Immunoglobulin G Subclass-Specific Glycosylation Changes in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
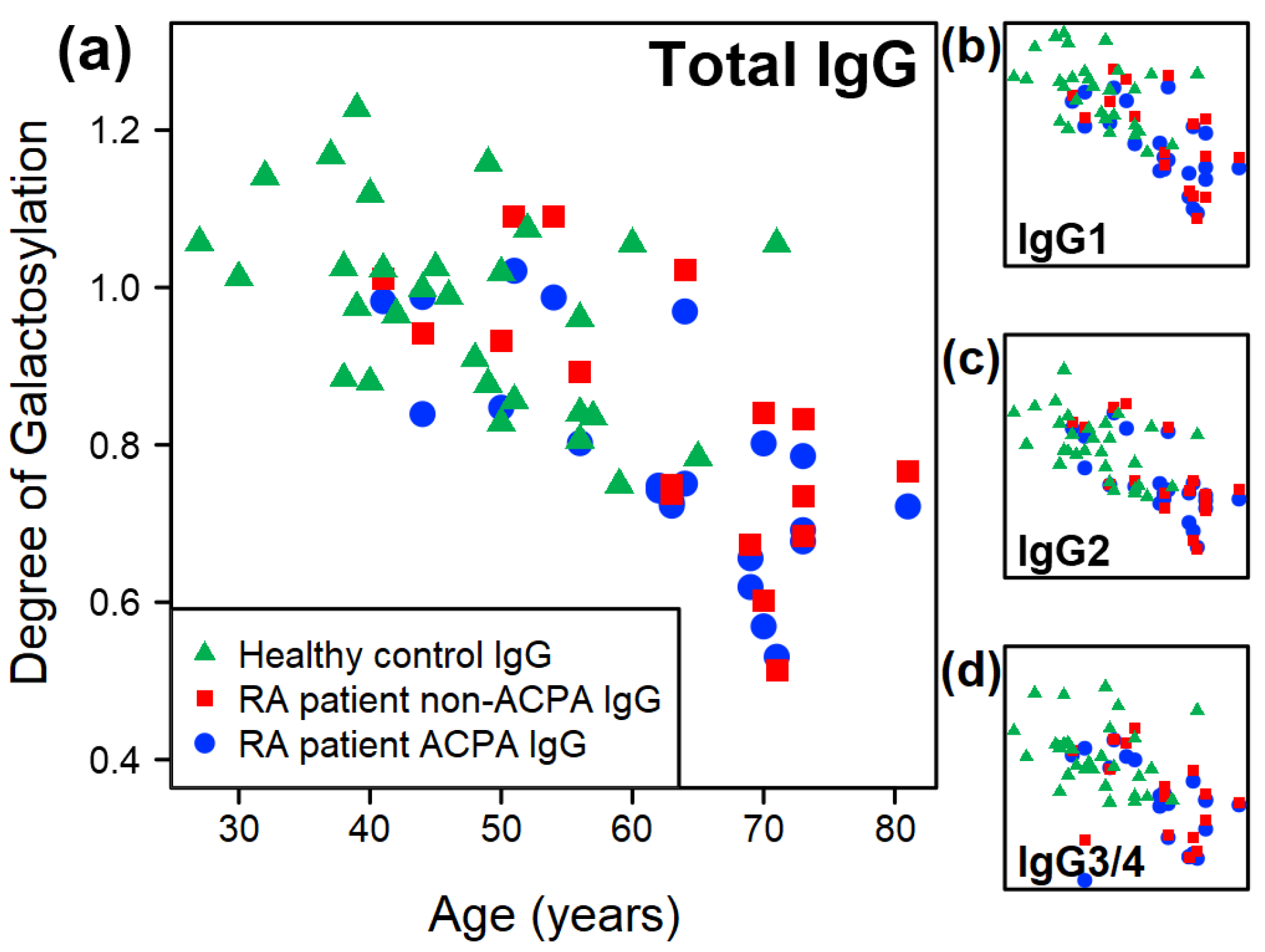
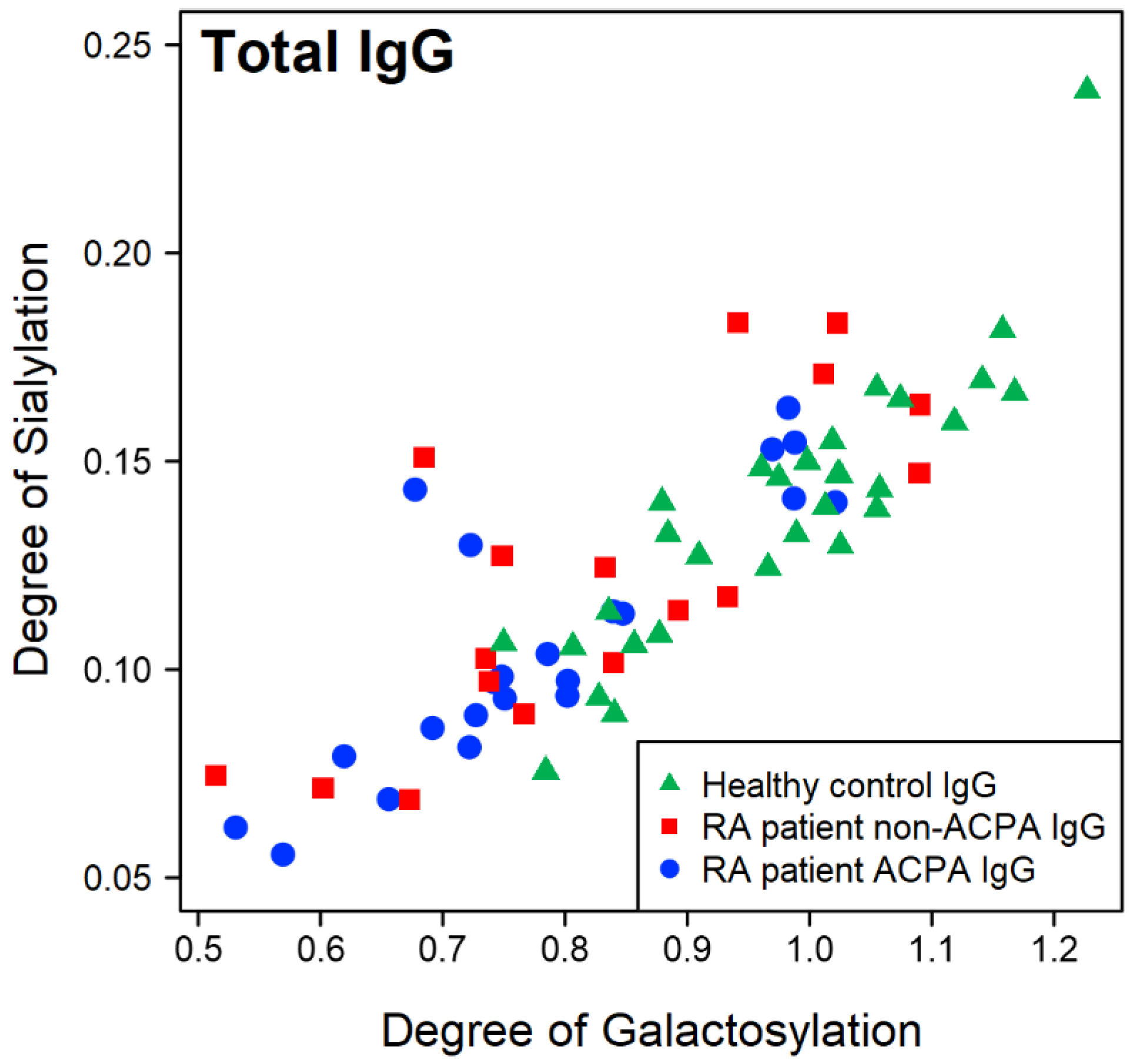
2.1. Overall Trends of Glycosylation of IgG from RA Patients and Healthy Controls
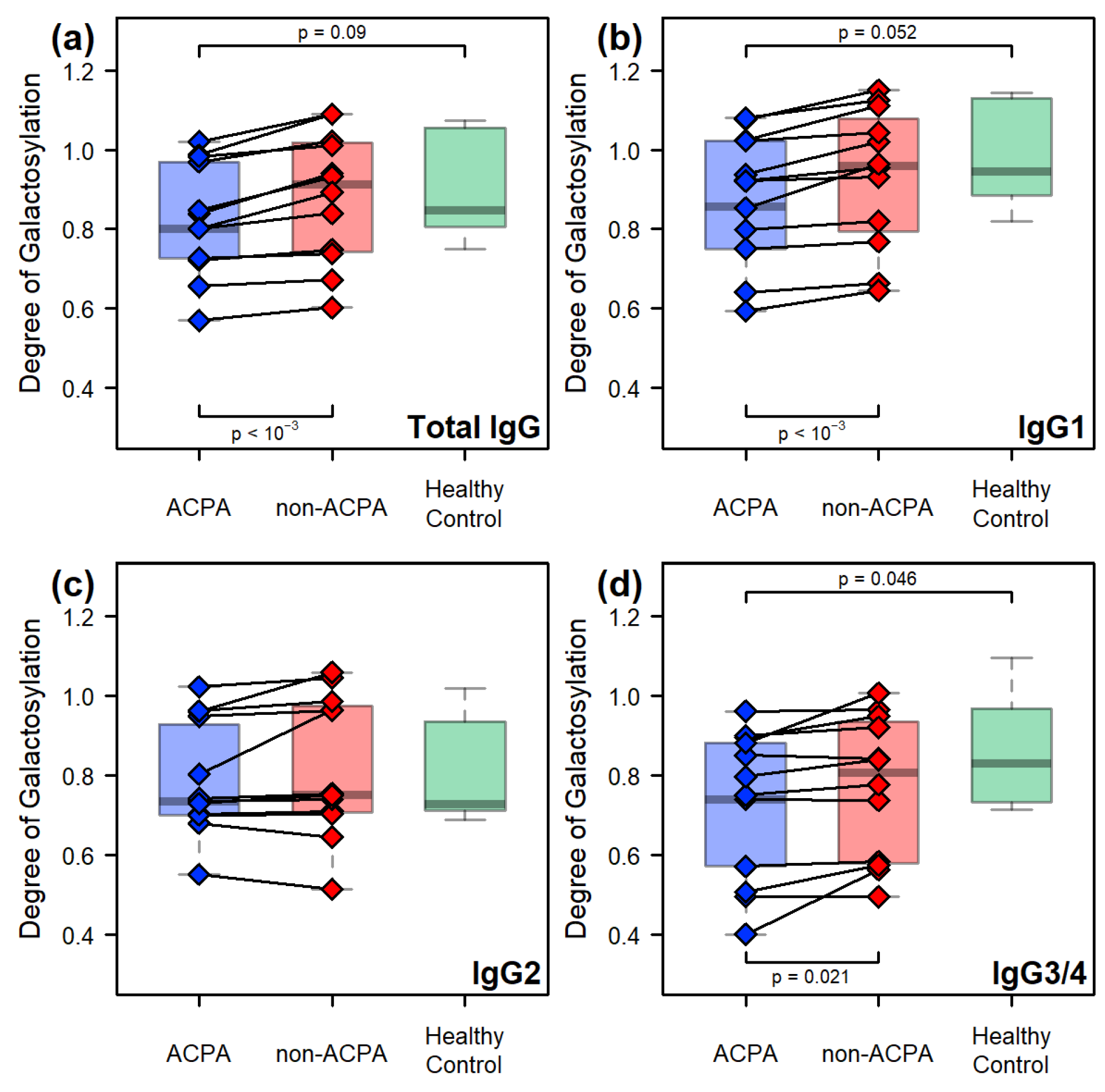
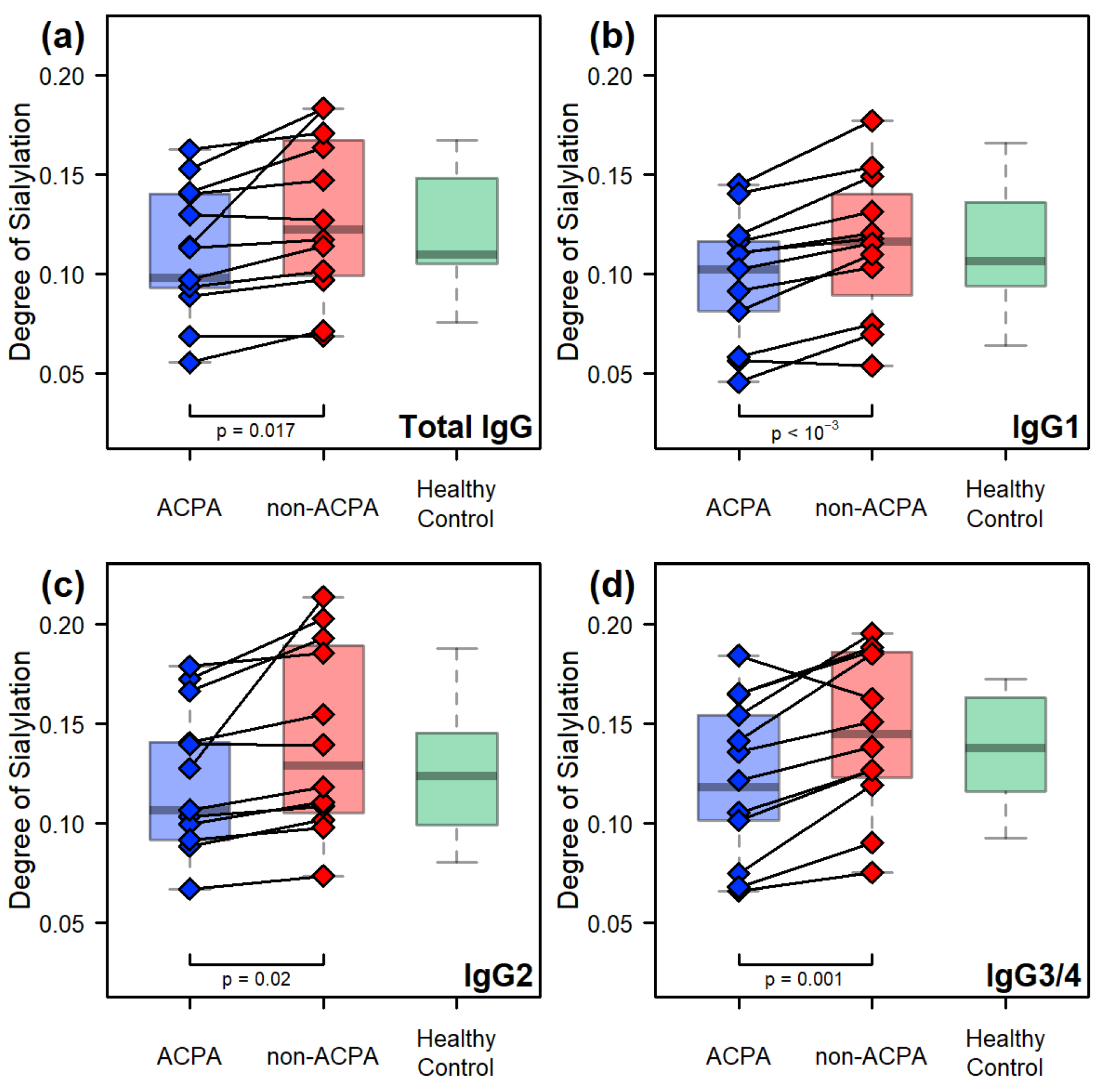
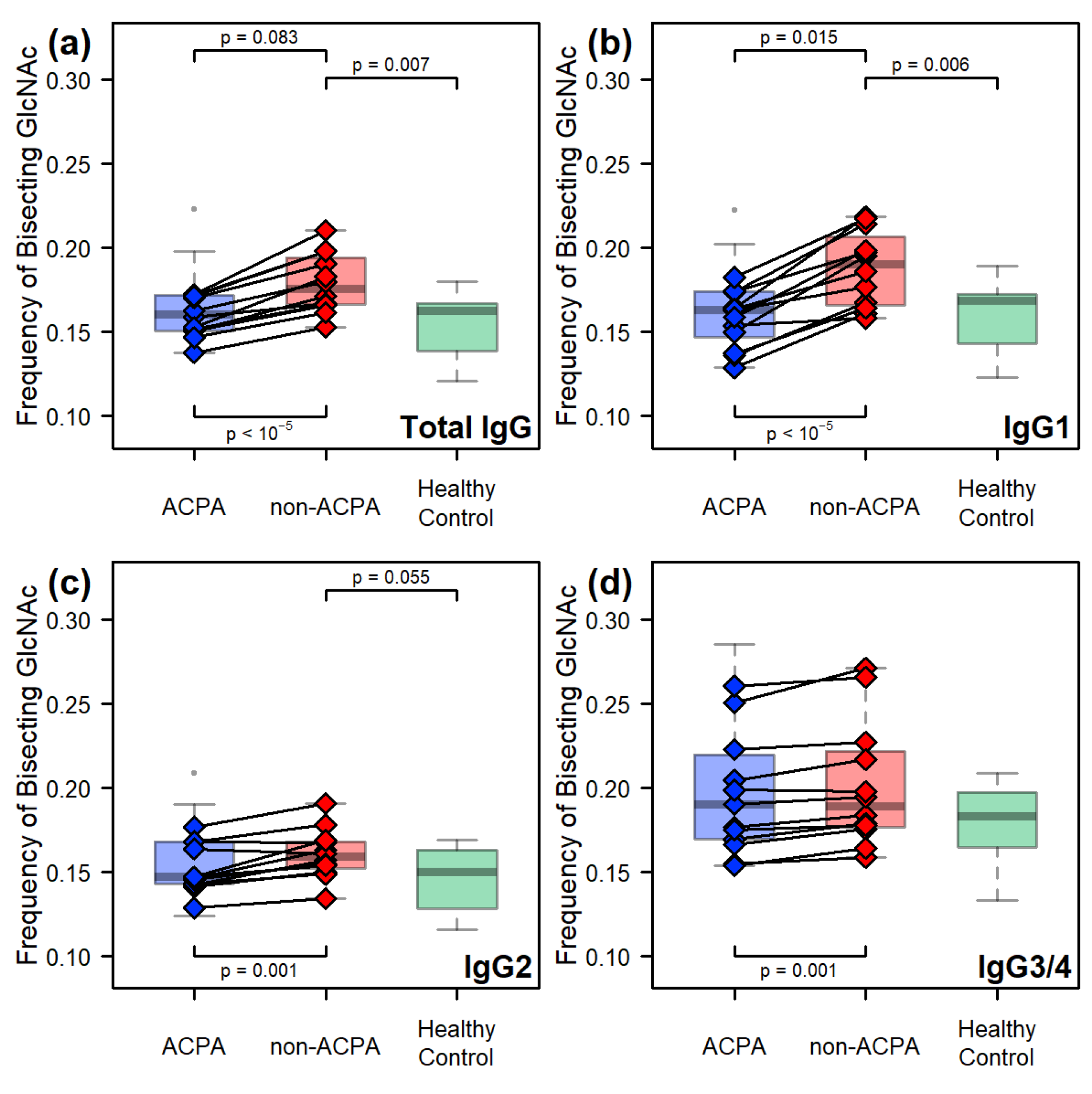
2.2. Comparative Results Between Age-Matched Groups
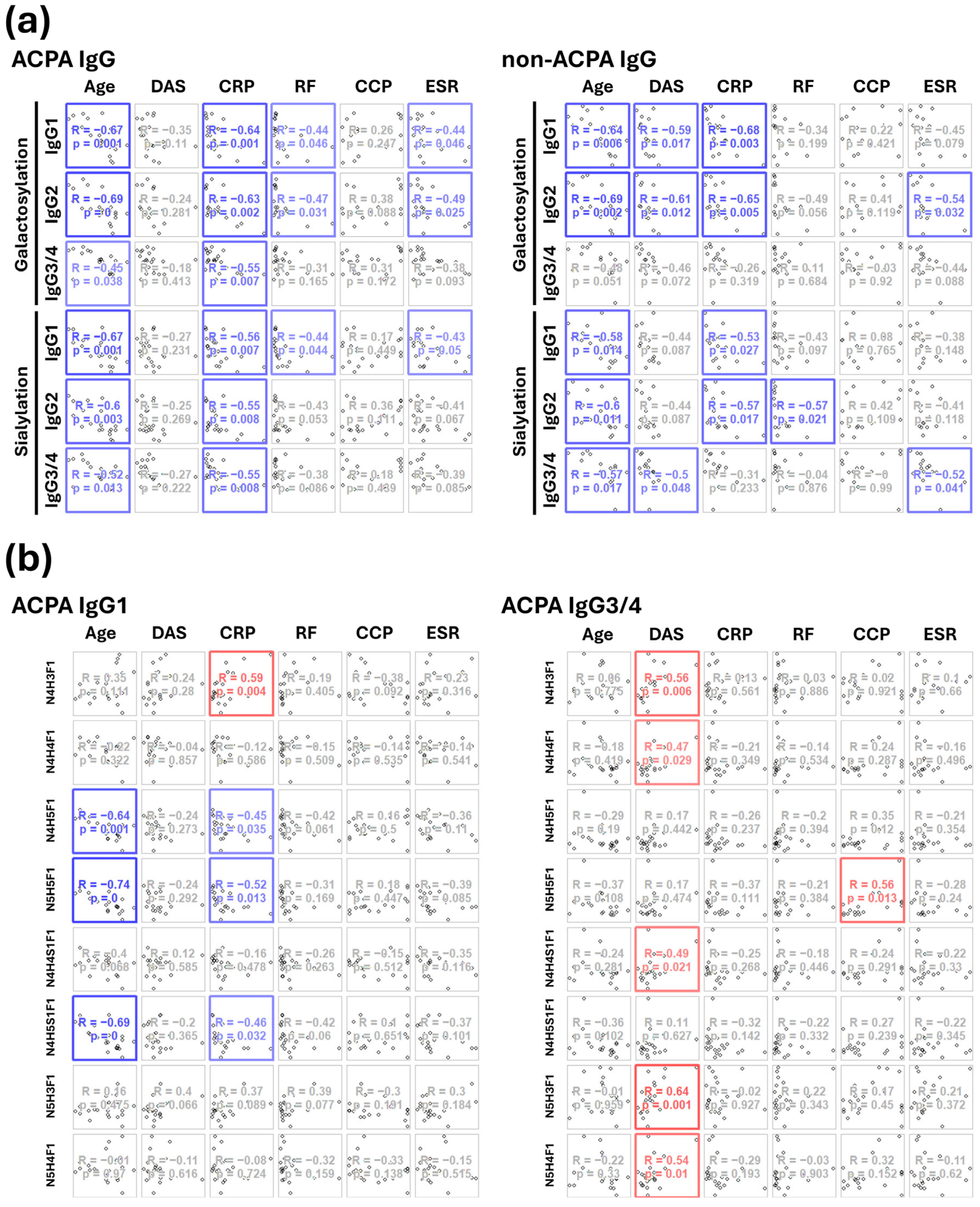
2.3. Correlations Between the IgG Fc Glycoforms and the Clinical Parameters of RA Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection of Blood Samples
4.2. IgG Isolation and ACPA Purification
4.3. Materials Used for Digestion and Chromatographic Separation
4.4. Enzymatic Digestion
4.5. Nano LC-MS(MS)
4.6. Data Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| ACPA | Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| DAS | Disease Activity Score |
| CCP | anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| ESR | Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate |
| GlcNAc | N-acetylglucosamine |
| FcγRIIIA | Fcγ receptor IIIA |
| HC | Healthy Control |
Appendix A
| ID | Age (Years) | DAS | CRP (mg/mL) | RF (IU/mL) | CCP (IU/mL) | ESR (mm/h) | Non-ACPA Sample Available | Included in Age-Matched Comparison | ID | Age (Years) | Included in Age-Matched Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA_01 | 41 | 3.1 | 16.88 | 51.8 | 281 | 14 | + | + | HC_01 | 51 | + |
| RA_02 | 44 | 2.8 | 9.9 | 14.9 | 2286 | 7 | + | + | HC_02 | 52 | + |
| RA_03 | 50 | 4.4 | 2.5 | 346 | 49.9 | 23 | + | + | HC_03 | 56 | + |
| RA_04 | 51 | 4 | 5.9 | 74 | 3090 | 14 | + | + | HC_04 | 56 | + |
| RA_05 | 54 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 34 | 3200 | 3 | + | + | HC_05 | 56 | + |
| RA_06 | 56 | 2.8 | 4.63 | 790 | 3200 | + | + | HC_06 | 57 | + | |
| RA_07 | 63 | 3.8 | 8.4 | 70 | 19 | + | + | HC_07 | 59 | + | |
| RA_08 | 63 | 5.1 | 10.5 | 262 | 1633 | 24 | + | + | HC_08 | 60 | + |
| RA_09 | 64 | 5.2 | 0.3 | 63 | 653 | 38 | + | + | HC_09 | 65 | + |
| RA_10 | 69 | 3.8 | 13.1 | 392 | 906 | 17 | + | + | HC_10 | 71 | + |
| RA_11 | 70 | 2.6 | 12 | 55 | 871 | 20 | + | + | HC_11 | 27 | |
| RA_12 | 70 | 5.2 | 30 | 974 | 700 | 89 | + | + | HC_12 | 30 | |
| RA_13 | 44 | 5.07 | 0.67 | 55 | 3200 | 20 | + | HC_13 | 32 | ||
| RA_14 | 62 | 3.3 | 1.82 | 16.3 | 510 | 7 | + | HC_14 | 37 | ||
| RA_15 | 64 | 6.9 | 8.6 | 105 | 48 | + | HC_15 | 38 | |||
| RA_16 | 69 | 7.2 | 34 | 1695 | 2424 | 95 | + | HC_16 | 38 | ||
| RA_17 | 62 | 13 | 3 | 104 | 1995 | 11 | + | HC_17 | 39 | ||
| RA_18 | 71 | 6.2 | 55 | 129 | 68 | 23 | + | HC_18 | 39 | ||
| RA_19 | 73 | 3.6 | 2.9 | 65 | 853 | 45 | + | HC_19 | 40 | ||
| RA_20 | 73 | 3.9 | 8.5 | 296 | 3200 | 51 | + | HC_20 | 40 | ||
| RA_21 | 73 | 4.2 | 19.5 | 164 | 1138 | 29 | + | HC_21 | 41 | ||
| RA_22 | 81 | 4.8 | 15 | 457 | 431 | 74 | + | HC_22 | 42 | ||
| HC_23 | 44 | ||||||||||
| HC_24 | 45 | ||||||||||
| HC_25 | 46 | ||||||||||
| HC_26 | 48 | ||||||||||
| HC_27 | 49 | ||||||||||
| HC_28 | 49 | ||||||||||
| HC_29 | 50 | ||||||||||
| HC_30 | 50 |

References
- Almutairi, K.; Nossent, J.; Preen, D.; Keen, H.; Inderjeeth, C. The Global Prevalence of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis Based on a Systematic Review. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapira, Y.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Shoenfeld, Y. Geoepidemiology of Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Fu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liang, C. Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 686155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deane, K.D.; Holers, V.M. The Natural History of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Ther. 2019, 41, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensvold, A.; Klareskog, L. Towards Prevention of Autoimmune Diseases: The Example of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.W.; Bemis, E.A.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Striebich, C.C.; Brake, S.; Feser, M.L.; Moss, L.; Clare-Salzler, M.; Holers, V.M.; Deane, K.D.; et al. The Association between Omega-3 Fatty Acid Biomarkers and Inflammatory Arthritis in an Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody Positive Population. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakieh, C.; Nam, J.L.; Hunt, L.; Hensor, E.M.A.; Das, S.; Bissell, L.-A.; Villeneuve, E.; McGonagle, D.; Hodgson, R.; Grainger, A.; et al. Predicting the Development of Clinical Arthritis in Anti-CCP Positive Individuals with Non-Specific Musculoskeletal Symptoms: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, M.; Gil-Vila, A.; Selva-O’Callaghan, A. Role of Autoantibodies in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Interstitial Lung Disease in Autoimmune Rheumatic Disorders. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. 2021, 13, 1759720X211032457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588, Erratum in Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haan, N.; Falck, D.; Wuhrer, M. Monitoring of Immunoglobulin N- and O-Glycosylation in Health and Disease. Glycobiology 2020, 30, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Bovenkamp, F.S.; Hafkenscheid, L.; Rispens, T.; Rombouts, Y. The Emerging Importance of IgG Fab Glycosylation in Immunity. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baković, M.P.; Selman, M.H.J.; Hoffmann, M.; Rudan, I.; Campbell, H.; Deelder, A.M.; Lauc, G.; Wuhrer, M. High-Throughput IgG Fc N-Glycosylation Profiling by Mass Spectrometry of Glycopeptides. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trbojević-Akmačić, I.; Lageveen-Kammeijer, G.S.M.; Heijs, B.; Petrović, T.; Deriš, H.; Wuhrer, M.; Lauc, G. High-Throughput Glycomic Methods. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 15865–15913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, G.P.; Barb, A.W. The Structural Role of Antibody N-Glycosylation in Receptor Interactions. Structure 2015, 23, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrok, M.J.; Jung, S.T.; Kang, T.H.; Monzingo, A.F.; Georgiou, G. Revisiting the Role of Glycosylation in the Structure of Human IgG Fc. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, V.A.; Doutch, J.; Rambo, R.P.; Gor, J.; Dalby, P.A.; Perkins, S.J. Solution Structure of Deglycosylated Human IgG1 Shows the Role of CH2 Glycans in Its Conformation. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 1814–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, B.A. The History of IgG Glycosylation and Where We Are Now. Glycobiology 2020, 30, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, I.S.; Lovell, S.; Mehzabeen, N.; Battaile, K.P.; Tolbert, T.J. Structural Characterization of the Man5 Glycoform of Human IgG3 Fc. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 92, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, G.; Treffers, L.; Plomp, R.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; de Boer, M.; Koeleman, C.A.M.; Lissenberg-Thunnissen, S.N.; Visser, R.; Brouwer, M.; Mok, J.Y.; et al. Decoding the Human Immunoglobulin G-Glycan Repertoire Reveals a Spectrum of Fc-Receptor- and Complement-Mediated-Effector Activities. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, C.W.; Dekkers, G.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; Treffers, L.W.; Nagelkerke, S.Q.; Lissenberg-Thunnissen, S.; Koeleman, C.A.M.; Wuhrer, M.; van den Berg, T.K.; Rispens, T.; et al. Enhanced Effector Functions Due to Antibody Defucosylation Depend on the Effector Cell Fcγ Receptor Profile. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maverakis, E.; Kim, K.; Shimoda, M.; Gershwin, M.E.; Patel, F.; Wilken, R.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Ruhaak, L.R.; Lebrilla, C.B. Glycans in the Immune System and The Altered Glycan Theory of Autoimmunity: A Critical Review. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeling, M.; Brückner, C.; Nimmerjahn, F. Differential Antibody Glycosylation in Autoimmunity: Sweet Biomarker or Modulator of Disease Activity? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, R.B.; Dwek, R.A.; Sutton, B.J.; Fernandes, D.L.; Leung, A.; Stanworth, D.; Rademacher, T.W.; Mizuochi, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Matsuta, K.; et al. Association of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Primary Osteoarthritis with Changes in the Glycosylation Pattern of Total Serum IgG. Nature 1985, 316, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espy, C.; Morelle, W.; Kavian, N.; Grange, P.; Goulvestre, C.; Viallon, V.; Chéreau, C.; Pagnoux, C.; Michalski, J.-C.; Guillevin, L.; et al. Sialylation Levels of Anti–Proteinase 3 Antibodies Are Associated with the Activity of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener’s). Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, M.H.J.; Niks, E.H.; Titulaer, M.J.; Verschuuren, J.J.G.M.; Wuhrer, M.; Deelder, A.M. IgG Fc N-Glycosylation Changes in Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome and Myasthenia Gravis. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vučković, F.; Krištić, J.; Gudelj, I.; Teruel, M.; Keser, T.; Pezer, M.; Pučić-Baković, M.; Štambuk, J.; Trbojević-Akmačić, I.; Barrios, C.; et al. Association of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Decreased Immunosuppressive Potential of the IgG Glycome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2978–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T.; Vidarsson, G. Novel Concepts of Altered Immunoglobulin G Galactosylation in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, M.; Terrier, A.; Jacque, E.; Dehenne, A.; Pochet-Béghin, V.; Beghin, C.; Dezetter, A.-S.; Dupont, G.; Engrand, A.; Beaufils, B.; et al. Fc Sialylation Prolongs Serum Half-Life of Therapeutic Antibodies. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1582–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.M.; Kobayashi, T.; Wermeling, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Intravenous Gammaglobulin Suppresses Inflammation through a Novel TH2 Pathway. Nature 2011, 475, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séïté, J.-F.; Cornec, D.; Renaudineau, Y.; Youinou, P.; Mageed, R.A.; Hillion, S. IVIg Modulates BCR Signaling through CD22 and Promotes Apoptosis in Mature Human B Lymphocytes. Blood 2010, 116, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Yang, S.-W.; Joo, J.-S.; Park, M.; Jin, Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, S.-V.; Yun, T.-J.; Cho, M.-L.; et al. Sialylated IVIg Binding to DC-SIGN+ Hofbauer Cells Induces Immune Tolerance through the Caveolin-1/NF-kB Pathway and IL-10 Secretion. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 246, 109215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.G.-H.; Scott, J.G. Investigations of the Constitutive Overexpression of CYP6D1 in the Permethrin resistantLPR Strain of House Fly (Musca Domestica). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 100, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, A.; Shoji-Hosaka, E.; Nakamura, K.; Wakitani, M.; Uchida, K.; Kakita, S.; Tsumoto, K.; Kumagai, I.; Shitara, K. Fucose Depletion from Human IgG1 Oligosaccharide Enhances Binding Enthalpy and Association Rate Between IgG1 and FcγRIIIa. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 336, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG Subclasses and Allotypes: From Structure to Effector Functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Ochiai, H.; Huang, W.; Yang, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, L.-X. Chemoenzymatic Synthesis and Fcγ Receptor Binding of Homogeneous Glycoforms of Antibody Fc Domain. Presence of a Bisecting Sugar Moiety Enhances the Affinity of Fc to FcγIIIa Receptor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18975–18991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, E.; Pučić-Baković, M.; Keser, T.; Wahl, A.; Hassinen, A.; Yang, J.-Y.; Liu, L.; Trbojević-Akmačić, I.; Razdorov, G.; Štambuk, J.; et al. Network Inference from Glycoproteomics Data Reveals New Reactions in the IgG Glycosylation Pathway. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1483, Erratum in Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.H.J.; de Jong, S.E.; Soonawala, D.; Kroon, F.P.; Adegnika, A.A.; Deelder, A.M.; Hokke, C.H.; Yazdanbakhsh, M.; Wuhrer, M. Changes in Antigen-Specific IgG1 Fc N-Glycosylation Upon Influenza and Tetanus Vaccination. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, M111.014563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahan, A.E.; Jennewein, M.F.; Suscovich, T.; Dionne, K.; Tedesco, J.; Chung, A.W.; Streeck, H.; Pau, M.; Schuitemaker, H.; Francis, D.; et al. Antigen-Specific Antibody Glycosylation Is Regulated via Vaccination. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005456, Erratum in PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, H.U.; van der Woude, D.; Ioan-Facsinay, A.; el Bannoudi, H.; Trouw, L.A.; Wang, J.; Häupl, T.; Burmester, G.-R.; Deelder, A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; et al. Glycan Profiling of Anti–Citrullinated Protein Antibodies Isolated from Human Serum and Synovial Fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, Y.; Ewing, E.; van de Stadt, L.A.; Selman, M.H.J.; Trouw, L.A.; Deelder, A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Wuhrer, M.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Toes, R.E.M.; et al. Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies Acquire a pro-Inflammatory Fc Glycosylation Phenotype Prior to the Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomp, R.; Ruhaak, L.R.; Uh, H.-W.; Reiding, K.R.; Selman, M.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Slagboom, P.E.; Beekman, M.; Wuhrer, M. Subclass-Specific IgG Glycosylation Is Associated with Markers of Inflammation and Metabolic Health. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundström, S.L.; Fernandes-Cerqueira, C.; Ytterberg, A.J.; Ossipova, E.; Hensvold, A.H.; Jakobsson, P.-J.; Malmström, V.; Catrina, A.I.; Klareskog, L.; Lundberg, K.; et al. IgG Antibodies to Cyclic Citrullinated Peptides Exhibit Profiles Specific in Terms of IgG Subclasses, Fc-Glycans and a Fab-Peptide Sequence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.; Adua, E.; Ugrina, I.; Laws, S.; Wang, W. Unravelling Immunoglobulin G Fc N-Glycosylation: A Dynamic Marker Potentiating Predictive, Preventive and Personalised Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krištić, J.; Vučković, F.; Menni, C.; Klarić, L.; Keser, T.; Beceheli, I.; Pučić-Baković, M.; Novokmet, M.; Mangino, M.; Thaqi, K.; et al. Glycans Are a Novel Biomarker of Chronological and Biological Ages. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2014, 69, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pučić, M.; Knežević, A.; Vidič, J.; Adamczyk, B.; Novokmet, M.; Polašek, O.; Gornik, O.; Šupraha-Goreta, S.; Wormald, M.R.; Redžić, I.; et al. High Throughput Isolation and Glycosylation Analysis of IgG–Variability and Heritability of the IgG Glycome in Three Isolated Human Populations*. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, M111.010090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyebrovszki, B.; Ács, A.; Szabó, D.; Auer, F.; Novozánszki, S.; Rojkovich, B.; Magyar, A.; Hudecz, F.; Vékey, K.; Drahos, L.; et al. The Role of IgG Fc Region N-Glycosylation in the Pathomechanism of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blöchl, C.; Stork, E.M.; Scherer, H.U.; Toes, R.E.M.; Wuhrer, M.; Domínguez-Vega, E. Fc Proteoforms of ACPA IgG Discriminate Autoimmune Responses in Plasma and Synovial Fluid of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Associate with Disease Activity. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2408769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Ito, K.; Furukawa, J.-I.; Nakata, J.; Alvarez, M.; Verbeek, J.S.; Shinohara, Y.; Izui, S. Galactosylation of IgG1 Modulates FcγRIIB-Mediated Inhibition of Murine Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 47, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, E.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Yagyu, K.; Takahashi, N. Structural Changes of Immunoglobulin G Oligosaccharides with Age in Healthy Human Serum. Glycoconj. J. 1997, 14, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Braicu, E.I.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L.; Sehouli, J.; Blanchard, V. Immunoglobulin G Subclass-Specific Glycosylation Changes in Primary Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.R.; Skold, M.; Ramsden, D.B.; Ocejo-Vinyals, J.G.; López-Hoyos, M.; Harding, S. The Clinical Utility of Measuring IgG Subclass Immunoglobulins During Immunological Investigation for Suspected Primary Antibody Deficiencies. Lab. Med. 2017, 48, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Immunoglobulin G Resulting from Fc Sialylation. Science 2006, 313, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayboroda, O.A.; Lageveen-Kammeijer, G.S.M.; Wuhrer, M.; Dolhain, R.J.E.M. An Integrated Glycosylation Signature of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, M.V.; Schett, G.; Steffen, U. Autoantibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Historical Background and Novel Findings. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 63, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, J.E.; Choy, E.H. C-Reactive Protein and Implications in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Associated Comorbidities. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beers, J.J.; Willemze, A.; Jansen, J.J.; Engbers, G.H.; Salden, M.; Raats, J.; Drijfhout, J.W.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.; Toes, R.E.; Pruijn, G.J. ACPA Fine-Specificity Profiles in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Do Not Correlate with Clinical Features at Baseline or with Disease Progression. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.C. Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cureus 2021, 13, e15063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornik, I.; Maravić, G.; Dumić, J.; Flögel, M.; Lauc, G. Fucosylation of IgG Heavy Chains Is Increased in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Biochem. 1999, 32, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Abberant Immunoglobulin G Glycosylation in Rheumatoid Arthritis by LTQ-ESI-MS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, T.; Yagi, H.; Takemoto, E.; Shibata-Koyama, M.; Isoda, Y.; Iida, S.; Masuda, K.; Satoh, M.; Kato, K. Structural Basis for Improved Efficacy of Therapeutic Antibodies on Defucosylation of Their Fc Glycans. Genes Cells 2011, 16, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Coillie, J.; Schulz, M.A.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; de Haan, N.; Ye, Z.; Geerdes, D.M.; van Esch, W.J.E.; Hafkenscheid, L.; Miller, R.L.; Narimatsu, Y.; et al. Role of N-Glycosylation in FcγRIIIa Interaction with IgG. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 987151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, G.; Plomp, R.; Koeleman, C.A.M.; Visser, R.; von Horsten, H.H.; Sandig, V.; Rispens, T.; Wuhrer, M.; Vidarsson, G. Multi-Level Glyco-Engineering Techniques to Generate IgG with Defined Fc-Glycans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tan, Z.; Guan, F.; Ren, Y. The Essential Functions and Detection of Bisecting GlcNAc in Cell Biology. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, M.; Mishra, S.K.; Tokoro, Y.; Sato, K.; Nakajima, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Taniguchi, N.; Kizuka, Y. Bisecting GlcNAc Is a General Suppressor of Terminal Modification of N-Glycan. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2019, 18, 2044–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, W.W.; Shen, R.-F.; Bern, M.; Cipollo, J. Identification of Sialic Acid Linkages on Intact Glycopeptides via Differential Chemical Modification Using IntactGIG-HILIC. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2018, 29, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarka, E.; Aradi, P.; Huber, K.; Pozsgay, J.; Végh, L.; Magyar, A.; Gyulai, G.; Nagy, G.; Rojkovich, B.; Kiss, É.; et al. Affinity Purification and Comparative Biosensor Analysis of Citrulline-Peptide-Specific Antibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiák, L.; Ozohanics, O.; Marino, F.; Drahos, L.; Vékey, K. Digestion Protocol for Small Protein Amounts for Nano-HPLC-MS(MS) Analysis. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozohanics, O.; Turiák, L.; Puerta, A.; Vékey, K.; Drahos, L. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry Methodology for Analyzing Site-Specific N-Glycosylation Patterns. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1259, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Team: Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szabó, D.; Gyebrovszki, B.; Szarka, E.; Auer, F.; Rojkovich, B.; Nagy, G.; Telekes, A.; Vékey, K.; Drahos, L.; Ács, A.; et al. Immunoglobulin G Subclass-Specific Glycosylation Changes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199626
Szabó D, Gyebrovszki B, Szarka E, Auer F, Rojkovich B, Nagy G, Telekes A, Vékey K, Drahos L, Ács A, et al. Immunoglobulin G Subclass-Specific Glycosylation Changes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199626
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzabó, Dániel, Balázs Gyebrovszki, Eszter Szarka, Felícia Auer, Bernadette Rojkovich, György Nagy, András Telekes, Károly Vékey, László Drahos, András Ács, and et al. 2025. "Immunoglobulin G Subclass-Specific Glycosylation Changes in Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199626
APA StyleSzabó, D., Gyebrovszki, B., Szarka, E., Auer, F., Rojkovich, B., Nagy, G., Telekes, A., Vékey, K., Drahos, L., Ács, A., & Sármay, G. (2025). Immunoglobulin G Subclass-Specific Glycosylation Changes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199626







