Assessment of a Helium/Argon-Generated Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device’s Safety Utilizing a Pig Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
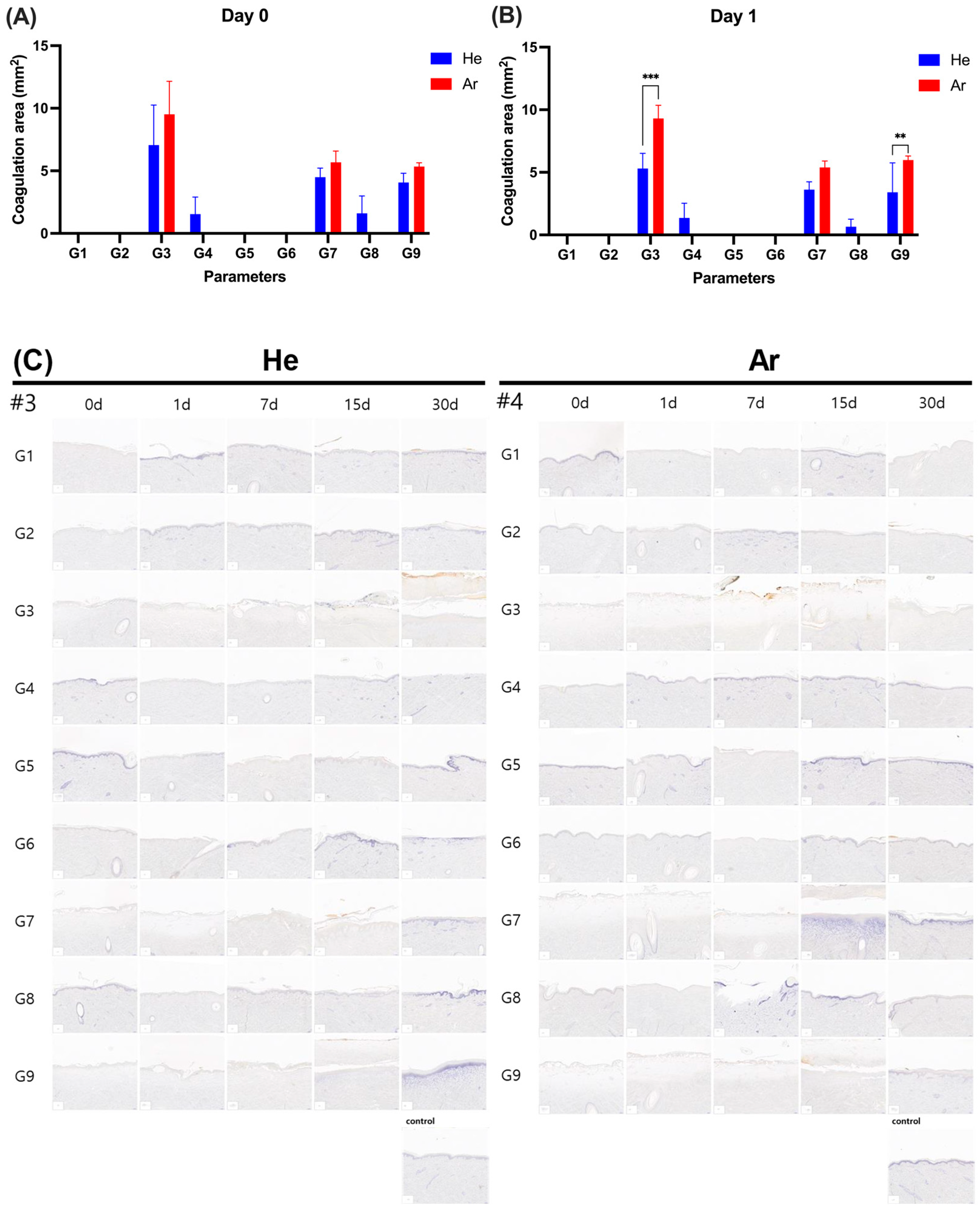
2.1. Experimental Schematic and Assessment of Clinical Value Following Plasma Irradiation
2.2. Measurement of Temperature Change on Pig Skin Surface Immediately After Plasma Irradiation
2.3. Dermatoscopic Observation of Skin Damage and Healing Process Following Plasma Device Application
2.4. Blood Serum Biochemistry Measurements
2.5. Evaluation of Inflammatory Cell Infiltration and Epidermal Proliferation of Skin After Plasma Irradiation
2.6. Evaluation of Skin Proliferation After Plasma Irradiation
2.7. Evaluation of Skin Elasticity Post-Irradiation
2.8. Evaluation of Elasticity Proliferation of Skin After Plasma Irradiation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Approval
4.2. Plasma Equipment
4.3. Animals, Breeding Conditions, and Experiment Handling
4.3.1. Environmental Conditions
4.3.2. Identification of Cage, Breeding Density, and Breeding Box
4.3.3. Method of Feeding, Feed, and Water
4.3.4. Experiment Design
4.3.5. Application of Anesthesia and Testing Equipment
4.4. Skin Surface Temperature Evaluation
4.5. Skin Visual Observation
4.6. Blood Biochemical Evaluation
4.7. Histopathological Evaluation
4.8. Evaluation of the Coagulation Area
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALB | Albumin |
| ALP | Akaline phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| Ar | Argon |
| ARRIVE | Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| Ca | Calcium |
| CAP | Cold atmospheric plasma |
| Cr | Creatinine |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| He | Helium |
| IP | Inorganic phosphorus |
| MT | Masson’s trichrome |
| NBTC | Nitro Blue Tetrazolium Chloride |
| T-bil | Total bilirubin |
| TP | Total protein |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| VB | Victoria blue |
References
- Grinin, L.; Grinin, A.; Korotayev, A. Anti-Aging as a Key Challenge for the Medicine of the Future; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 459–485. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Duan, E. Fighting against Skin Aging: The Way from Bench to Bedside. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Rho, N.-K.; Park, K.Y. Skin Aging from Mechanisms to Interventions: Focusing on Dermal Aging. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1195272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, P.; Duan, R.; Luo, J.; Yang, T.; Liu, N.; Wen, C. Development of Home Beauty Devices for Facial Rejuvenation: Establishment of Efficacy Evaluation System. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganceviciene, R.; Liakou, A.I.; Theodoridis, A.; Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.C. Skin Anti-Aging Strategies. Dermatoendocrinology 2012, 4, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors in Skin Ageing: A Review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shui, R.; Chen, J. Plasma Dermatology: Skin Therapy Using Cold Atmospheric Plasma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 918484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakouri, R.; Khani, M.R.; Samsavar, S.; Jezeh, M.A.; Abdollahimajd, F.; Hosseini, S.I.; Dilmaghanian, A.; Ghasemi, E.; Alihoseini, M.R.; Shokri, B. In Vivo Study of the Effects of a Portable Cold Plasma Device and Vitamin C for Skin Rejuvenation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Woedtke, T.; Laroussi, M.; Gherardi, M. Foundations of Plasmas for Medical Applications. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2022, 31, 054002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, R.; Evangelina, R.; Samuel, J.P.; Singh, P.; Saha, S.; Singhal, M.; Gandhirajan, R.K. Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) in Wound Healing: Harnessing a Dual-Edged Sword. Redox Exp. Med. 2024, 2024, e230026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.B. The Emerging Role of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in Redox Biology and Some Implications for Plasma Applications to Medicine and Biology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 263001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, A.; Nicol, M.J.; Bilén, S.G.; Kirimanjeswara, G.S.; Knecht, S.D. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Medicine: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities for Predictive Control. Plasma 2024, 7, 233–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Woedtke, T.; Emmert, S.; Metelmann, H.-R.; Rupf, S.; Weltmann, K.-D. Perspectives on Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) Applications in Medicine. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 070601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, A.T.; Abdalla, A.N.; Ren, K.; Liu, X. Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP): A Revolutionary Approach in Dermatology and Skincare. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Dietrich, S.; Steuer, A.; Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T.; Masur, K.; Wende, K. Non-Thermal Plasma Activates Human Keratinocytes by Stimulation of Antioxidant and Phase II Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 6731–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdabak Karaca, G.; Bulbul, Y.E.; Oksuz, A.U. Gold-Hyaluranic Acid Micromotors and Cold Atmospheric Plasma for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Therapeutic Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, A.; Yan, D.; Soni, V.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. Combination Drug Delivery Using Cold Atmospheric Plasma Technology. In Nanocarriers for the Delivery of Combination Drugs; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 393–423. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. Cold Atmospheric Plasma, a Novel Promising Anti-Cancer Treatment Modality. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15977–15995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-S.; Wong, T.-H.; Hou, C.-W.; Chu, T.-P.; Lee, J.-W.; Lou, B.-S.; Lin, M.-H. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jet Promotes Wound Healing Through CK2-Coordinated PI3K/AKT and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2025, 24, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, G.R.; Park, H.J.; Koh, Y.G.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Song, M.G.; Lee, J.O.; Hong, H.K.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, B.J. Low-intensity Cold Atmospheric Plasma Reduces Wrinkles on Photoaged Skin through Hormetic Induction of Extracellular Matrix Protein Expression in Dermal Fibroblasts. Lasers Surg. Med. 2022, 54, 978–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, G.R.; Park, H.J.; Koh, Y.G.; Kim, K.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.O.; Seok, J.; Yoo, K.H.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, B.J. The Effect of Low-intensity Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jet on Photoaging-induced Hyperpigmentation in Mouse Model. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 2799–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, T.P.; Eaglstein, W.H.; Davis, S.C.; Mertz, P. The pig as a model for human wound healing. Wound Repair. Regen. 2001, 9, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastar, I.; Liang, L.; Sawaya, A.P.; Wikramanayake, T.C.; Glinos, G.D.; Drakulich, S.; Chen, V.; Stojadinovic, O.; Davis, S.C.; Tomic-Canic, M. Preclinical Models for Wound-Healing Studies. In Skin Tissue Models for Regenerative Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 223–253. [Google Scholar]
- Seaton, M.; Hocking, A.; Gibran, N.S. Porcine Models of Cutaneous Wound Healing. ILAR J. 2015, 56, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiao In, M.; Richardson, K.C.; Loewa, A.; Hedtrich, S.; Kaessmeyer, S.; Plendl, J. Histological and Functional Comparisons of Four Anatomical Regions of Porcine Skin with Human Abdominal Skin. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2019, 48, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollina, U.; Berger, U.; Mahrle, G. Immunohistochemistry of Porcine Skin. Acta Histochem. 1991, 90, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo, G.M.; Bernatchez, S.F.; Diegelmann, R.; Di Pietro, L.A.; Eriksson, E.; Hinz, B.; Hopf, H.W.; Kirsner, R.; Liu, P.; Parnell, L.K.S.; et al. Preclinical Models of Wound Healing: Is Man the Model? Proceedings of the Wound Healing Society Symposium. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 2013, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, T.; Semmler, M.L.; Schäfer, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Emmert, S.; Boeckmann, L. Plasma Medicine: Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma in Dermatology. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 3873928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmler, M.L.; Bekeschus, S.; Schäfer, M.; Bernhardt, T.; Fischer, T.; Witzke, K.; Seebauer, C.; Rebl, H.; Grambow, E.; Vollmar, B.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of the Efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma (CAP) in Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN SPEC 91315:2025-07; Allgemeine Anforderungen an Plasmaquellen Für Die Erzeugung Eines Kalten Atmosphärendruckplasmas_(CAP) Für Medizinische Anwendungen; Text Deutsch Und Englisch. DIN Media: Berlin, Germany, 2025.
- Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Gutsol, A.; Shekhter, A.B.; Vasilets, V.N.; Fridman, A. Applied Plasma Medicine. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, T.P.; Stalder, K.R. Overview of Current Applications in Plasma Medicine. In Proceedings of the SPIE BiOS 2017, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22 February 2017; Ryan, T.P., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; p. 1006606. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, O.; Smits, P.; van Weersch, C.; Quaaden, M.; Bruls, E.; van Loon, A.; van der Kleij, J. Improved Wound Healing by Direct Cold Atmospheric Plasma Once or Twice a Week: A Randomized Controlled Trial on Chronic Venous Leg Ulcers. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 2025, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, O.; Orgill, D.P. An Overview of Recent Clinical Trials for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Therapies. J Clin Med 2024, 13, 7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrand, R.S.; Sabelis, L.W.; de Groot, V.; Peters, E.J. Cold Plasma Treatment Is Safe for Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Decreases Staphylococcus Aureus Bacterial Load. J Wound Care 2023, 32, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinlin, J.; Isbary, G.; Stolz, W.; Morfill, G.; Landthaler, M.; Shimizu, T.; Steffes, B.; Nosenko, T.; Zimmermann, J.; Karrer, S. Plasma Applications in Medicine with a Special Focus on Dermatology. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T. Plasma Medicine—Current State of Research and Medical Application. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2017, 59, 014031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busco, G.; Robert, E.; Chettouh-Hammas, N.; Pouvesle, J.-M.; Grillon, C. The Emerging Potential of Cold Atmospheric Plasma in Skin Biology. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 161, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, S.; Fukuhara, H.; Szili, E.J.; Kawada, C.; Hong, S.-H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shirafuji, T.; Tsuda, M.; Kurabayashi, A.; Furihata, M.; et al. Understanding the Role of Plasma Bullet Currents in Heating Skin to Mitigate Risks of Thermal Damage Caused by Low-Temperature Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Jets. Plasma 2023, 6, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmer, S.; Semchyshyn, N.; Shah, G.; Fitzpatrick, R. A Pilot Study on the Use of a Plasma Skin Regeneration Device (Portrait® PSR3) in Full Facial Rejuvenation Procedures. Lasers Med. Sci. 2007, 22, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, Y.; Elhelaly, A.E.; Hyodo, F.; Ichihashi, K.; Tomita, H.; Noda, Y.; Kato, H.; Matsuo, M. In Vivo Redox Imaging of Plasma-Induced Skin-Inflammation in Mice. Npj Imaging 2024, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; De, S. Thermal Injury of Skin and Subcutaneous Tissues: A Review of Experimental Approaches and Numerical Models. Burns 2017, 43, 909–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarmolenko, P.S.; Moon, E.J.; Landon, C.; Manzoor, A.; Hochman, D.W.; Viglianti, B.L.; Dewhirst, M.W. Thresholds for Thermal Damage to Normal Tissues: An Update. Int. J. Hyperth. 2011, 27, 320–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelmann, H.-R.; Vu, T.T.; Do, H.T.; Le, T.N.B.; Hoang, T.H.A.; Phi, T.T.T.; Luong, T.M.L.; Doan, V.T.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.M.; et al. Scar Formation of Laser Skin Lesions after Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma (CAP) Treatment: A Clinical Long Term Observation. Clin. Plasma Med. 2013, 1, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Nakamura, K.; Mizuno, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Takeda, K.; Kajiyama, H.; Utsumi, F.; Kikkawa, F.; Hori, M. Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Activates Lactate in Ringer’s Solution for Anti-Tumor Effects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratis, D.N.; Eland, K.L.; Angel, S.M. Effect of Pulse Delay Time on a Pre-Ablation Dual-Pulse LIBS Plasma. Appl. Spectrosc. 2001, 55, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drogoff, B.L.; Margot, J.; Vidal, F.; Laville, S.; Chaker, M.; Sabsabi, M.; Johnston, T.W.; Barthélemy, O. Influence of the Laser Pulse Duration on Laser-Produced Plasma Properties. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2004, 13, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stańczyk, B.; Wiśniewski, M. The Promising Potential of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Therapies. Plasma 2024, 7, 465–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barré-Sinoussi, F.; Montagutelli, X. Animal Models Are Essential to Biological Research: Issues and Perspectives. Future Sci OA 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenina, E.; Iannuccelli, N.; Billon, Y.; Fève, K.; Gress, L.; Bazovkina, D.; Mormede, P.; Larzul, C. Genetic Determinism of Cortisol Levels in Pig. Front Genet 2025, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nastuta, A.V.; Gerling, T. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Operated in Ar and He: From Basic Plasma Properties to Vacuum Ultraviolet, Electric Field and Safety Thresholds Measurements in Plasma Medicine. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, J.A.; Aragón, C. A Comparison of the Temperatures and Electron Densities of Laser-Produced Plasmas Obtained in Air, Argon, and Helium at Atmospheric Pressure. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 1999, 69, S475–S478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yambe, K.; Izumida, T.; Ohyama, I.; Akatsuka, H. Comparison of Electron Densities and Temperatures in Helium and Argon Nonthermal Atmospheric-Pressure Plasmas by Continuum Spectral Analysis. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2024, 52, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, I.M.; Van Hoosier, G. Clinical Biochemistry and Hematology. In The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 57–116. [Google Scholar]
- Eugster, A.K.; Albert, P.J.; Kalter, S.S. Multiple Enzyme Determinations in Sera and Livers of Tumor Bearing Hamsters. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966, 123, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.O. (Ed.) Animal Clinical Chemistry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781420080124. [Google Scholar]
- Sattler, T.; Fürll, M. Creatine Kinase and Aspartate Aminotransferase in Cows as Indicators for Endometritis. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 2004, 51, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, M.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Feng, P.; He, R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, C. Ratio of Creatine Kinase to Alanine Aminotransferase as a Biomarker of Acute Liver Injury in Dystrophinopathy. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 6484610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroussi, M.; Akan, T. Arc-Free Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma Jets: A Review. Plasma Process. Polym. 2007, 4, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M. Cold Plasma in Medicine and Healthcare: The New Frontier in Low Temperature Plasma Applications. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoorgashti, R.; Nikmaram, R.; Azimi, Y.; Rouientan, A.; Ebrahimi, H.; Lesan, S. Effectiveness of Cold Plasma Application in Oral Wound Healing Process: A Scoping Review. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 5062–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, S.; Blagus, T.; Cemazar, M.; Filipic, G.; Sersa, G.; Cvelbar, U. Safety Aspects of Atmospheric Pressure Helium Plasma Jet Operation on Skin: In Vivo Study on Mouse Skin. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belum, V.R.; de Barros Silva, G.; Laloni, M.T.; Ciccolini, K.; Goldfarb, S.B.; Norton, L.; Sklarin, N.T.; Lacouture, M.E. Cold Thermal Injury from Cold Caps Used for the Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Alopecia. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 157, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Q.; Fang, Z. Comparison of Atmospheric-Pressure He and Ar Plasma Jets Driven by Microsecond Pulses. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2015, 43, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, T.; Uehara, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Miyahara, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Iwasawa, A.; Ito, N.; Azuma, T.; Kohno, M.; Okino, A. Investigation of Reactive Species Using Various Gas Plasmas. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 39901–39905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, H.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Hassan, M.A.; Andocs, G.; Nojima, N.; Takeda, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Hori, M.; Kondo, T. EPR-Spin Trapping and Flow Cytometric Studies of Free Radicals Generated Using Cold Atmospheric Argon Plasma and X-Ray Irradiation in Aqueous Solutions and Intracellular Milieu. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiyari-Ramezani, M.; Nasiri, M.; Baniasadi, M. Helium and Argon Cold Plasma Effects on the 4T1 Cancer Cells and a Triple Negative Mouse Model of Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, L.E.; Terry, R.; Whittaker, A.L.; Hiendleder, S.; Ralph, C.R. Pronounced Inter-Individual Variation in Plasma Cortisol Response to Fluoxetine Hydrochloride in the Pig. Animals 2020, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrynin, D.; Wu, A.; Kalghatgi, S.; Park, S.; Shainsky, N.; Wasko, K.; Dumani, E.; Ownbey, R.; Joshi, S.; Sensenig, R.; et al. Live Pig Skin Tissue and Wound Toxicity of Cold Plasma Treatment. Plasma Med. 2011, 1, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maisch, T.; Shimizu, T.; Li, Y.-F.; Heinlin, J.; Karrer, S.; Morfill, G.; Zimmermann, J.L. Decolonisation of MRSA, S. Aureus and E. Coli by Cold-Atmospheric Plasma Using a Porcine Skin Model In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apelqvist, J.; Robson, A.; Helmke, A.; Rousseau, A.; Boekema, B.; den Braber, E.; Szili, E.; Stuermer, E.; Boeckmann, L.; Gaur, N.; et al. Cold Plasma: An Emerging Technology for Clinical Use in Wound Healing. J. Wound Manag. 2024, 25, S1–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

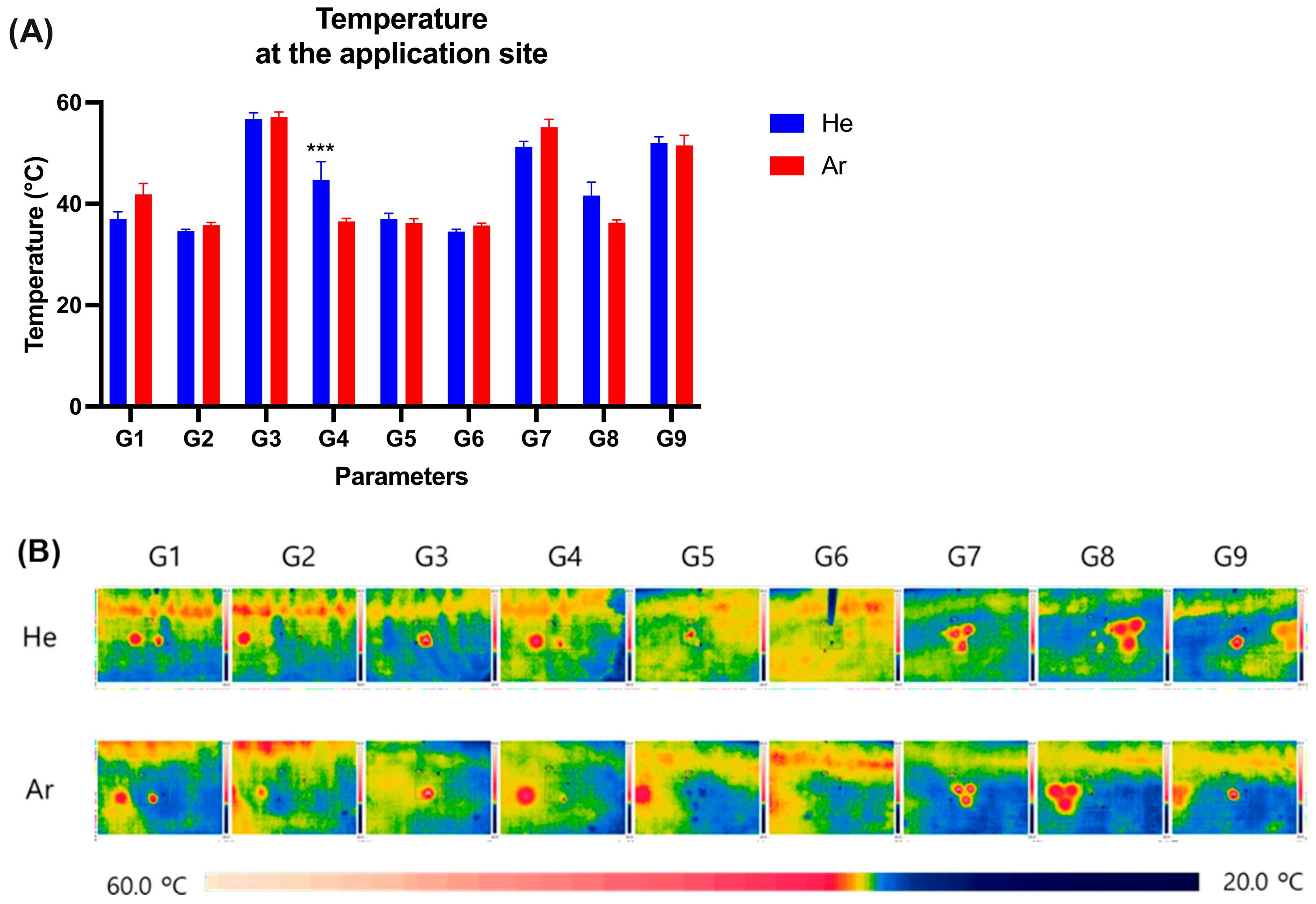
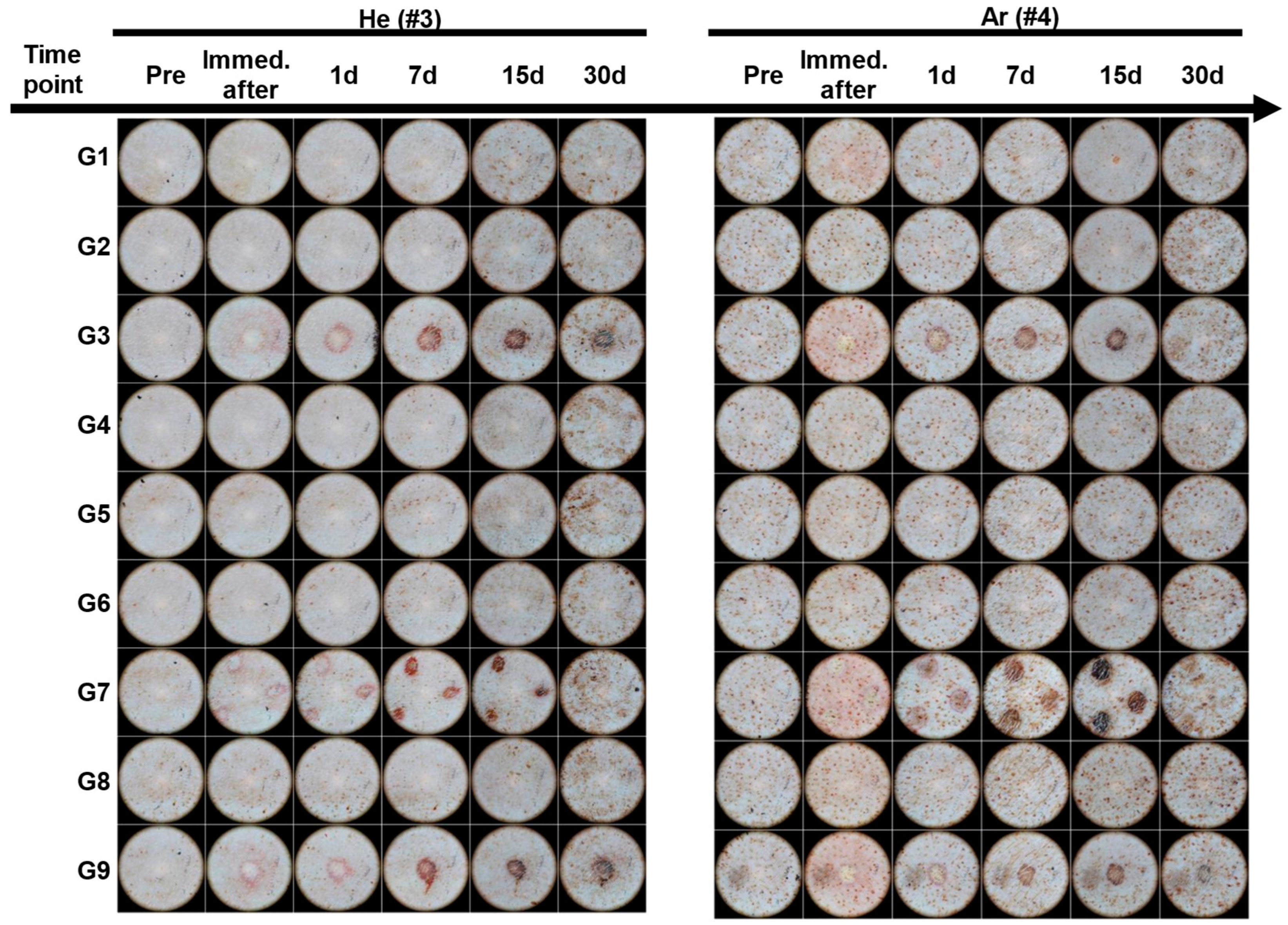


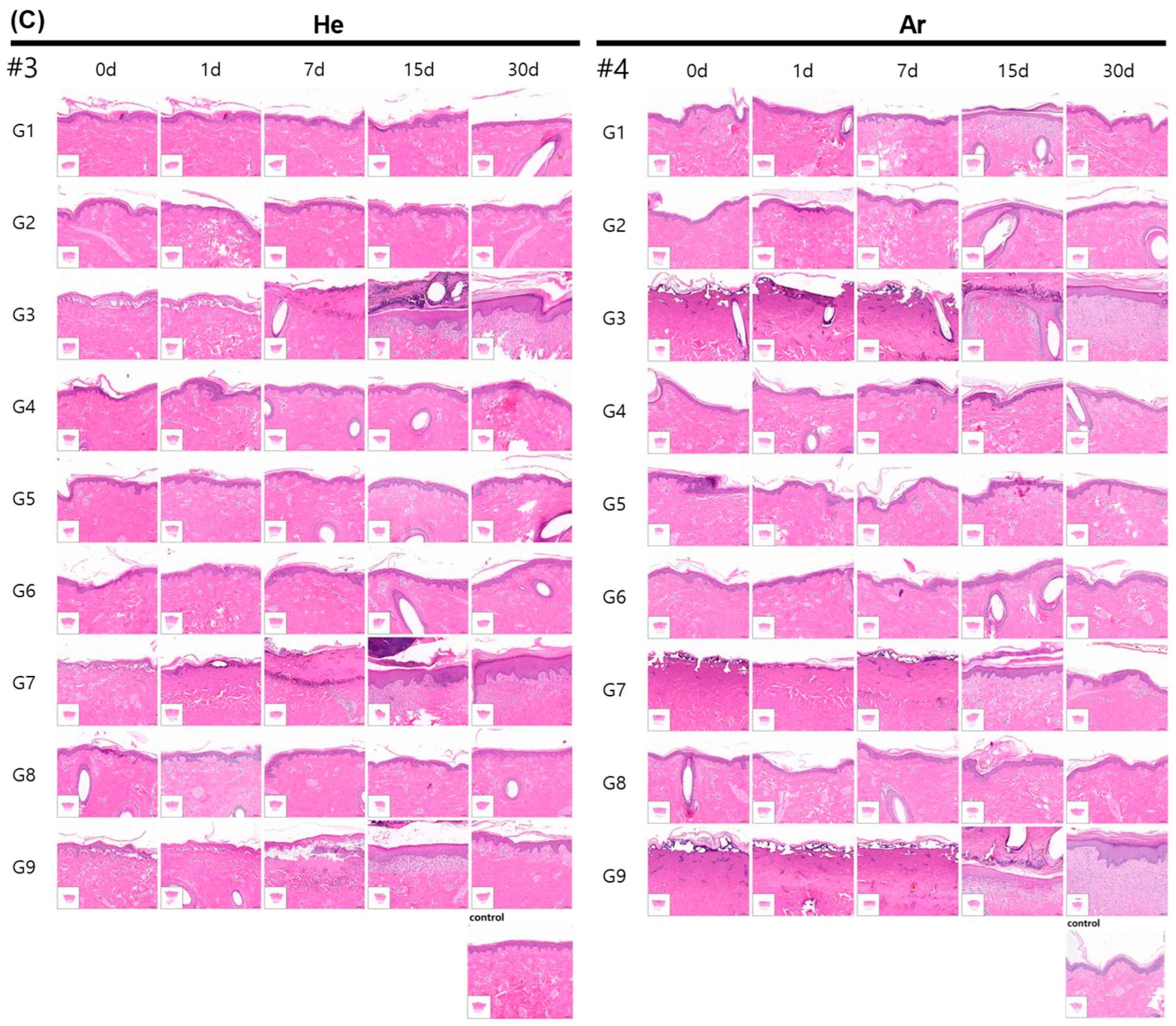


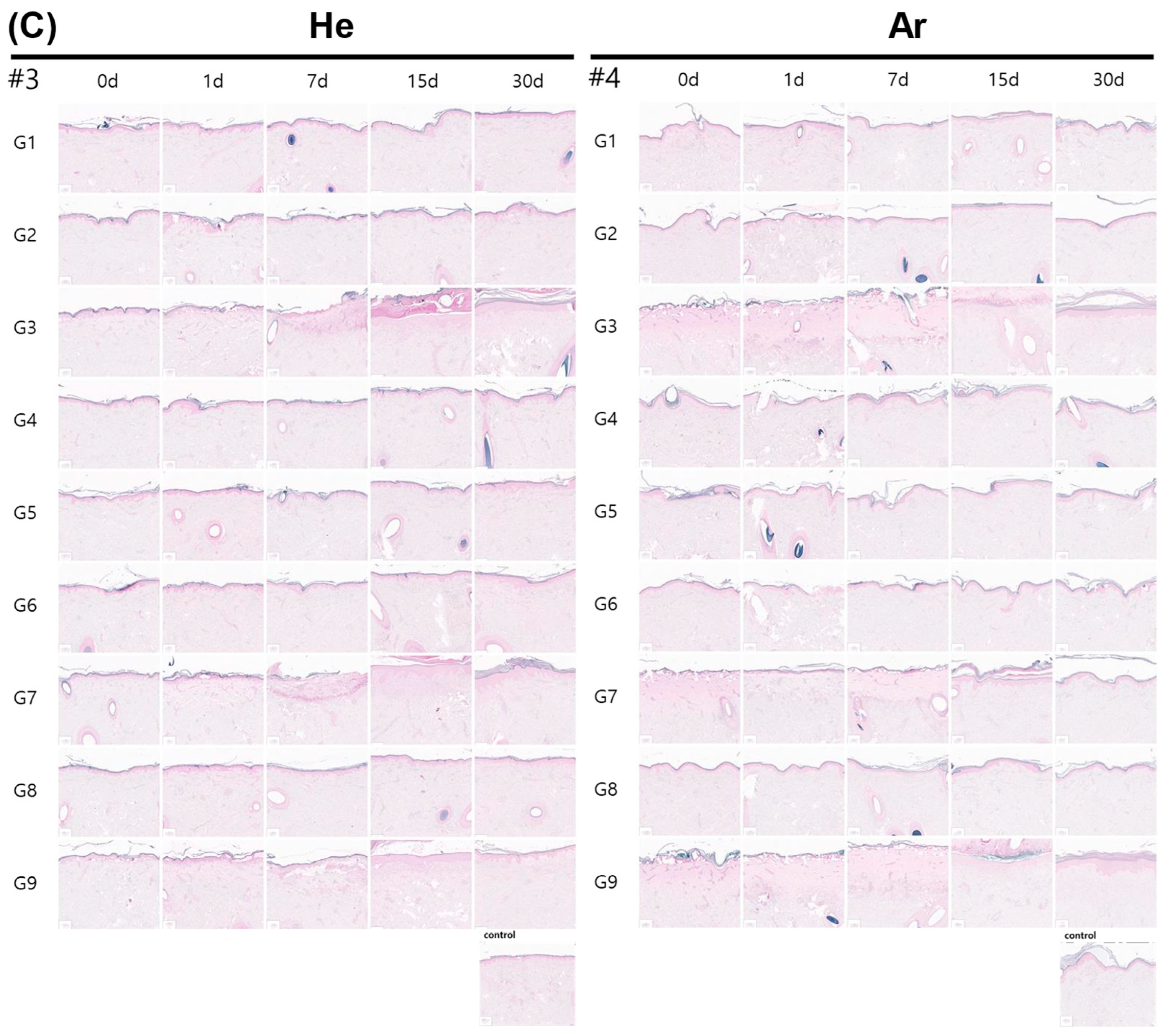
| Condition Name | Parameter Conditions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handpiece Type | Plasma Output * (kV) | Gas Output Mode (kPa) | Operation Mode * | Irradiation Time (s) | Clinical Outcomes | |
| G1 | Single # | 2.6 ± 10% | 7 ± 20% | Continuous | 10 s | Safe but Ar gas showed immediately epithelial cell shrinkage |
| G2 | Single | 2.6 ± 10% | 7 ± 20% | Pulse | 10 s | Gentle and safe |
| G3 | Single | 4 ± 10% | 11 ± 20% | Continuous | 10 s | Skin erosion and erythema |
| G4 | Single | 4 ± 10% | 11 ± 20% | Pulse | 10 s | Gentle and safe |
| G5 | Triple ## | 2 ± 10% | 13.5 ± 20% | Continuous | 10 s | Gentle and safe |
| G6 | Triple | 2 ± 10% | 13.5 ± 20% | Pulse | 10 s | Gentle and safe |
| G7 | Triple | 3.2 ± 10% | 21.5 ± 20% | Continuous | 10 s | Skin erosion and erythema |
| G8 | Triple | 3.2 ± 10% | 21.5 ± 20% | Pulse | 10 s | Gentle and safe |
| G9 | Single | 4 ± 10% | 11 ± 20% | continuous | 5 s | Skin erosion and erythema |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.-R.; Trinh, T.-T.T.; Thuy, L.L.T.; Giang, N.N.; Jin, Y.-X.; Lee, Y.-H.; Ahn, G.-Y.; Goo, B.L.; Jung, K.-S.; Hwang, H.-S.; et al. Assessment of a Helium/Argon-Generated Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device’s Safety Utilizing a Pig Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167854
Zhang X-R, Trinh T-TT, Thuy LLT, Giang NN, Jin Y-X, Lee Y-H, Ahn G-Y, Goo BL, Jung K-S, Hwang H-S, et al. Assessment of a Helium/Argon-Generated Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device’s Safety Utilizing a Pig Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167854
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xin-Rui, Thuy-Tien Thi Trinh, Linh Le Thi Thuy, Nguyen Ngan Giang, Yong-Xun Jin, Young-Hyun Lee, Gun-Young Ahn, Boncheol Leo Goo, Kyoung-Su Jung, Hyun-Soo Hwang, and et al. 2025. "Assessment of a Helium/Argon-Generated Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device’s Safety Utilizing a Pig Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167854
APA StyleZhang, X.-R., Trinh, T.-T. T., Thuy, L. L. T., Giang, N. N., Jin, Y.-X., Lee, Y.-H., Ahn, G.-Y., Goo, B. L., Jung, K.-S., Hwang, H.-S., Chien, P. N., & Heo, C.-Y. (2025). Assessment of a Helium/Argon-Generated Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device’s Safety Utilizing a Pig Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167854






