Dysregulation of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Targeting Oncogenic Signaling Pathways for Innovative Therapies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. miRNA Biogenesis and Regulation in HCC
3. PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway
4. Hippo–YAP/TAZ Pathway
5. Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
6. RAS/MAPK Pathway
7. p53 Pathway
8. miRNA-Based Therapeutics in HCC: Clinical Progress and Delivery Strategies
9. miRNA-Based Combination Therapies
10. Clinical Trials on miRNA Biomarkers and Therapies in HCC
11. Challenges and Future Perspectives
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarlashat, Y.; Mushtaq, H.; Pham, L.; Abbas, W.; Sato, K. Advancements in Immunotherapeutic Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Potential of Combination Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarlashat, Y.; Abbas, S.; Ghaffar, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Beyond the Border of Advanced Stage Therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarlashat, Y.; Ghaffar, A.; Guerra, F.; Picca, A. Immunological Landscape and Molecular Therapeutic Targets of the Tumor Microenvironment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarlashat, Y.; Tayyeba, A.; Hussain, S. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios in hepatocellular carcinoma: From inflammation to clinical applications. Cancer Plus 2024, 6, 5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Mackowiak, B.; Gao, B. MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Gut 2021, 70, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majem, B.; Rigau, M.; Reventós, J.; Wong, D.T. Non-coding RNAs in saliva: Emerging biomarkers for molecular diagnostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 8676–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Quintero, B. Cell-free microRNAs in blood and other body fluids, as cancer biomarkers. Cell Prolif. 2016, 49, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzeniewski, N.; Tosev, G.; Pahernik, S.; Hadaschik, B.; Hohenfellner, M.; Duensing, S. Identification of cell-free microRNAs in the urine of patients with prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2015, 33, 16.e17–16.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, G.; Pezzi, M.E.; Viani, M.V.; Pertinhez, T.A.; Cassi, D.; Magnoni, C.; Bellini, P.; Musolino, A.; Vescovi, P.; Meleti, M. Salivary MicroRNA for Diagnosis of Cancer and Systemic Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Halim, A.S.; Rudayni, H.A.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Ali, M.A.M. MicroRNAs: Small molecules with big impacts in liver injury. J. Cell Physiol. 2023, 238, 32–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorolyai, S.; Shajari, N.; Baghbani, E.; Sadreddini, S.; Baradaran, B. The relation between PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and cancer. Gene 2019, 698, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloudizargari, M.; Asghari, M.H.; Nabavi, S.F.; Gulei, D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Bishayee, A.; Nabavi, S.M. Targeting Hippo signaling pathway by phytochemicals in cancer therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 80, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.; Elkady, M.A.; Yehia, A.M.; Elsakka, E.G.E.; Abulsoud, A.I.; Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; Elshafei, A.; Abdelghany, T.M.; Elkhawaga, S.Y.; Ismail, A.; et al. The role of miRNAs in laryngeal cancer pathogenesis and therapeutic resistance-A focus on signaling pathways interplay. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 246, 154510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masliah-Planchon, J.; Garinet, S.; Pasmant, E. RAS-MAPK pathway epigenetic activation in cancer: miRNAs in action. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38892–38907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenyev, S.; Singh, A.; Fedorova, O.; Daks, A.; Kulshreshtha, R.; Barlev, N.A. Interplay between p53 and non-coding RNAs in the regulation of EMT in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadh, M.J.; Hussain, Q.M.; Alazzawi, T.S.; Fahdil, A.A.; Athab, Z.H.; Yarmukhamedov, B.; Al-Nuaimi, A.M.A.; Alsaikhan, F.; Farhood, B. MicroRNA as Key Players in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insights into Their Role in Metastasis. Biochem. Genet. 2025, 63, 1014–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Yu, X.; Shi, H.; Sun, B.; Amateau, S. miRNAs in HCC, pathogenesis, and targets. Hepatology 2024, 1177, 10-1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, L.A.; Mastebroek, D.J.; Ten Voorde, N.; van der Wall, E.; van Diest, P.J.; Moelans, C.B. The microRNA Lifecycle in Health and Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Dai, Q.; Su, X.; Fu, J.; Feng, X.; Peng, J. Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: The framework of malignant behavior. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4587–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.S.; Moglad, E.; Afzal, M.; Gupta, G.; Almalki, W.H.; Kazmi, I.; Alzarea, S.I.; Kukreti, N.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, D.; et al. Non-coding RNA mediated regulation of PI3K/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma: Therapeutic perspectives. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 258, 155303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oura, K.; Morishita, A.; Masaki, T. Molecular and Functional Roles of MicroRNAs in the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Wu, Q.M.; Chang, L.Y.; Liu, J.C. miR-34a and miR-125a-5p inhibit proliferation and metastasis but induce apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via repressing the MACC1-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Hoshino, H.; Wang, J.; Ono, S.; Iida, Y.; Hata, K.; Huang, S.K.; Colquhoun, S.; Hoon, D.S. MicroRNA-93 activates c-Met/PI3K/Akt pathway activity in hepatocellular carcinoma by directly inhibiting PTEN and CDKN1A. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3211–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Manriquez, L.M.; Carrasco-Morales, O.; Sanchez, Z.E.A.; Osorio-Perez, S.M.; Estrada-Meza, C.; Pathak, S.; Banerjee, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Paul, S. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of key signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma: A mechanistic insight. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 910733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ni, Q.; Li, M. MiR-660-5p promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by interaction with YWHAH via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 531, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Zhang, X.; Wan, Z. miR-3691-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through activating PI3K/Akt signaling by targeting PTEN. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 4897–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, H. miR-30b-3p Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Suppressing PI3K/Akt Pathway. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dong, J. Overexpression of microRNA-133b is associated with the increased survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatectomy: Involvement of the EGFR/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, T.; Yao, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, W.; Liu, Z. microRNA-1914, which is regulated by lncRNA DUXAP10, inhibits cell proliferation by targeting the GPR39-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in HCC. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 8292–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cui, M.; Qu, F.; Cheng, D.; Yu, J.; Tang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Wei, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, X. MiR-92a-3p Promotes the Malignant Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Mediating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 3244–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Zhang, B.L.; Yang, M.Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, C.H.; Zhang, S.G.; Liu, R. MicroRNA-106b-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development via modulating FOG2. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 5639–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F. MicroRNA in HCC: Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. Oncologie 2021, 23, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.Y.; Xie, H.J.; Li, Z.; Kong, L.F.; Gou, X.N.; Li, D.J.; Shi, Y.J.; Ding, Y.Z. miR-34a regulates HDAC1 expression to affect the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, F. MicroRNA-148a Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Growth via Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways by Targeting Death Receptor-5. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2731–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zheng, N.; Teng, F.; Bao, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M.; Guo, W.; Ding, G.; Wang, Q. MiR-199a/b-5p inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by post-transcriptionally suppressing ROCK1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 67169–67180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Benedetto, G.; Parisi, S.; Russo, T.; Passaro, F. YAP and TAZ Mediators at the Crossroad between Metabolic and Cellular Reprogramming. Metabolites 2021, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, W.; Song, Y.; Kim, J.R.; Cho, K.; Moon, H.; Ro, S.W.; Seo, E.; Ryu, Y.M.; Myung, S.J.; et al. Deubiquitinase YOD1 potentiates YAP/TAZ activities through enhancing ITCH stability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4691–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Ye, M.; Wang, F.; Fang, J.; Wang, C.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Q.; et al. MiR-21-3p Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via SMAD7/YAP1 Regulation. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 642030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Yang, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; He, X.; Zhan, M. MiR-135b promotes HCC tumorigenesis through a positive-feedback loop. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 530, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, L.; Tu, J.; Wu, T. Hypoxia-Induced Placenta-Specific microRNA (miR-512-3p) Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 2. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 6073–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Li, T.; Ai, N.; Wang, W.; He, B.; Bai, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, M.; Dong, S.; Zhu, Q.; et al. MEIS2C and MEIS2D promote tumor progression via Wnt/β-catenin and hippo/YAP signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Yao, B.; Liu, Q.; Guo, C. miR-1307-3p promotes tumor growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing DAB2 interacting protein. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Gong, J.; Shen, W.; Liu, C. miR-29c-3p regulates DNMT3B and LATS1 methylation to inhibit tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lung, R.W.M.; Tong, J.H.M.; Chan, A.W.H.; Zhang, B.; Wong, C.C.; Wu, F.; et al. miR-375 is involved in Hippo pathway by targeting YAP1/TEAD4-CTGF axis in gastric carcinogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhu, H.R.; Liu, T.T.; Shen, X.Z.; Zhu, J.M. The Hippo pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma: Non-coding RNAs in action. Cancer Lett. 2017, 400, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, A.M.; Fuentes, D.; Morshid, A.I.; Burke, M.R.; Kaseb, A.O.; Hassan, M.; Hazle, J.D.; Elsayes, K.M. Role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma, pathogenesis, and clinical significance. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2018, 5, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Apaer, S.; Yao, G.; Li, T. microRNA-19a-3p and microRNA-376c-3p Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through SOX6-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, P.; Lin, J.; Zheng, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, G.; Chen, D.; Xie, J.; Gao, Z.; Peng, L.; et al. MicroRNA-197 Promotes Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 470–486, Erratum in Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 56, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, C.; Yu, C. MicroRNA-500a promotes migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.; Ng, K.Y.; Tong, M.; Lau, E.Y.; Lee, T.K.; Chan, K.W.; Yuan, Y.F.; Cheung, T.T.; Cheung, S.T.; Wang, X.Q.; et al. Octamer 4/microRNA-1246 signaling axis drives Wnt/β-catenin activation in liver cancer stem cells. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2062–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, H.; Yu, Z.Y.; Feng, X.; Fu, B.S.; Qiu, C.H.; Zhang, J.W. MicroRNA-194 inhibits cell invasion and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma through PRC1-mediated inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, R.Q.; Li, W.B.; Hu, Z.W.; Wu, Z.X.; Sun, W. MiR-329-3p inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration through USP22-Wnt/β-Catenin pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 9932–9939. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Jia, S.; Zhao, S.; Shao, X. MiR-342 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Biomarks 2019, 25, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Qiu, L.; He, G.L.; Cai, L.; Peng, B.J.; Cao, Y.L.; Pan, M.X. MicroRNA-361-5p suppresses the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting WT1 and suppressing WNT/β-cadherin pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8823–8832. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.C.; Xiao, G.; Zhou, R.; Huang, X.P.; Li, N.L.; Tan, C.L.; Xie, F.J.; Weng, J.; Liu, L.X. MicroRNA-361-5p Inhibits Tumorigenesis and the EMT of HCC by Targeting Twist1. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8891876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Xu, B.W.; Shen, D.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Meng, G.X.; Li, G.Z.; Zhang, Z.L. BRF2 is mediated by microRNA-409-3p and promotes invasion and metastasis of HCC through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Dai, C.; Yu, X.; Yin, X.B.; Zhou, F. microRNA-485-5p inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through blocking the WBP2/Wnt signaling pathway. Cell. Signal. 2020, 66, 109466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.H.; Cai, K.T.; Lu, H.P.; Guo, Y.N.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.H.; Tang, W.; Huang, S.N. Overexpression of MiR-452-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and its prospective signaling pathways. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 4041–4056. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Khoshbakht, T.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Samadian, M. A Review on the Role of miR-1246 in the Pathoetiology of Different Cancers. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 8, 771835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, N. Role of Oncogenic Pathways on the Cancer Immunosuppressive Microenvironment and Its Clinical Implications in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarlashat, Y.; Ambreen, A.; Zafar, M.; Mushtaq, H.; Munir, B.; Mujahid, M.; Ghaffar, A. Effect of doxorubicin and paclitaxel on the selective oncogenes expression level of hepatocellular carcinoma RASRAF/MEK/ERK pathway in Huh-7 cell line. Agrobiol. Rec. 2024, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq, H.; Zarlashat, Y.; Ambreen, A.; Mujahid, M.; Kausar, S.; Shafqat, D. Reviewing advances in understanding and targeting the MAPK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma progression and therapeutics. Agrobiol. Rec. 2024, 15, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delire, B.; Stärkel, P. The Ras/MAPK pathway and hepatocarcinoma: Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Lin, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Zhu, S.; Wei, Y.; Huo, L.; Chen, Y.; Shang, C. miR-126-3p contributes to sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulating SPRED1. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 38, Erratum in Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Yang, M.; Yang, H.; Chang, R.; Fang, F.; Yang, L. miR-330-5p targets SPRY2 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression via MAPK/ERK signaling. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 90, Erratum in Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.T.; Shi, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Y.F.; Liu, W.R.; Shi, G.M.; Gao, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Song, K.; Fan, J.; et al. MicroRNA-30a suppresses autophagy-mediated anoikis resistance and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, C.; Shi, W.; Liu, M.; Tu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Hu, L. Reciprocal negative feedback loop between EZH2 and miR-101-1 contributes to miR-101 deregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chun, K.H. Molecular Targets and Signaling Pathways of microRNA-122 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Z.; Yang, M.; Yang, T.; Ma, M.; Yang, Z. Metal-Regulatory Transcription Factor-1 Targeted by miR-148a-3p Is Implicated in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 700649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Li, L.; Deng, N.; Xu, Y.; Wang, G.; Luo, H.; Xu, C.; Li, X. microRNA-203 functions as a natural Ras inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Dou, Z.; Lu, F.; Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Li, X. MicroRNA-6838-5p suppresses the self-renewal and metastasis of human liver cancer stem cells through downregulating CBX4 expression and inactivating ERK signaling. Biol. Chem. 2022, 404, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J.H.; Jiang, C.P. Diverse roles of miR-29 in cancer (review). Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.D.; Zhao, W.M.; Wang, X.N.; Li, Q.; Huang, H.; Cheng, W.P.; Jin, J.F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, M.J.; Tai, S.; et al. MicroRNA-107: A novel promoter of tumor progression that targets the CPEB3/EGFR axis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.M.; Li, L.X.; Bian, X.Y.; Shi, X.J.; Lu, L.L.; Zhou, H.X.; Pan, T.J.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Wu, W.Z. miR-296-5p suppresses EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma via attenuating NRG1/ERBB2/ERBB3 signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, H.B.; Mandlik, S.K.; Mandlik, D.S. Role of p53 suppression in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2023, 14, 46–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.I.; Yamagata, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Iwamoto, T.; Kato, S.; Miyazono, K. Modulation of microRNA processing by p53. Nature 2009, 460, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollutri, D.; Gramantieri, L.; Bolondi, L.; Fornari, F. TP53/MicroRNA Interplay in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fründt, T.; Krause, L.; Hussey, E.; Steinbach, B.; Köhler, D.; von Felden, J.; Schulze, K.; Lohse, A.W.; Wege, H.; Schwarzenbach, H. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of miR-16, miR-146a, miR-192 and miR-221 in Exosomes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver Cirrhosis Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupini, L.; Pepe, F.; Ferracin, M.; Braconi, C.; Callegari, E.; Pagotto, S.; Spizzo, R.; Zagatti, B.; Lanuti, P.; Fornari, F.; et al. Over-expression of the miR-483-3p overcomes the miR-145/TP53 pro-apoptotic loop in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 31361–31371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Milazzo, M.; Chieco, P.; Negrini, M.; Marasco, E.; Capranico, G.; Mantovani, V.; Marinello, J.; Sabbioni, S.; Callegari, E.; et al. In hepatocellular carcinoma miR-519d is up-regulated by p53 and DNA hypomethylation and targets CDKN1A/p21, PTEN, AKT3 and TIMP2. J. Pathol. 2012, 227, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; Deng, H.; Wan, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Tang, H. miR-1228 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of hepatoma cells through a p53 forward feedback loop. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ju, W.; Wang, D.; Zhu, X.; He, X. MicroRNA-26a targets the mdm2/p53 loop directly in response to liver regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, M.; Ying, M.; Ling, M. miRNA-125a-5p inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting TP53 regulated inhibitor of apoptosis 1 and Bcl-2-like-2 protein. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Feng, Y.G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, F.; Feng, Y. microRNA-23a in Human Cancer: Its Roles, Mechanisms and Therapeutic Relevance. Cancers 2018, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabáková, E.; Culig, Z.; Remšík, J.; Souček, K. Alternative mechanisms of miR-34a regulation in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3100, Erratum in Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, Y. The Emerging Roles of miR-125b in Cancers. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wen, F.; Cui, Y. Integrative transcriptome analysis identifies a crotonylation gene signature for predicting prognosis and drug sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tao, Y.; Shan, L.; Chen, R.; Jiang, H.; Qian, Z.; Cai, F.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y. The Role of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3557–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misso, G.; Di Martino, M.T.; De Rosa, G.; Farooqi, A.A.; Lombardi, A.; Campani, V.; Zarone, M.R.; Gullà, A.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; et al. Mir-34: A new weapon against cancer? Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 847–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.L.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA: Trends in clinical trials of cancer diagnosis and therapy strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogheim, G.; Chinnam, S.; Amralla, M.T. Lipid Nanoparticles as a Platform for miRNA and siRNA Delivery in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 22, 837–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; He, L.; Lai, Z.; Wan, Z.; Chen, Q.; Pan, S.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Xue, F.; et al. Gold nano-particles (AuNPs) carrying miR-326 targets PDK1/AKT/c-myc axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2830–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Cheng, L.; Liang, Y.; Lei, H.; Qin, M.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. MicroRNA therapeutic delivery strategies: A review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 93, 105430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Sharma, G.; Sarkar, B.K.; Lee, S.S. The novel strategies for next-generation cancer treatment: miRNA combined with chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 10164–10174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raniolo, S.; Unida, V.; Vindigni, G.; Stolfi, C.; Iacovelli, F.; Desideri, A.; Biocca, S. Combined and selective miR-21 silencing and doxorubicin delivery in cancer cells using tailored DNA nanostructures. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.Z.; Sun, P.; Wang, J.P.; Liu, Y.; Gong, W.; Liu, J. MiR-34a overexpression enhances the inhibitory effect of doxorubicin on HepG2 cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2752–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Elzallat, M.; Aboushousha, T.; Elhusseny, Y.; El-Ahwany, E. MicroRNA-122 mimic/microRNA-221 inhibitor combination as a novel therapeutic tool against hepatocellular carcinoma. NonCoding RNA Res. 2022, 8, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, L.; Fang, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhan, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. MiR-338-3p inhibits hepatocarcinoma cells and sensitizes these cells to sorafenib by targeting hypoxia-induced factor 1α. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ding, B.; Lou, W.; Lin, S. Promoter Hypomethylation and miR-145-5p Downregulation-Mediated HDAC11 Overexpression Promotes Sorafenib Resistance and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, M.; Lambert, B.; Meryet-Figuière, M.; Brotin, E.; Weiswald, L.B.; Paysant, H.; Vigneron, N.; Wambecke, A.; Abeilard, E.; Giffard, F.; et al. Functional miRNA Screening Identifies Wide-ranging Antitumor Properties of miR-3622b-5p and Reveals a New Therapeutic Combination Strategy in Ovarian Tumor Organoids. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1506–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D.P.; Conde, J. Gold Nanoconjugates for miRNA Modulation in Cancer Therapy: From miRNA Silencing to miRNA Mimics. ACS Mater. Au 2022, 2, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.T.; Hsu, W.F.; Huang, H.S.; Yen, J.H.; Lin, M.C.; Peng, C.Y.; Yen, H.R. Improved Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Cardiac Arrhythmia by Amiodarone Treatment through Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
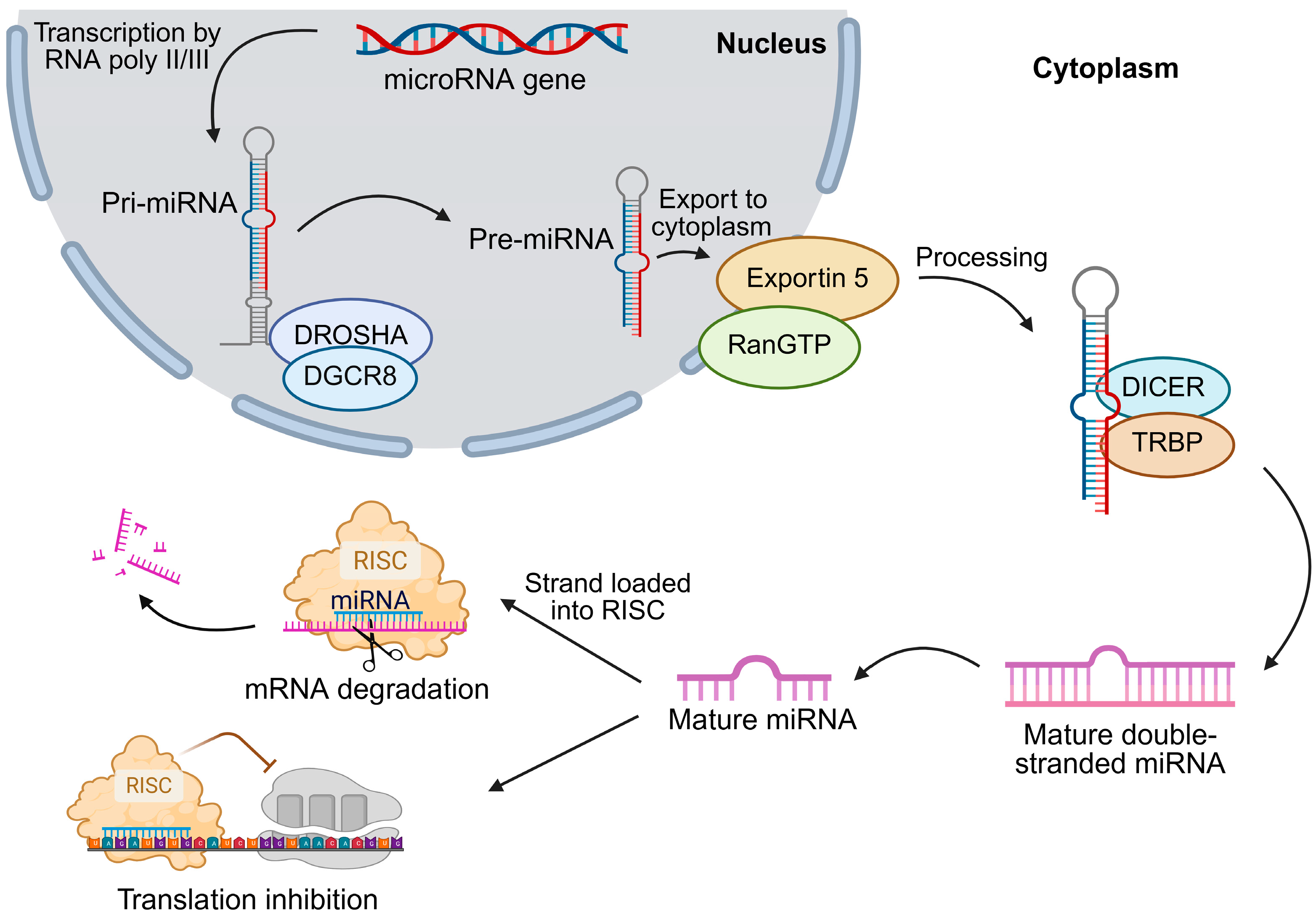
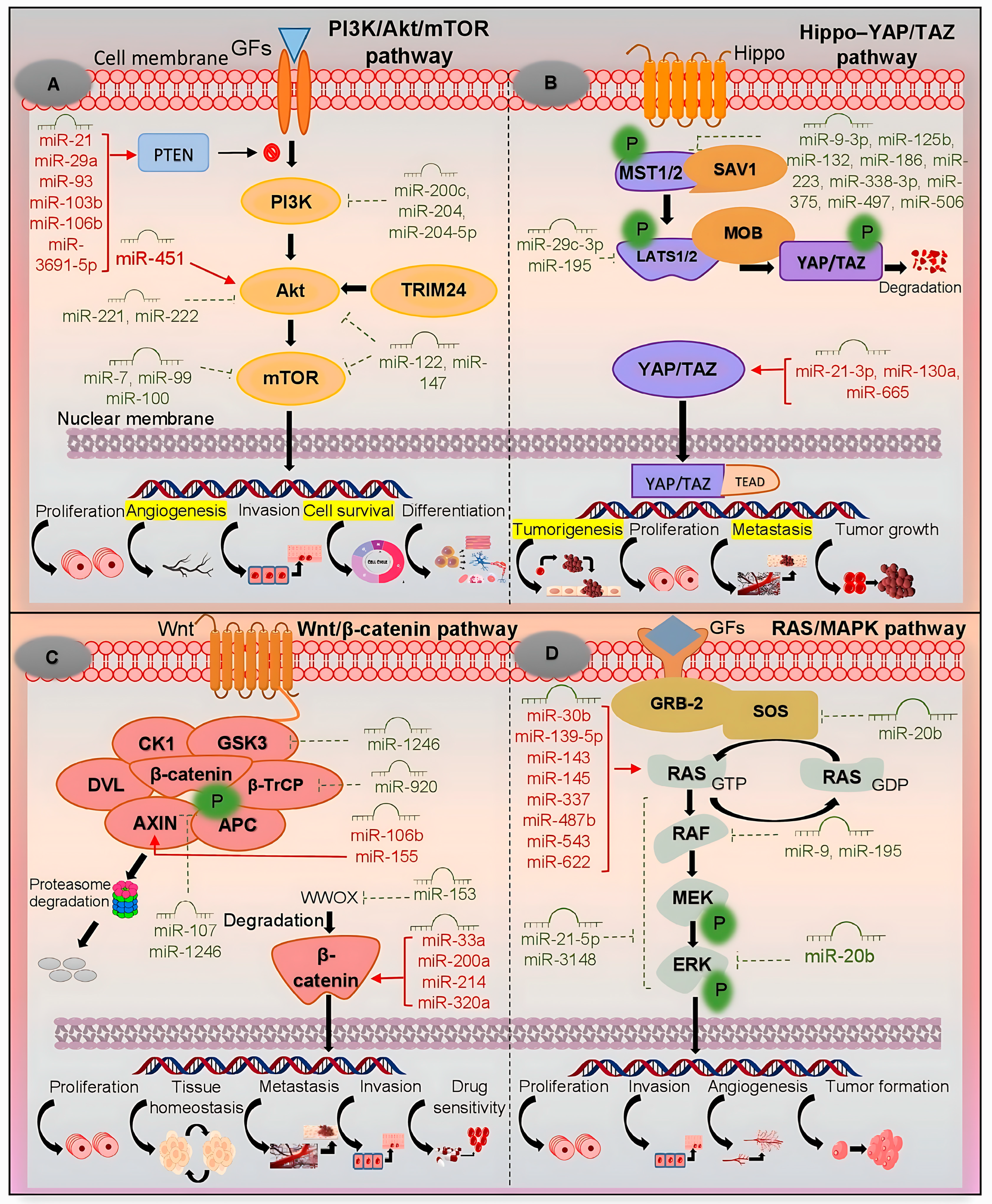

| miRNA (↑/↓) | Target(s) | Biochemical Role (Gene/Protein) | Affected Biological Process(es) | miRNA Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway | |||||
| miR-92a-3p ↑ | N-cadherin; vimentin | N-cadherin: adhesion protein; vimentin: cytoskeletal EMT marker | Proliferation; migration; invasion; EMT; apoptosis | OncomiR | [31] |
| miR-93 ↑ | PTEN; CDKN1A | PTEN: PIP3 phosphatase; CDKN1A (p21): cell-cycle inhibitor | Tumor progression; migration; invasion; apoptosis | OncomiR | [24] |
| miR-106b-5p ↑ | FOG2 | Transcriptional cofactor; regulates stem-cell differentiation | Proliferation; stem-cell differentiation and self-renewal | OncomiR | [32] |
| miR-660-5p ↑ | KLF3; YWHAH | KLF3: transcription factor; YWHAH (14-3-3η): scaffold protein | Proliferation; migration; invasion; EMT | OncomiR | [33] |
| miR-3691-5p ↑ | PTEN | PIP3 phosphatase; inhibits PI3K/Akt signaling | Tumor progression; cell proliferation | OncomiR | [27] |
| miR-30b-3p ↓ | TRIM27 | E3 ubiquitin ligase; activates PI3K/Akt signaling | Proliferation; migration; invasion; EMT | Tumor suppressor | [28] |
| miR-34a ↓ | HDAC1; MACC1 | HDAC1: histone deacetylase; MACC1: activates c-Met/PI3K/Akt signaling | Cell proliferation; apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | [34] |
| miR-125a-5p ↓ | MACC1 | Activates c-Met/PI3K/Akt signaling; promotes metastasis | Proliferation; metastasis; apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | [23] |
| miR-133b ↓ | EGFR | Receptor tyrosine kinase; activates MAPK/PI3K pathways | Cell proliferation; apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | [29] |
| miR-148a ↓ | DR5 | Death receptor; mediates caspase-dependent apoptosis | S phase regulation; apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | [35] |
| miR-199a/b-5p ↓ | ROCK1 | Rho kinase; regulates cytoskeleton and motility | Proliferation; migration; invasion | Tumor suppressor | [36] |
| miR-1914 ↓ | GPR39 | Zinc-activated GPCR; suppresses PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling | Cell-cycle control; apoptosis; tumor growth | Tumor suppressor | [30] |
| miRNA (↑/↓) | Target(s) | Biochemical Role (Gene/Protein) | Affected Biological Process(es) | miRNA Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hippo–YAP/TAZ Pathway | |||||
| miR-21 ↑ | YOD1 | Deubiquitinase; stabilizes YAP/TAZ by preventing degradation | Proliferation | OncomiR | [38] |
| miR-21-3p ↑ | SMAD7 | Negative regulator of TGF-β signaling; loss leads to YAP1 activation | Tumor progression | OncomiR | [39] |
| miR-130a ↑ | VGLL4 | TEAD-binding protein; competes with YAP/TAZ to inhibit Hippo signaling | Over-proliferation; tumorigenesis | OncomiR | [46] |
| miR-135b ↑ | MST1 | Serine/threonine kinase, phosphorylates LATS1/2 to activate Hippo pathway | Proliferation; invasion; migration | OncomiR | [40] |
| miR-512-3p ↑ | LATS2 | Kinase; phosphorylates/inactivates YAP/TAZ | Proliferation; invasion; migration | OncomiR | [41] |
| miR-1307-3p ↑ | LATS1 | Kinase in Hippo pathway; phosphorylates YAP/TAZ | Proliferation; migration; invasion | OncomiR | [42] |
| miR-9-3p ↓ | TAZ | Transcriptional co-activator; binds TEADs to promote proliferation | Proliferation; invasion; migration | Tumor suppressor | [46] |
| miR-29c-3p ↓ | DNMT3B | DNA methyltransferase; epigenetically silences tumor suppressors | Proliferation; migration; tumor growth | Tumor suppressor | [44] |
| miR-186 ↓ | YAP1 | Transcriptional co-activator; drives oncogenic gene expression | Tumorigenesis | Tumor suppressor | [38] |
| miR-375 ↓ | YAP1; CTGF; TEAD4 | YAP1: co-activator; CTGF: pro-fibrotic factor; TEAD4: transcription factor | Proliferation; tumor growth | Tumor suppressor | [45] |
| miRNA (↑/↓) | Target(s) | Biochemical Role (Gene/Protein) | Affected Biological Process(es) | miRNA Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway | |||||
| miR-19a-3p, miR-376c-3p ↑ | SOX6 | Binds β-catenin; blocks nuclear translocation | Proliferation; invasion; migration | OncomiR | [49] |
| miR-197 ↑ | AXIN2; DKK2; NKD1 | Negative Wnt regulators | Invasion; metastasis | OncomiR | [50] |
| miR-409-3p ↑ | BRF2 | Transcription factor; activates Wnt/β-catenin | Invasion; metastasis | OncomiR | [58] |
| miR-452-5p ↑ | CDKN1B | Cell-cycle inhibitor; loss promotes stemness | Cancer stem-cell differentiation; self-renewal | OncomiR | [60] |
| miR-500 ↑ | SFPR2; GSK3β | Wnt antagonists; inhibition activates β-catenin | Invasion; migration; prognosis | OncomiR | [51] |
| miR-1246 ↑ | RORα; CADM1; GSK3β; AXIN2 | AXIN2/GSK3β: degrade β-catenin; RORα: nuclear receptor modulating Wnt | Proliferation; invasion; migration; drug resistance | OncomiR | [61] |
| miR-194 ↓ | PRC1; β-catenin | Cytokinesis regulator; stabilizes β-catenin | Proliferation; invasion; migration | Tumor suppressor | [53] |
| miR-329-3p ↓ | USP22 | Deubiquitinase; stabilizes β-catenin | Proliferation; migration | Tumor suppressor | [54] |
| miR-342 ↓ | CXCL12 | Chemokine-activating Wnt/β-catenin | Proliferation; apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | [62] |
| miR-361-5p ↓ | WT1 | Transcriptional regulator; modulates EMT | Proliferation; invasion; migration | Tumor suppressor | [56] |
| miR-485-5p ↓ | WBP2 | Scaffold protein; promotes β-catenin nuclear entry | Proliferation; invasion; migration | Tumor suppressor | [59] |
| miRNA (↑/↓) | Target(s) | Biochemical Role (Gene/Protein) | Affected Biological Process(es) | miRNA Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAS/MAPK Pathway | |||||
| miR-29 ↑ | TTP | RNA-binding protein; destabilizes mRNAs | Invasion; metastasis; angiogenesis | OncomiR | [74] |
| miR-107 ↑ | CPEB3 | RNA-binding protein; regulates mRNA translation | Proliferation; invasion; migration | OncomiR | [75] |
| miR-126-3p ↑ | SPRED1 | Negative regulator of RAS/RAF/MAPK signaling | Invasion; metastasis; recurrence; sorafenib resistance | OncomiR | [66] |
| miR-148a-3p ↑ | MTF1 | Transcription factor; MAPK effector in AP-1 complex | Proliferation; metastasis; apoptosis | OncomiR | [71] |
| miR-330-5p ↑ | SPRY2 | Negative regulator of RTK/MAPK signaling | Proliferation; tumor growth | OncomiR | [67] |
| miR-30a ↓ | Beclin 1; ATG5 | Autophagy regulators; promote cell survival | Tumor growth; apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | [68] |
| miR-101 ↓ | EZH2 | Histone methyltransferase; epigenetically silences tumor suppressors | Proliferation; metastasis | Tumor suppressor | [69] |
| miR-122 ↓ | IGF-1R | Tyrosine kinase receptor; activates RAS/MAPK and PI3K/Akt | Proliferation; invasion; migration; survival | Tumor suppressor | [70] |
| miR-203 ↓ | NRAS | GTPase; activates RAS/MAPK and PI3K/Akt | Proliferation; apoptosis; tumor growth | Tumor suppressor | [72] |
| miR-296-5p ↓ | NRG1 | Growth factor; activates ERBB receptors upstream of RAS | Invasion; migration; EMT | Tumor suppressor | [76] |
| miR-6838-5p ↓ | CBX4 | Chromobox protein; promotes ERK signaling | CSC self-renewal; metastasis | Tumor suppressor | [73] |
| miRNA (↑/↓) | Target(s) | Biochemical Role (Gene/Protein) | Affected Biological Process(es) | miRNA Function | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p53 Pathway | |||||
| miR-221 ↑ | CDKN2B; CDKN2C; PTEN; TIMP3; MDM2 | CDKN2B/C: cell-cycle inhibitors; PTEN: PI3K/Akt antagonist; TIMP3: metalloproteinase inhibitor | Proliferation; tumor growth | OncomiR | [80] |
| miR-483-3p ↑ | BBC3/PUMA; IGF2 | PUMA: pro-apoptotic protein; IGF2: growth factor | Cell survival; tumor growth | OncomiR | [81] |
| miR-519d ↑ | CDKN1A/p21; PTEN; MDM2; TIMP2 | p21: CDK inhibitor; TIMP2: metalloproteinase inhibitor | Proliferation; invasion; apoptosis | OncomiR | [82] |
| miR-1228 ↑ | p53 | Master tumor suppressor; regulates cell-cycle and apoptosis | Cell-cycle progression; migration | OncomiR | [83] |
| miR-23a ↓ | XIAP | Inhibitor of apoptosis; blocks caspase activation | Tumor development; progression | Tumor suppressor | [86] |
| miR-26a ↓ | MDM2 | E3 ubiquitin ligase; degrades p53 | Cell-cycle arrest (p21/p27); apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | [84] |
| miR-30e ↓ | SIRT7 | NAD+-dependent deacetylase; stabilizes oncoproteins | Tumor growth; progression | Tumor suppressor | [79] |
| miR-34 ↓ | c-Met; caspase-3; ERK1/2 | c-Met: RTK activating survival; caspase-3: apoptosis executor; ERK1/2: MAPK kinases | Tumor progression; invasion; metastasis | Tumor suppressor | [87] |
| miR-122 ↓ | MDM2; cyclin G1 | MDM2: E3 ubiquitin ligase for p53; cyclin G1: cell-cycle regulator | Tumor growth; invasion; metastasis | Tumor suppressor | [79] |
| miR-125a-5p, miR-125b ↓ | LATS1; TRIAP1; BCL2L2 | LATS1: Hippo kinase; TRIAP1/BCL2L2: anti-apoptotic proteins | Proliferation; invasion; apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | [88] |
| miR-145-5p ↓ | MDM2 | Negative regulator of p53 stability | Tumor progression; metastasis | Tumor suppressor | [81] |
| Trial ID | Treatment | Disease | Patients (n) | Study Aim | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02412579 | Observational | HCC | 40 | IsomiR profiling as a non-invasive biomarker in liver transplantation candidates | Completed |
| NCT04720430 | LRT | HCC | 7 | Circulating miRNAs to predict LRT response before transplantation | Completed |
| NCT04965259 | N/A | HCC | 2000 | Development of miRNA-based diagnostic kit for early detection in high-risk patients (with MRI-AI, microbiome/metabolome profiling) | Ongoing |
| NCT05148572 | Surgical resection | HCC | 100 | Validation of circulating miRNAs for recurrence prediction | Ongoing |
| NCT05449847 | Observational | HCV (±HCC, cirrhosis, steatohepatitis) | 100 | Plasma miR-21 and miR-126 as biomarkers to predict HCC in HCV patients | Completed |
| NCT06342414 | N/A | HCC/intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | 400 | Exosomal miRNAs and machine learning for presurgical diagnosis and differentiation of liver cancers | Ongoing |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarlashat, Y.; Halász, J.; Dósa, E. Dysregulation of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Targeting Oncogenic Signaling Pathways for Innovative Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178365
Zarlashat Y, Halász J, Dósa E. Dysregulation of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Targeting Oncogenic Signaling Pathways for Innovative Therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178365
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarlashat, Yusra, Judit Halász, and Edit Dósa. 2025. "Dysregulation of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Targeting Oncogenic Signaling Pathways for Innovative Therapies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178365
APA StyleZarlashat, Y., Halász, J., & Dósa, E. (2025). Dysregulation of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Targeting Oncogenic Signaling Pathways for Innovative Therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178365







