Caspase-3 in Brain Death Donors Is Associated with Reduced Primary Graft Dysfunction After Heart Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics and HTx Process
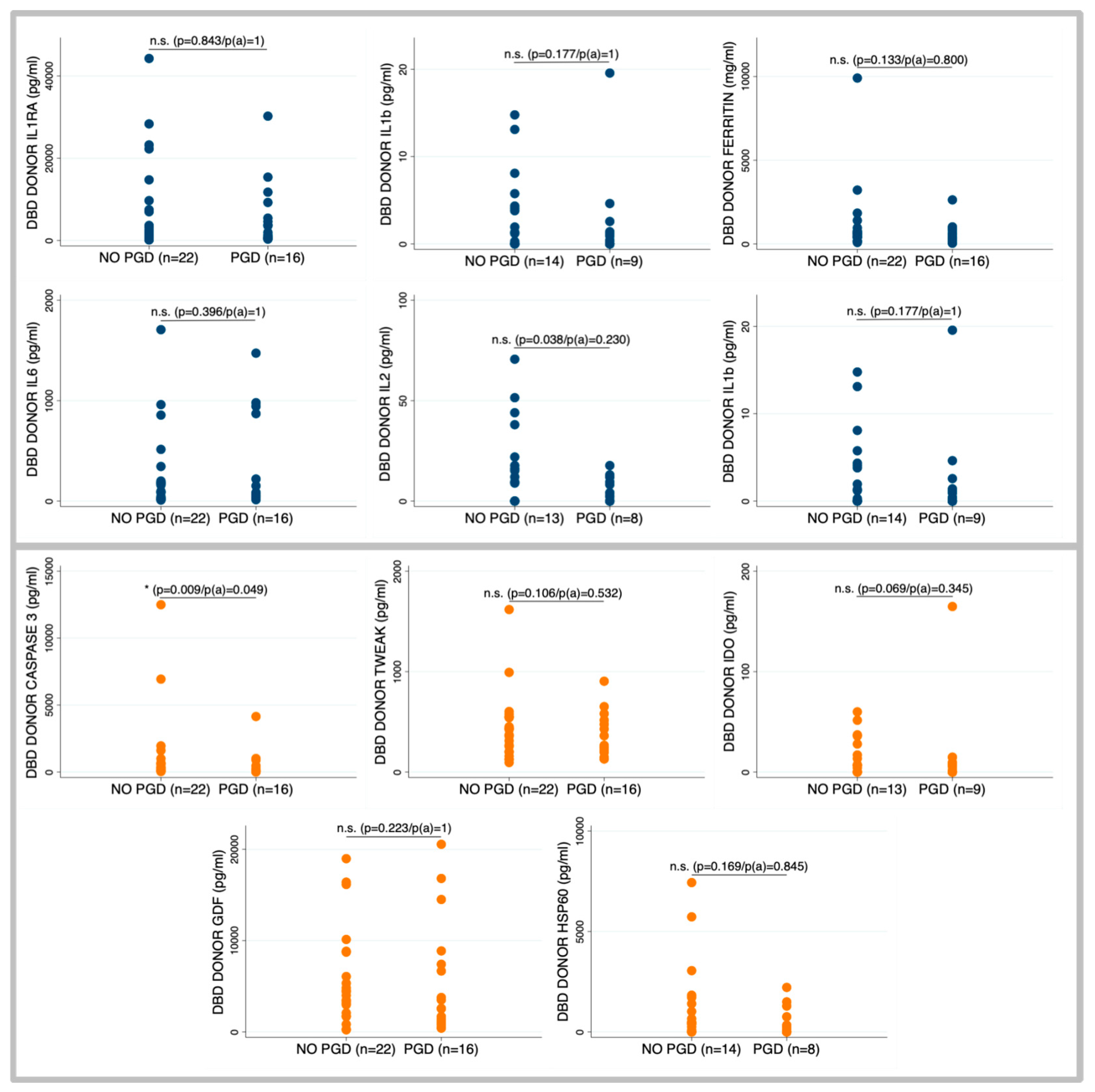
2.2. Primary Graft Dysfunction According to Brain Death Donor Profile
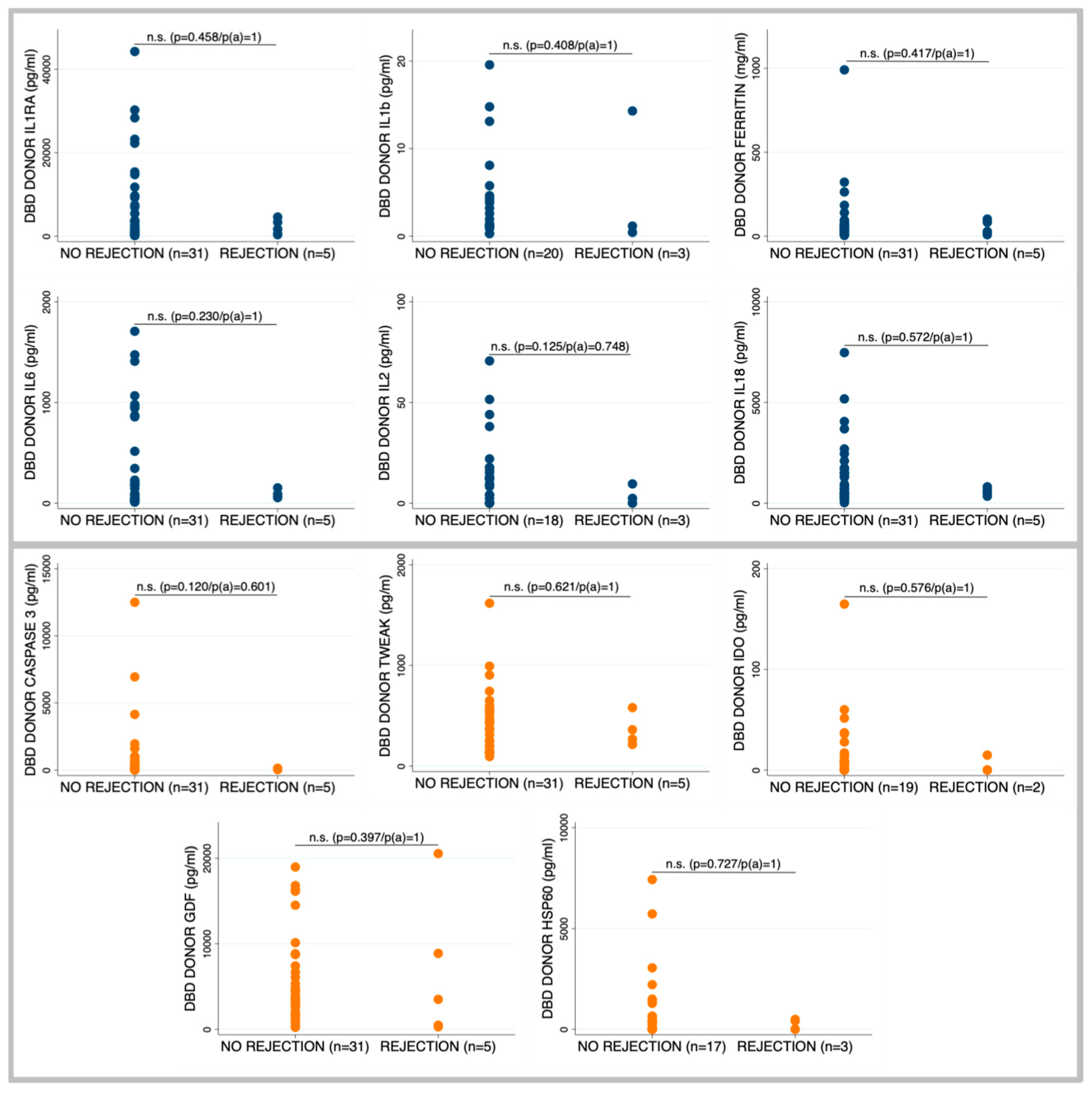
2.3. Occurrence of Rejection According to Brain Death Donor Profile
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
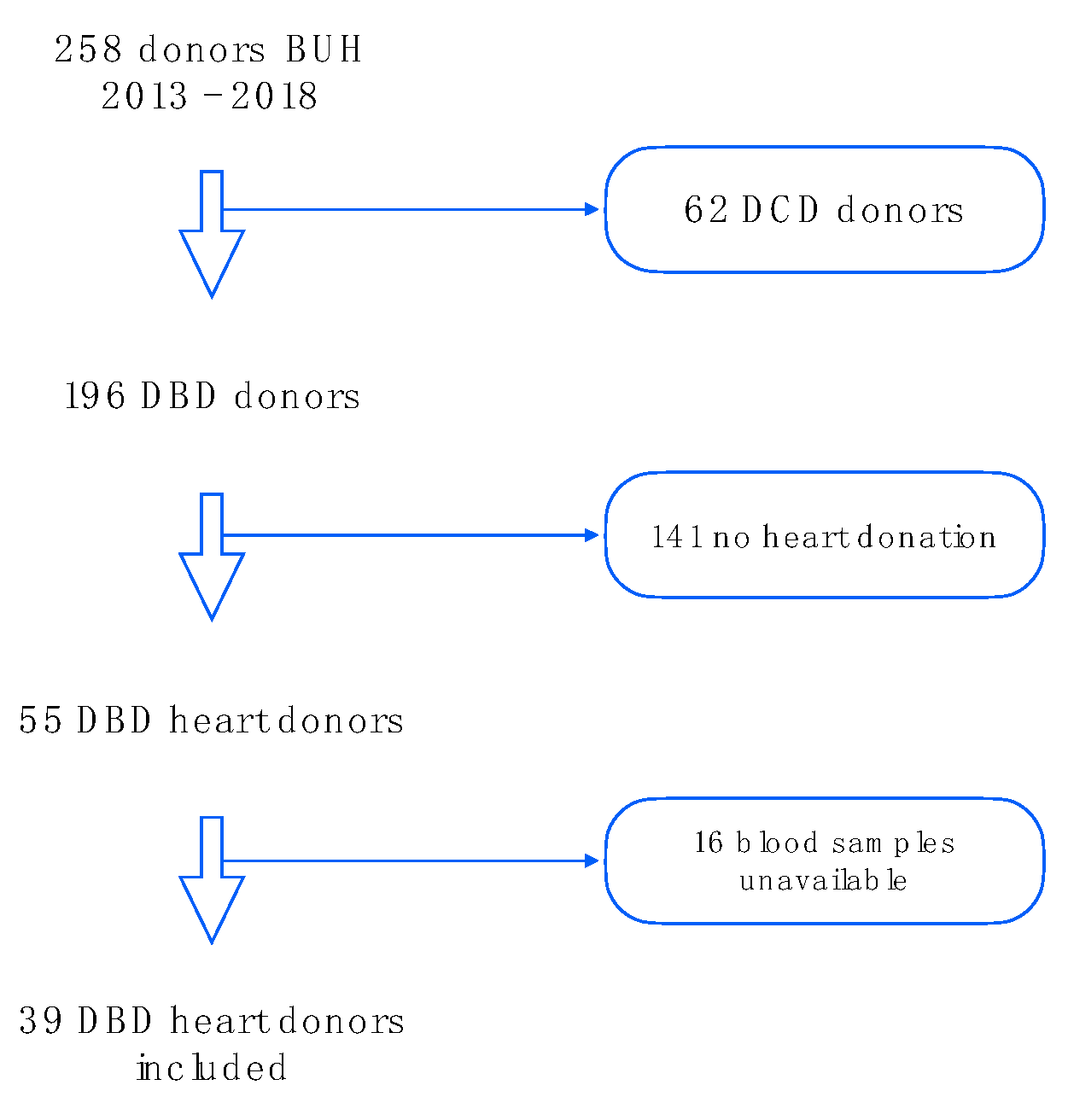
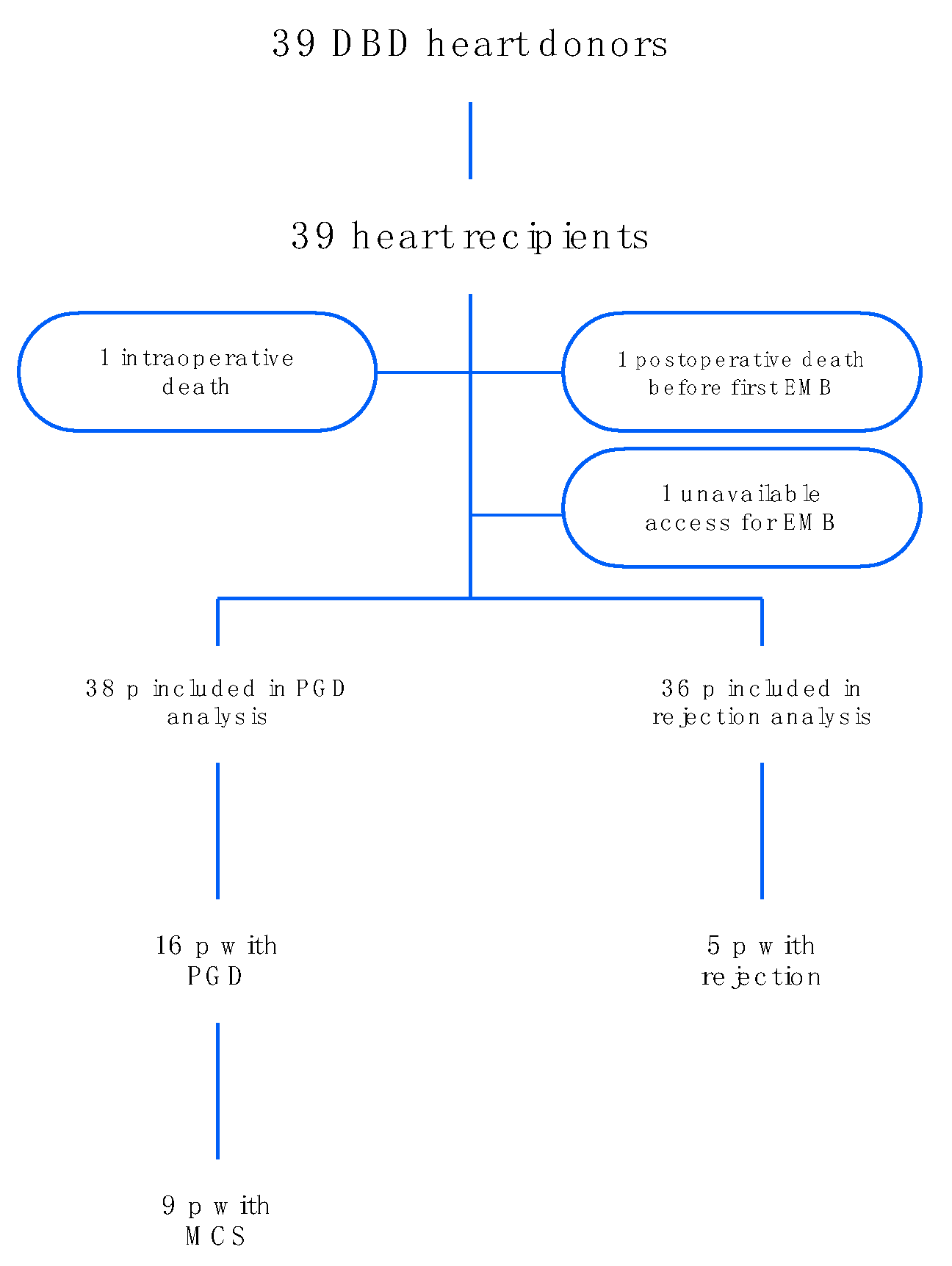
4.1. Patient Selection
4.2. Data Collection
4.3. Sample Acquisition
4.4. Multiplex Analysis
4.5. Mitochondrial and Genomic DNA
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BiVAD | Biventricular assist device |
| C5A | Complement component 5a |
| CD28 | Cluster of differentiation 28 |
| DCD | Donation after circulatory death |
| DBD | Donation after brain death |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| EMB | Endomyocardial biopsy |
| EV | Extracellular vesicles |
| GDF | Growth differentiation factor |
| gDNA | Genomic deoxyribonucleic acid |
| Hsp60 | Heat shock protein 60 |
| HTx | Heart transplant |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IL1RA | Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist |
| INTERMACS | Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support |
| IP-10 | Interferon gamma-induced protein 10 |
| ISHLT | International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation |
| IABP | Intra-aortic balloon pump |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| MCS | Mechanical circulatory support |
| mtDNA | Mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid |
| PGD | Primary graft dysfunction |
| RVAD | Right ventricular assist device |
| sFAS-L | Soluble Fas ligand |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TRAIL | Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand |
| TREM-1 | Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 |
| TWEAK | Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis |
Appendix A
References
- González-Vílchez, F.; Gómez-Bueno, M.; Almenar-Bonet, L.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Arizón Del Prado, J.M.; Blázquez-Bermejo, Z.; Delgado-Jiménez, J.F.; de Antonio-Ferrer, M.; Sobrino-Márquez, J.M.; García-Romero, E. Spanish heart transplant registry. 33rd official report of the Heart failure Association of the Spanish Society of Cardiology. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2022, 75, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khush, K.K.; Hsich, E.; Potena, L.; Cherikh, W.S.; Chambers, D.C.; Harhay, M.O.; Hayes, D., Jr.; Perch, M.; Sadavarte, A.; Toll, A.; et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-eighth adult heart transplantation report—2021; Focus on recipient characteristics. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2021, 40, 1035–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.F.; Salehi Omran, S.; Genuardi, M.V.; Horn, E.T.; Kilic, A.; Sciortino, C.M.; Keebler, M.E.; Kormos, R.L.; Hickey, G.W. Primary Graft Dysfunction in Heart Transplant Recipients—Risk Factors and Longitudinal Outcomes. ASAIO J. 2022, 68, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avtaar Singh, S.S.; Banner, N.R.; Rushton, S.; Simon, A.R.; Berry, C.; Al-Attar, N. ISHLT Primary Graft Dysfunction Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcome: A UK National Study. Transplantation 2019, 103, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivella, A.; Almenar-Bonet, L.; González-Vilchez, F.; Díez-López, C.; Díaz-Molina, B.; Blázquez-Bermejo, Z.; Sobrino-Márquez, J.M.; Gómez-Bueno, M.; Garrido-Bravo, I.P.; Barge-Caballero, E.; et al. Mechanical circulatory support in severe primary graft dysfunction: Peripheral cannulation but not earlier implantation improves survival in heart transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2023, 42, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auråen, H.; Mollnes, T.E.; Bjørtuft, Ø.; Bakkan, P.A.; Geiran, O.; Kongerud, J.; Fiane, A.; Holm, A.M. Multiorgan procurement increases systemic inflammation in brain dead donors. Clin. Transplant. 2013, 27, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, R.P.; Thom, O.; Fraser, J.F. Inflammatory Signalling Associated with Brain Dead Organ Donation: From Brain Injury to Brain Stem Death and Posttransplant Ischaemia Reperfusion Injury. J. Transplant. 2013, 2013, 521369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez López, S.; Otero Hernández, J.; Vázquez Moreno, N.; Escudero Augusto, D.; Alvarez Menéndez, F.; Astudillo González, A. Brain Death Effects on Catecholamine Levels and Subsequent Cardiac Damage Assessed in Organ Donors. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2009, 28, 815–820. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolakis, E.; Parissis, H.; Dougenis, D. Brain death and donor heart dysfunction: Implications in cardiac transplantation. J. Card. Surg. 2010, 25, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barklin, A.; Larsson, A.; Vestergaard, C.; Koefoed-Nielsen, J.; Bach, A.; Nyboe, R.; Wogensen, L.; Tønnesen, E. Does brain death induce a pro-inflammatory response at the organ level in a porcine model? Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2008, 52, 621–627. [Google Scholar]
- Amado, J.A.; López-Espadas, F.; Vázquez-Barquero, A.; Salas, E.; Riancho, J.A.; López-Cordovilla, J.J.; García-Unzueta, M.T. Blood levels of cytokines in brain-dead patients: Relationship with circulating hormones and acute-phase reactants. Metabolism 1995, 44, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullerits, R.; Oltean, S.; Flodén, A.; Oltean, M. Circulating resistin levels are early and significantly increased in deceased brain dead organ donors, correlate with inflammatory cytokine response and remain unaffected by steroid treatment. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrabal, C.A.; Thompson, L.O.; Potapov, E.V.; Southard, R.E.; Joyce, D.L.; Youker, K.A.; Noon, G.P.; Loebe, M. Organ-specific regulation of pro-inflammatory molecules in heart, lung, and kidney following brain death. J. Surg. Res. 2005, 123, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Roldán, J.M.; García-Alfaro, C.; Jimenéz-González, P.I.; Hernández-Hazañas, F.; Gascón Castillo, M.L.; Egea Guerrero, J.J. Muerte encefálica: Repercusión sobre órganos y tejidos. Med. Intensiv. 2009, 33, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, Z.; Chen, V.; Sidhu, K.; Lin, D.; Ng, R.T.; Balshaw, R.; Cohen-Freue, G.V.; Ignaszewski, A.; Imai, C.; Kaan, A.; et al. Predicting acute cardiac rejection from donor heart and pre-transplant recipient blood gene expression. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2013, 32, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemonti, L.; Sordi, V.; Pellegrini, S.; Scotti, G.M.; Scavini, M.; Sioli, V.; Gianelli Castiglione, A.; Cardillo, M. Circulating CXCL10 and IL-6 in solid organ donors after brain death predict graft outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaj, A.; Dewachter, L.; Rorive, S.; Remmelink, M.; Weynand, B.; Melot, C.; Galanti, L.; Hupkens, E.; Sprockeels, T.; Dewachter, C.; et al. Roles of inflammation and apoptosis in experimental brain death–induced right ventricular failure. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, R.V.; Dronavalli, V.; Lambert, P.A.; Steeds, R.P.; Wilson, I.C.; Thompson, R.D.; Mascaro, J.G.; Bonser, R.S. The proinflammatory environment in potential heart and lung donors: Prevalence and impact of donor management and hormonal therapy. Transplantation 2009, 88, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braulio, R.; Sanches, M.D.; Teixeira Junior, A.L.; Costa, P.H.; Moreira Mda, C.; Rocha, M.A.; Andrade, S.A.; Gelape, C.L. Associated clinical and laboratory markers of donor on allograft function after heart transplant. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 31, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayedi, Y.; Truby, L.K.; Foroutan, F.; Han, J.; Guzman, J.; Angleitner, P.; Sabatino, M.; Felius, J.; Van Zyl, J.S.; Rodenas-Alesina, E.; et al. The International Consortium on Primary Graft Dysfunction: Redefining Clinical Risk Factors in the Contemporary Era of Heart Transplantation. J. Card. Fail. 2024, 30, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Bautista, C.; Fernández-Avilés, F.; Delgado Jiménez, J.F. Serum biomarkers of acute rejection: Towards precision medicine in heart transplant. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2021, 40, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronavalli, V.B.; Banner, N.R.; Bonser, R.S. Assessment of the potential heart donor: A role for biomarkers? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorlat, A.; De Hous, N.; Vervaecke, A.J.; Vermeulen, T.; Van Craenenbroeck, E.; Heidbuchel, H.; Rodrigus, I.; Van Donink, W.; Ancion, A.; Van Cleemput, J.; et al. Biomarkers and Donor Selection in Heart Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, R.; Marklin, G.F.; Klinkenberg, W.D.; Wang, J.; Goss, C.W.; Lele, A.V.; Kensinger, C.D.; Lange, P.A.; Lebovitz, D.J. Intravenous Levothyroxine for Unstable Brain-Dead Heart Donors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2029–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.E.; Jaishankar, D.; Ho, J.W.; Alam, H.B.; Bharat, A.; Nadig, S.N. Mitochondrial responses to brain death in solid organ transplant. Front. Transplant. 2023, 2, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez López, S.; Vázquez Moreno, N.; Escudero Augusto, D.; Astudillo González, A.; Alvarez Menéndez, F.; Goyache Goñi, F.; Otero Hernández, J. A molecular approach to apoptosis in the human heart during brain death. Transplantation 2008, 86, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.; Cullen, S.; Martin, S. Apoptosis: Controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulatovic, I.; Ibarra, C.; Österholm, C.; Wang, H.; Beltrán-Rodríguez, A.; Varas-Godoy, M.; Månsson-Broberg, A.; Uhlén, P.; Simon, A.; Grinnemo, K.H. Sublethal caspase activation promotes generation of cardiomyocytes from embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häcker, G.; Haimovici, A. Sub-lethal signals in the mitochondrial apoptosis apparatus: Pernicious by-product or physiological event? Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Dellar, E.R.; Baena-Lopez, L.A. Caspases help to spread the message via extracellular vesicles. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 1954–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaj, A.; Dewachter, L.; Monier, A.; Vegh, G.; Rorive, S.; Remmelink, M.; Closset, M.; Melot, C.; Creteur, J.; Salmon, I.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Tacrolimus on Brain-Death-Associated Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Pigs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, S.; Amiel, J.A.; Desgroseilliers, M.; Williamson, D.R.; Thiboutot, Z.; Serri, K.; Perreault, M.M.; Marsolais, P.; Frenette, A.J. Corticosteroids in the management of brain-dead potential organ donors: A systematic review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 113, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Kainz, A.; Jelencsics, K.; Heinzel, A.; Berlakovich, G.; Remport, Á.; Heinze, G.; Langer, R.; Oberbauer, R. Steroid pretreatment of organ donors does not impact on early rejection and long-term kidney allograft survival: Results from a multicenter randomized, controlled trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, S.F.; Sheeran, F.L.; Chaudhuri, K.; Vale, M.; Bailey, M.; Pepe, S. Molecular markers of programmed cell death in donor hearts before transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2014, 33, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobashigawa, J.; Zuckermann, A.; Macdonald, P.; Leprince, P.; Esmailian, F.; Luu, M.; Mancini, D.; Patel, J.; Razi, R.; Reichenspurner, H.; et al. Report from a consensus conference on primary graft dysfunction after cardiac transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2014, 33, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Winters, G.L.; Fishbein, M.C.; Tazelaar, H.D.; Kobashigawa, J.; Abrams, J.; Andersen, C.B.; Angelini, A.; Berry, G.J.; Burke, M.M.; et al. Revision of the 1990 working formulation for the standardization of nomenclature in the diagnosis of heart rejection. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2005, 24, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajaz, S.; Czajka, A.; Malik, A. Accurate measurement of circulating mitochondrial DNA content from human blood samples using real-time quantitative PCR. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1264, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Donor Baseline Characteristics (N = 39) | |
|---|---|
| Comorbidities | |
| Age (years) | 46.4 ± 12.4 |
| Women, n (%) | 14 (35.9) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 0 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 6 (15.4) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 6 (15.4) |
| Kidney disease, n (%) | 0 |
| Lung disease, n (%) | 0 |
| Liver disease, n (%) | 2 (5.13) |
| Cardiac arrest, n (%) | 5 (12.8) |
| Laboratory results | |
| Troponin T (ng/L) | 156 ± 316 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 1.66 ± 1.07 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 88.2 ± 47.8 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 148 ± 27.7 |
| PaCO2 (mmHg) | 38.7 ± 5.98 |
| PaO2 (mmHg) | 298 ± 122 |
| HCO3 (mmol/L) | 25.8 ± 3.80 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 35.7 ± 7.38 |
| Prealbumin (g/L) | 178 ± 101 |
| ALT (U/L) | 0.91 ± 1.01 |
| Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 12.2 ± 10.3 |
| LDH (U/L) | 4.73 ± 1.71 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.9 ± 2.67 |
| Leucocytes (109/L) | 15.58 ± 6.32 |
| Cause of death, n (%) | |
| Hanging | 1 (2.56) |
| Anoxic encephalopathy | 3 (7.69) |
| Stroke | 13 (33.3) |
| Suicide | 1 (2.56) |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | 12 (30.8) |
| Traumatic brain injury | 8 (20.5) |
| Infections, n (%) | |
| Respiratory infection | 20 (55.6) |
| Microbiological isolation | 18 (46.15) |
| Treatments, n (%) | |
| Steroids | 6 (15.4) |
| Levothyroxine | 5 (12.8) |
| Desmopressin | 32 (82.1) |
| Mineralocorticoids | 12 (30.8) |
| Heart Recipient Baseline Characteristics (N = 39) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 55.3 ± 11.2 |
| Height (cm) | 164 ± 28.7 |
| Weight (kg) | 73.3 ± 15.5 |
| Women, n (%) | 7 (17.9) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 13 (33.3) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 12 (30.8) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 16 (41.0) |
| Prior smoker, n (%) | 19 (48.7) |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) | 11 (28.2) |
| Ischemic cardiomyopathy, n (%) | 16 (41.0) |
| Chronic inotrope support, n (%) | 6 (15.4) |
| Previous MCS, n (%) | 11 (28.2) |
| Emergency 0 status, n (%) | 14 (35.9) |
| Emergency 1 status, n (%) | 5 (12.8) |
| Sensitization, n (%) | 0 |
| Time on waiting list (days) | 107.2 ± 141.2 |
| INTERMACS profile n (%) | |
| 1 | 7 (17.9) |
| 2 | 5 (12.8) |
| 3 | 6 (15.4) |
| ≥4 | 21 (53.8) |
| Variable | No Rejection | Rejection | p | No PGD | PGD | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gDNA | 5.8 [1.6–13.7] | 11.5 [2.5–27.7] | 0.327 | 5.8 [1.3–13.7] | 6.2 [2.5–23.6] | 0.534 |
| mtDNA | 63.5 [18.4–170.0] | 108.6 [28.6–306.1] | 0.385 | 74.4 [18.8–274.4] | 26.7 [19.6–143.0] | 0.438 |
| Ratio | 7.8 [5.1–25.2] | 10.9 [5.9–14.5] | 0.117 | 10.5 [5.4–24.6] | 6.5 [3.3–10.7] | 0.067 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrador, L.; González-Costello, J.; Niubo-Bosch, J.; Calatayud-Samper, L.; Maestro-Benedicto, A.; Farrero-Torres, M.; Blasco-Peiro, T.; Almenar-Bonet, L.; Blázquez-Bermejo, Z.; Garrido-Bravo, I.; et al. Caspase-3 in Brain Death Donors Is Associated with Reduced Primary Graft Dysfunction After Heart Transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199434
Herrador L, González-Costello J, Niubo-Bosch J, Calatayud-Samper L, Maestro-Benedicto A, Farrero-Torres M, Blasco-Peiro T, Almenar-Bonet L, Blázquez-Bermejo Z, Garrido-Bravo I, et al. Caspase-3 in Brain Death Donors Is Associated with Reduced Primary Graft Dysfunction After Heart Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199434
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrador, Lorena, José González-Costello, Jordi Niubo-Bosch, Laura Calatayud-Samper, Alba Maestro-Benedicto, Marta Farrero-Torres, Teresa Blasco-Peiro, Luis Almenar-Bonet, Zorba Blázquez-Bermejo, Iris Garrido-Bravo, and et al. 2025. "Caspase-3 in Brain Death Donors Is Associated with Reduced Primary Graft Dysfunction After Heart Transplantation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199434
APA StyleHerrador, L., González-Costello, J., Niubo-Bosch, J., Calatayud-Samper, L., Maestro-Benedicto, A., Farrero-Torres, M., Blasco-Peiro, T., Almenar-Bonet, L., Blázquez-Bermejo, Z., Garrido-Bravo, I., Gran-Ipiña, F., Grande-Trillo, A., Manito, N., & Moreno-Gonzalez, G. (2025). Caspase-3 in Brain Death Donors Is Associated with Reduced Primary Graft Dysfunction After Heart Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199434






