Recent Updates on Diabetes and Bone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
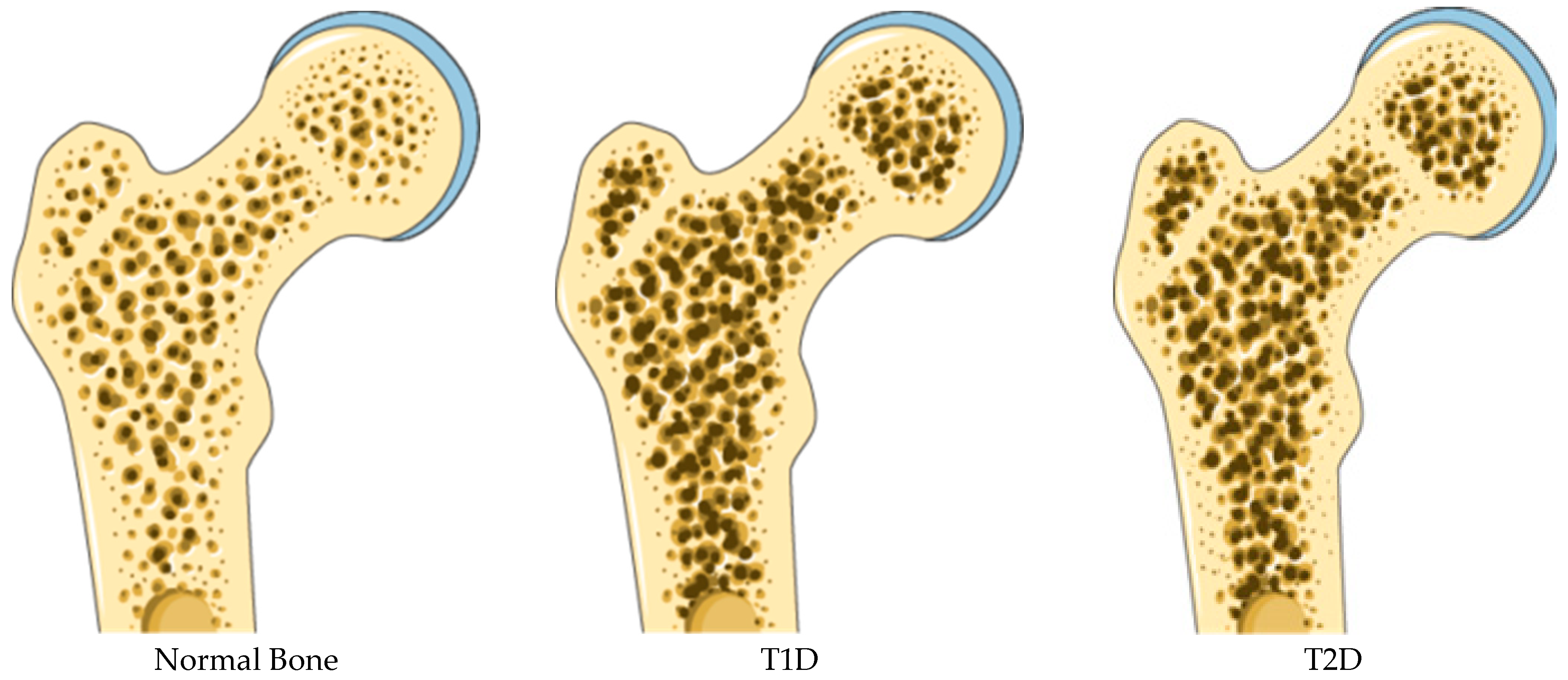
3. Skeletal Fragility in Diabetes
4. Vitamin D and Diabetes
5. Incretins and Glucagon-like Peptide 2 (GLP-2)
6. Neuropeptides and Diabetes
7. Asprosin
8. Irisin
9. Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein (TXNIP)
10. Bone Health Monitoring and Cure in Diabetes
11. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarez-Cubela, S.; Altilio, I.D.; Doke, M.; Klein, D.; Tamayo, A.; Alcazar, O.; Santana, C.G.; Qadir, M.M.F.; Alver, C.G.; Cruz, F.; et al. Pancreatic beta-cell regeneration in situ by the ALK3 agonist THR-123. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in diabetes prevalence and treatment from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 1108 population-representative studies with 141 million participants. Lancet 2024, 404, 2077–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annicchiarico, A.; Barile, B.; Buccoliero, C.; Nicchia, G.P.; Brunetti, G. Alternative therapeutic strategies in diabetes management. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 1142–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anelli, S.; Mazzilli, R.; Zamponi, V.; Giorgini, B.; Golisano, B.; Mancini, C.; Russo, F.; Panzuto, F.; Faggiano, A. Glucagonoma and Glucagonoma Syndrome: An Updated Review. Clin. Endocrinol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, A.; White, C.P.; Center, J.R. Bone metabolism in diabetes: A clinician’s guide to understanding the bone-glucose interplay. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerzian, S.R.; Johannesdottir, F.; Yu, E.W.; Bouxsein, M.L. Use of noninvasive imaging to identify causes of skeletal fragility in adults with diabetes: A review. JBMR Plus 2024, 8, ziae003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, N.H.; Driessen, J.H.M.; Kvist, A.V.; Souverein, P.C.; van den Bergh, J.P.; Vestergaard, P. Fracture patterns and associated risk factors in pediatric and early adulthood type 1 diabetes: Findings from a nationwide retrospective cohort study. Bone 2024, 180, 116997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Ji, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liang, X.; Zhao, Y. The association between prediabetes and bone mineral density: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2023, 39, e3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubago-Guisado, E.; Moratalla-Aranda, E.; Gonzalez-Salvatierra, S.; Gil-Cosano, J.J.; Garcia-Fontana, B.; Garcia-Fontana, C.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Munoz-Torres, M. Do patients with type 2 diabetes have impaired hip bone microstructure? A study using 3D modeling of hip dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1069224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmpa, E.; Karamagkiolis, S.; Tigas, S.; Navrozidou, P.; Vlychou, M.; Fezoulidis, I.; Koukoulis, G.N.; Bargiota, A. Bone Mineral Density in Adult Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Assessed by Both DXA and QCT. J. Diabetes Res. 2023, 2023, 8925956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Akesson, K.E.; Al-Daghri, N.; Biver, E.; Chandran, M.; Chevalley, T.; Josse, R.G.; Kendler, D.L.; Lane, N.E.; Makras, P.; et al. Bone microstructure and TBS in diabetes: What have we learned? A narrative review. Osteoporos. Int. 2025, 36, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerzian, S.R.; Chow, J.; Behzad, R.; Unal, M.; Brooks, D.J.; Wu, I.H.; Gauthier, J.; Jangolla, S.V.T.; Yu, M.G.; Shah, H.S.; et al. Long-duration type 1 diabetes is associated with deficient cortical bone mechanical behavior and altered matrix composition in human femoral bone. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2024, 40, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj, M.; Schwartz, A.V.; Burghardt, A.J.; Black, D.; Orwoll, E.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Fogolari, M.; Angeletti, S.; Banfi, G.; et al. Risk Factors for Bone Microarchitecture Impairments in Older Men With Type 2 Diabetes-The MrOS Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, e1660–e1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Refaie, A.; Baldassini, L.; Mondillo, C.; Ceccarelli, E.; Tarquini, R.; Gennari, L.; Gonnelli, S.; Caffarelli, C. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Diabetic Osteopathy: Another Positive Effect of Incretines? A 12 Months Longitudinal Study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2024, 115, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, N.H.; Dal, J.; Kvist, A.V.; van den Bergh, J.P.; Jensen, M.H.; Vestergaard, P. Bone parameters in T1D and T2D assessed by DXA and HR-pQCT—A cross-sectional study: The DIAFALL study. Bone 2023, 172, 116753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, C.; Eastell, R.; Pierroz, D.D.; Lane, N.E.; Al-Daghri, N.; Suzuki, A.; Napoli, N.; Mithal, A.; Chakhtoura, M.; Fuleihan, G.E.; et al. Biochemical Markers of Bone Fragility in Patients With Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e923–e936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, N.H.; Kvist, A.V.; Lykkeboe, S.; Starup-Linde, J.; Handberg, A.; van den Bergh, J.P.; Vestergaard, P. Bone turnover markers and mineral density in type 1 diabetes—A cross-sectional study: DIAFALL. Bone 2025, 198, 117548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Hou, X.; Nie, Q.; Xia, Q.; Hu, R.; Yang, X.; Song, G.; Ren, L. Association of Bone Turnover Markers with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Microvascular Complications: A Matched Case-Control Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 1177–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swolin-Eide, D.; Pundziute Lycka, A.; Novak, D.; Andersson, B.; Forsander, G.; Magnusson, P. Adolescents with long-duration type 1 diabetes have low bone mass and reduced levels of bone indices reflecting altered bone resorption. Bone 2025, 199, 117560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Majid, H.; Khan, P.; Sharma, N.; Kohli, S.; Islam, S.U.; Vohora, D.; Nidhi. CTX-1 and TRACP-5b as biomarkers for osteoporosis risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2024, 23, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddaloni, E.; Coleman, R.L.; Holman, R.R. Risk factors for bone fractures in type 2 diabetes and the impact of once-weekly exenatide: Insights from an EXSCEL post-hoc analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2025, 223, 112125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergdahl, E.; Forsander, G.; Sundberg, F.; Milkovic, L.; Dangardt, F. Investigating the presence and detectability of structural peripheral arterial changes in children with well-regulated type 1 diabetes versus healthy controls using ultra-high frequency ultrasound: A single-centre cross-sectional and case-control study. eClinicalMedicine 2025, 81, 103097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha Gregory, N.; Burghardt, A.J.; Backlund, J.C.; Rubin, M.R.; Bebu, I.; Braffett, B.H.; Kenny, D.J.; Link, T.M.; Kazakia, G.J.; Barnie, A.; et al. Diabetes Risk Factors and Bone Microarchitecture as Assessed by High-Resolution Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography in Adults With Long-standing Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 1548–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavati, G.; Pirrotta, F.; Merlotti, D.; Ceccarelli, E.; Calabrese, M.; Gennari, L.; Mingiano, C. Role of Advanced Glycation End-Products and Oxidative Stress in Type-2-Diabetes-Induced Bone Fragility and Implications on Fracture Risk Stratification. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesdottir, F.; Tedtsen, T.; Cooke, L.M.; Mahar, S.; Zhang, M.; Nustad, J.; Garrahan, M.A.; Gehman, S.E.; Yu, E.W.; Bouxsein, M.L. Microvascular disease and early diabetes onset are associated with deficits in femoral neck bone density and structure among older adults with longstanding type 1 diabetes. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2024, 39, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draghici, A.E.; Zahedi, B.; Taylor, J.A.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Yu, E.W. Vascular deficits contributing to skeletal fragility in type 1 diabetes. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2023, 4, 1272804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Huang, D.; Peng, L. Sclerostin as a new target of diabetes-induced osteoporosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1491066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Barria, H.; Aguilera-Eguia, R.; Flores-Fernandez, C.; Angarita-Davila, L.; Rojas-Gomez, D.; Alarcon-Rivera, M.; Lopez-Soto, O.; Maureira-Sanchez, J. Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melake, A.; Mengstie, M.A. Vitamin D deficiency and VDR TaqI polymorphism on diabetic nephropathy risk among type 2 diabetes patients. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1567716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Song, X.; Yan, L.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, W. Molecular insights into the interplay between type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoporosis: Implications for endocrine health. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1483512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, I.; Pantazidou, G.; Kokkalis, Z.; Georgopoulos, N.; Jelastopulu, E.; Baikousis, A.G. A Comparison of Vitamin D Levels and Hip Fracture Severity in Elderly Patients With and Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Clinical Study. Cureus 2025, 17, e81574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emini Sadiku, M. Impact of vitamin D and vitamin D receptor activator in diabetic nephropathy. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2025, 6, 1537336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.; Okada, Y.; Tanaka, Y. Vitamin D efficacy in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2024, 42, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittas, A.G.; Kawahara, T.; Jorde, R.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Balk, E.M. Vitamin D and Risk for Type 2 Diabetes in People With Prediabetes. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, eL230202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hands, J.M.; Patrick, R.; Frame, L.A. Vitamin D and Risk for Type 2 Diabetes in People With Prediabetes. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, eL230201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Veronese, N.; Marrone, E.; Di Palermo, C.; Iommi, C.; Ruggirello, R.; Caffarelli, C.; Gonnelli, S.; Barbagallo, M. Vitamin D and Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes in Older Adults: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Zhou, C.; Gan, X.; Huang, Y.; He, P.; Ye, Z.; Liu, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Relationship of Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations, Diabetes, Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphisms and Incident Venous Thromboembolism. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2025, 41, e70014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, A.; Alouffi, S.; Shahab, U.; Akasha, R.; Fazal-Ur-Rehman, M.; Ghoniem, M.E.; Ahmad, N.; Kaur, K.; Pandey, R.P.; Alshammari, A.; et al. Vitamin D supplementation modulates glycated hemoglobin (HBA1c) in diabetes mellitus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 753, 109911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 4. Comprehensive Medical Evaluation and Assessment of Comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S59–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viggers, R.; Rasmussen, N.H.; Vestergaard, P. Effects of Incretin Therapy on Skeletal Health in Type 2 Diabetes—A Systematic Review. JBMR Plus 2023, 7, e10817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koefoed-Hansen, F.; Helsted, M.M.; Kizilkaya, H.S.; Lund, A.B.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Gasbjerg, L.S. The evolution of the therapeutic concept ‘GIP receptor antagonism’. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1570603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkilde, M.M.; Lindquist, P.; Kizilkaya, H.S.; Gasbjerg, L.S. GIP-derived GIP receptor antagonists—A review of their role in GIP receptor pharmacology. Peptides 2024, 177, 171212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Deng, W.; Ye, Y.; Xu, J.; Han, D.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, Q. Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, inhibits bone loss in an animal model of osteoporosis with or without diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1378291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Park, S.E.; Kim, E. Evaluation of bone health and fracture risk in type 2 diabetes: A network meta-analysis of anti-diabetic treatments versus placebo. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2025, 48, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, P.; Estrin, N.; Farshidfar, N.; Zhang, Y.; Miron, R.J. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1RAs) Improve Periodontal and Peri-Implant Health in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Periodontal Res. 2025, 60, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, W.; Yang, D.; Zhu, D.; Jing, Y. Association of Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists use with fracture risk in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Bone 2025, 192, 117338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.N.; Akturk, H.K.; Kruger, D.; Ahmann, A.; Bhargava, A.; Bakoyannis, G.; Pyle, L.; Snell-Bergeon, J.K. Semaglutide in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity. NEJM Evid. 2025, 4, EVIDoa2500173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, L.; Bhadada, S.K.; Arjunan, D.; Duseja, A. Effect of Oral Semaglutide on Volumetric BMD and Bone Microarchitecture in Overweight/Obese Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2025, 116, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Cai, X.; Lin, C.; Yang, W.; Ji, L. Effects of Semaglutide and Tirzepatide on Bone Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Bao, X.; Li, Y. Semaglutide promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells through activation of the Wnt/LRP5/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1539411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddio, A.E.; Gouzoulis, M.J.; Vasudevan, R.S.; Dhodapkar, M.M.; Jabbouri, S.S.; Varthi, A.G.; Rubio, D.R.; Grauer, J.N. Semaglutide utilization associated with reduced 90-day postoperative complications following single-level posterior lumbar fusion for patients with type II diabetes. Spine J. 2025, 25, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Efficacy and Safety of GLP-1 Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 1873–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Frias, J.P.; Jastreboff, A.M.; le Roux, C.W.; Sattar, N.; Aizenberg, D.; Mao, H.; Zhang, S.; Ahmad, N.N.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity in people with type 2 diabetes (SURMOUNT-2): A double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Chao, A.M.; Machineni, S.; Kushner, R.; Ard, J.; Srivastava, G.; Halpern, B.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Author Correction: Tirzepatide after intensive lifestyle intervention in adults with overweight or obesity: The SURMOUNT-3 phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronne, L.J.; Sattar, N.; Horn, D.B.; Bays, H.E.; Wharton, S.; Lin, W.Y.; Ahmad, N.N.; Zhang, S.; Liao, R.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Continued Treatment with Tirzepatide for Maintenance of Weight Reduction in Adults With Obesity: The SURMOUNT-4 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 331, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Frias, J.; Jastreboff, A.M.; Du, Y.; Lou, J.; Gurbuz, S.; Thomas, M.K.; Hartman, M.L.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; et al. Retatrutide, a GIP, GLP-1 and glucagon receptor agonist, for people with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, double-blind, placebo and active-controlled, parallel-group, phase 2 trial conducted in the USA. Lancet 2023, 402, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, P.; Kumar, S. Diabetes and Bone Health: A Comprehensive Review of Impacts and Mechanisms. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2025, 41, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov-Jeppesen, K.; Christiansen, C.B.; Hansen, L.S.; Windelov, J.A.; Hedback, N.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Hindso, M.; Svane, M.S.; Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J.; et al. Effects of Exogenous GIP and GLP-2 on Bone Turnover in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchetta, I.; Dule, S.; Cimini, F.A.; Sentinelli, F.; Oldani, A.; Passarella, G.; Filardi, T.; Venditti, V.; Bleve, E.; Romagnoli, E.; et al. Circulating Proneurotensin Levels Predict Impaired Bone Mineralisation in Postmenopausal Women With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2025, 41, e70018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Abo El-Matty, D.M.; Abd ElSalam, E.A.; Hussein, M.A.; Hafez, W.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Shaheen, E.A.H.; Awad, E.A.; Osman, M.A.; Abd El-Raouf, M.S.; et al. Evaluating the Feasibility of Pro-Neurotensin and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 as Possible Indicators for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roomi, A.B.; Ali, E.A.; Nori, W.; Rahmah, M.I. Asprosin is a Reliable Predictor of Osteoporosis in Type 2 Diabetic Postmenopausal Women: A Case-Control Study. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2025, 40, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Lin, S.; Zhang, X.; Pan, H. The relationship between the expression of serum asprosin and miR-21 in patients with osteoporosis and delayed healing after OVCF surgery. J. Orthop. Surg. 2025, 33, 10225536251331325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, I.; Coccurello, R. Irisin: A Multifaceted Hormone Bridging Exercise and Disease Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Han, Z.; Gao, M.; Tian, L. FNDC5/irisin ameliorates bone loss of type 1 diabetes by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated ferroptosis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, S.; Brock, F.; Kaimala, S.; Greenwood, C.; Sulaiman, M.; Rogers, K.; Adeghate, E. A pilot study: Effect of irisin on trabecular bone in a streptozotocin-induced animal model of type 1 diabetic osteopathy utilizing a micro-CT. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Xing, B.; Zhang, G.; Wu, H.; Feng, N.; Li, Y.; Han, G. Serum Irisin is Associated with Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal T2dm Patients Complicated with Osteoporosis and in Mice with Diabetic Osteoporosis. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2023, 24, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, K.; Yuan, J.; Hua, Q.; Rong, K.; Zhou, T.; He, W.; Pang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of Rankl by Txnip-Ecd in aging and diabetic related osteoporosis. J. Adv. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarry, S.; Kover, K.; Luca, F. Thioredoxin Interacting Protein Expressed in Osteoblasts Mediates the Anti-Proliferative Effects of High Glucose and Modulates the Expression of Osteocalcin. J. Bone Metab. 2024, 31, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Ma, R.; Huang, Y.; Pan, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, E.; Bu, Y.; Luo, J.; et al. Rosmarinic Acid Ameliorates Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis by Reducing NLRP3 Expression and Alleviating Osteoblast Pyroptosis via the FOXO1/TXNIP Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 16557–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairoli, E.; Grassi, G.; Gaudio, A.; Palermo, A.; Vescini, F.; Falchetti, A.; Merlotti, D.; Eller-Vainicher, C.; Carnevale, V.; Scillitani, A.; et al. Validation of the clinical consensus recommendations on the management of fracture risk in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, T.N.; Flora, S.S.; Bhadada, S.K.; Yadav, U.; Pal, R. Anti-resorptive and anabolic therapies improve Falls Risk Assessment Score (FRAS) in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos. Int. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| T1D | T2D | |
|---|---|---|
| aBMD | low | Normal/elevated |
| TBS | decreased | decreased |
| Trabecular Number | reduced | |
| Cortical Bone | Reduced Cortical Thickness | Increased Cortical Porosity |
| CTX | Reduced levels | Reduced levels |
| TRACP-5b | Increased levels | Reduced levels |
| P1NP | Reduced levels | Reduced levels |
| Bone-ALP | Reduced levels | Reduced levels |
| Osteocalcin | Reduced levels | Reduced levels |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brunetti, G. Recent Updates on Diabetes and Bone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178140
Brunetti G. Recent Updates on Diabetes and Bone. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178140
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrunetti, Giacomina. 2025. "Recent Updates on Diabetes and Bone" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178140
APA StyleBrunetti, G. (2025). Recent Updates on Diabetes and Bone. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178140





