Diet and Lifestyle Interventions in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis of MASLD
3. Role of Diet and Lifestyle in MASLD
4. Role of Weight Loss

5. Role of Dietary Modifications
5.1. Role of Macronutrients
5.1.1. Fats
Saturated Fats
Monounsaturated Fats
Polyunsaturated Fats
Trans Fats
5.1.2. Carbohydrates
Fructose
5.1.3. Dietary Fiber
5.1.4. Proteins

5.2. Role of Micronutrients
5.2.1. Vitamins
Vitamin E
Vitamin C
Vitamin D
Vitamin A
Vitamin B3
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B9
Vitamin B12

5.3. Role of Minerals
5.3.1. Calcium and Phosphorus
5.3.2. Zinc and Magnesium
5.3.3. Iron and Selenium

5.4. Role of Herbal Supplements
5.4.1. Milk Thistle
5.4.2. Turmeric
5.4.3. Garlic
5.4.4. Basil, Lavender, Peppermint, Oregano, and Rosemary
5.4.5. Ginger
5.4.6. Gingko Biloba
5.4.7. Ginseng
5.4.8. Licorice
5.4.9. Rosa Damascena, Plantago Major
5.4.10. Berberine

5.5. Role of Other Supplements
5.5.1. Probiotics
5.5.2. Caffeine
5.5.3. Green Tea
5.5.4. Low-Calorie Sweeteners
5.5.5. Resveratrol
5.5.6. Choline
5.5.7. Fish Oil
5.5.8. Co-Enzyme Q10

5.6. Role of Alcohol, Cannabis, and Tobacco
5.6.1. Alcohol
5.6.2. Cannabinoids
5.6.3. Tobacco

6. Role of Various Dietary Patterns
6.1. Mediterranean Diet
6.2. Diet Approach to Stop Hypertension Diet
6.3. Low-Carbohydrate Diet
6.4. Ketogenic Diet
6.5. Low-Fat Diet
6.6. Intermittent Fasting

7. Role of Physical Activity and Exercise
7.1. Aerobic Exercise
7.2. High-Intensity Interval Training
7.3. Resistance Exercise

8. Role of Circadian Rhythm in MASLD
9. Psychosocial Determinants
10. Barriers to Implementing Lifestyle Interventions
11. Future Directions
12. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; A King, J.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.-A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, E.M.; Janney, C.G.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Bacon, B.R. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Proposal for Grading and Staging The Histological Lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Loomis, A.K.; van der Lei, J.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Ansell, D.; Pasqua, A.; Lapi, F.; Rijnbeek, P.; Mosseveld, M.; et al. Risks and clinical predictors of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma diagnoses in adults with diagnosed NAFLD: Real-world study of 18 million patients in four European cohorts. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, B.; Lindén, D.; Brolén, G.; Liljeblad, M.; Bjursell, M.; Romeo, S.; Loomba, R. Review article: The emerging role of genetics in precision medicine for patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danpanichkul, P.; Suparan, K.; Kim, D.; Wijarnpreecha, K. What Is New in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Lean Individuals: From Bench to Bedside. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Apovian, C.M.; Balapattabi, K.; Bannuru, R.R.; Barb, D.; Bardsley, J.K.; Beverly, E.A.; Corbin, K.D.; ElSayed, N.A.; et al. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in People with Diabetes: The Need for Screening and Early Intervention. A Consensus Report of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, 1057–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J. International Consensus Panel. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Ekstedt, M.; Hammar, U.; Stål, P.; Hultcrantz, R.; Kechagias, S. Fibrosis stage but not NASH predicts mortality and time to development of severe liver disease in biopsy-proven NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.-F.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Sun, Y.-M.; Wu, X.-N.; Yang, L.-L.; Lu, Z.-Z.; Ou, X.-J.; Jia, J.-D.; You, H. Histological assessment based on liver biopsy: The value and challenges in NASH drug development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilagan-Ying, Y.C.; Banini, B.A.; Do, A.; Lam, R.; Lim, J.K. Screening, Diagnosis, and Staging of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Application of Society Guidelines to Clinical Practice. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2023, 25, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathcart, J.; Barrett, R.; Bowness, J.S.; Mukhopadhya, A.; Lynch, R.; Dillon, J.F. Accuracy of Non-Invasive Imaging Techniques for the Diagnosis of MASH in Patients with MASLD: A Systematic Review. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddin, M.; Truong, E.; Mayo, R.; Martínez-Arranz, I.; Mincholé, I.; Banales, J.M.; Arrese, M.; Cusi, K.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bruha, R.; et al. Serum identification of at-risk MASH: The metabolomics-advanced steatohepatitis fibrosis score (MASEF). Hepatology 2024, 79, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Shubrook, J.H.; Adams, L.A.; Pfotenhauer, K.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Wright, E.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Harrison, S.A.; Loomba, R.; Mantzoros, C.S.; et al. Clinical Care Pathway for the Risk Stratification and Management of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattacheril, J.J.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Lim, J.K.; Sanyal, A.J. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Role of Noninvasive Biomarkers in the Evaluation and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Morandin, R.; Fiorio, V.; Lando, M.G.; Stefan, N.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Improve MASH and Liver Fibrosis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e70256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero-Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, W.; Schürmann, A. Genetic and epigenetic factors determining NAFLD risk. Mol. Metab. 2020, 50, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.; Peng, X.; Li, X.; An, K.; He, H.; Fu, X.; Li, S.; An, Z. Unmasking the enigma of lipid metabolism in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: From mechanism to the clinic. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1294267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, B.; Marjanovic-Haljilji, M.; Mijac, D.; Lukic, S.; Kapor, S.; Kapor, S.; Starcevic, A.; Popovic, D.; Djokovic, A. Molecular Aspects of MAFLD—New Insights on Pathogenesis and Treatment. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9132–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, M.Z.; Virgolici, B.; Cioarcă-Nedelcu, R. Lipid Hormones at the Intersection of Metabolic Imbalances and Endocrine Disorders. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, C.; Singer, K.; Renner, K.; Bruss, C.; Hellerbrand, C.; Dorn, C.; Reichelt-Wurm, S.; Gronwald, W.; Pukrop, T.; Herr, W.; et al. The spleen-liver axis supports obesity-induced systemic and fatty liver inflammation via MDSC and NKT cell enrichment. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2025, 601, 112518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Luo, F.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W.; Hu, M. Gut microbiota and metabolic biomarkers in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0310, Erratum in Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti-Aguado, D.; Calleja, J.L.; Vilar-Gomez, E.; Iruzubieta, P.; Rodríguez-Duque, J.C.; Del Barrio, M.; Puchades, L.; Rivera-Esteban, J.; Perelló, C.; Puente, A.; et al. Low-to-moderate alcohol consumption is associated with increased fibrosis in individuals with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, H.; Sun, H. Phthalate Biomarkers Composition in Relation to Fatty Liver: Evidence from Epidemiologic and in vivo studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Yao, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Cui, X.T.; Sun, A.; Cao, J.Y.; Wang, Z.S. Bisphenols exposure and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From environmental trigger to molecular pathogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1606654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, C.S.; Aboona, M.B.; Surendra, L.; Rangan, P.; Ng, C.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Muthiah, M.; Kim, D.; Fallon, M.B.; Noureddin, M.; et al. Neighborhood Social Determinants of Health Are Associated with Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease Outcomes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 23, 1577–1587.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maidstone, R.; Rutter, M.K.; Marjot, T.; Ray, D.W.; Baxter, M. Shift work and evening chronotype are associated with hepatic fat fraction and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in 282,303 UK biobank participants. Endocr. Connect. 2024, 13, e230472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Shahzil, M.; Moond, V.; Shahzad, M.; Thandavaram, A.; Sehar, A.; Waseem, H.; Siddiqui, T.; Dahiya, D.S.; Patel, P.; et al. Non-Pharmacological Approach to Diet and Exercise in Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: Bridging the Gap between Research and Clinical Practice. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadefi, A.; Arvanitakis, M.; Trépo, E.; Zelber-Sagi, S. Dietary strategies in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients: From evidence to daily clinical practice, a systematic review. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2023, 11, 663–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, M.; Solga, S.F.; Horska, A.; Bonekamp, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Brancati, F.L.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Kahn, S.E.; Clark, J.M.; et al. Effect of a 12-Month Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Hepatic Steatosis in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2156–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promrat, K.; Kleiner, D.E.; Niemeier, H.M.; Jackvony, E.; Kearns, M.; Wands, J.R.; Fava, J.L.; Wing, R.R. Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Befroy, D.; Lehrke, M.; Hendler, R.E.; Shulman, G.I. Reversal of Nonalcoholic Hepatic Steatosis, Hepatic Insulin Resistance, and Hyperglycemia by Moderate Weight Reduction in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, S.E.; Hackett, D.A.; George, J.; Johnson, N.A. Exercise and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobler, H.; Schattner, A.; Zhornicki, T.; Malnick, S.; Keter, D.; Sokolovskaya, N.; Lurie, Y.; Bass, D. Fatty liveran additional and treatable feature of the insulin resistance syndrome. Qjm 1999, 92, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.H.; Yockey, S.R. Weight Loss and Improvement in Comorbidity: Differences at 5%, 10%, 15%, and Over. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutoukidis, D.A.; Koshiaris, C.; Henry, J.A.; Noreik, M.; Morris, E.; Manoharan, I.; Tudor, K.; Bodenham, E.; Dunnigan, A.; Jebb, S.A.; et al. The effect of the magnitude of weight loss on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2021, 115, 154455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, S.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Comparison of Calorie-Restricted Diet and Resveratrol Supplementation on Anthropo-metric Indices, Metabolic Parameters, and Serum Sirtuin-1 Levels in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Ran-domized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maston, G.; Gibson, A.A.; Kahlaee, H.R.; Franklin, J.; Manson, E.; Sainsbury, A.; Markovic, T.P. Effectiveness and Characterization of Severely Energy-Restricted Diets in People with Class III Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parretti, H.M.; Jebb, S.A.; Johns, D.J.; Lewis, A.L.; Christian-Brown, A.M.; Aveyard, P. Clinical effectiveness of very-low-energy diets in the management of weight loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, P.; Larsen, T.M.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.; Macdonald, I.; Martinez, J.A.; Handjiev, S.; Poppitt, S.; Hansen, S.; Ritz, C.; Astrup, A.; et al. Men and women respond differently to rapid weight loss: Metabolic outcomes of a multi-centre intervention study after a low-energy diet in 2500 overweight, individuals with pre-diabetes (PREVIEW). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2840–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Caldwell, S.; Barb, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Loomba, R. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1797–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Lee, H.W.; Yoo, J.-J.; Cho, Y.; Kim, S.U.; Lee, T.H.; Jang, B.K.; Kim, S.G.; Ahn, S.B.; Kim, H.; et al. KASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 363–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Chan, W.K.; Chitturi, S.; Chawla, Y.; Dan, Y.Y.; Duseja, A.; Fan, J.; Goh, K.-L.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hashimoto, E.; et al. Asia-Pacific Working Party on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease guidelines 2017-Part 1: Definition, risk factors and assessment. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Guideline Centre (UK). Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Assessment and Management; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (UK): London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, G.G.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Murphy, A.J.; Febbraio, M.A. Diet-induced gut dysbiosis and inflammation: Key drivers of obesity-driven NASH. iScience 2022, 26, 105905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Lotan, R.; Shlomai, A.; Webb, M.; Harrari, G.; Buch, A.; Kaluski, D.N.; Halpern, Z.; Oren, R. Predictors for incidence and remission of NAFLD in the general population during a seven-year prospective follow-up. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, K.E.; Caan, M.W.; Nederveen, A.J.; Pels, A.; Ackermans, M.T.; Fliers, E.; la Fleur, S.E.; Serlie, M.J. Hypercaloric diets with increased meal frequency, but not meal size, increase intrahepatic triglycerides: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 2014, 60, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordain, L.; Eaton, S.B.; Sebastian, A.; Mann, N.; Lindeberg, S.; Watkins, B.A.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Brand-Miller, J. Origins and evolution of the Western diet: Health implications for the 21st century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Sahlabadi, A.; Sadat, S.; Beigrezaei, S.; Pourmasomi, M.; Feizi, A.; Ghiasvand, R.; Hadi, A.; Clark, C.C.T.; Miraghajani, M. Dietary patterns and risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcason, W. What Are the Components to the MIND Diet? J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, D.; Ranjbar, G.; Rezvani, R.; Goshayeshi, L.; Razmpour, F.; Nematy, M. Dietary patterns in relation to hepatic fibrosis among patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Qi, X.; Li, N.; Kaifi, J.T.; Chen, S.; Wheeler, A.A.; Kimchi, E.T.; Ericsson, A.C.; Rector, R.S.; Staveley-O’cArroll, K.F.; et al. Western diet contributes to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in male mice via remodeling gut microbiota and increasing production of 2-oleoylglycerol. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, I.J.; Tzoulaki, I.; Candeias, V.; Elliott, P. Salt intakes around the world: Implications for public health. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 38, 791–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, A.; Lauterbach, M.; Latz, E. Western Diet and the Immune System: An Inflammatory Connection. Immunity 2019, 51, 794–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srour, B.; Kordahi, M.C.; Bonazzi, E.; Deschasaux-Tanguy, M.; Touvier, M.; Chassaing, B. Ultra-processed foods and human health: From epidemiological evidence to mechanistic insights. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, B.; Reiter, F.P.; Leicht, H.B.; Fiessler, C.; Bergheim, I.; Heuschmann, P.U.; Geier, A.; Rau, M. Salt-Intake-Related Behavior Varies between Sexes and Is Strongly Associated with Daily Salt Consumption in Obese Patients at High Risk for MASLD. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, P.; Martin, A.; Lang, S.; Kütting, F.; Goeser, T.; Demir, M.; Steffen, H.-M. NAFLD and cardiovascular diseases: A clinical review. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemayor, S.; García, S.; Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Tur, J.A.; Bouzas, C. Dietary Patterns, Foods, and Nutrients to Ameliorate Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R. Dietary habits and their relations to insulin resistance and postprandial lipemia in nonalcoholic stea-tohepatitis. Hepatology 2003, 37, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshimitsu, K.; Matsuura, B.; Ohkubo, I.; Niiya, T.; Furukawa, S.; Hiasa, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Ebihara, K.; Onji, M. Dietary habits and nutrient intake in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Nutrition 2007, 23, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alferink, L.J.; Jong, J.C.K.-D.; Erler, N.S.; Veldt, B.J.; Schoufour, J.D.; de Knegt, R.J.; Ikram, M.A.; Metselaar, H.J.; LA Janssen, H.; Franco, O.H.; et al. Association of dietary macronutrient composition and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in an ageing population: The Rotterdam Study. Gut 2019, 68, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan, P.V.; Esmel, E.V.; Meseguer, E.S. Overview of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and the Role of Sugary Food Consumption and Other Dietary Components in Its Development. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramlich, L.; Ireton-Jones, C.; Miles, J.M.; Morrison, M.; Pontes-Arruda, A. Essential Fatty Acid Requirements and Intravenous Lipid Emulsions. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Tang, Y.L.M.; Althumiri, N.A.; Garcia-Larsen, V.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Alqahtani, S.A. Fatty acid composition but not quantity is an important indicator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 77, 1113–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Sädevirta, S.; Zhou, Y.; Kayser, B.; Ali, A.; Ahonen, L.; Lallukka, S.; Pelloux, V.; Gaggini, M.; Jian, C.; et al. Saturated Fat Is More Metabolically Harmful for the Human Liver Than Unsaturated Fat or Simple Sugars. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessby, B.; Uusitupa, M.; Hermansen, K.; Riccardi, G.; Rivellese, A.A.; Tapsell, L.C.; Nälsén, C.; Berglund, L.; Louheranta, A.; Rasmussen, B.M.; et al. Substituting dietary saturated for monounsaturated fat impairs insulin sensitivity in healthy men and women: The KANWU study. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosqvist, F.; Iggman, D.; Kullberg, J.; Cedernaes, J.; Johansson, H.-E.; Larsson, A.; Johansson, L.; Ahlström, H.; Arner, P.; Dahlman, I.; et al. Overfeeding Polyunsaturated and Saturated Fat Causes Distinct Effects on Liver and Visceral Fat Accumulation in Humans. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2356–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guveli, H.; Kenger, E.B.; Ozlu, T.; Kaya, E.; Yilmaz, Y. Macro- and micronutrients in metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease: Association between advanced fibrosis and high dietary intake of cholesterol/saturated fatty acids. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 33, e390–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosqvist, F.; Kullberg, J.; Ståhlman, M.; Cedernaes, J.; Heurling, K.; Johansson, H.-E.; Iggman, D.; Wilking, H.; Larsson, A.; Eriksson, O.; et al. Overeating Saturated Fat Promotes Fatty Liver and Ceramides Compared with Polyunsaturated Fat: A Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 6207–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Pacini, G.; De Michieli, F.; Cassader, M. Prolonged saturated fat–induced, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide elevation is associated with adipokine imbalance and liver injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Dysregulated enteroadipocyte axis as a novel feature of fatty liver. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caesar, R.; Tremaroli, V.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Cani, P.D.; Bäckhed, F. Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and Dietary Lipids Aggravates WAT Inflammation through TLR Signaling. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, E.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Costanzo, S.; Esposito, S.; De Curtis, A.; Persichillo, M.; Cerletti, C.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G.; Iacoviello, L.; et al. Incremental monounsaturated to saturated fat ratio and fibre consumption is associated with a reduction in a composite score of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: Prospective results from the Moli-sani study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Luo, R.; Liao, G.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Cheng, J.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y. Oleic acid protects saturated fatty acid mediated lipotoxicity in hepatocytes and rat of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assy, N.; Nassar, F.; Nasser, G.; Grosovski, M. Olive oil consumption and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Milanović, M.; Milić, N.; Luzza, F.; Giuffrè, A.M. Olive oil antioxidants and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Miranda, J.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Ros, E.; De Caterina, R.; Badimón, L.; Covas, M.; Escrich, E.; Ordovás, J.; Soriguer, F.; Abiá, R.; et al. Olive oil and health: Summary of the II international conference on olive oil and health consensus report, Jaén and Córdoba (Spain) 2008. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2010, 20, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Strasser, B.; Hoffmann, G. Effects of Monounsaturated Fatty Acids on Glycaemic Control in Patients with Abnormal Glucose Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 58, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, N.J.; Afman, L.A.; Mensink, M.; Müller, M. Phenotyping the effect of diet on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.-S. Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Dietary sources, metabolism, and significance—A review. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, G.S.; Calder, P.C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its treatment with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.H.; Guan, B.J. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A me-ta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine 2018, 97, e12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellem, F.; Pesando, D.; Bodennec, G.; Girard, J.-P.; Simopoulos, A.P. An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the Risk for Obesity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, J.P.; Aghdassi, E.; Mohammed, S.; Raman, M.; Avand, G.; Arendt, B.M.; Jalali, P.; Kandasamy, T.; Prayitno, N.; Sherman, M.; et al. Nutritional assessment and hepatic fatty acid composition in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A cross-sectional study. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capanni, M.; Calella, F.; Biagini, M.R.; Genise, S.; Raimondi, L.; Bedogni, G.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Sofi, F.; Milani, S.; Abbate, R.; et al. Prolonged n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation ameliorates hepatic steatosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorletti, E.; Bhatia, L.; McCormick, K.G.; Clough, G.F.; Nash, K.; Hodson, L.; Moyses, H.E.; Calder, P.C.; Byrne, C.D.; WELCOME Study. Effects of purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Results from the WELCOME study. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.A.; Oliveira, C.P.; Ferreira-Alves, V.A.; Stefano, J.T.; dos Rodrigues, L.S.R.; Torrinhas, R.S.; Cogliati, B.; Barbeiro, H.; Carrilho, F.J.; Waitzberg, D.L. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in treating non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argo, C.K.; Patrie, J.T.; Lackner, C.; Henry, T.D.; de Lange, E.E.; Weltman, A.L.; Shah, N.L.; Al-Osaimi, A.M.; Pramoonjago, P.; Jayakumar, S.; et al. Effects of n-3 fish oil on metabolic and histological parameters in NASH: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yari, Z.; Rahimlou, M.; Eslamparast, T.; Ebrahimi-Daryani, N.; Poustchi, H.; Hekmatdoost, A. Flaxseed supplementation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot randomized, open labeled, controlled study. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhibi, M.; Brahmi, F.; Mnari, A.; Houas, Z.; Chargui, I.; Bchir, L.; Gazzah, N.; Alsaif, M.A.; Hammami, M. The intake of high fat diet with different trans fatty acid levels differentially induces oxidative stress and non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in rats. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetri, L.H.; Basaranoglu, M.; Brunt, E.M.; Yerian, L.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Severe NAFLD with hepatic necroinflammatory changes in mice fed trans fats and a high-fructose corn syrup equivalent. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G987–G995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Ford, D.A. Dietary trans-fatty acid-induced NASH is normalized following loss of trans-fatty acids from hepatic lipid pools. Lipids 2012, 47, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Xin, X.; An, Z.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, Q. A high-trans fat, high-carbohydrate, high-cholesterol, high-cholate diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis mouse model and its hepatic immune response. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowman, J.K.; Hopkins, L.J.; Reynolds, G.M.; Nikolaou, N.; Armstrong, M.J.; Shaw, J.C.; Houlihan, D.D.; Lalor, P.F.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Hübscher, S.G.; et al. Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Murine Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Induced by Use of a High-Fat/Fructose Diet and Sedentary Lifestyle. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1550–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hua, R.; Peng, K.; Yin, Y.; Zeng, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Qiu, Y.; et al. High-starchy carbohydrate diet aggravates NAFLD by increasing fatty acids influx mediated by NOX2. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 1081–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Nitzan-Kaluski, D.; Goldsmith, R.; Webb, M.; Blendis, L.; Halpern, Z.; Oren, R. Long term nutritional intake and the risk for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A population based study. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volynets, V.; Küper, M.A.; Strahl, S.; Maier, I.B.; Spruss, A.; Wagnerberger, S.; Königsrainer, A.; Bischoff, S.C.; Bergheim, I. Nutrition, Intestinal Permeability, and Blood Ethanol Levels Are Altered in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yki-Järvinen, H.; Luukkonen, P.K.; Hodson, L.; Moore, J.B. Dietary carbohydrates and fats in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 770–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietman, A.; Sluik, D.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Kok, F.J.; Mensink, M. Associations between dietary factors and markers of NAFLD in a general Dutch adult population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Huang, L.; Shuai, P.; Wan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xue, J.; Liu, Y. Effect of a High Protein, Low Glycemic Index Dietary Intervention on Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 863834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawden, S.; Stephenson, M.; Falcone, Y.; Lingaya, M.; Ciampi, E.; Hunter, K.; Bligh, F.; Schirra, J.; Taylor, M.; Morris, P.; et al. Increased liver fat and glycogen stores after consumption of high versus low glycaemic index food: A randomized crossover study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 19, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geidl-Flueck, B.; Hochuli, M.; Németh, Á.; Eberl, A.; Derron, N.; Köfeler, H.C.; Tappy, L.; Berneis, K.; Spinas, G.A.; Gerber, P.A. Fructose- and sucrose- but not glucose-sweetened beverages promote hepatic de novo lipogenesis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, A.C.; Adeli, K. Fructose and the Metabolic Syndrome: Pathophysiology and Molecular Mechanisms. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basciano, H.; Federico, L.; Adeli, K. Fructose, insulin resistance, and metabolic dyslipidemia. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Yamanouchi, T. The role of fructose-enriched diets in mechanisms of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.D.; Stephenson, M.C.; Crossland, H.; Cordon, S.M.; Palcidi, E.; Cox, E.F.; Taylor, M.A.; Aithal, G.P.; Macdonald, I.A. No Difference Between High-Fructose and High-Glucose Diets on Liver Triacylglycerol or Biochemistry in Healthy Overweight Men. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1016–1025.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, H.; Du, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Dietary patterns are associated with prevalence of fatty liver disease in adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A.; Guy, C.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Colvin, R.; Johnson, R.J.; Diehl, A.M.; Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Increased fructose consumption is associated with fibrosis severity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maersk, M.; Belza, A.; Stødkilde-Jørgensen, H.; Ringgaard, S.; Chabanova, E.; Thomsen, H.; Pedersen, S.B.; Astrup, A.; Richelsen, B. Sucrose-sweetened beverages increase fat storage in the liver, muscle, and visceral fat depot: A 6-mo randomized intervention study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.Y.; Yiannakou, I.; Petersen, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Ma, J.; Long, M.T. Sugar-Sweetened Beverage, Diet Soda, and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Over 6 Years: The Framingham Heart Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2524–2532.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.; Herath, C.B. Dietary glycotoxins exacerbate progression of experimental fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Ying, Z.; Su, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. Fasting serum fructose is associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: A prospective study. Hepatol. Res. 2023, 53, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, S.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, W. Dietary fiber intake and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The mediating role of obesity. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1038435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddin, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wilkens, L.R.; Porcel, J.; Boushey, C.J.; Le Marchand, L.; Rosen, H.R.; Setiawan, V.W. Diet Associations with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in an Ethnically Diverse Population: The Multiethnic Cohort. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, J.A.; Raman, M.; Rioux, K.P.; Reimer, R.A. The potential role of prebiotic fibre for treatment and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and associated obesity and insulin resistance. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, A.; Dallio, M.; Godos, J.; Loguercio, C.; Salomone, F. Targeting gut-liver axis for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Translational and clinical evidence. Transl. Res. 2016, 167, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Ge, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Xia, Y. Co-interventions with Clostridium butyricum and soluble dietary fiber targeting the gut microbiota improve MAFLD via the Acly/Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5807–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, H.; Goel, P.; Srinivasan, V.M.; Tang, D.W.T.; Wong, S.H.; Lal, D. Gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and therapeutics. World J. Hepatol. 2025, 17, 106849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockman, D.A.; Chen, X.; Gallaher, D.D. High-Viscosity Dietary Fibers Reduce Adiposity and Decrease Hepatic Steatosis in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomhof, M.R.; Parnell, J.A.; Ramay, H.R.; Crotty, P.; Rioux, K.P.; Probert, C.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Raman, M.; Reimer, R.A. His-tological improvement of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with a prebiotic: A pilot clinical trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowska, E.; Portincasa, P.; Jamioł-Milc, D.; Maciejewska-Markiewicz, D.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K. The Relationship between Prebiotic Supplementation and Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters in Patients with NAFLD—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yan, Y.; Meng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Gu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, S.; et al. Protein foods from animal sources and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in representative cohorts from North and South China. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 293, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhong, L.; Tang, S. Food groups and the likelihood of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupoli, R.; Vitale, M.; Calabrese, I.; Giosuè, A.; Riccardi, G.; Vaccaro, O. White Meat Consumption, All-Cause Mortality, and Cardiovascular Events: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancovsky-Wajcman, D.; Fliss-Isakov, N.; Grinshpan, L.S.; Salomone, F.; Lazarus, J.V.; Webb, M.; Shibolet, O.; Kariv, R.; Zelber-Sagi, S. High Meat Consumption Is Prospectively Associated with the Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Presumed Significant Fibrosis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chuang, C.-C.; Kandaswamy, E.; Zhou, T.; Zuo, L. Role of ROS and Nutritional Antioxidants in Human Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oseini, A.M.; Sanyal, A.J. Therapies in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Liver Int. 2017, 37 (Suppl. 1), 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.-M.; Wu, W.-J.; Fu, N.; Liang, B.-L.; Wang, R.-Q.; Li, L.-X.; Zhao, S.-X.; Zhao, J.-M.; Yu, J. Antioxidants vitamin E and 1-aminobenzotriazole prevent experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Song, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Li, Z.; Cheng, L.; Ren, H. Protective Efficacy of Vitamins C and E on p,p′-DDT-Induced Cytotoxicity via the ROS-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway and NF-κB/FasL Pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, H.; Ahad, A.; Iqbal, J.; Siddiqui, W.A. Pharmacological potential of tocotrienols: A review. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niki, E. Role of vitamin E as a lipid-soluble peroxyl radical scavenger: In vitro and in vivo evidence. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.V.; McCullough, A.; Diehl, A.M.; Bass, N.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lavine, J.E.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; et al. Pioglitazone, Vitamin E, or Placebo for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, F.; Biernacki, D.M.; Kalavalapalli, S.; Lomonaco, R.; Subbarayan, S.K.; Lai, J.; Tio, F.; Suman, A.; Orsak, B.K.; Hecht, J.; et al. Role of Vitamin E for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podszun, M.C.; Frank, J. Impact of vitamin E on redox biomarkers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogli, S.; Naska, A.; Marinos, G.; Kasdagli, M.-I.; Orfanos, P. The Effect of Vitamin E Supplementation on Serum Aminotransferases in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Akhter, A. Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials of Pharmacologic Agents in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedarisetty, C.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Kumar, G.; Rastogi, A.; Bihari, C.; Kumar, M.; Sarin, S.K. Efficacy of combining pentoxiphylline and vitamin E versus vitamin E alone in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis—A randomized pilot study. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 40, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Maboud, M.; Menshawy, A.; Menshawy, E.; Emara, A.; Alshandidy, M.; Eid, M. The efficacy of vitamin E in reducing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820974917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njus, D.; Kelley, P.M.; Tu, Y.-J.; Schlegel, H.B. Ascorbic acid: The chemistry underlying its antioxidant properties. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 159, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righi, N.C.; Schuch, F.B.; De Nardi, A.T.; Pippi, C.M.; De Almeida Righi, G.; Puntel, G.O.; Da Silva, A.M.V.; Signori, L.U. Effects of vitamin C on oxidative stress, inflammation, muscle soreness, and strength following acute exercise: Meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2827–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, E.; Matos, M.D.; Kawiecki, D.; Ballard, K.; Guo, Y.; Volek, J.S.; Bruno, R.S. Vitamin C Status Is Related to Proinflammatory Responses and Impaired Vascular Endothelial Function in Healthy, College-Aged Lean and Obese Men. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, F.J.; Webster, J.; Barry, J.B.; Phillips, L.K.; Richards, A.A.; Whitehead, J.P. Synergistic effects of ascorbic acid and thiazolidinedione on secretion of high molecular weight adiponectin from human adipocytes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.B.; Wan, Z.; Frier, B.C.; Bell, R.C.; Field, C.J.; Wright, D.C. Dietary supplementation with vitamin E and C attenuates dexamethasone-induced glucose intolerance in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 302, R49–R58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Jo, A.N.; Lee, S.M.; Bae, H.S.; Jun, D.W.; Cho, Y.K.; Suk, K.T.; Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, S.B.; Cho, Y.J.; et al. Associations between intakes of individual nutrients or whole food groups and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among Korean adults. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, H.E.; Arendt, B.M. A cross-sectional study assessing dietary intake and physical activity in Canadian patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease vs healthy controls. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancovsky-Wajcman, D.; Fliss-Isakov, N.; Salomone, F.; Webb, M.; Shibolet, O.; Kariv, R.; Zelber-Sagi, S. Dietary vitamin E and C intake is inversely associated with the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Torgerson, S.; Hayashi, P.; Ward, J.; Schenker, S. Vitamin E and vitamin C treatment improves fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanaka, M.; Nishino, K.; Nakamura, J.; Suehiro, M.; Goto, D.; Urata, N.; Oka, T.; Kawamoto, H.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J.; et al. Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with vitamins E and C: A pilot study. Hepatic Med. 2013, 5, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Wu, P.; Wang, S.; Cao, D.; Guo, X.; Xu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Effects of Oral Vitamin C Supplementation on Liver Health and Associated Parameters in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 745609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobili, V.; Reif, S. Vitamin D and liver fibrosis: Let’s start soon before it’s too late. Gut 2015, 64, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Larsson, S.C. Inverse Association Between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 21, 398–405.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghooti, H.; Ghanavati, F.; Seyedian, S.S.; Cheraghian, B.; Mohammadtaghvaei, N. The efficacy of calcitriol treatment in non-alcoholic fatty liver patients with different genotypes of vitamin D receptor FokI polymorphism. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wei, C.-B.; Gu, W.; Hou, L.-L. Relevance of vitamin D on NAFLD and liver fibrosis detected by vibration controlled transient elastography in US adults: A cross-sectional analysis of NHANES 2017–2018. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2209335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, N.; Amani, R.; Hajiani, E.; Cheraghian, B. Does vitamin D improve liver enzymes, oxidative stress, and inflammatory biomarkers in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? A randomized clinical trial. Endocrine 2014, 47, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjalarsdottir, L.; Tersey, S.A.; Vishwanath, M.; Chuang, J.-C.; Posner, B.A.; Mirmira, R.G.; Repa, J.J. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mouse and human islets: A role for transcriptional regulation of voltage-gated calcium channels by the vitamin D receptor. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 185, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroomand, M.; Fotouhi, A.; Irannejad, N.; Hosseinpanah, F. Does high-dose vitamin D supplementation impact insulin resistance and risk of development of diabetes in patients with pre-diabetes? A double-blind randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 148, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, L.; Asadi, S.; Al-Mousavi, Z.; Niknam, R. A randomized controlled clinical trial comparing calcitriol versus cholecalciferol supplementation to reduce insulin resistance in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2999–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Ohnishi, H. Role of gut microbiota and Toll-like receptors in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7381–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Guo, E.; Yang, J. 1,25(OH)2 D3 attenuates hepatic steatosis by inducing autophagy in mice. Obesity 2017, 25, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour-Ghanaei, F.; Pourmasoumi, M.; Hadi, A.; Ramezani-Jolfaie, N.; Joukar, F. The Efficacy of Vitamin D Supplementation against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. J. Diet. Suppl. 2019, 17, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanko, V.L.; Domislovic, V.; Trkulja, V.; Krznaric-Zrnic, I.; Turk-Wensveen, T.; Krznaric, Z.; Kanizaj, T.F.; Radic-Kristo, D.; Bilic-Zulle, L.; Orlic, L.; et al. Vitamin D for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease detected by transient elastography: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimpour, Z.; Hoseini, R.; Behpour, N. Alterations of liver enzymes and lipid profile in response to exhaustive eccentric exercise: Vitamin D supplementation trial in overweight females with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. The link between Hepatic Vitamin A Metabolism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaker, M.W.; Vaandrager, A.B.; Helms, J.B. Retinoids in health and disease: A role for hepatic stellate cells in affecting retinoid levels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Dullaart, R.P.F.; Schreuder, T.C.M.A.; Blokzijl, H.; Faber, K.N. Disturbed Vitamin A Metabolism in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Nutrients 2017, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, X.; Peng, J.; Yu, H.; Lu, J.; Feng, Y. Association between dietary vitamin A intake from different sources and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among adults. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, M.V.; Trammell, S.A.; Migaud, M.E. The chemistry of the vitamin B3 metabolome. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganji, S.H.; Kashyap, M.L.; Kamanna, V.S. Niacin inhibits fat accumulation, oxidative stress, and inflammatory cytokine IL-8 in cultured hepatocytes: Impact on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2015, 64, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Allah, H.; Nasr, M.; Ahmed-Farid, O.A.; Ibrahim, B.M.; Bakeer, R.M.; Ahmed, R.F. Nicotinamide and ascorbic acid nanoparticles against the hepatic insult induced in rats by high fat high fructose diet: A comparative study. Life Sci. 2020, 263, 118540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loza-Medrano, S.S.; Baiza-Gutman, L.A.; Manuel-Apolinar, L.; García-Macedo, R.; Damasio-Santana, L.; Martínez-Mar, O.A.; Sánchez-Becerra, M.C.; Cruz-López, M.; Ibáñez-Hernández, M.A.; Díaz-Flores, M. High fructose-containing drinking water-induced steatohepatitis in rats is prevented by the nicotinamide-mediated modulation of redox homeostasis and NADPH-producing enzymes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, K.; Willmann, C.; Kantartzis, K.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Graf, M.; Kümmerle, S.; Häring, H.-U.; Fritsche, A.; Stefan, N.; et al. Dietary Niacin Intake Predicts the Decrease of Liver Fat Content During a Lifestyle Intervention. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Chu, W.C.W.; Yamashita, S.; Yeung, D.K.W.; Shi, L.; Wang, D.; Masuda, D.; Yang, Y.; Tomlinson, B. Liver fat reduction with niacin is influenced by DGAT-2 polymorphisms in hypertriglyceridemic patients. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, E.; Mohammed, B.S.; Korenblat, K.M.; Magkos, F.; McCrea, J.; Patterson, B.W.; Klein, S. Effect of Fenofibrate and Niacin on Intrahepatic Triglyceride Content, Very Low-Density Lipoprotein Kinetics, and Insulin Action in Obese Subjects with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemskerk, M.M.; van den Berg, S.A.A.; Pronk, A.C.M.; van Klinken, J.-B.; Boon, M.R.; Havekes, L.M.; Rensen, P.C.N.; van Dijk, K.W.; van Harmelen, V. Long-term niacin treatment induces insulin resistance and adrenergic responsiveness in adipocytes by adaptive downregulation of phosphodiesterase 3B. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E808–E813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, Y.; Carè, I.; Mazza, E.; Provenzano, F.; Colica, C.; Torti, C.; Romeo, S.; Pujia, A.; Montalcini, T. Protein and vitamin B6 intake are associated with liver steatosis assessed by transient elastography, especially in obese individuals. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2017, 23, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kessoku, T.; Ozaki, A.; Iwaki, M.; Honda, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Imajo, K.; Yoneda, M.; Saito, S.; Nakajima, A. Vitamin B6 efficacy in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An open-label, single-arm, single-center trial. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2021, 68, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.N.G.d.S.; Silvares, R.R.; Flores, E.E.I.; Rodrigues, K.L.; Daliry, A. Pyridoxamine improves metabolic and microcirculatory complications associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Microcirculation 2020, 27, e12603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sid, V.; Siow, Y.L.; O, K. Role of folate in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 95, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Min, H. Folic acid supplementation prevents high fructose-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating the AMPK and LKB1 signaling pathways. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2020, 14, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sid, V.; Shang, Y.; Siow, Y.L.; Hewage, S.M.; House, J.D.; O, K. Folic Acid Supplementation Attenuates Chronic Hepatic Inflammation in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice. Lipids 2018, 53, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssry, S.; Kamel, M.A. Effect of folate supplementation on immunological and autophagy markers in experimental nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2019, 30, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamid, M.; Mahroum, N.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Shalaata, K.; Yavne, Y.; Adawi, M.; Amital, H.; Watad, A. Folate and B12 Levels Correlate with Histological Severity in NASH Patients. Nutrients 2018, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.-F.; Bian, H.; Zhu, X.-P.; Yan, H.-M.; Chang, X.-X.; Zhang, L.-S.; Lin, H.-D.; Hu, X.-Q.; Gao, X. Serum folic acid levels are associated with the presence and severity of liver steatosis in Chinese adults. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaqanbari, M.R.; Zarringol, S.; Talari, H.R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Bahmani, F.; Mohtashamian, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Sharifi, N. Effects of Folic Acid Supplementation on Liver Enzymes, Lipid Profile, and Insulin Resistance in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2023, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, F.; Samman, S. Vitamin B12 in health and disease. Nutrients 2010, 2, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.S.; Guahnon, M.P.; Seganfredo, F.B.; Pinto, L.P.; Tovo, C.V.; Fernandes, S.A. Vitamin B12 and homocysteine levels in patients with NAFLD: A systematic review and metanalysis. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2021, 58, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talari, H.R.; Molaqanbari, M.R.; Mokfi, M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Bahmani, F.; Tabatabaei, S.M.H.; Sharifi, N. The effects of vitamin B12 supplementation on metabolic profile of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, L.; Tuo, B. Role of Ca2+ channels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and their implications for therapeutic strategies (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 50, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, T.; Wei, X.; Zhang, D.; Lv, W.; Luo, Z. Dietary Phosphorus Reduced Hepatic Lipid Deposition by Activating Ampk Pathway and Beclin1 Phosphorylation Levels to Activate Lipophagy in Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 841187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyczyńska, M.; Hunek, G.; Szczasny, M.; Brachet, A.; Januszewski, J.; Forma, A.; Portincasa, P.; Flieger, J.; Baj, J. Supplementation of Micro- and Macronutrients—A Role of Nutritional Status in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Sun, X.; Mao, Y.; Ye, D. Genetically determined circulating micronutrients and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheong, C.W.; Mustapha, N.R.N.; Mahadeva, S. A Randomized Trial of Silymarin for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1940–1949.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomone, F.; Barbagallo, I.; Godos, J.; Lembo, V.; Currenti, W.; Cinà, D.; Avola, R.; D’orazio, N.; Morisco, F.; Galvano, F.; et al. Silibinin Restores NAD+ Levels and Induces the SIRT1/AMPK Pathway in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hai, J. Silibinin ameliorates steatosis and insulin resistance during non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development partly through targeting IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalopitas, G.; Antza, C.; Doundoulakis, I.; Siargkas, A.; Kouroumalis, E.; Germanidis, G.; Samara, M.; Chourdakis, M. Impact of Silymarin in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition 2021, 83, 111092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhashemi, S.H.; Hakakzadeh, A.; Yeganeh, F.E.; Oshidari, B.; Rezaee, S.P. Effect of 8 Weeks milk thistle powder (silymarin extract) supplementation on fatty liver disease in patients candidates for bariatric surgery. Metabol. Open 2022, 14, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Fan, Y. The therapeutic effect of silymarin in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty disease: A meta-analysis (PRISMA) of randomized control trials. Medicine 2017, 96, e9061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; et al. Silymarin decreases liver stiffness associated with gut microbiota in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Duan, F.; Li, S.; Lu, B. Administration of silymarin in NAFLD/NASH: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y. Dihydrocurcumin ameliorates the lipid accumulation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance in oleic acid-induced L02 and HepG2 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi-Karimian, M.; Keshvari, M.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Salehizadeh, L.; Rahmani, S.; Behnam, B.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Asgary, S.; Sahebkar, A. Effects of curcuminoids on inflammatory status in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, R.; Arumugam, S.; Rahman, A.; Wahed, M.I.I.; Karuppagounder, V.; Harima, M.; Suzuki, H.; Miyashita, S.; Suzuki, K.; Yoneyama, H.; et al. Curcumin ameliorates liver damage and progression of NASH in NASH-HCC mouse model possibly by modulating HMGB1-NF-κB translocation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 44, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scazzocchio, B.; Minghetti, L.; D’Archivio, M. Interaction between Gut Microbiota and Curcumin: A New Key of Understanding for the Health Effects of Curcumin. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Huang, F.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y. Curcumin inhibits lipolysis via suppression of ER stress in adipose tissue and prevents hepatic insulin resistance. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Yu, Z.; Chiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chai, T.; Foltz, W.; Lu, H.; Fantus, I.G.; Jin, T. Curcumin Prevents High Fat Diet Induced Insulin Resistance and Obesity via Attenuating Lipogenesis in Liver and Inflammatory Pathway in Adipocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Mohseni, S.; Safargar, M.; Mohtashamian, A.; Niknam, S.; Bakhoda, M.; Afshari, S.; Jafari, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Fooladshekan, S.; et al. Curcumin effects on glycaemic indices, lipid profile, blood pressure, inflammatory markers and anthropometric measurements of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2024, 80, 103025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Mosallanezhad, Z.; Jalali, R.; Imanieh, M.H.; Moosavian, S.P. The effects of curcumin supplementation on liver function, metabolic profile and body composition in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 48, 102283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Guo, R.; Fung, M.-L.; Liong, E.C.; Chang, R.C.C.; Ching, Y.-P.; Tipoe, G.L. Garlic-Derived S-Allylmercaptocysteine Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Rat Model through Inhibition of Apoptosis and Enhancing Autophagy. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 642920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.-R.; Chen, P.; Li, Y.; Li, J.-Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, D.-D.; Cui, L.; Guan, Q.-G.; Li, H.-Y. Two cinnamoyloctopamine antioxidants from garlic skin attenuates oxidative stress and liver pathology in rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastkar, M.; Nikniaz, L.; Farhangi, M.A.; Nikniaz, Z. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of garlic in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 41, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhao, R.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Chu, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; et al. Effects of garlic supplementation on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 99, 105294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Meng, F.; Liao, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Meng, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Therapeutic Role of Ursolic Acid on Ameliorating Hepatic Steatosis and Improving Metabolic Disorders in High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86724, Correction in PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Takikawa, Y.; Satoh, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kosaka, K.; Tatemichi, Y.; Suzuki, K. Carnosic acid prevents obesity and hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Lu, W.-P.; Cui, Z.-H.; Zhou, L.; Yao, D.; Zhang, H.-M. Carnosic acid protects mice from high-fat diet-induced NAFLD by regulating MARCKS. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-S.; Lee, W.-C.; Lin, Y.-E.; Ho, C.-T.; Lu, K.-H.; Lin, S.-H.; Panyod, S.; Chu, Y.-L.; Sheen, L.-Y. Ginger Essential Oil Ameliorates Hepatic Injury and Lipid Accumulation in High Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimlou, M.; Yari, Z.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Alavian, S.M.; Keshavarz, S.A. Ginger supplementation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Hepat. Mon. 2016, 16, e34897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, M.; Moradinazar, M.; Khosravy, T.; Soleimani, D.; Jahangiri, P.; Kamari, N. A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical and clinical studies on the efficacy of ginger for the treatment of fatty liver disease. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1182–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.D.; Xie, Z.Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Wei, T.; Zhao, A.H.; Zhang, Q.H. Inhibitory effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on fatty liver: Regulation of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a and fatty acid metabolism. J. Dig. Dis. 2012, 13, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Xiong, F.-F.; Wang, S.-D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-H. Flavonoid ingredients of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract regulate lipid metabolism through Sp1-mediated carnitine palmitoyltranferase 1A up-regulation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 21, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, F.; Zhao, X.-L.; Xue, S.; Gong, F.-H. Ginkgo biloba Extract 50 (GBE50) Ameliorates Insulin Resistance, Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Suk, K.T.; Bang, C.S.; Yoon, J.H.; Baik, G.H.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, M.J. Anti-inflammatory and antifatigue effect of Korean Red Ginseng in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Yoo, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Park, E.-J.; Lee, H.-J. Ameliorative effects of black ginseng on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in free fatty acid–induced HepG2 cells and high-fat/high-fructose diet-fed mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.-Y. Ginsenoside Rb2 Alleviates Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Restoring Autophagy via Induction of Sirt1 and Activation of AMPK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiaghamohammadi, A.A.; Ziaee, A.; Samimi, R. The Efficacy of Licorice Root Extract in Decreasing Transaminase Activities in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1381–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamizadeh, P.; Asl, S.M.K.H.; Far, Z.G.; Ahmadijoo, P.; Mahmudiono, T.; Bokov, D.O.; Alsaikhan, F.; Jannat, B.; Mazloom, Z. Effects of licorice root supplementation on liver enzymes, hepatic steatosis, metabolic and oxidative stress parameters in women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 3949–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravej, S.A.A.-H.; Shojaii, A.; Dabaghian, F.H.; Jazayeri, S.F.; Khadem, E.; Agah, S.; Ghods, R. The Efficacy of Rosa damascena on Liver Enzymes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 6628911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, S.F.; Ghods, R.; Dabaghian, F.H.; Shojaii, A.; Moravej, S.A.A.-H.; Khadem, E.; Seyedian, S.S. The Efficacy of Plantago major Seed on Liver Enzymes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 6693887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yi, H.; Wu, J.; Kuang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Du, H.; Xu, T.; Jiang, G.; Fan, G. Therapeutic effect of berberine on metabolic diseases: Both pharmacological data and clinical evidence. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Li, D.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, M. Multi-Pharmacology of Berberine in Atherosclerosis and Metabolic Diseases: Potential Contribution of Gut Microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 709629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Q.; Li, M.; Huang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, Q.; Ma, X.; Qiu, T.; Li, J. The clinical efficacy and safety of berberine in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Chu, Y.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, J. Berberine prevents NAFLD and HCC by modulating metabolic disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 254, 108593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, R.Z.; Barbalho, S.M.; Sloan, K.P.; Laurindo, L.F.; Gonzaga, H.F.; Grippa, P.C.; Zutin, T.L.M.; Girio, R.J.S.; Repetti, C.S.F.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; et al. The Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics in Non-Alcoholic Fat Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Vitetta, L. Gut Microbiota Metabolites in NAFLD Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.; De Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Conde, R.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Primo, D.; De La Fuente, B.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of a probiotic on liver aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: A double blind randomized clinical trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Nor, M.H.M.; Ayob, N.; Mokhtar, N.M.; Ali, R.A.R.; Tan, G.C.; Wong, Z.; Shafiee, N.H.; Wong, Y.P.; Mustangin, M.; Nawawi, K.N.M. The Effect of Probiotics (MCP® BCMC® Strains) on Hepatic Steatosis, Small Intestinal Mucosal Immune Function, and Intestinal Barrier in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Vacante, M. Bifidobacterium longum with fructo-oligosaccharides in patients with non-alcoholic steato-hepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Ch’NG, D.; Jia, P.; Tsoi, K.K.F.; Wong, S.H.; Sung, J.J.Y. Use of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 38, 1682–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, R.; Yang, X.; Dai, J.; Huang, M.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Okekunle, A.P.; Gao, G.; Onwuka, J.U.; et al. Yogurt improves insulin resistance and liver fat in obese women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshimoghaddam, F.; Shateri, K.; Sina, M.; Hashemian, M.; Alizadeh, M. Daily Consumption of Synbiotic Yogurt Decreases Liver Steatosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, A.A.; Feld, J.J.; Park, Y.; Kleiner, D.E.; Everhart, J.E.; Liang, J.T.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Increased Caffeine Consumption Is Associated with Reduced Hepatic Fibrosis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marventano, S.; Salomone, F.; Godos, J.; Pluchinotta, F.; Del Rio, D.; Mistretta, A.; Grosso, G. Coffee and tea consumption in relation with non-alcoholic fatty liver and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, S.; Mallam, D.; Cox, G.A.; Tong, M.J. Impact of coffee on liver diseases: A systematic review. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Lu, F.-B.; Hu, Y.-B.; Xu, L.-M.; Zheng, M.-H.; Hu, E.-D. A systematic review and a dose–response meta-analysis of coffee dose and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2552–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, J.; Ahn, S.B. Different Associations of Coffee Consumption with the Risk of Incident Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Advanced Liver Fibrosis. Nutrients 2023, 16, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Koh, W.-P.; Wang, R.; Govindarajan, S.; Yu, M.C.; Yuan, J.-M. Coffee consumption and reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: Findings from the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Cancer Causes Control. 2011, 22, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Micek, A.; Marranzano, M.; Salomone, F.; Del Rio, D.; Ray, S. Coffee Consumption and Risk of Biliary Tract Cancers and Liver Cancer: A Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Nutrients 2017, 9, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaquet, M.; Rochat, I.; Moulin, J.; Cavin, C.; Bibiloni, R. Impact of coffee consumption on the gut microbiota: A human volunteer study. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 130, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Oishi, K. Influence of coffee (Coffea arabica) and galacto-oligosaccharide consumption on intestinal microbiota and the host responses. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 343, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askari, G.; Pezeshki, A.; Safi, S.; Feizi, A.; Karami, F. The effect of green tea extract supplementation on liver enzymes in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Xu, L.; Tang, S. Green tea polyphenols attenuate hepatic steatosis, and reduce insulin resistance and inflammation in high-fat diet-induced rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Hosseini, R.; Kazemi, A.; Ofori-Asenso, R.; Mazidi, M.; Mazloomi, S.M. Effects of green tea or green tea catechin on liver enzymes in healthy individuals and people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, R.; Nakamura, T.; Torimura, T.; Ueno, T.; Sata, M. Green tea with high-density catechins improves liver function and fat infiltration in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients: A double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, S.S.; Nagle, H.T. Revisited: Assessing the in vivo data on low/no-calorie sweeteners and the gut microbiota. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 132, 110692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.K.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Anderson, C.A.; Carson, J.A.; Després, J.P.; Hu, F.B.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Otten, J.J.; Towfighi, A.; Wylie-Rosett, J.; et al. Low-Calorie Sweetened Beverages and Cardiometabolic Health: A Science Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 138, e126–e140. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Resveratrol supplement inhibited the NF-κB inflammation pathway through activating AMPKα-SIRT1 pathway in mice with fatty liver. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 422, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, G.; Bu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, X. Resveratrol and caloric restriction prevent hepatic steatosis by regulating SIRT1-autophagy pathway and alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress in high-fat diet-fed rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihzadeh, F.; Adibi, P.; Hekmatdoost, A. The effects of resveratrol supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Ran, L.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Shu, F.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Resveratrol improves insulin resistance, glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, X.; Ge, A.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Zeng, L.; Ge, J. Efficacy and safety of dietary polyphenol supplementation in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 949746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangouni, A.A.; Abdollahi, S.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H. Effect of resveratrol supplementation on hepatic steatosis and cardiovascular indices in overweight subjects with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2022, 22, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, L.; Asghari, S.; Rafraf, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Shirmohammadi, M. No beneficial effects of resveratrol supplementation on atherogenic risk factors in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2020, 90, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, S.; Mohammadi, H.; Ghavami, A.; Sadeghi, E.; Safari, Z.; Askari, G. Efficacy of resveratrol supplementation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2021, 42, 101281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, S.B.; Mayr, J.A. Choline-related-inherited metabolic diseases-A mini review. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, N.; Arboleya, S.; Allison, J.; Kaliszewska, A.; Higarza, S.G.; Gueimonde, M.; Arias, J.L. The Relationship between Choline Bioavailability from Diet, Intestinal Microbiota Composition, and Its Modulation of Human Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, K.D.; Zeisel, S.H. Choline metabolism provides novel insights into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its progression. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 28, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yuan, M.; Wang, L. The effect of omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmíd, V.; Dvořák, K.; Šedivý, P.; Kosek, V.; Leníček, M.; Dezortová, M.; Hajšlová, J.; Hájek, M.; Vítek, L.; Bechyňská, K.; et al. Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome and NAFLD. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.M.; Cohn, J.S.; O’Connor, H.T.; Garg, M.L.; Caterson, I.D.; George, J.; Johnson, N.A. Effect of Fish Oil Supplementation on Hepatic and Visceral Fat in Overweight Men: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, L.N.; Salarini, J.; Leite, N.C.; Villela-Nogueira, C.A.; Dávalos, A.; Carmo, M.d.G.T.; Peres, W.A.F. Effect of fish oil supplementation on the concentration of miRNA-122, FGF-21 and liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 57, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardekani, A.; Tabrizi, R.; Maleki, E.; Lankarani, K.B.; Heydari, S.T.; Moradinazar, M.; Akbari, M. Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on lipid profiles and liver enzymes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 2580–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. How Safe Is Moderate Alcohol Consumption in Overweight and Obese Individuals? Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1698–1703.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.; Sanyal, A.J.; Brunt, E.M.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Donohue, M.; McCullough, A.J.; Schwimmer, J.B. Modest alcohol consumption is associated with decreased prevalence of steatohepatitis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmera, V.; Belt, P. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Among Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Modest Alcohol Use Is Associated with Less Improvement in Histologic Steatosis and Steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1511–1520.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åberg, F.; Puukka, P.; Salomaa, V.; Männistö, S.; Lundqvist, A.; Valsta, L.; Perola, M.; Jula, A.; Färkkilä, M. Combined Effects of Alcohol and Metabolic Disorders in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 995–997.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, L.A.; Arab, J.P.; Louvet, A.; Bataller, R.; Arrese, M. The intersection between alcohol-related liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 764–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åberg, F.; Byrne, C.D.; Pirola, C.J.; Männistö, V.; Sookoian, S. Alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome: Clinical and epidemiological impact on liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, H.; O’KEefe, H.; Craig, D.; Stow, D.; Hanratty, B.; Anstee, Q.M. Does moderate alcohol consumption accelerate the progression of liver disease in NAFLD? A systematic review and narrative synthesis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e049767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.T.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Benjamin, E.J.; Naimi, T.S. Alcohol Use Is Associated with Hepatic Steatosis Among Persons with Presumed Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1831–1841.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, P.; Lin, W.; Huang, C.; Lin, H.; Tseng, T.; Chen, P. Exclusive liquor and cocktail consumption is associated with at-risk fibrosis among nonheavy alcohol users with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 48, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, L.X. Risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 11890–11903. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, Y.; Arase, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Akuta, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Saitoh, S.; Suzuki, F.; Suzuki, Y.; Inao, M.; Mochida, S.; et al. Effects of Alcohol Consumption on Hepatocarcinogenesis in Japanese Patients with Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.; Poklepovic, A.; Moyneur, E.; Barghout, V. Population-based risk factors and resource utilization for HCC: US perspective. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010, 26, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoolchund, A.G.S.; Khakoo, S.I. MASLD and the Development of HCC: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Challenges. Cancers 2024, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Ong, J.; Yilmaz, Y.; Duseja, A.; Eguchi, Y.; El Kassas, M.; Castellanos-Fernandez, M.; George, J.; Jacobson, I.M.; et al. Effects of Alcohol Consumption and Metabolic Syndrome on Mortality in Patients with Nonalcoholic and Alcohol-Related Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 1625–1633.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajifathalian, K.; Sagvand, B.T.; McCullough, A.J. Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Survival in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A National Prospective Cohort Study. Hepatology 2019, 70, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adejumo, A.C.; Alliu, S.; Ajayi, T.O.; Adejumo, K.L.; Adegbala, O.M.; Onyeakusi, N.E.; Akinjero, A.M.; Durojaiye, M.; Bukong, T.N. Cannabis use is associated with reduced prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, W.; Kwak, M.-S.; Chung, G.E.; Yim, J.Y.; Ahmed, A. Inverse association of marijuana use with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among adults in the United States. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazwinsky-Wutschke, I.; Zipprich, A.; Dehghani, F. Endocannabinoid System in Hepatic Glucose Metabolism, Fatty Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Does Cannabis Intake Protect Against Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease? A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.J.; Weiss, S.H.; Nasir, U.M.; Pyrsopoulos, N.T. Cannabis use history is associated with increased prevalence of ascites among patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A nationwide analysis. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-J.; Park, M.Y.; Cho, E.J.; Yu, S.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yoon, J.-H. Smoking Increases the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignini, I.; Galasso, L.; Piccirilli, G.; Calvez, V.; Termite, F.; Esposto, G.; Borriello, R.; Miele, L.; Ainora, M.E.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Interplay of Oxidative Stress, Gut Microbiota, and Nicotine in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Karaketklang, K.; Aekplakorn, W. Cigarette Smoking Increased Risk of Overall Mortality in Patients with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 604919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Manson, J.E. A prospective study of red meat consumption and type 2 diabetes in middle-aged and elderly women: The women’s health study. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2108–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babio, N.; Sorlí, M.; Bulló, M.; Basora, J.; Ibarrola-Jurado, N.; Fernández-Ballart, J.; Martínez-González, M.; Serra-Majem, L.; González-Pérez, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Association between red meat consumption and metabolic syndrome in a Mediterranean population at high cardiovascular risk: Cross-sectional and 1-year follow-up assessment. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Liu, Z.W. The prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with lifestyle/dietary habits among university faculty and staff in Chengdu. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.C.; Sacks, F.; Trichopoulou, A.; Drescher, G.; Ferro-Luzzi, A.; Helsing, E.; Trichopoulos, D. Mediterranean diet pyramid: A cultural model for healthy eating. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61 (Suppl. 6), 1402S–1406S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.C.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Thodis, T.; Ward, G.; Trost, N.; Hofferberth, S.; O’dEa, K.; Desmond, P.V.; Johnson, N.A.; Wilson, A.M. The Mediterranean diet improves hepatic steatosis and insulin sensitivity in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Lista, J.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Fuentes, F.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Ortiz-Morales, A.M.; I Perez-Caballero, A.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; A Rangel-Zuñiga, O.; et al. Long-term secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet and a low-fat diet (CORDIOPREV): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Bulló, M. Prevention of diabetes with Mediterranean diets: A subgroup analysis of a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 160, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Bulló, M. PREDIMED Study Investigators. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with the Mediter-ranean diet: Results of the PREDIMED-Reus nutrition intervention randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.; Masulli, M.; Calabrese, I.; Rivellese, A.A.; Bonora, E.; Signorini, S.; Perriello, G.; Squatrito, S.; Buzzetti, R.; Sartore, G.; et al. Impact of a Mediterranean Dietary Pattern and Its Components on Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Glucose Control, and Body Weight in People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Real-Life Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaacks, L.M.; Sher, S.; De Staercke, C.; Porkert, M.; Alexander, W.R.; Jones, D.P.; Vaccarino, V.; Ziegler, T.R.; Quyyumi, A.A. Pilot randomized controlled trial of a Mediterranean diet or diet supplemented with fish oil, walnuts, and grape juice in overweight or obese US adults. BMC Nutr. 2018, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Tomás, N.; Blanco Mejía, S.; Viguiliouk, E.; Khan, T.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Kahleova, H.; Rahelić, D.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Mediterranean diet, cardiovascular disease and mortality in diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies and randomized clinical trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1207–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyogo, H.; Yamagishi, S.; Iwamoto, K.; Arihiro, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Sato, T.; Ochi, H.; Nonaka, M.; Nabeshima, Y.; Inoue, M.; et al. Elevated levels of serum advanced glycation end products in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; de la Fuente, B.; De Luis Román, D.A. Mediterranean diet is associated with liver histology in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 2518–2524. [Google Scholar]
- Montemayor, S.; Mascaró, C.M.; Ugarriza, L.; Casares, M.; Llompart, I.; Abete, I.; Zulet, M.Á.; Martínez, J.A.; Tur, J.A.; Bouzas, C. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and NAFLD in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: The FLIPAN Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Properzi, C.; O’Sullivan, T.A.; Sherriff, J.L.; Ching, H.L.; Jeffrey, G.P.; Buckley, R.F.; Tibballs, J.; MacQuillan, G.C.; Garas, G.; Adams, L.A. Ad Libitum Mediterranean and Low-Fat Diets Both Significantly Reduce Hepatic Steatosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1741–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, E.S.; Reddy, A.; Nicoll, A.J.; Ryan, M.C.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Abbott, G.; Johnson, N.A.; Sood, S.; Roberts, S.K.; Tierney, A.C. Impact of a Mediterranean diet on hepatic and metabolic outcomes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The MEDINA randomised controlled trial. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouvari, M.; Boutari, C.; Chrysohoou, C.; Fragkopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Tousoulis, D.; Pitsavos, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Mantzoros, C.S.; ATTICA study Investigators. Mediterranean diet is inversely associated with steatosis and fibrosis and de-creases ten-year diabetes and cardiovascular risk in NAFLD subjects: Results from the ATTICA perspective cohort study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3314–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsagoni, C.N.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Ioannidou, P.; Deutsch, M.; Alexopoulou, A.; Papadopoulos, N.; Papageorgiou, M.-V.; Fragopoulou, E.; Kontogianni, M.D. Improvements in clinical characteristics of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, after an intervention based on the Mediterranean lifestyle: A randomised controlled clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, J.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Bulló, M.; Lopez, J.V.; Corella, D.; Castañer, O.; Vidal, J.; Atzeni, A.; Fernandez-García, J.C.; Torres-Collado, L.; et al. Effect on gut microbiota of a 1-y lifestyle intervention with Mediterranean diet compared with energy-reduced Mediterranean diet and physical activity promotion: PREDIMED-Plus Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Loomba, R.; Rinella, M.E.; Bugianesi, E.; Marchesini, G.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Serfaty, L.; Negro, F.; Caldwell, S.H.; Ratziu, V.; et al. Current and future therapeutic regimens for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2018, 68, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, A.Y.; Rinott, E.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; Kaplan, A.; Rosen, P.; Shelef, I.; Youngster, I.; Shalev, A.; Blüher, M.; et al. Effect of green-Mediterranean diet on intrahepatic fat: The DIRECT PLUS randomised controlled trial. Gut 2021, 70, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraschek, S.P.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Weaver, C.M.; Appel, L.J. Effects of Sodium Reduction and the DASH Diet in Relation to Baseline Blood Pressure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmatdoost, A.; Shamsipour, A.; Meibodi, M.; Gheibizadeh, N.; Eslamparast, T.; Poustchi, H. Adherence to the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) and risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doustmohammadian, A.; Clark, C.C.T.; Maadi, M.; Motamed, N.; Sobhrakhshankhah, E.; Ajdarkosh, H.; Mansourian, M.R.; Esfandyari, S.; Hanjani, N.A.; Nikkhoo, M.; et al. Favorable association between Mediterranean diet (MeD) and DASH with NAFLD among Iranian adults of the Amol Cohort Study (AmolCS). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi Zade, M.; Telkabadi, M.H.; Bahmani, F.; Salehi, B.; Farshbaf, S.; Asemi, Z. The effects of DASH diet on weight loss and metabolic status in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized clinical trial. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, S.; Chitsazi, M.J.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. The effect of dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) on serum inflammatory markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, R.; Gilani, B.; Uppaluri, K.R. Low Carbohydrate Diet; (Updated 12 July 2021); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Astrup, A.; Larsen, T.M.; Harper, A. Atkins and other low-carbohydrate diets: Hoax or an effective tool for weight loss? Lancet 2004, 364, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, D.S.; Ebbeling, C.B. The Carbohydrate-Insulin Model of Obesity: Beyond “Calories In, Calories Out”. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbeling, C.B.; A Feldman, H.; Klein, G.L.; Wong, J.M.W.; Bielak, L.; Steltz, S.K.; Luoto, P.K.; Wolfe, R.R.; Wong, W.W.; Ludwig, D.S. Effects of a low carbohydrate diet on energy expenditure during weight loss maintenance: Randomized trial. BMJ 2018, 363, k4583, Correction in BMJ 2020, 371, m4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, D.S.; Aronne, L.J.; Astrup, A.; de Cabo, R.; Cantley, L.C.; Friedman, M.I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Johnson, J.D.; King, J.C.; Krauss, R.M.; et al. The carbo-hydrate-insulin model: A physiological perspective on the obesity pandemic. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.D.; Wyatt, H.R.; Hill, J.O.; McGuckin, B.G.; Brill, C.; Mohammed, B.S.; Szapary, P.O.; Rader, D.J.; Edman, J.S.; Klein, S. A Randomized Trial of a Low-Carbohydrate Diet for Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, C.D.; Trepanowski, J.F.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Hauser, M.E.; Rigdon, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Desai, M.; King, A.C. Effect of Low-Fat vs Low-Carbohydrate Diet on 12-Month Weight Loss in Overweight Adults and the Association with Genotype Pattern or Insulin Secretion: The DIETFITS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 319, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haufe, S.; Engeli, S.; Kast, P.; Böhnke, J.; Utz, W.; Haas, V.; Hermsdorf, M.; Mähler, A.; Wiesner, S.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; et al. Randomized comparison of reduced fat and reduced carbohydrate hypocaloric diets on intrahepatic fat in overweight and obese human subjects. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingsson, E.; Johansson, K.; Eriksson, J.; Sundström, J.; Neovius, M.; Marcus, C. Weight loss and dropout during a commercial weight-loss program including a very-low-calorie diet, a low-calorie diet, or restricted normal food: Observational cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidelmann, S.B.; Claggett, B. Dietary carbohydrate intake and mortality: A prospective cohort study and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health 2018, 3, e419–e428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noto, H.; Goto, A.; Tsujimoto, T.; Noda, M. Low-Carbohydrate Diets and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55030, Correction in PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghan, M.; Mente, A.; Zhang, X.; Swaminathan, S.; Li, W.; Mohan, V.; Iqbal, R.; Kumar, R.; Wentzel-Viljoen, E.; Rosengren, A.; et al. Associations of fats and carbohydrate intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 18 countries from five continents (PURE): A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2017, 390, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershuni, V.M.; Yan, S.L.; Medici, V. Nutritional Ketosis for Weight Management and Reversal of Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2018, 7, 97–106, Correction in Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2025, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, H.M.; Mathew, T.C.; Hussein, T.; Asfar, S.K.; Behbahani, A.; A Khoursheed, M.; Al-Sayer, H.M.; Bo-Abbas, Y.Y.; Al-Zaid, N.S. Long-term effects of a ketogenic diet in obese patients. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2004, 9, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Volek, J.S.; Phinney, S.D.; Forsythe, C.E.; Quann, E.E.; Wood, R.J.; Puglisi, M.J.; Kraemer, W.J.; Bibus, D.M.; Fernandez, M.L.; Feinman, R.D. Carbohydrate Restriction has a More Favorable Impact on the Metabolic Syndrome than a Low Fat Diet. Lipids 2009, 44, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volek, J.S.; Feinman, R.D. Carbohydrate restriction improves the features of Metabolic Syndrome. Metabolic Syndrome may be defined by the response to carbohydrate restriction. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 2, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larosa, J.C.; Fry, A.G.; Muesing, R.; Rosing, D.R. Effects of high-protein, low-carbohydrate dieting on plasma lipoproteins and body weight. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1980, 77, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, S.; Bistrian, B.; Evans, W.; Gervino, E.; Blackburn, G. The human metabolic response to chronic ketosis without caloric restriction: Preservation of submaximal exercise capability with reduced carbohydrate oxidation. Metabolism 1983, 32, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saslow, L.R.; Daubenmier, J.J.; Moskowitz, J.T.; Kim, S.; Murphy, E.J.; Phinney, S.D.; Ploutz-Snyder, R.; Goldman, V.; Cox, R.M.; Mason, A.E.; et al. Twelve-month outcomes of a randomized trial of a moderate-carbohydrate versus very low-carbohydrate diet in overweight adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, N.B.; de Melo, I.S. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, G.M.; Guzman, G.; De Mello, L.L.C.; Trein, B.; Spina, L.; Bussade, I.; Prata, J.M.; Sajoux, I.; Countinho, W. Efficacy of a 2-Month Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) Compared to a Standard Low-Calorie Diet in Reducing Visceral and Liver Fat Accumulation in Patients with Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yki-Järvinen, H. Nutritional Modulation of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9127–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Cerullo, G. Investigating the Link between Ketogenic Diet, NAFLD, Mitochondria, and Oxidative Stress: A Narrative Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendler, D.; Lin, S.; Yancy, W.S., Jr.; Mavropoulos, J.; Sylvestre, P.; Rockey, D.C.; Westman, E.C. The Effect of a Low-Carbohydrate, Ketogenic Diet on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Pilot Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seid, H.; Rosenbaum, M. Low Carbohydrate and Low-Fat Diets: What We Don’t Know and Why we Should Know It. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, D.K.; Chen, M.; E Manson, J.; Ludwig, D.S.; Willett, W.; Hu, F.B. Effect of low-fat diet interventions versus other diet interventions on long-term weight change in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkaneh, H.K.; Poursoleiman, F.; Al Masri, M.K.; Alras, K.A.; Shayah, Y.; Masmoum, M.D.; Alangari, F.A.; Alras, A.A.; Rinaldi, G.; Day, A.S.; et al. Low fat diet versus low carbohydrate diet for management of non-alcohol fatty liver disease: A systematic review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 987921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.; Thompson, C.H.; Luscombe-Marsh, N.D.; Wycherley, T.P.; Noakes, M.; Buckley, J.D.; Wittert, G.A.; Yancy, W.S., Jr.; Brinkworth, G.D. Effects of an energy-restricted low-carbohydrate, high unsaturated fat/low saturated fat diet versus a high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet in type 2 diabetes: A 2-year randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighatdoost, F.; Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Surkan, P.J.; Azadbakht, L. The effects of low carbohydrate diets on liver function tests in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasim, I.; Majeed, C.N.; DeBoer, M.D. Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, L.; Hamilton, S.; Azevedo, L.B.; Olajide, J.; De Brún, C.; Waller, G.; Whittaker, V.; Sharp, T.; Lean, M.; Hankey, C.; et al. Intermittent fasting interventions for treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JBI Database System Rev. Implement. Rep. 2018, 16, 507–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drinda, S.; Grundler, F.; Neumann, T.; Lehmann, T.; Steckhan, N.; Michalsen, A.; De Toledo, F.W. Effects of Periodic Fasting on Fatty Liver Index—A Prospective Observational Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Seo, Y.-G.; Paek, Y.-J.; Song, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Noh, H.-M. Effect of alternate-day fasting on obesity and cardiometabolic risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2020, 111, 154336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Nadkarni, D.; Martin, L.; Newberry, C.; Kumar, S.; Kushner, T. Intermittent fasting improves hepatic end points in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezpeleta, M.; Gabel, K.; Cienfuegos, S.; Kalam, F.; Lin, S.; Pavlou, V.; Song, Z.; Haus, J.M.; Koppe, S.; Alexandria, S.J.; et al. Effect of alternate day fasting combined with aerobic exercise on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 56–70.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.D.; Moehl, K.; Donahoo, W.T.; Marosi, K.; Lee, S.A.; Mainous, A.G., 3rd; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Mattson, M.P. Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying the Health Benefits of Fasting. Obesity 2018, 26, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Lindqvist, C.; Petersson, S.; Moshtaghi-Svensson, J.; Tillander, V.; Brismar, T.B.; Hagström, H.; Stål, P. Treatment of NAFLD with intermittent calorie restriction or low-carb high-fat diet—A randomised controlled trial. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Vazquez-Montesino, L.M.; Li, A.A.; Cholankeril, G.; Ahmed, A. Inadequate Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior Are Independent Predictors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, J. Association of sarcopenia and physical activity on the severity of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease among United States adults: NHANES 2017–2018. Front. Aging 2025, 6, 1573170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Lazarus, J.V.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Yilmaz, Y.; Duseja, A.; Eguchi, Y.; Castera, L.; Pessoa, M.G.; Oliveira, C.P.; et al. Global Consensus Recommendations for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2025, 169, 1017–1032.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.-C.; Ryu, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Wild, S.H.; Byrne, C.D. Effect of exercise on the development of new fatty liver and the resolution of existing fatty liver. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerage, A.M.; Ritti-Dias, R.M.; Balagopal, P.B.; Conceição, R.D.d.O.; Umpierre, D.; Santos, R.D.; Cucato, G.G.; Bittencourt, M.S. Physical activity levels and hepatic steatosis: A longitudinal follow-up study in adults. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Murag, S.; Cholankeril, G.; Cheung, A.; Harrison, S.A.; Younossi, Z.M.; Ahmed, A. Physical Activity, Measured Objectively, Is Associated with Lower Mortality in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 1240–1247.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, S.; Chang, Y.; Jung, H.-S.; Yun, K.E.; Kwon, M.-J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, C.-W.; Cho, J.; Suh, B.-S.; Cho, Y.K.; et al. Relationship of sitting time and physical activity with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; He, J. Effects of Moderate and Vigorous Exercise on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, L.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Lu, Y.; Han, C.; Lin, M.; Li, X.; et al. Long-term effect of exercise on improving fatty liver and cardiovascular risk factors in obese adults: A 1-year follow-up study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaee-Moradie, F.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Barrett, M.; Jackson, N.C.; Herring, R.; Thomas, E.L.; Bell, J.; Kemp, G.J.; Wright, J.; Umpleby, A.M. Exercise Training Reduces Liver Fat and Increases Rates of VLDL Clearance But Not VLDL Production in NAFLD. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4219–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Paik, J.M.; Ivancovsky-Wajcmen, D.; Henry, L.; Yilmaz, Y.; Alqahtani, S.A.; El-Kassass, M.; Pekas, E.J.; Gerber, L.H.; Younossi, Z.M. “Weekend Warrior” Exercise Pattern Protects Against MASLD and Mortality Comparable to Regular Exercise: National Cohort Study. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e70226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekelund, U.; Tarp, J.; Steene-Johannessen, J.; Hansen, B.H.; Jefferis, B.; Fagerland, M.W.; Whincup, P.; Diaz, K.M.; Hooker, S.P.; Chernofsky, A.; et al. Dose-response associations between accelerometry measured physical activity and sedentary time and all cause mortality: Systematic review and harmonised meta-analysis. BMJ 2019, 366, l4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøntved, A.; Hu, F.B. Television Viewing and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and All-Cause Mortality: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2011, 305, 2448–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, D.W.; Salmon, J.; Healy, G.N.; Shaw, J.E.; Jolley, D.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Owen, N.; on behalf of the AusDiab Steering Committee. Association of Television Viewing with Fasting and 2-h Postchallenge Plasma Glucose Levels in Adults Without Diagnosed Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascaró, C.M.; Bouzas, C.; Montemayor, S.; Casares, M.; Llompart, I.; Ugarriza, L.; Borràs, P.-A.; Martínez, J.A.; Tur, J.A. Effect of a Six-Month Lifestyle Intervention on the Physical Activity and Fitness Status of Adults with NAFLD and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; E Sahar, N.; Javaid, H.M.A.; Pak, E.S.; Liang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ha, H.; Huh, J.Y. Exercise-Induced Irisin Decreases Inflammation and Improves NAFLD by Competitive Binding with MD2. Cells 2021, 10, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, H.; Ge, X.; Ying, S.; Hu, M.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; et al. Inhibition of MD2-dependent inflammation attenuates the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredrickson, G.; Barrow, F.; Dietsche, K.; Parthiban, P.; Khan, S.; Robert, S.; Demirchian, M.; Rhoades, H.; Wang, H.; Adeyi, O.; et al. Exercise of high intensity ameliorates hepatic inflammation and the progression of NASH. Mol. Metab. 2021, 53, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Nitzan-Kaluski, D.; Goldsmith, R.; Webb, M.; Zvibel, I.; Goldiner, I.; Blendis, L.; Halpern, Z.; Oren, R. Role of leisure-time physical activity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based study. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallsworth, K.; Thoma, C.; Moore, S.; Ploetz, T.; Anstee, Q.M.; Taylor, R.; Day, C.P.; Trenell, M.I. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with higher levels ofobjectivelymeasured sedentary behaviour and lower levels of physical activity than matched healthy controls. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, D.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Albert, M.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J.W.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 140, e596–e646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-J.; Wu, C.-L.; Chiu, C.-H. High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise Increases Fat Oxidation Rate and Reduces Postprandial Triglyceride Concentrations. Nutrients 2018, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Pan, Y.; Zhong, T.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, A.S. Effects of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise on metabolic syndrome parameters and cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashida, R.; Kawaguchi, T.; Bekki, M.; Omoto, M.; Matsuse, H.; Nago, T.; Takano, Y.; Ueno, T.; Koga, H.; George, J.; et al. Aerobic vs. resistance exercise in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, M.B.; Shojaee-Moradie, F.; Sharaf, S.E.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Kemp, G.J.; Barrett, M.; Jackson, N.C.; Herring, R.A.; Wright, J.; Thomas, E.L.; et al. HDL-apoA-I kinetics in response to 16 wk of exercise training in men with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E839–E847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orci, L.A.; Gariani, K.; Oldani, G.; Delaune, V.; Morel, P.; Toso, C. Exercise-based Interventions for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-analysis and Meta-regression. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1398–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Kuljiratitikal, K.; Aksornchanya, O.; Chaiyasoot, K.; Bandidniyamanon, W.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, N. Moderate-Intensity Aerobic vs Resistance Exercise and Dietary Modification in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Kotani, K.; Tanaka, K.; Egucih, Y.; Anzai, K. Therapeutic Approaches to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Exercise Intervention and Related Mechanisms. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbasset, W.K.; Tantawy, S.A.; Kamel, D.M.; Alqahtani, B.A.; Soliman, G.S. A randomized controlled trial on the effectiveness of 8-week high-intensity interval exercise on intrahepatic triglycerides, visceral lipids, and health-related quality of life in diabetic obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Medicine 2019, 98, e14918, Correction in Medicine 2020, 99, e22388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, W.; Li, J.; Ossowski, Z. Effects of aerobic exercise on metabolic indicators and physical performance in adult NAFLD patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Medicine 2023, 102, e33147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’gOrman, P.; Naimimohasses, S.; Monaghan, A.; Kennedy, M.; Melo, A.M.; Fhloinn, D.N.; Doherty, D.G.; Beddy, P.; Finn, S.P.; Moore, J.B.; et al. Improvement in histological endpoints of MAFLD following a 12-week aerobic exercise intervention. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Tsujimoto, T.; Kim, B.; Uchida, F.; Suzuki, H.; Iizumi, S.; Isobe, T.; Sakae, T.; Tanaka, K.; Shoda, J. Weight-loss-independent benefits of exercise on liver steatosis and stiffness in Japanese men with NAFLD. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Björnsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated with Long-term Outcomes of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, A.M.; Joyner, M.J.; Little, J.P.; Jones, A.M.; Gibala, M.J. A Perspective on High-Intensity Interval Training for Perfor-mance and Health. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.-L.; Lim, J.; Yoo, J.-K.; Kim, H.-K.; Hwang, M.-H.; Handberg, E.M.; Petersen, J.W.; Holmer, B.J.; Casella, J.A.L.; Cusi, K.; et al. Effect of all-extremity high-intensity interval training vs. moderate-intensity continuous training on aerobic fitness in middle-aged and older adults with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 116, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibala, M.J.; Little, J.P.; MacDonald, M.J.; Hawley, J.A. Physiological adaptations to low-volume, high-intensity interval training in health and disease. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holten, M.K.; Zacho, M.; Gaster, M.; Juel, C.; Wojtaszewski, J.F.; Dela, F. Strength Training Increases Insulin-Mediated Glucose Uptake, GLUT4 Content, and Insulin Signaling in Skeletal Muscle in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitranun, W.; Deerochanawong, C.; Tanaka, H.; Suksom, D. Continuous vs interval training on glycemic control and macro- and microvascular reactivity in type 2 diabetic patients. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2014, 24, e69–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Buring, J.E.; Rifai, N.; Mora, S.; Sacks, F.M.; Ridker, P.M. Fasting Compared with Nonfasting Triglycerides and Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Women. JAMA 2007, 298, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, S.E.; Hackett, D.A.; Parker, H.M.; O’’Connor, H.T.; Gerofi, J.A.; Sainsbury, A.; Baker, M.K.; Chuter, V.H.; Caterson, I.D.; George, J.; et al. Effect of aerobic exercise training dose on liver fat and visceral adiposity. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Jessen, N.; Goodyear, L.J. AMP-activated protein kinase and the regulation of glucose transport. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, E867–E877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartee, G.D.; Hepple, R.T.; Bamman, M.M.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise Promotes Healthy Aging of Skeletal Muscle. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, A.; Niederseer, D.; Diem, G.; Finkenzeller, T.; Ledl-Kurkowski, E.; Forstner, R.; Pirich, C.; Patsch, W.; Weitgasser, R.; Niebauer, J. Different types of resistance training in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Effects on glycaemic control, muscle mass and strength. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2013, 20, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perseghin, G.; Price, T.B.; Petersen, K.F.; Roden, M.; Cline, G.W.; Gerow, K.; Rothman, D.L.; Shulman, G.I. Increased Glucose Transport–Phosphorylation and Muscle Glycogen Synthesis after Exercise Training in Insulin-Resistant Subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devries, M.C.; Samjoo, I.A.; Hamadeh, M.J.; McCready, C.; Raha, S.; Watt, M.J.; Steinberg, G.R.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. Endurance Training Modulates Intramyocellular Lipid Compartmentalization and Morphology in Skeletal Muscle of Lean and Obese Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4852–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.D.; Hu, D.; Greenaway, T.; Blackwood, S.J.; Dwyer, R.M.; Sharman, J.E.; Jones, G.; Squibb, K.A.; Brown, A.A.; Otahal, P.; et al. Skeletal Muscle Microvascular-Linked Improvements in Glycemic Control From Resistance Training in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larose, J.; Sigal, R.J. Effect of exercise training on physical fitness in type II diabetes mellitus. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuenke, M.D.; Mikat, R.P.; McBride, J.M. Effect of an acute period of resistance exercise on excess post-exercise oxygen consumption: Implications for body mass management. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 86, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.-N.; Zhou, B.-Q.; Ning, N.; Pan, T.; Xu, F.; He, S.-H.; Chen, N.-N.; Sun, M. Effects of lifestyle intervention on adults with metabolic associated fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1081096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, S.E.; Sabag, A.; Hallsworth, K.; Hickman, I.J.; Macdonal, G.A.; Stine, J.G.; George, J.; Johnson, N.A. Exercise in the Management of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Adults: A Position Statement from Exercise and Sport Science Australia. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 2347–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Jee, Y.S. Effect of treadmill walking on cardiometabolic risk factors and liver function markers in older adults with MASLD: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2025, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, M.; Shiroma, E.J.; Buring, J.E.; Miyachi, M.; Lee, I.M. Strength Training and All-Cause, Cardiovascular Disease, and Cancer Mortality in Older Women: A Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e007677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraji, H.; Minasian, V.; Kelishadi, R. Changes in Liver Enzymes and Metabolic Profile in Adolescents with Fatty Liver following Exercise Interventions. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2021, 24, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abassi, W.; Ouerghi, N.; Hammami, M.B.; Jebabli, N.; Feki, M.; Bouassida, A.; Weiss, K.; Knechtle, B. High-Intensity Interval Training Reduces Liver Enzyme Levels and Improves MASLD-Related Biomarkers in Overweight/Obese Girls. Nutrients 2025, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stine, J.G. Exercise in Patients with Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 21, 390–393. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Liu, C.J. Effects of Exercise Intervention in Subjects with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2025, 34, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogbe, M.; Hummer, B.; Stine, J.G.; Lizaola-Mayo, B.; Forman, D.E.; Vargas, H.E.; Duarte-Rojo, A. Advanced Liver Fibrosis Impairs Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2025, 70, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Shi, Y.H.; Guo, Y.X.; Li, Y.Y.; Yin, H.L.; Wu, T.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, J.X.; Bi, Y. Social Jetlag elicits fatty liver via perturbed circulating prolactin rhythm-mediated circadian remodeling of hepatic lipid metabolism. Mil. Med. Res. 2025, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graindorge, P.-H.; Paoli, J.; Yildirim, B.; Morel, C.; Herzine, A.; Collin, M.; Gallais, I.; Boucard, S.; Pouyatos, B.; Meyre, D.; et al. Early stage of metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease disrupts circadian rhythm and induces neuroinflammation in rats. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.V. Circadian Deregulation: Back Facing the Sun Toward Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Development. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, S.; Bogdanovic, A.; Hildebrandt, T.; Flint, E.; Geng, A.; Pecenko, S.; Lussier, P.; Strumberger, M.A.; Meyer, M.; Weber, J.; et al. Significant nocturnal wakefulness after sleep onset in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2024, 4, 1458665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Rajendran, R.; Rajakumari, S. Diet-induced obesity dampens the temporal oscillation of hepatic mitochondrial lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2025, 66, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, S.; Lionis, C.; Kite, C.; Lagojda, L.; Uthman, O.A.; Dallaway, A.; Atkinson, L.; Chaggar, S.S.; Randeva, H.S.; Kyrou, I. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coexisting depression, anxiety and/or stress in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1357664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, L.; Exley, C.; McPherson, S.; Trenell, M.I.; Anstee, Q.M.; Hallsworth, K. Lifestyle Behavior Change in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Qualitative Study of Clinical Practice. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1968–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, L.; Flynn, D.; Dombrowski, S.U.; van Wersch, A.; Sniehotta, F.F.; Trenell, M.I. Successful behavioural strategies to increase physical activity and improve glucose control in adults with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2015, 32, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, L.; Michie, S. Designing interventions to change eating behaviours. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carels, R.A.; Darby, L.A.; Rydin, S.; Douglass, O.M.; Cacciapaglia, H.M.; O’BRien, W.H. The relationship between self-monitoring, outcome expectancies, difficulties with eating and exercise, and physical activity and weight loss treatment outcomes. Ann. Behav. Med. 2005, 30, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
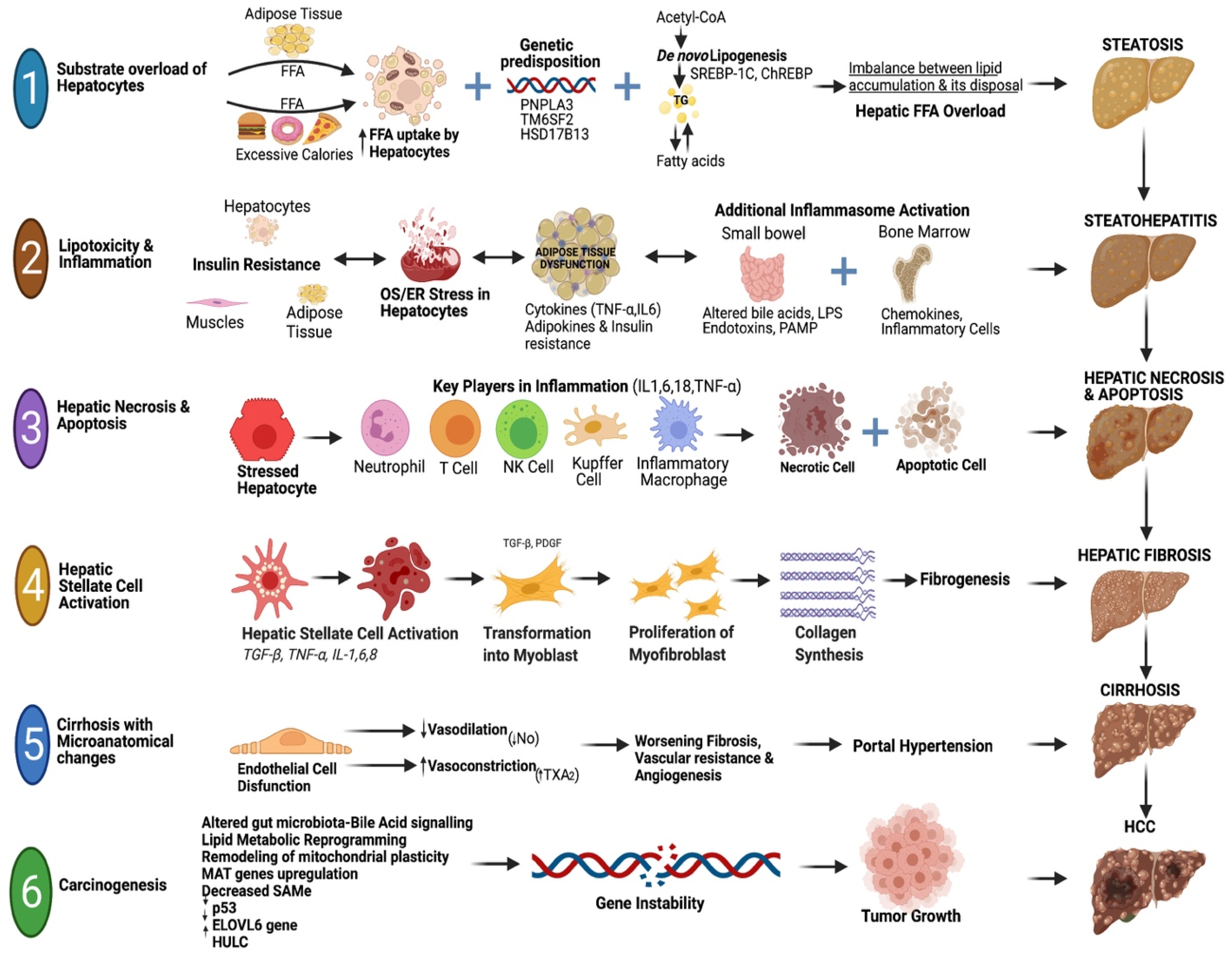
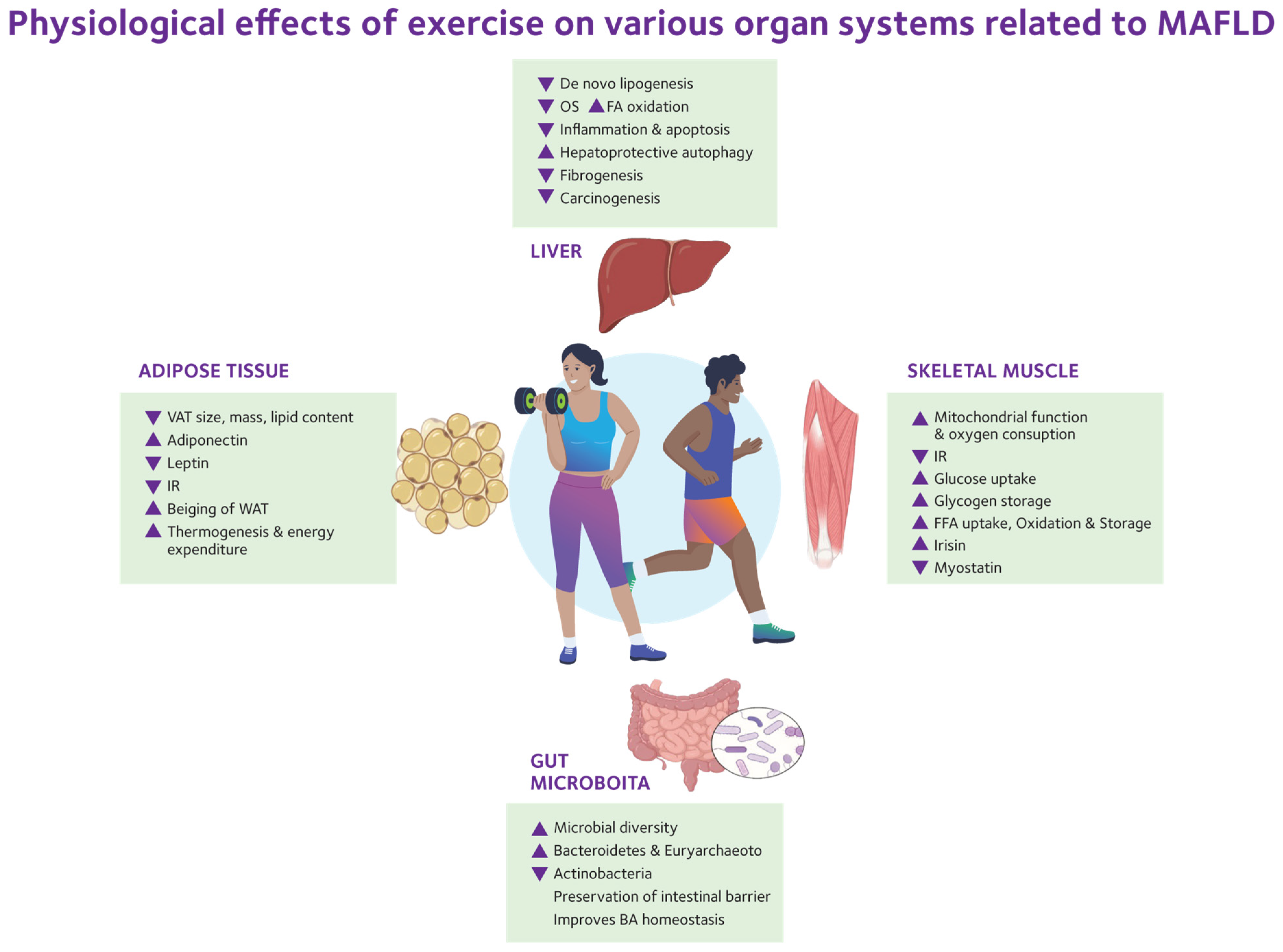

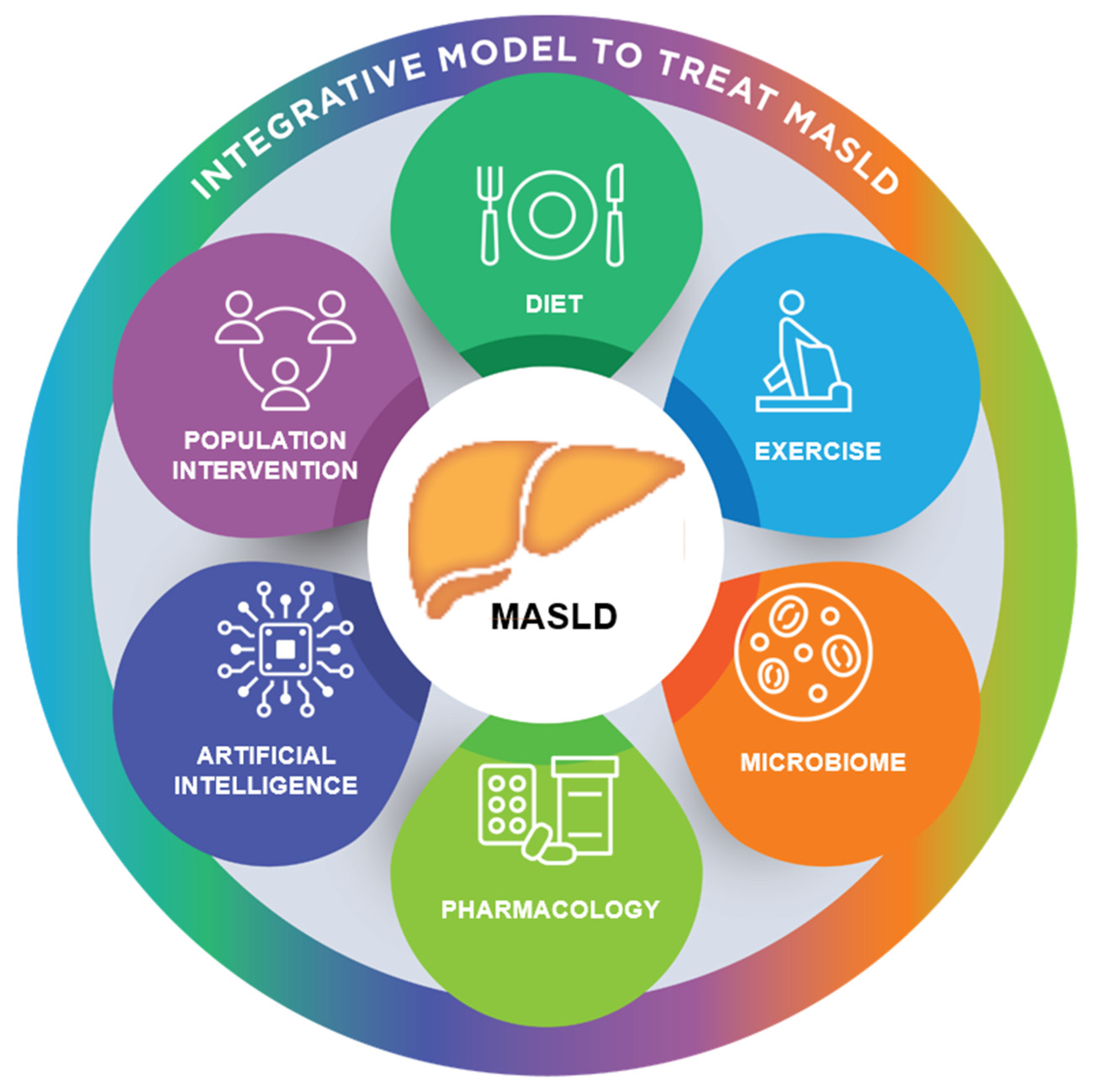
| Society Guidelines | % Weight Loss | Dietary Restrictions | Physical Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AASLD (2023) | 3–5% weight loss improves steatosis. 7–10% weight loss improves most histopathologic features of MASH, including fibrosis. | A diet that leads to a caloric deficit and is limited in carbohydrates and saturated fats. Mediterranean dietary pattern. | Aerobic exercise at least five times a week for a total of 150 min/week | [47] |
| EASL-EASD-EASO (2024) | 3–5% weight loss for MASLD with average weight ≥5% weight loss for steatosis reduction ≥7–10% weight loss for MASH and fibrosis reduction | Recommend the Mediterranean diet. Minimizing processed and ultra-processed foods while increasing the intake of unprocessed or minimally processed foods. | >150 min/week of moderate or 75 min of vigorous exercise. Minimizing sedentary time. | [48] |
| KASL (2021) | 7–10% weight loss. | Calorie restriction (500 kcal), low-carbohydrate, and low fructose diet. | Exercising for at least 30 min. Three times a week | [49] |
| APWP (2025) | >5% for steatosis reduction 7–10% for MASH resolution >10% improves liver fibrosis | 1200–1800 kcal/day or 500–750 kcal caloric restriction Low-carbohydrate and ultra-processed food abstinence Mediterranean diet, ketogenic diet, intermittent fasting, and time-restricted feeding are recommended | 150–240 min/week of moderate-to-vigorous intensity aerobic exercise 2–3 days/week of resistance training | [50] |
| NICE (2016) | Consider NICE guidelines for obesity and weight gain prevention. | Consider NICE guidelines for obesity and weight gain prevention. No specific diet. | Consider NICE guidelines for obesity and weight gain prevention. | [51] |
| ADA (2025) | ≥5% decreases steatosis ≥10% improves fibrosis | Mediterranean diet benefits on cardiometabolic factors; highly saturated fats, carbohydrates, and alcohol should be avoided | 150 min/week of moderate or 75 min/week of rigorous aerobic 2–3 times/week of resistance training | [8] |
| Summary of Current Nutritional Data in MASLD H = Human, A = Animal | ||
|---|---|---|
| Calories | Daily restriction of 500–1000 kcal results in an improvement in insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis (H) | [9,48] |
| MACRONUTRIENTS | ||
| Fats | SFAs (found in dairy products, vegetable oils, desserts, and red meat) increase intrahepatic triglycerides and plasma ceramides, impairing insulin sensitivity (H). RCTs show increased liver fat and ceramides with high SFA diets, with a strong link to fibrosis progression. | [72,73,74,75,76,77,78] |
| Increased intake of MUFAs (found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts) is associated with a healthier lipid profile (lower LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and a reduced total cholesterol/HDL ratio), decreased lipotoxicity, and improved insulin sensitivity (H). Olive oil, a key component of MD, has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antithrombotic properties, which help improve steatosis and reduce cardiovascular risk (H). | [79,80,81,82,83,84,85] | |
| Omega-3 and -6 PUFAs are essential fatty acids obtained solely through diet. Increasing intake of Omega-3 PUFAs (found in chia and flax seeds, walnuts, salmon, and dietary supplements) lowers hepatic triglyceride levels, reduces hepatic steatosis, and enhances insulin sensitivity (H). They have anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic properties. | [86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95] | |
| Increased intake of Omega-6 PUFAs (found in vegetable oils) is linked to a higher risk of CVD, cancer, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases. Omega-6 PUFAs are associated with inflammation if their ratio to Omega-3 is high. | [86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95] | |
| Increased intake of trans-fats (found in baked and refrigerated foods) has a pro-oxidative effect, leading to increased insulin resistance, obesity, and systemic inflammation, and is associated with an increased risk of developing MASLD in animal studies (A). Human evidence is limited. Clinical Guidance supports strict avoidance. | [68,96,97,98,99,100] | |
| Carbohydrates | Carbohydrates are the most abundant macronutrients and can be classified as simple or complex. The dietary source of carbohydrates plays a crucial role in determining its effect on patients with MASLD. Simple carbohydrates (found in sugar-sweetened beverages) pose a high-risk factor for MASLD patients (H). | [67,102] |
| Refined and added carbohydrates lead to an increase in glycemic load, causing hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, increased DNL, visceral adiposity, and hepatic fat. Observational and interventional studies show strong links with MASLD prevalence and progression. | [102,103,104,105,106,107,113,114,115,116,117,118] | |
| RCTs and cohort studies have linked fructose intake to steatosis, MASH, and fibrosis progression, and higher serum fructose levels have been correlated with MASLD risk. | [108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118] | |
| Lack of dietary fiber (a type of carbohydrate) in the diet has been linked to MASLD. Prebiotic fibers and non-digestible carbohydrates (e.g., resistant starch) modulate gut microbiota and significantly improve serum AST, ALT, insulin, and IHTG levels, while also reducing inflammation (H). A protective association has been observed between reduced steatosis and metabolic risk in cohort and dietary intervention studies. | [105,106,107,119,120,127] | |
| Proteins | Excessive consumption of red meat, especially processed meat, raises the risk of MASLD, T2DM, CVD, and death in patients by fostering insulin resistance (H). | [129,130,131,300,301,302] |
| Processed meat is strongly linked to MASLD and all-cause mortality. It is high in sodium, nitrates, and preservatives, and it worsens metabolic and inflammatory pathways. | [129,130,300,301,302] | |
| Fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins provide high-quality protein, along with omega-3 fatty acids and choline. This leads to decreased steatosis, as well as anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects. | [105,128,300,301] | |
| MICRONUTRIENTS | ||
| Vitamin E | Daily supplementation of Vitamin E (800 IU) in non-diabetic patients improved histologic features of MASH (H). | [47,48,144] |
| Vitamin C | Daily supplementation with a combination of Vitamin C and E (1000 mg and 1000 IU, respectively) is inversely related to the severity of MASLD and shows improvement in fibrosis scores (H). | [152] |
| Vitamin D | Vitamin D supplementation may exert antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory effects (H). Vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased IR and may predispose to MASLD (H). | [156,160,161] |
| Vitamin A | Vitamin A deficiency in patients with MASLD may be associated with the progression of MASLD (H). | [169] |
| Vitamin B3 | Vitamin B3 reduced IHTG (H). Niacin treatment showed improvement in TGs, VLDL, and insulin sensitivity (H). | [174,179] |
| Vitamin B6 | Vitamin B6 supplementation (90 mg daily) significantly ameliorated hepatic fat accumulation (HFA). | [182] |
| Vitamin B9 | Vitamin B9 deficiency was considered an independent risk factor in MASLD (A). Folate supplementation ameliorates hepatic steatosis and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines (A). | [187,188] |
| Vitamin B12 | Low levels of vitamin B12 are associated with increased severity of MASH (H). | [188] |
| Calcium and Phosphorus | High serum calcium and phosphorus levels may be associated with MASLD (H). | [194] |
| Magnesium | A high intake of magnesium may be associated with a reduced risk of MASLD (H). | [195] |
| Zinc and Selenium | In animal studies, zinc and selenium supplementation improved serum AST, ALT, triglycerides, and total cholesterol in MASLD (A). | [196] |
| Iron | Iron was associated with worsening steatohepatitis in animal models (A). | [197] |
| HERBAL SUPPLEMENTS | ||
| Milk Thistle | Silymarin (milk thistle plant extract) has been shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic effects (H). It reduces oxidative damage, hepatic steatosis, and IR in MASLD (H). | [199,200,203,205] |
| Turmeric | Curcumin, an active ingredient of turmeric, has anti-inflammatory (H) and antioxidant properties (A). It has been shown to reduce IR in mice (A). This active ingredient significantly reduces ALT, AST, total cholesterol, LDL, fasting blood glucose, and insulin resistance (H). | [206,207,211,212,213] |
| Garlic | In animal studies, SAMC (active ingredient) has been linked to alleviating inflammation and insulin resistance (A). In human studies, garlic supplementation has been associated with improved levels of ALT, AST, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, TG, and fasting blood glucose (H). | [214,215,216,217] |
| Basil, Lavender, Peppermint, Sage, Oregano, and Rosemary | Ursolic acid (found in rosemary, peppermint, basil, lavender, and oregano) and carnosic acid (found in rosemary) have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic effects in animal studies (A). | [218,220] |
| Ginger | In animal studies, ginger has been associated with anti-lipogenic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties (A). In human trials, ginger supplementation has been shown to significantly improve ALT, AST, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis (H). | [221,222,223] |
| Gingko Biloba | Ginkgo Biloba reduces oxidative stress and improves liver enzymes, hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and IR, as seen in animal studies (A). | [224,225,226] |
| Ginseng | Ginseng has been shown to improve liver enzyme function, thereby preventing hepatic inflammation, fibrosis, and steatosis in MASLD, as observed in animal studies (A). | [227,228,229] |
| Licorice | Chamomile and red clover may have hepatoprotective effects (A). Licorice is associated with improved IR and ALT levels (H). | [230,231] |
| Plantago major | Daily supplementation with 2 g of Plantago major seeds resulted in a substantial reduction in serum levels of ALT, TGs, and LDL, as well as alleviation of hepatic steatosis, compared to the placebo (H). | [233] |
| Berberine | Berberine (BBR) is an isoquinolone found in various medicinal plants; BBR improves intestinal barrier function and reduces inflammation caused by gut microbiota-derived LPS in metabolic diseases. This may improve glucose and lipid metabolism (H) (A). It has improved weight, HOMA-IR, AST, ALT, GGT, total cholesterol and LDL (H). | [234,235,236] |
| OTHERS | ||
| Probiotics | Yogurt may improve IR, ALT, and hepatic fat in patients with MASLD. Probiotic/symbiotic use in MASLD may enhance liver steatosis, AST, ALT, endotoxins, and IR (H). | [241,242,243,244] |
| Caffeine | A Moderate amount of caffeine-containing coffee consumption (2–3 cups/day) decreased the severity of hepatic fibrosis and was associated with reduced risk of advanced liver fibrosis in MASLD (H). | [250,251,252] |
| Green tea | Daily supplementation with green tea extract may improve liver enzymes in patients with MASLD. | [255] |
| Low-calorie Sweeteners | The American Heart Association (AHA) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommend reducing the consumption of sweeteners due to their adverse effects on body weight and cardiometabolic risk factors (H). | [260] |
| Resveratrol | Resveratrol in red wine has been shown to reduce oxidative stress, liver fat accumulation, and inflammation, as seen in animal models (A). | [261,262] |
| Some randomized controlled trials examining the effect of daily resveratrol supplements indicated improvements in AST, ALT, and insulin resistance (H). | [263,264] | |
| Although it is associated with some improvement in inflammatory markers, it does not impact the overall management of MASLD (H). | [268] | |
| Choline | Choline-deficient diets lead to intestinal dysbiosis and may be linked to MASH (H). | [270,271] |
| Fish oil | Daily fish oil supplementation (3 capsules each containing 0.315 g of omega-3 PUFAs) improved lipid profile, the function of liver enzymes, and steatosis (H). | [272] |
| Co-enzyme Q10 | Co-enzyme Q10 daily supplementation (100 mg) is associated with reduced AST, GGT levels (H). | [276] |
| Alcohol | Heavy alcohol use (4 standard drinks/day or greater than 14 drinks/week in men or greater than three drinks/day or seven drinks/week in women as defined by NIAAA) is not recommended in patients with MASLD. | http://rethinkingdrinking.niaaa.nih.gov/How-much-is-too-much (accessed on 29 July 2025) |
| Substantial evidence is not available to safely recommend light to moderate alcohol use in MASLD patients (H). | [277] | |
| Cannabinoids | A notably lower prevalence of MASLD is reported among cannabis users, but more research is needed to confirm this effect (H). | [292,293] |
| Tobacco | Although a direct relationship between tobacco use and MASLD has not been found, it is considered a significant risk factor for HCC, CVD (H). | [297,298] |
| Patient Group | Recommended Modality | Target Dose (Duration/Intensity) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Adults | Aerobic, Resistance, or combined | 150–300 min/week moderate aerobic (3–6 METs) OR 75–150 min vigorous (>6 METs); 2–3 RE sessions/week; Recommended activities include walking, cycling, jogging, swimming | [365,412] |
| Sarcopenia/Muscle loss | Resistance ± Aerobic | 2–3 RE sessions/ week (50–75% 1RM) | [364] |
| Older adults | Walking/treadmill, low-moderate aerobic | ~180 min/week (30 min/day × 6 days) | [413] |
| Women | Moderate aerobic, lifestyle activities | ≥150 min/week | [414] |
| Adolescents/Youth | HIIT, aerobic sports | ≥3 sessions/week | [415,416] |
| Advanced fibrosis/comorbidities | Aerobic ± RE (Supervised) | Individualized (≤moderate) | [417,418,419] |
| “Weekend Warrior” | Any | 1–2 longer weekly sessions | [373] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheikh, M.Y.; Younus, M.F.; Shergill, A.; Hasan, M.N. Diet and Lifestyle Interventions in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199625
Sheikh MY, Younus MF, Shergill A, Hasan MN. Diet and Lifestyle Interventions in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199625
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheikh, Muhammad Y., Muhammad F. Younus, Annie Shergill, and Muhammad N. Hasan. 2025. "Diet and Lifestyle Interventions in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199625
APA StyleSheikh, M. Y., Younus, M. F., Shergill, A., & Hasan, M. N. (2025). Diet and Lifestyle Interventions in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199625






