The X-Linked TLR7 rs179008 T Allele Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Severe Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children/Kawasaki-like Syndrome in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Boys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
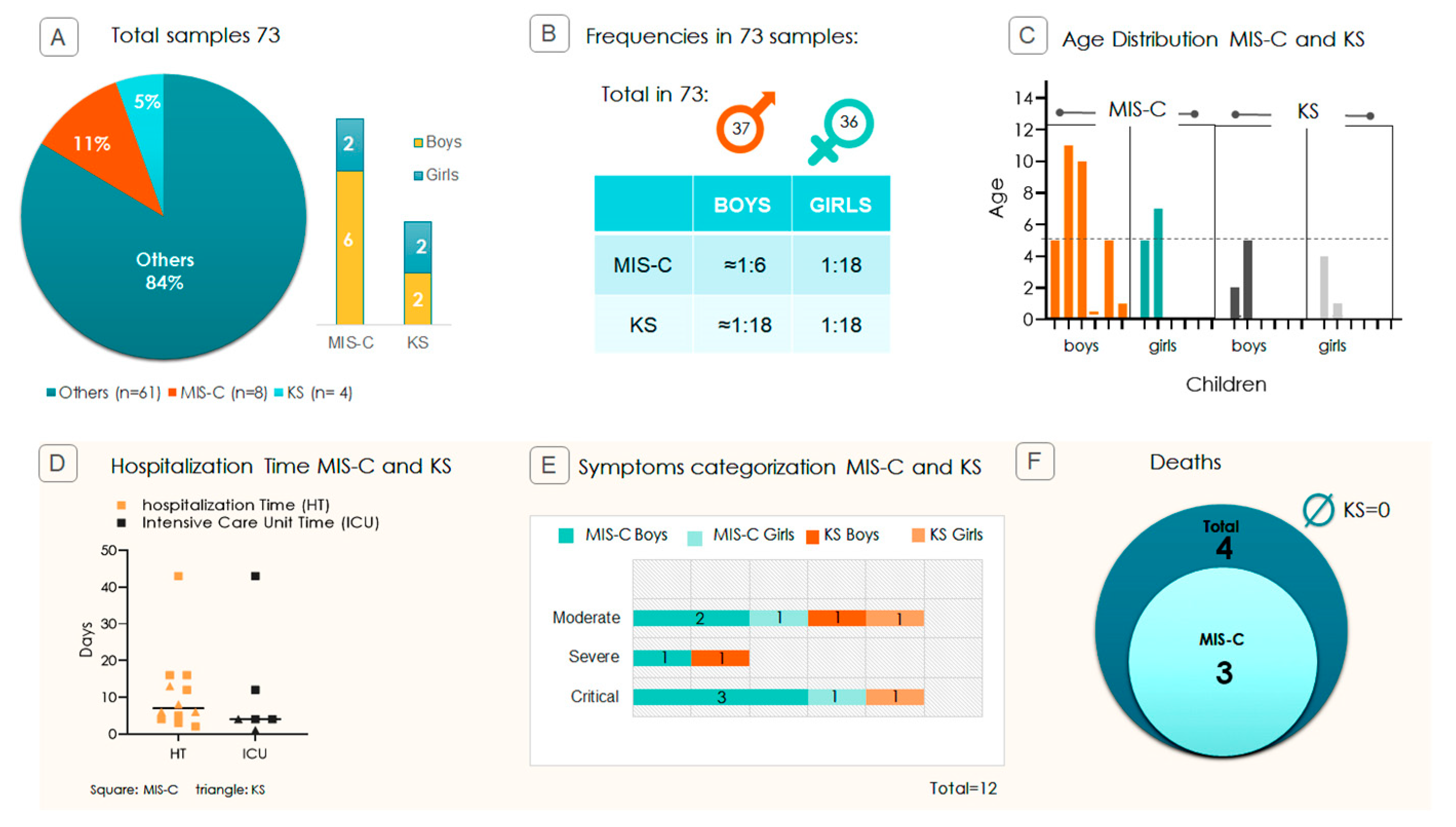
2.1. Pediatric Study Profile and Disease Severity
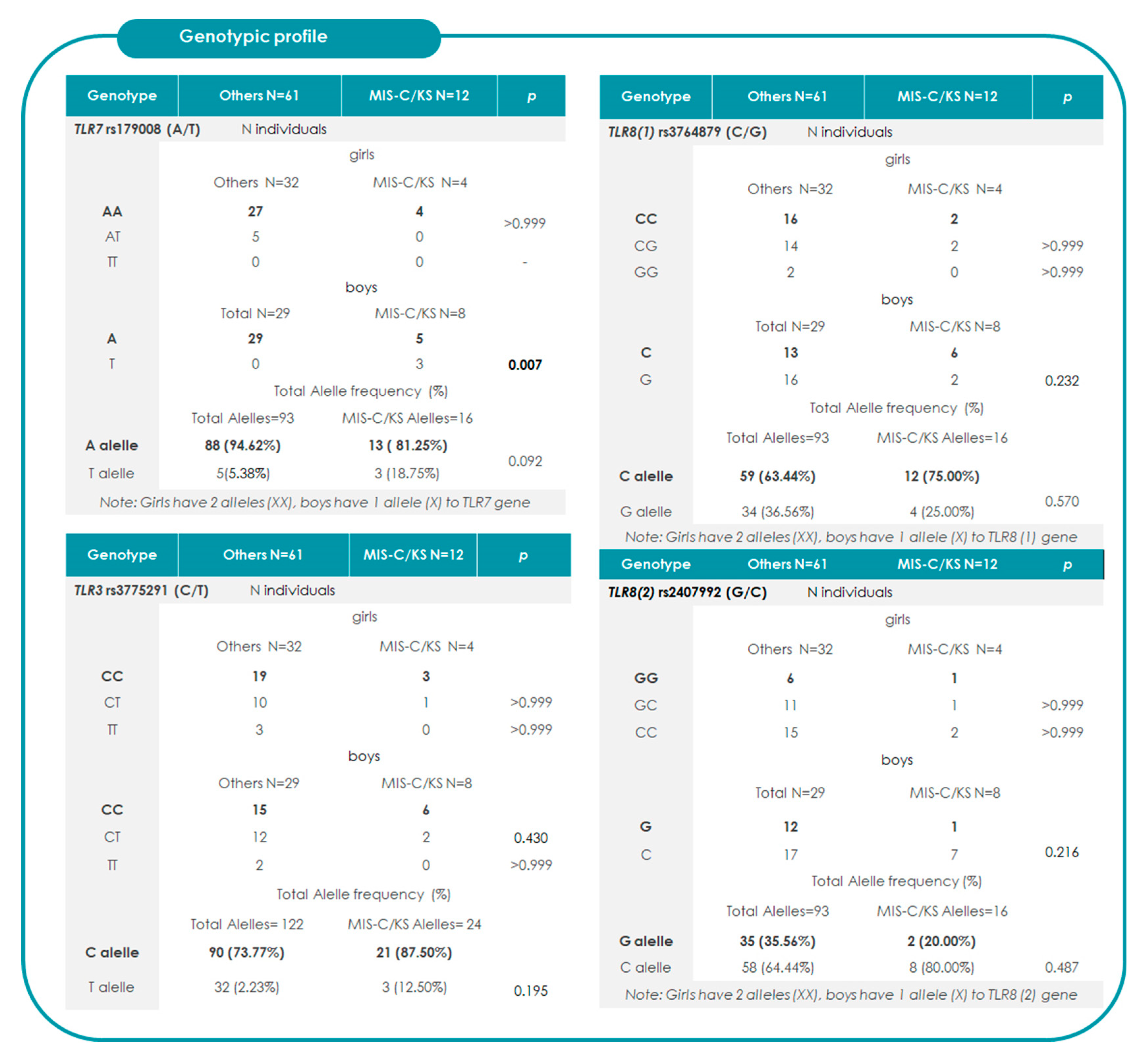
2.2. Association Between TRLs and the Risk of Progression to MIS-C/KS
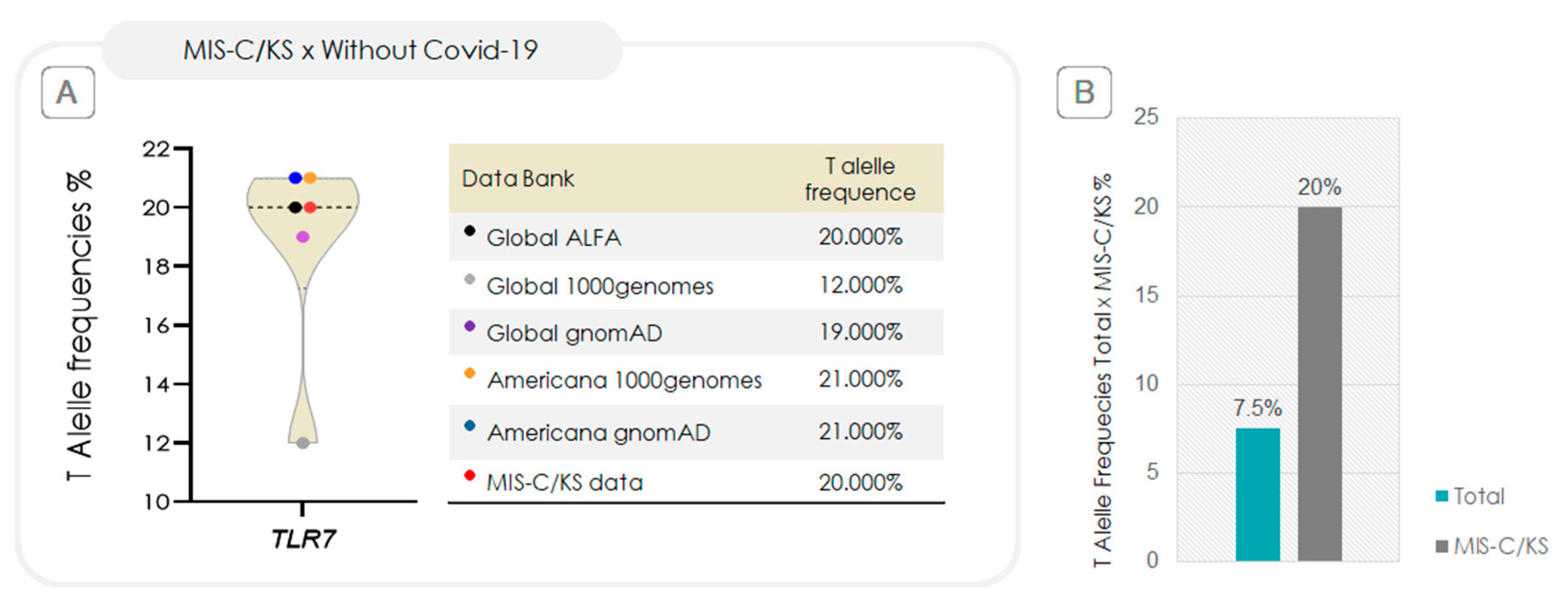
2.3. Relative-Risk Analysis for the Association of TLR7 rs179008 in Relation to Progression to MIS-C/KS and Clinical Severity
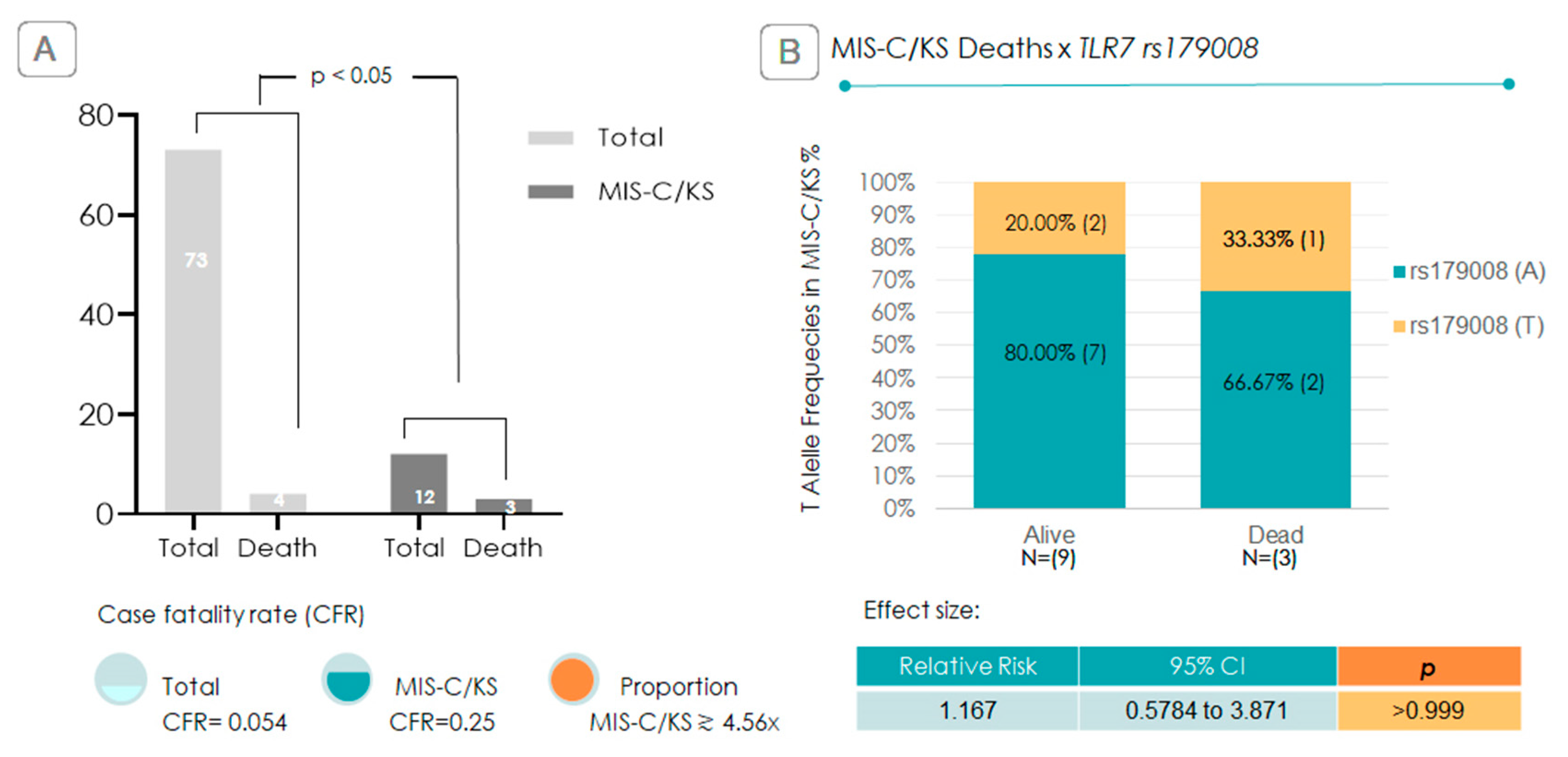
2.4. Is the TLR7 rs179008 T Allele Associated with Increased Mortality?
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Approval and Written Consent
4.2. Design and Sampling
4.3. Identification and Severity Classification
4.4. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
4.5. Sequencing and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HT | Hospitalization time |
| ICU | Intensive care units |
| IFN-I | Type I interferon |
| KS | Kawasaki disease |
| MIS-C | Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| RR | Relative risk |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphisms |
| TLR, TLR | Tolllike receptor, gene TLR |
References
- Kitano, T.; Kitano, M.; Krueger, C.; Jamal, H.; Al Rawahi, H.; Lee-Krueger, R.; Sun, R.D.; Isabel, S.; García-Ascaso, M.T.; Hibino, H.; et al. The differential impact of pediatric COVID-19 between high-income countries and low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review of fatality and ICU admission in children worldwide. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Child Mortality and COVID-19. 2023. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-survival/covid-19/ (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Instituto Butantan. COVID-19 Já Matou Mais De 1.400 Crianças De Zero A 11 Anos No Brasil E Deixou Outras Milhares Com Sequelas. 2022. Available online: https://butantan.gov.br/noticias/covid-19-ja-matou-mais-de-1.400-criancas-de-zero-a-11-anos-no-brasil-e-deixou-outras-milhares-com-sequelas (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Sun, Y.K.; Wang, C.; Lin, P.Q.; Hu, L.; Ye, J.; Gao, Z.G.; Lin, R.; Li, H.M.; Shu, Q.; Huang, L.S.; et al. Severe pediatric COVID-19: A review from the clinical and immunopathophysiological perspectives. World J. Pediatr. 2024, 20, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Information for Pediatric Healthcare Providers. 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/covid/hcp/clinical-care/for-pediatric-hcp.html (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) COVID-19 Response Team. Severe Outcomes Among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)—United States, February 12–March 16, 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/wr/mm6912e2.htm (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Jain, S.S.; Harahsheh, A.S.; Lee, S.; Raghuveer, G.; Dahdah, N.; Khoury, M.; Portman, M.A.; Wehrmann, M.; Sabati, A.A.; Fabi, M.; et al. Factors associated with shock at presentation in Kawasaki Disease versus Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children associated with COVID-19. Can. J. Cardiol. 2025, 41, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, A.H. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MISC) and Kawasaki disease: Two different illnesses with overlapping clinical features. J. Pediatr. 2020, 224, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Arditi, M. Kawasaki Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: Common Inflammatory Pathways of Two Distinct Diseases. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 49, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.J.; Jarovsky, D.; Almeida Farias, C.G.; Ramos Nantes de Castilho, T.R.; Gara Caetano, T.; Manzoni Ribeiro Borsetto, C.C.; Simões Aguiar, A.; Serafini de Araújo, C.; Badue Pereira, M.F.; de Sousa Marques, H.H.; et al. High Fatality Rates in Pediatric Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome: A Multicenter Experience From the Epicenter of Brazil’s Coronavirus Pandemic. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2024, 43, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Harahsheh, A.S.; Raghuveer, G.; Jain, S.; Choueiter, N.F.; Garrido-Garcia, L.M.; Dahdah, N.; Portman, M.A.; Misra, N.; Khoury, M.; et al. Emerging insights into the pathophysiology of multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with COVID-19 in children. Can. J. Cardiol. 2023, 39, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.A.; Huang, Y.L.; Chiang, B.L. Innate immune response analysis in COVID-19 and kawasaki disease reveals MISC predictors. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2022, 121, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, L.; Campbell, M.J.; Wu, E.Y. Multisystemic Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Kawasaki Disease: Parallels in Pathogenesis and Treatment. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023, 23, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.T.; Tzvetkov, E.; Pereira, A.; Wu, Y.; Kasar, S.; Przetak, M.M.; Vlach, J.; Niewold, T.B.; Jensen, M.A.; Okitsu, S.L. TLR7 and TLR8 differentially activate the IRF and NF-κB pathways in specific cell types to promote inflammation. ImmunoHorizons 2020, 4, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, S.; Daga, S.; Fallerini, C.; Baldassarri, M.; Benetti, E.; Picchiotti, N.; Fava, F.; Gallì, A.; Zibellini, S.; Bruttini, M. Rare variants in Toll-like receptor 7 result in functional impairment and downregulation of cytokine-mediated signaling in COVID-19 patients. Genes Immun. 2022, 23, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyavar, S.D.; Singh, R.D.; Emani, R.; Pawar, G.P.; Chaudhari, V.D.; Podany, A.T.; Avedissian, S.N.; Fletcher, C.V.; Salunke, D.B. Role of toll-like receptor 7/8 pathways in regulation of interferon response and inflammatory mediators during SARS-CoV2 infection and potential therapeutic options. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, B. Toll-like receptors: How they work and what they do. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2002, 9, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Lv, W.; Liu, P.; Huang, H.; Luan, J.; Zhang, L. Meta-analysis of the association between toll-like receptor gene polymorphisms and hepatitis C virus infection. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1254805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naushad, S.M.; Mandadapu, G.; Ramaiah, M.J.; Almajhdi, F.N.; Hussain, T. The role of TLR7 agonists in modulating COVID-19 severity in subjects with loss-of-function TLR7 variants. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.S.; Bentes, A.A.; Diniz, L.M.; Carvalho, S.H.; Kroon, E.G.; Campos, M.A. Association Between Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor 3 (tlr3), TLR7, tlr8 and tirap Genes with Severe Symptoms in Children Presenting COVID-19. Viruses 2024, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller-Larsen, S.; Nyegaard, M.; Haagerup, A.; Vestbo, J.; Kruse, T.A.; Børglum, A.D. Association analysis identifies TLR7 and TLR8 as novel risk genes in asthma and related disorders. Thorax 2008, 63, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.F.B.; Litvinov, N.; Farhat, S.C.L.; Eisencraft, A.P.; Gibelli, M.A.B.C.; Carvalho, W.B.; Fernandes, V.R.; Fink, T.T.; Framil, J.V.S.; Galleti, K.V.; et al. Severe clinical spectrum with high mortality in pediatric patients with COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome. Clinics 2020, 75, e2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, E.J.; Nakra, N.; Gale, C.; Dimitriades, V.R.; Lakshminrusimha, S. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MISC) and neonates (MIS-N) associated with COVID-19: Optimizing definition and management. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufnagel, M.; Armann, J.; Jakob, A.; Doenhardt, M.; Diffloth, N.; Hospach, A.; Schneider, D.T.; Trotter, A.; Roessler, M.; Schmitt, J.; et al. A comparison of pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporarily-associated with SARS-CoV-2 and Kawasaki disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Setta, F.; Magalhães-Barbosa, M.C.; Rodrigues-Santos, G.; Figueiredo, E.A.D.N.; Jacques, M.L.; Zeitel, R.S.; Sapolnik, R.; Borges, C.T.D.S.; Lanziotti, V.S.; Castro, R.E.V.; et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MISC) during SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in Brazil: A multicenter, prospective cohort study. J. Pediatr. 2021, 97, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravelli, A. MIS-C and Kawasaki disease: Different illnesses or part of the same spectrum? Glob. Pediatr. 2024, 8, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwani, M.; Yassin, A.; Al-Zoubi, R.M.; Aboumarzouk, O.M.; Nettleship, J.; Kelly, D.; Al-Qudimat, A.R.; Shabsigh, R. Sex-based differences in severity and mortality in COVID-19. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, e2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiering, A.E.; de Vries, T.J. Why Females Do Better: The X Chromosomal TLR7 Gene-Dose Effect in COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 756262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, G.; Rahimi, B.; Panahi, M.; Abkhiz, S.; Saraygord-Afshari, N.; Milani, M.; Alizadeh, E. An Overview of Betacoronaviruses-Associated Severe Respiratory Syndromes, Focusing on Sex-Type-Specific Immune Responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 92, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.L.; Huber, S. Sex Differences in Susceptibility to Viral Infection. In Sex Hormones and Immunity to Infection; Klein, S.L., Roberts, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 93–122. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, H.; Klein, S.L. Sex Differences in Immunity to Viral Infections. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 720952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.A.; Zolini, G.P.; Kroon, E.G. Impact of Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) and TLR Signaling Proteins in Trigeminal Ganglia Impairing Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1) Progression to Encephalitis: Insights from Mouse Models. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2024, 29, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, N.L.; Bentes, A.A.; de Carvalho, A.L.; de Souza Silva, T.B.; Alves, P.A.; de Sousa Reis, E.V.; Rodrigues, T.A.; Kroon, E.G.; Campos, M.A. Case report: Hepatitis in a child infected with SARS-CoV-2 presenting toll-like receptor 7 Gln11Leu single nucleotide polymorphism. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loske, J.; Röhmel, J.; Lukassen, S.; Stricker, S.; Magalhães, V.G.; Liebig, J.; Chua, R.L.; Thürmann, L.; Messingschlager, M.; Seegebarth, A.; et al. Pre-activated antiviral innate immunity in the upper airways controls early SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ji, W.; Guzman Rivera, J.; Madhvi, A.; Andrews, T.; Richlin, B.; Suarez, C.; Gaur, S.; Hasan, U.N.; Cuddy, W.; et al. A genetically modulated Toll-like receptor-tolerant phenotype in peripheral blood cells of children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome. J. Immunol. 2025, 214, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldstein, L.R.; Rose, E.B.; Horwitz, S.M.; Collins, J.P.; Newhams, M.M.; Son, M.B.F.; Newburger, J.W.; Kleinman, L.C.; Heidemann, S.M.; Martin, A.A.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in U.S. Children and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Farias, E.C.F.; Pavão Junior, M.J.C.; de Sales, S.C.D.; do Nascimento, L.M.P.P.; Pavão, D.C.A.; Pinheiro, A.P.S.; Pinheiro, A.H.O.; Alves, M.C.B.; Ferraro, K.M.M.M.; Aires, L.F.Q.; et al. Factors associated to mortality in children with critical COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in a resource-poor setting. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Information for Healthcare Providers about Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MISC). Available online: https://archive.cdc.gov/www_cdc_gov/mis/mis-c/hcp/index.html (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Yehya, N.; Khemani, R.G.; Erickson, S.; Smith, L.S.; Rowan, C.M.; Jouvet, P.; Willson, D.F.; Cheifetz, I.M.; Ward, S.; Thomas, N.J.; et al. Respiratory dysfunction criteria in critically ill children: The PODIUM consensus conference. Pediatrics 2022, 149 (Suppl. S1), S48–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucky, B. SeqTrace: A graphical tool for rapidly processing DNA sequencing chromatograms. J. Biomol. Tech. 2012, 23, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, E.G.M.; Ferreira, F.S.; Brito, W.R.S.; Lopes, F.T.; de Lima, A.C.R.; Neto, G.S.P.; Amoras, E.S.G.; Lima, S.S.; da Costa, C.A.; Souza, M.S.; et al. TLR7 rs179008 (A/T) and TLR7 rs3853839 (C/G) polymorphisms are associated with variations in IFN-α levels in HTLV-1 infection. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1462352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrade, A.d.S.; Bentes, A.A.; Diniz, L.M.; Hees Carvalho, S.; Kroon, E.G.; Campos, M.A. The X-Linked TLR7 rs179008 T Allele Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Severe Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children/Kawasaki-like Syndrome in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Boys. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178491
Andrade AdS, Bentes AA, Diniz LM, Hees Carvalho S, Kroon EG, Campos MA. The X-Linked TLR7 rs179008 T Allele Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Severe Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children/Kawasaki-like Syndrome in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Boys. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178491
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrade, Adriana de Souza, Aline Almeida Bentes, Lilian Martins Diniz, Silvia Hees Carvalho, Erna Geessien Kroon, and Marco Antonio Campos. 2025. "The X-Linked TLR7 rs179008 T Allele Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Severe Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children/Kawasaki-like Syndrome in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Boys" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178491
APA StyleAndrade, A. d. S., Bentes, A. A., Diniz, L. M., Hees Carvalho, S., Kroon, E. G., & Campos, M. A. (2025). The X-Linked TLR7 rs179008 T Allele Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Severe Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children/Kawasaki-like Syndrome in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Boys. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178491





