Targeting the Purinergic Axis with Phenolic Compounds to Disrupt the Oxidative-Inflammatory Cycle in Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
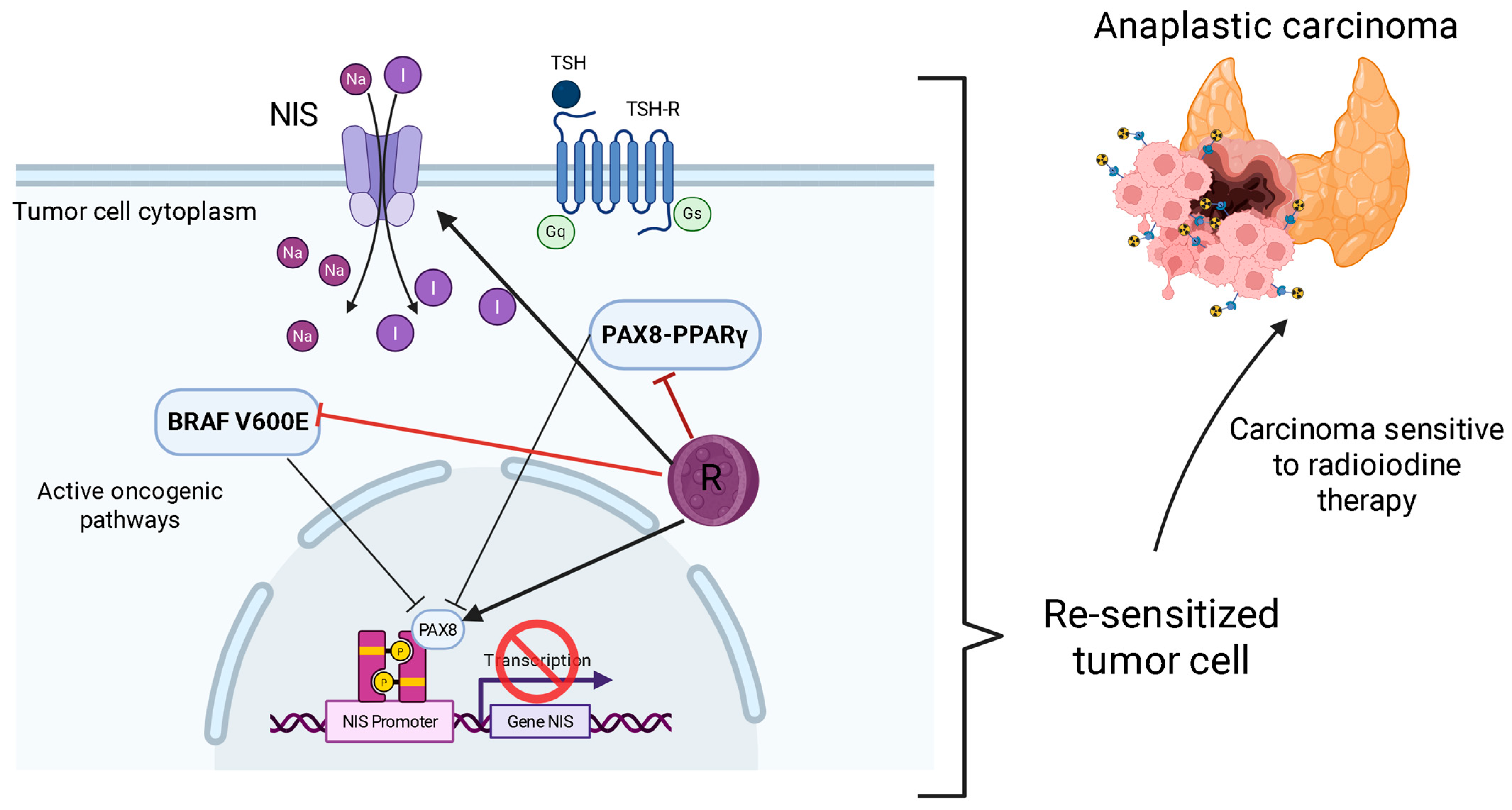
2. Molecular Heterogeneity and Challenges in Thyroid Cancer
3. The Oxidative Stress-Inflammation Axis: The Central Vulnerability of Thyroid Cancer
3.1. Limitations of Current Evidence
3.1.1. Correlation vs. Causation
3.1.2. Reliance on Preclinical Models
3.1.3. The Challenge of Therapeutic Selectivity
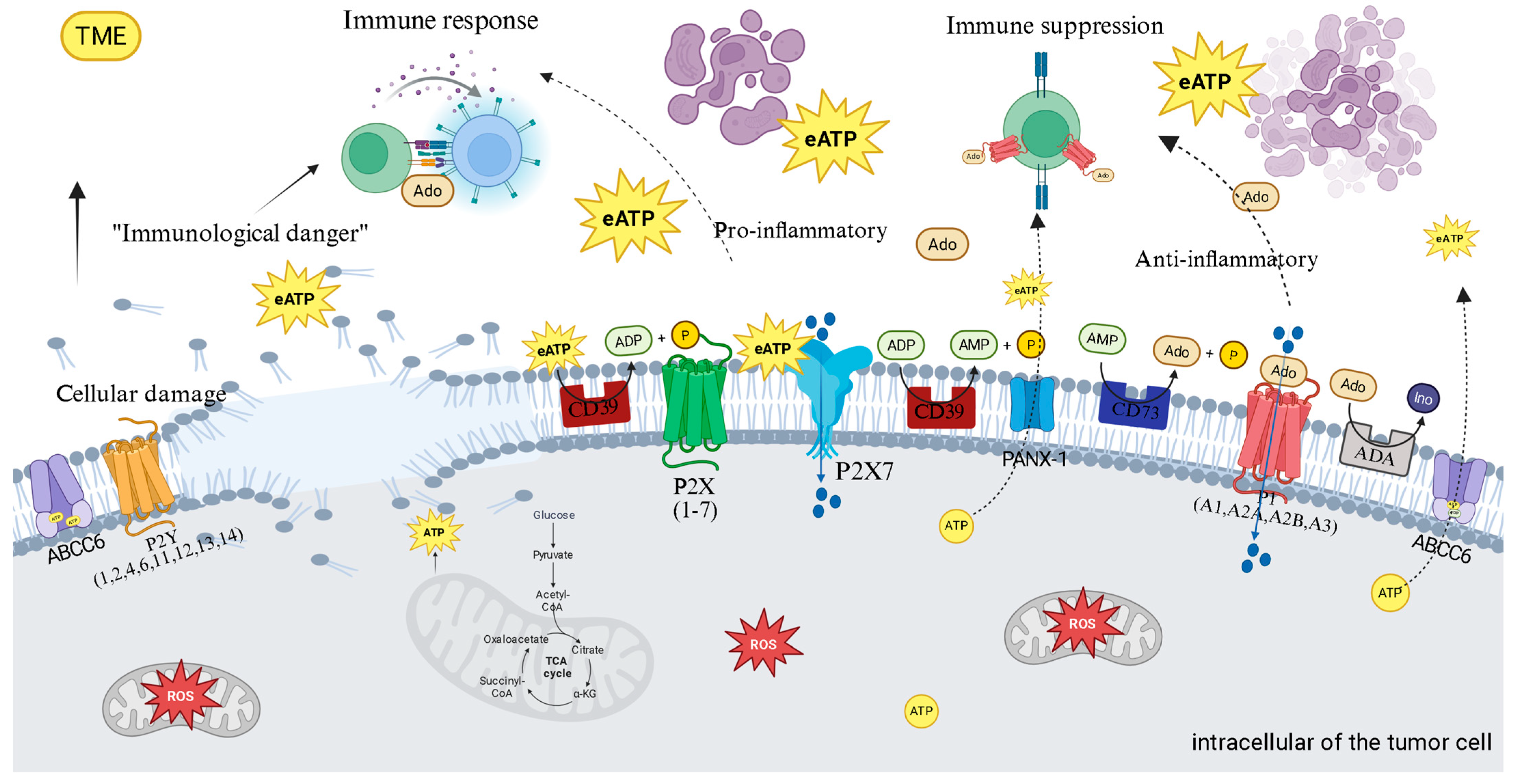
4. Purinergic Signaling: The Immunometabolic Switch of Thyroid Cancer
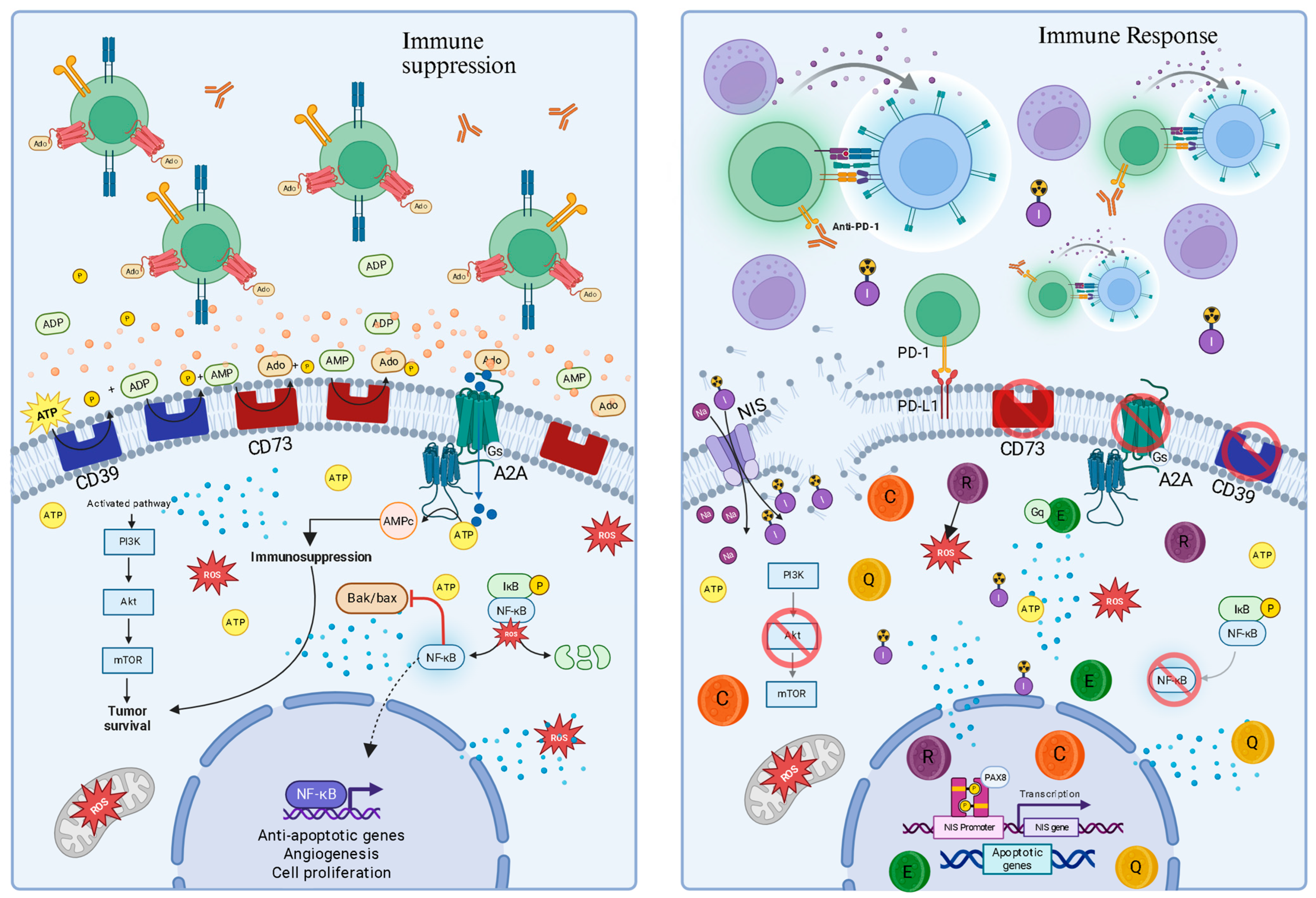
4.1. Therapeutic Implications: Targeting the Purinergic Axis
4.2. Therapeutic Strategies Based on Purinergic Modulation
4.3. Rational Combinations with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
4.4. Limitations of Current Evidence
4.4.1. Lack of Thyroid-Specific Clinical Data
4.4.2. Tumor Heterogeneity Is Understudied
4.4.3. Potential for Therapeutic Resistance
5. Phenolic Compounds as Pleiotropic Modulators in Thyroid Cancer
5.1. Compounds Phenolics
5.1.1. Curcumin
5.1.2. Resveratrol
5.1.3. Quercetin
5.1.4. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG)
5.2. Summary of Mechanistic Focus
5.3. Resensitization to Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Therapy
5.4. Enhancing with Checkpoint Immunotherapies
5.5. Clinical Landscape of ICIs in Thyroid Cancer and the Rationale for Combination with Purinergic Modulators
5.6. Overcoming the Translational Challenge with Nanotechnology
5.7. Limitations of Current Evidence
5.7.1. The Overwhelming Bioavailability Hurdle
5.7.2. Pleiotropy as a Double-Edged Sword
5.8. Discussion on Clinical Trials and Research Gaps
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TC | Thyroid Cancer |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| BRAF | proto-oncogene B-Raf |
| RAS | rat sarcoma virus |
| p53 | tumor suppressor protein or TP53 |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| Ado | Adenosine |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa B |
| OS | Oxidative Stress |
| PTC | Papillary Carcinoma |
| DTC | Differentiated Thyroid Carcinomas |
| FTC | Follicular Carcinoma |
| APC | Anaplastic Carcinoma |
| DAMP | Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern |
| MAPK | MAP Kinase |
| RET | Rearranged during transfection |
| PPAR | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor |
| PPFP | PAX8/PPARY fusion protein |
| NIS | Sodium/Iodine Symporter |
| RAI | Radioactive Iodine |
| TKIs | Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen Peroxide |
| TPO | Thyroid Peroxidase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| TAS | Total Antioxidant Status |
| TOS | Total Oxidant Status |
| OSI | Oxidative Stress Index |
| NOX4 | NADPH Oxidase 4 |
| DUOX | Dual Oxidase |
| 8-OHdG | 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositol-3-kinase |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| PTPs | Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases |
| ERα | Estrogen Receptor Alpha |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 |
| CT | Thyroid Cancer |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| CXCL8 | Chemokine 8 |
| eATP | Extracellular ATP |
| P1 | Purinoreceptors type 1 |
| P2 | Purinoreceptors type 2 |
| P2X7 | Purinoreceptor P2X subtype 7 |
| CD39 | Ectonucleoside Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolase E-NTPDase1 |
| CD73 | Ecto-5′-nucleotidase |
| AMP | Adenosine Monophosphate |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor beta |
| NK | Natural Killer (Natural killer cells) |
| cAMP | Cyclic AMP (3′-5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) |
| Tregs | Regulatory T Cells (regulatory T lymphocytes) |
| PD-1 | Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 |
| nfP2X7 | Non-functional P2X7 receptor |
| NLRP3 | Inflammasome coding gene |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-18 | Interleukin type 18 |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Reduced |
| OXPHOS | Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation |
| ABCB6 | ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter Subfamily B, Member 6 |
| PANX-1 | Pannexin-1 |
| P2X | Ionotropic P2 purinoreceptors |
| P2Y | Metabotropic P2 purinoreceptors |
| ADA | Adenosine Deaminase |
| ICIs | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors |
| PKA | Protein Kinase A |
| Akt/mTOR | protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NAG-1/GDF15 | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Activated Gene-1/Growth Differentiation Factor 15 |
| MMP3 | Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 |
| JAK/STAT | Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| EMT | Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition |
| EPR | Enhanced Permeability and Retention |
| CD38 | Differentiation cluster 38 |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Miao, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Zhu, L.; Liu, H.; Shen, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, B.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Drivers of Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Opportunities. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Di Virgilio, F. Purinergic signalling and cancer. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 491–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Adinolfi, E. Extracellular purines, purinergic receptors and tumor growth. Oncogene 2017, 36, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozac-Szőke, A.-R.; Cozac, D.A.; Negovan, A.; Tinca, A.C.; Vilaia, A.; Cocuz, I.-G.; Sabău, A.H.; Niculescu, R.; Chiorean, D.M.; Tomuț, A.N.; et al. Immune Cell Interactions and Immune Checkpoints in the Tumor Microenvironment of Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, L.J.; Durante, C.; Topliss, D.J.; Winquist, E.; Robenshtok, E.; Iwasaki, H.; Luster, M.; Elisei, R.; Leboulleux, S.; Tahara, M. Lenvatinib for the Treatment of Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Treatment Optimization for Maximum Clinical Benefit. Oncologist 2022, 27, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M. Molecular pathogenesis and mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuloria, S.; Mehta, J.; Chandel, A.; Sekar, M.; Rani, N.N.I.M.; Begum, M.Y.; Subramaniyan, V.; Chidambaram, K.; Thangavelu, L.; Nordin, R.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on the Therapeutic Potential of Curcuma longa Linn. in Relation to its Major Active Constituent Curcumin. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 820806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goring, S.; Mahood, Q. Radioiodine Resensitization for Radioiodine-Refractory Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: CADTH Health Technology Review; Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N.; Baharlouei, A.; Watson, D.G.; Lightfoot, D.A. Phytochemicals: Extraction, Isolation, and Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Plant Extracts. Plants 2017, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakrim, S.; El Omari, N.; El Hachlafi, N.; Bakri, Y.; Lee, L.H.; Bouyahya, A. Dietary Phenolic Compounds as Anticancer Natural Drugs: Recent Update on Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Trials. Foods 2022, 11, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, J.; Zimmerman, A.W.; Friedrich, V.L., Jr. Altered brain copper and zinc content in quaking mice. Exp. Neurol. 1983, 82, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyemi, U.; Caillou, B.; Talbot, M.; Ameziane-El-Hassani, R.; Lacroix, L.; Lagent-Chevallier, O.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Roos, D.; Bidart, J.M.; Virion, A.; et al. Intracellular expression of reactive oxygen species-generating NADPH oxidase NOX4 in normal and cancer thyroid tissues. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M. Oxidative stress: A new risk factor for thyroid cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, C7–C11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Sheng, J.; Tang, P.; Peng, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, X.; Hu, J.; Xu, T. The role and mechanism of NADPH oxidase in the development and progression of thyroid carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 4366–4375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z. Bisphenol A exposure enhances proliferation and tumorigenesis of papillary thyroid carcinoma through ROS generation and activation of NOX4 signaling pathways. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 292, 117946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, E.; Leonardi, A.; Pacifico, F. NF-κB in Thyroid Cancer: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenniche, S.; Oukabli, M.; Oubaddou, Y.; Chahdi, H.; Damiri, A.; Alghuzlan, A.; Laraqui, A.; Dakka, N.; Bakri, Y.; Dupuy, C.; et al. A Comparative Analysis of NOX4 Protein Expression in Malignant and Non-Malignant Thyroid Tumors. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 5811–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchi, E.; Orioli, E.; Pegoraro, A.; Sangaletti, S.; Portararo, P.; Curti, A.; Colombo, M.P.; Di Virgilio, F.; Adinolfi, E. The P2X7 receptor modulates immune cells infiltration, ectonucleotidases expression and extracellular ATP levels in the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3636–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinolfi, E.; Giuliani, A.L.; De Marchi, E.; Pegoraro, A.; Orioli, E.; Di Virgilio, F. The P2X7 receptor: A main player in inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, I.; Missiaglia, E.; Sciarra, A.; Santos, J.V.; Bouilly, J.; Romero, P.; Sempoux, C.; de Leval, L. CD73 expression in normal, hyperplastic, and neoplastic thyroid: A systematic evaluation revealing CD73 overexpression as a feature of papillary carcinomas. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2021, 479, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, R.; Adinolfi, E.; Harwood, C.A.; Philpott, M.; Barden, J.A.; Di Virgilio, F.; McNulty, S. P2X7 in Cancer: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagg, J.; Beavis, P.A.; Divisekera, U.; Liu, M.C.; Möller, A.; Darcy, P.K.; Smyth, M.J. CD73-deficient mice are resistant to carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Y.; Lu, D.; Xue, M. Purinergic signaling in thyroid disease. Purinergic Signal. 2023, 19, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deaglio, S.; Dwyer, K.M.; Gao, W.; Friedman, D.; Usheva, A.; Erat, A.; Chen, J.F.; Enjyoji, K.; Linden, J.; Oukka, M.; et al. Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Yin, S.; To, K.K.W.; Fu, L. CD39/CD73/A2AR pathway and cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, F.; Capece, M.; Rotondo, A.; Cangelosi, D.; Ferracin, M.; Franceschini, A.; Raffaghello, L.; Pistoia, V.; Varesio, L.; Adinolfi, E. The P2X7 receptor is a key modulator of the PI3K/GSK3β/VEGF signaling network: Evidence in experimental neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5240–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Majem, M.; Barlesi, F.; Carcereny, E.; Chu, Q.; Monnet, I.; Sanchez-Hernandez, A.; Dakhil, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Winzer, L.; et al. COAST: An Open-Label, Phase II, Multidrug Platform Study of Durvalumab Alone or in Combination with Oleclumab or Monalizumab in Patients with Unresectable, Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3383–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drill, M.; Jones, N.C.; Hunn, M.; O’bRien, T.J.; Monif, M. Antagonism of the ATP-gated P2X7 receptor: A potential therapeutic strategy for cancer. Purinergic Signal. 2021, 17, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moesta, A.K.; Li, X.Y.; Smyth, M.J. Targeting CD39 in cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Tello, B.; García-Gómez, M.; Rekus-Polanska, E.; Malgue, F.; Charlín, S.; Hernández-Oliveras, A.; Reyes-Alvarez, J.; Rosemblatt, M.; Lundqvist, A.; Lladser, A.; et al. CD73 promotes the maturation of murine NK cells and their survival in the tumor microenvironment. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2025, 117, qiaf011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, M.; Wainwright, D.A.; Wu, J.D.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, B. Targeting CD73 to augment cancer immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 53, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, L.; Hotson, A.; Powderly, J.D.; Sznol, M.; Heist, R.S.; Choueiri, T.K.; George, S.; Hughes, B.G.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Shepard, D.R.; et al. Adenosine 2A Receptor Blockade as an Immunotherapy for Treatment-Refractory Renal Cell Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H. The progress and prospects of targeting the adenosine pathway in cancer immunotherapy. Biomark. Res. 2025, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeay, S.; Rodier, M.; Fillon, L.; Faure, S.; Clere, N. Epigallocatechin Gallate: A Review of Its Beneficial Properties to Prevent Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5443–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Ai, Z. Curcumin enhances anti-tumor immunity in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma by elevating CD8+ T cell function and downregulating the AKT/mTORC1/STAT3/PD-L1 axis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2025, 269, 155898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Kong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, N.; Ma, J. Curcumin inhibits the viability, migration and invasion of papillary thyroid cancer cells by regulating the miR-301a-3p/STAT3 axis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manica, D.; da Silva, G.B.; Narzetti, R.A.; Dallagnoll, P.; da Silva, A.P.; Marafon, F.; Cassol, J.; de Souza Matias, L.; Zamoner, A.; de Oliveira Maciel, S.F.V.; et al. Curcumin modulates purinergic signaling and inflammatory response in cutaneous metastatic melanoma cells. Purinergic Signal. 2025, 21, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, S.; Cheng, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Bao, J.; Yu, H. Curcumin induces autophagic cell death in human thyroid cancer cells. Toxicol. Vitr. Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2022, 78, 105254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, S. Bioavailability of phenolic compounds. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, H.; Gupta, D.S.; Kaur, G.; Singh, T.; Ramniwas, S.; Sak, K.; Aggarwal, D.; Chhabra, R.S.; Gupta, M.; Saini, A.K.; et al. Nanoformulations of quercetin for controlled delivery: A review of preclinical anticancer studies. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 3443–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H.X.; Bao, J.D.; Sun, Z.; Lu, R.R. Curcumin inhibits invasion and metastasis in K1 papillary thyroid cancer cells. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, S. Curcumin Inhibits Papillary Thyroid Cancer Cell Proliferation by Regulating lncRNA LINC00691. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2022, 2022, 5946670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bao, J.; Guan, H.; Yu, H.; Lu, R.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y. Curcumin inhibits metastasis in human papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells via down-regulation of the TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 341, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitz, K.T.; Bitterman, K.J.; Cohen, H.Y.; Lamming, D.W.; Lavu, S.; Wood, J.G.; Zipkin, R.E.; Chung, P.; Kisielewski, A.; Zhang, L.L.; et al. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature 2003, 425, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-López, S.; Sánchez-Melgar, A.; Martín, M.; Albasanz, J.L. Resveratrol enhances A1 and hinders A2A adenosine receptors signaling in both HeLa and SH-SY5Y cells: Potential mechanism of its antitumoral action. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1007801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kursvietiene, L.; Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Staneviciene, I.; Mongirdiene, A.; Kubová, K.; Masteikova, R.; Bernatoniene, J. Anti-Cancer Properties of Resveratrol: A Focus on Its Impact on Mitochondrial Functions. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinimehr, S.J.; Hosseini, S.A. Resveratrol sensitizes selectively thyroid cancer cell to 131-iodine toxicity. J. Toxicol. 2014, 2014, 839597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-M.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Ahmed, K.; Harrison, A.D.; Kunnimalaiyaan, M.; Chen, H. Resveratrol induces differentiation markers expression in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma via activation of Notch1 signaling and suppresses cell growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Quispe, C.; Mukazhanova, Z.; Knut, E.; Turgumbayeva, A.; Kipchakbayeva, A.; Seitimova, G.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Lobine, D.; Koay, A.; et al. Resveratrol-Based Nanoformulations as an Emerging Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 649395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wu, C.; Huang, C.; Xie, P.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. CD73, a Promising Therapeutic Target of Diclofenac, Promotes Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer through a Nucleotidase Independent Mechanism. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjala, L.; Tammela, P. Aggregating behavior of phenolic compounds--a source of false bioassay results? Molecules 2012, 17, 10774–10790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lee, J.; Moon, H.; Ryu, C.H.; Seok, J.; Jung, Y.-S.; Ryu, J.; Baek, S.J. Quercetin Induces Anticancer Activity by Upregulating Pro-NAG-1/GDF15 in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habza-Kowalska, E.; Kaczor, A.A.; Bartuzi, D.; Piłat, J.; Gawlik-Dziki, U. Some Dietary Phenolic Compounds Can Activate Thyroid Peroxidase and Inhibit Lipoxygenase-Preliminary Study in the Model Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, H.O.A.; Alshebremi, M.; Babiker, A.Y.; Rahmani, A.H. The Role of Quercetin, a Flavonoid in the Management of Pathogenesis Through Regulation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Biological Activities. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Cai, Y.; Chen, W.; Yuan, X.; He, Z.; Lin, F. Mechanistic study of quercetin in the treatment of thyroid cancer with diabetes based on network pharmacology and in vitro experiments. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1537799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Investigation of Scutellaria Barbata’s immunological mechanism against thyroid cancer using network pharmacology and experimental validation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, L.; De Masi, L.; Sirignano, C.; Maresca, V.; Basile, A.; Nebbioso, A.; Rigano, D.; Bontempo, P. Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG): Pharmacological Properties, Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potential. Molecules 2025, 30, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Amicis, F.; Perri, A.; Vizza, D.; Russo, A.; Panno, M.L.; Bonofiglio, D.; Giordano, C.; Mauro, L.; Aquila, S.; Tramontano, D.; et al. Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits growth and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human thyroid carcinoma cell lines. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, P.; Teng, T.; Chen, M.; Xie, Z.; Ji, A.; Li, Y. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the growth and increases the apoptosis of human thyroid carcinoma cells through suppression of EGFR/RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, M.; Carlomagno, F. Central role of RET in thyroid cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.E.; Naigeon, M.; Goldschmidt, V.; Roulleaux Dugage, M.; Seknazi, L.; Danlos, F.X.; Champiat, S.; Marabelle, A.; Michot, J.M.; Massard, C.; et al. Immunosenescence, inflammaging, and cancer immunotherapy efficacy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2022, 22, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, E.; McGlinchey, K.; Wang, J.; Martin, P.; Ching, S.L.; Floc’h, N.; Kurasawa, J.; Starrett, J.H.; Lazdun, Y.; Wetzel, L.; et al. Anti-PD-L1 and anti-CD73 combination therapy promotes T cell response to EGFR-mutated NSCLC. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e142843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Seidel, V.; Izabela, M.; Monserrat-Mequida, M.; Sureda, A.; Ormazabal, V.; Zuniga, F.A.; Mangalpady, S.S.; Pezzani, R.; Ydyrys, A.; et al. Phenolic compounds as Nrf2 inhibitors: Potential applications in cancer therapy. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, S.; Kalam, N.; Shaikh, M.F.; Hasnain, M.S.; Hafiz, A.K.; Ansari, M.T. Nanoencapsulation of Polyphenols as Drugs and Supplements for Enhancing Therapeutic Profile—A Review. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022, 15, 77–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, I.A.; Sanna, V.; Ahmad, N.; Sechi, M.; Mukhtar, H. Resveratrol nanoformulation for cancer prevention and therapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1348, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.Y.; Algazi, A.; Capdevila, J.; Longo, F.; Miller, W.; Jr Chun Bing, J.T.; Bonilla, C.E.; Chung, H.C.; Guren, T.K.; Lin, C.C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with advanced thyroid cancer in the phase 2 KEYNOTE-158 study. Cancer 2023, 129, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, C.; Kiyota, N.; Imamura, Y.; Goto, H.; Suto, H.; Chayahara, N.; Toyoda, M.; Ito, Y.; Miya, A.; Miyauchi, A.; et al. Exploratory Analysis to Predict Optimal Tumor Burden for Starting Lenvatinib in Patients with Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 638123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, J.D.; Haugen, B.R.; Worden, F.P.; Bowles, D.W.; Gianoukakis, A.G.; Konda, B.; Dadu, R.; Sherman, E.J.; McCue, S.; Foster, N.R.; et al. Combination Targeted Therapy with Pembrolizumab and Lenvatinib in Progressive, Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 3757–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumberger, M.; Tahara, M.; Wirth, L.J.; Robinson, B.; Brose, M.S.; Elisei, R.; Habra, M.A.; Newbold, K.; Shah, M.H.; Hoff, A.O.; et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorch, J.H.; Barletta, J.A.; Nehs, M.; Uppaluri, R.; Alexander, E.K.; Haddad, R.I.; Hanna, G.J.; Margalit, D.N.; Tishler, R.B.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; et al. A phase II study of nivolumab (N) plus ipilimumab (I) in radioidine refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (RAIR DTC) with exploratory cohorts in anaplastic (ATC) and medullary thyroid cancer (MTC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of curcumin: Problems and promises. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, R.; Valentino, A.; Sepe, F.; Gianfreda, F.; Condò, R.; Cerroni, L.; Calarco, A.; Peluso, G. Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Reinforced Hyaluronic Hydrogel: Multitarget Strategy for the Treatment of Diabetes-Related Periodontitis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-R.; Qi, L.; Zhang, X.-W.; Wei, C.; Yu, B.; Pei, T.-L. Quercetin and Nano-Derivatives: Potential and Challenges in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 6701–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, T.; Xu, H.; Ren, B.; Cheng, X.; Qi, R.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, L.; Chen, S.; et al. Curcumin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Enhanced Anticancer Efficiency in Breast Cancer. Molecules 2018, 23, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Lin, X.M.; Nie, J.H.; Ye, H.S.; Liu, J. Resveratrol and its Nanoparticle suppress Doxorubicin/Docetaxel-resistant anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells in vitro and in vivo. Nanotheranostics 2021, 5, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngcamu, A.N.; Nwabuife, J.C.; Ndimande, N.P.; Gabela, S.; Ghazi, T.; Sekhoacha, M.P.; Faya, M.A. Novel folic acid-functionalized smart Eicosapentaenoic acid liposomes for the targeted delivery of quercetin against cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 113, 107358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.; Generalov, R.; Pereira, M.d.o.C.; Peres, I.; Juzenas, P.; Coelho, M.A. Epigallocatechin gallate-loaded polysaccharide nanoparticles for prostate cancer chemoprevention. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Compound (Name/Code) | Molecular Target | Mechanism of Action | Highest Clinical Phase | Cancer Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTX-030 | CD39 | Allosteric inhibitory antibody | Phase I | Solid tumors (NCT04318536) |
| IPH5201 | CD39 | Inhibitory antibody | Phase I | Solid tumors (NCT04318536) |
| Oleclumab (MEDI9447) | CD73 | Non-competitive inhibitory antibody | Phase III (initiated) | Lung cancer, pancreatic, colorectal (NCT02503923) |
| CPI-006 | CD73 | Competitive inhibitory antibody | Phase I/II | Solid tumors, lymphoma (NCT03454451) |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2AR/A2BR | Small molecule dual antagonist | Phase II | Solid tumors (colorectal, prostate) (NCT03719129, NCT03719131) |
| Ciforadenant (CPI-444) | A2AR | Small molecule antagonist | Phase I/II | Renal cancer (NCT02657889) and solid tumors (NCT03167169) |
| Phenolic Compound | Key Molecular Targets | Primary Effects on Cancer Hallmarks | Specific Modulation of Oxidative Stress | Specific Modulation of Inflammation | Specific Modulation of Purinergic Signaling | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | PI3K/Akt/mTOR, NF-κB, STAT3, TGF-β/Smad2/3, MAPK, miR-301a-3p | Inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, inhibits migration/invasion, inhibits metastasis, and overcomes drug resistance | Prooxidant effect (ROS generation) causes mitochondrial damage | Inhibits NF-κB, modulates inflammatory cytokines | Decreases expression of CD39, CD73, and A2A | [37,38,39,40,43,44,45] |
| Resveratrol | SIRT1, Adenosine Receptors (A1, A2A), Notch1, Caspases | Induces redifferentiation, inhibits cell growth, induces cell death, reverses multidrug resistance, sensitizes to 131I | Induces cell death via oxidative stress, protects against ROS damage | Anti-inflammatory | Increases A1, reduces A2A | [47,48,49,50,51] |
| Quercetin | CD73, NAG-1/GDF15, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, MAPK/ERK, NF-κB, JAK/STAT, MMP3 | Induces apoptosis, inhibits proliferation, inhibits angiogenesis, inhibits migration/invasion, causes cell cycle arrest | Potent antioxidant (neutralizes ROS), mitigates oxidative stress | Anti-inflammatory, downregulates NF-κB, modulates JAK/STAT | Inhibits CD73 activity, a potential limitation of ATP efflux | [42,54,55,56,57,58] |
| EGCG | CD73, Bcl-2, EGFR/RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK, NF-κB, MAPK, AMPK, DNA methyltransferase | Modulates apoptosis, inhibits growth/proliferation, inhibits migration/invasion, inhibits angiogenesis, causes cell cycle arrest, inhibits EMT | Dual function (antioxidant and prooxidant), ROS generation | Anti-inflammatory, inhibits NF-κB | Inhibits CD73 | [36,59,60,61,62] |
| Trial Name/Identifier | Drug(s) | Phase | Thyroid Cancer Subtype | Key Outcome (ORR) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEYNOTE-158 (NCT02628067) | Pembrolizumab (Anti-PD-1) | II | RAI-Refractory DTC | 9.1% | [70] |
| LENVIMA/KEYTRUDA (NCT02973997) | Pembrolizumab + Lenvatinib (TKI) | II | RAI-Refractory DTC | 64.3% | [71] |
| SELECT (NCT01321554) | Lenvatinib (TKI) | III | RAI-Refractory DTC | 64.8% | [72] |
| NCT03246958 | Nivolumab (Anti-PD-1) + Ipilimumab (Anti-CTLA-4) | II | RAI-Refractory DTC | 9.4% | [73] |
| LENVIMA/KEYTRUDA (NCT0297397) | Pembrolizumab + Lenvatinib (TKI) | II | RAI-Refractory DTC | 64.3% | [70] |
| Phenolic Compound | Nanocarrier Type | Particle Size (nm) | Drug Loading/Encapsulation Efficiency | Study Model | In Vivo Efficacy Highlights | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) | ~40 nm | 23.38% Loading/72.47% Encapsulation | Breast Cancer (SKBR3 cells, in vitro) | Showed higher cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction in SKBR3 cells compared to free curcumin. | [77] |
| Resveratrol | Targeted Polymeric Nanoparticles (IL-13Rα2-targeting) | ~30 nm | 6.81% Loading/40.84% Encapsulation | Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer (Xenograft Mice) | Inhibited tumor growth by 69.23% compared to the untreated group (p < 0.01), without the toxicity of chemotherapy. | [78] |
| Quercetin | Folic Acid-EPA-Liposomes | 106.4 nm | 92.69% Encapsulation | Cervical (HeLa) and Liver (HepG2) Cancer cells (in vitro) | 16-fold increase in potency vs. free quercetin in HeLa cells (IC50: 3.76 µg/mL); showed low toxicity in healthy cells. | [79] |
| EGCG | Liposomes | ~100 nm | >80% Encapsulation | Prostate Cancer (Xenograft Mice) | Increased tumor accumulation by 4-fold and significantly improved tumor suppression vs. free EGCG. | [80] |
| Compound/Therapeutic Strategy | Study Type | Thyroid Cancer Model/Context | Main Finding/Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | In vitro | PTC cells (BCPAP, TPC-1) | Inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion; induces apoptosis and autophagy [38,39,40] |
| In vivo (murine model) | APC xenografts | Enhances CD8+ T cell function and downregulates AKT/mTORC1/STAT3/PD-L1 axis; synergistic with anti-PD-1 [37] | |
| Preclinical | PTC cells | Inhibits metastasis via downregulation of the TGF-β/Smad2/3 pathway [43,44,45] | |
| Resveratrol | In vitro | APC cells (HTh7, 8505C) | Induces expression of differentiation markers (NIS) via Notch1 activation; suppresses cell growth [47,48,49,50,51] |
| In vitro | Thyroid cancer cells | Increases 131I-induced cell death; protects normal cells from 131I toxicity [46,47,48,49,50] | |
| In vivo (nanoparticles) | APC xenografts | Sustained-release nanoparticles effectively inhibit tumor growth in vivo, overcoming the poor bioavailability of free resveratrol [66] | |
| Quercetin | In vitro | Differentiated thyroid cancer cells | Induces anticancer activity via upregulation of pro-NAG-1/GDF15; induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest [54,55,56,57,58] |
| In vitro | Thyroid cancer cells | Inhibits proliferation and MMP3 expression under high glucose conditions [2] | |
| Preclinical | PTC cells | Demonstrates strong anti-tumor efficacy; regulates TNF, PI3K-AKT, NF-κB pathways [61,62] | |
| EGCG | In vitro | Human thyroid carcinoma cells | Inhibits growth and enhances apoptosis via suppression of EGFR/RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway [59] |
| In vitro | Human thyroid carcinoma cells | Decreases migration and invasion; inhibits proliferation and motility with loss of EMT markers [59,60,61,62] | |
| Nanoformulations | General | Various cancer types, including thyroid | Improve bioavailability, solubility, and stability; enable targeted tumor delivery [6,36,62,65] |
| ICIs (anti-PD-1/PD-L1) | Clinical | Thyroid cancer | Ongoing trials, including monotherapy and combinations; investigation of biomarkers [9] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simões, J.L.B.; Bagatini, M.D. Targeting the Purinergic Axis with Phenolic Compounds to Disrupt the Oxidative-Inflammatory Cycle in Thyroid Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178474
Simões JLB, Bagatini MD. Targeting the Purinergic Axis with Phenolic Compounds to Disrupt the Oxidative-Inflammatory Cycle in Thyroid Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178474
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimões, Júlia Leão Batista, and Margarete Dulce Bagatini. 2025. "Targeting the Purinergic Axis with Phenolic Compounds to Disrupt the Oxidative-Inflammatory Cycle in Thyroid Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178474
APA StyleSimões, J. L. B., & Bagatini, M. D. (2025). Targeting the Purinergic Axis with Phenolic Compounds to Disrupt the Oxidative-Inflammatory Cycle in Thyroid Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178474






