Pharmacological Spectrum of Substances Derived from Albizia julibrissin Durazz
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Phytochemistry
2.1. Triterpenoid Saponins
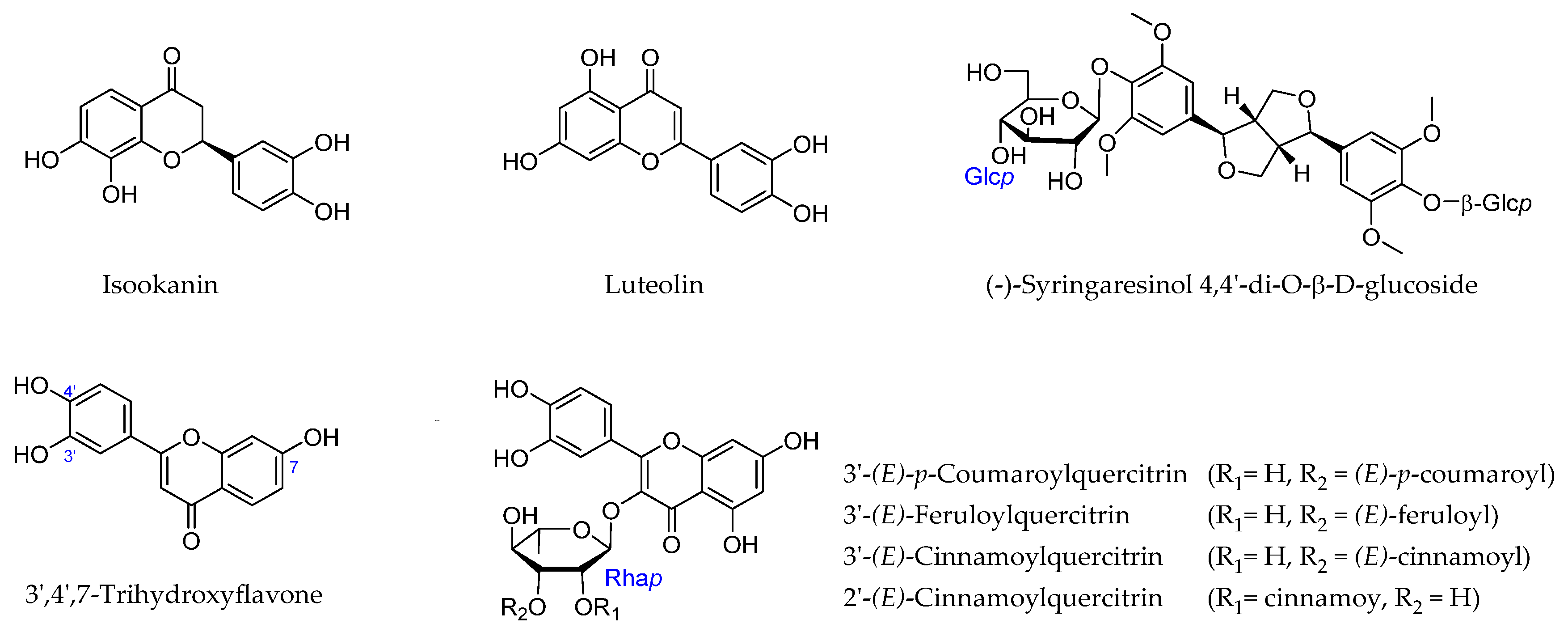
2.2. Flavonoids
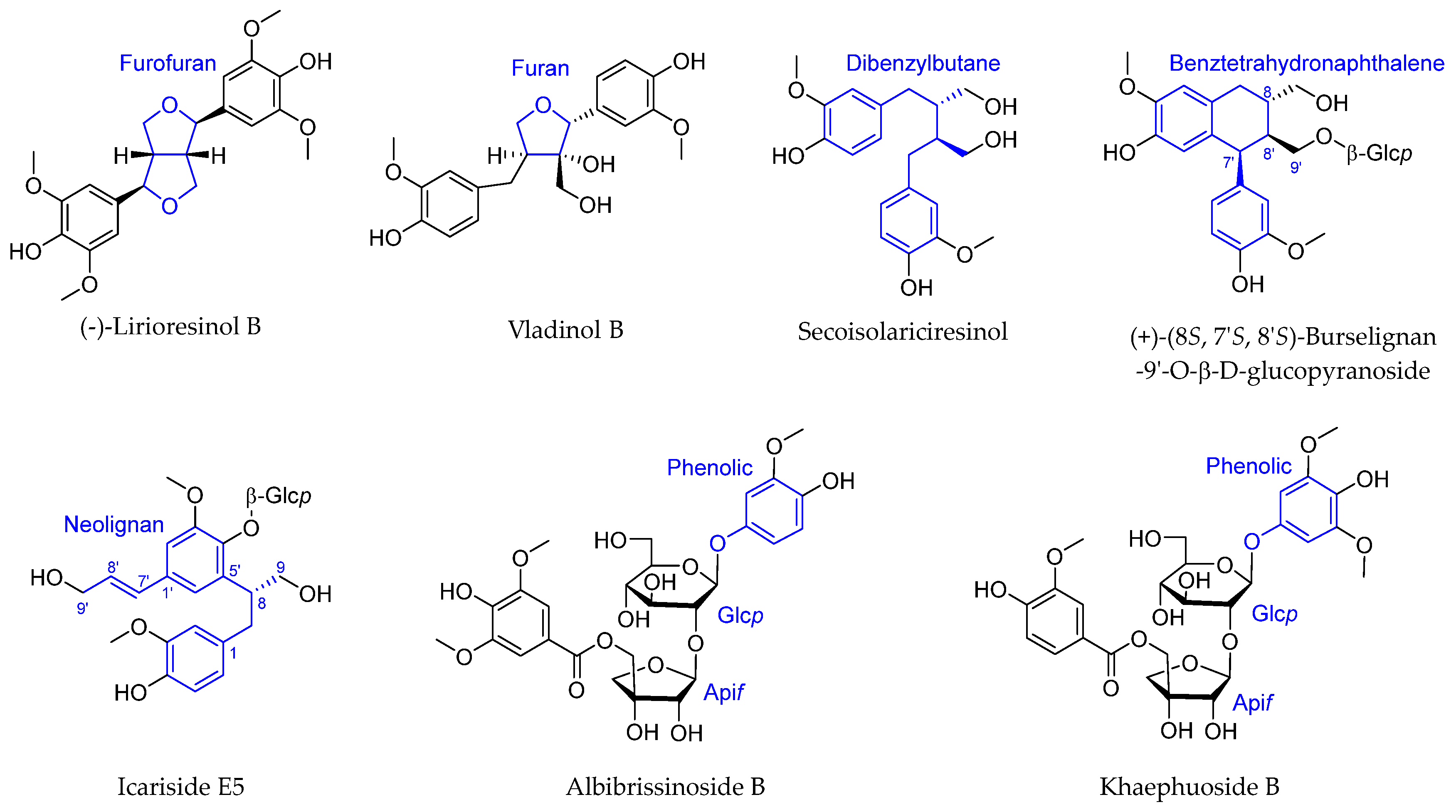
2.3. Lignans
3. Pharmacological Properties
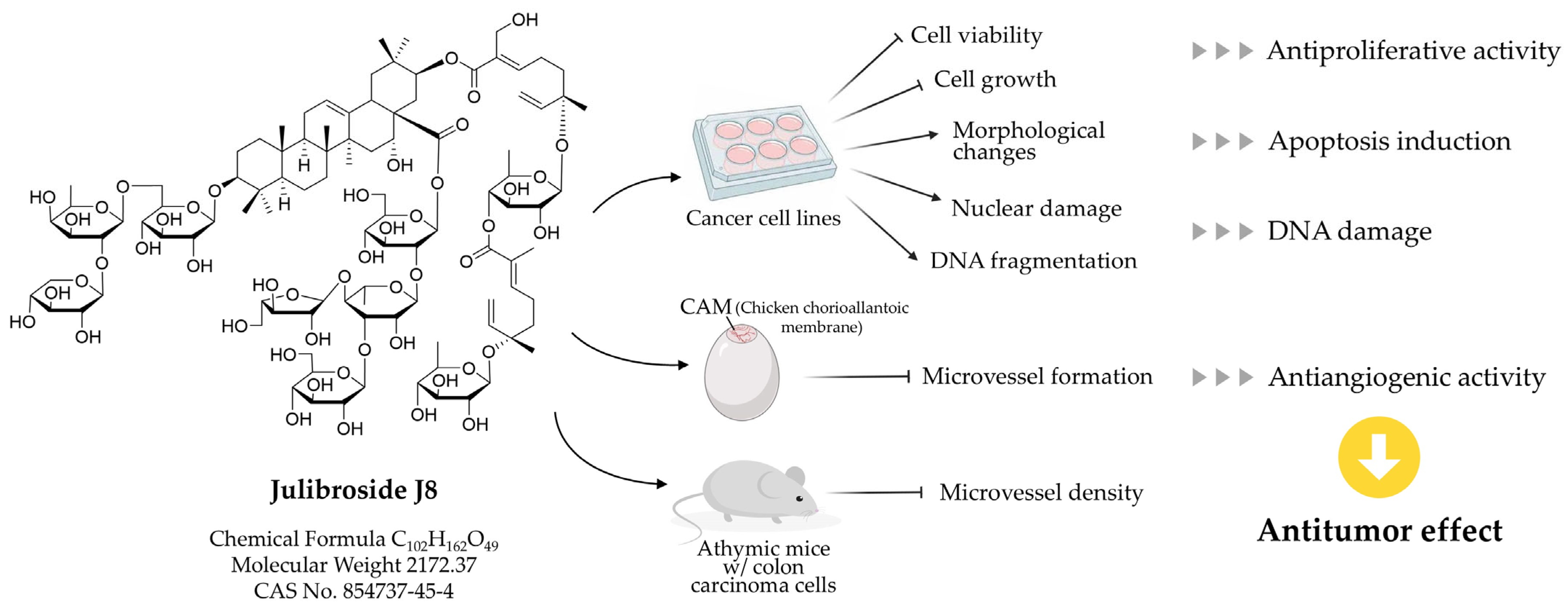
3.1. Antitumor Effect
3.1.1. Apoptosis-Inducing Effects
3.1.2. Antiangiogenic Effects
3.2. Antidepressant and Antianxiety Effect
3.3. Anti-Obesity Effect
3.4. Antibacterial Effect
3.5. Others
3.5.1. Immune Responses
3.5.2. Neuroprotective Effects
3.5.3. Antiparasitic Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, K.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Cho, S.-P.; Hong, G.-L.; Jung, J.-Y. Effects of Albizia julibrissin Durazz through Suppression of Mitochondrial Fission and Apoptosis in Cisplatin-induced Acute Kidney Injury. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2022, 28, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.P. Chinese Materia Medica: Chemistry, Pharmacology and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 191–193. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Molecular basis and mechanism of action of Albizia julibrissin in depression treatment and clinical application of its formulae. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 15, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, B. A comparison review of Hehuan flowers and Hehuan bark on the traditional applications, phytochemistry and pharmacological effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 303, 116002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, K.; Tong, W.Y.; Liang, H.; Cui, J.R.; Tu, G.Z.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, R.Y. Diastereoisomeric saponins from Albizia julibrissin. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.J.; Kang, S.S.; Jung, H.A.; Kim, G.J.; Choi, J.S. Isolation of flavonoids and a cerebroside from the stem bark of Albizzia julibrissin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahagi, T.; Daikonya, A.; Kitanaka, S. Flavonol acylglycosides from flower of Albizia julibrissin and their inhibitory effects on lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.H.; Hong, S.I.; Ma, S.X.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. 3′,4′,7-Trihydroxyflavone prevents apoptotic cell death in neuronal cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, H.J. Isolation and identification of lignans and other phenolic constituents from the stem bark of Albizia julibrissin Durazz and evaluation of their nitric oxide inhibitory activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zheng, J.; Wu, L.J.; Zhao, Y.Y. Julibroside J 8-induced HeLa cell apoptosis through caspase pathway. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Pramanik, K.; Mukhopadhyay, B. Synthesis of a tetra-and a trisaccharide related to an anti-tumor saponin “Julibroside J 28” from Albizia julibrissin. Glycoconj. J. 2008, 25, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, R.Y. A cytotoxic saponin from Albizia julibrissin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 1211–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, L.; Liang, H. Three anti-tumor saponins from Albizia julibrissin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2765–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Qian, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, J.; Tu, P.; Liang, H. Oleanane-type saponins and prosapogenins from Albizia julibrissin and their cytotoxic activities. Phytochemistry 2021, 185, 112674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.J.; Han, C.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, K.H. Induction of apoptosis in human acute leukemia Jurkat T cells by Albizzia julibrissin extract is mediated via mitochondria-dependent caspase-3 activation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Feng, L.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, L.F.; Jin, J. Anti-angiogenic activity of julibroside J8, a natural product isolated from Albizia julibrissin. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Yi, Q.; Xie, F.; Du, B.; Feng, L.; Qiu, L. Total saponins from Albizia julibrissin inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 3405–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Cho, J.H.; Ahn, N.Y.; Oh, H.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Jang, C.G.; Ryu, J.H. Effect of chronic Albizzia julibrissin treatment on 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptors in rat brain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 81, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Antidepressant-like effects of Albizzia julibrissin in mice: Involvement of the 5-HT1A receptor system. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2007, 87, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lv, Y.W.; Shi, J.L.; Ma, X.J.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.Q.; Wang, S.N.; Guo, J.Y. Anti-anxiety effect of (−)-Syringaresnol-4-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside from Albizzia julibrissin Durazz (Leguminosae). Molecules 2017, 22, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.S.; Liu, H.P.; Cheng, J.; Chen, C.J.; Hwang, S.L.; Tseng, C.C.; Hsu, L.F.; Lin, W.Y. Albizia julibrissin ameliorates memory loss induced by insomnia in drosophila. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 2019, 7395962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.H.; Ha, R.R.; Kwon, S.H.; Hong, S.I.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Anxiolytic effects of Julibroside C1 isolated from Albizzia julibrissin in mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2013, 44, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ji, H.; Ryu, D.; Cho, E.; Park, D.; Jung, E. Albizia julibrissin Exerts Anti-Obesity Effects by Inducing the Browning of 3T3L1 White Adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajalakshmi, P.V.; Senthil, K. Flavonoid content and antibacterial activity of Albizia julibrissin. Durazz leaf, stem and flower extracts against clinically isolated bacterial pathogens. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 506–508. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, T. Characterization of a novel natural fiber extracted from Albizia julibrissin plant stem: Advancing sustainable product development. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 103737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Fei, L.; Zhu, B.; Shi, M. Quick and improved immune responses to inactivated H9N2 avian influenza vaccine by purified active fraction of Albizia julibrissin saponins. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; He, T.; Gao, X.; Shi, M.; Sun, H. Evaluation and characteristics of immunological adjuvant activity of purified fraction of Albizia julibrissin saponins. Immunol. Investig. 2019, 48, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Fathi, H.; Ziar, A.; Mohammadi, H. Attenuation of brain mitochondria oxidative damage by Albizia julibrissin Durazz: Neuroprotective and antiemetic effects. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 42, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, I.; Safdar, N.; Akhtar, W.; Ayaz, A.; Ali, S.; Elansary, H.O.; Moussa, I.M.; Zaman, W. Green solvent-based extraction of three Fabaceae species: A potential antioxidant, anti-diabetic, and anti-leishmanial agents. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Appearance * | Division | Name |
|---|---|---|
 | Kingdom | Plantae |
| Phylum | Magnoliophyta | |
| Class | Magnoliopsida | |
| Subclass | Rosidae | |
| Order | Fabales | |
| Family | Fabaceae | |
| Genus | Albizia | |
| Species | Albizia julibrissin Durazz. |
| Core Structure | Name | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
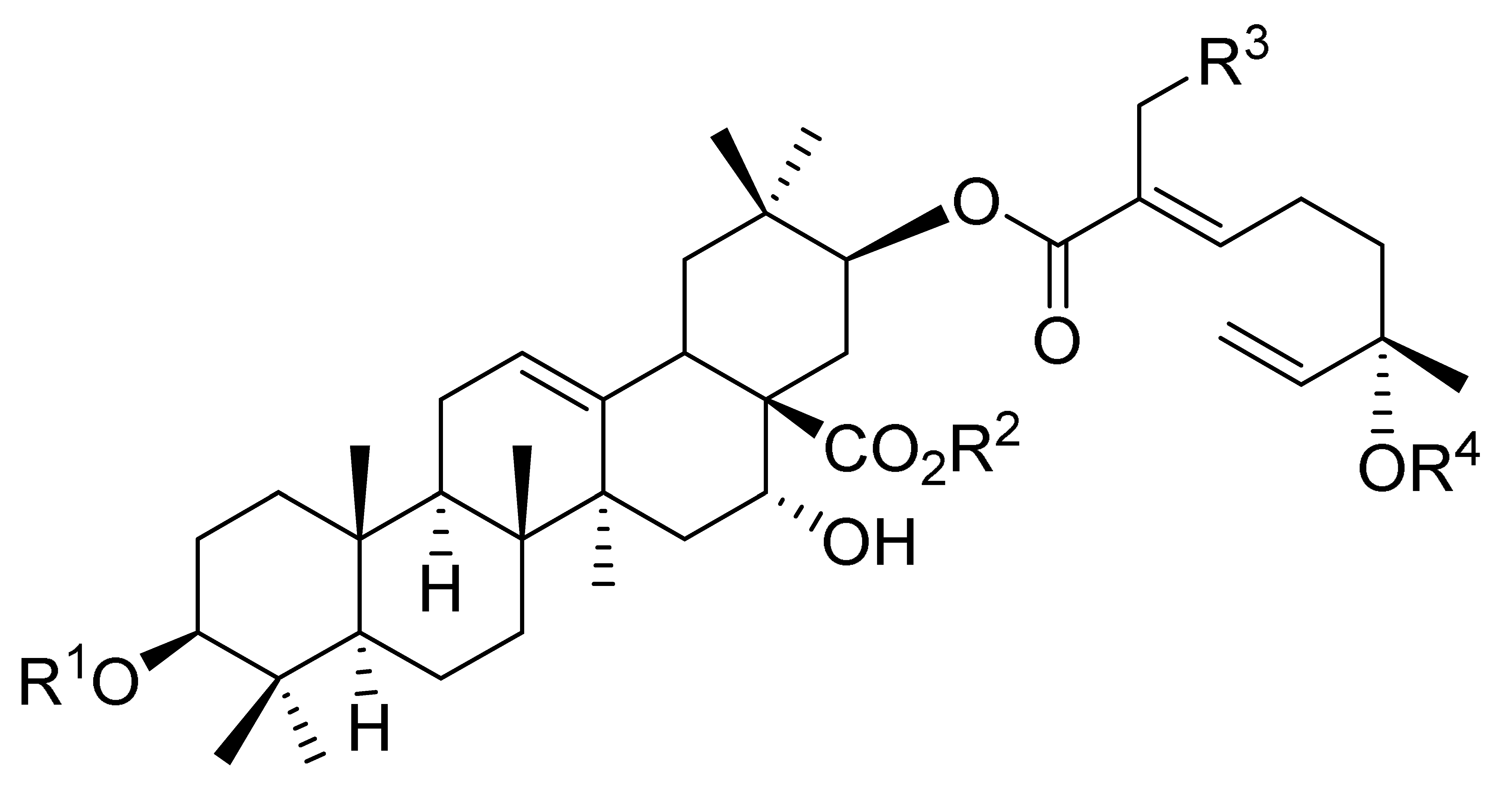 | Julibroside J8 | 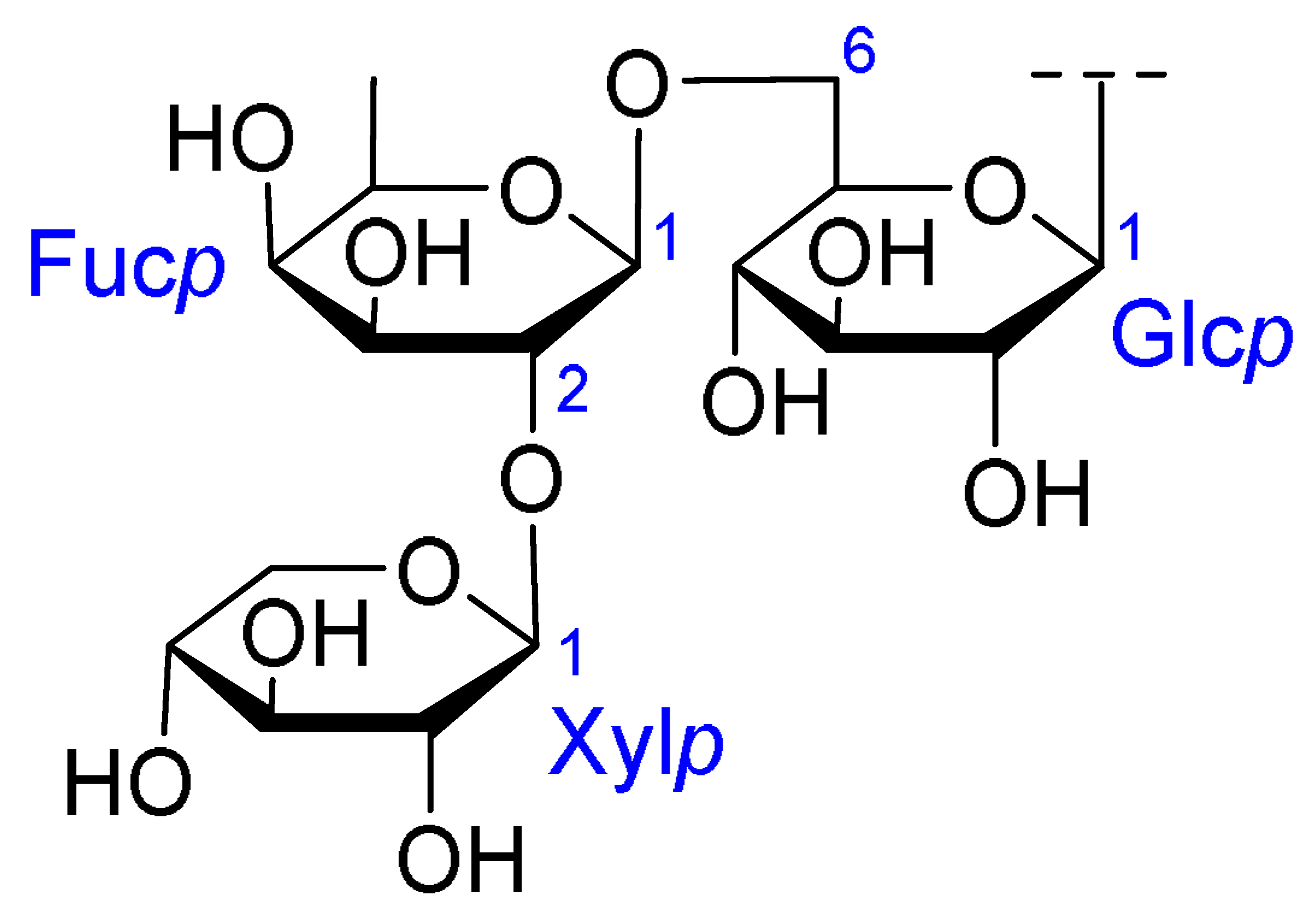 | 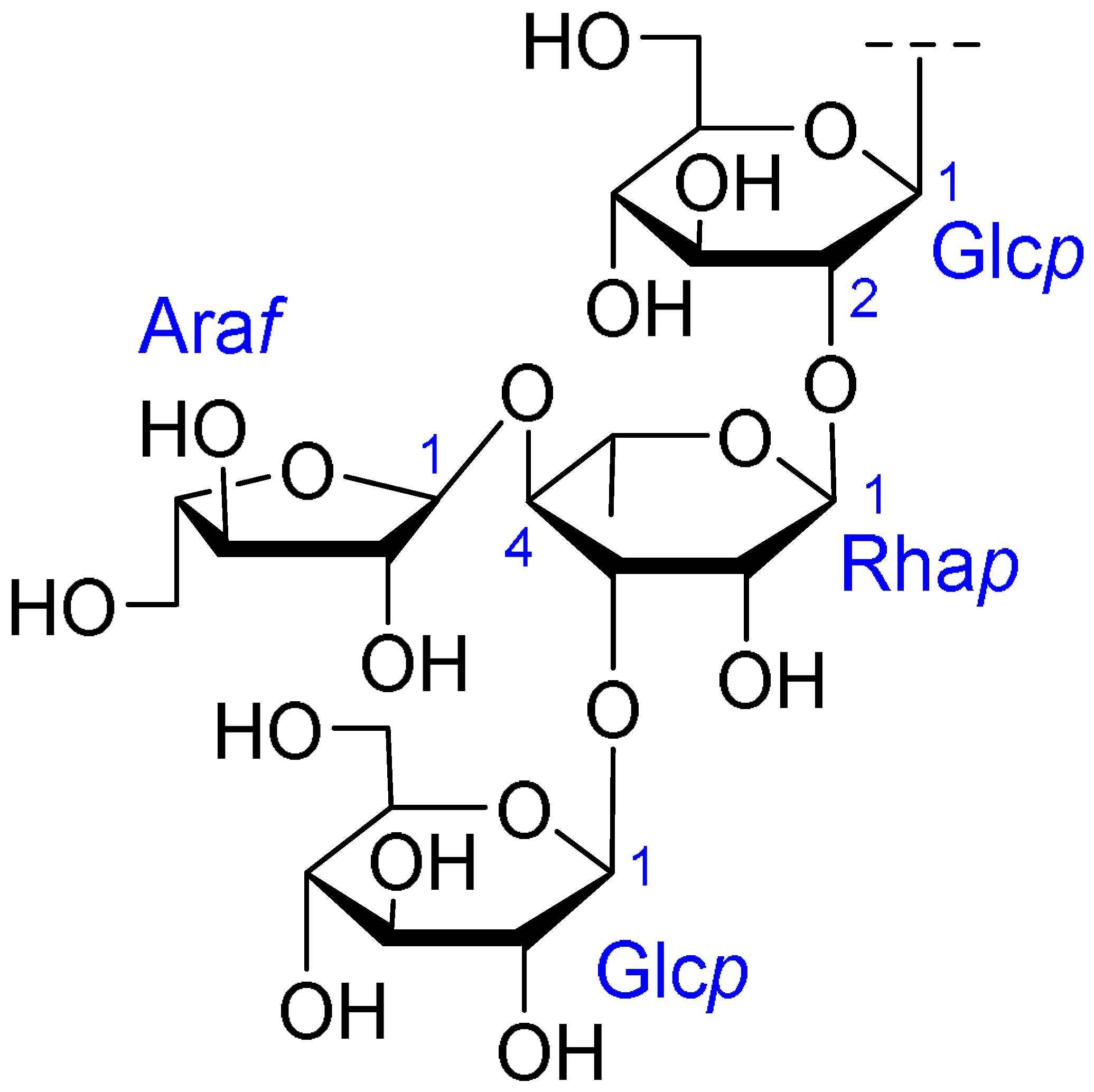 | OH | 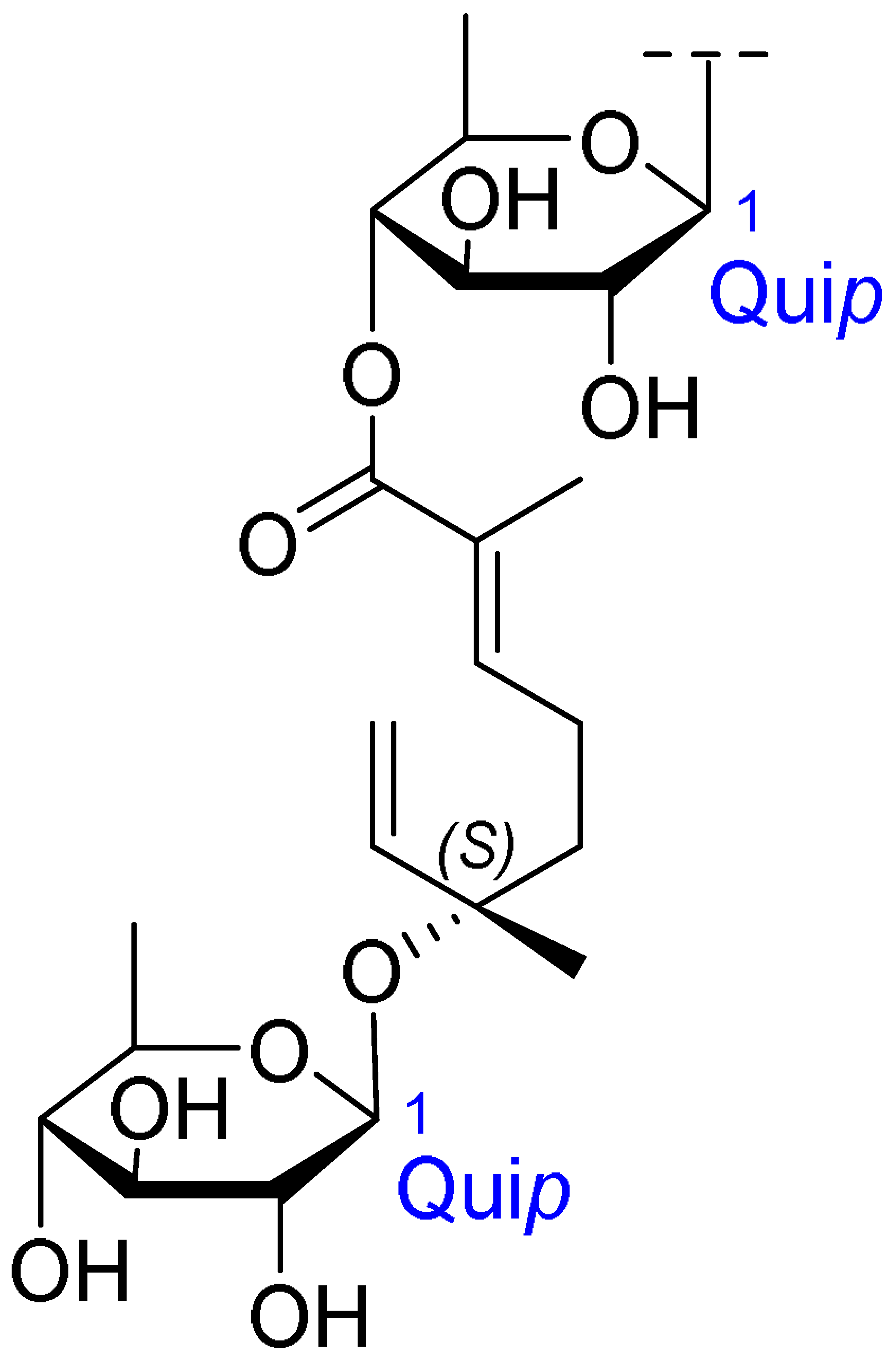 |
| Julibroside J21 | 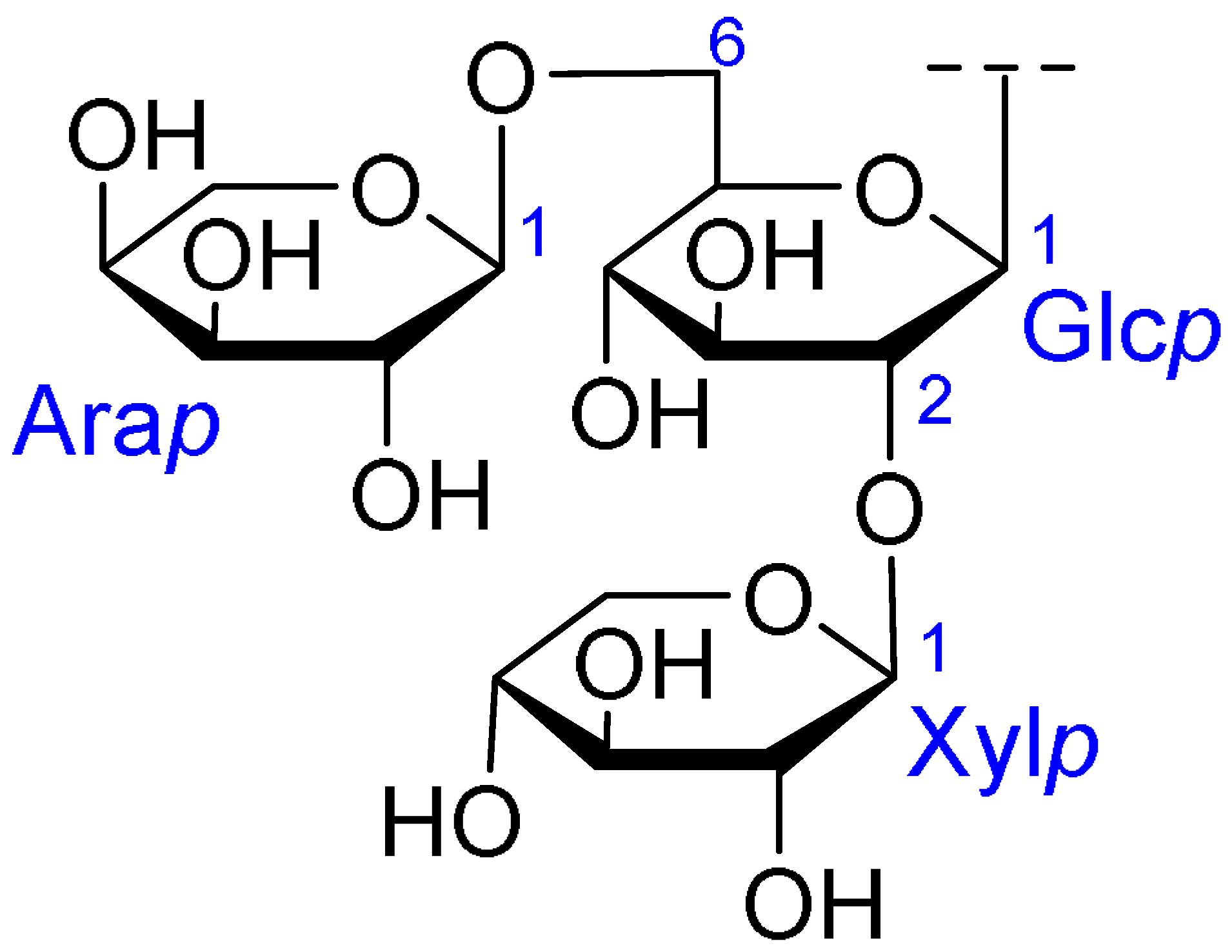 | OH | 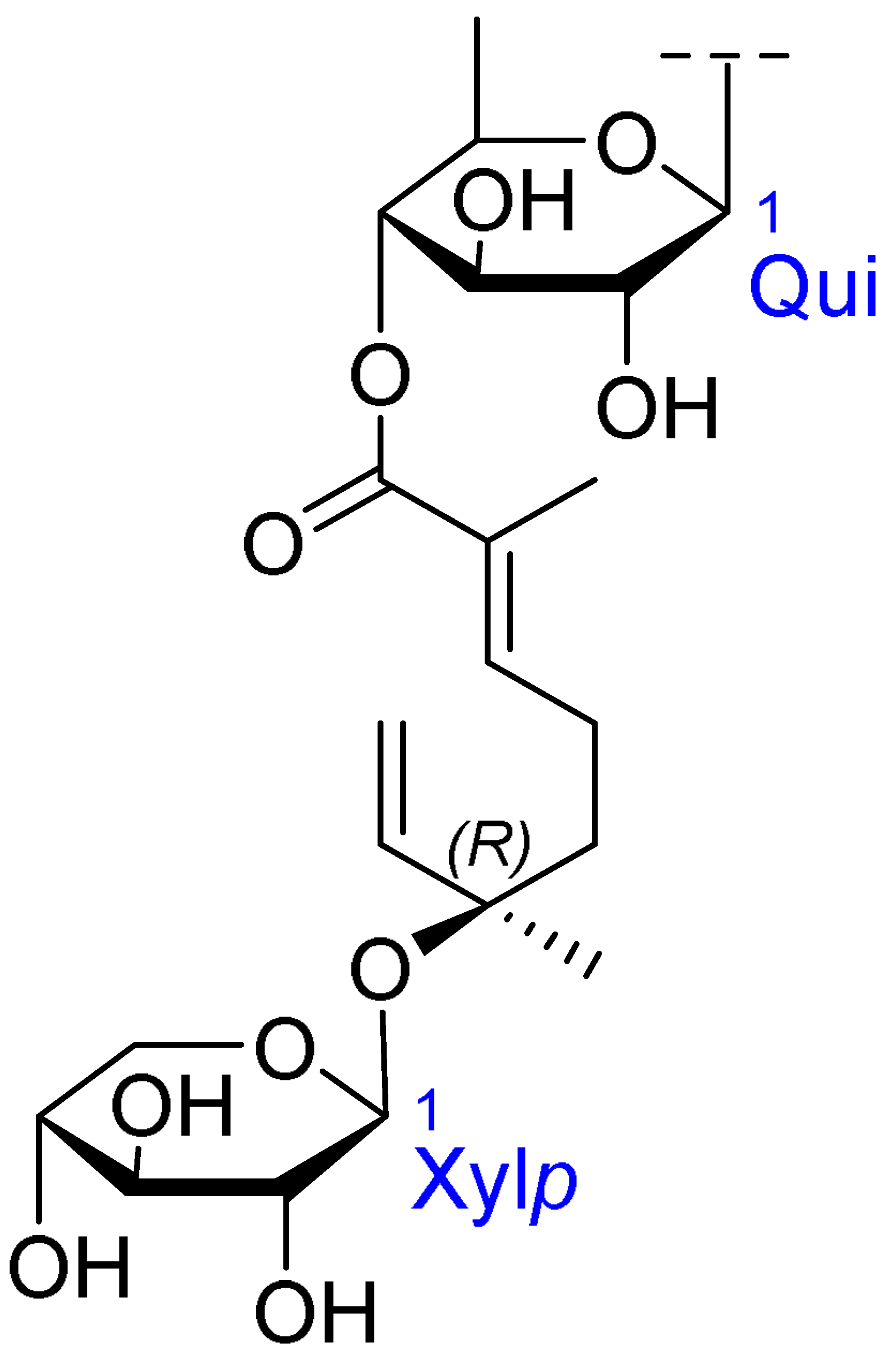 | ||
| Julibroside J28 |  | H |  | ||
| Julibroside J29 | OH | 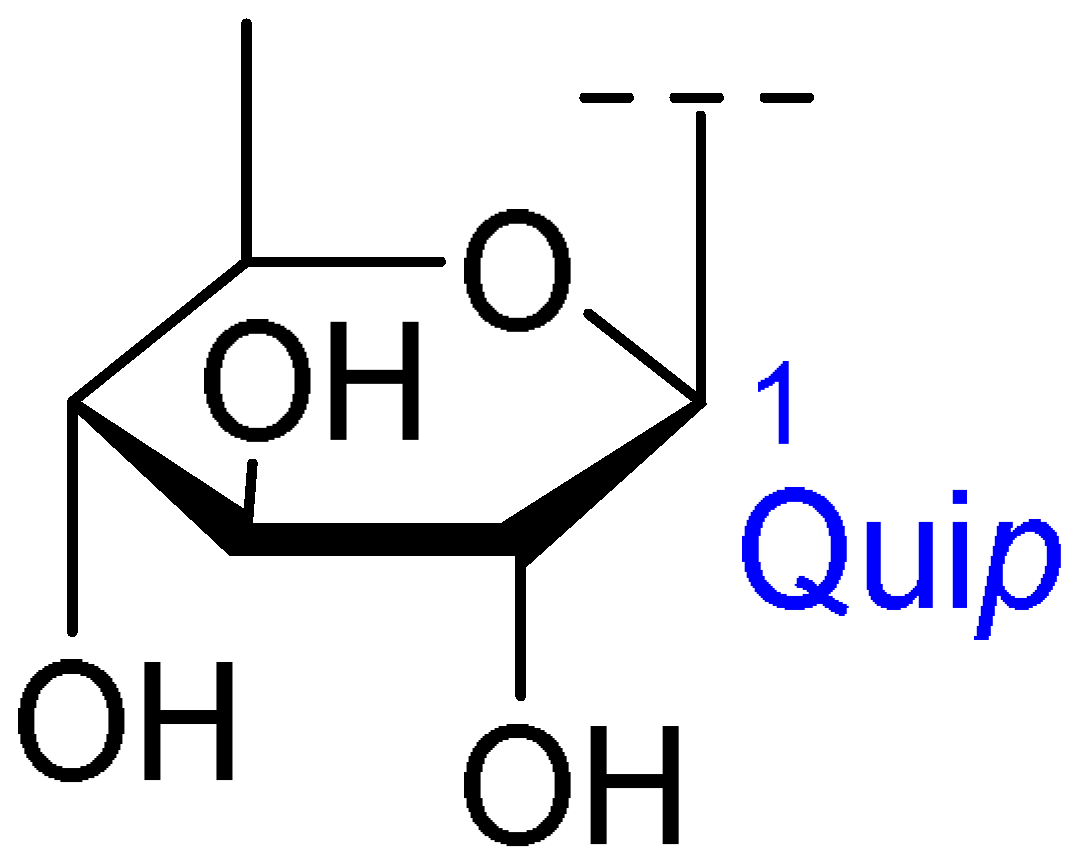 | |||
| Julibroside J30 | OH | 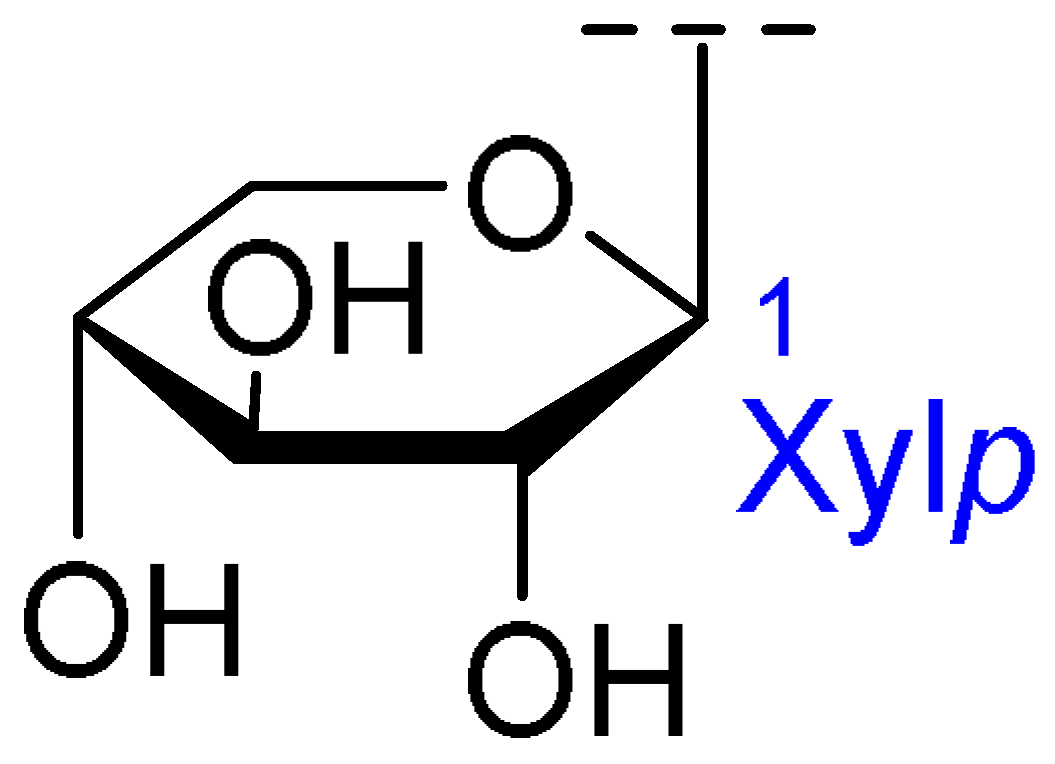 | |||
| Julibroside J31 |  | OH | 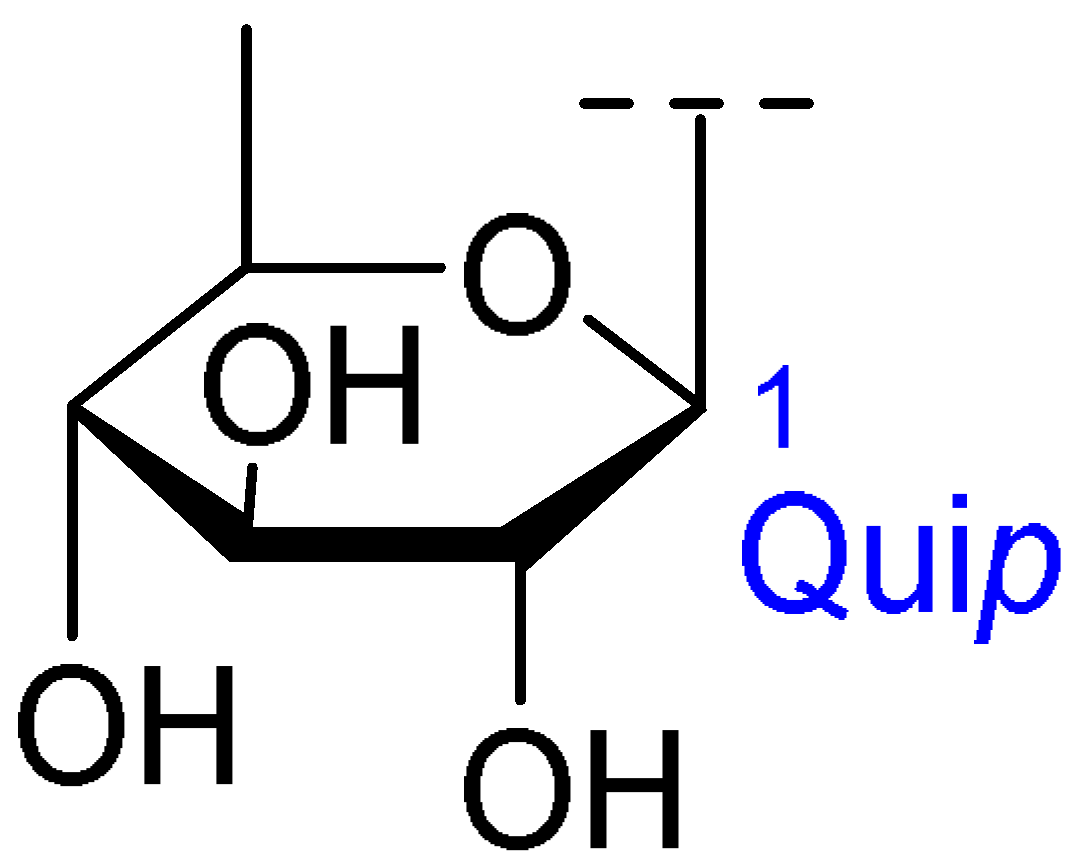 |
| Active Ingredient | Model | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Julibroside J8 | HeLa cells | Caspase-3 activation and cleavage of its substrate ICAD, and that the balance between Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Bax expression. | [11] |
| Julibroside J28 | HeLa, Bel-7402, PC-3M-1E8 cancer cells | Induces apoptosis in tumor cells through caspase-3 activation, ICAD cleavage, and modulation of the Bcl-2/Bax protein balance. | [12] |
| Julibroside J21 | Bel-7402 cell | Induces cytotoxicity in Bel-7402 cancer cells as measured by the SRB assay, potentially through modulation of apoptosis-related pathways. | [13] |
| Julibroside J29, Julibroside J30, Julibroside J31 | PC-3M-1E8, HeLa, MDA-MB-435 cancer cell | Induces cytotoxicity in cancer cells as measured by SRB and MTT assays, potentially through inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of cell death. | [14] |
| Oleanane-type saponins and prosapogenins from Albizia julibrissin | BGC-823, A549, HCT-116, and HepG2 cell | Julibrosides K–L and M–O exhibit cytotoxicity by inducing apoptosis and inhibiting cell proliferation through cell cycle arrest in cancer cells. | [15] |
| A partially purified substance (HaBC18) from Albizia julibrissin Durazz. | Jurkat T cells | Mediated via mitochondria-dependent caspase-3 activation. | [16] |
| Julibroside J8 | HMEC-1/ BALB/C-nu/nu mice were injected subcutaneously with 2 × 105 colon cancer cells (C51) | Inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing the VEGF signaling pathway, specifically impairing endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation. | [17] |
| Total saponins of A. julibrissin | BALB/c mice, VEGF-induced Ea.hy926 human endothelial cell | Inhibits of VEGFR2 activation and downstream signaling of Fak, Akt, and Erk in vitro and in vivo. | [18] |
| Active Ingredient | Model | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aqueous extract of Albizzia julibrissin (AEAJ) | Sprague-Dawley rat | Enhances serotonergic neurotransmission by upregulating 5-HT1A receptor expression in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. | [19] |
| Methylene chloride fraction of Albizzia julibrissin (MCAJ) | Male ICR mice | Mediated through the 5-HT1A receptor system. | [20] |
| (−)-Syringaresnol-4-O-β-d-apiofuranosyl-(1→2)-β-d-glucopyranoside (SAG) | Rats stimulated by the elevated plus maze | Enhances inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain through GABAa receptors. | [21] |
| Aqueous extract of Albizzia julibrissin | Sleep-deprived Drosophila | Inhibition of oxidative stress and neuroprotection. | [22] |
| Julibroside C1 | ICR mice stimulated by the elevated plus maze | Enhances of inhibitory neurotransmission through 5-HT1A and GABAa receptors. | [23] |
| Active Ingredient | Model | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albizia julibrissin Leaf extracts (AJLE) | 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes differentiated into white adipocytes | Activates AMPK pathway to inhibit fat differentiation, accumulation, Increases UCP1 and PGC-1a expression to promote browning and energy consumption of white adipocytes. | [24] |
| Flower of A. julibrissin | 3T3-L1 cells differentiated into white adipocytes | Flavonol acylglycosides inhibit fat production and accumulation through AMPK pathway activation and regulate fat metabolism gene expression. | [8] |
| Active Ingredient | Model | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. julibrissin leaf | Clinically isolated bacterial pathogens (Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli, Entero-coccus faecalis, and Proteus vulgaris) | Inhibits bacterial growth by disrupting cell membrane integrity and metabolic activity, likely mediated by high flavonoid content. | [25] |
| A. julibrissin fibers | Providencia | Inhibits bacterial growth by creating zones of inhibition in disk diffusion assay, possibly through membrane disruption by bioactive phytochemicals. | [26] |
| Active Ingredient | Model | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| A purified active saponin fraction from the stem bark of Albizzia julibrissin | ICR mice, SPF white Leghorn chickens | Enhances humoral and cellular immune responses and induces Th1 and Th2 responses. | [27] |
| Albizia julibrissin saponins (AJSAF) | BALB/c and ICR mice | Enhances both humoral and cellular immune responses by upregulating Th1 (IFN-γ, IL-2, T-bet, STAT4) and Th2 (IL-4, IL-10, GATA-3, STAT6) pathways, thereby boosting PRRSV vaccine immunogenicity. | [28] |
| Methanolic extract of the flower of A. julibrissin | Young chickens induced to vomit with copper sulfate and ipecac | Direct scavenging of free radicals and/or increasing the antioxidant status of the neurons stimulated by emesis. | [29] |
| Methanolic extract of the of A. julibrissin | Leishmania major parasites | Likely regulates cytotoxic enzymes involved in parasite survival, exerting anti-leishmanial activity. | [30] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Kwon, C.-H.; Ham, Y.-M.; Ha, M.W. Pharmacological Spectrum of Substances Derived from Albizia julibrissin Durazz. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167778
Yang Y, Kwon C-H, Ham Y-M, Ha MW. Pharmacological Spectrum of Substances Derived from Albizia julibrissin Durazz. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167778
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuji, Chan-Hyuk Kwon, Young-Min Ham, and Min Woo Ha. 2025. "Pharmacological Spectrum of Substances Derived from Albizia julibrissin Durazz" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167778
APA StyleYang, Y., Kwon, C.-H., Ham, Y.-M., & Ha, M. W. (2025). Pharmacological Spectrum of Substances Derived from Albizia julibrissin Durazz. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167778





