Early Insights from Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Patients: An Observational Study on Polygenic Risk and Liver Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
2.2. Liver Enzymes and Fibrosis Index
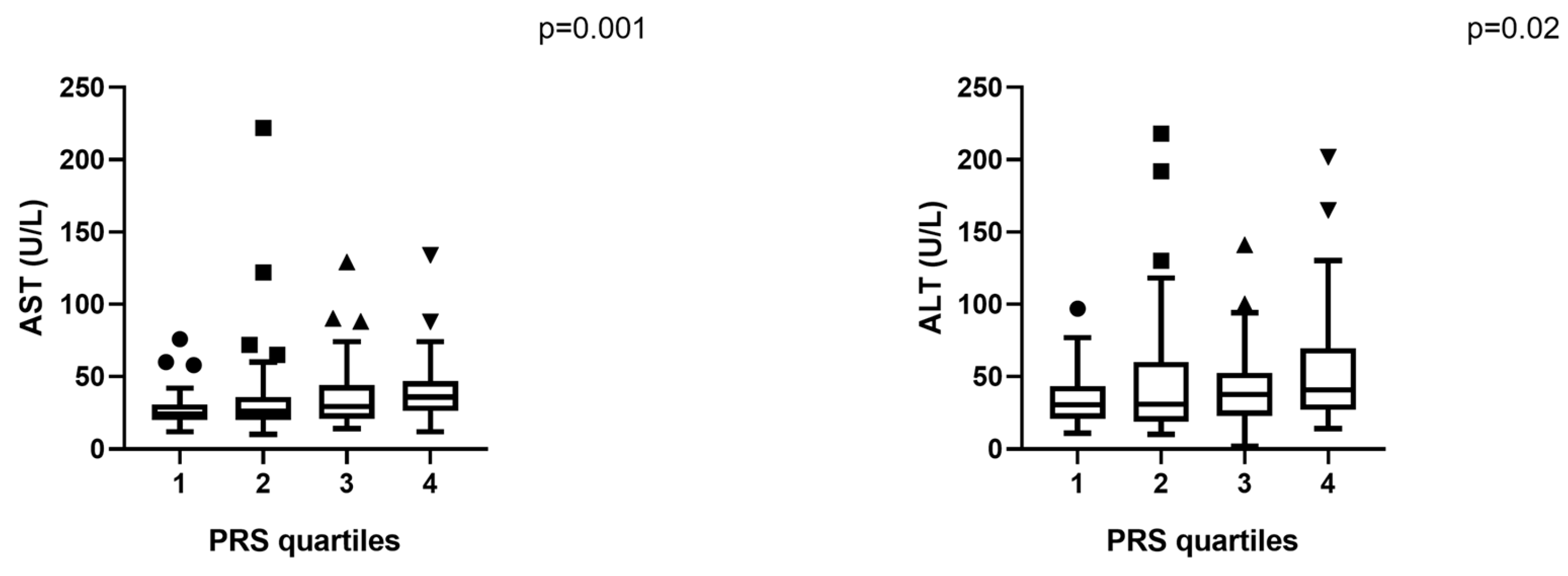
2.3. Hepatic Steatosis and Genetic Risk
2.4. Total Cohort Analysis
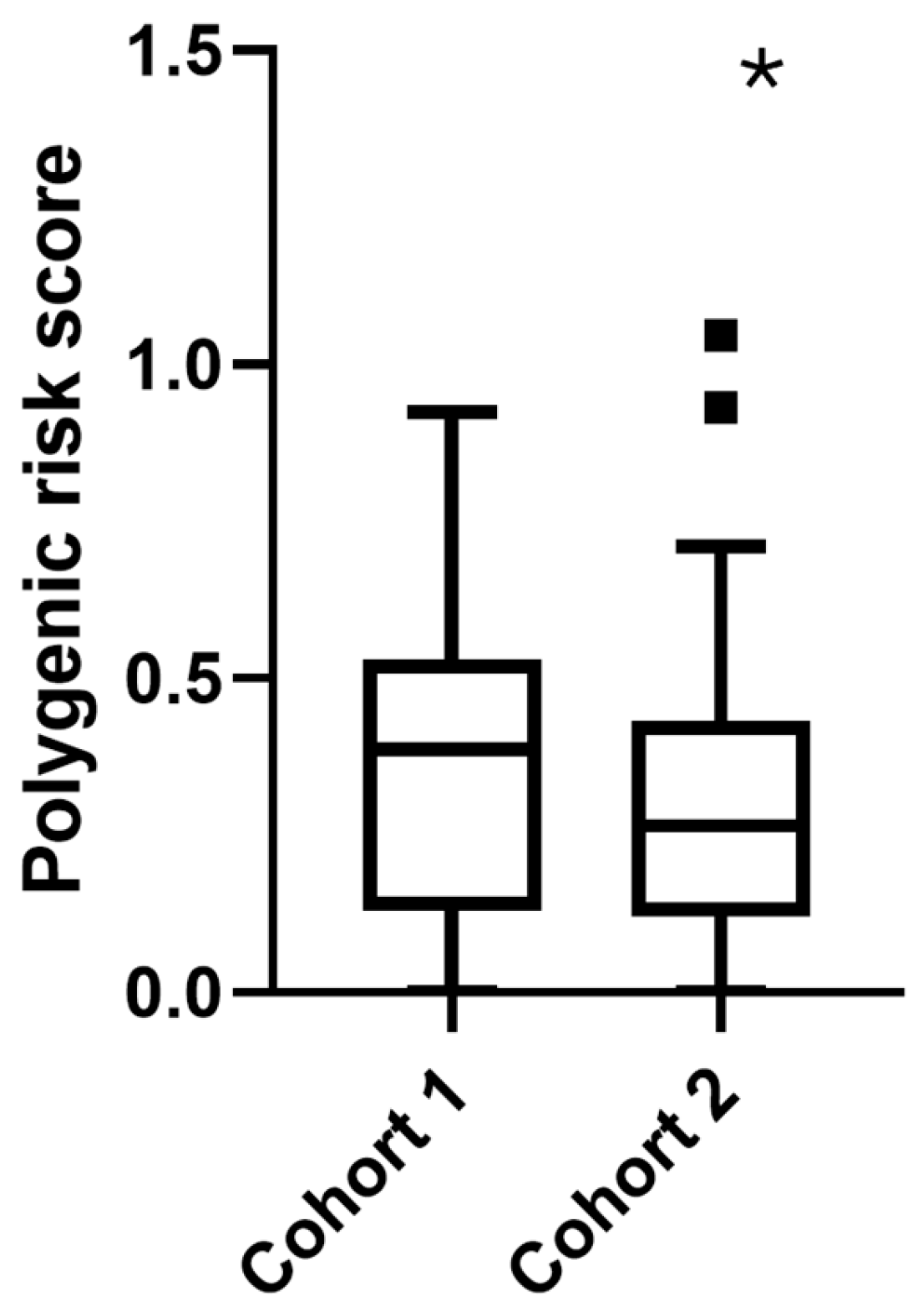
2.5. Cohort-Specific Analysis
2.5.1. Cohort 1: Internal Medicine
2.5.2. Cohort 2: Bariatric Surgery
2.6. SNP-Specific Associations in the Total Cohort
2.7. Cohort-Specific SNP Findings
2.7.1. Cohort 1: Internal Medicine
2.7.2. Cohort 2: Bariatric Surgery
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
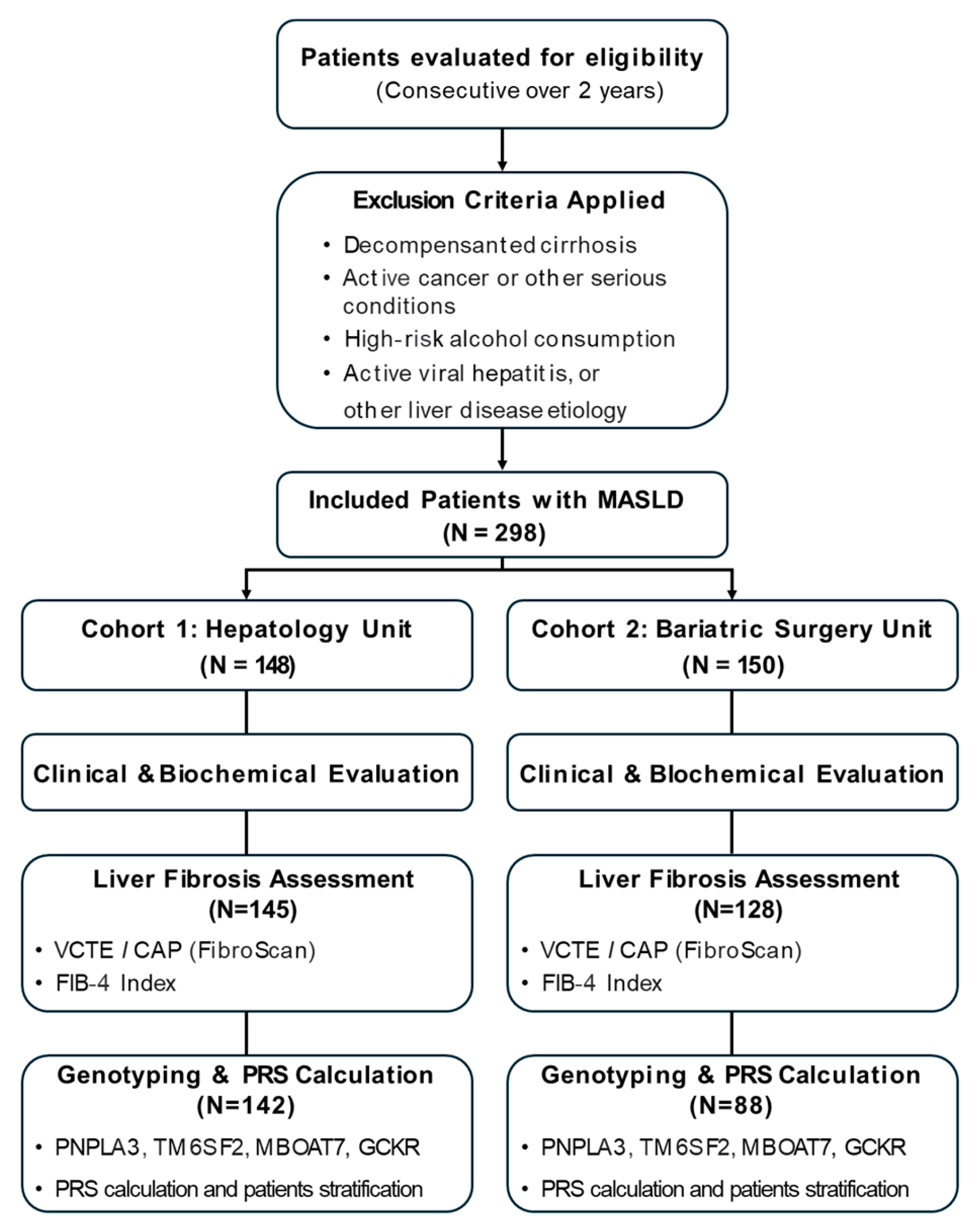
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Clinical and Biochemical Assessment
4.3. Liver Fibrosis and Steatosis Assessment
- Low-risk: <1.3 (or <2.0 for individuals > 65 years);
- Intermediate risk: 1.3–2.67;
- High-risk: >2.67.
4.4. Genotyping and PRS
- PNPLA3 (rs738409): dominant model;
- TM6SF2 (rs58542926): dominant model;
- MBOAT7 (rs641738): recessive model;
- GCKR (rs1260326): recessive model.
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MASLD | Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease |
| NAFLD | Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (former term for MASLD) |
| PRS | Polygenic Risk Score |
| SNP | Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| FIB-4 | Fibrosis-4 Index |
| LS | Liver Stiffness |
| CAP | Controlled Attenuation Parameter |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| VCTE | Vibration-Controlled Transient Elastography |
| LSM | Liver Stiffness Measurement |
| CMRF | Cardiometabolic Risk Factor |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| PNPLA3 | Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 |
| MBOAT7 | Membrane-bound O-acyltransferase domain-containing protein 7 |
| GCKR | Glucokinase regulatory |
| TM6SF2 | Transmembrane 6 superfamily 2 |
References
- Motta, B.M.; Masarone, M.; Torre, P.; Persico, M. From Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) to Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology, Incidence, Predictions, Risk Factors, and Prevention. Cancers 2023, 15, 5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated With Long-term Outcomes of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397.e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liver, E.A.f.t.S.o.t. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis-2021 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 659–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Kalligeros, M.; Henry, L. Epidemiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, S32–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofrad, P.; Contos, M.J.; Haque, M.; Sargeant, C.; Fisher, R.A.; Luketic, V.A.; Sterling, R.K.; Shiffman, M.L.; Stravitz, R.T.; Sanyal, A.J. Clinical and histologic spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated with normal ALT values. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golabi, P.; Otgonsuren, M.; Cable, R.; Felix, S.; Koenig, A.; Sayiner, M.; Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is associated with impairment of Health Related Quality of Life (HRQOL). Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2016, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, P.; Motta, B.M.; Sciorio, R.; Masarone, M.; Persico, M. Inflammation and Fibrogenesis in MAFLD: Role of the Hepatic Immune System. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 781567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlitina, J.; Smagris, E.; Stender, S.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Zhou, H.H.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Vogt, T.F.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Exome-wide association study identifies a TM6SF2 variant that confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancina, R.M.; Dongiovanni, P.; Petta, S.; Pingitore, P.; Meroni, M.; Rametta, R.; Borén, J.; Montalcini, T.; Pujia, A.; Wiklund, O.; et al. The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals of European Descent. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1219–1230.e1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, C.; Jamialahmadi, O.; Pelusi, S.; Baselli, G.; Dongiovanni, P.; Zanoni, I.; Santoro, L.; Maier, S.; Liguori, A.; Meroni, M.; et al. Non-invasive stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma risk in non-alcoholic fatty liver using polygenic risk scores. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Rotman, Y.; Valenti, L. Genetics of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease: The State of the Art Update. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 2177–2187.e2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, V.; Romeo, S.; Valenti, L. The contribution of genetics and epigenetics to MAFLD susceptibility. Hepatol. Int. 2024, 18, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yuan, H.; Suo, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X. Population stratification using MASLD polygenic risk score improves severe liver disease prediction by clinical fibrosis scores. Dig. Liver Dis. 2025, 57, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver; European Association for the Study of Diabetes. EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassailly, G.; Caiazzo, R.; Buob, D.; Pigeyre, M.; Verkindt, H.; Labreuche, J.; Raverdy, V.; Leteurtre, E.; Dharancy, S.; Louvet, A.; et al. Bariatric Surgery Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Morbidly Obese Patients. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 379–388, quiz e315-376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Meta-analysis of the influence of I148M variant of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene (PNPLA3) on the susceptibility and histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L.; Reeves, H.L.; Burt, A.D.; Tiniakos, D.; McPherson, S.; Leathart, J.B.; Allison, M.E.; Alexander, G.J.; Piguet, A.C.; Anty, R.; et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 influences hepatic fibrosis progression in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonett, D.G.; Wright, T.A. Sample Size Requirements for Estimating Pearson, Kendall and Spearman Correlations. Psychometrika 2000, 6, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Total (N = 298) | Cohort 1 (n = 148) | Cohort 2 (n = 150) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53.1 ± 13.1 | 58.3 ± 11.2 | 43.1 ± 10.4 | 2.7 × 10−19 |
| Female | 48.3% | 41.9% | 54.7% | 0.027 # |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 35.9 ± 6.4 | 33.1 ± 5.3 | 41.7 ± 4.6 | 3.9 × 10−24 |
| AST (U/L) | 34.3 ± 23.3 | 38.4 ± 26.6 | 25.8 ± 9.9 | 0.000013 |
| ALT (U/L) | 43.8 ± 33.4 | 48.3 ± 36.9 | 34.7± 22.1 | 0.005 |
| FIB-4 | 1.75 ± 1.77 | 2.09 ± 1.98 | 1.02 ± 0.87 | 4.0 × 10−5 |
| Liver Stiffness (kPa) | 9.4 ± 10.2 | 10.3 ± 11.2 | 8.3 ± 7.9 | NS |
| CAP (dB/m) | 307.0 ± 42 | 302.0 ± 43.7 | 312.5 ± 39.4 | NS |
| PRS | 0.342 ± 0.23 | 0.368 ± 0.24 | 0.302 ± 0.21 | 0.047 # |
| PRS | FIB-4 | AST | ALT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman’s rho | PRS | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | 0.189 ** | 0.300 ** | 0.224 ** |
| Sig. (1-tailed) | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.001 | |||
| N | 230 | 196 | 201 | 201 | ||
| FIB-4 | Correlation Coefficient | 0.189 ** | 1.000 | 0.552 ** | 0.174 ** | |
| Sig. (1-tailed) | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.007 | |||
| N | 196 | 203 | 203 | 203 | ||
| AST | Correlation Coefficient | 0.300 ** | 0.552 ** | 1.000 | 0.822 ** | |
| Sig. (1-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||
| N | 201 | 203 | 208 | 208 | ||
| ALT | Correlation Coefficient | 0.224 ** | 0.174 ** | 0.822 ** | 1.000 | |
| Sig. (1-tailed) | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.000 | |||
| N | 201 | 203 | 208 | 208 |
| Variant | Associated Marker | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Cohort 1 | Cohort 2 | ||
| PNPLA3 | AST ↑ BMI ↓ | AST ↑ ALT ↑ | - | Suggesting hepatic injury independently of adiposity |
| GCKR | LS and FIB-4 (p = 0.07) | LS ↑ | - | Possible fibrosis impact through altered glucose and lipid flux |
| MBOAT7 | CAP ↑ | CAP (p = 0.066) | AST ↑ ALT ↑ | Suggesting steatosis-driven injury |
| TM6SF2 | - | - | TG ↓ Cholesterol ↓ | Known cardioprotective/hepatotoxic profile |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torre, P.; Motta, B.M.; Sarcina, T.; Festa, M.; Masarone, M.; Persico, M. Early Insights from Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Patients: An Observational Study on Polygenic Risk and Liver Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178426
Torre P, Motta BM, Sarcina T, Festa M, Masarone M, Persico M. Early Insights from Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Patients: An Observational Study on Polygenic Risk and Liver Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178426
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorre, Pietro, Benedetta Maria Motta, Tommaso Sarcina, Mariano Festa, Mario Masarone, and Marcello Persico. 2025. "Early Insights from Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Patients: An Observational Study on Polygenic Risk and Liver Biomarkers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178426
APA StyleTorre, P., Motta, B. M., Sarcina, T., Festa, M., Masarone, M., & Persico, M. (2025). Early Insights from Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Patients: An Observational Study on Polygenic Risk and Liver Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178426











