The Role of Particle Inhalation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Smoking and IPF
3. Environmental Particle Exposures Other than Smoking and IPF
4. Occupational Particle Exposures and IPF
5. Synergy of Particle Exposures and IPF
6. Biochemical Pathogenesis of Particle-Associated IPF
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | alveolar macrophage |
| AD | alveolar duct |
| DIP | desquamative interstitial pneumonitis |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| IIP | idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis |
| ILD | interstitial lung disease |
| IPF | idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| NSIP | nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis |
| OP | organizing pneumonitis |
| PM2.5 | particulate matter with a diameter less than 2.5 micron |
| RB-ILD | respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease |
| RB | respiratory bronchiole |
| SEM/EDS | scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| TB | terminal bronchiole |
| UIP | usual interstitial pneumonitis |
References
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, N.W.; Atamas, S.P.; Hines, S.E.; Luzina, I.G.; Shah, N.G.; Britt, E.J.; Ghio, A.J.; Galvin, J.R. Demystifying idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: Time for more etiology-focused nomenclature in interstitial lung disease. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2022, 16, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, K.O. My approach to interstitial lung disease using clinical, radiological and histopathological patterns. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 62, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, M.B. The pathologist’s approach to acute lung injury. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2010, 134, 719–727. [Google Scholar]
- American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 646–664. [Google Scholar]
- Ley, B.; Collard, H.R.; King, T.E., Jr. Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trethewey, S.P.; Walters, G.I. The Role of Occupational and Environmental Exposures in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Narrative Literature Review. Medicina 2018, 54, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzieri, S.; Illica Magrini, E.; Mozzoni, P.; Andreoli, R.; Pela, G.; Bertorelli, G.; Corradi, M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and occupational risk factors. Med. Lav. 2019, 110, 407–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, S.K.; Schwarz, M.I. Update in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2009, 15, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolters, P.J.; Blackwell, T.S.; Eickelberg, O.; Loyd, J.E.; Kaminski, N.; Jenkins, G.; Maher, T.M.; Molina-Molina, M.; Noble, P.W.; Raghu, G.; et al. Time for a change: Is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis still idiopathic and only fibrotic? Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, J.; Panizo, A.; Sola, I.; Queipo, F.; Martinez-Penuela, A.; Carias, R. Prognostic value of clinical, morphologic, and immunohistochemical factors in patients with bronchiolitis obliterans-organizing pneumonia. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Dalurzo, M.; Panse, P.; Parish, J.; Leslie, K. Usual interstitial pneumonia-pattern fibrosis in surgical lung biopsies. Clinical, radiological and histopathological clues to aetiology. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 66, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritopoulos, G.A.; Vasarmidi, E.; Jacob, J.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M. Smoking and interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Akinci Ozyurek, B.; Erdogan, Y.; Cirit Kocer, B.; Demirag, F.; Dadali, Y.; Buyukyaylaci Ozden, S. Retrospective evaluation of patients with organizing pneumonia: Is cryptogenic organizing pneumonia different from secondary organizing pneumonia? Tuberk. Toraks 2017, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.; du Bois, R.M.; Colby, T.V.; Hansell, D.M.; Nicholson, A.G. Clinical significance of respiratory bronchiolitis on open lung biopsy and its relationship to smoking related interstitial lung disease. Thorax 1999, 54, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.U.; Nicholson, A.G.; Hansell, D.M. Challenges in pulmonary fibrosis·4: Smoking-induced diffuse interstitial lung diseases. Thorax 2007, 62, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Attili, A.K.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Gross, B.H.; Flaherty, K.R.; Myers, J.L.; Martinez, F.J. Smoking-related interstitial lung disease: Radiologic-clinical-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2008, 28, 1383–1396, discussion 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marten, K.; Milne, D.; Antoniou, K.M.; Nicholson, A.G.; Tennant, R.C.; Hansel, T.T.; Wells, A.U.; Hansell, D.M. Non-specific interstitial pneumonia in cigarette smokers: A CT study. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenstein, A.L.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Zanardi, C.; Dexter, E. Clinically occult interstitial fibrosis in smokers: Classification and significance of a surprisingly common finding in lobectomy specimens. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washko, G.R.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Fernandez, I.E.; Nishino, M.; Okajima, Y.; Yamashiro, T.; Ross, J.C.; Estepar, R.S.; Lynch, D.A.; Brehm, J.M.; et al. Lung volumes and emphysema in smokers with interstitial lung abnormalities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 897–906. [Google Scholar]
- Bak, S.H.; Lee, H.Y. Overlaps and uncertainties of smoking-related idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Int. J. Chron. Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 3221–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, C.B.; Gaensler, E.A.; Coutu, R.E.; FitzGerald, M.X.; Gupta, R.G. Natural history and treated course of usual and desquamative interstitial pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1978, 298, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Colby, T.V.; Hartman, T.E.; Vassallo, R. Smoking-related interstitial lung diseases: A concise review. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 17, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, W. Cigarette smoking, asbestos, and pulmonary fibrosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1971, 104, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.; Johnston, I.; Britton, J. What causes cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis? A case-control study of environmental exposure to dust. BMJ 1990, 301, 1015–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, K.B.; Samet, J.M.; Stidley, C.A.; Colby, T.V.; Waldron, J.A. Cigarette smoking: A risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, R.; Lewis, S.; Richards, K.; Johnston, I.; Britton, J. Occupational exposure to metal or wood dust and aetiology of cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Lancet 1996, 347, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, K.; Mori, T.; Yamada, N.; Yamaguchi, M.; Hosoda, Y. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Epidemiologic approaches to occupational exposure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskar, V.; Coultas, D. Exposures and idiopathic lung disease. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 29, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sancho, C.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Fernandez-Plata, M.R.; Navarro, C.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Vargas, M.H.; Loyd, J.E.; Selman, M. Familial pulmonary fibrosis is the strongest risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1902–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrom, M.; Gustafson, T.; Boman, K.; Nilsson, K.; Tornling, G.; Murgia, N.; Toren, K. Effects of smoking, gender and occupational exposure on the risk of severe pulmonary fibrosis: A population-based case-control study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Huang, K.; Ding, Y.; Lou, B.; Hou, Z.; Dai, H.; Wang, C. Cigarette smoking contributes to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis associated with emphysema. Chin. Med. J. 2014, 127, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Karkkainen, M.; Kettunen, H.P.; Nurmi, H.; Selander, T.; Purokivi, M.; Kaarteenaho, R. Effect of smoking and comorbidities on survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, M.J.; Murambadoro, T.; Alif, S.M.; Benke, G.P.; Dharmage, S.C.; Glaspole, I.; Hopkins, P.; Hoy, R.F.; Klebe, S.; Moodley, Y.; et al. Occupational and environmental risk factors for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Australia: Case-control study. Thorax 2020, 75, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Ahn, C.; Kim, T.H. Occupational and environmental risk factors of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.P.; Speer, M.C.; Loyd, J.E.; Brown, K.K.; Herron, A.; Slifer, S.H.; Burch, L.H.; Wahidi, M.M.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; Sporn, T.A.; et al. Clinical and pathologic features of familial interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.W.; Han, K.; Choi, S.M. Impact of smoking on the development of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a nationwide population-based cohort study. Thorax 2022, 77, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellou, V.; Belbasis, L.; Evangelou, E. Tobacco Smoking and Risk for Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Prospective Cohort Study from the UK Biobank. Chest 2021, 160, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkkainen, M.; Nurmi, H.; Kettunen, H.P.; Selander, T.; Purokivi, M.; Kaarteenaho, R. Underlying and immediate causes of death in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubairi, A.B.S.; Ahmad, H.; Hassan, M.; Sarwar, S.; Abbas, A.; Shahzad, T.; Irfan, M. Clinical characteristics and factors associated with mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An experience from a tertiary care center in Pakistan. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Richeldi, L.; Kim, D.S.; Taniguchi, H.; Tschoepe, I.; Luisetti, M.; Roman, J.; Tino, G.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Hallmann, C.; et al. Acute exacerbations in the INPULSIS trials of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Ding, L.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y. Early-life Exposure to Tobacco Smoke and the Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Population-based Cohort Study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2025, 22, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Gujral, M.; Abraham, J.L.; Scalzetti, E.M.; Iannuzzi, M.C. A case of hut lung: Scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy analysis of a domestically acquired form of pneumoconiosis. Chest 2013, 144, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.A.; Jagirdar, J.; Hay, J.G.; Addrizzo-Harris, D.J.; Naidich, D.P.; Rom, W.N. Hut lung. A domestically acquired particulate lung disease. Medicine 2000, 79, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, R.M.; Cosio, M.G.; Ghezzo, H.; Salazar, M.; Perez-Padilla, R. Comparison of lung morphology in COPD secondary to cigarette and biomass smoke. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2008, 12, 972–977. [Google Scholar]
- Kunal, S.; Pilaniya, V.; Shah, A. Bronchial anthracofibrosis with interstitial lung disease: An association yet to be highlighted. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2015213940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.; Harari, S. Now we know: Chronic exposure to air pollutants is a risk factor for the development of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2202113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, S.; Harari, S.; Caminati, A.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J.D.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Cesana, G.; Madotto, F. The association between air pollution and the incidence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Northern Italy. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1700397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Sun, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, D.; Wu, M.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; Tian, Y. Air pollutants, genetic susceptibility and risk of incident idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makela, K.; Ollila, H.; Sutinen, E.; Vuorinen, V.; Peltola, E.; Kaarteenaho, R.; Myllarniemi, M. Inorganic particulate matter in the lung tissue of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients reflects population density and fine particle levels. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 40, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterbottom, C.J.; Shah, R.J.; Patterson, K.C.; Kreider, M.E.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Rivera-Lebron, B.; Miller, W.T.; Litzky, L.A.; Penning, T.M.; Heinlen, K.; et al. Exposure to Ambient Particulate Matter Is Associated with Accelerated Functional Decline in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2018, 153, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannson, K.A.; Vittinghoff, E.; Lee, K.; Balmes, J.R.; Ji, W.; Kaplan, G.G.; Kim, D.S.; Collard, H.R. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis associated with air pollution exposure. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.G.; Richeldi, L. Air pollution and acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Back to miasma? Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sese, L.; Nunes, H.; Cottin, V.; Sanyal, S.; Didier, M.; Carton, Z.; Israel-Biet, D.; Crestani, B.; Cadranel, J.; Wallaert, B.; et al. Role of atmospheric pollution on the natural history of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2018, 73, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.L.; Dong, F.S.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, C.L.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.H.; Wang, K.; Qi, H. Retrospective Study of Effect of Fine Particulate Matter on Acute Exacerbation of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tahara, M.; Fujino, Y.; Yamasaki, K.; Oda, K.; Kido, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Kawanami, T.; Kataoka, K.; Egashira, R.; Hashisako, M.; et al. Exposure to PM2.5 is a risk factor for acute exacerbation of surgically diagnosed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A case-control study. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomos, I.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Manali, E.D.; Papiris, S.A.; Karakatsani, A. Long-term personal air pollution exposure and risk for acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, C.; Raghu, G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Unmasking cryptogenic environmental factors. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, P.D.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Balmes, J.R.; Cummings, K.J.; Fishwick, D.; Miedinger, D.; Murgia, N.; Naidoo, R.N.; Reynolds, C.J.; Sigsgaard, T.; et al. The Occupational Burden of Nonmalignant Respiratory Diseases. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1312–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Johannson, K.A. Occupational exposures and IPF: When the dust unsettles. Thorax 2020, 75, 828–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Blanc, P.D.; Toren, K.; Jarvholm, B. Smoking, occupational exposures, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis among Swedish construction workers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2021, 64, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.T.; Strek, M.E.; Adegunsoye, A.; Wong, A.W.; Assayag, D.; Cox, G.; Fell, C.D.; Fisher, J.H.; Gershon, A.S.; Halayko, A.J.; et al. Inhalational exposures in patients with fibrotic interstitial lung disease: Presentation, pulmonary function and survival in the Canadian Registry for Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respirology 2022, 27, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.T.; Feary, J.; Johannson, K.A. Environmental and occupational exposures in interstitial lung disease. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2022, 28, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, S.; Tonelli, R.; Murray, M.; Samarelli, A.V.; Spagnolo, P. Environmental Causes of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, K.B.; Samet, J.M.; Coultas, D.B.; Stidley, C.A.; Hunt, W.C.; Colby, T.V.; Waldron, J.A. Occupational and environmental risk factors for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A multicenter case-control study. Collaborating Centers. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burilkov, T.M.L.; Lukanova, R. Pneumociosis in a chalk plant. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. Suppl. 1991, 14, 361. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka, Y.; Munakata, M.; Homma, Y.; Masaki, Y.; Ohe, M.; Doi, I.; Amishima, M.; Kimura, K.; Ishikura, H.; Yoshiki, T.; et al. Three cases of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia with bullae seen in schoolteachers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1995, 28, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolocci, G.; Folletti, I.; Toren, K.; Ekstrom, M.; Dell’Omo, M.; Muzi, G.; Murgia, N. Occupational risk factors for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Southern Europe: A case-control study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadalla, N.J.; Hegazy, A.; Elmetwally, R.A.; Wahby, I. Occupational and environmental risk factors for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Egypt: A multicenter case-control study. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 3, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nett, R.J.; Cummings, K.J.; Cannon, B.; Cox-Ganser, J.; Nathan, S.D. Dental Personnel Treated for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis at a Tertiary Care Center—Virginia, 2000–2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenker, M. Exposures and health effects from inorganic agricultural dusts. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108 (Suppl. 4), 661–664. [Google Scholar]
- Schenker, M.B.; Pinkerton, K.E.; Mitchell, D.; Vallyathan, V.; Elvine-Kreis, B.; Green, F.H. Pneumoconiosis from agricultural dust exposure among young California farmworkers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenker, M.B. Inorganic agricultural dust exposure causes pneumoconiosis among farmworkers. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2010, 7, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauchet, A.; Chaussavoine, A.; Pairon, J.C.; Gabillon, C.; Didier, A.; Baldi, I.; Esquirol, Y. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: What do we Know about the Role of Occupational and Environmental Determinants? A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2022, 25, 372–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, J.M.; Syamlal, G.; Weissman, D.N. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Mortality by Industry and Occupation—United States, 2020–2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2025, 74, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Chung, M.P.; Uh, S.T.; Park, C.S.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, Y.B.; Lee, H.L.; Song, J.S.; et al. Association between occupational dust exposure and prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A Korean national survey. Chest 2015, 147, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of inorganic dusts in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP). Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi 1986, 61, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, H.; Tajima, H.; Mizoguchi, I.; Iwai, K. Elemental analysis of hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi 1992, 30, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, H.; Ichinose, S.; Hosoya, T.; Ando, T.; Ikushima, S.; Oritsu, M.; Takemura, T. Inhalation of inorganic particles as a risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis—Elemental microanalysis of pulmonary lymph nodes obtained at autopsy cases. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2007, 203, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, M.; Redlich, C.A. Asbestosis and environmental causes of usual interstitial pneumonia. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2015, 21, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monso, E.; Tura, J.M.; Marsal, M.; Morell, F.; Pujadas, J.; Morera, J. Mineralogical microanalysis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Arch. Environ. Health 1990, 45, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, G.I. Occupational exposures and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 20, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Inase, N.; Ichinose, S.; Usui, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Ohtani, Y.; Ando, N.; Akashi, T.; Kondoh, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; et al. Elemental analysis of inorganic dusts in lung tissues of interstitial pneumonias. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 2007, 54, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kang, D.M.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, J. Occupational and Environmental Risk Factors for Chronic Fibrosing idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia in South Korea. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 59, e221–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.; Hubbard, R. Recent advances in the aetiology of cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Histopathology 2000, 37, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monso, E.; Tura, J.M.; Pujadas, J.; Morell, F.; Ruiz, J.; Morera, J. Lung dust content in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A study with scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive x ray analysis. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1991, 48, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barber, C.M.; Wiggans, R.E.; Young, C.; Fishwick, D. UK asbestos imports and mortality due to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Occup. Med. 2016, 66, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskar, V.S.; Coultas, D.B. Is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis an environmental disease? Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brichet, A.; Tonnel, A.B.; Brambilla, E.; Devouassoux, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Copin, M.C.; Wallaert, B.; Groupe d’Etude en Pathologie Interstitielle de la Societe de Pathologie Thoracique du Nord. Chronic interstitial pneumonia with honeycombing in coal workers. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2002, 19, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, H.; Johkoh, T.; Honma, K.; Saito, Y.; Fukushima, Y.; Shida, H.; Suganuma, N. Chronic interstitial pneumonia in silicosis and mix-dust pneumoconiosis: Its prevalence and comparison of CT findings with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2007, 131, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Honma, K.; Suganuma, N.; Morikubo, H.; Saito, Y.; Shida, H.; Kaji, Y. Progression from near-normal to end-stage lungs in chronic interstitial pneumonia related to silica exposure: Long-term CT observations. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, B.; Shin, J.; Kim, E.Y.; Choi, S.; Cha, W.; Choi, B.S. Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Associated with Crystalline Silica Exposure in Pneumoconiosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2021, 63, e905–e910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, R.; Cooper, M.; Antoniak, M.; Venn, A.; Khan, S.; Johnston, I.; Lewis, S.; Britton, J. Risk of cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis in metal workers. Lancet 2000, 355, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Yokoyama, T.; Chida, K.; Azuma, A.; Suda, T.; Kudoh, S.; Sakamoto, N.; Okamoto, K.; Kobashi, G.; et al. Occupational and environmental factors and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Japan. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2005, 49, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, G.A.; Antao, V.C.; Wood, J.M.; Wassell, J.T. Occupational risks for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis mortality in the United States. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2008, 14, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.W.; Myong, J.P.; Yoon, H.K.; Rhee, C.K.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.S.; Jo, B.S.; Cho, Y.; Byun, J.; Choi, M.; et al. Occupational exposure and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A multicentre case-control study in Korea. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2017, 21, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assad, N.; Sood, A.; Campen, M.J.; Zychowski, K.E. Metal-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Collins, B.F.; Xia, D.; Schmidt, R.; Abraham, J.L. Pulmonary fibrosis associated with aluminum trihydrate (Corian) dust. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2154–2156. [Google Scholar]
- De Sadeleer, L.J.; Verleden, S.E.; De Dycker, E.; Yserbyt, J.; Verschakelen, J.A.; Verbeken, E.K.; Nemery, B.; Verleden, G.M.; Hermans, F.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; et al. Clinical behaviour of patients exposed to organic dust and diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2018, 23, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, M. Lung fibrosis and exposure to wood dusts: Two case reports and review of the literature. Med. Pr. 2015, 66, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, T.; Dahlman-Hoglund, A.; Nilsson, K.; Strom, K.; Tornling, G.; Toren, K. Occupational exposure and severe pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 2207–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.V.; Koff, J.; Gotway, M.B.; Nishimura, S.; Balmes, J.R. Case report: A case of wood-smoke-related pulmonary disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, K.M.; McLaughlin, A.M.; Beckett, W.S.; Sime, P.J. Asbestos-related lung disease. Am. Fam. Physician 2007, 75, 683–688. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, C.C.; Yu, I.T.; Chen, W. Silicosis. Lancet 2012, 379, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy-Jardin, M.; Sobaszek, A.; Duhamel, A.; Mastora, I.; Zanetti, C.; Remy, J. Asbestos-related pleuropulmonary diseases: Evaluation with low-dose four-detector row spiral CT. Radiology 2004, 233, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.I.S.; Muller, N.L.; Neder, J.A.; Nogueira, C.R.; Napolis, L.M.; Terra, M.; Bagatin, E.; Nery, L.E. Asbestos-related Disease Progression of Parenchymal Abnormalities on High-resolution CT. J. Thorac. Imaging 2008, 23, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehmas, T.; Oksa, P. Chest HRCT signs predict deaths in long-term follow-up among asbestos exposed workers. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 1983–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuaychoo, B.; Luangdansakun, N.; Chierakul, N.; Ruangchira-Urai, R.; Amornpichetkul, K.; Thongcharoen, P.; Muangman, N. Pathological confirmed diagnosis of asbestosis: The first case report in Thailand. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2015, 98, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Attanoos, R.L.; Alchami, F.S.; Pooley, F.D.; Gibbs, A.R. Usual interstitial pneumonia in asbestos-exposed cohorts—Concurrent idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis or atypical asbestosis? Histopathology 2016, 69, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Hoshi, E.; Murai, K.; Kanauchi, T.; Kurashima, K.; Sugita, Y. Asbestos exposure increases the incidence of histologically confirmed usual interstitial pneumonia. Histopathology 2016, 68, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topçu, F.; Bayram, H.; Simşek, M.; Kaya, K.; Ozcan, C.; Işik, R.; Senyiğit, A. High-resolution computed tomography in cases with environmental exposure to asbestos in Turkey. Respiration 2000, 67, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, Y.; Satoh, T.; Kaira, K.; Hachisu, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Yajima, T.; Hisada, T.; Yokoo, H.; Dobashi, K. Progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Is Associated with Silica/Silicate Inhalation. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, I.B.; Vestergaard, J.M.; Ohlander, J.; Peters, S.; Bendstrup, E.; Bonde, J.P.E.; Schlünssen, V.; Bønløkke, J.H.; Rasmussen, F.; Stokholm, Z.A.; et al. Occupational exposure to respirable crystalline silica and incident idiopathic interstitial pneumonias and pulmonary sarcoidosis: A national prospective follow-up study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2024, 81, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, J.; Hodgson, M.J.; DeGraff, C.A.; Godar, T. Case-control study of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and environmental exposures. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 1998, 40, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, V.E.; Renzetti, A.D.; Doggett, R.S.; Jarvis, J.Q.; Colby, T.V. Chronic diffuse interstitial fibrosis of the lung in uranium miners. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 1998, 40, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Göçmen Ocal, S.; Doruk, S.; Acu, B. Is tin fume exposure benign or not? Two case reports. Tuberk. Toraks 2009, 57, 422–426. [Google Scholar]
- Smolkova, P.; Nakladalova, M. The etiology of occupational pulmonary aluminosis—The past and the present. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014, 158, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, F.; Takemura, T.; Bando, M.; Kuroki, T.; Numao, T.; Moriyama, H.; Hagiwara, K. Progressive plasterer’s pneumoconiosis complicated by fib rotic interstitial pneumonia: A case report. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.J.; Sisodia, R.; Barber, C.; Moffatt, M.; Minelli, C.; De Matteis, S.; Cherrie, J.W.; Newman Taylor, A.; Cullinan, P. What role for asbestos in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Findings from the IPF job exposures case-control study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2023, 80, 97–103, Erratum in Occup. Environ. Med. 2023, 80, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, I.; Drummond, G.B.; Nirmalan, M. Distribution of blood flow and ventilation in the lung: Gravity is not the only factor. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 98, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.R.; O’Shaughnessy, P.; Tawhai, M.H.; Hoffman, E.A.; Lin, C.-L. Regional deposition of particles in an image-based airway model: Large-eddy simulation and left-right lung ventilation asymmetry. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ferin, J. Observations concerning alveolar dust clearance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1972, 200, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Oberdorster, G. Lung dosimetry: Pulmonary clearance of inhaled particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1993, 18, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, B.E. Pulmonary and thoracic macrophage subpopulations and clearance of particles from the lung. Environ. Health Perspect. 1992, 97, 17–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Cox, C.; Gelein, R. Intratracheal instillation versus intratracheal-inhalation of tracer particles for measuring lung clearance function. Exp. Lung Res. 1997, 23, 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, Y.; Ishii, H.; Hogg, J.C.; Shih, C.H.; Yatera, K.; Vincent, R.; van Eeden, S.F. Particulate matter air pollution stimulates monocyte release from the bone marrow. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H. A quantitative and qualitative study of blood monocytes in smokers. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. 1985, 66, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Nemmar, A.; Inuwa, I.M. Diesel exhaust particles in blood trigger systemic and pulmonary morphological alterations. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 176, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruske, I.; Hampel, R.; Socher, M.M.; Ruckerl, R.; Schneider, A.; Heinrich, J.; Oberdörster, G.; Wichmann, H.E.; Peters, A. Impact of ambient air pollution on the differential white blood cell count in patients with chronic pulmonary disease. Inhal. Toxicol. 2010, 22, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.C.; Hwang, J.J.; Yang, Y.R.; Chan, C.C. Association Between Long-term Exposure to Traffic-related Air Pollution and Inflammatory and Thrombotic Markers in Middle-aged Adults. Epidemiology 2017, 28 (Suppl. 1), S74–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekici, Y.; Yilmaz, M.; Secen, O. New inflammatory indicators: Association of high eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and low lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio with smoking. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 4292–4303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, N.; Jary, H.; Lea, S.; Khan, N.; Piddock, K.C.; Dockrell, D.H.; Donaldson, K.; Duffin, R.; Singh, D.; Parker, L.C.; et al. Diesel exhaust particle exposure in vitro alters monocyte differentiation and function. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51107. [Google Scholar]
- Rom, W.N. Basic mechanisms leading to focal emphysema in coal workers’ pneumoconiosis. Environ. Res. 1990, 53, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, W.A.; Gillooly, M.; Lamb, D. Intra-alveolar macrophage numbers in current smokers and non-smokers: A morphometric study of tissue sections. Thorax 1992, 47, 437–440. [Google Scholar]
- Clarà, P.C.; Jerez, F.R.; Ramírez, J.B.; González, C.M. Deposition and Clinical Impact of Inhaled Particles in the Lung. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2023, 59, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdorster, G. Lung particle overload: Implications for occupational exposures to particles. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1995, 21, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, P.E. Dust overloading of the lungs: Update and appraisal. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1992, 113, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.P.; Chen, Y.K.; Morrow, P.E. An analysis of alveolar macrophage mobility kinetics at dust overloading of the lungs. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1989, 13, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, A.G.; Muggenburg, B.A.; Snipes, M.B.; Bice, D.E. The role of macrophages in particle translocation from lungs to lymph nodes. Science 1985, 230, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.R.; Lambert, L.; Pantin, C.F.; Prowse, K.; Cole, R.B. Silicosis presenting as bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. Thorax 1996, 51, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.; Kirchner, E.M.; Goltz, J.P.; Lorenz, V.-M.; Kickuth, R. Prevalence of enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes in heavy smokers—A comparative study. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, A.P.C.; Justo, L.T.; Dos Santos, N.V.; Marquezini, M.V.; de André, P.A.; da Rocha, F.M.M.; Pasqualucci, C.A.; Barrozo, L.V.; Singer, J.M.; De André, C.D.S.; et al. Pleural anthracosis as an indicator of lifetime exposure to urban air pollution: An autopsy-based study in Sao Paulo. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferin, J.; Oberdörster, G. Translocation of particles from pulmonary alveoli into the interstitium. J. Aerosol. Med. 1992, 5, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, R.F.; Shepherd, S.; Levin, J.; Hammar, S.P. Characteristics of asbestos concentration in lung as compared to asbestos concentration in various levels of lymph nodes that collect drainage from the lung. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2007, 31, 95–133148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabeyrin, M.; Thivolet, F.; Ferretti, G.R.; Chalabreysse, L.; Jankowski, A.; Cottin, V.; Pison, C.; Cordier, J.F.; Lantuejoul, S. Usual interstitial pneumonia end-stage features from explants with radiologic and pathological correlations. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 19, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, A.G.; Fulford, L.G.; Colby, T.V.; du Bois, R.M.; Hansell, D.M.; Wells, A.U. The relationship between individual histologic features and disease progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
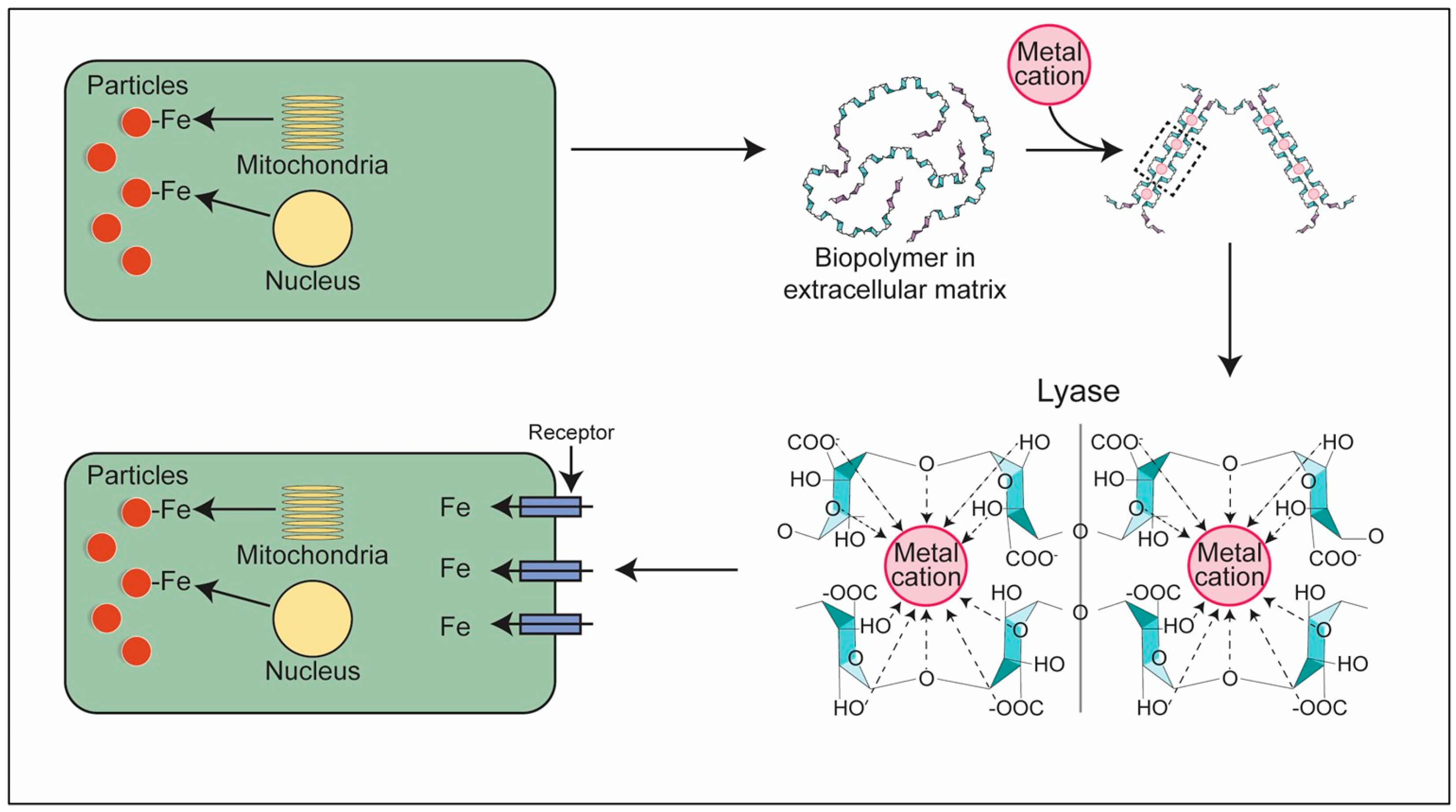
- Ghio, A.J.; Tong, H.; Soukup, J.M.; Dailey, L.A.; Cheng, W.Y.; Samet, J.M.; Kesic, M.J.; Bromberg, P.A.; Turi, J.L.; Upadhyay, D.; et al. Sequestration of mitochondrial iron by silica particle initiates a biological effect. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 305, L712–L724, Erratum in Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2018, 315, L919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghio, A.J.; Soukup, J.M.; Dailey, L.A.; Madden, M.C. Air pollutants disrupt iron homeostasis to impact oxidant generation, biological effects, and tissue injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 151, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, A.J.; Hilborn, E.D.; Stonehuerner, J.G.; Dailey, L.A.; Carter, J.D.; Richards, J.H.; Crissman, K.M.; Foronjy, R.F.; Uyeminami, D.L.; Pinkerton, K.E. Particulate matter in cigarette smoke alters iron homeostasis to produce a biological effect. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, S.E.; Murray, J.J.; Parrish, M.G. Iron binding, internalization, and fate in human alveolar macrophages. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1986, 108, 587–595. [Google Scholar]
- Wesselius, L.J.; Nelson, M.E.; Skikne, B.S. Increased release of ferritin and iron by iron-loaded alveolar macrophages in cigarette smokers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.E.; O’Brien-Ladner, A.R.; Wesselius, L.J. Regional variation in iron and iron-binding proteins within the lungs of smokers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, S.A.; Finley, T.N.; Smith, M.H.; Ladman, A.J. A comparison of alveolar macrophages and pulmonary surfactant (?) obtained from the lungs of human smokers and nonsmokers by endobronchial lavage. Anat. Rec. 1969, 163, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombat, M.; Mal, H.; Groussard, O.; Capron, F.; Thabut, G.; Jebrak, G.; Brugiere, O.; Dauriat, G.; Castier, Y.; Leseche, G.; et al. Pulmonary vascular lesions in end-stage idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Histopathologic study on lung explant specimens and correlations with pulmonary hemodynamics. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Maldonado, F.; Ryu, J.H.; Eiken, P.W.; Hartman, T.E.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Decker, P.A.; Yi, E.S. Iron deposition and increased alveolar septal capillary density in nonfibrotic lung tissue are associated with pulmonary hypertension in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2010, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxeddu, E.; Comandini, A.; Cavalli, F.; Pezzuto, G.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Senis, L.; Paci, M.; Curradi, G.; Sergiacomi, G.L.; Saltini, C. Iron laden macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: The telltale of occult alveolar hemorrhage? Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 28, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghio, A.J.; Roggli, V.L. Perls’ Prussian Blue Stains of Lung Tissue, Bronchoalveolar Lavage, and Sputum. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2021, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popper, H.; Murer, B. Chapter 22. Smoking-related diseases. In Pulmonary Pathology; Essentials of Diagnostic Pathology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 325–344. [Google Scholar]
- Sangiuolo, F.; Puxeddu, E.; Pezzuto, G.; Cavalli, F.; Longo, G.; Comandini, A.; Di Pierro, D.; Pallante, M.; Sergiacomi, G.; Simonetti, G.; et al. HFE gene variants and iron-induced oxygen radical generation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukihara, J.; Taniguchi, H.; Ando, M.; Kondoh, Y.; Kimura, T.; Kataoka, K.; Furukawa, T.; Johkoh, T.; Fukuoka, J.; Sakamoto, K.; et al. Hemosiderin-laden macrophages are an independent factor correlated with pulmonary vascular resistance in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A case control study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Kagawa, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Sugawara, R.; Sugimoto, C.; Tachibana, K.; Fujita, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Inoue, Y. Hemosiderin-Laden Macrophages in Bronchoalveolar Lavage: Predictive Role for Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Can. Respir. J. 2021, 2021, 4595019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutti, A.; Corradi, M.; Goldoni, M.; Vettori, M.V.; Bernard, A.; Apostoli, P. Exhaled metallic elements and serum pneumoproteins in asymptomatic smokers and patients with COPD or asthma. Chest 2006, 129, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumby, S.; Saito, J.; Adcock, I.M.; Chung, K.F.; Quinlan, G.J. Decreased breath excretion of redox active iron in COPD: A protective failure? Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, A.J.; Soukup, J.M.; McGee, J.; Madden, M.C.; Esther, C.R. Iron concentration in exhaled breath condensate decreases in ever-smokers and COPD patients. J. Breath. Res. 2018, 12, 046009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, J.J.; Kohlhepp, P.; Zhang, D.; Winzerling, J.J. Effects of sham air and cigarette smoke on A549 lung cells: Implications for iron-mediated oxidative damage. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 286, L866–L876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schonfeld, E.; Yasharel, I.; Yavin, E.; Brand, A. Docosahexaenoic acid enhances iron uptake by modulating iron transporters and accelerates apoptotic death in PC12 cells. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, C.; Jian, L.; Guo, S.; Chen, R.; Li, K.; Qu, F.; Tao, K.; Fu, Y.; Luo, F.; et al. Sulfasalazine induced ferroptosis in breast cancer cells is reduced by the inhibitory effect of estrogen receptor on the transferrin receptor. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Line, B.R.; Fulmer, J.D.; Reynolds, H.Y.; Roberts, W.C.; Jones, A.E.; Harris, E.K.; Crystal, R.G. Gallium-67 citrate scanning in the staging of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Correlation and physiologic and morphologic features and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1978, 118, 355–365. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Liang, G.; Qin, H.; Peng, X.; Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Qing, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Ye, L.; et al. p53-Dependent apoptosis induced in human bronchial epithelial (16-HBE) cells by PM2.5 sampled from air in Guangzhou, China. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2014, 24, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, R.U.; Wereley, J.P.; Chitambar, C.R. Induction of apoptosis by iron deprivation in human leukemic CCRF-CEM cells. Exp. Hematol. 1995, 23, 428–432. [Google Scholar]
- Hileti, D.; Panayiotidis, P.; Hoffbrand, A.V. Iron chelators induce apoptosis in proliferating cells. Br. J. Haematol. 1995, 89, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.H.; Chen, J.H.; Lin, H.H.; Chen, B.C.; Hsu, J.D.; Wang, C.J. Induction of apoptosis in the lung tissue from rats exposed to cigarette smoke involves p38/JNK MAPK pathway. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2005, 155, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, Q.; Deslee, G.; Adair-Kirk, T.L.; Woods, J.C.; Byers, D.; Conradi, S.; Dury, S.; Perotin, J.M.; Lebargy, F.; Cassan, C.; et al. Increased iron sequestration in alveolar macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96285, Correction in PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.H.; Soukup, J.M.; Madden, M.C.; Hays, M.; Berntsen, J.; Paulson, S.E.; Ghio, A.J. A Fulvic Acid-like Substance Participates in the Pro-inflammatory Effects of Cigarette Smoke and Wood Smoke Particles. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Retherford, R.D. Does biofuel smoke contribute to anaemia and stunting in early childhood? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutou, A.K.; Stanopoulos, I.; Pitsiou, G.G.; Kontakiotis, T.; Kyriazis, G.; Sichletidis, L.; Argyropoulou, P. Anemia of chronic disease in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A case-control study of cardiopulmonary exercise responses. Respiration 2011, 82, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, V.; Ish, P.; Singh, G.; Tiwari, M.; Goel, N.; Gaur, S.N. Iron deficiency in non-anemic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a predominantly male population: An ignored entity. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. Arch. Monaldi Mal. Torace 2020, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andarge, S.D.; Areba, A.S.; Kabthymer, R.H.; Legesse, M.T.; Kanno, G.G. Is Indoor Air Pollution from Different Fuel Types Associated with the Anemia Status of Pregnant Women in Ethiopia? J. Prim. Care Community Health 2021, 12, 21501327211034374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesina, A.M.; Vallyathan, V.; McQuillen, E.N.; Weaver, S.O.; Craighead, J.E. Bronchiolar inflammation and fibrosis associated with smoking. A morphologic cross-sectional population analysis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 143, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churg, A.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Onnervik, P.O.; Thim, K.; Wright, J.L. Effect of an MMP-9/MMP-12 inhibitor on smoke-induced emphysema and airway remodelling in guinea pigs. Thorax 2007, 62, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.L.; Postma, D.S.; Kerstjens, H.A.; Timens, W.; Whittaker, P.; Churg, A. Airway remodeling in the smoke exposed guinea pig model. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concórdio-Reis, P.; Martins, M.; Araújo, D.; Alves, V.D.; Moppert, X.; Guézennec, J.; Reis, M.A.M.; Freitas, F. Iron(III) cross-linked hydrogels based on Alteromonas macleodii Mo 169 exopolysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Yang, Z.; Fan, W.; Huang, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, W. Epigenetic modification of a pectin methylesterase gene activates apoplastic iron reutilization in tomato roots. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 2339–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.F.; Tun, H.C. The degradation of hyaluronic acid by ferrous ions. Carbohydr. Res. 1972, 22, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merce, A.L.; Marques Carrera, L.C.; Santos Romanholi, L.K.; Lobo Recio, M.A. Aqueous andsolid complexes of iron(III) with hyaluronic acid. Potentiometric titrations and infrared spectroscopy studies. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2002, 89, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracke, K.R.; Dentener, M.A.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Vernooy, J.H.; Demoor, T.; Pauwels, N.S.; Cleutjens, J.; van Suylen, R.J.; Joos, G.F.; Brusselle, G.G.; et al. Enhanced deposition of low-molecular-weight hyaluronan in lungs of cigarette smoke-exposed mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 42, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, H.; Tung, C.H.; Zhang, W. Hijacking the hyaluronan assisted iron endocytosis to promote the ferroptosis in anticancer photodynamic therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 351, 123123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galy, B.; Conrad, M.; Muckenthaler, M. Mechanisms controlling cellular and systemic iron homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 133–155, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Sindikubwabo, F.; Cañeque, T.; Lafon, A.; Versini, A.; Lombard, B.; Loew, D.; Wu, T.D.; Ginestier, C.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; et al. CD44 regulates epigenetic plasticity by mediating iron endocytosis. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Yao, X.; Xu, K.; Wu, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, N.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O.; Jiang, F. Trivalent iron induced gelation in Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch. polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R.; Qin, Z.; Ji, F.; Xu, M.; Tian, X.; Li, J.; Yao, F. Hybrid pectin-Fe3+/polyacrylamide double network hydrogels with excellent strength, high stiffness, superior toughness and notch-insensitivity. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 9237–9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.; Liu, S.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Tan, X.; Chi, B. Biomimetic poly(γ-glutamic acid) hydrogels based on iron (III) ligand coordination for cartilage tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Putman, R.K.; Hatabu, H.; Gao, W.; Dupuis, J.; Latourelle, J.C.; Nishino, M.; Zazueta, O.E.; Kurugol, S.; Ross, J.C.; et al. Development and Progression of Interstitial Lung Abnormalities in the Framingham Heart Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, A.J.; Soukup, J.M.; Dailey, L.A.; Roggli, V.L. Mucus increases cell iron uptake to impact the release of pro-inflammatory mediators after particle exposure. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peric, L.; Pereira, C.S.; Perez, S.; Hunenberger, P.H. Conformation, dynamics and ion-binding properties of single-chain polyuronates: A molecular dynamics study. Mol. Simul. 2008, 34, 421–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, G.Y.; Hong, Y.; Gu, Z.B.; Fang, F. Calcium cation triggers and accelerates the gelation of high methoxy pectin. Food Hydrocolloid 2013, 32, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawkowska, D.; Cybulska, J.; Zdunek, A. Structure-related gelling of pectins and linking with other natural compounds: A review. Polymers 2018, 10, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, H.; Schmut, O. The inability of superoxide dismutase to inhibit the depolymerization of hyaluronic acid by ferrous ions and ascorbate. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch. Klin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1980, 214, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, G.T.; Illes, J.; Szekely, Z.; Forrai, E.; Gere, A. Effect of different metal ions on the oxidative damage and antioxidant capacity of hyaluronic acid. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 410, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, W.; Wei, D.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Rahman, M.M.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z.; Ma, Y. Purification and characterisation of a bifunctional alginate lyase from novel Isoptericola halotolerans CGMCC 5336. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornsunthorntawee, O.; Katepetch, C.; Vanichvattanadecha, C.; Saito, N.; Rujiravanit, R. Depolymerization of chitosan-metal complexes via a solution plasma technique. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Long, J.X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, L.; Li, Y. Phenolics production through catalytic depolymerization of alkali lignin with metal chlorides. Bioresources 2014, 9, 3347–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Long, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Ma, L. Efficient and product-controlled depolymerization of lignin oriented by metal chloride cooperated with Pd/C. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Zhou, J.; Tan, Z.; Yuan, M.; Yao, P.; Liu, X. Characterization of a novel alginate lyase from marine bacterium Vibrio furnissii H1. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunter, E.A.; Popeyko, O.V.; Melekhin, A.K.; Belozerov, V.S.; Martinson, E.A.; Litvinets, S.G. Preparation and properties of the pectic gel microparticles based on the Zn2+, Fe3+ and Al3+ cross-linking cations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J. The pectin lyases in Arabidopsis thaliana: Evolution, selection and expression profiles. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franza, T.; Sauvage, C.; Expert, D. Iron regulation and pathogenicity in Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937: Role of the Fur repressor protein. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1999, 12, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; da Silva, R.; Silva, D.; Gomes, E. Production of pectate lyase by Penicillium viridicatum RFC3 in solid-state and submerged fermentation. Int. J. Microbiol. 2010, 2010, 276590. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Wen, S.; Liao, S.; Wang, Q.; Pan, S.; Zhang, R.; Lei, F.; Liao, W.; Feng, J.; Huang, S. Characterization of a bifunctional alginate lyase as a new member of the polysaccharide lyase family 17 from a marine strain BP-2. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, J.; Rodriguez-Eaton, S.; Ekanemesang, U.M.; Phillips, P. Characterization of metal-binding bioflocculants produced by the cyanobacterial component of mixed microbial mats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2311–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.J.; Soper, B.W.; Tang, J.; Bradley, R.L. Phenotypic variation in exopolysaccharide production in the marine, aerobic nitrogen-fixing unicellular cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 12, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franza, T.; Michaud-Soret, I.; Piquerel, P.; Expert, D. Coupling of iron assimilation and pectinolysis in Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Nout, M.J.; Liang, J. Effect of neutrase, alcalase, and papain hydrolysis of whey protein concentrates on iron uptake by Caco-2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4894–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Micheletti, E.; Zille, A.; Santos, A.; Moradas-Ferreira, P.; Tamagnini, P.; De Philippis, R. Using extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)-producing cyanobacteria for the bioremediation of heavy metals: Do cations compete for the EPS functional groups and also accumulate inside the cell? Microbiology 2011, 157 Pt 2, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asperti, M.; Stuemler, T.; Poli, M.; Gryzik, M.; Lifshitz, L.; Meyron-Holtz, E.G.; Vlodavsky, I.; Arosio, P. Heparanase overexpression reduces hepcidin expression, affects iron homeostasis and alters the response to inflammation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liang, W.; Xiong, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Rong, J.; Xiong, S.; Liu, R.; You, J.; Yin, T.; et al. Digestion and absorption characteristics of iron-chelating silver carp scale collagen peptide and insights into their chelation mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosmus, J.; Vancikova, O.; Marc, J.; Deyl, Z. Studies on the structure of collagen V. The site of binding of trivalent iron on collagen. Experientia 1967, 23, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannes, P.L. Cytochemical visualization of anions in collagenous and elastic fiber-associated connective tissue matrix in neonatal and adult rat lungs using iron-containing stains. Histochemistry 1986, 84, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Yang, J.I.; Li, Y.H.; Kuo, J.M. Evaluation of iron-binding activity of collagen peptides prepared from the scales of four cultivated fishes in Taiwan. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagy, J.R.; Kronstadt, R.A. Iron as a tanning agent. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1943, 31, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathima, N.N.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U. Effect of UV irradiation on the physico-chemical properties of iron crosslinked collagen. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2011, 105, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardi, C.; Arezzini, B.; Fortino, V.; Comporti, M. Effect of free iron on collagen synthesis, cell proliferation and MMP-2 expression in rat hepatic stellate cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairuae, N.; Connor, J.R.; Cheepsunthorn, P. Increased cellular iron levels affect matrix metalloproteinase expression and phagocytosis in activated microglia. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 500, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X. Inhibiting effects of common trivalent metal ions on transmembrane-type 2 matrix metalloproteinase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsuka, R.; Terashima, M.; Ishimura, A.; Suzuki, T.; Takino, T. Iron regulates MT1-MMP-mediated proMMP-2 activation and cancer cell invasion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 742, 151124. [Google Scholar]
- Pieraggi, M.; Nejjar, I.; Julian, M.; Bouissou, H. Staining of elastic tissue by Verhoeff’s iron hematoxylin. Ann. Pathol. 1986, 6, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Tilson, M.D. Histochemistry of aortic elastin in patients with nonspecific abdominal aortic aneurysmal disease. Arch. Surg. 1988, 123, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, H.; Wu, G.Y.; Wu, C.H. Evidence that an iron chelator regulates collagen synthesis by decreasing the stability of procollagen mRNA. Hepatology 1992, 15, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunda, S.; Kaviani, N.; Hinek, A. Fluctuations of intracellular iron modulate elastin production. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, F.; Fan, D.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y. Higher iron bioavailability of a human-like collagen iron complex. J. Biomater. Appl. 2017, 32, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, G.; Pigman, W. Catalytic role of copper and iron ions in the depolymerization of hyaluronic acid by ascorbic acid. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1965, 110, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.J.; Herp, A.; Pigman, W. Metal catalysis in the depolymerization of hyaluronic acid by autoxidants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 7570–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickrell, J.A.; Diel, J.H.; Slauson, D.O.; Halliwell, W.H.; Mauderly, J.L. Radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis resolves spontaneously if dense scars are not formed. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 1983, 38, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Kisseleva, T. Reversibility of liver fibrosis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2015, 39 (Suppl. 1), S60–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasser, S.W.; Hagood, J.S.; Wong, S.; Taype, C.A.; Madala, S.K.; Hardie, W.D. Mechanisms of Lung Fibrosis Resolution. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Juan, Y.H.; Hu, H.C.; Kao, K.C.; Lee, C.S. Reversal of lung fibrosis: An unexpected finding in survivor of acute respiratory distress syndrome. QJM 2018, 111, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, L.F.; Rubak, S. Reversible lung fibrosis in a 6-year-old girl after long term nitrofurantoin treatment. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, J.F. Cryptogenic organising pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 422–446. [Google Scholar]
- Akira, M.; Inoue, G.; Yamamoto, S.; Sakatani, M. Non-specific interstitial pneumonia: Findings on sequential CT scans of nine patients. Thorax 2000, 55, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, A.J.; Pavlisko, E.N.; Roggli, V.L.; Todd, N.W.; Sangani, R.G. Cigarette Smoke Particle-Induced Lung Injury and Iron Homeostasis. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2022, 17, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.W.; Liao, S.; Curci, J.A. Vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Coron. Artery Dis. 1997, 8, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentimalli, L.; Modesti, A.; Vignati, A.; Marchese, E.; Albanese, A.; Di Rocco, F.; Coletti, A.; Di Nardo, P.; Fantini, C.; Tirpakova, B.; et al. Role of apoptosis in intracranial aneurysm rupture. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 101, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, T.; Hingorani, A.; Ascher, E. Role of apoptosis and proteolysis in the pathogenesis of iliac artery aneurysms. Vascular 2005, 13, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, S.O.; Celik, S.; Erturhan, S.; Erbagci, A.; Yagci, F.; Ucak, R. Verapamil prevents the apoptotic and hemodynamic changes in response to unilateral ureteral obstruction. Int. J. Urol. 2008, 15, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, W.R. Thin-section CT of the secondary pulmonary lobule: Anatomy and the image—The 2004 Fleischner lecture. Radiology 2006, 239, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staats, P.; Kligerman, S.; Todd, N.; Tavora, F.; Xu, L.; Burke, A. A comparative study of honeycombing on high resolution computed tomography with histologic lung remodeling in explants with usual interstitial pneumonia. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2015, 211, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piciucchi, S.; Tomassetti, S.; Ravaglia, C.; Gurioli, C.; Gurioli, C.; Dubini, A.; Carloni, A.; Chilosi, M.; Colby, T.V.; Poletti, V. From “traction bronchiectasis” to honeycombing in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A spectrum of bronchiolar remodeling also in radiology? BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternostro, R.; Kapzan, L.; Mandorfer, M.; Schwarzer, R.; Benedikt, S.; Viveiros, A.; Bauer, D.; Ferlitsch, M.; Zoller, H.; Trauner, M.; et al. Anemia and iron deficiency in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis: Prevalence and impact on clinical outcomes. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

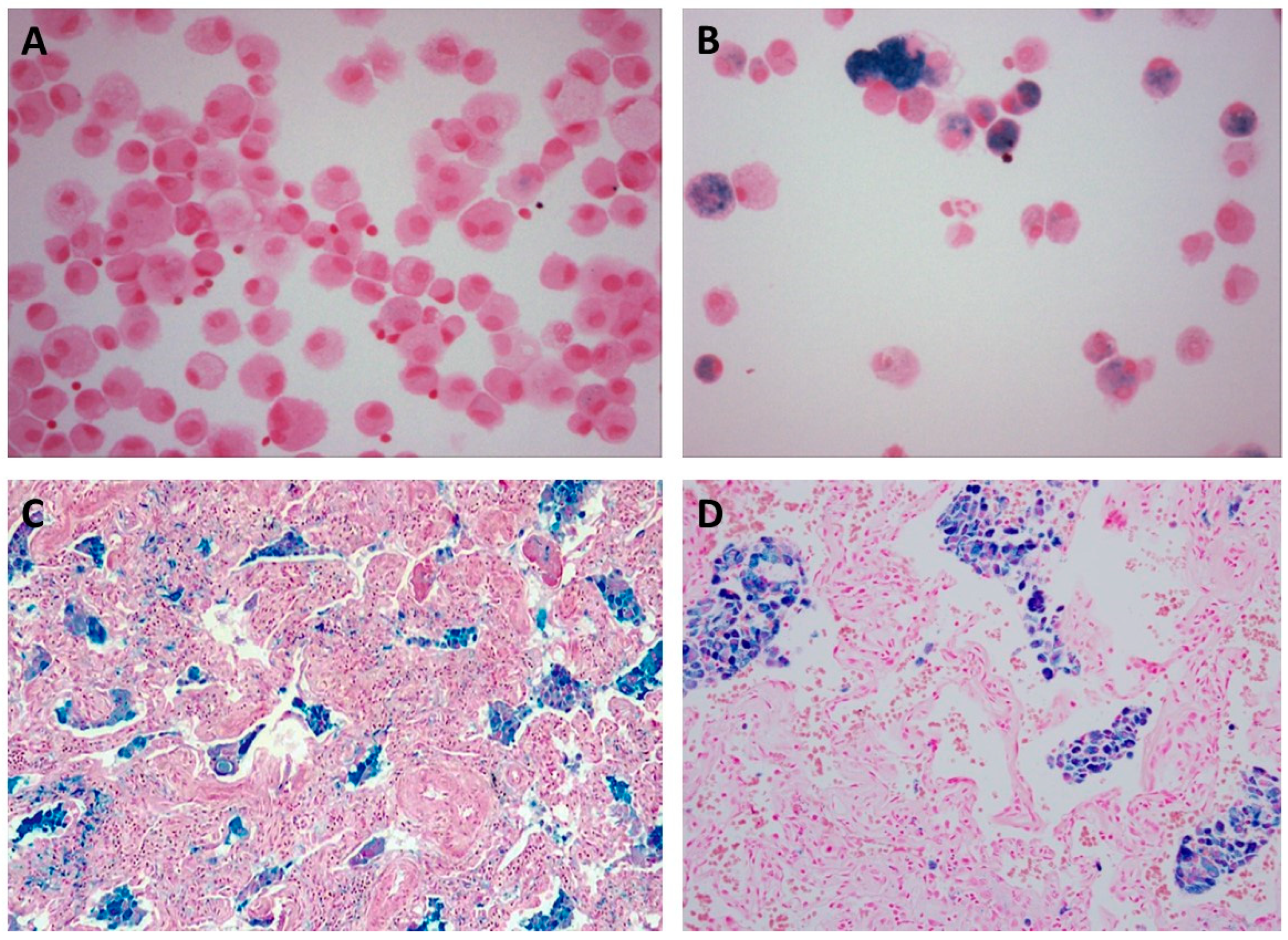


| Occupation(s) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|
| Stone cutting/polishing | [67] |
| Mining | [67] |
| Insulating | [67] |
| Work in a chalk plant | [68] |
| Teaching | [69] |
| Metallurgical and steel industry work | [70] |
| Dentist, dental hygienist, or dental technician | [71,72] |
| Agricultural work and farming | [31,37,70,71,73,74,75,76,77] |
| Livestock work | [67,70] |
| Veterinarians and gardeners | [70] |
| Carpentry work and woodworking | [67,71] |
| Hairdresser | [67] |
| Chemical and petrochemical industries | [67,71] |
| Exposure(s) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|
| Respirable dusts, smoke, gases, or chemicals | [32,36] |
| Inorganic particles | [63,79,80] |
| Silicon and aluminum | [81] |
| Silica and silicates | [82,83] |
| Silica and minerals | [84] |
| Aluminum silicate | [85] |
| Chalk/silica and silicates | [68,69] |
| Stone, sand, or silica | [86] |
| Stone and sand dust | [87] |
| Asbestos | [36,82,88,89,90] |
| Coal | [91] |
| Silica | [92,93,94] |
| Mineral dusts | [90] |
| Metal dusts and fumes | [37,67,70,76,84,87,90,95,96,97,98,99] |
| Aluminum trihydrate (Corian) dust | [100] |
| Organic dust | [70] |
| Vegetable dusts | [67] |
| Organic dusts | [76] |
| Organic dust (livestock/agriculture/farming) | [96,101] |
| Animal dusts | [69] |
| Animal feeds | [71] |
| Moulds/birds | [101] |
| Soil | [31,73,74,75] |
| Wood dust | [37,73,76,84,97,102] |
| Wood dusts (birch and hardwood) | [103] |
| Wood preservatives | [71] |
| Industrial wood smoke | [104] |
| Diesel exhaust particles | [30] |
| Pesticides | [37,71,76] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghio, A.J.; Sangani, R.G.; Todd, N.W. The Role of Particle Inhalation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8736. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178736
Ghio AJ, Sangani RG, Todd NW. The Role of Particle Inhalation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8736. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178736
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhio, Andrew J., Rahul G. Sangani, and Nevins W. Todd. 2025. "The Role of Particle Inhalation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8736. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178736
APA StyleGhio, A. J., Sangani, R. G., & Todd, N. W. (2025). The Role of Particle Inhalation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8736. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178736





