Effect of PGPRs on the Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure and Yield of Silage Maize in Saline–Alkaline Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Different PGPRs on the Growth Promotion of Silage Maize
2.2. Effects of Different PGPRs on Soil Nutrients and Enzyme Activities
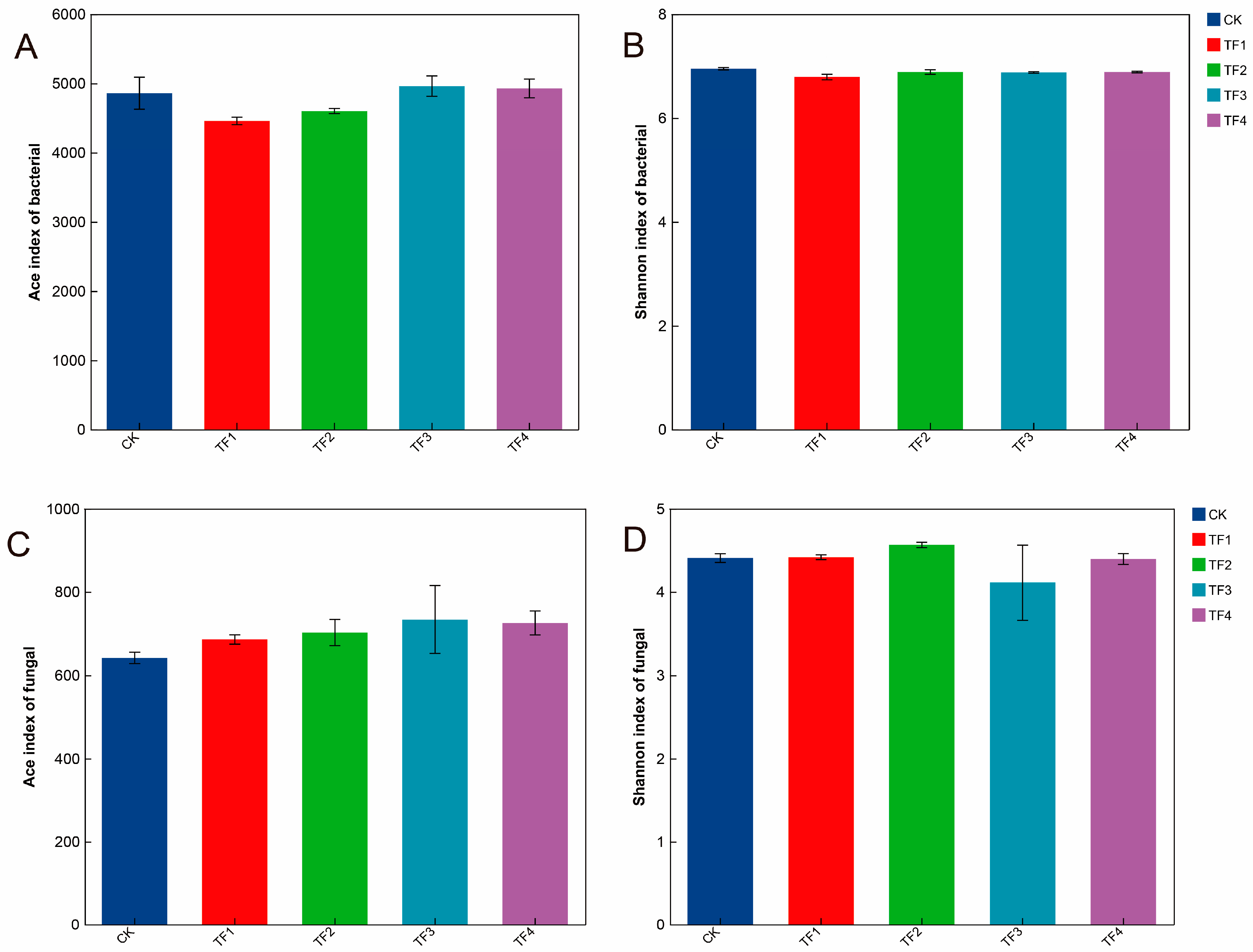
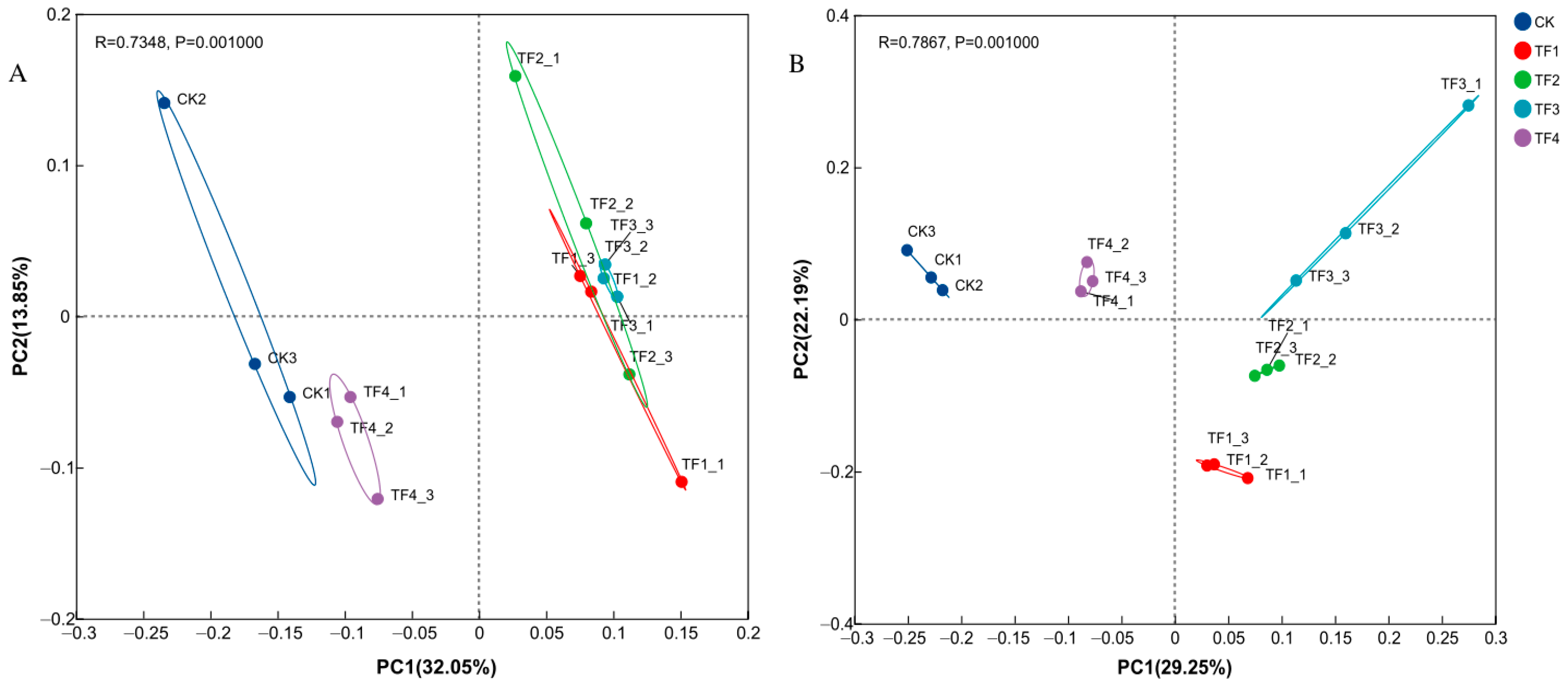
2.3. Alpha Diversity, Bacterial, and Fungal Community Structure Analysis Under Different PGPRs
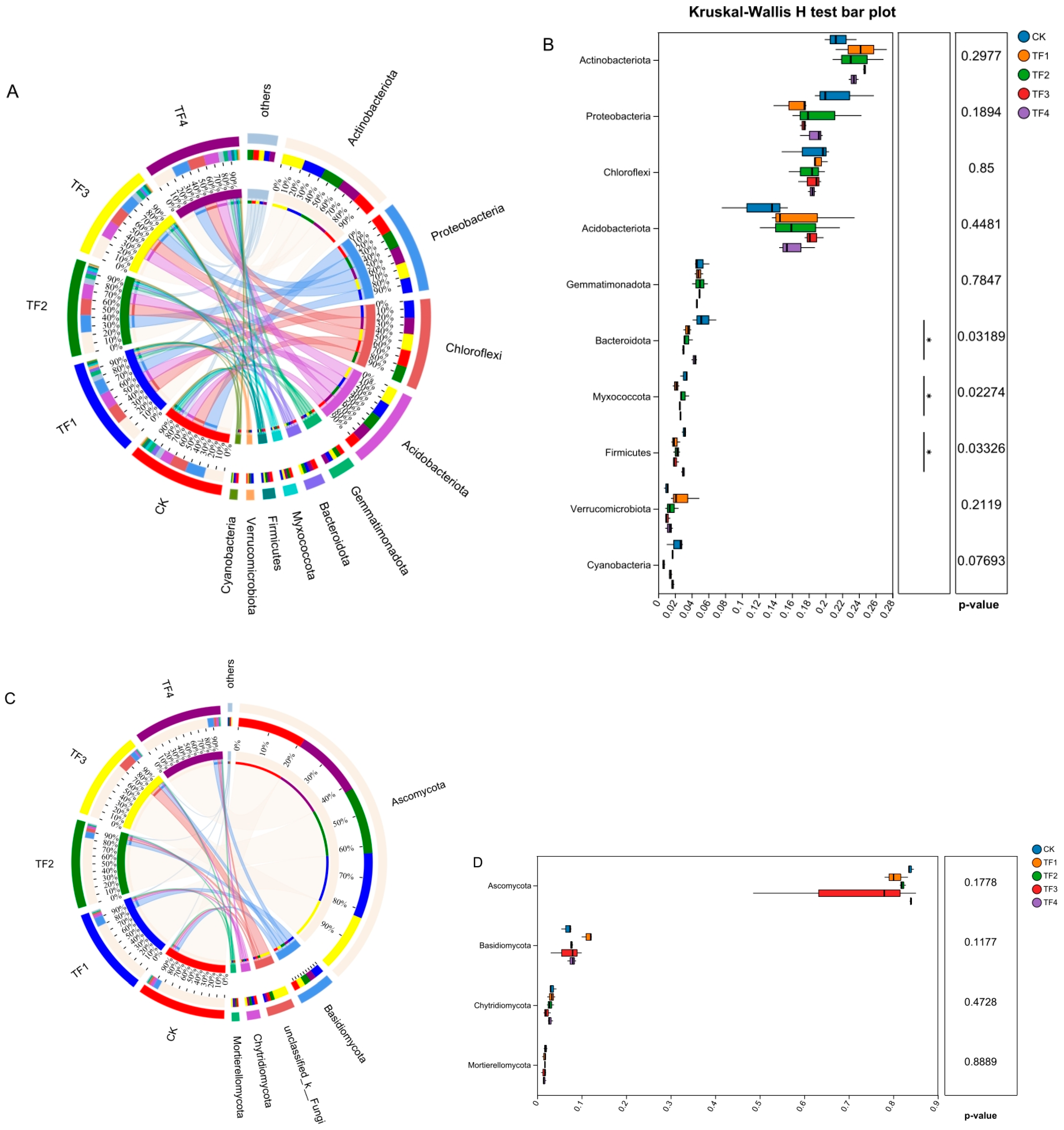
2.4. Effects of PGPRs on the Composition of Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities at the Phylum Level
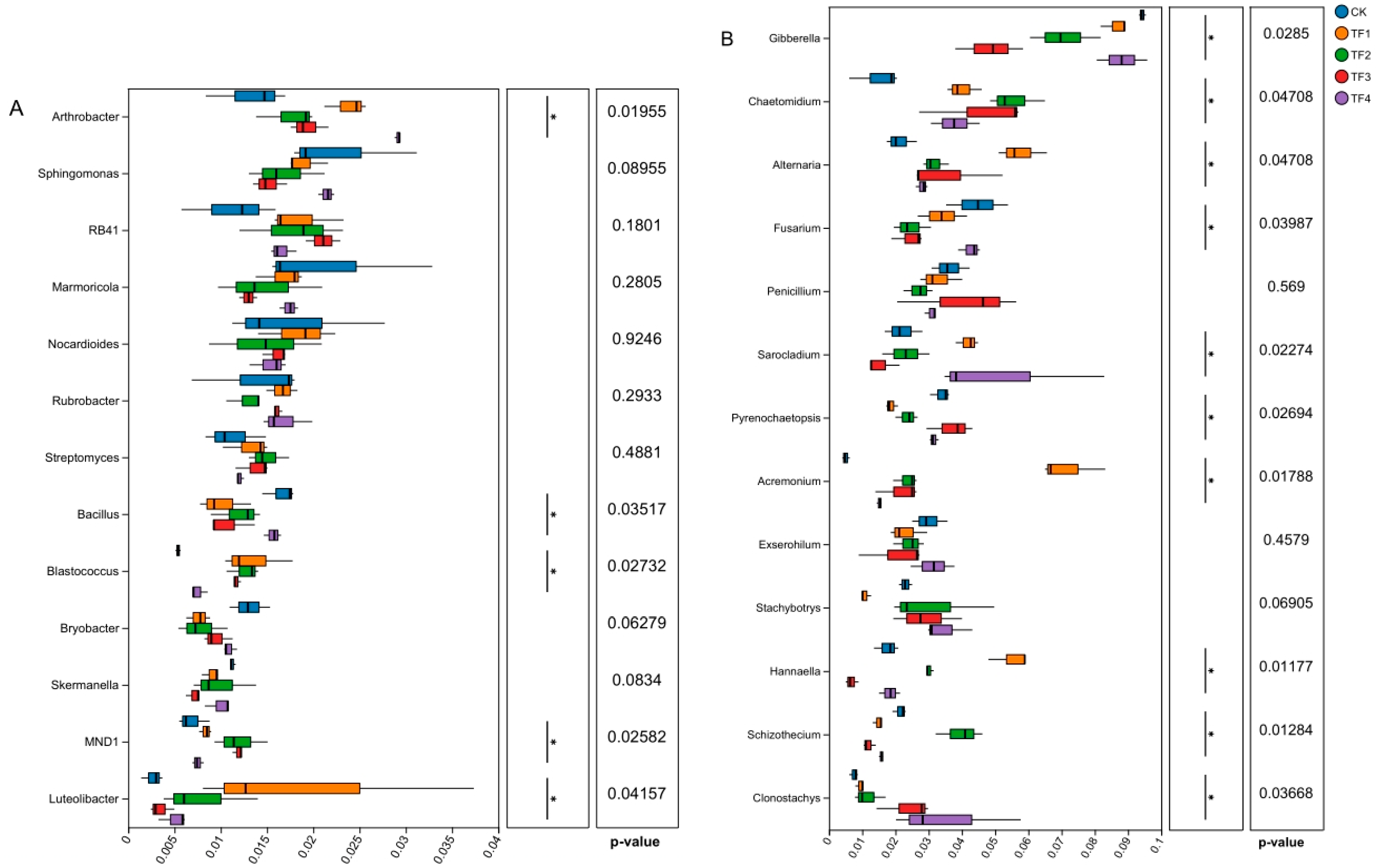
2.5. Effects of PGPRs on the Composition of Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities at the Genus Level
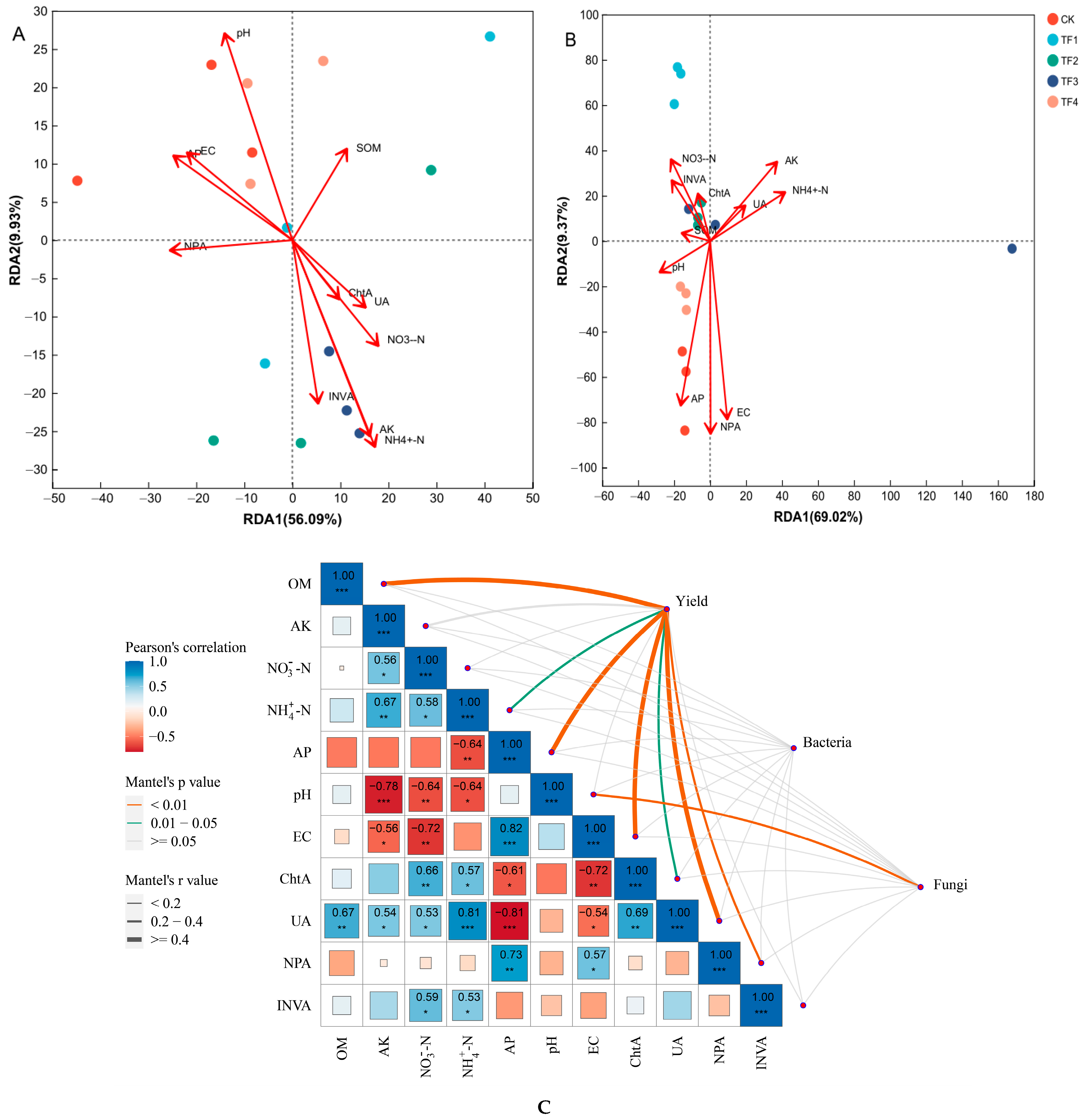
2.6. Relationships Between Soil Microbial Community, Yield, and Soil Biochemical Properties
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Field Site Description
4.2. Experimental Description
4.3. Plant Analysis
4.4. Soil Sample Collection
4.5. Soil Chemical Analysis
4.6. Soil Enzyme Assays
4.7. Soil DNA Extraction, Illumina MiSeq Sequencing, and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, K.Z.; Wu, Z.T.; Li, W.X.; Chang, H.; Wang, L.F.; Xu, Z.P.; Yang, X.L.; Liu, Q. Research progress on cultivation techniques of silage maize in China. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 2024, 9, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Yi, J. Visualization analysis of silage maize research field in China based on knowledge map. J. Maize Sci. 2021, 29, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.Y. New concept “Forage is a Part of Grains” to utmost spurring the development of forage industry. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2023, 31, 311–313. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Soil salinity: Historical perspectives and a world overview of the problem. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Haj-Amor, Z.; Araya, T.; Kim, D.G.; Bouri, S.; Lee, J.; Ghiloufi, W.; Yang, Y.R.; Kang, H.J.; Jhariya, M.K.; Banerjee, A.; et al. Soil salinity and its associated effects on soil microorganisms, greenhouse gas emissions, crop yield, biodiversity and desertification: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinizationunder changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, W.W.; Niu, L.Y.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, J.J.; Cao, J.F. Characteristics of soil salinization in coastal saline alkali area of Cangzhou. Adm. Tech. Environ. Monit. 2021, 33, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Feng, J.J.; Chen, S.H.; Sun, G.Z.; Wei, Z.H.; Hu, T.T. Effects of microbial fertilizer and irrigation amount on growth, physiology and water use efficiency of tomato in greenhouse. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 323, 112553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Li, L.; Wang, J.T.; Qi, X.W.; Fang, H.L.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Z.Q.; Yu, X.; Liang, C.Y. Effects of different microbial agent applications on the growth and quality of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) cormels. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 336, 113385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.N.; Hou, J.J.; Zhang, S.D.; Hu, W.J.; Yi, G.W.; Chen, W.J.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Q.Z. Preparation of a new biochar-based microbial fertilizer: Nutrient release patterns and synergistic mechanisms to improve soil fertility. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.M.; Cao, J.; Wang, G. Influence of land management on soil nutrients and microbial biomass in the central Loess Plateau, northwest China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2005, 16, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K. Microbial and enzyme activities of saline and sodic soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Liu, J.J.; Fu, L.; Lu, D.X.; Yue, S.T.; Yang, M.Y. Effects of phosphate solubilizing bacteria on the soil enzyme activities and microecology of soybean rhizosphere. J. China Agric. Univ. 2017, 22, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Wang, G.L.; Chang, F.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Pang, H.C.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, J.; Ji, H.J.; Li, Z.Y. Effects of microbial agents on physicochemical properties and microbial flora of rhizosphere saline-alkali soil. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhao, D.H.; Guan, F.C.; Shi, J.Y.; Cui, Y.R.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zong, X.C.; Liang, L.L. Effects of compound bacterial agents on growth, development and yield of soybean in saline alkali soil. Soybean Sci. 2022, 41, 588–593. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Q.Y.; Gong, M.; Jiang, Y.W.; Yang, X.; Kong, M.; He, J.X.; Zhang, Q.; Song, J.Q.; Li, X.Z.; Han, W.; et al. Microencapsulated microbial seed coating could improve soil environment and maize grain yield in saline soil. Plants 2024, 13, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Nawaz, A.; Khattak, Z.; Butt, M.A.; Fouillaud, M.; Dufossé, L.; Munir, M.; ul Haq, I.; Mukhtar, H. Microbial bio-control agents: A comprehensive analysis on sustainable pest management in agriculture. J. Agr. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.L.; Sun, Y.X.; Yao, Z.P.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, Y.S. Bacillus halophilus BH-8 combined with coal gangue as a composite microbial agent for the rehabilitation of saline-alkali land. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, A.K.; Das, A.B. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: A review. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 324–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, M.C.; Mucha, Â.; Ferreira, H.; Goncalves, B.; Bacelar, E.; Marques, G. Comparative study of plant growth-promoting bacteria on the physiology growth and fruit quality of strawberry. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2019, 99, 5341–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silambarasan, S.; Logeswari, P.; Cornejo, P.; Abraham, J.; Valentine, A. Simultaneous mitigation of aluminum, salinity and drought stress in Lactuca sativa growth via formulated plant growth promoting Rhodotorula mucilaginosa CAM4. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.Y.; Wei, J.K.; Xue, F.Y.; Li, W.C.; Guan, T.K.; Hu, B.Y.; Chen, Q.J.; Han, Y.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Zhang, G.Q. Microbial inoculation influences microbial communities and physicochemical properties during lettuce seedling using composted spent mushroom substrate. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 174, 104418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, W.X.; Zhao, Z. Effect of dynamic application of microbial modifier on growth and yield of spring maize in saline-alkali soil. J. Irrig. Drain. 2024, 43, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, T.; Tian, P.C.; Gao, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.Q. Effects of microbial agent and microbial fertilizer input on soil microbial community structure and diversity in a peanut continuous cropping system. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 64, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Chai, H.X.; Gao, P.L.; Gao, P.H.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.Z.; Guo, X.L.; Lv, Q.X. Effects of brackish water irrigation and biochar application on fertility, enzyme activity, and winter wheat yield in coastal saline-alkali soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 2437–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Sierra, N.D.; Posada, L.F.; Santa-María, G.; Romero-Tabarez, M.; Villegas-Escobar, V.; Alvarez, J.C. Bacillus subtilis EA-CB0575 genome reveals clues for plant growth promotion and potential for sustainable agriculture. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2020, 20, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Niu, W.Q.; Ma, L.; Du, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Legacy effects of wheat season organic fertilizer addition on microbial co-occurrence networks, soil function, and yield of the subsequent maize season in a wheat-maize rotation system. J. Environ. Manage 2023, 347, 119160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.J.; Shi, Y.J.; Yang, X.; Dong, L.L.; Lei, F.L.; Zheng, C.S.; Xie, A.Q.; Zhang, D.L.; Sun, L.M.; Sun, X. Analysis of growth and rhizosphere soil changes of herbaceous peony treated with a compound microbial agent under contrasted soil conditions. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Rakshit, A.; Parewa, H.P.; Danish, S.; Alfarraj, S.; Datta, R. Bio-priming with compatible rhizospheric microbes enhances growth and micronutrient uptake of red cabbage. Land 2022, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhegger, R.; Ihring, A.; Gantner, S.; Bahnweg, G.; Knappe, C.; Vogg, G. Induction of systemic resistance in tomato by N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone-producing rhizosphere bacteria. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rady, M.M. Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on growth, yield, antioxidant system and cadmium content of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) plants under salinity and cadmium stress. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wan, C.C.; Song, X.; Xia, G.F.; Ao, N.; Sang, J.J.; Wang, K.M.; Wang, J. Effects of effective microorganisms on growth promotion and the rhizosphere eukaryotic community structure of pepper in Xinjiang, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Shang, Q.X.; Zhang, W.Y.; Menghe, B.L.G. Effects of lactic acid bacteria compound preparation on improvement of saline-alkali soil and soil microbial community. J. South. Agric. 2019, 50, 710–718. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Mao, X.X.; Zhang, M.S.; Yang, W.; Di, H.J.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.J.; Li, B.W. The application of Bacillus megaterium alters soil microbial community composition, bioavailability of soil phosphorus and potassium, and cucumber growth in the plastic shed system of North China. Agric. Ecosyst. Enviro. 2021, 307, 107236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira-Paiva, C.A.; Bini, D.; de Sousa, S.M.; Ribeiro, V.P.; dos Santos, F.C.; de Paula Lana, U.G.; de Souza, F.F.; Gomes, E.A.; Marriel, I.E. Inoculation with Bacillus megaterium CNPMS B119 and Bacillus subtilis CNPMS B2084 improve P-acquisition and maize yield in Brazil. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1426166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira Velloso, C.C.; de Oliveira, C.A.; Gomes, E.A.; Lana, U.G.P.; de Carvalho, C.G.; Guimarães, L.J.M.; Pastina, M.M.; de Sousa, S.M. Genome-guided insights of tropical Bacillus strains efficient in maize growth promotion. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, S.M.; de Oliveira, C.A.; Andrade, D.L.; de Carvalho, C.G.; Ribeiro, V.P.; Pastina, M.M.; Marriel, I.E.; Ubiraci Gomes de Paula Lana, U.G.; Gomes, E.A. Tropical Bacillus strains inoculation enhances maize root surface area, dry weight, nutrient uptake and grain yield. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, V.P.; Marriel, I.E.; Sousa, S.M.; de Paula Lana, U.G.; Mattos, B.B.; de Oliveira, C.A.; Gomes, E.A. Endophytic Bacillus strains enhance pearl millet growth and nutrient uptake under low-P. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49 (Suppl. S1), 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiyhs, B.S.; Philippot, L. Insights into the resistance and resilience of the soil microbial community. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.C.; Li, Y.Y.; Yu, T.Y.; Liu, G.J.; Dong, L.H. Effects of microbial agents on soil salinity and alfalfa growth under different salt stress conditions. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 17, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Chen, Y.; Qu, S.; Zhao, W.S. Effects of different microbial fertilizers on soil quality and maize yield in coastal saline soil. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 4279–4292. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, N.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.Q.; Hu, Q.L.; Zhang, J.F. Application of compound microbial agent in improvement of soda saline-alkali soil. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2024, 46, 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.L. Effects of microbial inoculants on quality and soil environment of Huanghua brumal jujube. J. Hebei For. Sci. Technol. 2023, 1, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, S.X.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Jiang, G.Y.; Wu, J. Effect of microbial agents on soil physical and chemical properties and growth of pakchoi. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.J.; Wang, S.; Luan, H.A.; Li, H.; Guo, S.P.; Qi, G.H.; Zhang, X.M. Effects of microbial inoculum on red raspberry growth, fruit quality and activating soil phosphorus and potassium. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 198–209. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, X.X.; Chang, F.D.; Liu, N.; Pang, H.C.; Shi, W.J.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, Y.Y. Effects of applying functional microbial agents on sunflower growth and soil microorganism in severe saline alkali soil. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2021, 5, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Z.Y.; Huang, Q.W.; Zhang, R.F.; Li, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q.R. Effects of organic-inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice-wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.Q.; Liu, B.W.; Yin, Y.; Liang, F.; Xie, D.S.; Han, T.T.; Liu, Y.Z.; Yan, B.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; et al. Impact of biocontrol microbes on soil microbial diversity in ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 5537–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, J.W.; Liu, F.H.; Liu, Z.C.; Luo, S.L.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, J.; Yu, J.H. Reduced chemical fertilizer combined with bio-organic fertilizer affects the soil microbial community and yield and quality of lettuce. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 863325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.B.; Wan, S.X.; Hua, K.K.; Yin, Y.; Chu, H.Y.; Wang, D.Z.; Guo, X.S. Fertilization regime has a greater effect on soil microbial community structure than crop rotation and growth stage in an agroecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 149, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Lu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Guo, P.R.; Jia, B.B.; Hao, B.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Guo, W. Bioorganic fertilizers improve the adaptability and remediation efficiency of Puccinellia distans in multiple heavy metals-contaminated saline soil by regulating the soil microbial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Schlaeppi, K.; Banerjee, S.; Kuramae, E.E.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Fungal-bacterial diversity and microbiome complexity predict ecosystem functioning. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vasconcellos, R.L.F.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Rhizospheric streptomycetes as potential biocontrol agents of Fusarium and Armillaria pine rot and as PGPR for Pinus taeda. BioControl 2009, 54, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chen, K.; Li, H.M.; Zhao, Z.J.; Hu, J.D.; Li, J.S.; Yang, H.T. Biocontrol efficacy and action mechanism of Trichoderma harzianum LTR-2 and Arthrobacter ureafaciens DnL1-1 against crown rot of wheat. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2023, 35, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.Q.; Liu, L.L.; Wen, T.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, J.B.; Cai, Z.C. Illumina MiSeq investigations on the changes of microbial community in the Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense infected soil during and after reductive soil disinfestation. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 181, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhang, X.; Guo, D.D.; Zhou, W.; Huang, S.M. Distinct responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to changes in fertilization regime and crop rotation. Geoderma 2018, 319, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wen, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, M.L.; Penton, C.R.; Thomashow, L.S.; Shen, Q.R. Predicting disease occurrence with high accuracy based on soil macroecological patterns of fusarium wilt. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2936–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlawi, S.; Abusharkh, S.; Carroll, A.; McMullin, D.R.; Avis, T.J. Biological and chemical characterization of antimicrobial activity in Arthrobacter spp. isolated from disease-suppressive compost. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Islam, M.S.; Song, P.; Zhu, L.; Dong, W.B. Isolation and optimization of a broad-spectrum synthetic antimicrobial peptide, Ap920-WI, from Arthrobacter sp. H5 for the biological control of plant diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Xie, M.M.; Xue, T.T.; Sui, X.; Sun, H.; Li, C.W.; Song, F.Q. Short-term continuous cropping leads to a decline in rhizosphere soil fertility by modulating the perilla root exudates. Rhizosphere 2024, 32, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.M.; Wattanachai, P.; Kasem, S.; Poaim, S. Biological control of Phytophthora palmivora causing root rot of pomelo using Chaetomium spp. Mycobiology 2015, 43, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalinova, A.A.; Salimova, D.R.; Berestetskiy, A.O. Fungi of the genera Alternaria as producers of biological active compounds and mycoherbicides. Appl. Biochem. Micro. 2020, 56, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berestetskiy, A.O.; Gannibal, F.B.; Minkovich, E.V.; Osterman, I.V.; Salimova, D.R.; Sergiev, P.V.; Sokornova, S.V. Spectrum of biological activity of the Alternaria fungi isolated from the phyllosphere of herbaceous plants. Microbiology 2018, 87, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, N.D.; Vaughan, M.M.; McCormick, S.P.; Brown, J.A.; Bakker, M.G. Sarocladium zeae is a systemic endophyte of wheat and an effective biocontrol agent against Fusarium head blight. Biol. Control. 2020, 149, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comby, M.; Gacoin, M.; Robineau, M.; Rabenoelina, F.; Ptas, S.; Dupont, J.; Profizi, C.; Baillieul, F. Screening of wheat endophytes as biological control agents against Fusarium head blight using two different In Vitro tests. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 202, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, K.; Rajabpour, A.; Ghodoum Parizipour, M.H.; Yarahmadi, F. Biological and molecular characterization of Cladosporium sp. and Acremonium zeylanicum as biocontrol agents of Aphis fabae in a tri-trophic system. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2022, 170, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.N.; Lu, H.M.; Qi, X.; Lin, M.P.; Gao, C.H.; Luo, X.W. Recent advances in chemistry and bioactivities of secondary metabolites from the genus Acremonium. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Rocha, L.F.N.; Martinez, J.M.; Montalva, C.; Humber, R.A.; Luz, C. Clonostachys spp., natural mosquito antagonists, and their prospects for biological control of Aedes aegypti. Parasitol Res. 2022, 121, 2979–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cota, L.V.; Maffia, L.V.; Mizubuti, E.S.G.; Macedo, P.E.F.; Antunes, R.F. Biological control of strawberry gray mold by Clonostachys rosea under field conditions. Biol. Control 2008, 46, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Xiao, S.Q.; Chen, X.M.; Ali, I.; Gou, J.L.; Wang, D.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, W.K.; Shang, R.; Han, M.W. Biochar-based microbial agent reduces U and Cd accumulation in vegetables and improves rhizosphere microecology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.L.; Gong, T.; Wang, J.W.; Li, G.J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhen, J.; Ning, M.; Yue, D.D.; Du, Z.M.; Chen, G.C. Effects of compound microbial fertilizer on soil characteristics and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.G.; Zheng, X.H.; Oba, B.T.; Shen, C.B.; Wang, X.X.; Wang, H.; Luo, Q.; Sun, L.N. Activating soil microbial community using bacillus and rhamnolipid to remediate TPH contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.S.; Li, S.Z.; Dong, L.H.; Wang, P.P.; Lu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Su, Z.H.; Guo, Q.G.; Ma, P. Effects of different crop rotations on the incidence of cotton Verticillium wilt and structure and function of the rhizospheric microbial community. Plant Soil 2023, 485, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.S.; Guo, Q.G.; Li, S.Z.; Lu, X.Y.; Dong, L.H.; Wang, P.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Su, Z.H.; Ma, P. Application of Bacillus subtilis NCD-2 can suppress cotton verticillium wilt and its effect on abundant and rare microbial communities in rhizosphere. Biol. Control 2022, 165, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.H.; Tian, L.; Nasir, F.; Bahadur, A.; Batool, A.; Luo, S.S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.C.; Tian, C.J. Response of microbial communities and enzyme activities to amendments in saline-alkaline soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, M.M.; Song, W.F.; Wen, S.L.; Wang, B.R.; Zhu, C.Q.; Shen, R.F. Impact of 25 years of inorganic fertilization on diazotrophic abundance and community structure in an acidic soil in southern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Li, Y.P.; Li, W.X.; Xie, Z.S.; Fan, C.L.; Liu, P.X.; Deng, S.X. Bacterial community structure in atmospheric particulate matters of different sizes during the haze days in Xi’an, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.S.; Wang, P.P.; Dong, L.H.; Li, S.Z.; Lu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Su, Z.H.; Guo, Q.G.; Ma, P. Effect of broccoli residues into soil on occurrence of verticillium wilt of spring-sowing-cotton and on rhizosphere microbial communities structure and function. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1115656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Density (×1000 Plants/hm2) | Plant Height (cm) | Fresh Weight (kg/Plant) | Stem Diameter (mm) | Biomass (tons/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 47.29 ± 8.38 c | 213.58 ± 6.46 c | 0.80 ± 0.09 b | 15.53 ± 0.44 b | 39.56 ± 5.69 d |
| TF1 | 58.25 ± 3.09 b | 255.15 ± 2.44 a | 0.91 ± 0.05 ab | 22.64 ± 1.31 a | 52.69 ± 2.79 c |
| TF2 | 57.37 ± 7.95 b | 256.25 ± 5.61 a | 0.94 ± 0.05 ab | 20.69 ± 1.41 a | 54.69 ± 7.42 bc |
| TF3 | 57.85 ± 0.60 b | 252.60 ± 2.53 a | 1.06 ± 0.07 a | 20.89 ± 0.68 a | 60.94 ± 0.44 b |
| TF4 | 67.64 ± 2.08 a | 233.05 ± 4.67 b | 0.97 ± 0.09 ab | 20.20 ± 0.57 a | 65.41 ± 1.64 a |
| Index | CK | TF1 | TF2 | TF3 | TF4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM (%) | 1.77 ± 0.21 b | 1.93 ± 0.13 b | 1.81 ± 0.20 b | 2.10 ± 0.22 ab | 2.30 ± 0.09 a |
| NO3−-N (μg/g) | 4.44 ± 0.74 c | 5.38 ± 1.09 b | 7.34 ± 0.78 a | 5.46 ± 0.78 b | 5.89 ± 0.36 b |
| NH4+-N (μg/g) | 53.35 ± 7.34 d | 63.41 ± 3.96 c | 85.60 ± 5.29 b | 95.92 ± 3.20 a | 80.34 ± 2.34 b |
| AK (mg/kg) | 937.56 ± 3.90 c | 1006.85 ± 9.09 b | 1163.77 ± 15.22 a | 1116.81 ± 34.02 a | 1018.02 ± 8.50 b |
| AP (μg/g) | 168.98 ± 3.70 a | 31.43 ± 3.89 c | 43.17 ± 2.94 b | 41.71 ± 7.77 b | 19.19 ± 3.06 d |
| pH | 7.44 ± 0.01 a | 7.47 ± 0.05 a | 7.09 ± 0.02 c | 7.22 ± 0.03 b | 7.47 ± 0.01 a |
| EC (μS/cm) | 466.67 ± 0.58 a | 313.00 ± 2.00 d | 281.33 ± 0.58 e | 385.33 ± 2.08 b | 343.00 ± 1.00 c |
| ChtA (U/g) | 70.42 ± 1.17 c | 75.03 ± 1.97 b | 86.67 ± 4.91 a | 76.64 ± 1.99 b | 82.45 ± 1.78 a |
| UA (U/g) | 2916.10 ± 11.51 d | 3165.22 ± 7.85 c | 3437.84 ± 16.32 b | 3494.24 ± 23.03 b | 3682.26 ± 16.92 a |
| NPA (U/g) | 2088.78 ± 45.43 a | 1809.46 ± 12.14 d | 2006.63 ± 10.12 b | 1951.95 ± 11.52 c | 1918.76 ± 34.95 c |
| INVA (U/g) | 45.96 ± 1.82 a | 48.67 ± 3.56 a | 50.28 ± 4.17 a | 49.86 ± 2.66 a | 49.82 ± 0.94 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Cui, N.; Lu, X.; Mo, S.; Guo, Q.; Ma, P. Effect of PGPRs on the Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure and Yield of Silage Maize in Saline–Alkaline Fields. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168040
Zhao W, Li S, Yang W, Cui N, Lu X, Mo S, Guo Q, Ma P. Effect of PGPRs on the Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure and Yield of Silage Maize in Saline–Alkaline Fields. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168040
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Weisong, Shezeng Li, Wei Yang, Naqi Cui, Xiuyun Lu, Shaojing Mo, Qinggang Guo, and Ping Ma. 2025. "Effect of PGPRs on the Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure and Yield of Silage Maize in Saline–Alkaline Fields" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168040
APA StyleZhao, W., Li, S., Yang, W., Cui, N., Lu, X., Mo, S., Guo, Q., & Ma, P. (2025). Effect of PGPRs on the Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure and Yield of Silage Maize in Saline–Alkaline Fields. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168040





