Association Between Peach and Olive Pollen Non-Specific Lipid Transfer Protein Allergy and HLA Class II Phenotype
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Demographic Variables
2.2. Prick Test Results
2.3. nsLTP sIgE Profile
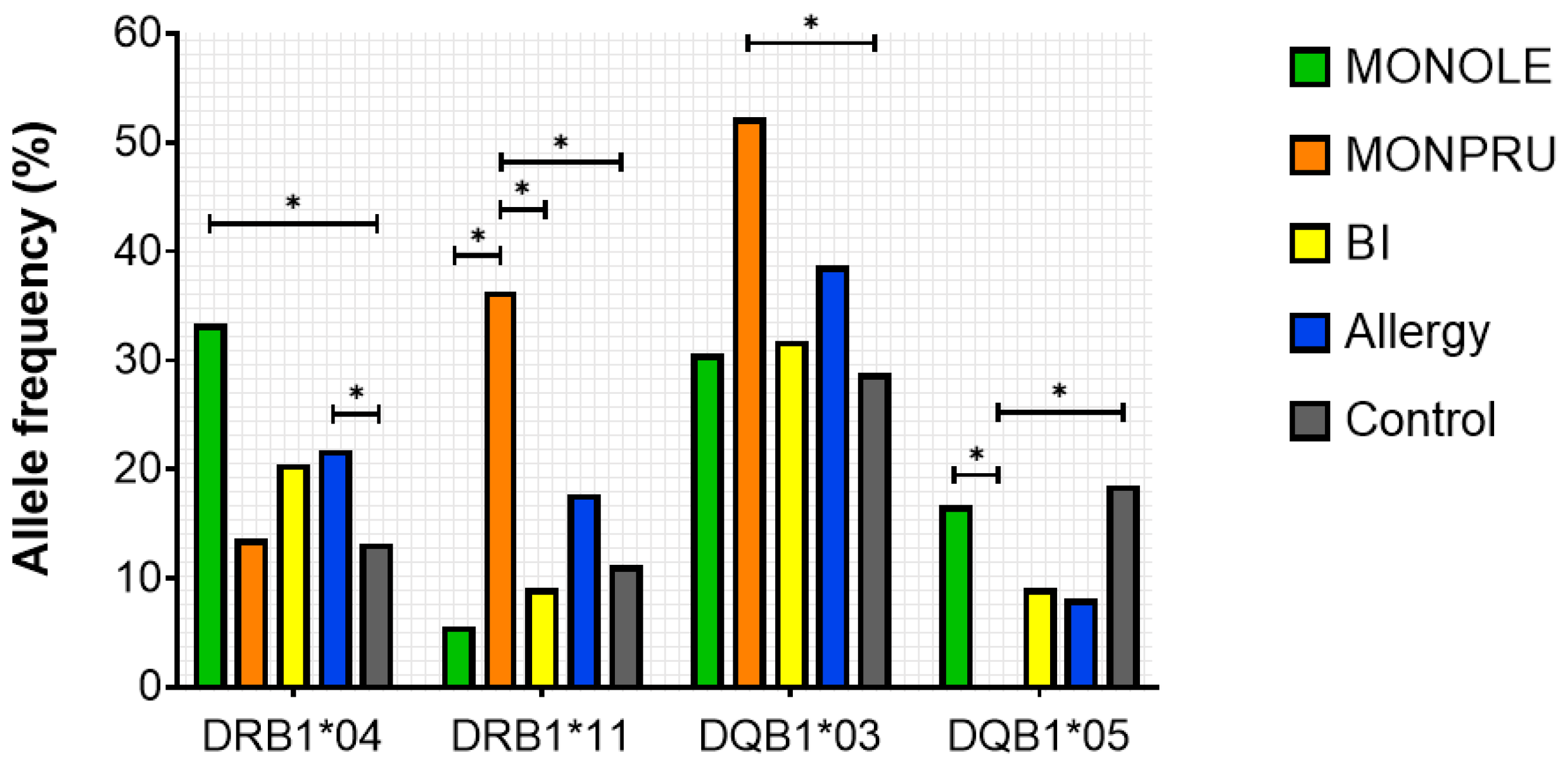
2.4. HLA Genotyping
2.5. Predicted T-Cell Epitopes for Ole e 7 and Pru p 3
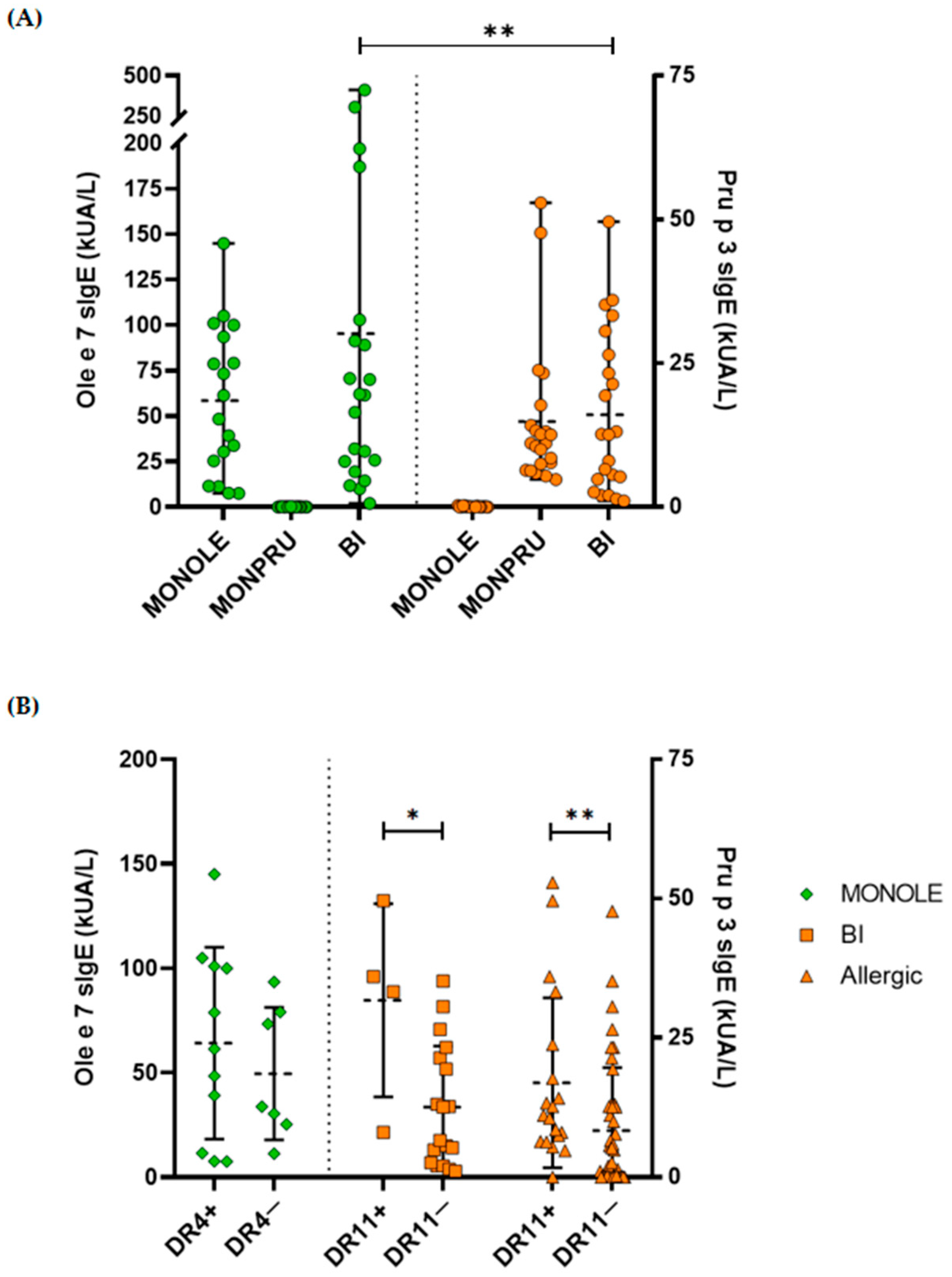
2.6. Correlation Between Specific IgE Levels and HLA Genotyping
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Controls
- (i)
- Patients monosensitised to Ole e 7 (sIgE to Ole e 7 > 0.35 kUA/L and sIgE to Pru p 3 < 0.35 kUA/L) were grouped as MONOLE (n = 18).
- (ii)
- Patients monosensitised to Pru p 3 (IgE to Pru p 3 > 0.35 kUA/L and sIgE to Ole e 7 < 0.35 kUA/L) were grouped as MONPRU (n = 22).
- (iii)
- Patients sensitised to both allergens (sIgE to Ole e 7 and Pru p 3 > 0.35 kUA/L) were grouped as BI (n = 22).
4.2. IgE Quantification
4.3. Prick Test
4.4. HLA Typing
4.5. T Cell Epitope Prediction
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APC | Antigen Presenting Cell |
| BI | Bisensitised to Ole e 7 and Pru p 3 |
| HLA | Human Leukocyte Antigen |
| IEDB | Immune Epitope Database |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography coupled to Mass Spectrometry |
| MONOLE | Monosensitised to Ole e 7 |
| MONPRU | Monosensitised to Pru p 3 |
| NGS | Next Generation Sequencing |
| nsLTP | Non-specific Lipid Transfer Protein |
| sIgE | Specific Immunoglobulin E |
| SPK | Skin Prick Test |
| TCR | T-cell Receptor |
References
- Finkina, E.I.; Melnikova, D.N.; Bogdanov, I.V.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Lipid transfer proteins as components of the plant innate immune system: Structure, functions, and applications. Acta Naturae 2016, 8, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, T.A.; Blomqvist, K.; Edqvist, J. Lipid transfer proteins: Classification, nomenclature, structure, and function. Planta 2016, 244, 971–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skypala, I.J.; Asero, R.; Barber, D.; Cecchi, L.; Perales, A.D.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Pastorello, E.A.; Swoboda, I.; Bartra, J.; Ebo, D.G.; et al. Non-specific lipid-transfer proteins: Allergen structure and function, cross-reactivity, sensitization, and epidemiology. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2021, 11, e12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Perales, A.; Garcia-Casado, G.; Sanchez-Monge, R.; Garcia-Selles, F.J.; Barber, D.; Salcedo, G. cDNA cloning and heterologous expression of the major allergens from peach and apple belonging to the lipid-transfer protein family. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacin, A.; Cumplido, J.; Figueroa, J.; Ahrazem, O.; Sanchez-Monge, R.; Carrillo, T.; Salcedo, G.; Blanco, C. Cabbage lipid transfer protein Bra o 3 is a major allergen responsible for cross-reactivity between plant foods and pollens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, I.; Miguel-Moncin, M.S.; Abel, T.; Foetisch, K.; Hartz, C.; Fortunato, D.; Cistero-Bahima, A.; Vieths, S.; Scheurer, S. Identification of a plane pollen lipid transfer protein (Pla a 3) and its immunological relation to the peach lipid-transfer protein, Pru p 3. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba, M.; Rodríguez, R.; Batanero, E. The spectrum of olive pollen allergens. From structures to diagnosis and treatment. Methods 2014, 66, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot, R.; Józefiak, D.; Sip, A.; Kuźma, D.; Musidlak, O.; Goździcka-Józefiak, A. Isolation and characterization of a non-specific lipid transfer protein from Chelidonium majus L. latex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asero, R.; Pravettoni, V.; Scala, E.; Villalta, D. Lipid transfer protein allergy: A review of current controversies. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2021, 52, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rial, M.J.; Sastre, J. Food Allergies Caused by Allergenic Lipid Transfer Proteins: What Is behind the Geographic Restriction? Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asero, R.; Brusca, I.; Cecchi, L.; Pignatti, P.; Pravettoni, V.; Scala, E.; Uasuf, C.; Villalta, D. Why lipid transfer protein allergy is not a pollen-food syndrome: Novel data and literature review. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 54, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Rivas, M.; González-Mancebo, E.; Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Benito, C.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; Salcedo, G.; Alonso, M.D.; Rosado, A.; Tejedor, M.A.; Vila, C.; et al. Clinically relevant peach allergy is related to peach lipid transfer protein, Pru p 3, in the Spanish population. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogas, G.; Muñoz-Cano, R.; Mayorga, C.; Casas, R.; Bartra, J.; Pérez, N.; Pascal, M.; Palomares, F.; Torres, M.J.; Gómez, F. Phenotyping peach-allergic patients sensitized to lipid transfer protein and analysing severity biomarkers. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 75, 3228–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barni, S.; Caimmi, D.; Chiera, F.; Comberiati, P.; Mastrorilli, C.; Pelosi, U.; Paravati, F.; Marseglia, G.L.; Arasi, S. Phenotypes and Endotypes of Peach Allergy: What Is New? Nutrients 2022, 14, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G.; Cecchi, L.; Bonini, S.; Nunes, C.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Behrendt, H.; Liccardi, G.; Popov, T.; Van Cauwenberge, P. Allergenic pollen and pollen allergy in Europe. Allergy 2007, 62, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.; De La Torre, F.; Feo, F.; Florido, F.; Guardia, P.; Moreno, C.; Quiralte, J.; Lombardero, M.; Villalba, M.; Salcedo, G.; et al. Understanding patient sensitization profiles in complex pollen areas: A molecular epidemiological study. Allergy 2008, 63, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeo-Santos, C.; Navas, A.; Benedé, S.; Ruíz-León, B.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Vogel, L.; Moreno-Aguilar, C.; Jurado, A.; Villalba, M.; Barderas, R. New insights into the sensitization to nonspecific lipid transfer proteins from pollen and food: New role of allergen Ole e 7. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 75, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, P.; Aguado, R.; Molina, J.; Trujillo-Aguilera, A.; Villalba, M.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Oeo-Santos, C.; Chicano, E.; Blanco, N.; Navas, A.; et al. Pollen-Food Allergy Syndrome: From Food Avoidance to Deciphering the Potential Cross-Reactivity between Pru p 3 and Ole e 7. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Cong, L.; Wang, Q. Pathogenesis of allergic diseases and implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spínola, H. HLA Loci and Respiratory Allergic Diseases. J. Respir. Res. 2017, 3, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamji, M.H.; Durham, S.R. Mechanisms of allergen immunotherapy for inhaled allergens and predictive biomarkers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Casado, G.; Pacios, L.F.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; Lombardero, M.; García-Selles, F.J.; Polo, F.; Barber, D.; Salcedo, G. Identification of IgE-binding epitopes of the major peach allergen Pru p 3. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.-P.; Barre, A.; Culerrier, R.; Granier, C.; Didier, A.; Rougé, P. Lipid transfer proteins from Rosaceae fruits share consensus epitopes responsible for their IgE-binding cross-reactivity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordesillas, L.; Cuesta-Herranz, J.; Gonzalez-Muñoz, M.; Pacios, L.F.; Compés, E.; Garcia-Carrasco, B.; Sanchez-Monge, R.; Salcedo, G.; Diaz-Perales, A. T-cell epitopes of the major peach allergen, Pru p 3: Identification and differential T-cell response of peach-allergic and non-allergic subjects. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, E.; Monza, M.; Pravettoni, V.; Longhi, R.; Bonara, P.; Scibilia, J.; Primavesi, L.; Scorza, R. Characterization of the T-cell epitopes of the major peach allergen Pru p 3. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 153, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, L.; Núñez, C. The HLA complex and coeliac disease. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 358, 47–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, J.; He, C.; Li, D.; Tong, W.; Zou, Y.; Xu, W. Role of HLA-B27 in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brézin, A.P.; Monnet, D.; Cohen, J.H.; Levinson, R.D. HLA-A29 and Birdshot Chorioretinopathy. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2011, 19, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, A.; Cárdaba, B.; Jara, P.; Cuadrado, P.; Hierro, L.; de Andrés, B.; del Pozo, V.; Cortegano, M.I.; Gallardo, S.; Camarena, C.; et al. Autoimmune hepatitis type 2 and hepatitis C virus infection: Study of HLA antigens. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torío, A.; Sánchez-Guerrero, I.; Muro, M.; Villar, L.M.; Minguela, A.; Marín, L.; Moya-Quiles, M.R.; Montes-Ares, O.; Pagán, J.; Alvarez-López, M.R. HLA class II genotypic frequencies in atopic asthma: Association of DRB1*01-DQB1*0501 Genotype with Artemisia vulgaris allergic asthma. Hum. Immunol. 2003, 64, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlin, E.; Phillips, E. Genotyping for severe drug hypersensitivity. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontakioti, E.; Domvri, K.; Papakosta, D.; Daniilidis, M. HLA and asthma phenotypes/endotypes: A review. Hum. Immunol. 2014, 75, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waage, J.; Standl, M.; Curtin, J.A.; Jessen, L.E.; Thorsen, J.; Tian, C.; Schoettler, N.; Flores, C.; Abdellaoui, A.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; et al. Genome-wide association and HLA fine-mapping studies identify risk loci and genetic pathways underlying allergic rhinitis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, K.; Bovijn, J.; Zheng, N.; Lepamets, M.; Censin, J.C.; Jürgenson, T.; Särg, D.; Abner, E.; Laisk, T.; Luo, Y.; et al. Genome-wide Study Identifies Association between HLA-B*55:01 and Self-Reported Penicillin Allergy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, S.-S.; Morino, R.; Nakazono, K.; Kamitsuji, S.; Akita, M.; Kawajiri, M.; Yamasaki, T.; Kami, A.; Hoshi, Y.; Tada, A.; et al. Genome-wide association study of self-reported food reactions in Japanese identifies shrimp and peach specific loci in the HLA-DR/DQ gene region. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucera, E.; Valentini, M.; Mezzacappa, S.; Migliara, G.; Chini, R.; Rizzi, A.; Aruanno, A.; Ria, F. HLA-DRB1 haplotype associates with selection of lipid transfer protein variants as targets of food allergy. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Montero-Martín, G.; Mallempati, K.C.; Gangavarapu, S.; Sánchez-Gordo, F.; Herrero-Mata, M.J.; Balas, A.; Vicario, J.L.; Sánchez-García, F.; González-Escribano, M.F.; Muro, M.; et al. High-resolution characterization of allelic and haplotypic HLA frequency distribution in a Spanish population using high-throughput next-generation sequencing. Hum. Immunol. 2019, 80, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulten, V.; Radakovics, A.; Hartz, C.; Mari, A.; Vazquez-Cortes, S.; Fernandez-Rivas, M.; Lauer, I.; Jahn-Schmid, B.; Eiwegger, T.; Scheurer, S.; et al. Characterization of the allergic T-cell response to Pru p 3, the nonspecific lipid transfer protein in peach. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdaba, B.; De Pablo, R.; Vilches, C.; Martín, E.; Geller-Bernstein, C.; De Andres, B.; Zaharan, Y.; Del Pozo, V.; Gallardo, S.; Chaves, E.D.A.; et al. Allergy to olive pollen: T-cell response from olive allergic patients is restricted by DR7-DQ2 antigens. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1996, 26, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdaba, B.; Pozo, D.; Jurado, A.; Gallardo, S.; Cortegano, I.; Arrieta, I.; Amo, D.; Tramón, P.; Florido, F.; Sastre, J.; et al. Olive pollen allergy: Searching for immunodominant T-cell epitopes on the Ole e 1 molecule. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1998, 28, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheerbrant, H.; Guillien, A.; Vernet, R.; Lupinek, C.; Pison, C.; Pin, I.; Demenais, F.; Nadif, R.; Bousquet, J.; Pickl, W.F.; et al. Associations between specific IgE sensitization to 26 respiratory allergen molecules and HLA class II alleles in the EGEA cohort. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 76, 2575–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreborg, S.; Frew, A. Position paper: Allergen standardization and skin tests. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1993, 48, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeo-Santos, C.; Mas, S.; Benedé, S.; López-Lucendo, M.; Quiralte, J.; Blanca, M.; Mayorga, C.; Villalba, M.; Barderas, R. A recombinant isoform of the Ole e 7 olive pollen allergen assembled by de novo mass spectrometry retains the allergenic ability of the natural allergen. J. Proteom. 2018, 187, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynisson, B.; Alvarez, B.; Paul, S.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M. NetMHCpan-4.1 and NetMHCIIpan-4.0: Improved predictions of MHC antigen presentation by concurrent motif deconvolution and integration of MS MHC eluted ligand data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W449–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NetMHCIIpan 4.3-DTU Health Tech-Bioinformatic Services. Available online: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/NetMHCIIpan-4.3/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
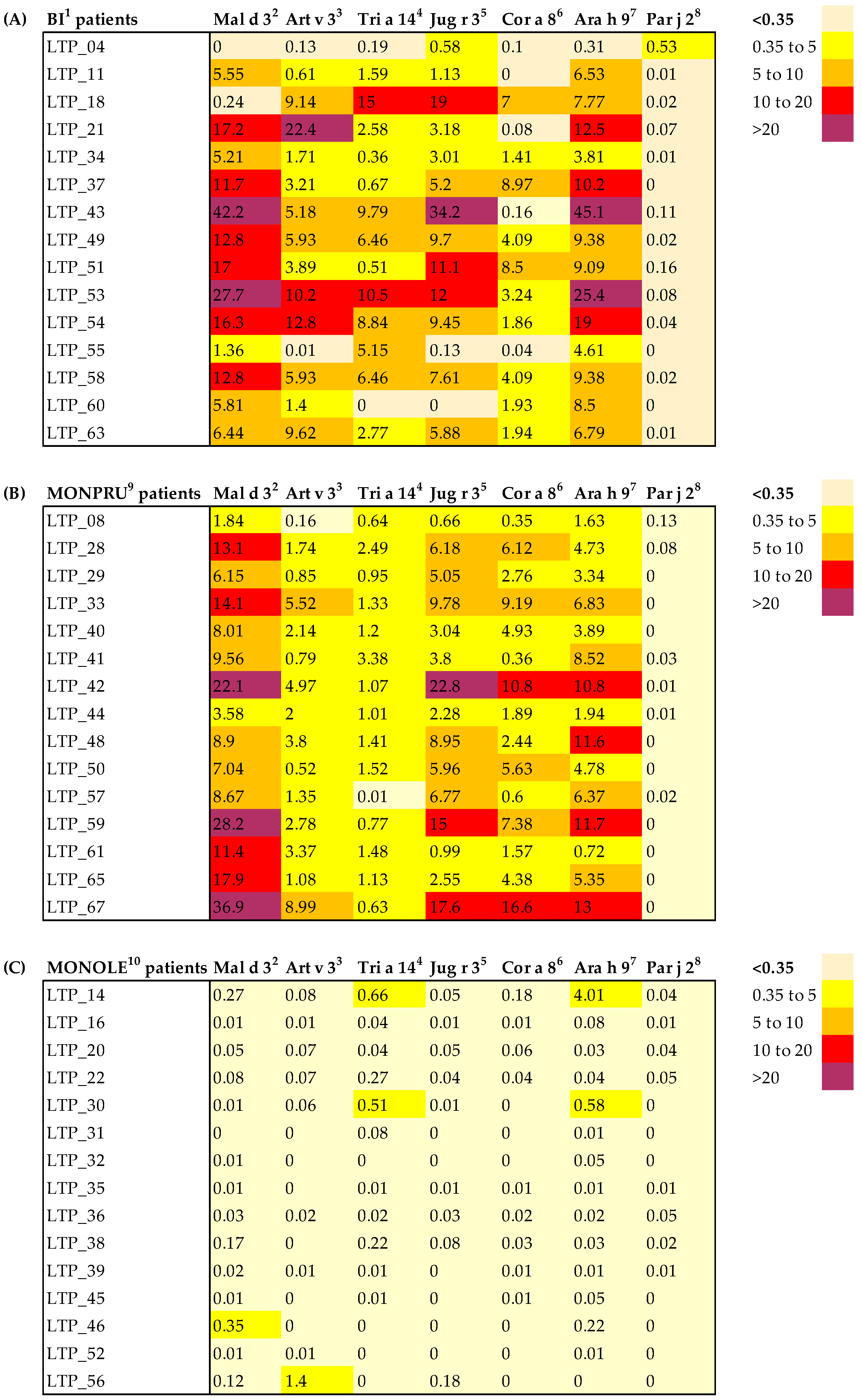
| MONOLE n = 18 | MONPRU n = 22 | BI n = 22 | p-Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 38.3 (11.8) | 37.0 (10.2) | 33.6 (11.1) | 0.383 |
| Female, n (%) | 14 (77.8) | 17 (77.3) | 11 (50.0) | 0.086 |
| Rural habitat, n (%) | 9 (50.0) | 13 (59.1) | 11 (50.0) | 0.790 |
| Respiratory symptoms | ||||
| Rhinoconjunctivitis, n (%) | 17 (94.4) | 15 (68.2) | 22 (100.0) | 0.004 |
| Asthma, n (%) | 16 (88.9) | 7 (31.8) | 15 (68.2) | 0.001 |
| Rosaceae symptoms | ||||
| Oral symptoms, n (%) | 1 (5.6) | 2 (9.1) | 7 (31.8) | 0.043 |
| Mild systemic-cutaneous symptoms, n (%) | 0 | 13 (59.1) | 3 (13.6) | <0.001 |
| Moderate systemic-respiratory symptoms, n (%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (9.1) | 0.153 |
| Anaphylaxis, n (%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (4.5) | 0.397 |
| sIgE levels | ||||
| Pru p 3 sIgE (kUA/L), mean (SD) | 0.09 (0.10) | 14.85 (12.59) | 16.06 (14.06) | <0.001 |
| Ole e 7 sIgE (kUA/L), mean (SD) | 58.47 (40.62) | 0.12 (0.12) | 95.30 (106.42) | <0.001 |
| Ole e 1 sIgE 2 (kUA/L), mean (SD) | 17.85 (38.37) | NA | 23.73 (44.40) | 0.838 |
| Positive SPT 3 with Olea europaea extract, n (%) | 18 (100.0) | 8 (47.1) | 17 (94.4) | <0.001 |
| Positive SPT 3 with peach extract, n (%) | 0 | 19 (95.0) | 14 (77.8) | <0.001 |
| Allergy | Total Allergy Group N = 62 | Control Group N = 548 | p-Value 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MONOLE N = 18 | MONPRU N = 22 | BI N = 22 | p-Value 1 | ||||
| DRB1*01 | 8.33 | 0 | 6.82 | ns | 4.84 | 13.68 | ns |
| DRB1*03 | 13.89 | 11.36 | 6.82 | ns | 10.48 | 10.95 | ns |
| DRB1*04 | 33.33 | 13.64 | 20.45 | ns | 21.77 | 10.58 | <0.001 |
| DRB1*04:01 | 0 | 2.27 | 0 | ns | 0.81 | 1.46 | ns |
| DRB1*04:02 | 2.78 | 4.55 | 2.27 | ns | 3.23 | 1.82 | ns |
| DRB1*04:03 | 5.56 | 0 | 4.55 | ns | 3.23 | 2.19 | ns |
| DRB1*04:04 | 22.22 | 0 | 4.55 | <0.001 | 8.06 | 2.01 | <0.001 |
| DRB1*04:05 | 2.78 | 4.55 | 6.82 | ns | 4.84 | 2.01 | ns |
| DRB1*04:06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ns | 0 | 0.36 | ns |
| DRB1*04:07 | 0 | 2.27 | 2.27 | ns | 1.61 | 0.73 | ns |
| DRB1*07 | 13.89 | 9.09 | 15.91 | ns | 12.90 | 16.42 | ns |
| DRB1*08 | 2.78 | 4.55 | 0 | ns | 2.42 | 3.10 | ns |
| DRB1*09 | 0 | 2.27 | 4.55 | ns | 2.42 | 1.46 | ns |
| DRB1*10 | 2.78 | 0 | 0 | ns | 0.81 | 1.46 | ns |
| DRB1*11 | 5.56 | 36.36 | 9.09 | <0.001 | 17.74 | 13.87 | ns |
| DRB1*11:01 | 2.78 | 25.0 | 4.55 | 0.001 | 11.29 | 4.56 | ns |
| DRB1*11:02 | 0 | 2.27 | 0 | ns | 0.81 | 2.55 | ns |
| DRB1*11:03 | 0 | 0 | 2.27 | ns | 0.81 | 1.10 | ns |
| DRB1*11:04 | 2.78 | 9.09 | 2.27 | ns | 4.84 | 5.66 | ns |
| DRB1*12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ns | 0 | 0.91 | ns |
| DRB1*13 | 2.78 | 11.36 | 13.64 | ns | 9.68 | 12.59 | ns |
| DRB1*14 | 2.78 | 0 | 0 | ns | 0.81 | 4.02 | ns |
| DRB1*15 | 13.89 | 11.36 | 20.45 | ns | 15.32 | 9.67 | ns |
| DRB1*16 | 0 | 0 | 2.27 | ns | 0.81 | 1.28 | ns |
| Allergy | Total Allergy Group N = 62 | Control Group N = 151 | p-Value 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MONOLE N = 18 | MONPRU N = 22 | BI N = 22 | p-Value 1 | ||||
| DQB1*02 | 30.56 | 22.73 | 25.00 | ns | 25.81 | 29.14 | ns |
| DQB1*03 | 30.56 | 52.27 | 31.82 | 0.048 | 38.71 | 25.83 | ns |
| DQB1*03:01 | 5.56 | 40.91 | 9.09 | <0.001 | 19.35 | 15.89 | ns |
| DQB1*03:02 | 22.22 | 9.09 | 15.91 | ns | 15.32 | 5.30 | ns |
| DQB1*03:03 | 0 | 2.27 | 6.82 | ns | 3.23 | 3.97 | ns |
| DQB1*03:04 | 2.78 | 0 | 0 | ns | 0.81 | 0 | ns |
| DQB1*03:05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ns | 0 | 0.66 | ns |
| DQB1*04 | 8.33 | 4.55 | 0 | ns | 4.03 | 1.99 | ns |
| DQB1*05 | 16.67 | 0 | 9.09 | 0.038 | 8.06 | 19.87 | ns |
| DQB1*05:01 | 11.11 | 0 | 6.82 | ns | 5.65 | 14.57 | ns |
| DQB1*05:02 | 2.78 | 0 | 2.27 | ns | 1.61 | 1.99 | ns |
| DQB1*05:03 | 2.78 | 0 | 0 | ns | 0.81 | 3.31 | ns |
| DQB1*06 | 13.89 | 20.45 | 34.09 | ns | 23.39 | 23.17 | ns |
| Protein | Allele | Peptide | Start Position | End Position | Score 1 | Percentile Rank 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ole e 7 | DRB1 | |||||
| DRB1*04:03 | KSALALVGNKVDTGR | 54 | 68 | 0.73 | 1.1 | |
| DRB1*04:04 | GVKTVLAQATSKPDK | 32 | 46 | 0.63 | 2.4 | |
| DRB1*04:05 | KSALALVGNKVDTGR | 54 | 68 | 0.79 | 0.8 | |
| DRB1*11:01 | TGRVSSLPKKCGMSV | 66 | 80 | 0.33 | 5.8 | |
| DRB1*11:02 | TGRVSSLPKKCGMSV | 66 | 80 | 0.19 | 13.0 | |
| DRB1*11:04 | TGRVSSLPKKCGMSV | 66 | 80 | 0.54 | 3.3 | |
| DQB1 | ||||||
| DQB1*03:01 | GNKVDTGRVSSLPKK | 61 | 75 | 0.63 | 1.2 | |
| DQB1*03:02 | TAKLTSCVSYLDDKS | 8 | 22 | 0.01 | 2.5 | |
| DQB1*03:03 | GNKVDTGRVSSLPKK | 61 | 75 | 0.24 | 0.69 | |
| DQB1*05:01 | TSCVSYLDDKSAKPT | 12 | 26 | 0.02 | 2.1 | |
| DQB1*05:03 | TSCVSYLDDKSAKPT | 12 | 26 | 0.06 | 2.5 | |
| Pru p 3 | DRB1 | |||||
| DRB1*04:03 | NVNNLARTTPDRQAA | 33 | 47 | 0.38 | 6.5 | |
| DRB1*04:04 | NGIRNVNNLARTTPD | 29 | 43 | 0.32 | 7.2 | |
| DRB1*04:05 | SIPYKISASTNCATV | 76 | 90 | 0.16 | 11.0 | |
| DRB1*11:01 | IRNVNNLARTTPDRQ | 31 | 45 | 0.33 | 5.9 | |
| DRB1*11:02 | NGIRNVNNLARTTPD | 29 | 43 | 0.59 | 2.5 | |
| DRB1*11:04 | IRNVNNLARTTPDRQ | 31 | 45 | 0.61 | 2.7 | |
| DQB1 | ||||||
| DQB1*03:01 | LKQLSASVPGVNPNN | 51 | 65 | 0.59 | 1.5 | |
| DQB1*03:02 | VPGVNPNNAAALPGK | 58 | 72 | 0.0054 | 14.0 | |
| DQB1*03:03 | VPGVNPNNAAALPGK | 58 | 72 | 0.21 | 1.1 | |
| DQB1*05:01 | VPGVNPNNAAALPGK | 58 | 72 | 0.0073 | 13.0 | |
| DQB1*05:03 | NVNNLARTTPDRQAA | 33 | 47 | 0.05 | 4.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez, P.; Molina, J.; Bernardo, R.; González, R.; Manzanares, B.; Aguado, R.; Carrero, L.; Jurado, A.; Ruiz-León, B.; Navas, A. Association Between Peach and Olive Pollen Non-Specific Lipid Transfer Protein Allergy and HLA Class II Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167755
Álvarez P, Molina J, Bernardo R, González R, Manzanares B, Aguado R, Carrero L, Jurado A, Ruiz-León B, Navas A. Association Between Peach and Olive Pollen Non-Specific Lipid Transfer Protein Allergy and HLA Class II Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167755
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez, Paula, Juan Molina, Raquel Bernardo, Rafael González, Bárbara Manzanares, Rocío Aguado, Laura Carrero, Aurora Jurado, Berta Ruiz-León, and Ana Navas. 2025. "Association Between Peach and Olive Pollen Non-Specific Lipid Transfer Protein Allergy and HLA Class II Phenotype" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167755
APA StyleÁlvarez, P., Molina, J., Bernardo, R., González, R., Manzanares, B., Aguado, R., Carrero, L., Jurado, A., Ruiz-León, B., & Navas, A. (2025). Association Between Peach and Olive Pollen Non-Specific Lipid Transfer Protein Allergy and HLA Class II Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167755








