Enhancing Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in Lung Cancer Cells Through Synergistic Targeting of the PI3K/AKT Pathway with Small Molecule Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
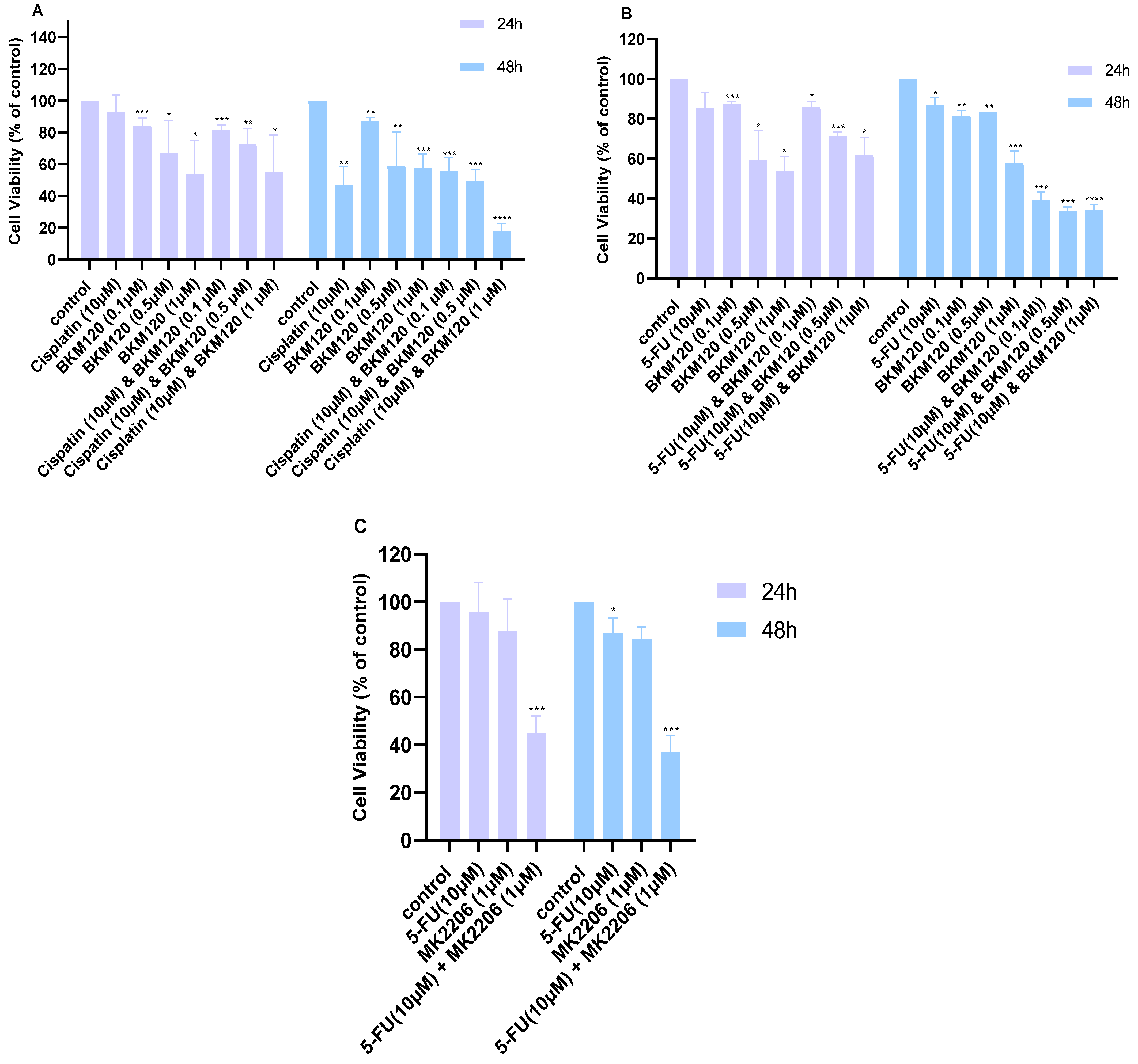
2.1. Combination of Cisplatin or 5-FU with Small Molecule Inhibitors Improves Their Cytotoxicity in Lung Cancer Cells
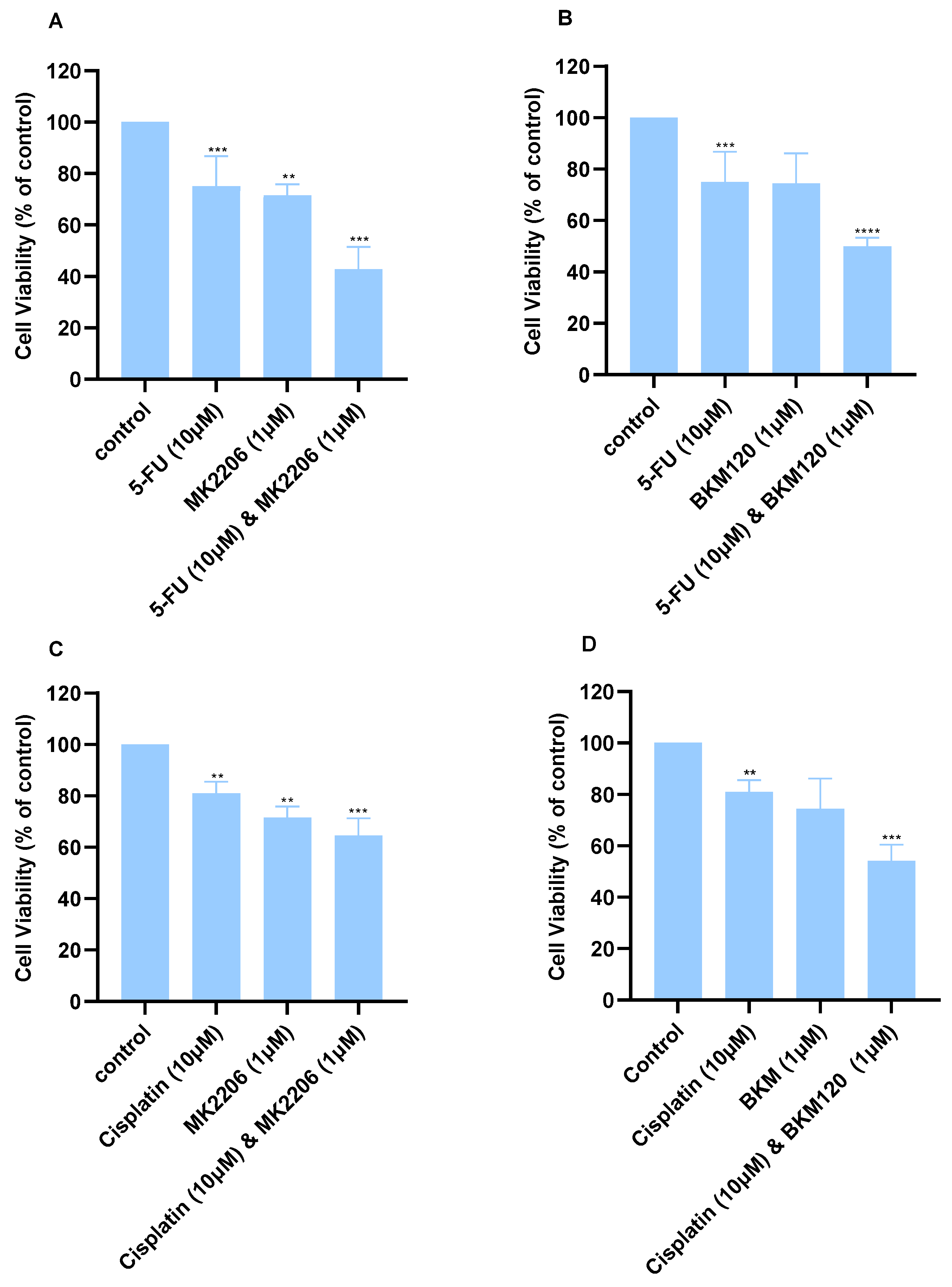
2.2. Chou–Talalay Analysis Reveals Synergistic Interactions Between Drug Concentrations
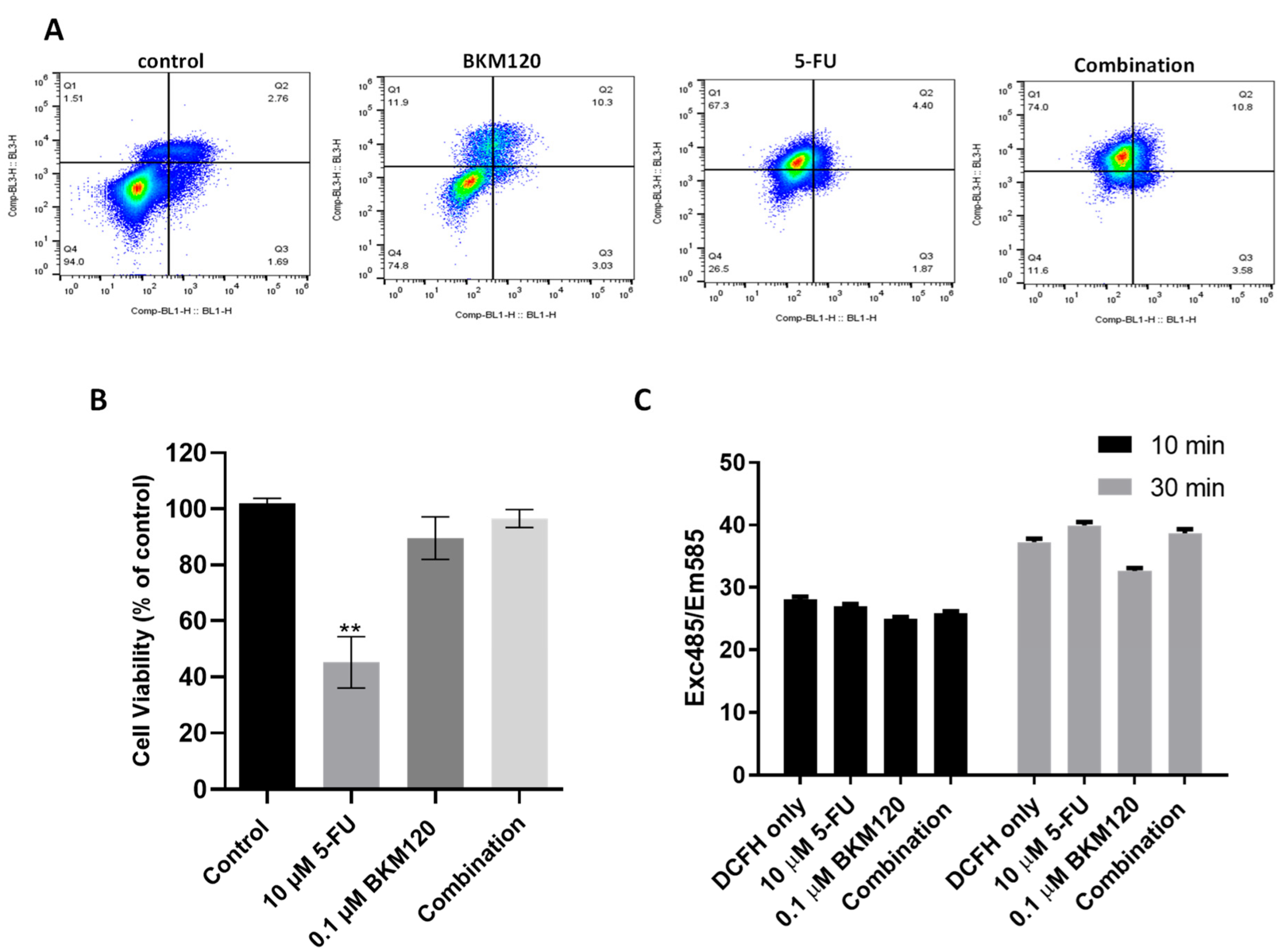
2.3. Combination of Selected Concentrations of 5-FU and BKM120 in H460 Cells Induces Apoptosis Without Affecting Normal Lung Cells
2.4. The Combination of Selected Agents Modifies the Expression Levels of Pro- and Anti-Apoptotic Proteins in H460 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. DCFH-DA
4.4. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide Staining
4.5. Total RNA Preparation and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (q-PCR)
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-FU | 5-Fluorouracil |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| CI | Combination Index |
| DCFH-DA | 2′-7′-Diclorofluorescein Diacetate |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| LCLC | Large cell lung carcinoma |
| LC | Lung cancer |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-monotetrazolium bromide |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| PI | Propidium Iodide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute |
| SCLC | Small cell lung cancer |
| SMIs | Small molecule inhibitors |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabath, M.B.; Cote, M.L. Cancer Progress and Priorities: Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Hu, R.; Xue, X.; Qu, M.; Sun, G. Novel therapeutic strategies for non-small cell lung cancer: Combination therapies with immune checkpoint inhibitors (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2025, 30, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemjabbar-Alaoui, H.; Hassan, O.U.; Yang, Y.W.; Buchanan, P. Lung cancer: Biology and treatment options. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2015, 1856, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neophytou, C.M.; Trougakos, I.P.; Erin, N.; Papageorgis, P. Apoptosis Deregulation and the Development of Cancer Multi-Drug Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The first metal based anticancer drug. Bioorgan. Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkovicova, D.; Neophytou, C.M.; Gasparovic, A.C.; Goncalves, A.C. DNA Damage Response in Cancer Therapy and Resistance: Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharati, A.; Rajabloo, Y.; Moghbeli, M. Molecular mechanisms of mTOR-mediated cisplatin response in tumor cells. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yin, Y.; Xu, S.J.; Chen, W.S. 5-Fluorouracil: Mechanisms of resistance and reversal strategies. Molecules 2008, 13, 1551–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.; Vale, N. Novel Drug Combinations in Lung Cancer: New Potential Synergies Between 5-FU and Repurposed Drugs. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Singh, S.K.; Mishra, M.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, R. Promising Combinatorial Therapeutic Strategies against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Wang, S.; Jiang, W.J.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Fan, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, H.J.; Sheng, R.; Fei, T. Chemoresistance mechanisms to 5-Fluorouracil and reversal strategies in lung and breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Pi, W.; Lan, Y.; Wu, X.; Lv, D.; Meng, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, W. Synergistic Antitumor Effects of Anlotinib Combined with Oral 5-Fluorouracil/S-1 via Inhibiting Src/AKT Signaling Pathway in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2022, 2022, 4484211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Liang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Xu, Q.; Zhong, M.; et al. ROS/PI3K/Akt and Wnt/beta-catenin signalings activate HIF-1alpha-induced metabolic reprogramming to impart 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2022, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in cancer: Mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, G.G.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.S.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vera, A.A.; Reznik, S.E. Combining PI3K/Akt/mTOR Inhibition with Chemotherapy; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sarris, E.G.; Saif, M.W.; Syrigos, K.N. The biological role of PI3K pathway in lung cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 1236–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Sootome, H.; Nakatsuru, Y.; Miyama, K.; Taguchi, S.; Tsujioka, K.; Ueno, Y.; Hatch, H.; Majumder, P.K.; Pan, B.S.; et al. MK-2206, an allosteric akt inhibitor, enhances antitumor efficacy by standard chemotherapeutic agents or molecular targeted drugs in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1956–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, M.; Brand, T.M.; Campbell, D.A.; Starr, M.M.; Luthar, N.; Traynor, A.M.; Wheeler, D.L. Targeting AKT with the allosteric AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in non-small cell lung cancer cells with acquired resistance to cetuximab. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yan, S.; Attayan, N.; Ramalingam, S.; Thiele, J.C. Combination of an allosteric Akt Inhibitor MK-2206 with etoposideor rapamycin enhances the anti-tumor growth effect in Neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3603–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Deng, X.; Xiang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.; Liu, Q. Plk3 Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity of Nonsmall-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT Pathway via Stabilizing PTEN. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 8995–9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaei, Z.N.; Khalili-Tanha, G.; Zangouei, A.S.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Moghbeli, M. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as a critical regulator of Cisplatin response in tumor cells. Oncol. Res. 2021, 29, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraud, J.; Bouriez, D.; Seeneevassen, L.; Rousseau, B.; Sifre, E.; Giese, A.; Megraud, F.; Lehours, P.; Dubus, P.; Gronnier, C.; et al. Orthotopic Patient-Derived Xenografts of Gastric Cancer to Decipher Drugs Effects on Cancer Stem Cells and Metastatic Dissemination. Cancers 2019, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, H.; Fang, J.; Yu, R. Metformin and buparlisib synergistically induce apoptosis of non-small lung cancer (NSCLC) cells via Akt/FoxO3a/Puma axis. Toxicol. Vitr. 2024, 97, 105801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ji, B.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Bain, D.J.; Sun, J.; et al. Advanced hierarchical computational modeling-based rational development of platinum (II) nanocomplex to improve lung cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2411334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khameneh, S.C.; Sari, S.; Razi, S.; Yousefi, A.M.; Bashash, D. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling using BKM120 reduced the proliferation and migration potentials of colorectal cancer cells and enhanced cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralhan, R.; Kaur, J. Alkylating agents and cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2007, 17, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, N.A.G.; Martins, N.M.; Curti, C.; Pires Bianchi, M.d.L.; dos Santos, A.C. Dimethylthiourea protects against mitochondrial oxidative damage induced by cisplatin in liver of rats. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2007, 170, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, M.K.; Burkhardt, G.; Köhler, H. Insights into potential cellular mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity and their clinical application. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1997, 12, 2478–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethy, C.; Kundu, C.N. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) resistance and the new strategy to enhance the sensitivity against cancer: Implication of DNA repair inhibition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, G.; Song, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Xu, Y. ABCG2 regulates the pattern of self-renewing divisions in cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2168–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, N.; Elshewy, A.; El-Askary, H.; Mohamed, K.O.; Helwa, A.A. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile derivatives as novel anti-cancer, dual EGFR(WT)/COX-2 inhibitors with docking studies. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 32296–32320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Soares, J.; Greninger, P.; Edelman, E.J.; Lightfoot, H.; Forbes, S.; Bindal, N.; Beare, D.; Smith, J.A.; Thompson, I.R.; et al. Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC): A resource for therapeutic biomarker discovery in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D955–D961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanaei, M.J.; Razi, S.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Bashash, D. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in lung cancer; oncogenic alterations, therapeutic opportunities, challenges, and a glance at the application of nanoparticles. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 18, 101364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopleva, M.Y.; Walter, R.B.; Faderl, S.H.; Jabbour, E.J.; Zeng, Z.; Borthakur, G.; Huang, X.; Kadia, T.M.; Ruvolo, P.P.; Feliu, J.B.; et al. Preclinical and early clinical evaluation of the oral AKT inhibitor, MK-2206, for the treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2226–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Lin, N.U.; Maurer, M.A.; Chen, H.; Mahvash, A.; Sahin, A.; Akcakanat, A.; Li, Y.; Abramson, V.; Litton, J.; et al. Phase II trial of AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in patients with advanced breast cancer who have tumors with PIK3CA or AKT mutations, and/or PTEN loss/PTEN mutation. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Zhou, Y.S.; Yang, J.X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Liu, Q.Q.; Yuan, C.; Wang, F.Z. MK-2206 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HepG2 cells and sensitizes TRAIL-mediated cell death. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 382, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, G.; Pierobon, M.; Kim, I.K.; Hsu, W.H.; Deng, J.; Moon, Y.W.; Petricoin, E.F.; Zhang, Y.W.; Wang, Y.; Giaccone, G. Inhibition of AKT1 signaling promotes invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells with K-RAS or EGFR mutations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Weng, H.C.; Hsu, J.L.; Lin, S.W.; Guh, J.H.; Hsu, L.C. The Combination of MK-2206 and WZB117 Exerts a Synergistic Cytotoxic Effect Against Breast Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Saura, C.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Guo, H.; Ciruelos, E.; Bermejo, B.; Gavilá, J.; Serra, V.; Prat, A.; Paré, L.; et al. Phase 2 study of buparlisib (BKM120), a pan-class I PI3K inhibitor, in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Canon, J.L.; De Braud, F.; Grossi, F.; De Pas, T.; Gray, J.E.; Su, W.C.; Felip, E.; Yoshioka, H.; Gridelli, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Buparlisib (BKM120) in Patients with PI3K Pathway-Activated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results from the Phase II BASALT-1 Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Inada-Inoue, M.; Mitsuma, A.; Yoshino, T.; Ohtsu, A.; Suenaga, N.; Sato, M.; Kakizume, T.; Robson, M.; Quadt, C.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of buparlisib (BKM120), an oral pan-class I PI3K inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, D.; Fu, J.; Shen, R.; LaFortune, T.A.; Wang, S.; Tiao, N.; Kim, Y.W.; Liu, J.L.; Ramnarian, D.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Antitumor activity of NVP-BKM120--a selective pan class I PI3 kinase inhibitor showed differential forms of cell death based on p53 status of glioma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Qian, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, H.; Lan, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, J.; et al. Novel phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor NVP-BKM120 induces apoptosis in myeloma cells and shows synergistic anti-myeloma activity with dexamethasone. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.K.; Machado-Neto, J.A.; Lopes, M.R.; Morini, B.C.; Traina, F.; Costa, F.F.; Saad, S.T.; Favaro, P. Molecular effects of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor NVP-BKM120 on T and B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, X.; Guan, W.; Qian, M.; Yao, Z.; Yin, X.; Zhao, H. NVP-BKM120 inhibits colon cancer growth via FoxO3a-dependent PUMA induction. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 83052–83062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendell, J.C.; Rodon, J.; Burris, H.A.; de Jonge, M.; Verweij, J.; Birle, D.; Demanse, D.; De Buck, S.S.; Ru, Q.C.; Peters, M.; et al. Phase I, dose-escalation study of BKM120, an oral pan-Class I PI3K inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, M.; Santiskulvong, C.; Eng, C.; Dorigo, O. Effect of PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition-mediated G1 arrest on chemosensitization in ovarian cancer cells. Anticancer. Res. 2012, 32, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Hu, H. The Influence of Cell Cycle Regulation on Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Leung, P.C.; Cho, W.C.; Wong, C.K.; Wang, D. Targeting PI3K signaling in Lung Cancer: Advances, challenges and therapeutic opportunities. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N. Targeting the DNA Damage Response Machinery for Lung Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Na, T.; Wang, L.; Gao, Q.; Yin, W.; Wang, J.; Yuan, B.Z. Human diploid MRC-5 cells exhibit several critical properties of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6820–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, R. Effect of small molecule phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor combined with 5-fluorouracil on regulating progression of breast cancer cells. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2025, 18, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, R.; Hande, M.P. A comparative study of protein kinase C activation in gamma-irradiated proliferating and confluent human lung fibroblast cells. J. Radiat. Res. 2009, 50, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, K.S.; Joo, S.H. Modulation of Reactive Oxygen Species to Overcome 5-Fluorouracil Resistance. Biomol. Ther. 2022, 30, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Tondro Anamag, F.; Shoorei, H.; Fattahi, F.; Javadinia, S.A.; Basiri, A.; Taheri, M. 5-Fluorouracil: A Narrative Review on the Role of Regulatory Mechanisms in Driving Resistance to This Chemotherapeutic Agent. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 658636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Peng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, B.; Elkabets, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, R.; Zhong, Y.; et al. BKM120 sensitizes glioblastoma to the PARP inhibitor rucaparib by suppressing homologous recombination repair. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
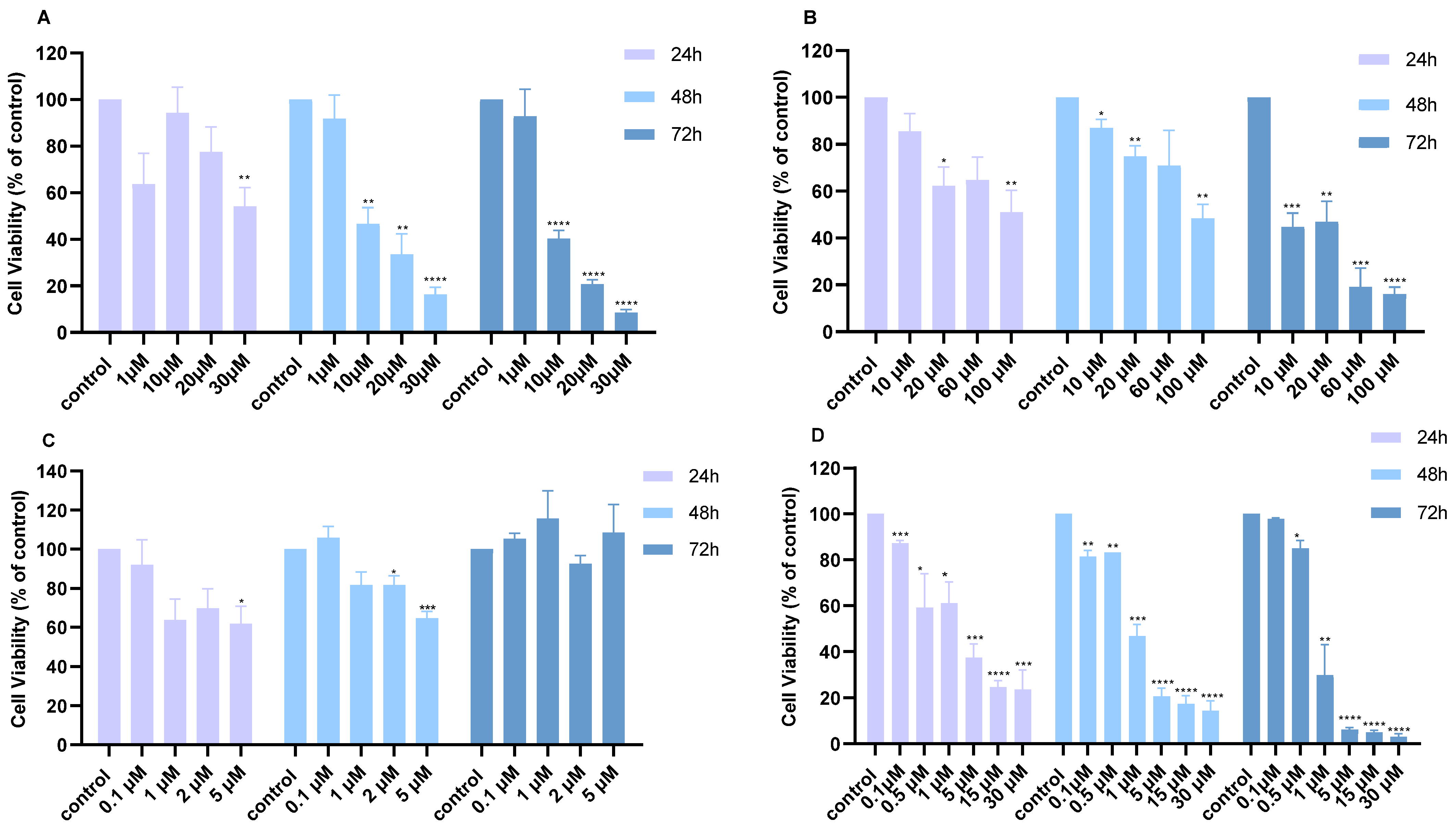


| H460 | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
| Cisplatin | 50.4 | 8.6 | 6.0 |
| 5-FU | 85.5 | 105.2 | 12.3 |
| MK2206 | 117.5 | 202.3 | N/A |
| BKM120 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| A549 | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
| Cisplatin | 109.4 | 37.3 | 25.7 |
| 5-FU | 134.5 | 110.2 | 38.6 |
| MK2206 | 6.2 | 4.8 | 13.6 |
| BKM120 | 13.3 | 4.8 | 6.2 |
| Dose Cisplatin 48 h | Dose BKM120 48 h | Effect | CI |
| 10.0 | 0.1 | 0.56 | 1.84 |
| 10.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.61 |
| 10.0 | 1.0 | 0.18 | 0.22 |
| Dose 5-FU 48 h | Dose BKM120 48 h | Effect | CI |
| 10.0 | 0.1 | 0.39 | 0.08 |
| 10.0 | 0.5 | 0.34 | 0.16 |
| 10.0 | 1.0 | 0.35 | 0.32 |
| Dose Cisplatin 48 h | Dose BKM120 48 h | Effect | CI |
| 10.0 | 1.0 | 0.54 | 0.48 |
| Dose Cisplatin 48 h | Dose MK2206 48 h | Effect | CI |
| 10.0 | 1.0 | 0.64 | 0.88 |
| Dose 5-FU 48 h | Dose BKM120 48 h | Effect | CI |
| 10.0 | 1.0 | 0.49 | 0.23 |
| Dose 5-FU 48 h | Dose MK2206 48 h | Effect | CI |
| 10.0 | 1.0 | 0.42 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michael, M.; Christou, M.; Kanakas, I.; Neophytou, C.M. Enhancing Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in Lung Cancer Cells Through Synergistic Targeting of the PI3K/AKT Pathway with Small Molecule Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178378
Michael M, Christou M, Kanakas I, Neophytou CM. Enhancing Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in Lung Cancer Cells Through Synergistic Targeting of the PI3K/AKT Pathway with Small Molecule Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178378
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichael, Maria, Maria Christou, Iason Kanakas, and Christiana M. Neophytou. 2025. "Enhancing Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in Lung Cancer Cells Through Synergistic Targeting of the PI3K/AKT Pathway with Small Molecule Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178378
APA StyleMichael, M., Christou, M., Kanakas, I., & Neophytou, C. M. (2025). Enhancing Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in Lung Cancer Cells Through Synergistic Targeting of the PI3K/AKT Pathway with Small Molecule Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178378








