Patient Stratification for Serum LDH Levels Reveals Distinct CLA+ T-Cell Cytokine Secretion in Response to HDM, Clinical Features and Allergic Comorbidities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
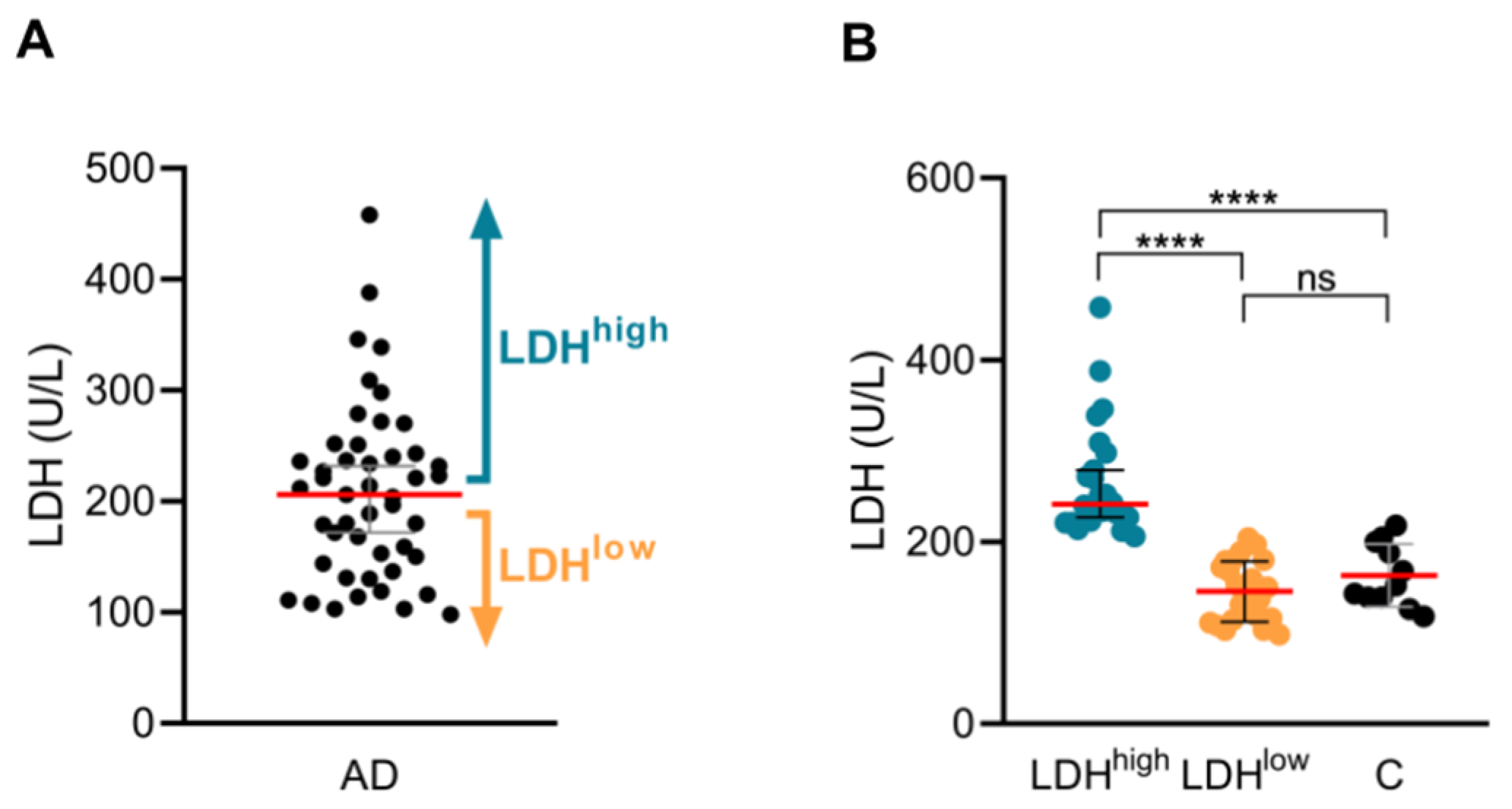
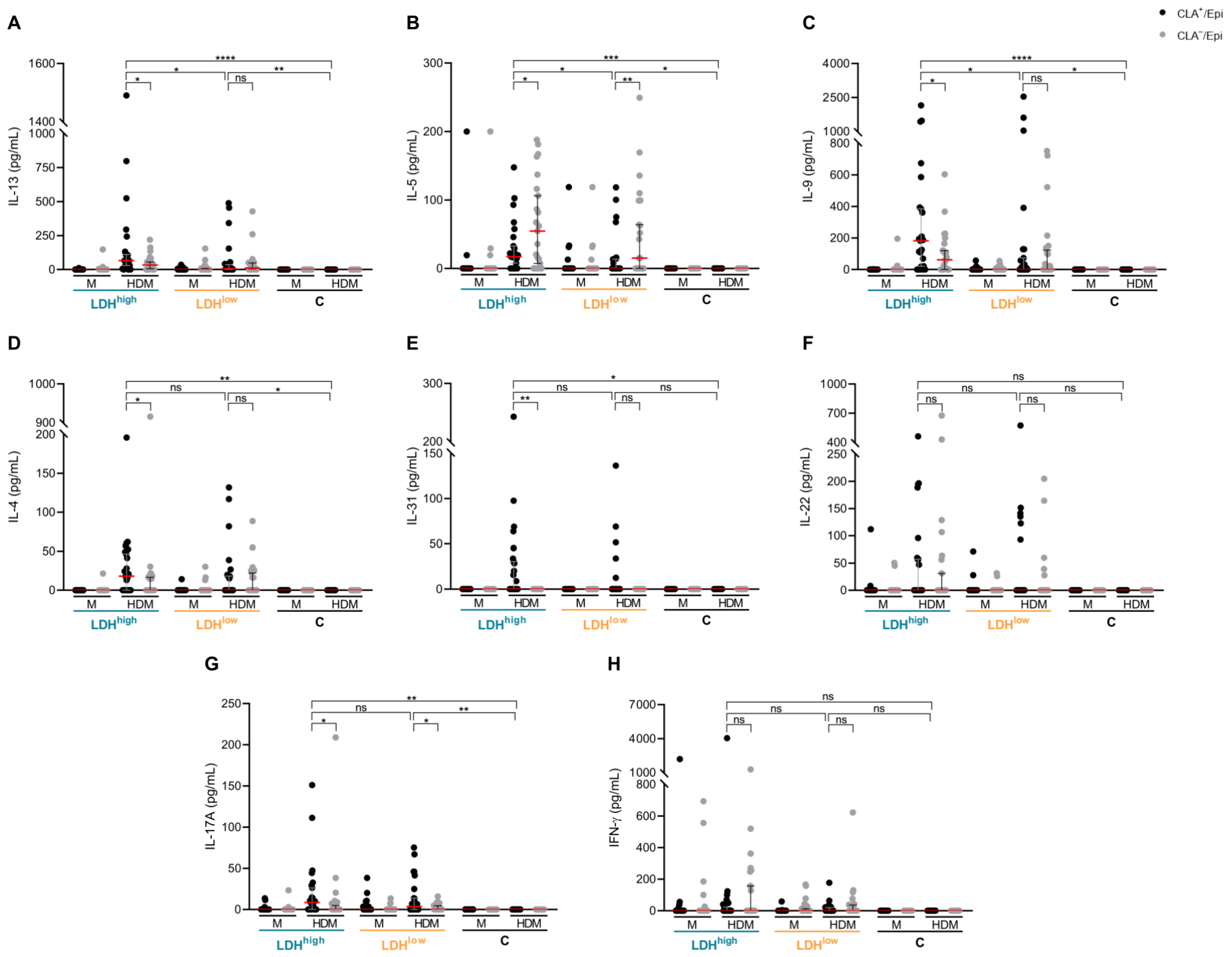
2.1. Patients with High Serum LDH Show Higher IL-13, IL-5 and IL-9 Production by CLA+ Memory T Cells in Respose to HDM than Patients with Low Serum LDH
2.2. Patients with High Serum LDH Present a Specific Phenotype and a Higher Prevalence of Allergic Comorbidities in Comparison with Patients with Low Serum LDH
2.3. Stratification According to Disease Severity, Eosinophil Count or Serum Total IgE in the Same Patients Fails to Reflect LDHhigh Endotype
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Isolation of Circulating CLA+/− Memory T Cells and Epidermal Cell Suspension
4.3. Coculture and Stimulation of Circulating CLA+/− Memory T Cells with Epidermal Cells
4.4. Cytokine and Chemokine Quantification
4.5. Quantification of Total and Specific IgE Against HDM and SEB
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langan, S.M.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Brunner, P.M. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2025, 405, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livesey, A.; Garty, F.; Shipman, A.R.; Shipman, K.E. Lactate dehydrogenase in dermatology practice. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, H.; Noguchi, T.; Kamimura, K.; Nishioka, K.; Nishiyama, S. Significance of elevated serum LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) activity in atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 1990, 17, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renert-Yuval, Y.; Thyssen, J.P.; Bissonnette, R.; Bieber, T.; Kabashima, K.; Hijnen, D.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Biomarkers in atopic dermatitis-a review on behalf of the International Eczema Council. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1174–1190.e1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Villarreal, M.; Jepson, B.; Rafaels, N.; David, G.; Hanifin, J.; Taylor, P.; Boguniewicz, M.; Yoshida, T.; De Benedetto, A.; et al. Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Colonized with Staphylococcus aureus Have a Distinct Phenotype and Endotype. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2224–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, K.; Aihara, M.; Matsunaga, T.; Chen, H.; Taguri, M.; Morita, S.; Fujita, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kambara, T.; Ikezawa, Z. Association of serum interleukin-18 and other biomarkers with disease severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2012, 304, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Kamata, M.; Ito, M.; Uchida, H.; Nagata, M.; Fukaya, S.; Hayashi, K.; Fukuyasu, A.; Tanaka, T.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Higher baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase level is associated with poor effectiveness of dupilumab in the long term in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnowicki, T.; Santamaria-Babí, L.F.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Circulating CLA(+) T cells in atopic dermatitis and their possible role as peripheral biomarkers. Allergy 2017, 72, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, D.S.; Nierkens, S.; Knol, E.F.; Giovannone, B.; Delemarre, E.M.; van der Schaft, J.; van Wijk, F.; de Bruin-Weller, M.S.; Drylewicz, J.; Thijs, J.L. Confirmation of multiple endotypes in atopic dermatitis based on serum biomarkers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, C.; der Wal, M.M.V.; El Amrani, M.; Luin, M.V.; Bakker, D.S.; Bruin-Weller, M.; van Wijk, F. Biological Tipping Point in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Treated with Different Dosing Intervals of Dupilumab. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 1822–1825.e1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.; Allakhverdi, Z.; Dupuis, F. 185 High-dimensional analysis identifies variability persistent skin-homing Th2/Tc2 populations in AD patients under remission with dupilumab. In Proceedings of the ISID 2023, Tokyo, Japan, 10–13 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Starrenburg, M.; Dekkers, C.; van der Wal, M.; Meermans, M.; Bakker, D.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; van Wijk, F. 121 Impact Of Tralokinumab on Skin-homing T cells and IL-4 and IL13 Receptor Dynamics In Patients With Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, S249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, J.S.; Carlsson, M.; Stougaard, J.K.; Nygaard, U.; Buchner, M.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Hvid, M.; Vestergaard, C.; Deleuran, M.; Deleuran, B. The OX40 Axis is Associated with Both Systemic and Local Involvement in Atopic Dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, S.; Bieber, T.; Cork, M.J.; Reich, A.; Wilson, R.; Quaratino, S.; Stebegg, M.; Brennan, N.; Gilbert, S.; O′Malley, J.T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of amlitelimab, a fully human nondepleting, noncytotoxic anti-OX40 ligand monoclonal antibody, in atopic dermatitis: Results of a phase IIa randomized placebo-controlled trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 189, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans-De San Nicolàs, L.; Figueras-Nart, I.; Bonfill-Ortí, M.; De Jesús-Gil, C.; García-Jiménez, I.; Guilabert, A.; Curto-Barredo, L.; Bertolín-Colilla, M.; Ferran, M.; Serra-Baldrich, E.; et al. SEB-induced IL-13 production in CLA(+) memory T cells defines Th2 high and Th2 low responders in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2022, 77, 3448–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans-de San Nicolàs, L.; Figueras-Nart, I.; García-Jiménez, I.; Bonfill-Ortí, M.; Guilabert, A.; Curto-Barredo, L.; Bertolín-Colilla, M.; Ferran, M.; Serra-Baldrich, E.; Pujol, R.M.; et al. Allergen sensitization stratifies IL-31 production by memory T cells in atopic dermatitis patients. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1124018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Jiménez, I.; Sans-de San Nicolás, L.; Curto-Barredo, L.; Bertolín-Colilla, M.; Sensada-López, E.; Figueras-Nart, I.; Bonfill-Ortí, M.; Guilabert-Vidal, A.; Ryzhkova, A.; Ferran, M.; et al. Heterogeneous IL-9 Production by Circulating Skin-Tropic and Extracutaneous Memory T Cells in Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Bianchelli, T.; Gesuita, R.; Foti, C.; Malara, G.; Micali, G.; Amerio, P.; Rongioletti, F.; Corazza, M.; Patrizi, A.; et al. Comorbidities and treatment patterns in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: Results from a nationwide multicenter study. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2022, 314, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, H.; Kouda, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Takigawa, M.; Masamoto, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Ochi, H. 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine in urine as an index of oxidative damage to DNA in the evaluation of atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1998, 138, 1033–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Takekuma, K.; Hoshika, A. Changes in serum lactate dehydrogenase activity in children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Int. 2010, 52, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Rodriguez, E.; Degenhardt, F.; Baurecht, H.; Wehkamp, U.; Volks, N.; Szymczak, S.; Swindell, W.R.; Sarkar, M.K.; Raja, K.; et al. Atopic Dermatitis Is an IL-13-Dominant Disease with Greater Molecular Heterogeneity Compared to Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsborough, J.; Leung, D.Y.; Maurer, M.; Howell, M.; Boguniewicz, M.; Yao, L.; Storey, H.; LeCiel, C.; Harder, B.; Gross, J.A. IL-31 is associated with cutaneous lymphocyte antigen-positive skin homing T cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, N.; Benfeitas, R.; Katayama, S.; Bruhn, S.; Andersson, A.; Wikberg, G.; Lundeberg, L.; Lindvall, J.M.; Greco, D.; Kere, J.; et al. Epigenetic alterations in skin homing CD4(+)CLA(+) T cells of atopic dermatitis patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnowicki, T.; Gonzalez, J.; Shemer, A.; Malajian, D.; Xu, H.; Zheng, X.; Khattri, S.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; et al. Severe atopic dermatitis is characterized by selective expansion of circulating TH2/TC2 and TH22/TC22, but not TH17/TC17, cells within the skin-homing T-cell population. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 104–115.e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, D.S.; van der Wal, M.M.; Heeb, L.E.M.; Giovannone, B.; Asamoah, M.; Delemarre, E.M.; Drylewicz, J.; Nierkens, S.; Boyman, O.; de Bruin-Weller, M.S.; et al. Early and Long-Term Effects of Dupilumab Treatment on Circulating T-Cell Functions in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1943–1953.E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, C.M.; Holm, J.G.; Nørreslet, L.B.; Serup, J.V.; Thomsen, S.F.; Agner, T. Treatment of atopic dermatitis with dupilumab: Experience from a tertiary referral centre. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, M.E.; Nahm, D.H. Real Clinical Practice Data of Monthly Dupilumab Therapy in Adult Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical Efficacy and Predictive Markers for a Favorable Clinical Response. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2021, 13, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Nowaczyk, J.; Blicharz, L.; Waśkiel-Burnat, A.; Czuwara, J.; Olszewska, M.; Rudnicka, L. Immunopathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis: Focus on Interleukins as Disease Drivers and Therapeutic Targets for Novel Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Interleukin-13: Targeting an underestimated cytokine in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2020, 75, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria Babi, L.F.; Picker, L.J.; Perez Soler, M.T.; Drzimalla, K.; Flohr, P.; Blaser, K.; Hauser, C. Circulating allergen-reactive T cells from patients with atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis express the skin-selective homing receptor, the cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trier, A.M.; Kim, B.S. Insights into atopic dermatitis pathogenesis lead to newly approved systemic therapies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 188, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jura-Szoltys, E.; Niemiec-Górska, A.; Glück, J.; Branicka, O.; Gawlik, R. Evaluation of Rhinological Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Allergic or Eosinophilic Severe Uncontrolled Asthma Treated with Anti-IgE or Anti-IL5 Therapy: A Real-Live Study. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2025, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soendergaard, M.B.; Hansen, S.; Bjerrum, A.S.; Hilberg, O.; Lock-Johansson, S.; Håkansson, K.E.J.; Ingebrigtsen, T.S.; Johnsen, C.R.; Rasmussen, L.M.; von Bülow, A.; et al. Complete response to anti-interleukin-5 biologics in a real-life setting: Results from the nationwide Danish Severe Asthma Register. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00238-202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugas, B.; Renauld, J.C.; Pène, J.; Bonnefoy, J.Y.; Peti-Frère, C.; Braquet, P.; Bousquet, J.; Van Snick, J.; Mencia-Huerta, J.M. Interleukin-9 potentiates the interleukin-4-induced immunoglobulin (IgG, IgM and IgE) production by normal human B lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit-Frere, C.; Dugas, B.; Braquet, P.; Mencia-Huerta, J.M. Interleukin-9 potentiates the interleukin-4-induced IgE and IgG1 release from murine B lymphocytes. Immunology 1993, 79, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar, S.R.; Hoyte, E.G.; Loza, A.; Bonaccorso, S.; Chiang, D.; Umetsu, D.T.; Nadeau, K.C. Immunologic effects of omalizumab in children with severe refractory atopic dermatitis: A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 162, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesner, L.M.; Farag, A.K.; Pospich, R.; Traidl, S.; Werfel, T. T-cell receptor sequencing specifies psoriasis as a systemic and atopic dermatitis as a skin-focused, allergen-driven disease. Allergy 2022, 77, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff, M.; Ahmad, F.; Pandey, A.; Datsi, A.; AlHammadi, A.; Al-Khawaga, S.; Al-Malki, A.; Meng, J.; Alam, M.; Buddenkotte, J. Neuroimmune communication regulating pruritus in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1875–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Lu, J.; Choi, E.B.; Oh, M.H.; Jeong, M.; Barmettler, S.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, T. Expression of IL-22 in the Skin Causes Th2-Biased Immunity, Epidermal Barrier Dysfunction, and Pruritus via Stimulating Epithelial Th2 Cytokines and the GRP Pathway. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 2543–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siiskonen, H.; Harvima, I. Mast Cells and Sensory Nerves Contribute to Neurogenic Inflammation and Pruritus in Chronic Skin Inflammation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.A.; Thaçi, D.; Hamilton, J.D.; Graham, N.M.; Bieber, T.; Rocklin, R.; Ming, J.E.; Ren, H.; Kao, R.; Simpson, E.; et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Pinter, A.; Alavi, A.; Lynde, C.; Bouaziz, J.D.; Wollenberg, A.; Murrell, D.F.; Alpizar, S.; Laquer, V.; Chaouche, K.; et al. Nemolizumab is associated with a rapid improvement in atopic dermatitis signs and symptoms: Subpopulation (EASI ≥ 16) analysis of randomized phase 2B study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Brunner, P.M.; Neumann, A.U.; Khattri, S.; Pavel, A.B.; Malik, K.; Singer, G.K.; Baum, D.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of fezakinumab (an IL-22 monoclonal antibody) in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis inadequately controlled by conventional treatments: A randomized, double-blind, phase 2a trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 872–881.e876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaçi, D. IL-22 receptor blocker reduces itch and skin lesions in AD. In Proceedings of the Ammerican Academy of Dermatology (AAD), New Orleans, LA, USA, 17–21 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Zeng, N.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Xia, Q.; Luo, D. Atopic dermatitis and risk of autoimmune diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferran, M.; Galván, A.B.; Rincón, C.; Romeu, E.R.; Sacrista, M.; Barboza, E.; Giménez-Arnau, A.; Celada, A.; Pujol, R.M.; Santamaria-Babí, L.F. Streptococcus induces circulating CLA(+) memory T-cell-dependent epidermal cell activation in psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Clinical Features | LDHhigh, n (%) | N | LDHlow, n (%) | N | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 10 (41.7%) | 24 | 13 (56.5%) | 23 | 0.614 |
| Rhinitis | 19 (79.2%) | 24 | 9 (39.1%) | 23 | 0.039 |
| Conjunctivitis | 13 (54.2%) | 24 | 5 (21.7%) | 23 | 0.089 |
| Asthma | 11 (45.8%) | 24 | 11 (47.8%) | 23 | >0.999 |
| Food allergy | 6 (27.3%) | 22 | 4 (17.4%) | 23 | 0.614 |
| Clinical Features | Total IgEhigh, n (%) | N | Total IgElow, n (%) | N | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhinitis | 17 (70.8%) | 24 | 11 (47.8%) | 23 | 0.285 |
| Conjunctivitis | 12 (50.0%) | 24 | 6 (26.1%) | 23 | 0.285 |
| Asthma | 13 (54.2%) | 24 | 9 (39.1%) | 23 | 0.514 |
| Food allergy | 4 (18.2%) | 22 | 6 (26.1%) | 23 | 0.722 |
| Clinical Features | Eosinophiliahigh, n (%) | N | Eosinophilialow, n (%) | N | p Value |
| Rhinitis | 18 (75.0%) | 24 | 10 (45.5%) | 22 | 0.277 |
| Conjunctivitis | 12 (50.0%) | 24 | 6 (27.3%) | 22 | 0.281 |
| Asthma | 13 (54.2%) | 24 | 8 (36.4%) | 22 | 0.337 |
| Food allergy | 4 (17.4%) | 20 | 6 (27.3%) | 20 | 0.491 |
| Clinical Features | EASIhigh, n (%) | N | EASIlow, n (%) | N | p Value |
| Rhinitis | 17 (63.0%) | 27 | 11 (55.0%) | 20 | 0.765 |
| Conjunctivitis | 13 (48.2%) | 27 | 5 (25.0%) | 20 | 0.273 |
| Asthma | 14 (51.9%) | 27 | 8 (40.0%) | 20 | 0.742 |
| Food allergy | 9 (36.0%) | 25 | 1 (5.0%) | 20 | 0.108 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Jiménez, I.; Figueras-Nart, I.; Sans-de San Nicolás, L.; Curto-Barredo, L.; Bertolín-Colilla, M.; Bonfill-Ortí, M.; Díez-Ribas, S.; Llobet-del Pino, A.; Guilabert-Vidal, A.; Ryzhkova, A.; et al. Patient Stratification for Serum LDH Levels Reveals Distinct CLA+ T-Cell Cytokine Secretion in Response to HDM, Clinical Features and Allergic Comorbidities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167821
García-Jiménez I, Figueras-Nart I, Sans-de San Nicolás L, Curto-Barredo L, Bertolín-Colilla M, Bonfill-Ortí M, Díez-Ribas S, Llobet-del Pino A, Guilabert-Vidal A, Ryzhkova A, et al. Patient Stratification for Serum LDH Levels Reveals Distinct CLA+ T-Cell Cytokine Secretion in Response to HDM, Clinical Features and Allergic Comorbidities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167821
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Jiménez, Irene, Ignasi Figueras-Nart, Lídia Sans-de San Nicolás, Laia Curto-Barredo, Marta Bertolín-Colilla, Montserrat Bonfill-Ortí, Sandra Díez-Ribas, Alex Llobet-del Pino, Antonio Guilabert-Vidal, Anna Ryzhkova, and et al. 2025. "Patient Stratification for Serum LDH Levels Reveals Distinct CLA+ T-Cell Cytokine Secretion in Response to HDM, Clinical Features and Allergic Comorbidities" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167821
APA StyleGarcía-Jiménez, I., Figueras-Nart, I., Sans-de San Nicolás, L., Curto-Barredo, L., Bertolín-Colilla, M., Bonfill-Ortí, M., Díez-Ribas, S., Llobet-del Pino, A., Guilabert-Vidal, A., Ryzhkova, A., Ferran, M., Pujol, R. M., & Santamaria-Babí, L. F. (2025). Patient Stratification for Serum LDH Levels Reveals Distinct CLA+ T-Cell Cytokine Secretion in Response to HDM, Clinical Features and Allergic Comorbidities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167821






