Identification of Salivary Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Non-Invasive Diagnosis and Proactive Monitoring of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
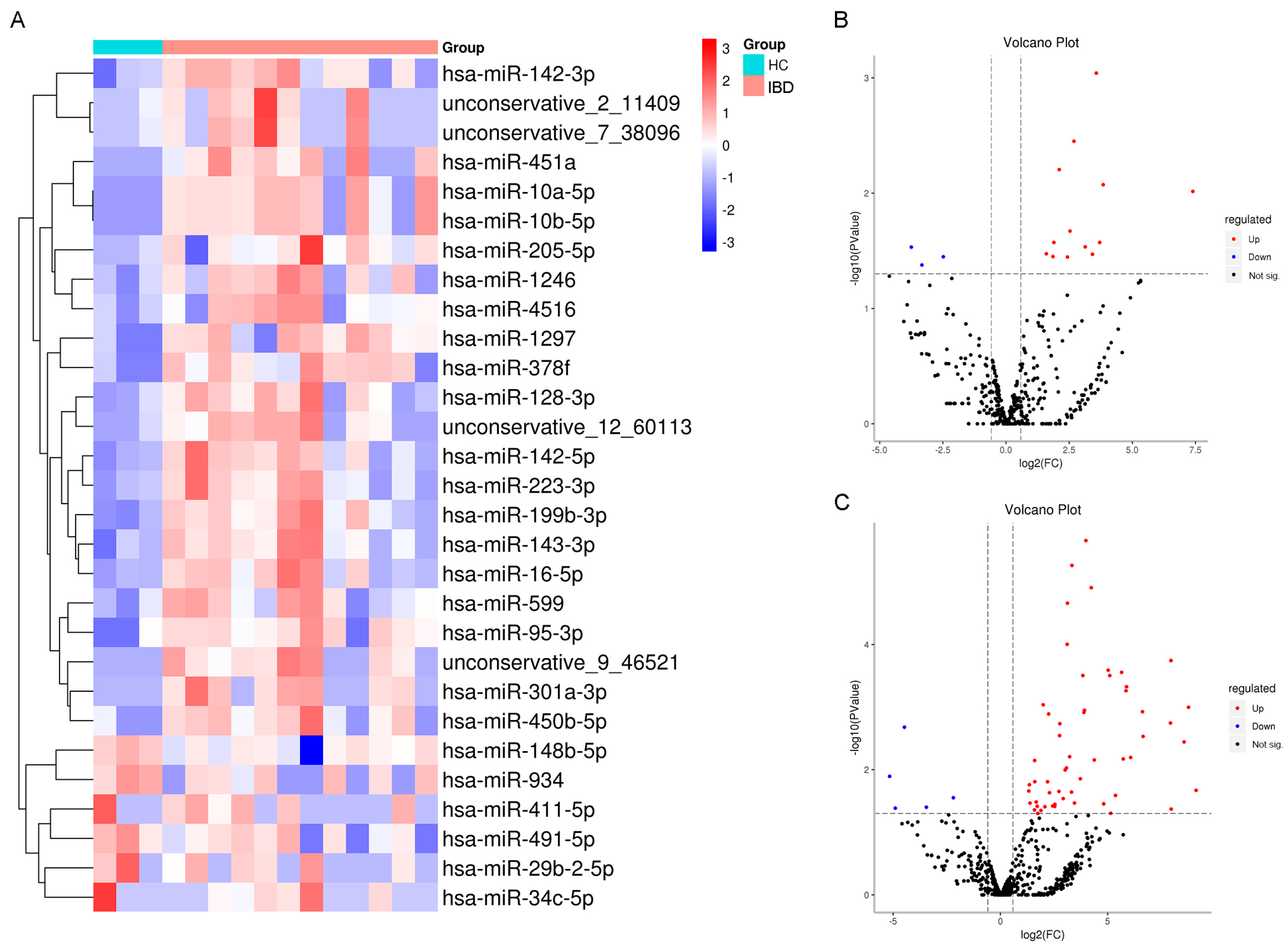
2.1. Identifying Expression Patterns of Salivary Exosomal miRNAs in IBD
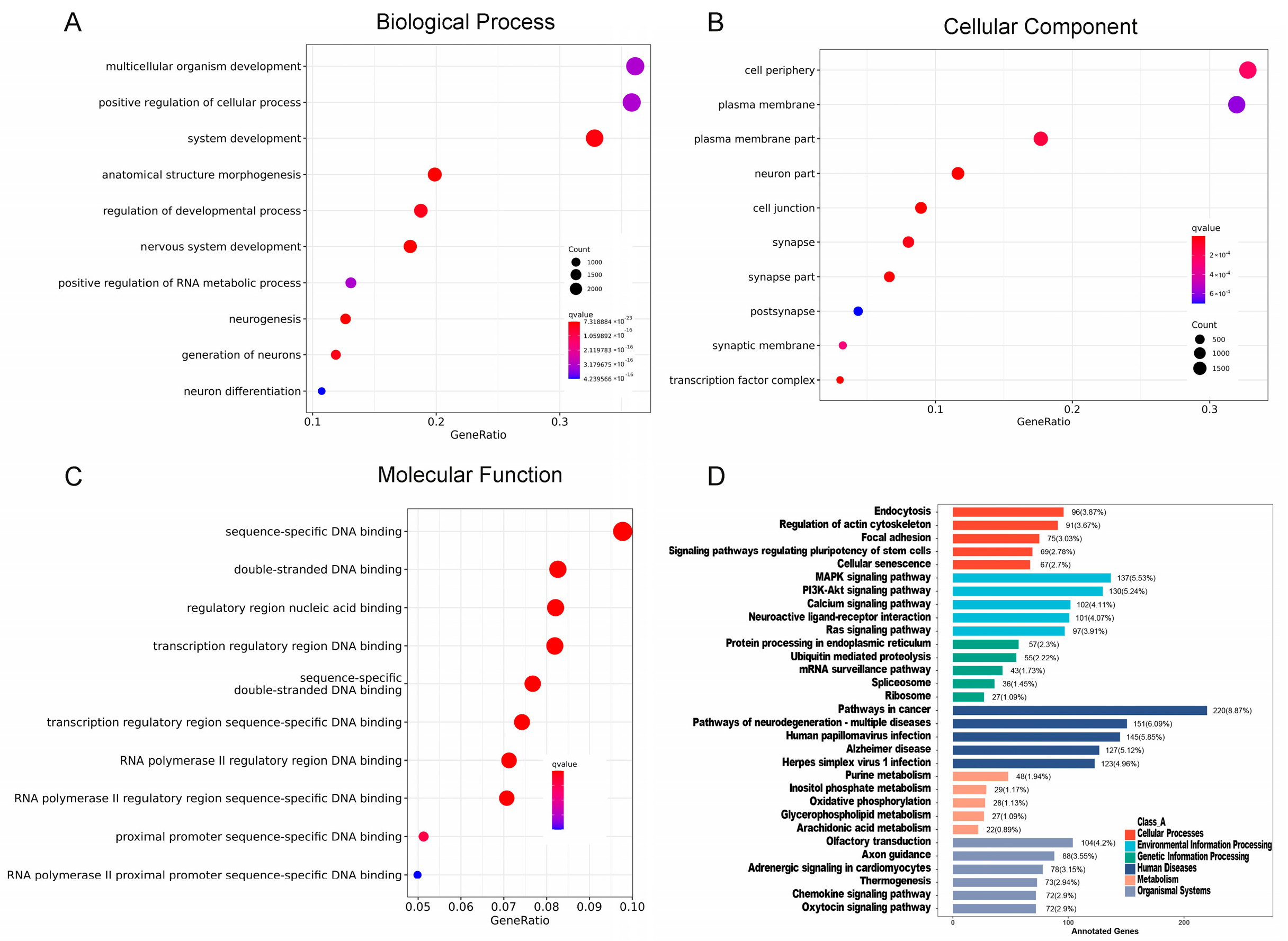
2.2. Functional Analysis of Differentially Expressed miRNAs (DEMs) of Salivary Exosomes
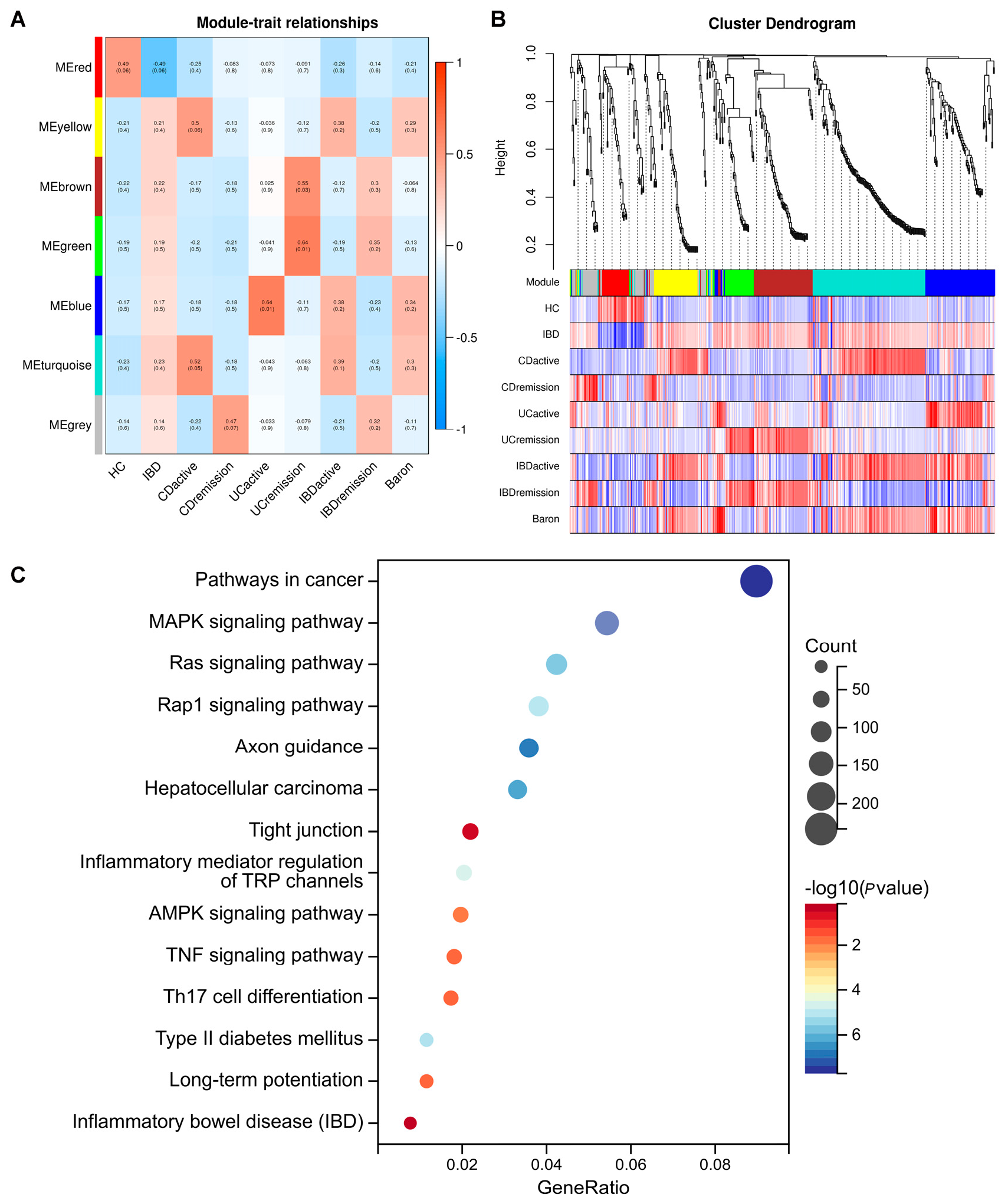
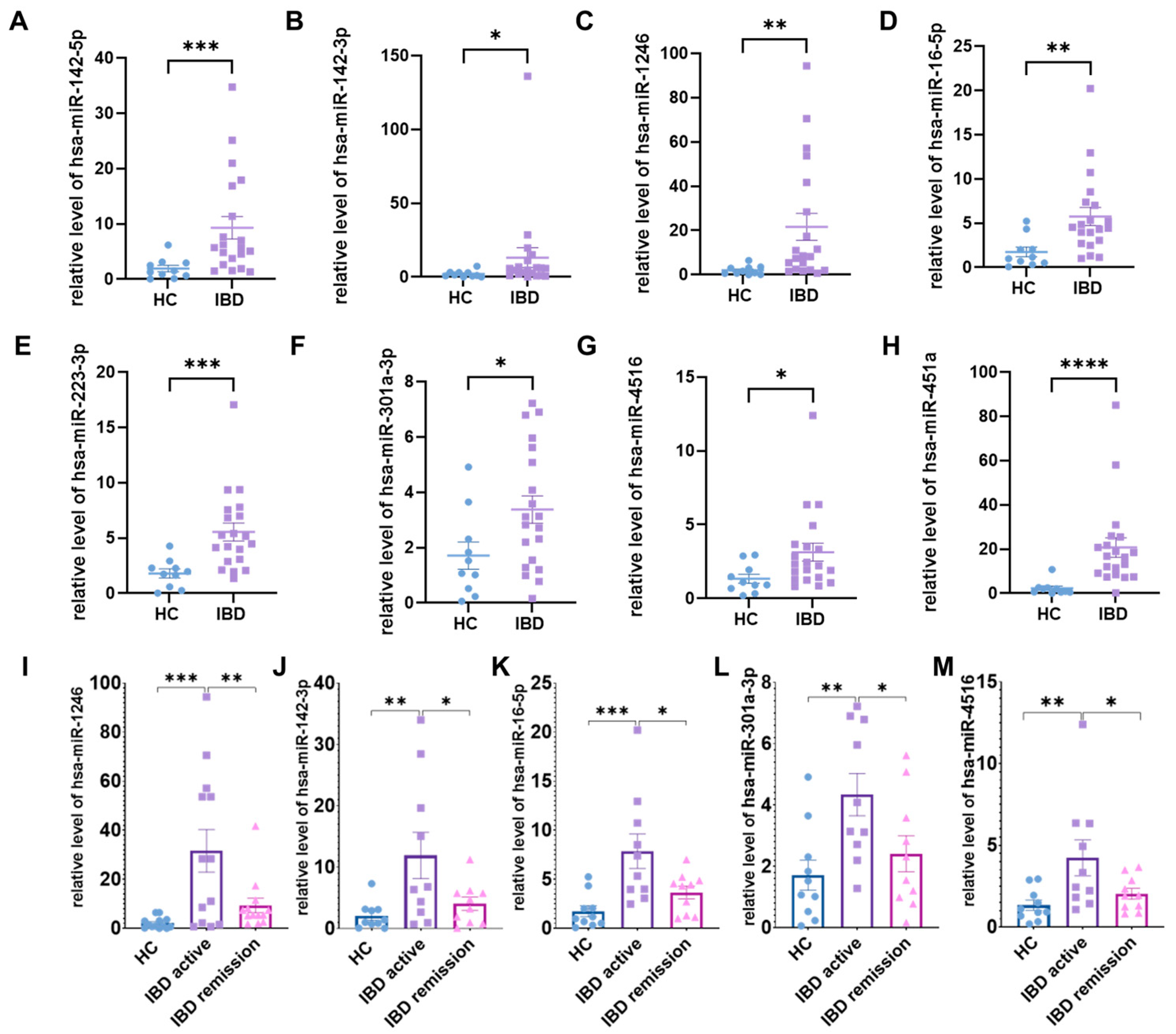
2.3. Identification of the Salivary Exosomal miRNAs Signature Correlated with IBD Disease Activity
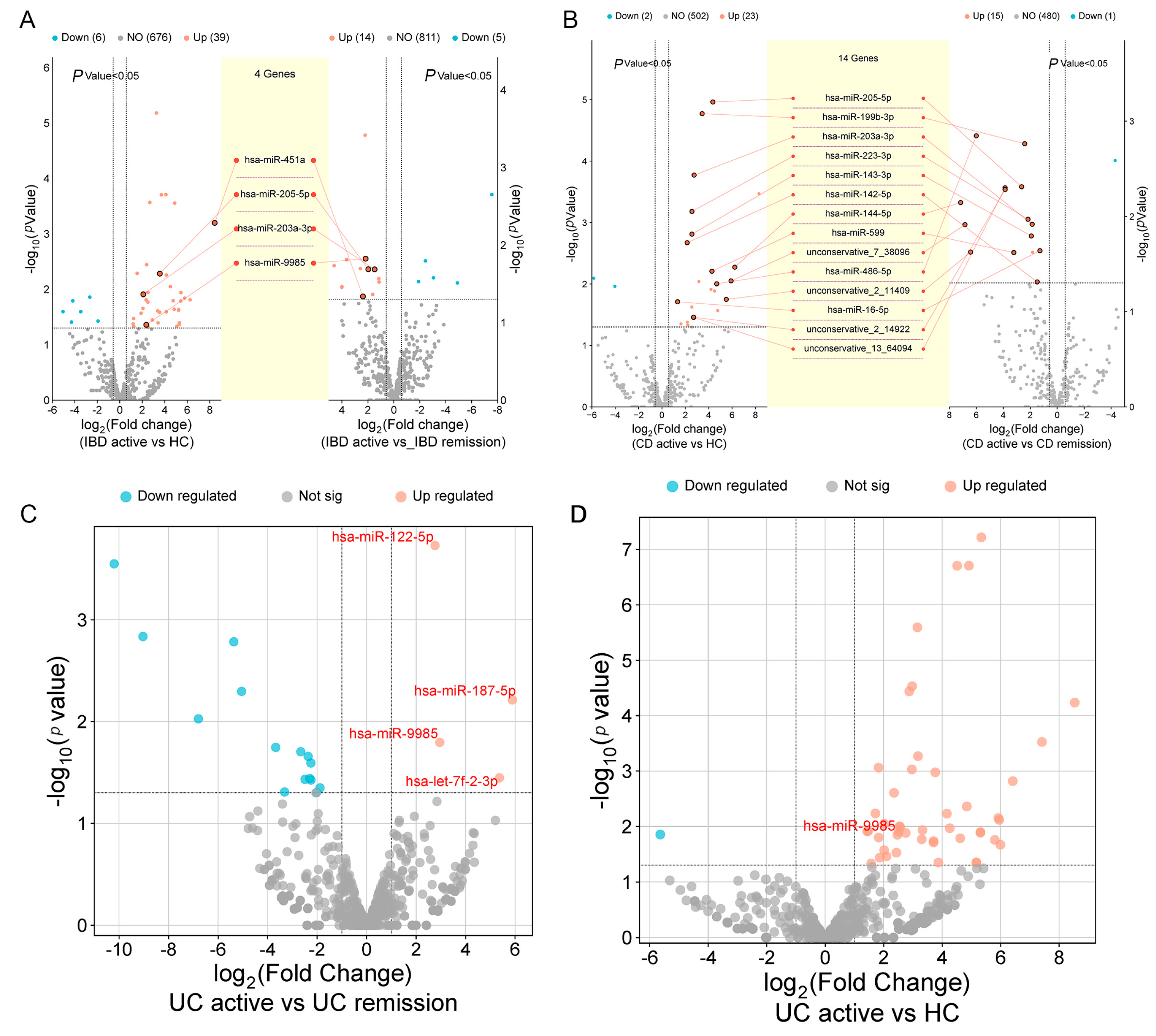
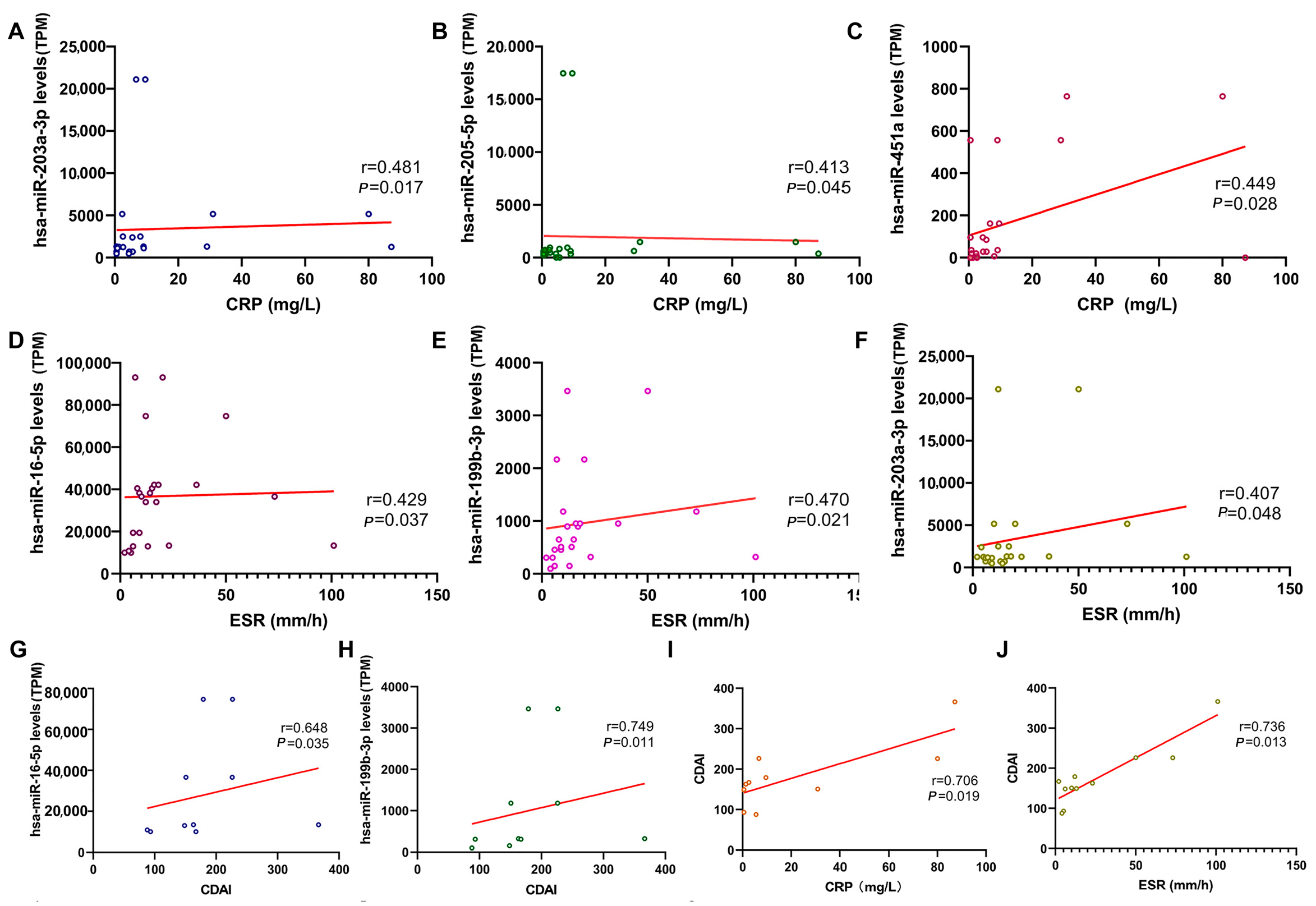
2.4. Correlation Between Salivary Exosomal miRNAs with Clinical Parameters
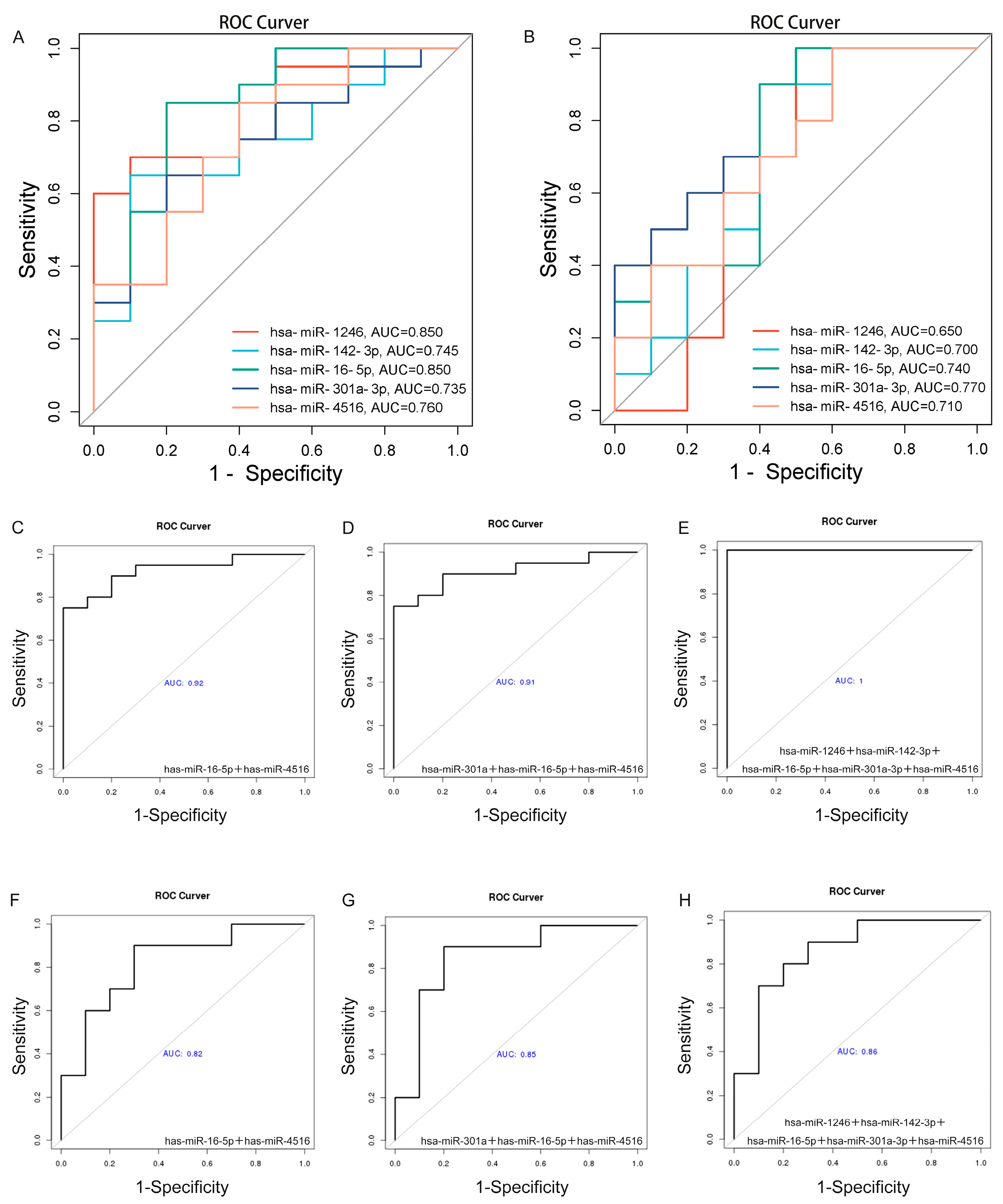
2.5. Validation Analysis of Salivary Exosomal miRNAs in Independent Cohort
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. IBD Diagnosis and Activity
4.2. Cohort for Extraction of Salivary Exosomal miRNAs and Clinical Information
4.3. Western Blot
4.4. Extraction and Classification of Salivary Exosomes
4.5. Exosomal RNA Isolation and RNA Analyses
4.6. The Preparation and Sequencing of the Library
4.7. Profiling miRNA Expression and Comparative Analysis
4.8. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4.9. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
4.10. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.11. Statistical Analysis
4.12. Data and Code Availability
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel diseases |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| HC | Healthy control |
| MiRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| NTA | Nanoparticle tracking analysis |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| WGCNA | Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis |
| DEMs | Differentially expressed miRNAs |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| qRT-PCR | Real-Time Quantitative PCR |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
References
- Argollo, M.; Gilardi, D.; Peyrin-Biroulet, C.; Chabot, J.F.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Comorbidities in inflammatory bowel disease: A call for action. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, F.; Langner, C.; Driessen, A.; Ensari, A.; Geboes, K.; Mantzaris, G.J.; Villanacci, V.; Becheanu, G.; Borralho Nunes, P.; Cathomas, G.; et al. European consensus on the histopathology of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 827–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, S.; Van Assche, G.; Rutgeerts, P. Laboratory markers in IBD: Useful, magic, or unnecessary toys? Gut 2006, 55, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, H.S.; Fiocchi, C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: Current state of the art. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crunkhorn, S. Improving liquid biopsy for cancer detection. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.; Ganeshalingam, J.; Wan, J.C.M. The future of liquid biopsy. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Casati, S.; Goldoni, R.; Thomaz, D.V.; Kehr, N.S.; Galimberti, D.; Del Fabbro, M.; Tartaglia, G.M. Salivary biomarkers: Novel non-invasive tools to diagnose chronic inflammation. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Bai, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, X.; Ying, B. Promising applications of human-derived saliva biomarker testing in clinical diagnostics. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Z.; Cheng, X.Q.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, P.; Yi, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X.D. Saliva in the diagnosis of diseases. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 8, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczeklik, K.; Krzyściak, W.; Cibor, D.; Domagała-Rodacka, R.; Pytko-Polończyk, J.; Mach, T.; Owczarek, D. Markers of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in the serum and saliva of patients with active Crohn disease. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2018, 128, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enver, A.; Ozmeric, N.; Isler, S.C.; Toruner, M.; Fidan, C.; Demirci, G.; Elgun, S.; Silva, A. Evaluation of periodontal status and cytokine levels in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, J.S.; Attumi, T.; Opekun, A.R.; Abraham, B.; Hou, J.; Shelby, H.; Graham, D.Y.; Streckfus, C.; Klein, J.R. MicroRNA signatures differentiate Crohn’s disease from ulcerative colitis. BMC Immunol. 2015, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijakowski, K.; Surdacka, A. Salivary Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jia, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, W. Salivary Exosomes: Emerging Roles in Systemic Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, V.; O’Brien, M.H.; Yadav, S. High-Quality and High-Yield RNA Extraction Method from Whole Human Saliva. Biomark. Insights 2020, 15, 1177271920929705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Gu, J.; Xu, W.; Cai, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Hefley, B.; Escandon, P.; Nicholas, S.E.; Karamichos, D. Salivary Exosomes in Health and Disease: Future Prospects in the Eye. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshmi, B.; Cheshomi, H. Salivary exosomes: Properties, medical applications, and isolation methods. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6295–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Fu, W.; Yi, J.; Wang, J.; Du, G. The biology, function, and applications of exosomes in cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2783–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Ni, J.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L.Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.D.; Fang, X.; Wang, P.; Pan, H.F. Exosomes as biomarkers and therapeutic delivery for autoimmune diseases: Opportunities and challenges. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; You, P.; Sun, S.; Lin, J.; Chen, N. Salivary exosomal PSMA7: A promising biomarker of inflammatory bowel disease. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.A.; Ludwig, R.G.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Brandão, B.B.; Kahn, C.R. Extracellular miRNAs: From Biomarkers to Mediators of Physiology and Disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 656–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, L.; Zhu, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Wei, R.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, G.; Li, P.; et al. Evaluation of circulating small extracellular vesicles derived miRNAs as biomarkers of early colon cancer: A comparison with plasma total miRNAs. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1643670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martin, R.; Wang, G.; Brandão, B.B.; Zanotto, T.M.; Shah, S.; Kumar Patel, S.; Schilling, B.; Kahn, C.R. MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention. Nature 2022, 601, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Lin, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wang, L.; Durante, K.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. A signature of saliva-derived exosomal small RNAs as predicting biomarker for esophageal carcinoma: A multicenter prospective study. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, H.; Deng, W.; Lin, W.; Li, K.; Xiong, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, F.; Ma, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Evaluation of Salivary Exosomal Chimeric GOLM1-NAA35 RNA as a Potential Biomarker in Esophageal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3035–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jing, J.; Zhou, C.; Fan, Y. Emerging roles of exosomes in oral diseases progression. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2024, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, T.; Tomofuji, T.; Maruyama, T.; Yoneda, T.; Ekuni, D.; Azuma, T.; Miyai, H.; Mizuno, H.; Kato, H.; Tsutsumi, K.; et al. miR-1246 and miR-4644 in salivary exosome as potential biomarkers for pancreatobiliary tract cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2375–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Lu, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, B.; Li, N.; Tang, B. A portable point-of-care testing system to diagnose lung cancer through the detection of exosomal miRNA in urine and saliva. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8968–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Akanyibah, F.A.; Xia, Y.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Mao, F.; Liang, Y. Emerging role of small RNAs in inflammatory bowel disease and associated colorectal cancer (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 55, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocansey, D.K.W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Mao, F. Exosome-mediated effects and applications in inflammatory bowel disease. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2020, 95, 1287–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Eisenhut, M.; Shin, J.I. IBD immunopathogenesis: A comprehensive review of inflammatory molecules. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.G. The global burden of IBD: From 2015 to 2025. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ye, C.; Wu, Y.; Yang, P.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. Exosomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: What Have We Learned So Far? Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhashi, S.; Feldbrügge, L.; Csizmadia, E.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Robson, S.C.; Moss, A.C. Luminal Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Exhibit Proinflammatory Effects on Epithelial Cells and Macrophages. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Jin, Y.; Shao, C.; Fan, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, G. Serum exosomal pregnancy zone protein as a promising biomarker in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2021, 26, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Tang, A.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, Z.; Shen, S. Inhibition of lncRNA NEAT1 suppresses the inflammatory response in IBD by modulating the intestinal epithelial barrier and by exosome-mediated polarization of macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, S.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Yumiseba, S.; Yang, J.D.; Hariri, R.; Ye, Q.; He, S.; et al. Characterization of human placenta-derived exosome (pExo) as a potential osteoarthritis disease modifying therapeutic. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Qing, Q.; Pan, Q.; Hu, M.; Yu, H.; Yue, X. Serum exosomal miR-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogler, G.; Singh, A.; Kavanaugh, A.; Rubin, D.T. Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Concepts, Treatment, and Implications for Disease Management. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1118–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K. The oral-gut axis in IBD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, D.; Boccalari, E.; Di Stasio, D.; Della Vella, F.; Carinci, F.; Lucchese, A.; Petruzzi, M. Prevalence of Oral Lesions and Correlation with Intestinal Symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, T.; Chen, N.; Chen, F. Dysbiosis and Ecotypes of the Salivary Microbiome Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and the Assistance in Diagnosis of Diseases Using Oral Bacterial Profiles. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zang, S.Q.; Wei, J.; Yu, H.C.; Yang, Z.; Wu, H.M.; Kang, Y.; Tao, H.; Yang, M.F.; Jin, L.; et al. High-throughput sequencing provides insights into oral microbiota dysbiosis in association with inflammatory bowel disease. Genomics 2021, 113, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Saliva Diagnostics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 15, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmerhorst, E.J.; Oppenheim, F.G. Saliva: A dynamic proteome. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.; Lin, J. MicroRNA in inflammatory bowel disease: Translational research and clinical implication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12274–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S.; Zhou, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Zhao, L. Extracellular vesicles isolated by size-exclusion chromatography present suitability for RNomics analysis in plasma. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cully, M. Exosome-based candidates move into the clinic. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.; Man Law, I.K.; Pothoulakis, C. Role and mechanisms of exosomal miRNAs in IBD pathophysiology. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G646–G654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polytarchou, C.; Oikonomopoulos, A.; Mahurkar, S.; Touroutoglou, A.; Koukos, G.; Hommes, D.W.; Iliopoulos, D. Assessment of Circulating MicroRNAs for the Diagnosis and Disease Activity Evaluation in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis by Using the Nanostring Technology. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönauen, K.; Le, N.; von Arnim, U.; Schulz, C.; Malfertheiner, P.; Link, A. Circulating and Fecal microRNAs as Biomarkers for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, J.S.; Montufar-Solis, D.; Vigneswaran, N.; Klein, J.R. Selective Upregulation of microRNA Expression in Peripheral Blood Leukocytes in IL-10−/− Mice Precedes Expression in the Colon. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 5834–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-T.; Zheng, X.-B.; Fan, D.-J.; Yao, Q.-Q.; Hu, J.-C.; Lian, L.; Wu, X.-J.; Lan, P.; He, X.-S. MicroRNA-143 Targets ATG2B to Inhibit Autophagy and Increase Inflammatory Responses in Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, H.; Yan, S.; Ruijin, W.; Mingming, S.; Leilei, F.; Wei, W.; Changqin, L.; Maochun, T.; Zhong, L.; Ping, W.; et al. miR-301a promotes intestinal mucosal inflammation through induction of IL-17A and TNF-α in IBD. Gut 2016, 65, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yu, T.; Shi, Y.; Ma, C.; Yang, W.; Fang, L.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Xiao, F.; Guo, F.; et al. MicroRNA 301A Promotes Intestinal Inflammation and Colitis-Associated Cancer Development by Inhibiting BTG1. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1434–1448.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krissansen, G.W.; Yang, Y.; McQueen, F.M.; Leung, E.; Peek, D.; Chan, Y.C.; Print, C.; Dalbeth, N.; Williams, M.; Fraser, A.G. Overexpression of miR-595 and miR-1246 in the Sera of Patients with Active Forms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdier, J.; Breunig, I.R.; Ohse, M.C.; Roubrocks, S.; Kleinfeld, S.; Roy, S.; Streetz, K.; Trautwein, C.; Roderburg, C.; Sellge, G. Faecal Micro-RNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Fu, H.; Kuang, S.; He, F.; Zhang, M.; Shen, Z.; Qin, W.; Lin, Z.; Huang, S. Exosomes derived from 3D-cultured MSCs improve therapeutic effects in periodontitis and experimental colitis and restore the Th17 cell/Treg balance in inflamed periodontium. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Gao, J.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, K. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes loaded miR-451a targets ATF2 to improve rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 127, 111365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J.; Harp, K.O.; Bashi, A.; Hood, J.L.; Botchway, F.; Wilson, M.D.; Thompson, W.E.; Stiles, J.K.; Driss, A. MiR-451a and let-7i-5p loaded extracellular vesicles attenuate heme-induced inflammation in hiPSC-derived endothelial cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1082414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moret-Tatay, I.; Cerrillo, E.; Hervás, D.; Iborra, M.; Sáez-González, E.; Forment, J.; Tortosa, L.; Nos, P.; Gadea, J.; Beltrán, B. Specific Plasma MicroRNA Signatures in Predicting and Confirming Crohn’s Disease Recurrence: Role and Pathogenic Implications. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, A.; Light, D.; Lamm, A.T. QsRNA-seq: A method for high-throughput profiling and quantifying small RNAs. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Description of Validation Cohort | Total | UC | CD | Control | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Patients (no. %) | 120, 100% | 60, 50% | 42, 35% | 18, 15% | |
| Sex (f/m) | 49/71 | 28/32 | 12/30 | 9/9 | ||
| Age (mean + SD) | 40 ± 16.5 | 46.4 ± 14.6 | 32.8 ± 16.2 | |||
| Clinical Course (year, mean + SD) | 6.1 ± 5.7 | 6.6 ± 5.9 | 5.5 ± 5.5 | |||
| Active | Patients (no. %) | 53, 100% | 37, 69.8% | 16, 30.2% | ||
| Sex (f/m) | 23/30 | 16/21 | 7/9 | |||
| Age (mean + SD) | 40 ± 15 | 44.3 ± 14.0 | 30.8 ± 14.9 | |||
| Clinical Course (year, mean + SD) | 5.6 ± 5.2 | 6.3 ± 5.7 | 4.2 ± 3.6 | |||
| Mayo (mean + SD) | 4.5 ± 2.0 | |||||
| CDAI (mean + SD) | 177.2 ± 69.8 | |||||
| Serum (mean + SD) | Patients (no. %) | 45, 100% | 29, 64.4% | 16, 35.6% | ||
| CRP (mg/L) | 19.0 ± 29.5 | 14.3 ± 23.5 | 27.6 ± 37.4 | |||
| Patients (no. %) | 43, 100% | 27, 60.0% | 16, 40.0% | |||
| ESR (mm/h) | 25.6 ± 20.6 | 28.7 ± 23.3 | 20.5 ± 14.1 | |||
| Remission | Patients (no. %) | 49, 100% | 23, 46.9% | 26, 53.1% | ||
| Sex (f/m) | 17/32 | 12/11 | 5/21 | |||
| Age (mean + SD) | 41.4 ± 17.9 | 49.7 ± 15.2 | 34.1 ± 17.1 | |||
| Clinical Course (year, mean + SD) | 6.7 ± 6.2 | 7.1 ± 6.3 | 6.4 ± 6.3 | |||
| Mayo (mean + SD) | 0.4 ± 0.8 | |||||
| CDAI (mean + SD) | 40.1 ± 28.4 | |||||
| Serum (mean + SD) | Patients (no. %) | 41, 100% | 15, 36.6% | 26, 63.4% | ||
| CRP (mg/L) | 1.4 ± 1.3 | 1.2 ± 1.2 | 1.5 ± 1.3 | |||
| Patients (no. %) | 39, 100% | 14, 35.9% | 25, 64.1% | |||
| ESR (mm/h) | 9.5 ± 9.4 | 11.8 ± 11.4 | 8.2 ± 8.1 | |||
| Treatment | Corticosteroids (no. %) | 5, 100% | 3, 60% | 2, 40% | ||
| 5-ASA (no. %) | 52, 100% | 40, 76.9% | 12, 23.1% | |||
| Immunosuppressive treatment (no. %) | 6, 100% | 5, 83.3% | 1, 16.7% | |||
| TNFα Inhibitor (no. %) | 31, 100% | 13, 41.9% | 18, 58.1% | |||
| IL-12/23 Inhibitor (no. %) | 14, 100% | 1, 7.1% | 13, 92.9% | |||
| Integrin Inhibitor (no. %) | 16, 100% | 10, 62.5% | 6, 37.5% | |||
| Surgery (no. %) | 0% | 0% | 0% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, N. Identification of Salivary Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Non-Invasive Diagnosis and Proactive Monitoring of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167750
Yang C, Chen J, Zhao Y, Xu Y, Wu J, Xu J, Chen F, Chen N. Identification of Salivary Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Non-Invasive Diagnosis and Proactive Monitoring of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167750
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Congyi, Jingyi Chen, Yuzheng Zhao, Yalan Xu, Jushan Wu, Jun Xu, Feng Chen, and Ning Chen. 2025. "Identification of Salivary Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Non-Invasive Diagnosis and Proactive Monitoring of Inflammatory Bowel Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167750
APA StyleYang, C., Chen, J., Zhao, Y., Xu, Y., Wu, J., Xu, J., Chen, F., & Chen, N. (2025). Identification of Salivary Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Non-Invasive Diagnosis and Proactive Monitoring of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167750






