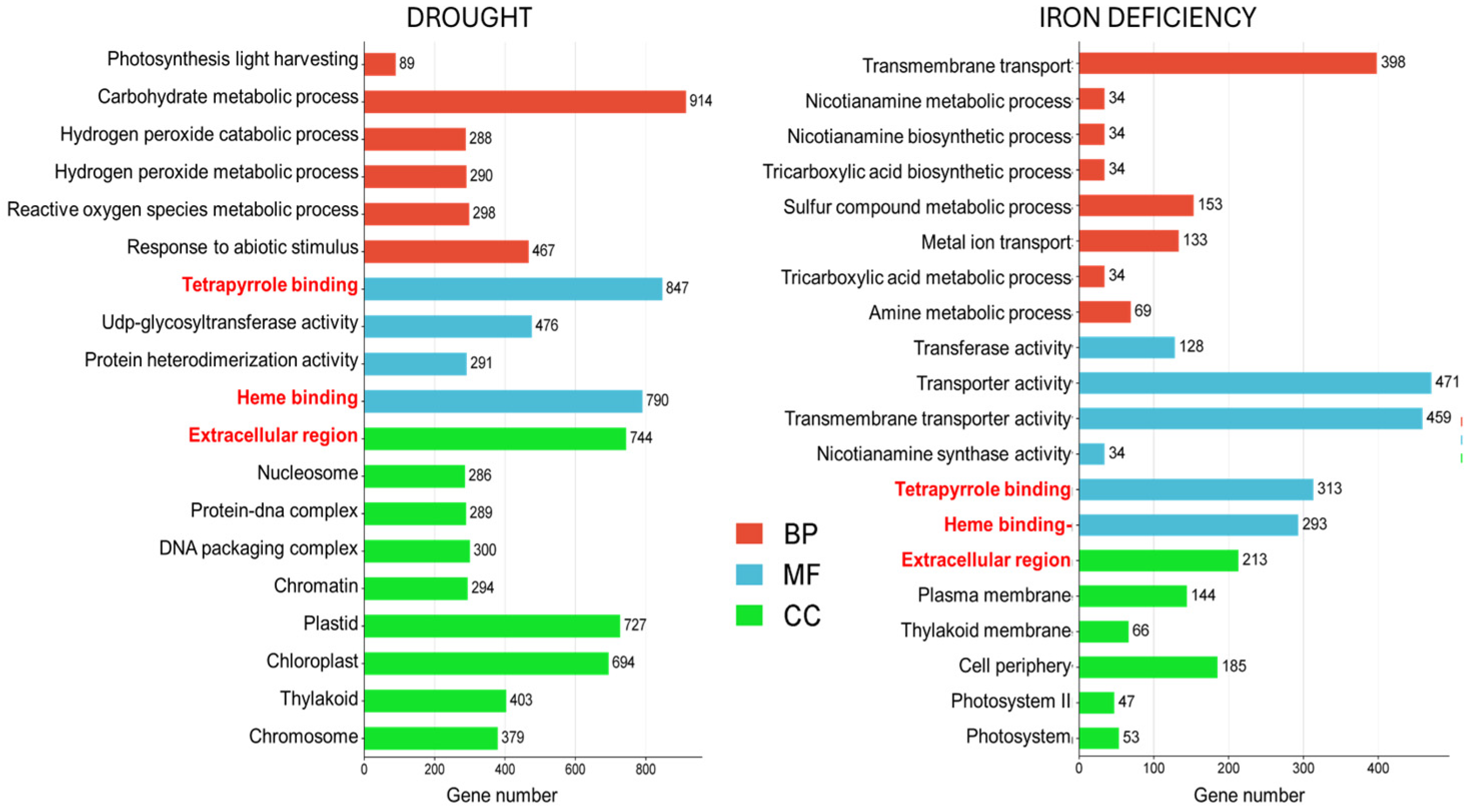
2.2. GO Enrichment Revealed Biological Process Related to Drought and Fe Uptake
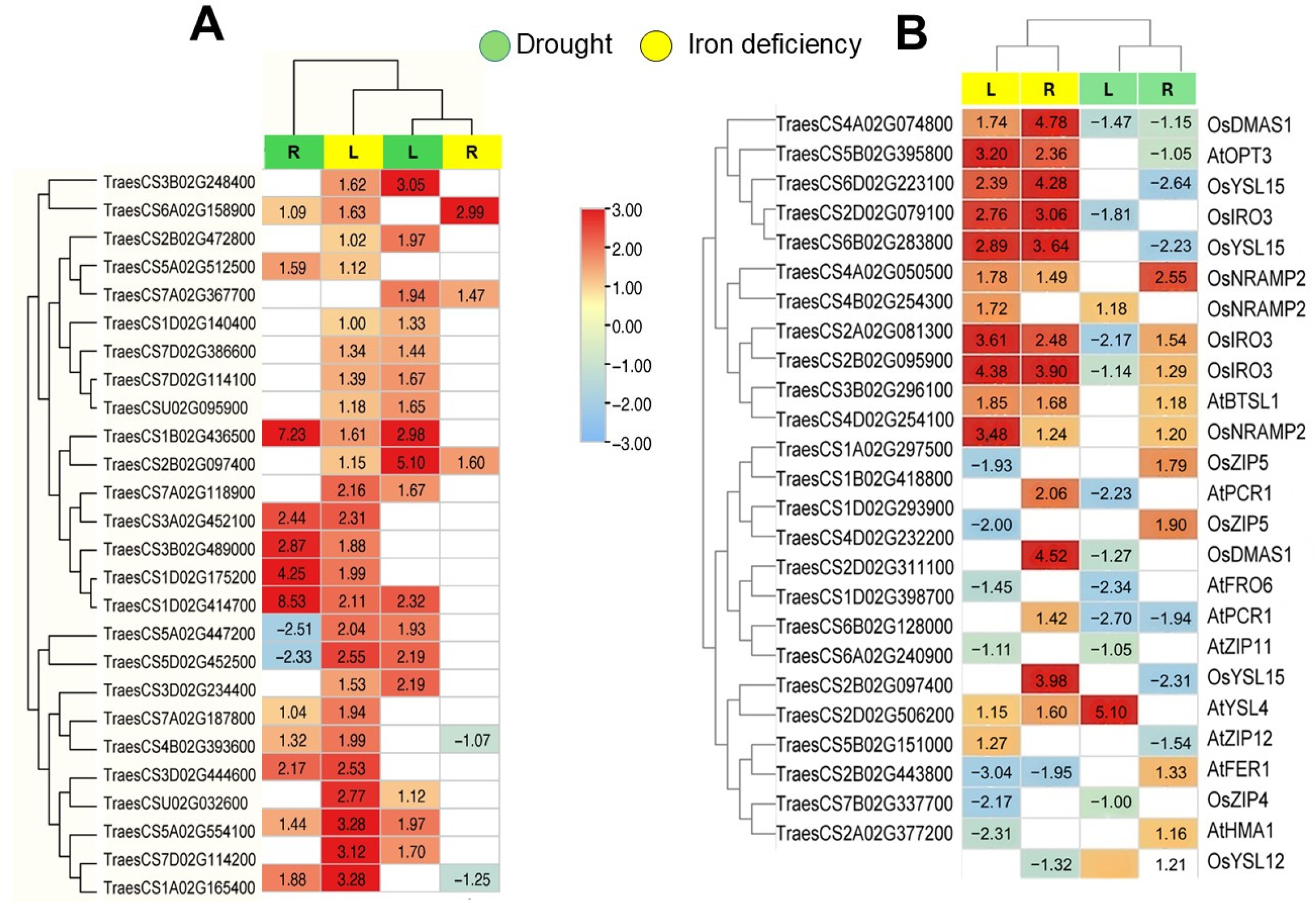
2.3. Fe Homeostasis Genes Are Modulated Under Fe Deficiency and Drought Conditions
2.4. Drought and Fe Deficiency Affect Phytohormone Signaling
2.5. Transcription Factors Controlling Fe Uptake Under Drought and Fe Deficiency
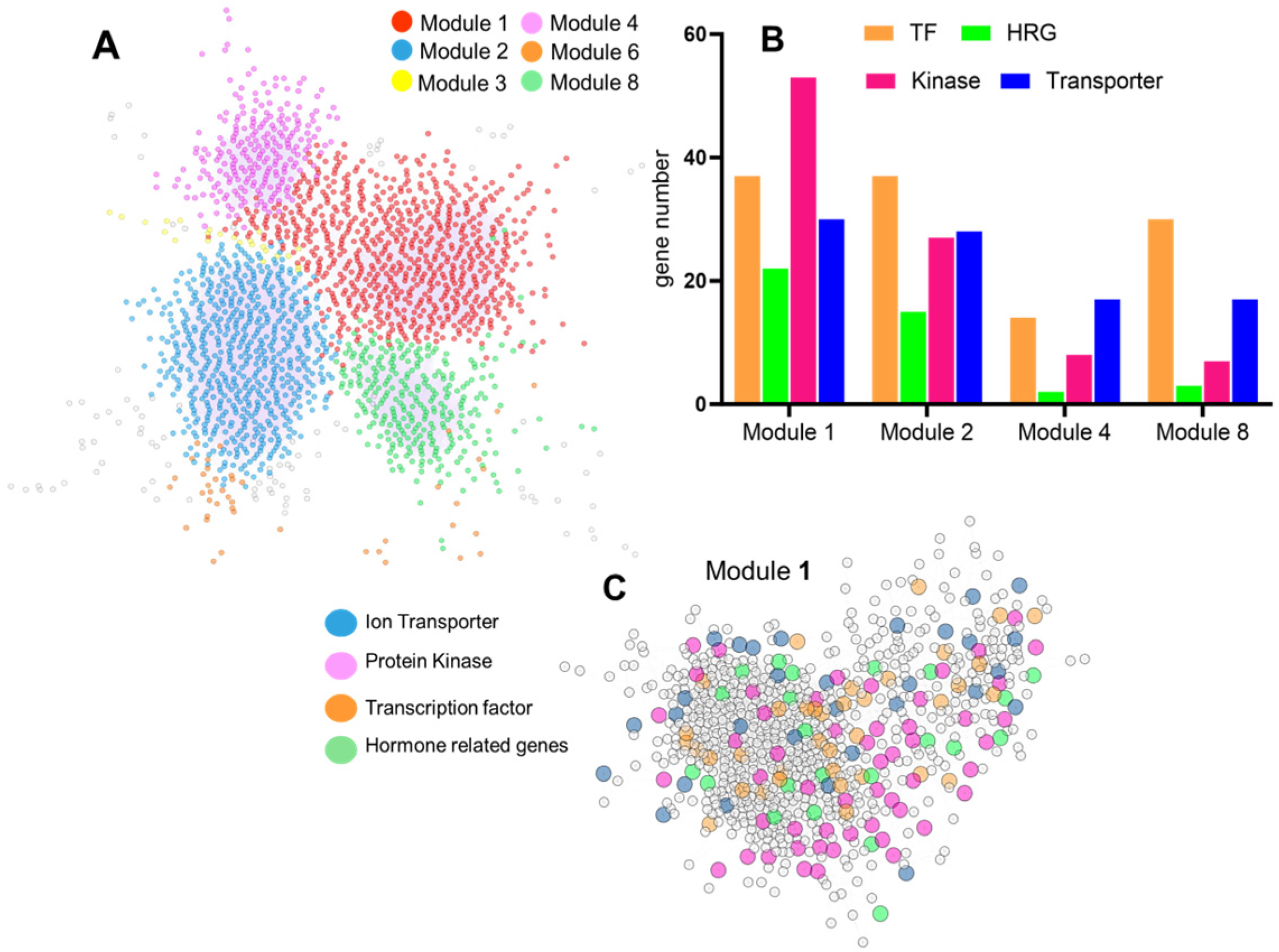
2.6. Co-Expression Network Analysis Revealed Hub Gene for Fe Transport Under Drought
2.7. Validation of Candidate TFs by RT-qPCR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material Stress Treatment
4.2. Expression Analysis of Candidate Genes by qRT-PCR
4.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
4.4. Functional Enrichment Analyses
4.5. Co-Expression Network Analysis
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, D.K.; Kumar Sharma, P. Wheat as a Nutritional Powerhouse: Shaping Global Food Security. In Triticum—The Pillar of Global Food Security; Meena, V.S., Jaiswal, J.P., Jinger, D., Paramesh, V., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Capurso, C. Whole-Grain Intake in the Mediterranean Diet and a Low Protein to Carbohydrates Ratio Can Help to Reduce Mortality from Cardiovascular Disease, Slow Down the Progression of Aging, and to Improve Lifespan: A Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, N.; Wahid, A.; Hafeez, M.B.; Ullah, A.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Farooq, M. Grain development in wheat under combined heat and drought stress: Plant responses and management. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 188, 104517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaupane, S.; Poudel, M.R.; Panthi, B.; Dhakal, A.; Paudel, H.; Bhandari, R. Drought stress effect, tolerance, and management in wheat—A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2024, 10, 2296094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrebi, M.; Marín-Sanz, M.; Miras Moreno, M.B.; Quagliata, G.; Caldo, F.; Gatti, N.; Mannino, G.; Pesenti, M.; D’Alessandro, S.; Nocito, F.F.; et al. The drought-induced plasticity of mineral nutrients contributes to drought tolerance discrimination in durum wheat. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 215, 109077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quagliata, G.; Maghrebi, M.; Marín-Sanz, M.; Palombieri, S.; Sestili, F.; Lafiandra, D.; Barro, F.; Vigani, G.; Astolfi, S. Rye-durum wheat 1BL.1RS translocation: Implications for drought tolerance and nutritional status. Physiol. Plant 2024, 176, e14579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, D.T. Marschner H. 1995. Mineral nutrition of higher plants. second edition. 889pp. London: Academic Press, £29.95 (paperback). Ann. Bot. 1996, 78, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Singh, S.; Gaur, S.; Singh, S.; Yadav, V.; Liu, S.; Singh, V.P.; Sharma, S.; Srivastava, P.; Prasad, S.M.; et al. Acquisition and Homeostasis of Iron in Higher Plants and Their Probable Role in Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotz, N.; Guerinot, M.L. Molecular aspects of Cu, Fe and Zn homeostasis in plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, J.; Guerinot, M.L. Iron uptake and transport in plants: The good, the bad, and the ionome. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4553–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogo, Y.; Itai, R.N.; Nakanishi, H.; Inoue, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Suzuki, M.; Takahashi, M.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, N.K. Isolation and characterization of IRO2, a novel iron-regulated bHLH transcription factor in graminaceous plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperotto, R.A.; Boff, T.; Duarte, G.L.; Santos, L.S.; Grusak, M.A.; Fett, J.P. Identification of putative target genes to manipulate Fe and Zn concentrations in rice grains. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uauy, C.; Distelfeld, A.; Fahima, T.; Blechl, A.; Dubcovsky, J. A NAC Gene regulating senescence improves grain protein, zinc, and iron content in wheat. Science 2006, 314, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogo, Y.; Itai, R.N.; Kobayashi, T.; Aung, M.S.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K. OsIRO2 is responsible for iron utilization in rice and improves growth and yield in calcareous soil. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 75, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ogo, Y.; Itai, R.N.; Nakanishi, H.; Takahashi, M.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, N.K. The transcription factor IDEF1 regulates the response to and tolerance of iron deficiency in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19150–19155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Q.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Guo, Y. Transcription factor MYB8 regulates iron deficiency stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2024, 340, 111973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, N.; Guerinot, M.L. All together now: Regulation of the iron deficiency response. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 2045–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.M.; Hindt, M.N.; Schmidt, H.; Clemens, S.; Guerinot, M.L. MYB10 and MYB72 are required for growth under iron-limiting conditions. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romera, F.J.; Lucena, C.; Alcàntara, E. Plant Hormones Influencing Iron Uptake in Plants. In Iron Nutrition in Plants and Rhizospheric Microorganisms; Barton, L.L., Abadia, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 251–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, F.; Muller, S.; Bauer, P. Suppression of Fe deficiency gene expression by jasmonate. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 49, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguela, M.; Briat, J.F.; Vert, G.; Curie, C. Cytokinins negatively regulate the root iron uptake machinery in Arabidopsis through a growth-dependent pathway. Plant J. 2008, 55, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.J.; Zhu, X.F.; Wang, Z.W.; Dong, F.; Dong, N.Y.; Zheng, S.J. Abscisic acid alleviates iron deficiency by promoting root iron reutilization and transport from root to shoot in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Aslam, M.; Waseem, M.; Jakada, B.H.; Okal, E.J.; Lei, Z.; Saqib, H.S.A.; Yuan, W.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q. Mechanisms of Abscisic Acid-Mediated Drought Stress Responses in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharath, P.; Gahir, S.; Raghavendra, A.S. Abscisic Acid-Induced Stomatal Closure: An Important Component of Plant Defense Against Abiotic and Biotic Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 615114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.; Wahid, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Fujita, D.; Basra, S.M.A. Plant drought stress: Effects, mechanisms and management. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, D.R.; Heckathorn, S.A.; Jayawardena, D.M.; Mishra, S.; Boldt, J.K. Effects of Drought on Nutrient Uptake and the Levels of Nutrient-Uptake Proteins in Roots of Drought-Sensitive and -Tolerant Grasses. Plants 2018, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, M.; Urrea, C.A.; Habib, R.; Bhide, K.; Thimmapuram, J.; Kalavacharla, V. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Tolerant and Sensitive Genotypes of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Response to Terminal Drought Stress. Plants 2023, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gong, J.; Bhullar, N.K. Iron deficiency triggered transcriptome changes in bread wheat. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2709–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Rasheed, A.; Li, M.; Xia, X.; He, Z.; Hao, Y. Dissection of Molecular Processes and Genetic Architecture Underlying Iron and Zinc Homeostasis for Biofortification: From Model Plants to Common Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-D.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, F.-J. The vacuolar transporter OsNRAMP2 mediates Fe remobilization during germination and affects Cd distribution to rice grain. Plant Soil 2022, 476, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Celma, J.; Connorton, J.M.; Kruse, I.; Green, R.T.; Franceschetti, M.; Chen, Y.T.; Cui, Y.; Ling, H.Q.; Yeh, K.C.; Balk, J. Arabidopsis BRUTUS-LIKE E3 ligases negatively regulate iron uptake by targeting transcription factor FIT for recycling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17584–17591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, P.; Liang, G. OsIRO3 negatively regulates Fe homeostasis by repressing the expression of OsIRO2. Plant J. 2022, 111, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidi, M.N.; Mahjoubi, H.; Yacoubi, I. Transcriptome meta-analysis of abiotic stresses-responsive genes and identification of candidate transcription factors for broad stress tolerance in wheat. Protoplasma 2023, 260, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connorton, J.M.; Balk, J.; Rodríguez-Celma, J. Iron homeostasis in plants—A brief overview. Metallomics 2017, 9, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-U.; Song, W.-Y.; Hong, D.; Ko, D.; Yamaoka, Y.; Jang, S.; Yim, S.; Lee, E.; Khare, D.; Kim, K.; et al. Plant ABC Transporters Enable Many Unique Aspects of a Terrestrial Plant’s Lifestyle. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 338–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Itai, R.N.; Ogo, Y.; Kakei, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, N.K. The rice transcription factor IDEF1 is essential for the early response to iron deficiency, and induces vegetative expression of late embryogenesis abundant genes. Plant J. 2009, 60, 948–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, P.; Baby, D.; Bauer, P. Interconnection of iron and osmotic stress signalling in plants: Is FIT a regulatory hub to cross-connect abscisic acid responses? Plant Biol. 2021, 23 (Suppl. 1), 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divol, F.; Couch, D.; Conéjéro, G.; Roschzttardtz, H.; Mari, S.; Curie, C. The Arabidopsis YELLOW STRIPE LIKE4 and 6 transporters control iron release from the chloroplast. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1040–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chiecko, J.C.; Kim, S.A.; Walker, E.L.; Lee, Y.; Guerinot, M.L.; An, G. Disruption of OsYSL15 leads to iron inefficiency in rice plants. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldoni, E.; Genga, A.; Cominelli, E. Plant MYB Transcription Factors: Their Role in Drought Response Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15811–15851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Zou, C.; Yu, D. The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant abiotic stresses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Tang, X. NAC transcription factors in plant multiple abiotic stress responses: Progress and prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergby, D.; Hanin, M.; Saidi, M.N. The durum wheat NAC transcription factor TtNAC2A enhances drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 186, 104439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, M.N.; Mergby, D.; Souibgui, A.; Yacoubi, I. Overexpression of durum wheat NAC transcription factor TtNTL3A promotes early flowering and increases multiple stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 192, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.; Luang, S.; Li, Y.; Bazanova, N.; Morran, S.; Song, Z.; Perera, M.A.; Hrmova, M.; Borisjuk, N.; Lopato, S. Identification and characterization of wheat drought-responsive MYB transcription factors involved in the regulation of cuticle biosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5363–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, P.J.; Park, C.M. Cuticular wax biosynthesis as a way of inducing drought resistance. Plant Signal Behav. 2011, 6, 1043–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Karemera, N.J.U.; Wu, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, Z. The ethylene response factor AtERF4 negatively regulates the iron deficiency response in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Guan, Z.; Lang, K.; Shen, D.; Huang, W.; Dou, D. PlantExp: A platform for exploration of gene expression and alternative splicing based on public plant RNA-seq samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1483–D1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.H.; Apeltsin, L.; Newman, A.M.; Baumbach, J.; Wittkop, T.; Su, G.; Bader, G.D.; Ferrin, T.E. clusterMaker: A multi-algorithm clustering plugin for Cytoscape. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saidi, M.N.; Rebai, O.; Hachani, F.; Vigani, G.; Astolfi, S. Transcriptomics Data Mining to Identify Novel Regulatory Genes of Iron Uptake in Drought-Stressed Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210955
Saidi MN, Rebai O, Hachani F, Vigani G, Astolfi S. Transcriptomics Data Mining to Identify Novel Regulatory Genes of Iron Uptake in Drought-Stressed Wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210955
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaidi, Mohamed Najib, Omeima Rebai, Fadhila Hachani, Gianpiero Vigani, and Stefania Astolfi. 2025. "Transcriptomics Data Mining to Identify Novel Regulatory Genes of Iron Uptake in Drought-Stressed Wheat" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210955
APA StyleSaidi, M. N., Rebai, O., Hachani, F., Vigani, G., & Astolfi, S. (2025). Transcriptomics Data Mining to Identify Novel Regulatory Genes of Iron Uptake in Drought-Stressed Wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210955






