Integrin β Regulates the Hepatopancreas Antiviral Innate Immune System by Affecting the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Penaeus vannamei
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pv-Integrin β Gene Sequence Information
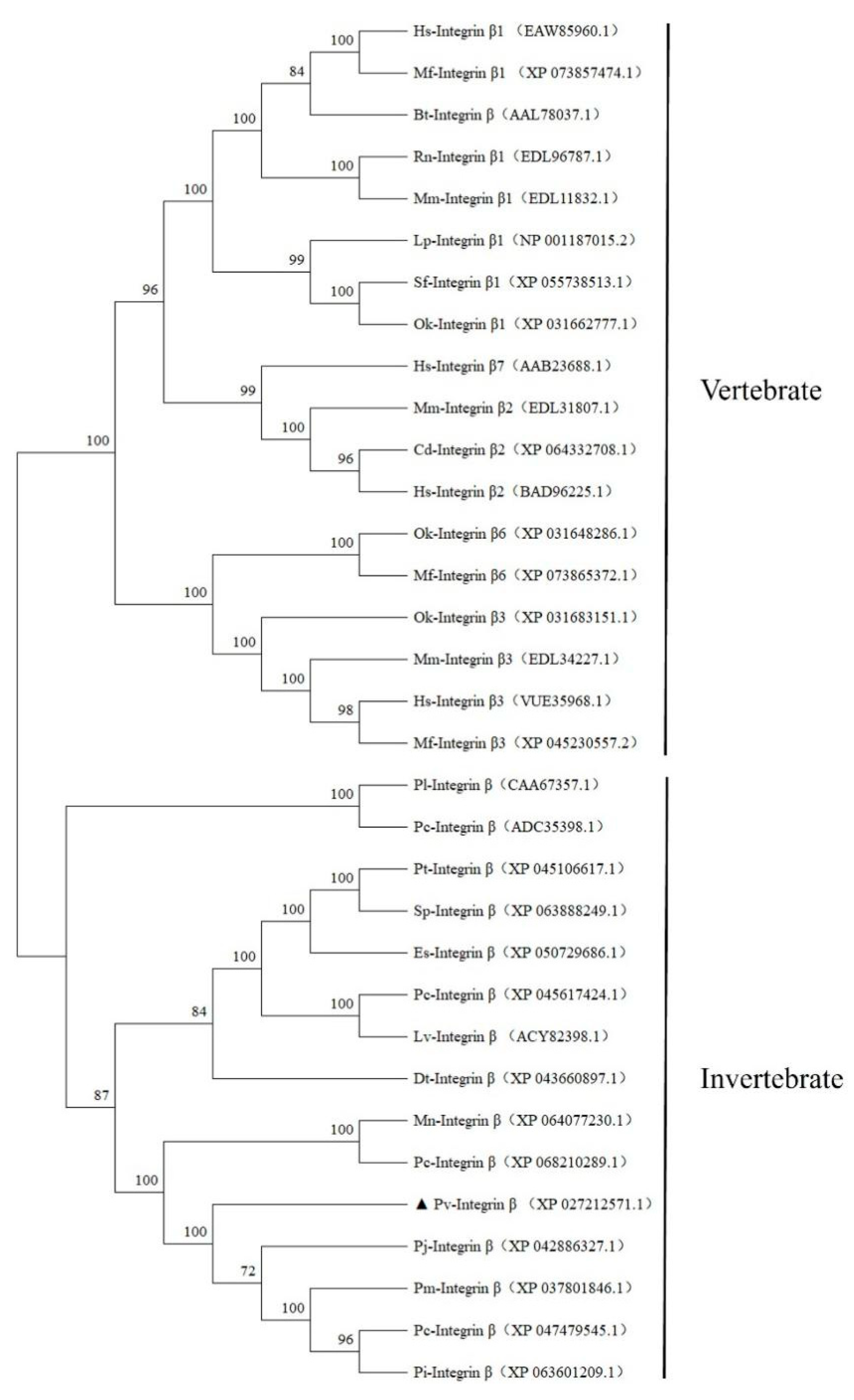
2.2. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree
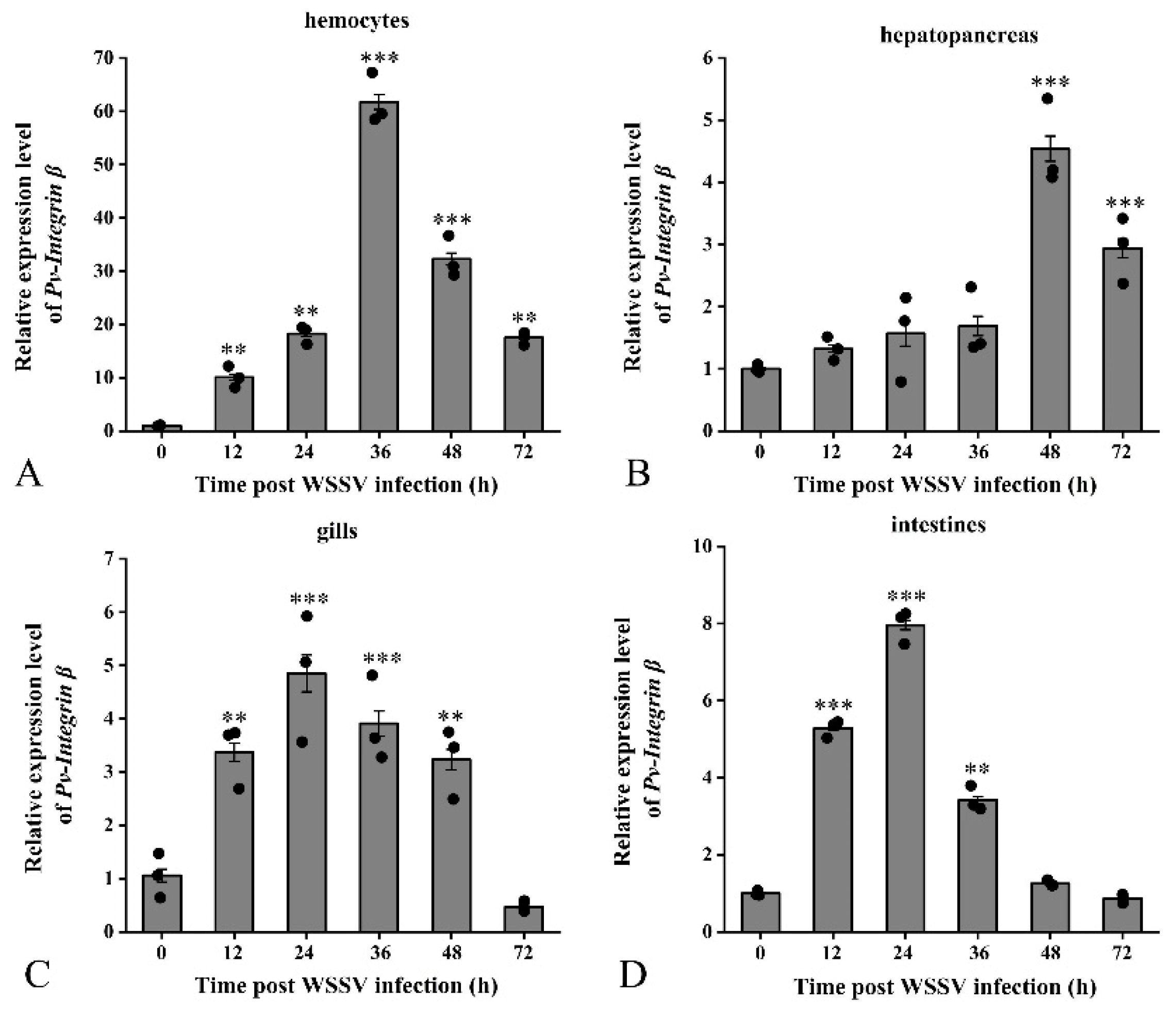
2.3. Analysis of Pv-Integrin β Expression Patterns Following WSSV Infection
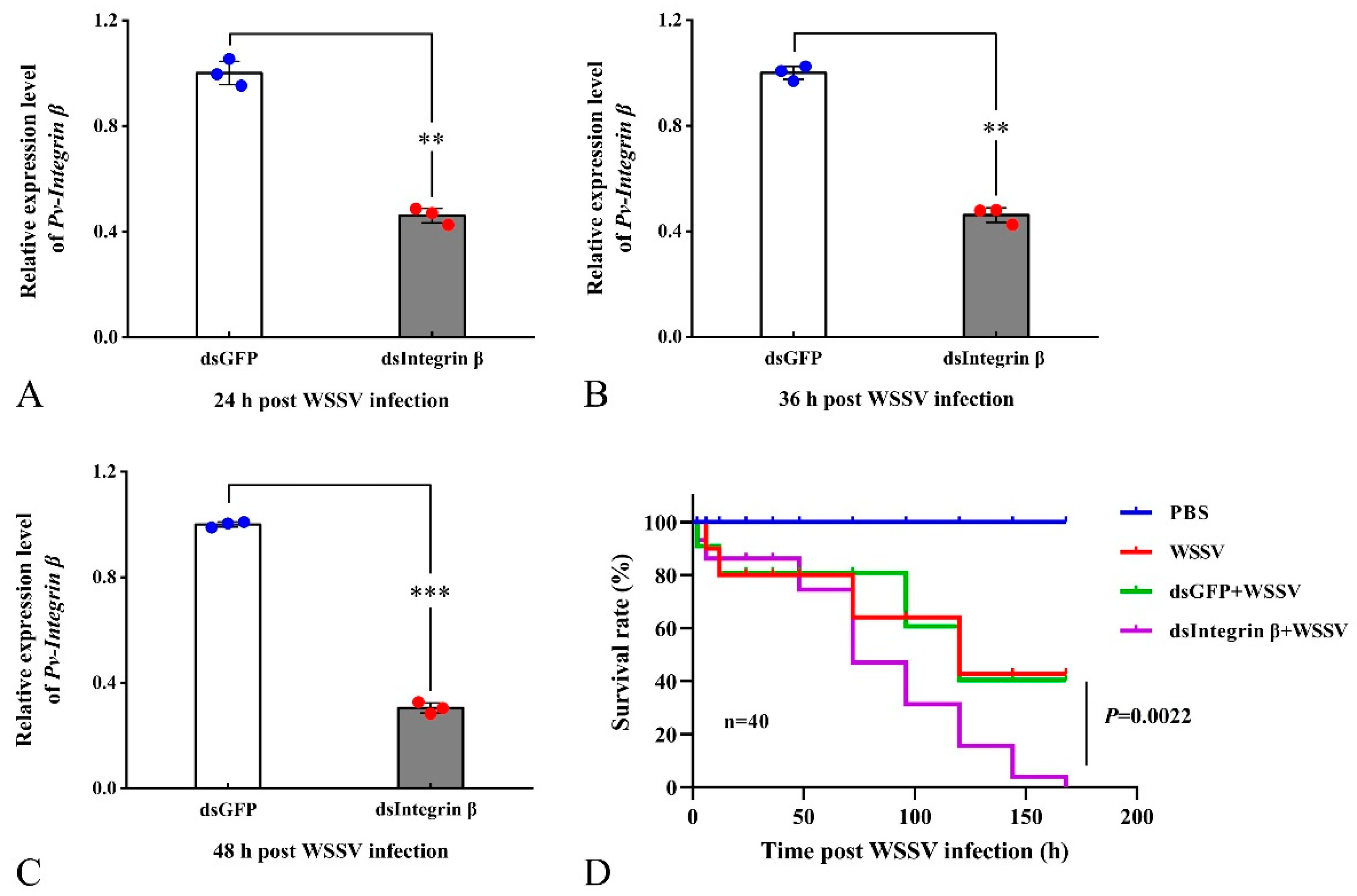
2.4. Analysis of dsRNA Interference Efficiency and Survival Rate of P. vannamei
2.5. Knockdown of the Pv-Integrin β Gene Promotes WSSV replication
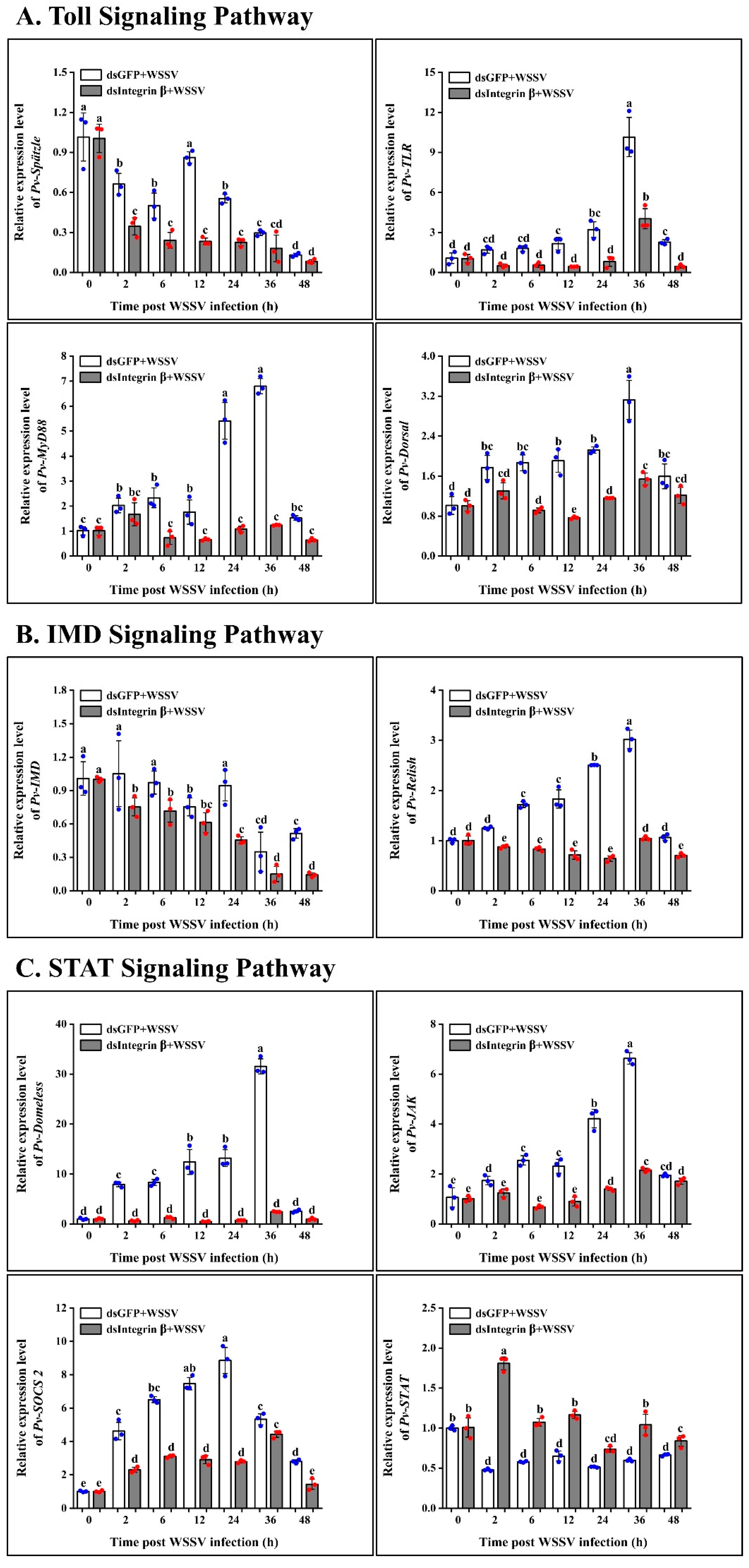
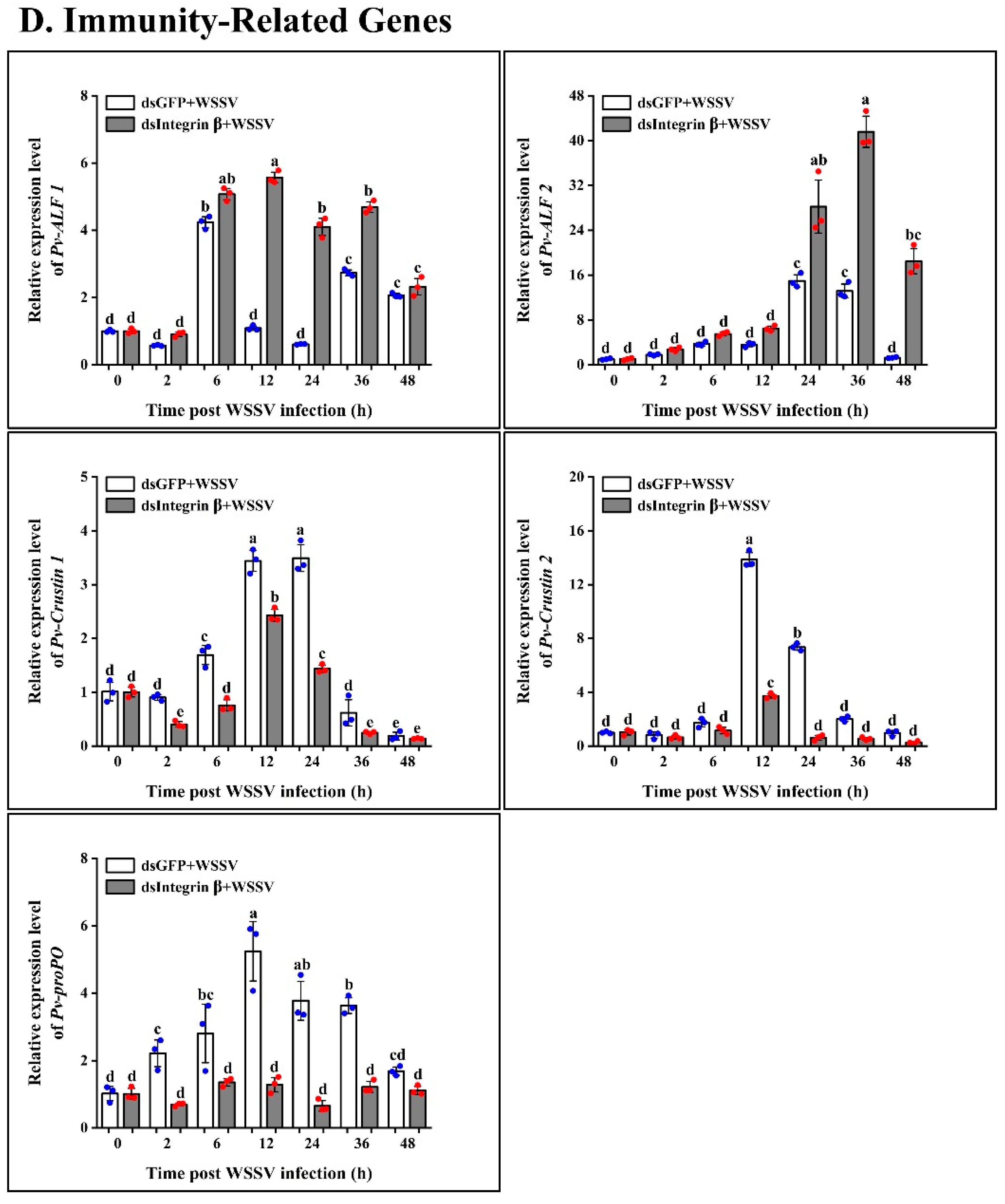
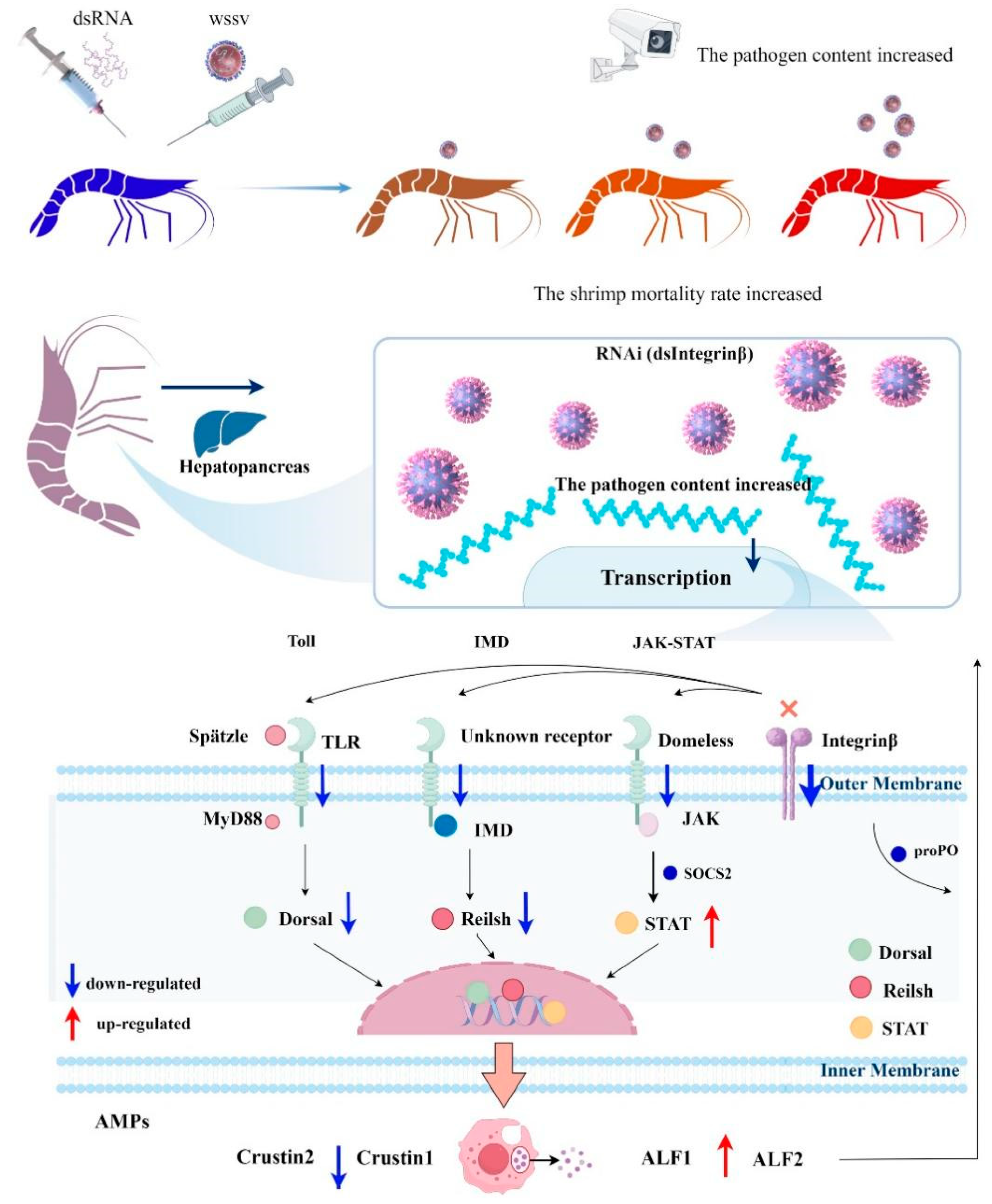
2.6. Role of Pv-Integrin β in the Regulation of Innate Immune Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Samples Collection
4.2. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. Gene Cloning and Bioinformatic Analysis
4.4. Tissue Distribution and Expression Pattern Analysis of the Pv-Integrin β Gene
4.5. Double-Stranded RNA Preparation
4.6. Survival Rate Analysis After Pv-Integrin β Knockdown
4.7. Pathogen Detection After Pv-Integrin β Knockdown
4.8. Detection of Innate Immune Signaling Pathway Genes Following the Knockdown of the Pv-Integrin β Gene
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desrina; Slamet, B.P.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Verreth, J.A.J.; Vlak, J.M. White spot syndrome virus host range and impact on transmission. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1843–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Hirono, I.; Maningas, M.B.B.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Stentiford, G.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Nimaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1053–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leu, J.H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Kou, G.H.; Lo, C.F. Whispovirus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 328, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wißing, M.H.; Brüggemann, Y.; Steinmann, E.; Todt, D. Virus-Host Cell Interplay during Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Xu, L.; Yang, F. Proteomic analysis of the major envelope and nucleocapsid proteins of white spot syndrome virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10615–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hulten, M.C.W.; Goldbach, R.W.; Vlak, J.M. Three functionally diverged major structural proteins of white spot syndrome virus evolved by gene duplication. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2525–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Yin, Z.X.; Xu, X.P.; Weng, S.P.; Rao, X.Y.; Dai, Z.X.; Luo, Y.W.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.S.; Guan, H.J. A novel C-type lectin from the shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei possesses anti-white spot syndrome virus activity. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, N.T.; Liang, H.; Zhang, M.; Bakky, M.A.H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Role of Cellular Receptors in the Innate Immune System of Crustaceans in Response to White Spot Syndrome Virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, S.K. Integrins in cell adhesion and signaling. Hum. Cell 1996, 9, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, M.S.; Ponniah, A.G. Recent insights into host-pathogen interaction in white spot syndrome virus infected penaeid shrimp. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhai, F.; Sheng, X.; Xing, J.; Zhan, W. The Roles of β-Integrin of Chinese Shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis) in WSSV Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feire, A.L.; Koss, H.; Compton, T. Cellular integrins function as entry receptors for human cytomegalovirus via a highly conserved disintegrin-like domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15470–15475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.Q.; Wang, X.L.; Zhan, W. An integrin β subunit of Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis involved in WSSV infection. Aquaculture. 2012, 368–369, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Cheng, W.; Hsu, C.H.; Tsui, W.C. Characterization of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei integrin β and its role in immunomodulation by dsRNA-mediated gene silencing. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 40, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Tran, N.T.; Huang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ma, H.; Li, S. Innate immune responses and metabolic alterations of mud crab (Scylla paramamosain) in response to Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 1992, 69, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, B.; Spatz, J.P.; Bershadsky, A.D. Environmental sensing through focal adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, D. White spot syndrome virus IE1 protein blocks the integrin-FAK signaling to enhance viral infection in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 157, 110073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancotti, F.G.; Ruoslahti, E. Integrin signaling. Science 1999, 285, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, T.; Leoni, V.; Campadelli-Fiume, G. Type I interferon and NF-κB activation elicited by herpes simplex virus gH/gL via αvβ3 integrin in epithelial and neuronal cell lines. J Virol. 2013, 87, 13911–13916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, T.; Campadelli-Fiume, G. The epithelial αvβ3-integrin boosts the MYD88-dependent TLR2 signaling in response to viral and bacterial components. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Hu, L.; Li, J.; Yan, W.; Song, E.; Kuang, M.; Liu, S.; He, J.; Weng, S. The NF-κB family member dorsal plays a role in immune response against Gram-positive bacterial infection in mud crab (Scylla paramamosain). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 106, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, W.D.; Kirkpatrick, R.B. Cactus-independent nuclear translocation of Drosophila RELISH. J. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 82, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, J.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, L. Molecular cloning and expression of a Relish gene in Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2010, 37, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yan, H.; Wang, D.; Priya, T.A.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, J. Identification of a novel relish homolog in Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis and its function in regulating the transcription of antimicrobial peptides. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.G.; Wang, P.H.; Xu, X.P.; Li, C.Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Fan, W.Z.; Yan, H.; Weng, S.P. Litopenaeus vannamei NF-κB is required for WSSV replication. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 45, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visetnan, S.; Supungul, P.; Hirono, I.; Tassanakajon, A.; Rimphanitchayakit, V. Activation of PmRelish from Penaeus monodon by yellow head virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, D.; Li, S.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, J. A Dorsal homolog (FcDorsal) in the Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis is responsive to both bacteria and WSSV challenge. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanji, T.; Hu, X.; Weber, A.N.; Ip, Y.T. Toll and IMD pathways synergistically activate an innate immune response in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4578–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Lǚ, K.; Yin, B.; He, J.; Li, C. Shrimp with knockdown of LvSOCS2, a negative feedback loop regulator of JAK/STAT pathway in Litopenaeus vannamei, exhibit enhanced resistance against WSSV. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 65, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Lin, S.; Shen, X.; Du, Z. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of peroxiredoxin 4 (prx 4) in freshwater crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 137, 108781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, S.V.; Lightner, D.V. Quantitative real time PCR for the measurement of white spot syndrome virus in shrimp. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Primer Name | Sequence (5′~3′) |
|---|---|
| Amplified sequence | |
| Pv-Integrin-β-F | GTCAGGGGTCTCTGCAAATCA |
| Pv-Integrin-β-R | CAGGTCTGTTCATCAGGTACT |
| For the qRT-PCR assay | |
| Integrin-β-F | TGCAAGAAGCCAGCAGATCC |
| Integrin-β-R | GAACATGTTGGCCCACTCCA |
| 18 S-F | TATACGCTAGTGGAGCTGGAA |
| 18 S-R | GGGGAGGTAGTGACGAAAAAT |
| VP 28-F | TTCTTTCACTCTTTCGGTCGT |
| VP 28-R | GCCAACTTCATCCTCATCAAT |
| IE 1-F | TGGCACAACAACAGACCCTA |
| IE 1-R | CTTTCCTTGAAGTACGAGAC |
| SOCS 2-F | CTGCCAAACGCCCACTTC |
| SOCS 2-R | CGTGGCAGGCATTGTGTG |
| MyD88-F | GGCAAAGGGCTATTGGAACTAT |
| MyD88-R | ATGATCCAGACACCTCTCGTATTC |
| proPO-F | TACATGCACCAGCAAATTATCG |
| proPO-R | AGTTTGGGGAAGTAGCCGTC |
| ALF1-F | TTACTTCAATGGCAGGATGTGG |
| ALF1-R | GTCCTCCGTGATGAGATTACTCTG |
| ALF2-F | GGCCATTGCGAACAAACTCAC |
| ALF2-R | GTCCATCCTGGGCACCACAT |
| Crustin1-F | GTAGGTGTTGGTGGTGGTTTC |
| Crustin1-R | CTCGCAGCAGTAGGCTTGAC |
| Crustin2-F | GGTACGTCTGCTGCAAGCC |
| Crustin2-R | CTGAGAACCTGCCACGATGG |
| Domeless-F | TCAGACAGGAGGTCTCATAC |
| Domeless-R | GTACCAGTGTGAAGCCTTAC |
| JAK-F | TACCCTGGTCTACGCTATAC |
| JAK-R | TGAGACGGTAGTACCCATTC |
| Spätzle-F | TGGGGACTCTCCTTACGATG |
| Spätzle-R | GGGAACAGACAGGTCTCCAA |
| Dorsal-F | GATGGAATGATAGAATGGGAAGC |
| Dorsal-R | CACTGGTACTCTTGTCTGGTGGTC |
| Relish-F | CTACATTCTGCCCTTGACTCTGG |
| Relish-R | GGCTGGCAAGTCGTTCTCG |
| IMD-F | CGGCTCTGCGGTTCACAT |
| IMD-R | CCTCGACCTTGTCTCGTTCCT |
| STAT-F | AGCCCCTGTCTGAGCGAAA |
| STAT-R | GGTGTTCTCTTGTGACCTTCATCA |
| TLR-F | GGGGTACCATGGTGTCAGGACTGGAGTCAGGCAACC |
| TLR-R | TGCTCTAGATACACTTTTCGAGTTTGATTTAACAAG |
| Pathogen detection primers | |
| WSSV-F | TGGTCCCGTCCTCATCTCAG |
| WSSV-R | GCTGCCTTGCCGGAAATTA |
| WSSV-probe | AGCCATGAAGAATGCCGTCTATCACACA |
| For dsRNA synthesis | |
| dsGFP-Fi | GCGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGCATCTTCTTCAAGGACGACGG |
| dsGFP-Ri | GCGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGAGTTCACCTTGATGCCGTTCT |
| Pv-Integrin-β-Fi | GCGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGACGACCGCAAGGGCAAAT |
| Pv-Integrin-β-Ri | GCGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGACGCAGGGCTTGTAGTCTGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.; Zhang, L.; Luo, K.; Luan, S.; Kong, J.; Fu, Q.; Cao, J.; Chen, B.; Dai, P.; Li, X.; et al. Integrin β Regulates the Hepatopancreas Antiviral Innate Immune System by Affecting the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Penaeus vannamei. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178478
Yang B, Zhang L, Luo K, Luan S, Kong J, Fu Q, Cao J, Chen B, Dai P, Li X, et al. Integrin β Regulates the Hepatopancreas Antiviral Innate Immune System by Affecting the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Penaeus vannamei. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178478
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Bingbing, Li Zhang, Kun Luo, Sheng Luan, Jie Kong, Qiang Fu, Jiawang Cao, Baolong Chen, Ping Dai, Xupeng Li, and et al. 2025. "Integrin β Regulates the Hepatopancreas Antiviral Innate Immune System by Affecting the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Penaeus vannamei" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178478
APA StyleYang, B., Zhang, L., Luo, K., Luan, S., Kong, J., Fu, Q., Cao, J., Chen, B., Dai, P., Li, X., & Meng, X. (2025). Integrin β Regulates the Hepatopancreas Antiviral Innate Immune System by Affecting the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Penaeus vannamei. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178478







