Mutation Spectrum of GJB2 in Taiwanese Patients with Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Prevalence, Pathogenicity, and Clinical Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
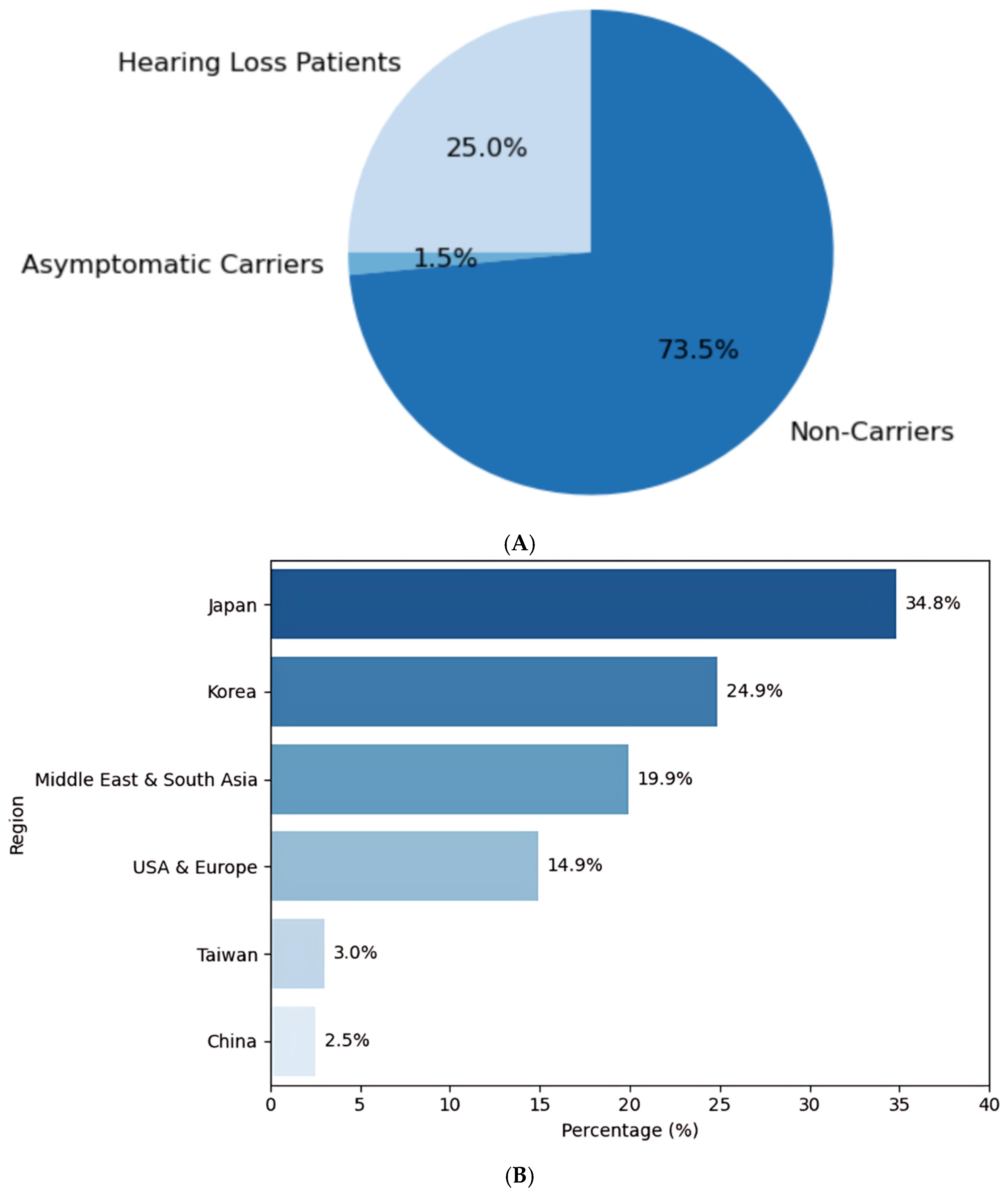
2.1. Global and Taiwanese Prevalence of GJB2 Variants
2.2. Structural and Pathogenic Insights into Common GJB2 Missense Mutations
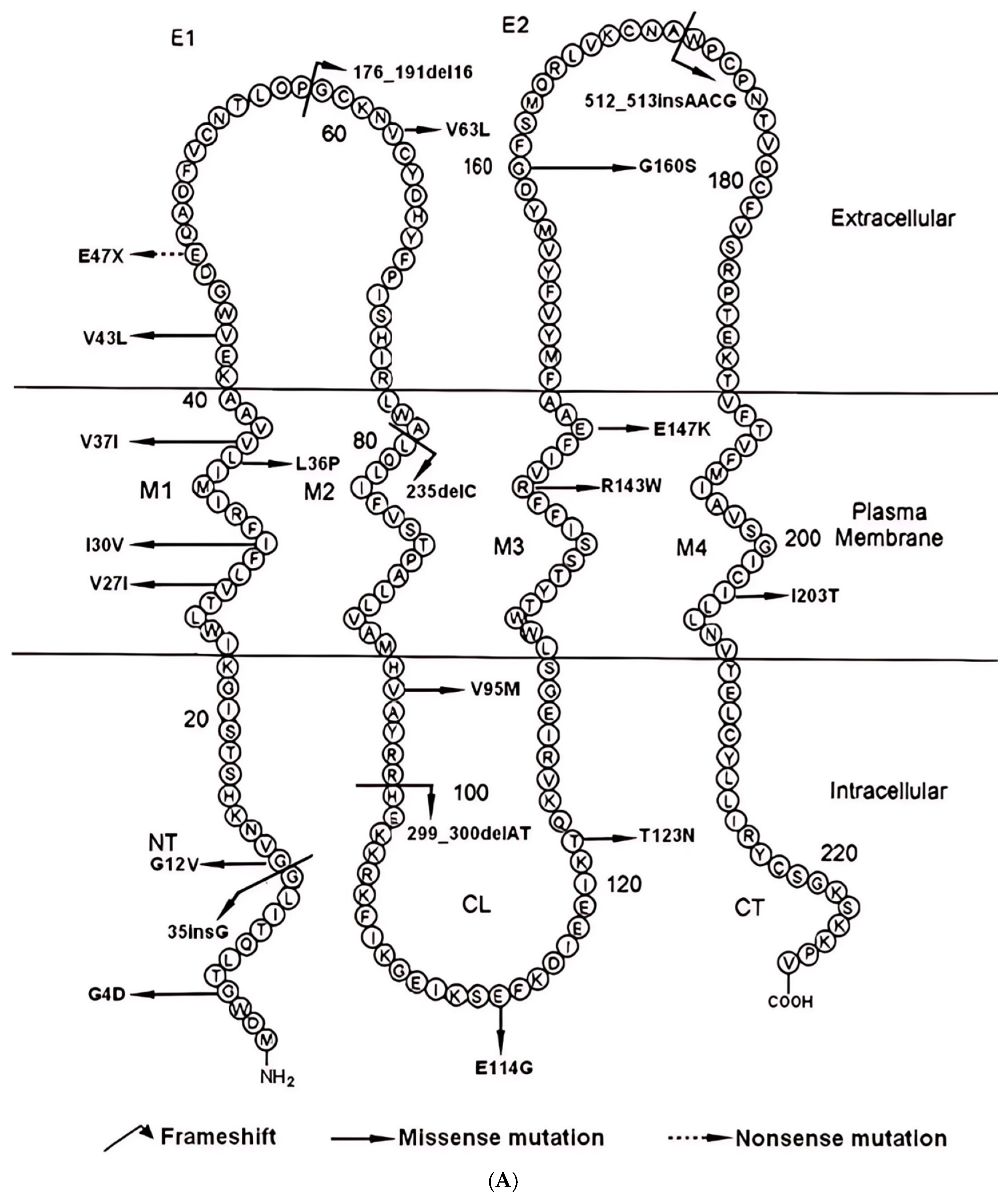
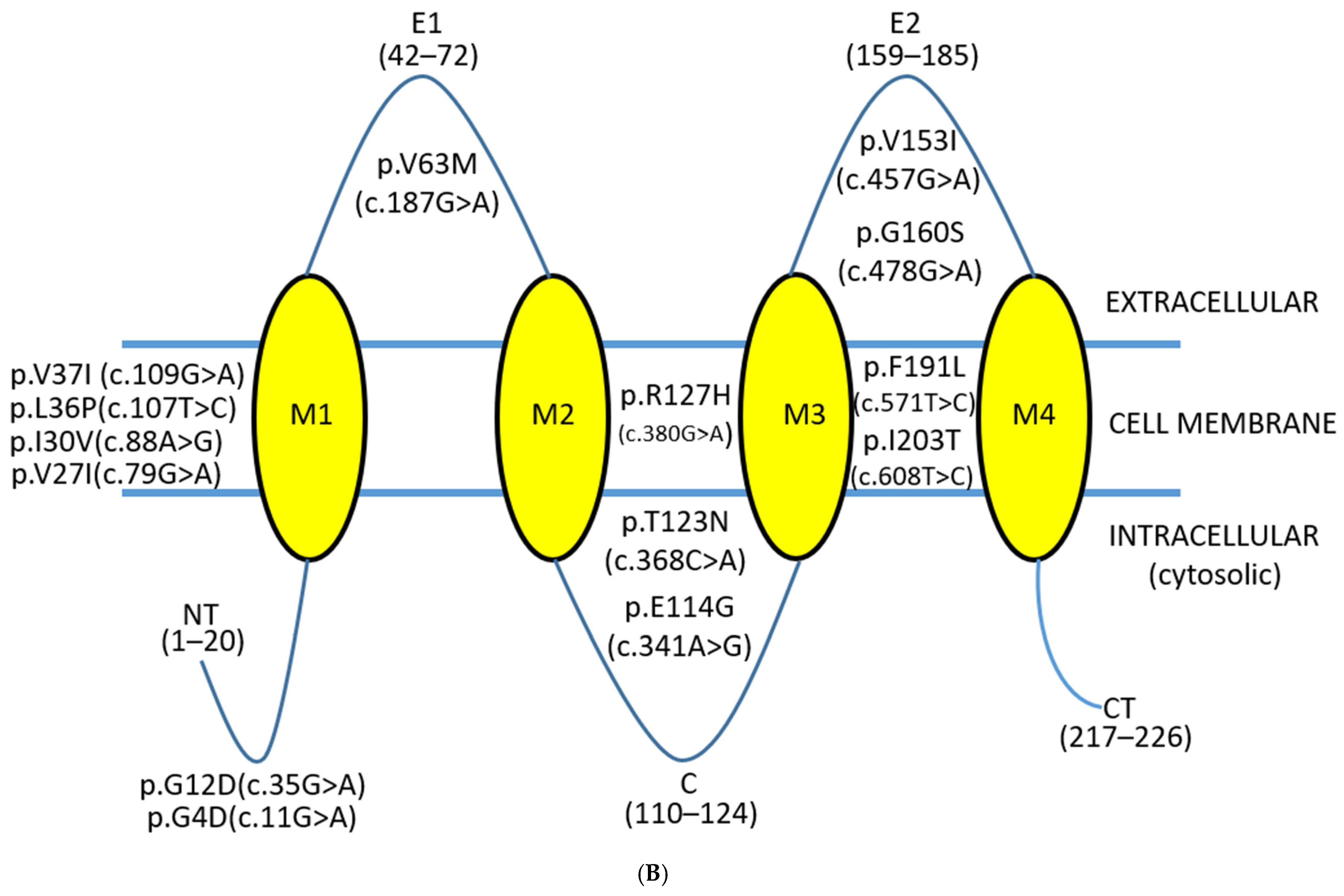
| GRCh37 (hg19) | ID | Domain | cDNA Position | Amino Acid Substitution | Polyphen2 | SIFT | Mutationaster | Alphamissense | Freq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr13:20763710 | rs111033222 | IC1 | c.11G>A | p.G4D | Ben (0.029) | TOLERATED (0.21) | polymorphism | benign | C:0.996042 T:0.003958 |
| chr13:20763686 | rs1801002 | IC1 | c.35G>A | p.G12D | Dam (0.999) | TOLERATED (0.45) | DC (0.999) | Pathogenic (0.8012) | C:0.999658 A:0.000342 |
| chr13:20763642 | rs2274084 | TM1 | c.79G>A | p.V27I | Dam (0.999) | TOLERATED (0.13) | polymorphism | benign | C:0.692815 T:0.307185 |
| chr13:20763633 | rs374625633 | TM1 | c.88A>G | p.I30V | Ben (0.226) | TOLERATED (0.31) | DC (0.999) | benign | T:0.998022 C:0.001978 |
| chr13:20763614 | TM1 | c.107T>C | p.L36P | Dam (1.000) | AFFECT PROTEIN FUNCTION (0.00) | DC (0.999) | Pathogenic (0.991) | A:0.999670 G:0.000330 | |
| chr13:20763612 | rs72474224 | TM1 | c.109G>A | p.V37I | Dam (1.000) | TOLERATED (0.66) | DC (0.999) | benign | C:0.923204 T:0.076796 |
| chr13:20763534 | EC1 | c.187G>A | p.V63M | Dam (1.000) | AFFECT PROTEIN FUNCTION (0.00) | DC (0.999) | Pathogenic (0.817) | C:0.999670 A:0.000330 | |
| chr13:20763380 | rs2274083 | IC2 | c.341A>G | p.E114G | Ben (0.001) | TOLERATED (0.32) | polymorphism | benign | T:0.778034 C:0.221966 |
| chr13:20763353 | rs111033188 | IC2 | c.368C>A | p.T123N | Ben (0.000) | TOLERATED (0.51) | polymorphism | benign | G:0.991760 T:0.008240 |
| chr13:20763341 | IC2 | c.380G>A | p.R127H | Ben (0.006) | TOLERATED (0.22) | polymorphism | benign | C:0.999341 A:0.000659 | |
| chr13:20763264 | rs111033186 | EC2 | c.457G>A | p.V153I | Ben (0.002) | TOLERATED (1.00) | DC (0.815) | benign | C:0.999670 T:0.000330 |
| chr13:20763243 | rs34988750 | EC2 | c.478G>A | p.G160S | Dam (0.947) | AFFECT PROTEIN FUNCTION (0.02) | DC (0.999) | benign | C:0.999670 T:0.000330 |
| chr13:20763150 | EC2 | c.571T>C | p.F191L | Dam (1.000) | AFFECT PROTEIN FUNCTION (0.00) | DC (0.999) | Pathogenic (0.997) | A:0.997034 G:0.002966 | |
| chr13:20763113 | rs76838169 | TM4 | c.608T>C | p.I203T | Dam (0.994) | AFFECT PROTEIN FUNCTION (0.01) | DC (0.999) | Pathogenic (0.646) | A:0.939024 G:0.060976 |

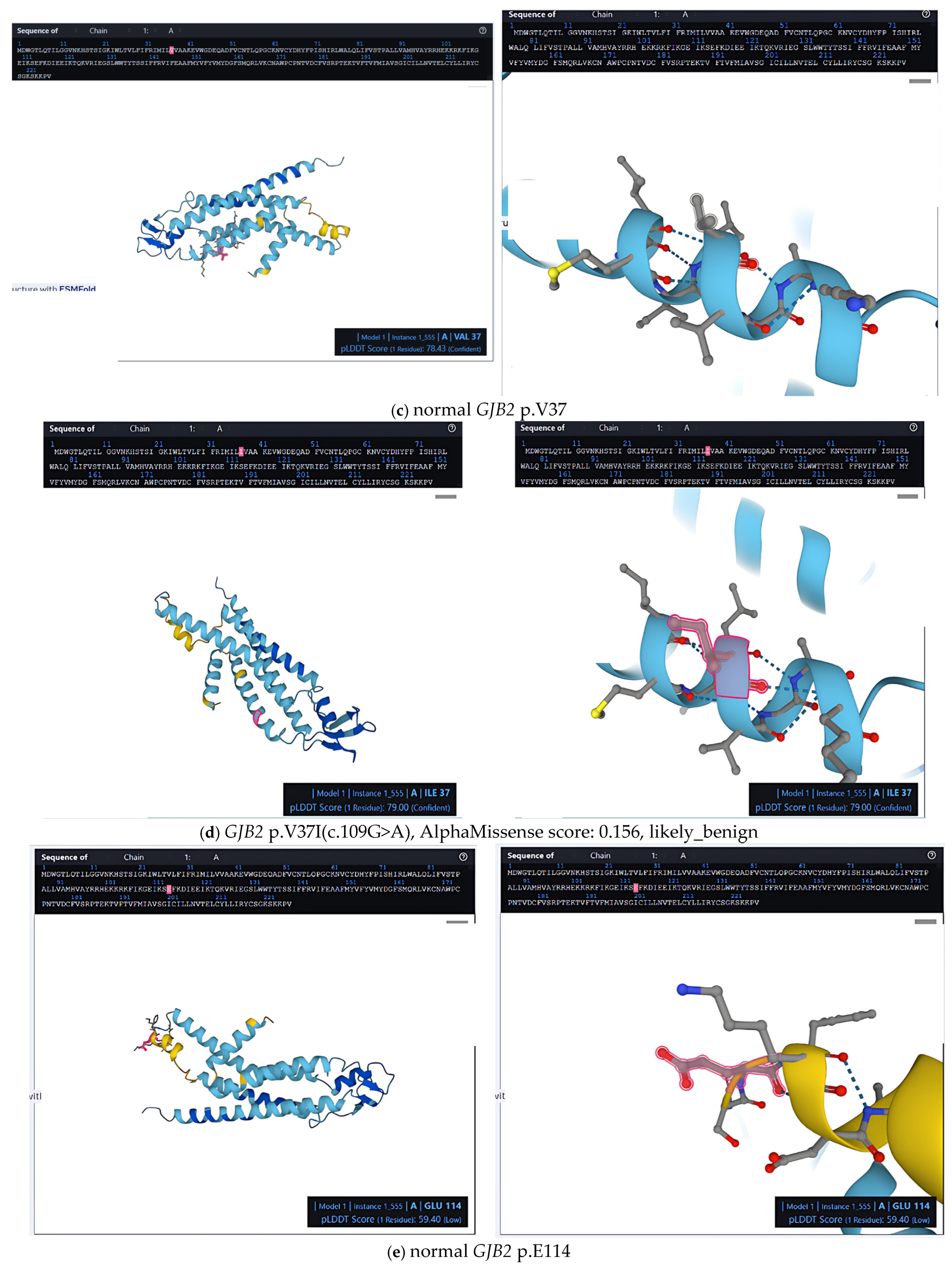
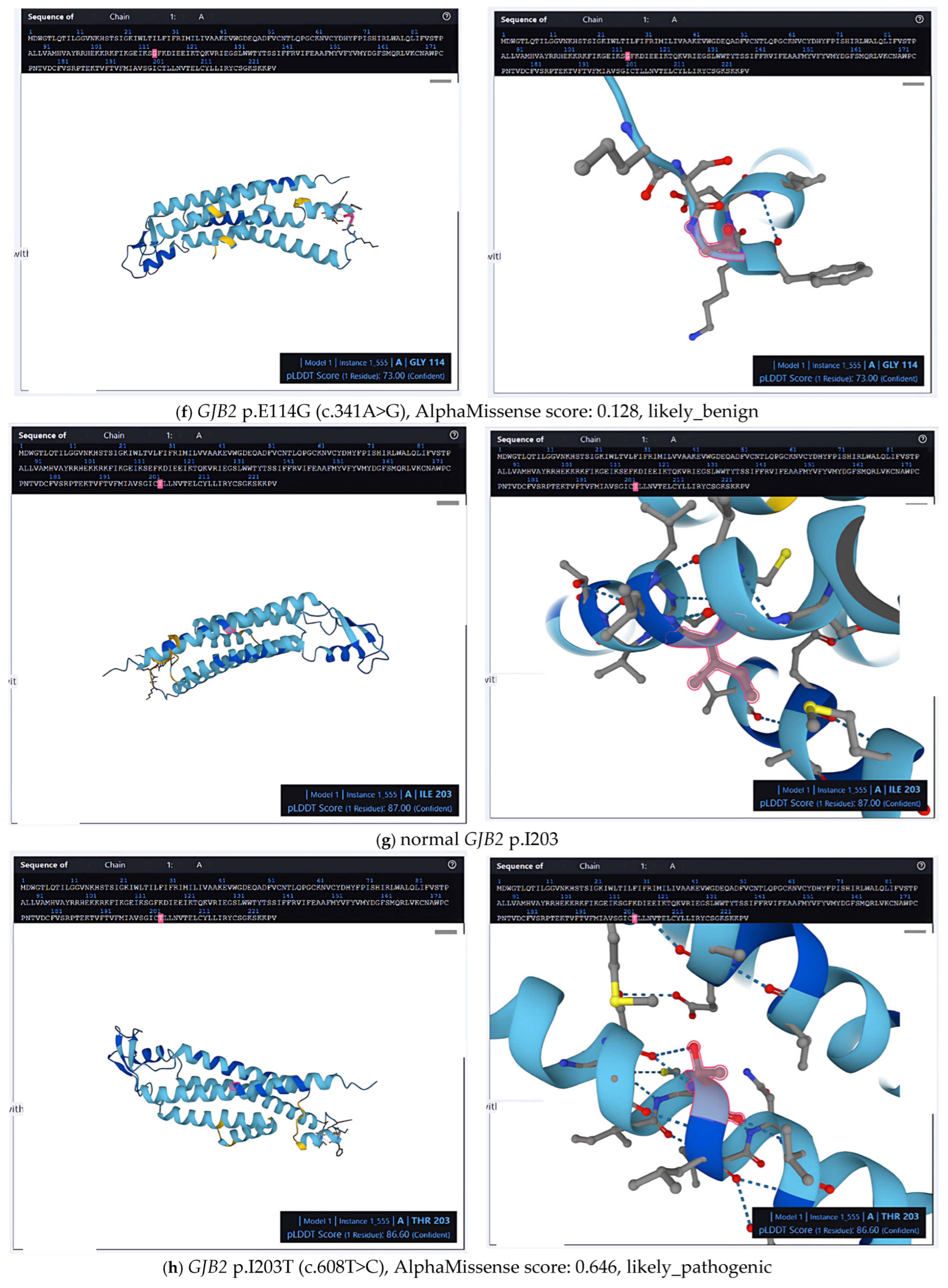
2.3. Population-Level Analysis of Missense Mutations in the Taiwanese Cohort
2.4. Clinical Implications and Observed Genotype–Phenotype Correlations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Methods
4.1.1. Ethical Approvals
4.1.2. Patient Recruitment
4.1.3. Audiological Assessments
- Normal hearing: −10 to 15 dB HL
- Slight hearing loss: 16 to 25 dB HL
- Mild hearing loss: 26 to 40 dB HL
- Moderate hearing loss: 41 to 55 dB HL
- Moderately severe hearing loss: 56 to 70 dB HL
- Severe hearing loss: 71 to 90 dB HL
- Profound hearing loss: >91 dB HL
4.1.4. GJB2 Mutations, PCR, and Sanger Sequencing
4.1.5. GJB2 Whole Exome Sequencing
4.1.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parzefall, T.; Frohne, A.; Koenighofer, M.; Kirchnawy, A.; Streubel, B.; Schoefer, C.; Frei, K.; Lucas, T. Whole-exome sequencing to identify the cause of congenital sensorineural hearing loss in carriers of a heterozygous GJB2 mutation. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 3619–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Yang, T.W.; Tseng, Y.S.; Tsai, C.Y.; Yeh, C.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Lin, P.H.; Lin, T.C.; Wu, Y.J.; Yang, T.H.; et al. Machine learning-based longitudinal prediction for GJB2-related sensorineural hearing loss. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 176, 108597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, C.C.; Nance, W.E. Newborn hearing screening—A silent revolution. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.F.; Lin, H.C.; Tsai, C.L.; Hsu, Y.C. GJB2 mutation spectrum in the Taiwanese population and genotype-phenotype comparisons in patients with hearing loss carrying GJB2 c.109G>A and c.235delC mutations. Hear. Res. 2022, 413, 108135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Hung, C.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Huang, F.L.; Tsao, P.N.; Su, Y.N.; Lee, Y.L.; Hsieh, W.S.; et al. Newborn genetic screening for hearing impairment: A population-based longitudinal study. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Kang, E.J.; Ryu, J.S.; Lee, A.; Yang, Y.H.; Lee, K.R. Carrier frequency of GJB2 (connexin-26) mutations causing inherited deafness in the Korean population. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 53, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Matsuo, H.; Shimizu, S.; Nakayama, A.; Suzuki, K.; Hamajima, N.; Shinomiya, N.; Nishio, S.; Kosugi, S.; Usami, S.; et al. Carrier frequency of the GJB2 mutations that cause hereditary hearing loss in the Japanese population. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, S.; Yao, J.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xing, G.; Cao, X. Genetic mutations of GJB2 and mitochondrial 12S rRNA in nonsyndromic hearing loss in Jiangsu Province of China. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.Q.; Lin, X.; Wang, Z.T.; Wang, L.L.; Song, M.H.; Yang, H.O.; Huang, W.D. Three-dimensional reconstruction of anomalous eutectic in laser remelted Ni-30 wt.% Sn alloy. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 065007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, N.; Zhang, L.S.; Gong, K.; Cai, Y.; Gao, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Han, Q.; Zhang, Y. Proteomic profiling reveals comprehensive insights into adrenergic receptor-mediated hypertrophy in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2009, 3, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiana, G.; Sun, R.; Huang, J.; Napolioni, V.; Ciccocioppo, R. Contribution of infectious diseases to the selection of ADH1B and ALDH2 gene variants in Asian populations. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 48, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Pan, J.; Mei, C.; Cui, M.; He, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; et al. Sirtuin 5-Mediated Desuccinylation of ALDH2 Alleviates Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Following Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2402710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, P.M.; Harris, D.J.; Comer, B.C.; Askew, J.W.; Fowler, T.; Smith, S.D.; Kimberling, W.J. Novel mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) that cause autosomal recessive (DFNB1) hearing loss. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 62, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.T.; Lin, P.H.; Lo, M.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Lee, C.Y.; Tsai, C.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Tsai, S.F.; Liu, T.C.; Hsu, C.J.; et al. Genetic Factors Contribute to the Phenotypic Variability in GJB2-Related Hearing Impairment. J. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 25, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Z. Analysis of GJB2 gene mutations spectrum and the characteristics of individuals with c.109G>A in Western Guangdong. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2023, 11, e2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Nicholson, B.J. The role of connexins in ear and skin physiology—Functional insights from disease-associated mutations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, A.; Tani, K.; Hiroaki, Y.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Sosinsky, G.E. Three-dimensional structure of a human connexin26 gap junction channel reveals a plug in the vestibule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10034–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, T.; Ikeda, K.; Kure, S.; Matsubara, Y.; Oshima, T.; Watanabe, K.; Kawase, T.; Narisawa, K.; Takasaka, T. Novel mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) responsible for childhood deafness in the Japanese population. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 90, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.L.; Lindeman, N.; Lip, V.; Adams, A.; Amato, R.S.; Cox, G.; Irons, M.; Kenna, M.; Korf, B.; Raisen, J.; et al. Effectiveness of sequencing connexin 26 (GJB2) in cases of familial or sporadic childhood deafness referred for molecular diagnostic testing. Genet. Med. 2002, 4, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwa, H.L.; Ko, T.M.; Hsu, C.J.; Huang, C.H.; Chiang, Y.L.; Oong, J.L.; Chen, C.C.; Hsu, C.K. Mutation spectrum of the connexin 26 (GJB2) gene in Taiwanese patients with prelingual deafness. Genet. Med. 2003, 5, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Dai, P.; Wang, G.J.; Yuan, Y.Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Kang, D.Y.; Han, D.Y. Genetic counseling and instruction of marriage for deaf young people: Study of 115 cases. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2009, 89, 677–679. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yu, F.; Dai, P.; Han, D.Y.; Yang, S.M.; Wang, G.J.; Hong, M.D.; Kang, D.Y.; Zhang, X. Mutation of Gap junction protein beta 2 gene and treatment outcome of cochlear implantation in cochlear implantation recipients. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2009, 89, 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.Y.; Huang, D.L.; Han, D.Y.; Jin, Z.C.; Dai, P. Real-time Taqman probe technique system for detecting the MtDNA 1555 A > G mutation. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2009, 44, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Lin, X.; Li, L.; Mei, L.; Huang, Z.; Yang, T.; Wu, H. Characterization of a knock-in mouse model of the homozygous p.V37I variant in Gjb2. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, S.B.; Gersak, K.; Michaelson-Cohen, R.; Walsh, T.; Lee, M.K.; Malach, D.; Klevit, R.E.; King, M.C.; Levy-Lahad, E. Mutations in LARS2, encoding mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase, lead to premature ovarian failure and hearing loss in Perrault syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 92, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Song, Y.; Yan, S.; Cao, M.; Huang, J.; Jia, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fan, W.; Cai, L.; et al. CUEDC1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the TbetaRI/Smad signaling pathway and suppresses tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Aging 2020, 12, 20047–20068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Zhai, B.; Pissios, P. Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase Interacts with Enzymes of the Methionine Cycle and Regulates Methyl Donor Metabolism. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5775–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.S.; Oh, E.S.; Lin, F.R.; Deal, J.A. Hearing Impairment and Cognition in an Aging World. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2021, 22, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, H.M.; Yan, W.J.; Qin, Y. Identification of the Signature Genes and Network of Reactive Oxygen Species Related Genes and DNA Repair Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 833829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadhimi, Y.; Llano, D.A. Does hearing loss lead to dementia? A review of the literature. Hear. Res. 2021, 402, 108038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, A.; La Via, L.; Lechien, J.R.; Sangiorgio, G.; Iannella, G.; Magliulo, G.; Pace, A.; Mat, Q.; Lavalle, S.; Lentini, M. Hearing Loss and Oxidative Stress: A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimoni, C.; Crema, L.; Savini, S.; Negossi, L.; Rosignoli, M.; Sacchetto, L.; Bianchini, C.; Ciorba, A. Hearing threshold estimation by auditory steady state responses (ASSR) in children. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Wakamatsu, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Ota, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Yamashita, R.; Yamamoto, J.; Sekine, M.; Tsuritani, K.; Wakaguri, H.; et al. Diversification of transcriptional modulation: Large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Castillo, F.J.; Del Castillo, I. DFNB1 Non-syndromic Hearing Impairment: Diversity of Mutations and Associated Phenotypes. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Subject | Age | Gender | p.V27I | p.V37I | p.E114G | p.I203T | R’t PTA (dB HL) | L’t PTA (dB HL) | Other Mutation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | Female | Het | WT | Het | Het | 111.3 | 113.8 | |
| 2 | 38 | Male | WT | Hom | WT | WT | 90 | 106.3 | |
| 3 | 20 | Female | Het | WT | WT | WT | 115 | 90.3 | CMV |
| 4 | 17 | Male | Hom | WT | Hom | WT | >100 | >100 | |
| 5 | 18 | Female | WT | WT | WT | WT | >100 | >100 | GJB2:c.301_303del (p.Glu101del) (+/−); GJB2:c.235del (p.Leu79fs) (+/−) |
| 6 | 13 | Male | WT | WT | WT | WT | 102.5 | 101.3 | suspect noonan syndrome with multiple letigenes or LEOPARD syndrome |
| 7 | 24 | Female | WT | WT | WT | Het | >100 | >100 | |
| 8 | 44 | Female | WT | WT | WT | WT | 125 | 121.3 | suspect MELAS syndrome X |
| 9 | 58 | Female | Het | WT | Het | WT | 101.3 | 101.3 | |
| 10 | 12 | Male | Het | Het | Het | WT | 77.5 | 75 | |
| 11 | 8 | Female | WT | Het | WT | WT | 111.7 | 111.7 | |
| 12 | 7 | Male | Het | WT | Het | WT | 110 | 110 | R’t Mondini dysplasia; L’t common cavity, cochlear nerve aplasia |
| 13 | 53 | Female | WT | WT | WT | WT | 95 | 106.3 | |
| 14 | 14 | Female | Het | WT | Het | WT | 83.75 | 115 | |
| 15 | 23 | Female | Het | Het | Het | WT | 98.75 | 125 | |
| 16 | 11 | Male | WT | WT | WT | WT | 100 | 86.7 | |
| 17 | 2 | Female | Het | Het | Het | WT | 107.5 | 103.75 | |
| 18 | 11 | Male | Het | WT | Het | WT | 115 | 92.5 | |
| 19 | 16 | Female | WT | WT | WT | WT | >100 | >100 | |
| 20 | 5 | Male | Het | Het | WT | WT | 115 | 115 | |
| 21 | 11 | Male | Het | WT | Het | WT | 101.25 | 105 | |
| 22 | 10 | Female | Het | WT | Het | WT | 97.5 | 88.75 | SLC26A4 (c.919-2A>G/WT) OTOF (c.5098G>C/WT) |
| 23 | 18 | Male | WT | WT | WT | Het | 100 | 101.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-F.; Chen, C.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Hsu, Y.-C. Mutation Spectrum of GJB2 in Taiwanese Patients with Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Prevalence, Pathogenicity, and Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178213
Lin Y-F, Chen C-H, Lee C-Y, Lin H-C, Hsu Y-C. Mutation Spectrum of GJB2 in Taiwanese Patients with Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Prevalence, Pathogenicity, and Clinical Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178213
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yi-Feng, Che-Hong Chen, Chang-Yin Lee, Hung-Ching Lin, and Yi-Chao Hsu. 2025. "Mutation Spectrum of GJB2 in Taiwanese Patients with Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Prevalence, Pathogenicity, and Clinical Implications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178213
APA StyleLin, Y.-F., Chen, C.-H., Lee, C.-Y., Lin, H.-C., & Hsu, Y.-C. (2025). Mutation Spectrum of GJB2 in Taiwanese Patients with Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Prevalence, Pathogenicity, and Clinical Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178213






