Effects of Nutritional Conditions on Growth, Biofilm Formation, and Enterotoxin Production in Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Food Poisoning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. S. aureus Growth Dynamics Under Different Nutritional Conditions
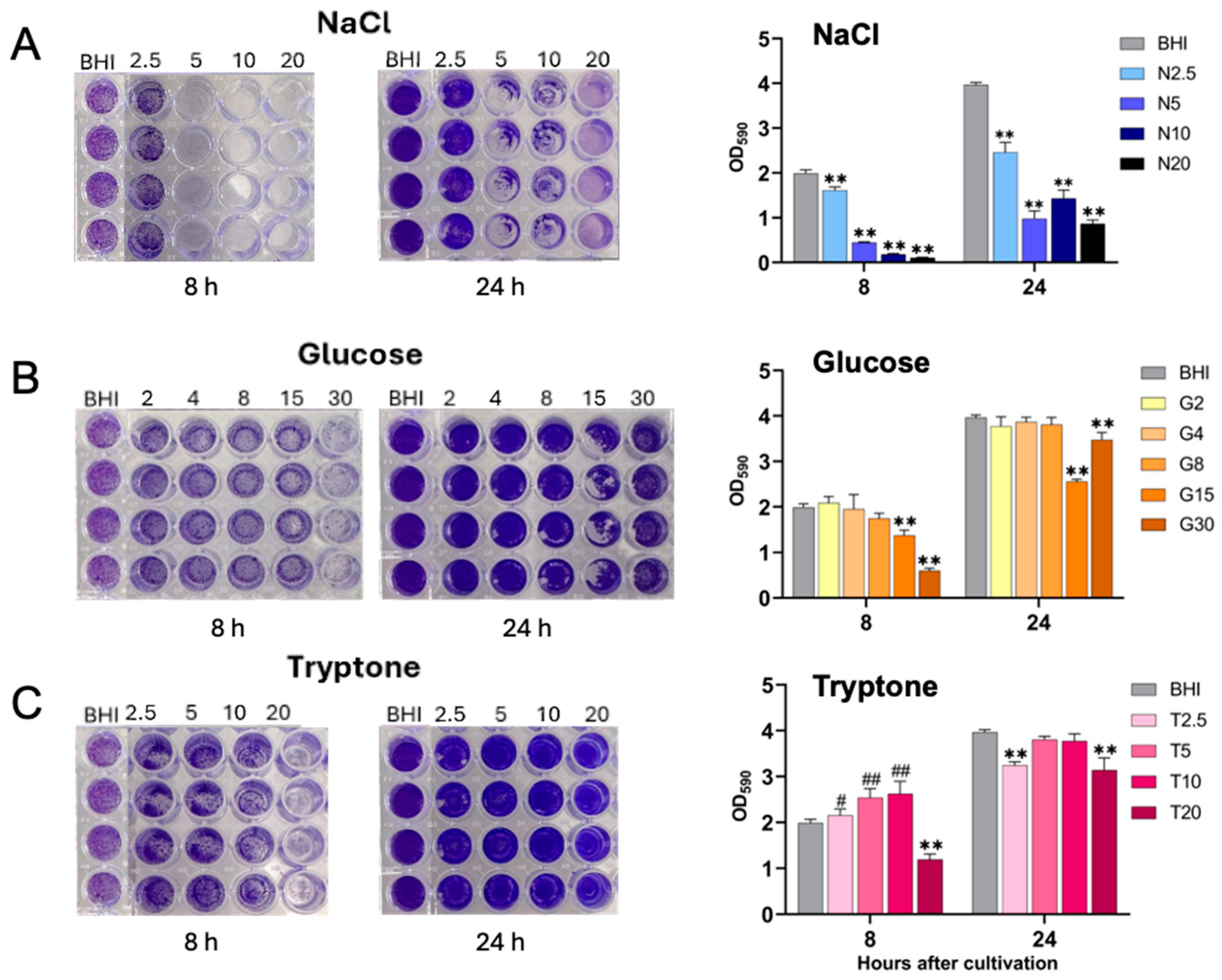
2.2. Biofilm Formation of S. aureus Under Different Nutritional Conditions
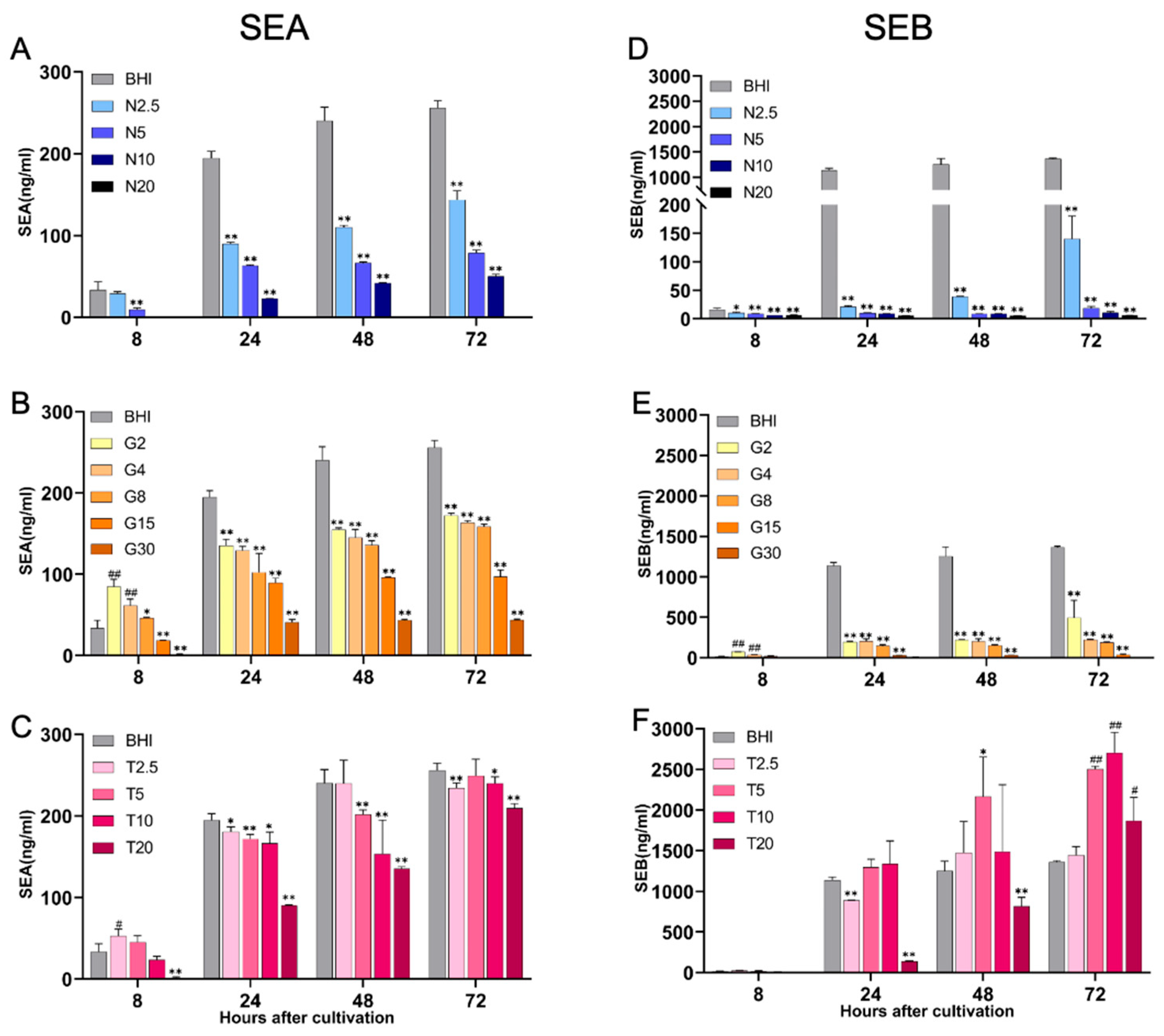
2.3. Production of Staphylococcal Enterotoxins, SEA and SEB, Under Different Nutritional Conditions
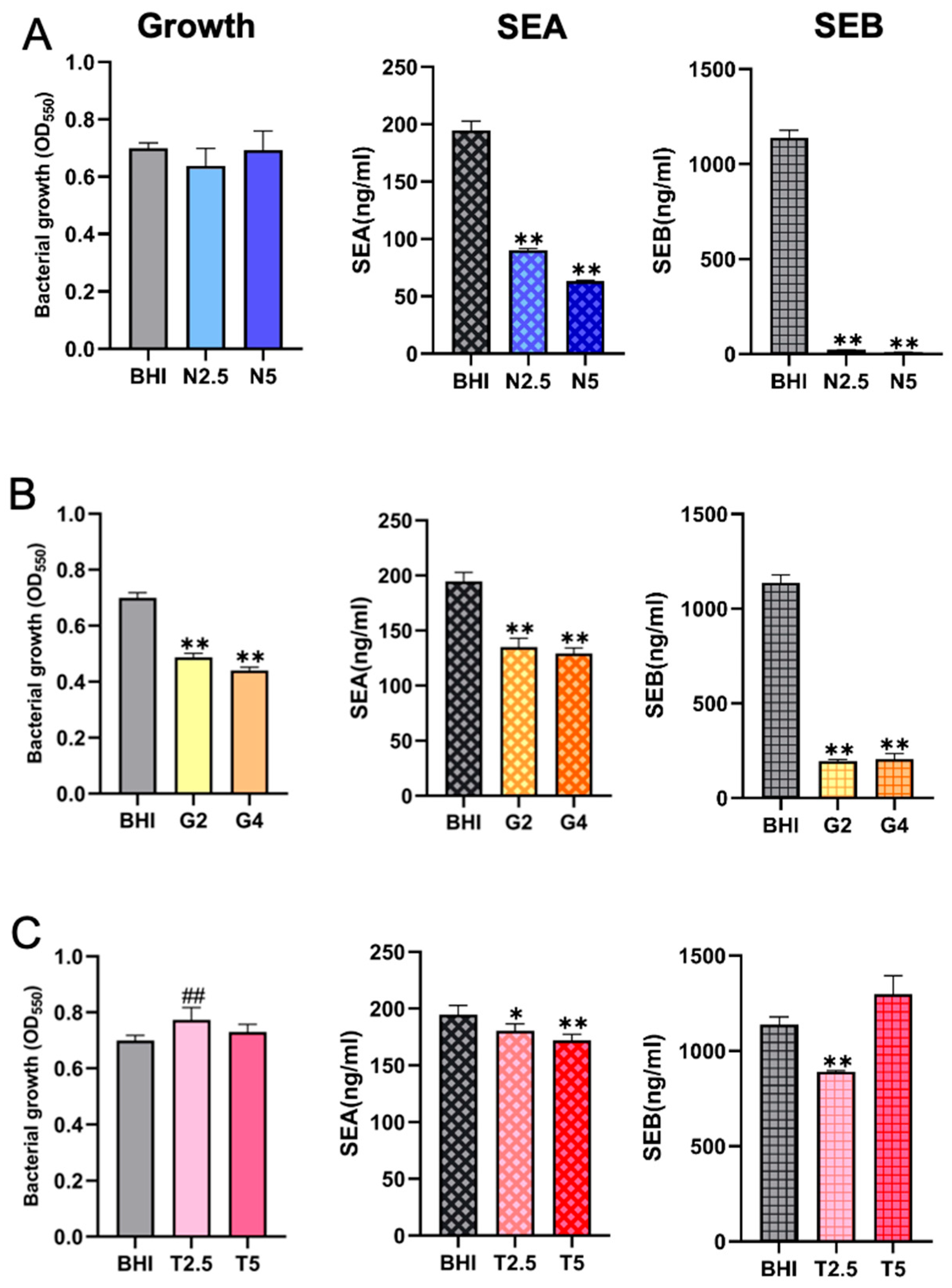
2.4. Comparison of SE Production Under Different Nutritional Conditions with Comparable Bacterial Cell Densities
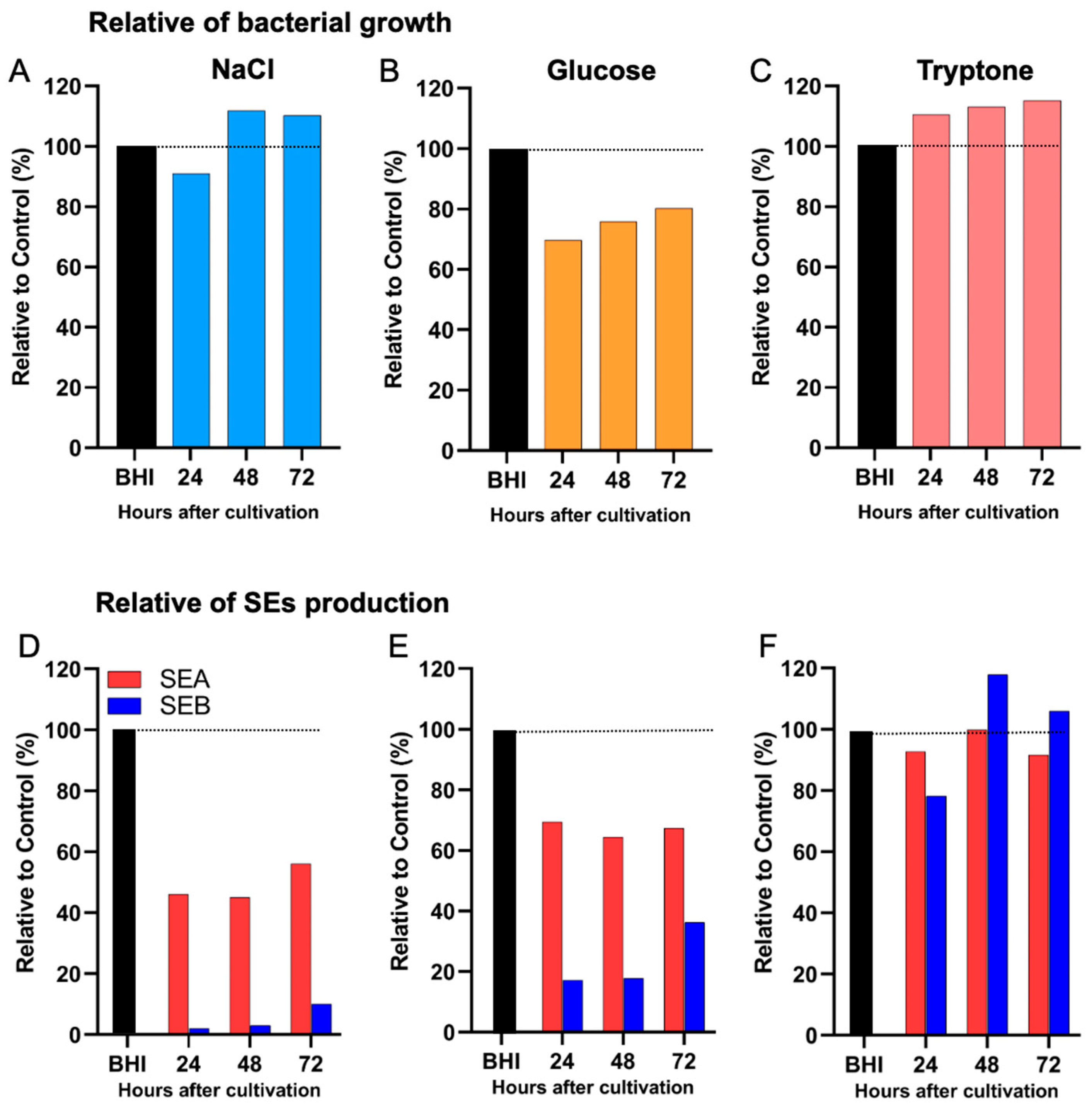
2.5. Differential Effects of Nutritional Conditions on the Production of Distinct Enterotoxin Types
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Preparation of Different Nutritional Culture Media
4.3. Determination of Bacterial Growth
4.4. Detection and Analysis of Biofilm Formation
4.5. Determination of Enterotoxin Production by Sandwich ELISA
4.6. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Fang, R.; Ono, H.K.; Hu, D.-L. Molecular characteristics and pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus exotoxins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Li, S.; Fang, R.; Ono, H. Update on molecular diversity and multipathogenicity of staphylococcal superantigen toxins. Anim. Dis. 2021, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Ketchakmadze, D.; Durglishvili, N.; Ketchakmadze, K. Staphylococcus aureus: A major pathogen of food poisoning: A rare research report. Nutr. Food Process. 2022, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Haghi, F.; Zeighami, H.; Hajiloo, Z.; Torabi, N.; Derakhshan, S. High frequency of enterotoxin encoding genes of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food and clinical samples. J. Health Popul Nutr. 2021, 40, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union one health 2019 zoonoses report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2015. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04634. [Google Scholar]
- Asao, T.; Kumeda, Y.; Kawai, T.; Shibata, T.; Oda, H.; Haruki, K.; Nakazawa, H.; Kozaki, S. An extensive outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning due to low-fat milk in Japan: Estimation of enterotoxin A in the incriminated milk and powdered skim milk. Epidemiol. Infect. 2003, 130, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudyal, N.; Pan, H.; Liao, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Fang, W.; Yue, M. A Meta-analysis of major foodborne pathogens in Chinese food commodities between 2006 and 2016. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Lei, G.; Huang, W.; Lv, H.; Yang, X. Molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates form food-poisoning outbreaks (2011–2022) in Sichuan, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2024, 21, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarawak Trubune. Bacteria Found in Bento Box Lunches in Japan that Poisoned Nearly 400 People. 27 September 2023. Available online: https://www.sarawaktribune.com/bacteria-found-in-bento-box-lunches-in-japan-that-poisoned-nearly-400-people/ (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Kyodo News. 130 People Suffer Food Poisoning in Japan After Eating Eel. Kyodo News (English). 30 July 2024. Available online: https://english.kyodonews.net/news/2024/07/ede485cdc28a-130-people-suffer-food-poisoning-in-japan-after-eating-eel.html (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Suzuki, Y.; Ono, H.K.; Shimojima, Y.; Kubota, H.; Kato, R.; Kakuda, T.; Hirose, S.; Hu, D.-L.; Nakane, A.; Takai, S. A novel staphylococcal enterotoxin SE02 involved in a staphylococcal food poisoning outbreak that occurred in Tokyo in 2004. Food Microbiol. 2020, 92, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.L.; Zhu, G.; Mori, F.; Omoe, K.; Okada, M.; Wakabayashi, K.; Kaneko, S.; Shinagawa, K.; Nakane, A. Staphylococcal enterotoxin induces emesis through increasing serotonin release in intestine and it is downregulated by cannabinoid receptor 1. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2267–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.K.; Hirose, S.; Narita, K.; Sugiyama, M.; Asano, K.; Hu, D.-L.; Nakane, A. Histamine release from intestinal mast cells induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) evokes vomiting reflex in common marmoset. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, S.H.; Tremaine, M.T.; Betley, M.J.; Welch, R.A. Identification and characterization of staphylococcal enterotoxin types G and I from Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.K.; Omoe, K.; Imanishi, K.i.; Iwakabe, Y.; Hu, D.-L.; Kato, H.; Saito, N.; Nakane, A.; Uchiyama, T.; Shinagawa, K. Identification and characterization of two novel staphylococcal enterotoxins, types S and T. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4999–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-F.; Cui, Y.; Shi, X. Identification and Characterization of Two Novel Staphylococcal Enterotoxins. In Proceedings of the IAFP 2018 Annual Meeting, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 8–11 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Aung, M.S.; Urushibara, N.; Kawaguchiya, M.; Ito, M.; Habadera, S.; Kobayashi, N. Prevalence and genetic diversity of staphylococcal enterotoxin (-Like) genes sey, selw, selx, selz, sel26 and sel27 in community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Toxins 2020, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, J.; Turnbull, J.D.; Russell, J.; Parkhill, J.; Alexander, S. Genome sequencing of a historic Staphylococcus aureus collection reveals new enterotoxin genes and sheds light on the evolution and genomic organization of this key virulence gene family. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieza, M.Y.R.; Bonsaglia, E.C.R.; Rall, V.L.M.; Santos, M.V.d.; Silva, N.C.C. Staphylococcal enterotoxins: Description and importance in food. Pathogens 2024, 13, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, N.; Rasooly, A. Staphylococcal enterotoxins. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeaki, N.; Budi Susilo, Y.; Pregiel, A.; Rådström, P.; Schelin, J. Prophage-encoded staphylococcal enterotoxin A: Regulation of production in Staphylococcus aureus strains representing different sea regions. Toxins. 2015, 7, 5359–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haag, A.F.; Podkowik, M.; Ibarra-Chávez, R.; Gallego del Sol, F.; Ram, G.; Chen, J.; Marina, A.; Novick, R.P.; Penadés, J.R. A regulatory cascade controls Staphylococcus aureus pathogenicity island activation. Nat Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadariya, J.; Smith, T.C.; Thapaliya, D. Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal food-borne disease: An ongoing challenge in public health. Int. B.R. 2014, 2014, 827965. [Google Scholar]
- Macori, G.; Bellio, A.; Bianchi, D.M.; Chiesa, F.; Gallina, S.; Romano, A.; Zuccon, F.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Cauquil, A.; Merda, D. Genome-wide profiling of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus strains used for the production of naturally contaminated cheeses. Genes 2019, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Hua, D.; You, Y.; Wu, Q.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Hu, Y. A food poisoning caused by ST7 Staphylococcal aureus harboring sea gene in Hainan province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1110720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.-L.; Omoe, K.; Sashinami, H.; Shinagawa, K.; Nakane, A. Immunization with a nontoxic mutant of staphylococcal enterotoxin A, SEAD227A, protects against enterotoxin-induced emesis in house musk shrews. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwan, W.R.; Wetzel, K.J. Osmolyte transport in Staphylococcus aureus and the role in pathogenesis. World J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, M.K.; Sturd, N.A.; Razvi, F.; Wellems, D.L.; Carson, S.D.; Fey, P.D. Proline transporters ProT and PutP are required for Staphylococcus aureus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prax, M.; Mechler, L.; Weidenmaier, C.; Bertram, R. Glucose augments killing efficiency of daptomycin challenged Staphylococcus aureus persisters. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yue, S.; Chen, T.; She, P.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y. Reduced growth of Staphylococcus aureus under high glucose conditions is associated with decreased pentaglycine expression. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 537290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Poudel, S.; Seif, Y.; Shen, Z.; Palsson, B.O. Elucidating the CodY regulon in Staphylococcus aureus USA300 substrains TCH1516 and LAC. mSystems 2023, 8, e0027923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanaugh, J.S.; Horswill, A.R. Impact of environmental cues on staphylococcal quorum sensing and biofilm development. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12556–12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, N.K.; Mazaitis, M.J.; Costerton, J.W.; Leid, J.G.; Powers, M.E.; Shirtliff, M.E. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Properties, regulation, and roles in human disease. Virulence 2011, 2, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelin, J.; Susilo, Y.B.; Johler, S. Expression of staphylococcal enterotoxins under stress encountered during food production and preservation. Toxins 2017, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato’o, Y.; Hisatsune, J.; Aziz, F.; Tatsukawa, N.; Shibata-Nakagawa, M.; Ono, H.K.; Naito, I.; Omoe, K.; Sugai, M. Coordination of prophage and global regulator leads to high enterotoxin production in staphylococcal food poisoning-associated lineage. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0292723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.A.; Donegan, N.P.; Kwan, J.; William, A.; Cheung, A. Influences of σB and agr on expression of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (seb) in Staphylococcus aureus. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, R.P.; Ram, G. Staphylococcal pathogenicity islands—Movers and shakers in the genomic firmament. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 38, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidl, K.; Müller, S.; François, P.; Kriebitzsch, C.; Schrenzel, J.; Engelmann, S.; Bischoff, M.; Berger-Bächi, B. Effect of a glucose impulse on the CcpA regulon in Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Kaito, C.; Omae, Y.; Sekimizu, K. Sugar-responsive gene expression and the agr system are required for colony spreading in Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2011, 51, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, G.V.; Bastos, C.P.; da Silva, W.P. The effect of sodium chloride and temperature on the levels of transcriptional expression of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from broiler carcasses. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.D.; Walsh, K.A.; Gould, L.H. Foodborne disease outbreaks caused by Bacillus cereus, Clostridium perfringens, and Staphylococcus aureus—United States, 1998–2008. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Buyser, M.-L.; Dufour, B.; Maire, M.; Lafarge, V. Implication of milk and milk products in food-borne diseases in France and in different industrialised countries. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nia, Y.; Mutel, I.; Assere, A.; Lombard, B.; Auvray, F.; Hennekinne, J.-A. Review over a 3-year period of European Union proficiency tests for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins in food matrices. Toxins 2016, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, J.C.; King, A.N.; Grigg, J.C.; Sheldon, J.R.; Edgell, D.R.; Murphy, M.E.; Brinsmade, S.R.; Heinrichs, D.E. Repression of branched-chain amino acid synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus is mediated by isoleucine via CodY, and by a leucine-rich attenuator peptide. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, N.E.; Sweeney, E.; Harrison, F. Building a better biofilm-formation of in vivo-like biofilm structures by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a porcine model of cystic fibrosis lung infection. Biofilm 2020, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Ono, H.K.; Hirose, S.; Hara-Kudo, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, D.-L. Effects of Nutritional Conditions on Growth, Biofilm Formation, and Enterotoxin Production in Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Food Poisoning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199791
Hu Z, Zhu Z, Ono HK, Hirose S, Hara-Kudo Y, Li S, Hu D-L. Effects of Nutritional Conditions on Growth, Biofilm Formation, and Enterotoxin Production in Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Food Poisoning. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199791
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zuo, Zhihao Zhu, Hisaya K. Ono, Shouhei Hirose, Yukiko Hara-Kudo, Shaowen Li, and Dong-Liang Hu. 2025. "Effects of Nutritional Conditions on Growth, Biofilm Formation, and Enterotoxin Production in Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Food Poisoning" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199791
APA StyleHu, Z., Zhu, Z., Ono, H. K., Hirose, S., Hara-Kudo, Y., Li, S., & Hu, D.-L. (2025). Effects of Nutritional Conditions on Growth, Biofilm Formation, and Enterotoxin Production in Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Food Poisoning. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199791





