Syringic Acid Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity Through PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf-2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Male Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Silico ADMET Analysis for SYA and DOX
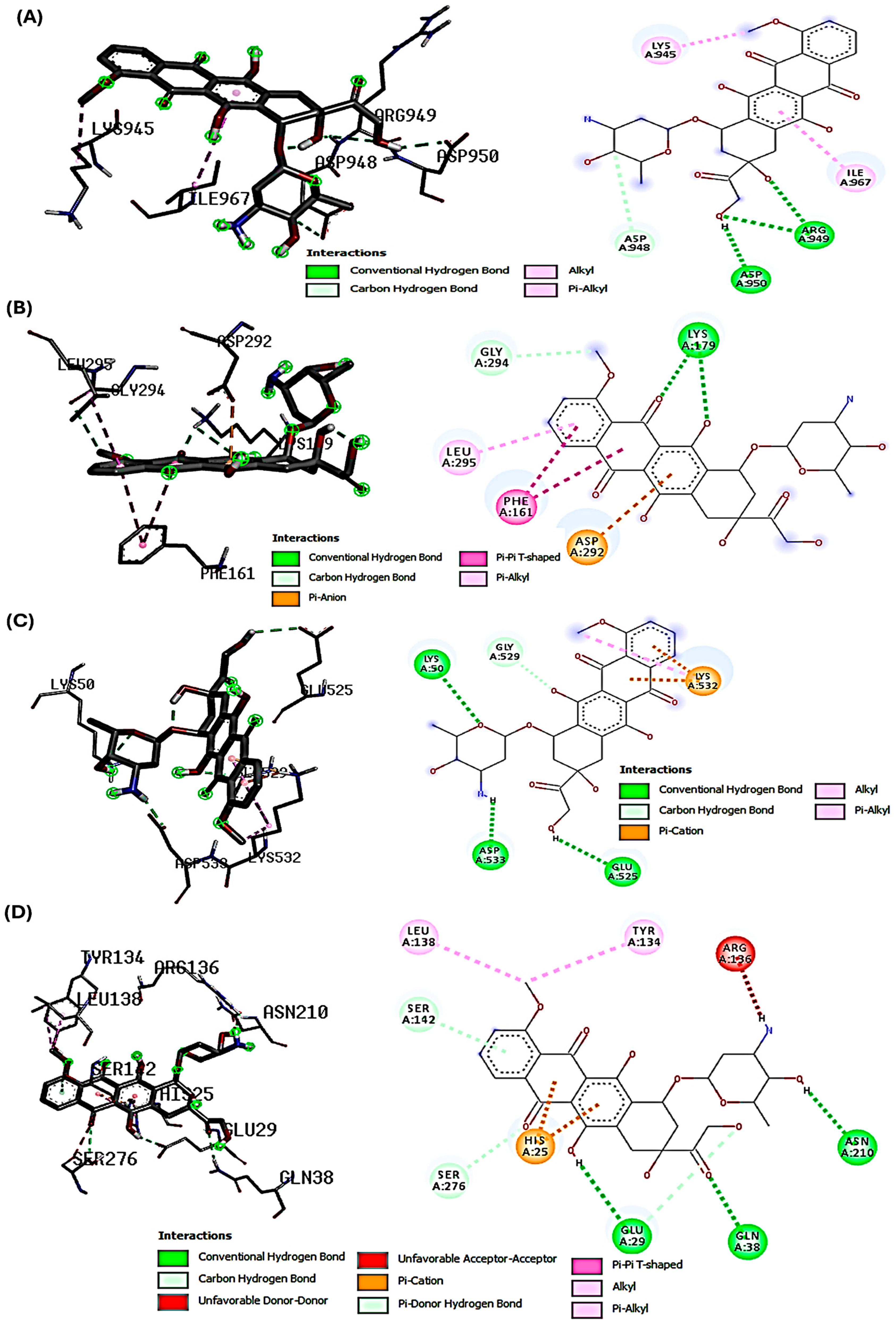
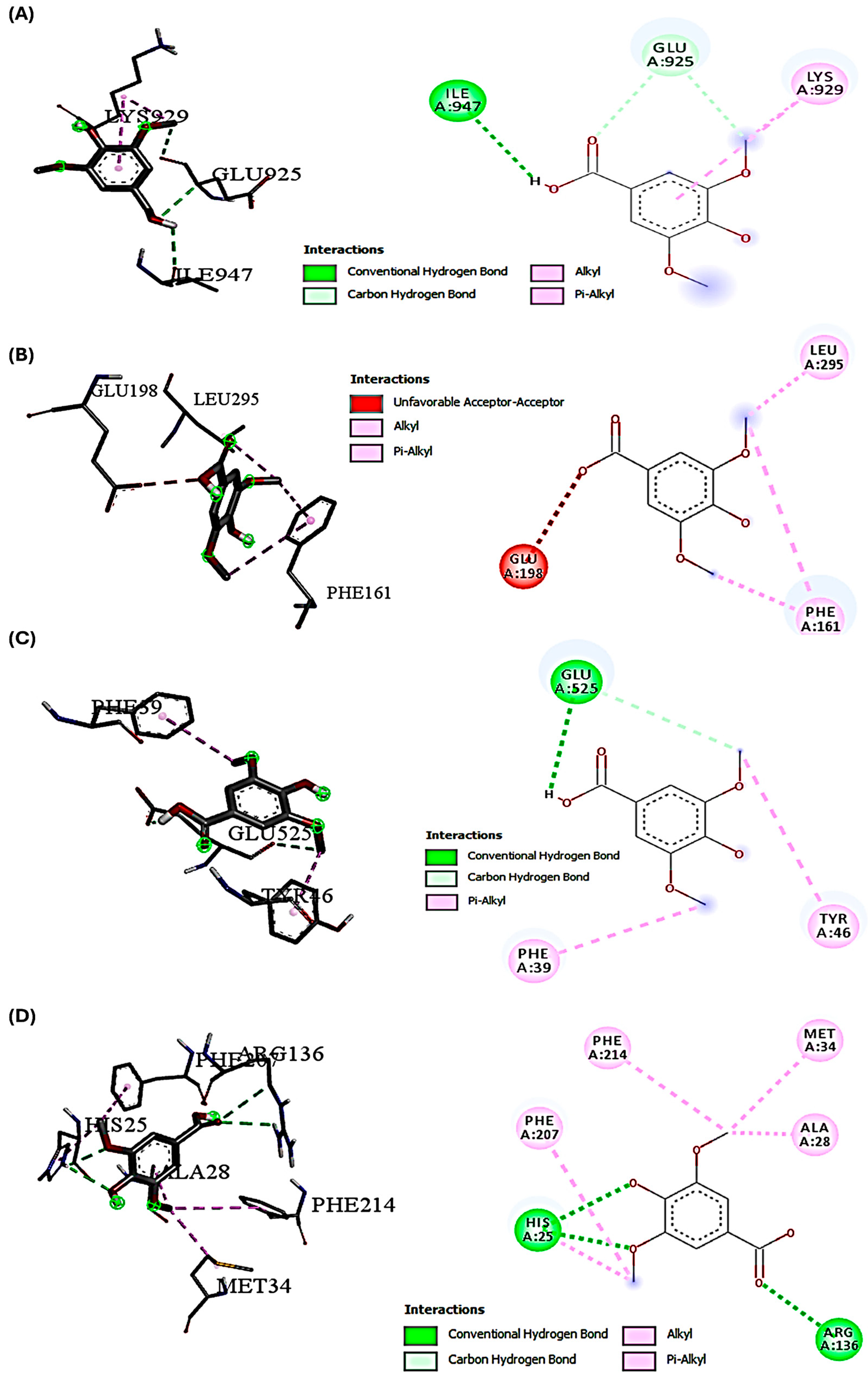
2.2. Molecular Docking Interactions of SYA and DOX with PI3K, Akt, Nrf-2, and HO-1
2.3. Impact of DOX/SYA Therapy on Changes in Liver and Body Weight
2.4. Treatment with SYA Has Mitigated Liver Dysfunction Induced by DOX in Rats
2.5. SYA Treatment Reduces DOX-Induced Hepatic Oxidative Stress in Rats
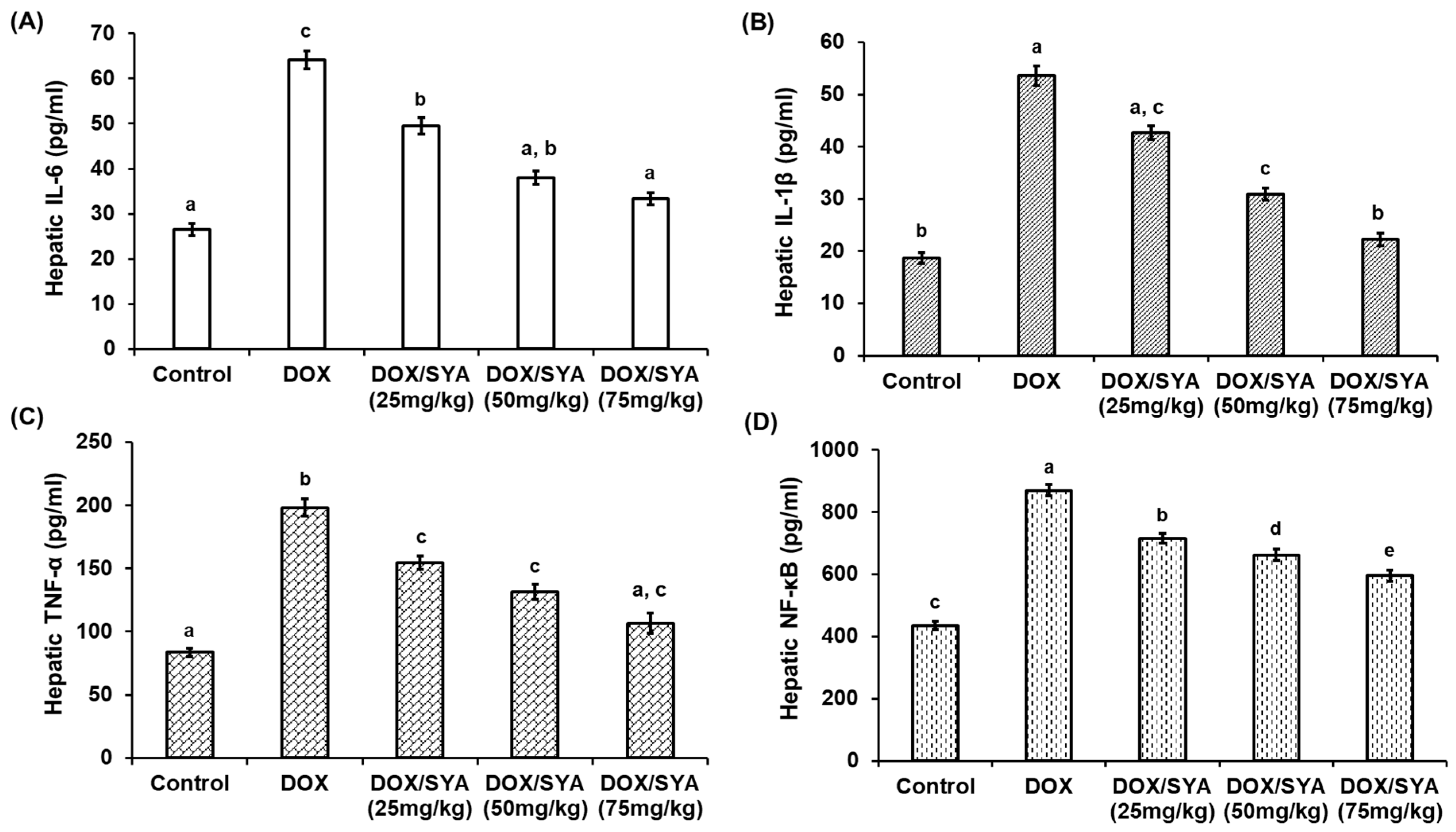
2.6. Treatment with SYA Mitigates Inflammation in the Liver Tissues of DOX-Injected Rats
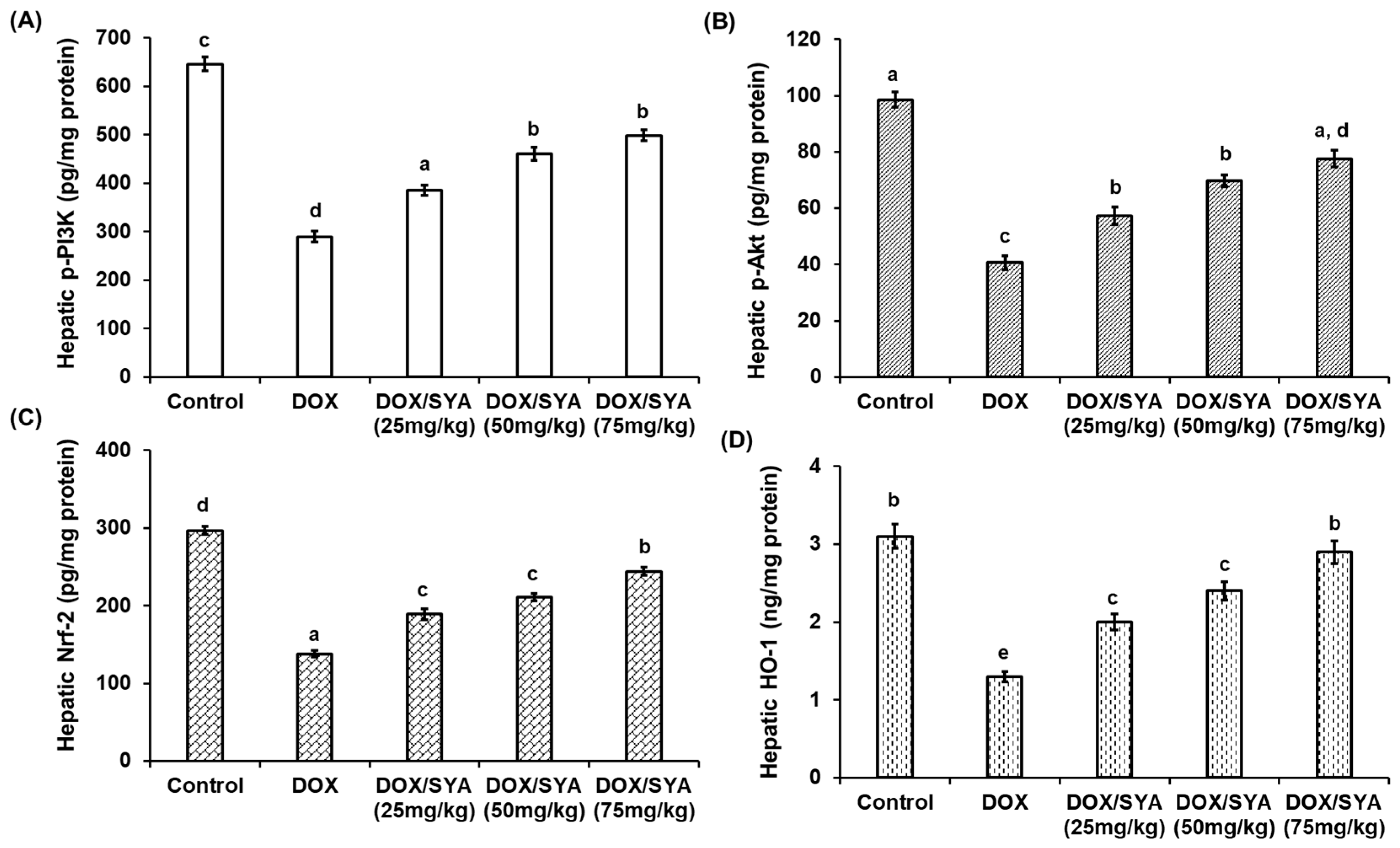
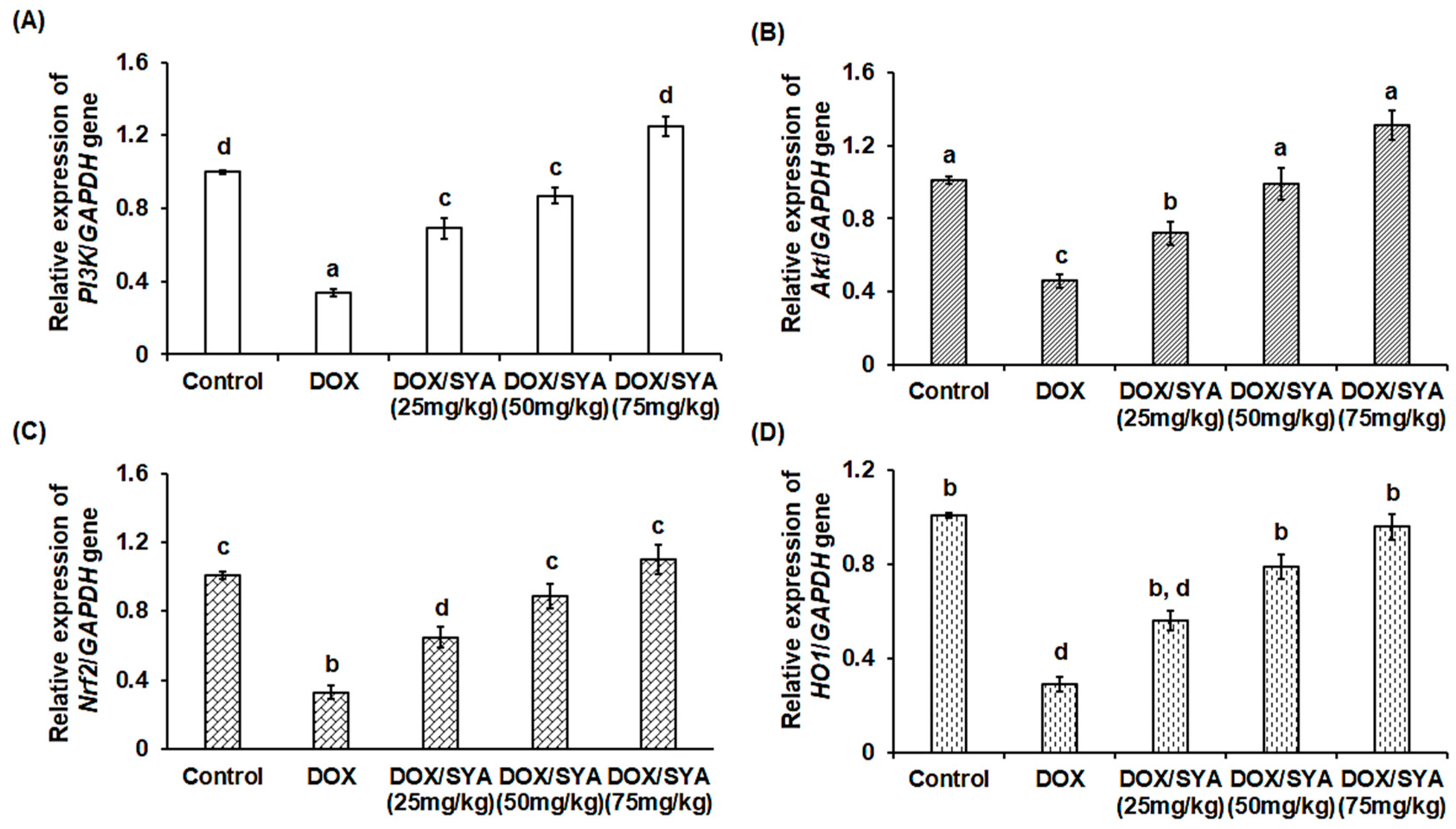
2.7. Treatment with SYA Targeting the PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathway in DOX-Challenged Rats
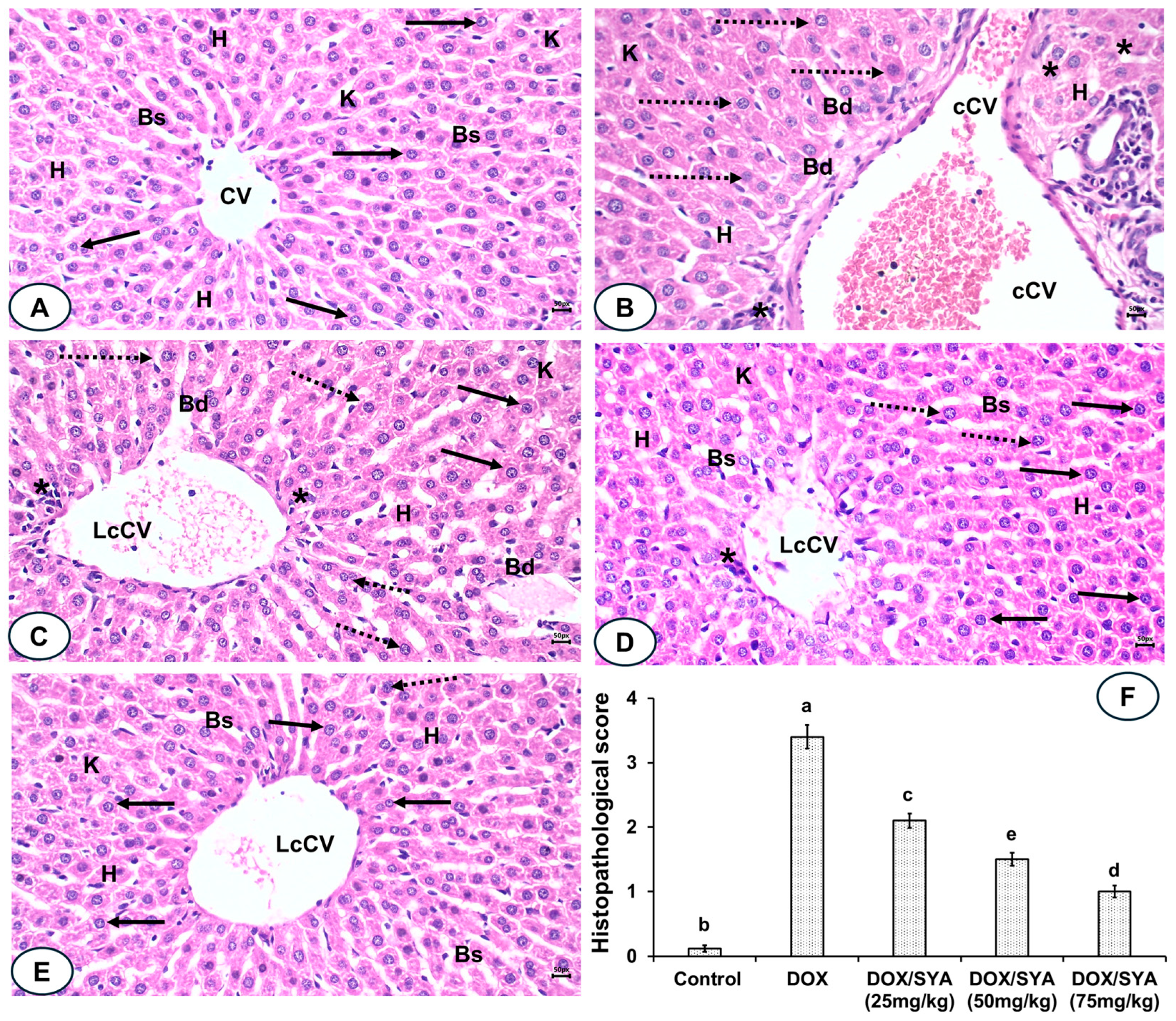
2.8. Treatment with SYA Reduces Histopathological Alterations Caused by DOX in Rat Liver Tissues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. In Silico Studies
4.3. Rats and Experimental Design
4.4. Biochemical Analysis
4.5. Molecular Analysis
4.6. Histopathological Investigations
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kciuk, M.; Gielecińska, A.; Mujwar, S.; Kołat, D.; Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż.; Celik, I.; Kontek, R. Doxorubicin-an agent with multiple mechanisms of anticancer activity. Cells 2023, 12, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, P.L.; Renu, K.; Valsala Gopalakrishnan, A. New molecular and biochemical insights of doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity. Life Sci. 2020, 250, 117599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Said, K.S.; Haidyrah, A.S.; Mobasher, M.A.; Khayyat, A.I.A.; Shakoori, A.; Al-Sowayan, N.S.; Barnawi, I.O.; Mariah, R.A. Artemisia annua extract attenuate doxorubicin-induced hepatic injury via PI-3K/Akt/Nrf-2-mediated signaling pathway in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, D.O.; Mahmoud, S.S.; Hassan, A.; Sanad, E.F. Doxorubicin-induced hepatic toxicity in rats: Mechanistic protective role of Omega-3 fatty acids through Nrf2/HO-1 activation and PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β axis modulation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danan, G.; Teschke, R. RUCAM in drug and herb induced liver injury: The update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschke, R.; Danan, G. Diagnosis and causality assessment of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) in daily clinical practice: The liver injury case database and the RUCAM algorithm. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 155–168. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi, F.; Arasteh, O.; Elyasi, S. Preventive and therapeutic use of herbal compounds against doxorubicin induced hepatotoxicity: A comprehensive review. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 1595–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Tong, N.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y. Protective effects of berberine on doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Chu, L.; Liang, H.; Chen, J.; Liang, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X. Protective effects of dioscin against doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity via regulation of Sirt1/FOXO1/NF-κb signal. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, N.; Hua, C.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Lu, J.; Song, P.; Xu, J.; et al. Citronellal ameliorates doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity via antioxidative stress, antiapoptosis, and proangiogenesis in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.M.; Elkomy, M.H.; Fahim, H.I.; Ashour, M.B.; Naguib, I.A.; Alghamdi, B.S.; Mahmoud, H.U.R.; Ahmed, N.A. Rutin and quercetin counter doxorubicin-induced liver toxicity in Wistar rats via their modulatory effects on inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and Nrf2. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 2710607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwaili, M.A.; Abu-Almakarem, A.S.; Aljohani, S.; Alkhodair, S.A.; Al-Bazi, M.M.; Eid, T.M.; Alamri, J.; Mobasher, M.A.; Algarza, N.; Khayyat, A.I.A.; et al. Avenanthramide-C ameliorate doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity via modulating Akt/GSK-3β and Wnt-4/β-Catenin pathways in male rats. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1507786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Said, K.S.; Hussein, S.; Alrashdi, B.M.; Mahmoud, H.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Elbakry, M.; El-Tantawy, H.; Kabil, D.I.; El-Naggar, S.A. Musa sp. leaves extract ameliorates the hepato-renal toxicities induced by cadmium in mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasulu, C.; Ramgopal, M.; Ramanjaneyulu, G.; Anuradha, C.M.; Suresh Kumar, C. Syringic acid (SA)—A review of its occurrence, biosynthesis, pharmacological and industrial importance. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, A.C.; Panchal, S.S. Safety evaluation of syringic acid: Subacute oral toxicity studies in Wistar rats. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somade, O.T.; Ajiboye, B.O.; Osukoya, O.A.; Jarikre, T.A.; Oyinloye, B.E. Syringic acid ameliorates testicular oxidative stress via the conservation of endogenous antioxidant markers and inhibition of the activated Nrf2-Keap1-NQO1-HO1 signaling in methyl cellosolve-administered rats. Pharmacol. Res. Mod. Chin. Med. 2023, 6, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somade, O.T.; Oyinloye, B.E.; Ajiboye, B.O.; Osukoya, O.A. Syringic acid demonstrates an anti-inflammatory effect via modulation of the NF-κB-iNOS-COX-2 and JAK-STAT signaling pathways in methyl cellosolve-induced hepato-testicular inflammation in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 34, 101484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.C.; Panchal, S.S.; Allam, A.A.; Othman, S.I.; Satia, M.; Mandhane, S.N. Syringic acid ameliorates cardiac, hepatic, renal and neuronal damage induced by chronic hyperglycaemia in Wistar rats: A behavioural, biochemical and histological analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferah Okkay, I.; Okkay, U.; Gundogdu, O.L.; Bayram, C.; Mendil, A.S.; Ertugrul, M.S.; Hacimuftuoglu, A. Syringic acid protects against thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy: Behavioral, biochemical, and molecular evidence. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 769, 136385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Mao, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Xu, L. Protective effects of syringic acid in nonalcoholic fatty liver in rats through regulation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2024, 38, e23809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, V.; Raja, B. Protective effects of syringic acid against acetaminophen-induced hepatic damage in albino rats. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 21, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyi, O.E.; Somade, O.T.; Ajayi, B.O.; James, A.S.; Adeyi, A.O.; Olayemi, Z.M.; Tella, N.B. Syringic acid demonstrates better anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects than ascorbic acid via maintenance of the endogenous antioxidants and downregulation of pro-inflammatory and apoptotic markers in DMN-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 33, 101428. [Google Scholar]
- Rashedinia, M.; Alimohammadi, M.; Shalfroushan, N.; Khoshnoud, M.J.; Mansourian, M.; Azarpira, N.; Sabahi, Z. Neuroprotective effect of syringic acid by modulation of oxidative stress and mitochondrial mass in diabetic rats. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8297984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, S.A.; Gür, C.; İleritürk, M.; Akaras, N.; Küçükler, S.; Kandemir, F.M. Effect of syringic acid on oxidative stress, autophagy, apoptosis, inflammation pathways against testicular damage induced by lead acetate. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 80, 127315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Velu, P.; Zareian, M.; Feng, Z.; Vijayalakshmi, A. Effects of syringic acid on apoptosis, inflammation, and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in gastric cancer cells. Front. Nut. 2021, 8, 788929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liang, Y. Chemoprotective effect of syringic acid on cyclophosphamide induced ovarian damage via inflammatory pathway. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal Singh, S.; Thakur, G.; Dahiya, R. Evaluation of the reno-protective effect of syringic acid against nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin in rats. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 11, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Vredenburg, G.; Kapitein, B.; Claessen, S.M.; Rosing, H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H. Hepatotoxicity of chemotherapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Octavia, Y.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Gabrielson, K.L.; Janssens, S.; Crijns, H.J.; Moens, A.L. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 52, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, F.; Deng, Z. Oxidative stress: Signaling pathways, biological functions, and disease. Med. Comm. 2025, 6, e70268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsirhani, A.M.; Abu-Almakarem, A.S.; Alwaili, M.A.; Aljohani, S.; Alali, I.; AlRashidi, A.A.; Abuzinadah, N.Y.; Alkhodair, S.A.; Mobasher, M.A.; Alothaim, T.; et al. Syzygium aromaticum extract mitigates doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity in male rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasher, M.A.; Alsirhani, A.M.; Alwaili, M.A.; Baakdah, F.; Eid, T.M.; Alshanbari, F.A.; Alzahri, R.Y.; Alkhodair, S.A.; El-Said, K.S. Annona squamosa fruit extract ameliorates lead acetate-induced testicular injury by modulating JAK-1/STAT-3/SOCS-1 signaling in male rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, I.; Mandryk, I.; Horbańczuk, J.O.; Wierzbicka, A.; Koszarska, M. Nutraceutical properties of syringic acid in civilization diseases—Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschke, R.; Eickhoff, A.; Danan, G. Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis: Robust causality assessment using two different validated and scoring diagnostic algorithms. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairi, L.A.; Abu-Almakarem, A.S.; Al-Sowayan, N.S.; Alkhodair, S.A.; Albishi, H.M.; Eid, T.M.; Alshanbari, F.A.; Abuzinadah, N.Y.; Mobasher, M.A.; El-Said, K.S. Colpomenia sinuosa extract mitigates lead acetate-induced testicular dysfunctions in male rats. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2025, 12, 1551773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwaili, M.A.; Abu-Almakarem, A.S.; El-Said, K.S.; Eid, T.M.; Mobasher, M.A.; Alsabban, A.H.; Alburae, N.A.; Banjabi, A.A.; Soliman, M.M. Shikimic acid protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alherz, F.A.; Negm, W.A.; El-Masry, T.A.; Elmorshedy, K.E.; El-Kadem, A.H. The potential beneficial role of Ginkgetin in doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity: Elucidating the underlying claim. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedikli, E.; Barış, V.Ö.; Yersal, N.; Dinçsoy, A.B.; Müftüoğlu, S.F.; Erdem, A. Taurine protects doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity via its membrane-stabilizing effect in rats. Life 2023, 13, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Xiao, M.; Gao, T.; Zhang, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wen, P.; et al. Co-treatment with resveratrol and FGF1 protects against acute liver toxicity after doxorubicin treatment via the AMPK/NRF2 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 940406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, M.U.; Fatima, T.; Batool, M.; Azmat, R.; Sadaf, A.; Ghafoor, N.; Khalil, M. Therapeutic efficacy of chrysoeriol on doxorubicin induced liver damage by improving biochemical and histological profile in rats. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 11, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, R.; Aminzadeh, S.; Khodayar, M.J.; Khorsandi, L.; Salehcheh, M. Protective effects of zingerone on oxidative stress in doxorubicin-induced rat hepatotoxicity. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 12, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, E.; Busletta, C.; Bonzo, L.V.; Povero, D.; Paternostro, C.; Mareschi, K.; Ferrero, I.; David, E.; Bertolani, C.; Caligiuri, A.; et al. Intracellular reactive oxygen species are required for directional migration of resident and bone marrow- derived hepatic pro-fibrogenic cells. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Chi, Z.; Tao, X.; Zhai, X.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, J.; Yang, S.; Dong, D. Naringin against doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity in mice through reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis via the up-regulation of SIRT1. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani Hekmat, A.; Hekmat, M.; Ramezanipour, S.; Javanmardi, K. Protective effects of Alamandine against doxorubicin-induced liver injury in rats. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2025, 26, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, O. Camellia sinensis and epicatechin abate doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity in male Wistar rats via their modulatory effects on oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. J. App. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 30–44. [Google Scholar]
- AlAsmari, A.F.; Alharbi, M.; Alqahtani, F.; Alasmari, F.; AlSwayyed, M.; Alzarea, S.I.; Al-Alallah, I.A.; Alghamdi, A.; Hakami, H.M.; Alyousef, M.K.; et al. Diosmin alleviates doxorubicin-induced liver injury via modulation of oxidative stress-mediated hepatic inflammation and apoptosis via NfkB and MAPK pathway: A preclinical study. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Niu, Q.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, Z.; Dong, H. The role of the interleukin family in liver fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1497095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laftah, A.H.; Alhelfi, N.; Salait, S.K.; Altemimi, A.B.; Tabandeh, M.R.; Tsakali, E.; Van Impe, J.F.M.; Abd El-Maksoud, A.A.; Abedelmaksoud, T.G. Mitigation of doxorubicin-induced liver toxicity in mice breast cancer model by green tea and Moringa oleifera combination: Targeting apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 124, 106626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnam, S.; Pal, A. Relevance of Erk1/2-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in CEES-induced oxidative stress regulates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2019, 35, 541–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, C.; Peng, L. Hydrazinocurcumin and 5-fluorouracil enhance apoptosis and restrain tumorigenicity of HepG2 cells via disrupting the PTEN-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 109851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Emam, S.Z.; Soubh, A.A.; Al-Mokaddem, A.K.; Abo El-Ella, D.M. Geraniol activates Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway mediating protection against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, S.M.; Patil, C.R. Asiatic acid ameliorates doxorubicin induced cardiac and hepato-renal toxicities with Nrf2 transcriptional factor activation in rats. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2018, 18, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Fu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zou, H.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, Z.; Bian, J. Role of PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in resveratrol alleviation of zearalenone-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in TM4 cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daly, A.K. Pharmacogenomics and the genetics of drug-induced liver injury. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lucena, M.I.; Molokhia, M.; Shen, Y.; Urban, T.J.; Aithal, G.P.; Andrade, R.J.; Daly, A.K. Susceptibility to amoxicillin–clavulanate-induced liver injury is influenced by multiple HLA class I and II alleles. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Hsieh, C.; Yin, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, A.; et al. ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Novati, G.; Pan, J.; Bycroft, C.; Žemgulytė, A.; Applebaum, T.; Pritzel, A.; Wong, L.H.; Zielinski, M.; Sargeant, T.; et al. Accurate proteome-wide missense variant effect prediction with Alpha Missense. Science 2023, 381, eadg7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gan, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.X.; Cao, Y. CB-Dock2: Improved protein-ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template fitting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W159–W164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warpe, V.S.; Mali, V.R.; Arulmozhi, S.; Bodhankar, S.L.; Mahadik, K.R. Cardioprotective effect of ellagic acid on doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats. J. Acute Med. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancroft, J.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Orabi, S.H.; Abd Eldaium, D.; Hassan, A.; Sabagh, H.S.E.; Abd Eldaim, M.A. Allicin modulates diclofenac sodium induced hepatonephro toxicity in rats via reducing oxidative stress and caspase 3 protein expression. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 74, 103306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
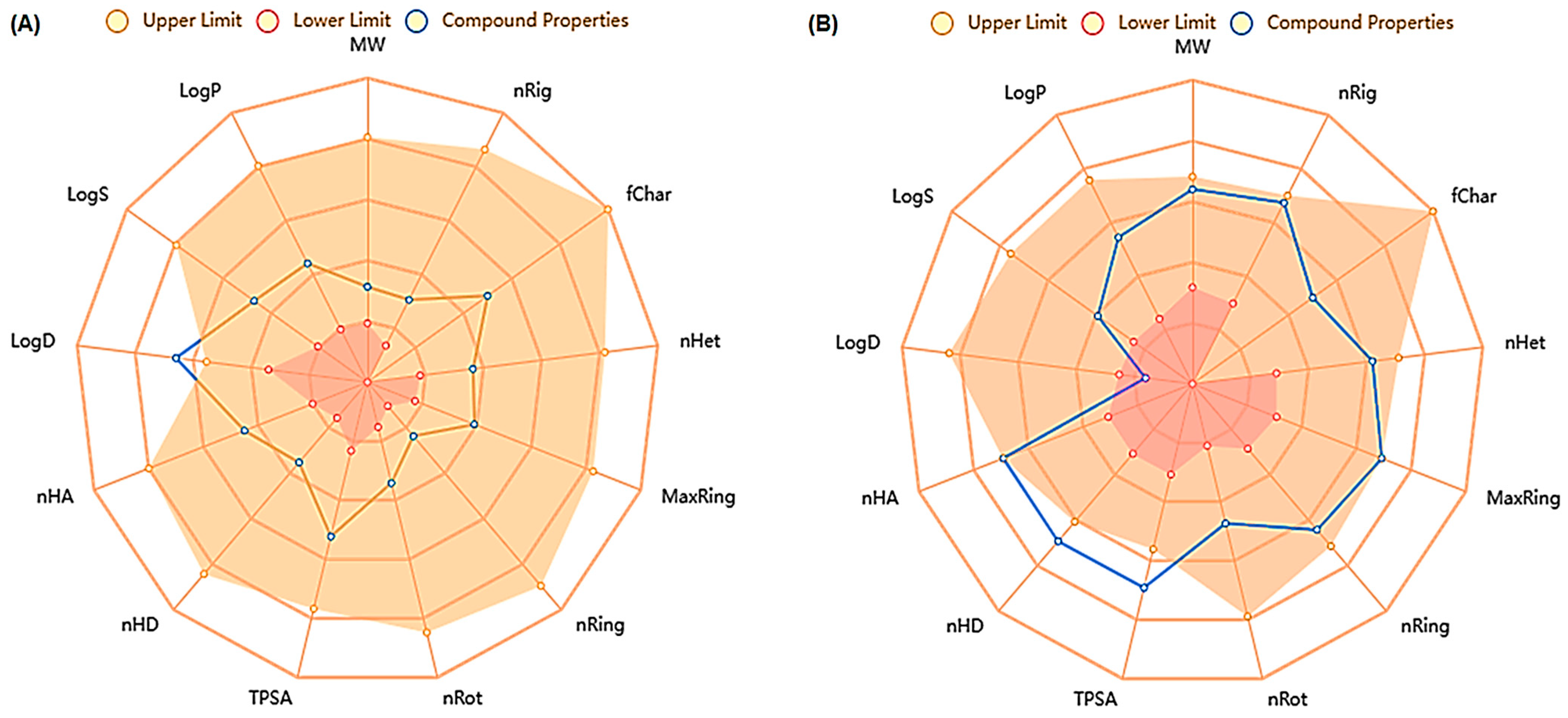
| Name | Syringic Acid (SYA) | Doxorubicin (DOX) |
|---|---|---|
| LogS | −1.975 | −2.69 |
| LogD | 3.978 | 0.689 |
| LogP | 1.212 | 1.76 |
| Pgp-inh | 0.002 | 0.024 |
| Pgp-sub | 0.003 | 0.999 |
| HIA | 0.028 | 0.751 |
| F(20%) | 0.011 | 0.024 |
| F(30%) | 0.067 | 0.168 |
| Caco-2 | −5.142 | −6.006 |
| MDCK | 1.09 × 105 | 6.24 × 106 |
| PPB | 50.89% | 91.29% |
| VDss | 0.459 | 1.01 |
| Fu | 38.57% | 12.38% |
| CYP1A2-inh | 0.032 | 0.489 |
| CYP1A2-sub | 0.911 | 0.452 |
| CYP2C19-inh | 0.025 | 0.013 |
| CYP2C19-sub | 0.058 | 0.064 |
| CYP2C9-inh | 0.028 | 0.016 |
| CYP2C9-sub | 0.131 | 0.431 |
| CYP2D6-inh | 0.012 | 0.005 |
| CYP2D6-sub | 0.141 | 0.168 |
| CYP3A4-inh | 0.016 | 0.103 |
| CL | 7.208 | 9.566 |
| T12 | 0.946 | 0.847 |
| hERG | 0.034 | 0.019 |
| H-HT | 0.154 | 0.257 |
| DILI | 0.795 | 0.964 |
| Ames | 0.009 | 0.811 |
| ROA | 0.011 | 0.022 |
| FDAMDD | 0.023 | 0.453 |
| SkinSen | 0.129 | 0.418 |
| Carcinogenicity | 0.034 | 0.776 |
| EC | 0.292 | 0.003 |
| EI | 0.977 | 0.073 |
| Respiratory | 0.044 | 0.92 |
| BCF | 0.401 | 0.451 |
| IGC50 | 2.487 | 3.709 |
| LC50 | 2.55 | 3.784 |
| LC50DM | 3.357 | 5.493 |
| NR-AR | 0.012 | 0.017 |
| NR-AR-LBD | 0.046 | 0.964 |
| NR-AhR | 0.196 | 0.906 |
| NR-Aromatase | 0.021 | 0.834 |
| NR-ER | 0.112 | 0.619 |
| NR-ER-LBD | 0.007 | 0.536 |
| NR-PPAR-gamma | 0.235 | 0.165 |
| SR-ARE | 0.061 | 0.813 |
| SR-ATAD5 | 0.191 | 0.549 |
| SR-HSE | 0.139 | 0.01 |
| SR-MMP | 0.043 | 0.959 |
| SR-p53 | 0.053 | 0.988 |
| MW | 198.05 | 543.17 |
| Vol | 189.069 | 516.727 |
| Dense | 1.048 | 1.051 |
| nHA | 5 | 12 |
| nHD | 2 | 9 |
| TPSA | 75.99 | 212.39 |
| nRot | 3 | 5 |
| nRing | 1 | 5 |
| MaxRing | 6 | 18 |
| nHet | 5 | 12 |
| nRig | 7 | 28 |
| Flex | 0.429 | 0.179 |
| nStereo | 0 | 5 |
| NonBiodegradable | 0 | 3 |
| SureChEMBL | 0 | 1 |
| Skin_Sensitization | 4 | 8 |
| Toxicophores | 1 | 3 |
| Genotoxic_Carcinogenicity_Mutagenicity | 0 | 4 |
| QED | 0.76 | 0.147 |
| Synth | 1.726 | 5.015 |
| Fsp3 | 0.222 | 0.37 |
| MCE-18 | 8 | 118.243 |
| Natural Product-likeness | 0.544 | 1.37 |
| Lipinski | Accepted | Rejected |
| Pfizer | Accepted | Accepted |
| GlaxoSmithKline | Accepted | Rejected |
| Compound/Protein | PI3K | Akt | Nrf-2 | HO-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOX | −6.5 | −7.9 | −6.9 | −7.7 |
| SYA | −4.4 | −5.6 | −4.5 | −5.4 |
| Groups | Control | DOX | DOX/SYA (25 mg/kg) | DOX/SYA (50 mg/kg) | DOX/SYA (75 mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I.B.W (g) | 155.21 ± 6.54 a | 162.74 ± 5.83 a | 165.42 ± 4.87 a | 157.62 ± 5.81 a | 160.78 ± 6.23 a |
| F.B.W (g) | 215.23 ± 7.69 a | 185.44 ± 8.16 c | 195.12 ± 6.15 a,c | 196.47 ± 5.79 a,c | 204.77 ± 7.12 a |
| B.W.C (%) | 38.71% a | 13.94% e | 17.95% e,c | 24.64% e | 27.40% a,e |
| R.L.W (%) | 4.61 ± 0.25 e | 5.07 ± 0.31 e | 4.87 ± 0.29 e | 4.71 ± 0.33 e | 4.70 ± 0.27 e |
| Groups | AST (U/L) | ALT (U/L) | ALP (U/L) | GGT (U/L) | TP (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 48.38 ± 3.16 c | 34.67 ± 2.25 a | 192.83 ± 4.87 a | 7.64 ± 0.79 b | 8.19 ± 0.65 c |
| DOX | 114.85 ± 4.87 e | 89.64 ± 3.69 c | 325.68 ± 6.93 b | 19.14 ± 1.95 a | 3.95 ± 0.29 b |
| DOX/SYA (25 mg/kg) | 81.65 ± 3.78 a | 68.82 ± 2.97 e | 274.73 ± 6.88 c | 11.05 ± 1.48 c | 5.54 ± 0.44 a |
| DOX/SYA (50 mg/kg) | 69.74 ± 3.56 a | 60.84 ± 3.12 e | 242.61 ± 4.79 c | 9.23 ± 1.17 b | 6.21 ± 0.64 a |
| DOX/SYA (75 mg/kg) | 60.93 ± 3.17 c,d | 53.69 ± 2.95 e,d | 239.33 ± 5.94 c | 10.46 ± 1.08 b,c | 5.93 ± 0.59 a |
| Groups | MDA (nmol/mg Protein) | SOD (U/mg Protein) | GST (U/mg Protein) | GPX (U/mg Protein) | GSH (nmol/mg Protein) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2.16 ± 0.18 a | 12.35 ± 0.95 c | 36.45 ± 1.48 c | 73.69 ± 3.28 b | 24.87 ± 1.54 c |
| DOX | 6.85 ± 0.57 b | 5.79 ± 0.48 a | 17.29 ± 1.12 d | 41.58 ± 2.97 a | 10.79 ± 1.15 b |
| DOX/SYA (25 mg/kg) | 5.57 ± 0.39 b | 8.13 ± 0.66 b | 25.37 ± 1.74 a | 52.74 ± 2.65 c | 16.15 ± 1.64 a |
| DOX/SYA (50 mg/kg) | 4.41 ± 0.51 b, c | 9.37 ± 0.58 b | 29.82 ± 2.01 a | 64.18 ± 3.14 b,c | 19.07 ± 1.90 a |
| DOX/SYA (75 mg/kg) | 3.29 ± 0.33 a,c | 10.95 ± 1.06 b,c | 33.44 ± 1.95 c | 67.95 ± 2.48 b,c | 19.93 ± 1.84 a |
| Gene | Accession Number | Forward Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K | NM_053481.2 | CGAGAGTACGCTGTAGGCTG | AGAAACTGGCCAATCCTCCG |
| Akt1 | NM_033230.3 | GAAGGAGAAGGCCACAGGTC | TTCTGCAGGACACGGTTCTC |
| Nrf2 | NM_031789.3 | CACATCCAGACAGACACCAGT | CTACAAATGGGAATGTCTCTGC |
| HO1 | NM_012580.2 | ACAGGGTGACAGAAGAGGCTAA | CTGTGAGGGACTCTGGTCTTTG |
| GAPDH | NM_017008.4 | CCGCATCTTCTTGTGCAGTG | GAGAAGGCAGCCCTGGTAAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alwaili, M.A.; Eid, T.M.; Abu-Almakarem, A.S.; Alsirhani, A.M.; Al-Sowayan, N.S.; Aljarari, R.M.; Al-Judaibi, E.A.; AlRashidi, A.A.; Mobasher, M.A.; El-Said, K.S. Syringic Acid Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity Through PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf-2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Male Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7779. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167779
Alwaili MA, Eid TM, Abu-Almakarem AS, Alsirhani AM, Al-Sowayan NS, Aljarari RM, Al-Judaibi EA, AlRashidi AA, Mobasher MA, El-Said KS. Syringic Acid Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity Through PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf-2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Male Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7779. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167779
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlwaili, Maha Abdullah, Thamir M. Eid, Amal S. Abu-Almakarem, Alaa Muqbil Alsirhani, Noorah Saleh Al-Sowayan, Rabab Mohamed Aljarari, Effat A. Al-Judaibi, Aljazi Abdullah AlRashidi, Maysa A. Mobasher, and Karim Samy El-Said. 2025. "Syringic Acid Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity Through PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf-2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Male Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7779. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167779
APA StyleAlwaili, M. A., Eid, T. M., Abu-Almakarem, A. S., Alsirhani, A. M., Al-Sowayan, N. S., Aljarari, R. M., Al-Judaibi, E. A., AlRashidi, A. A., Mobasher, M. A., & El-Said, K. S. (2025). Syringic Acid Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity Through PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf-2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Male Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7779. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167779





