Cobalt Ion Removal by Activated Carbon and Biochar Derived from Sargassum sp.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the AC/BC Samples
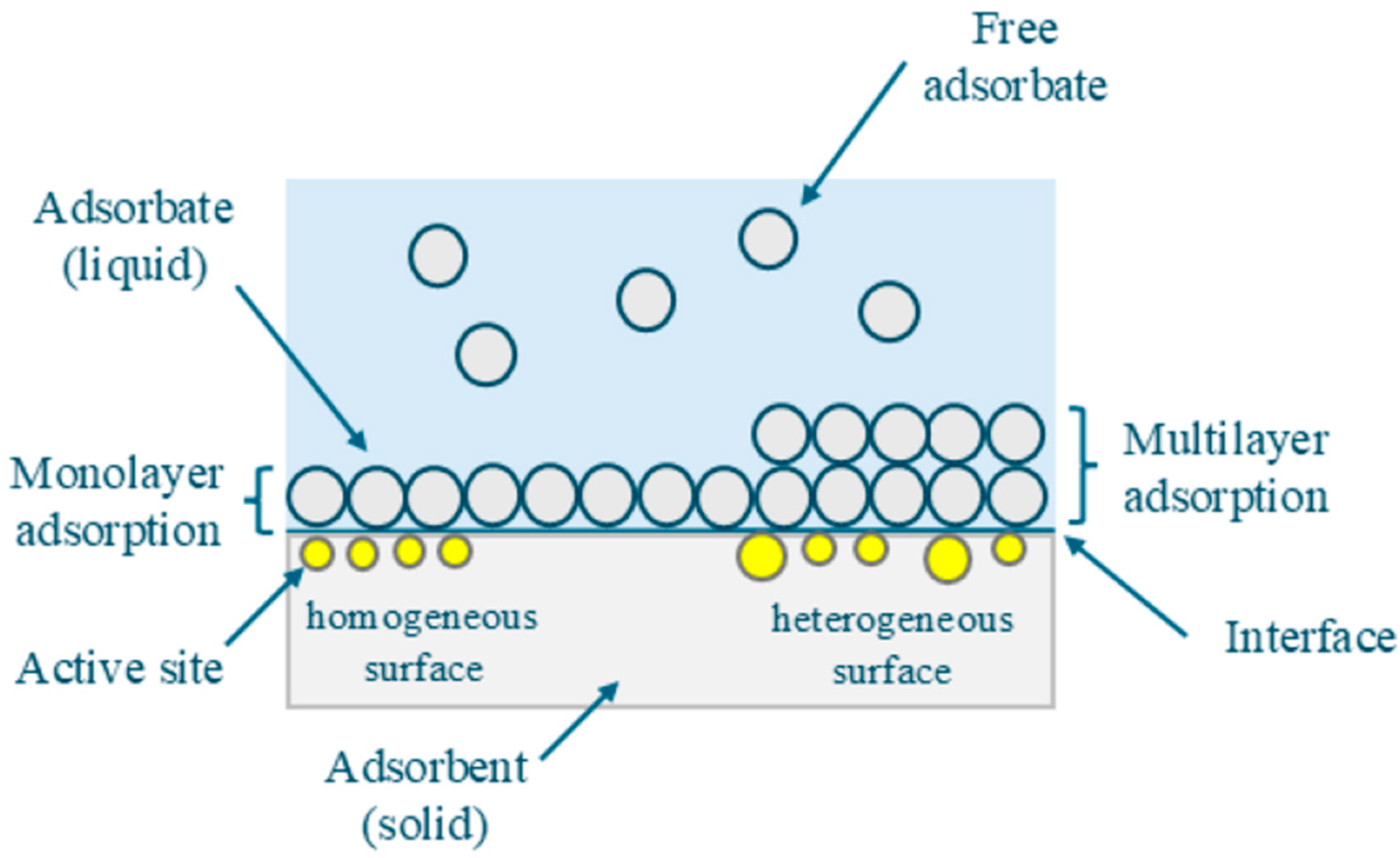
2.2. Adsorption Test
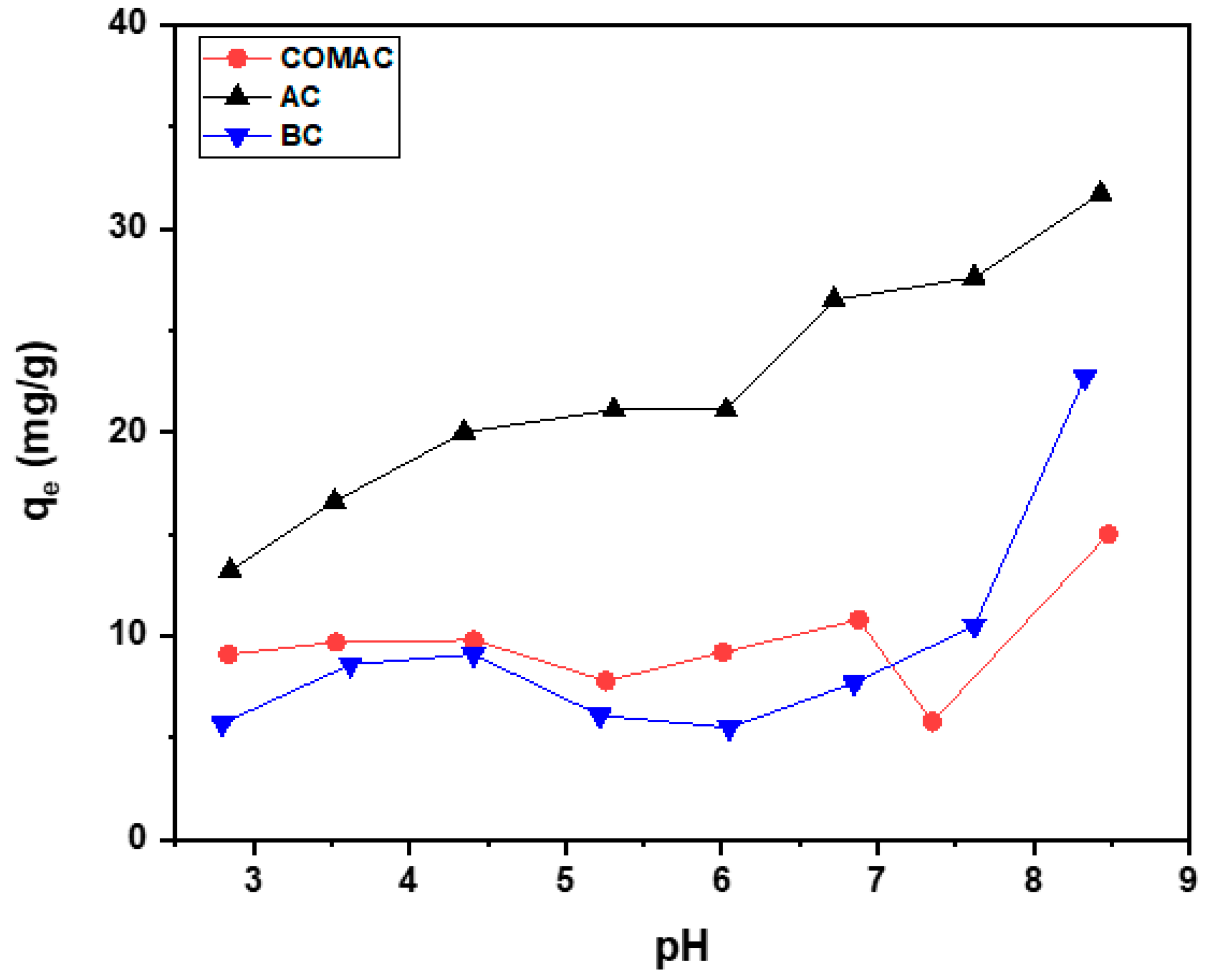
2.2.1. Influence of pH
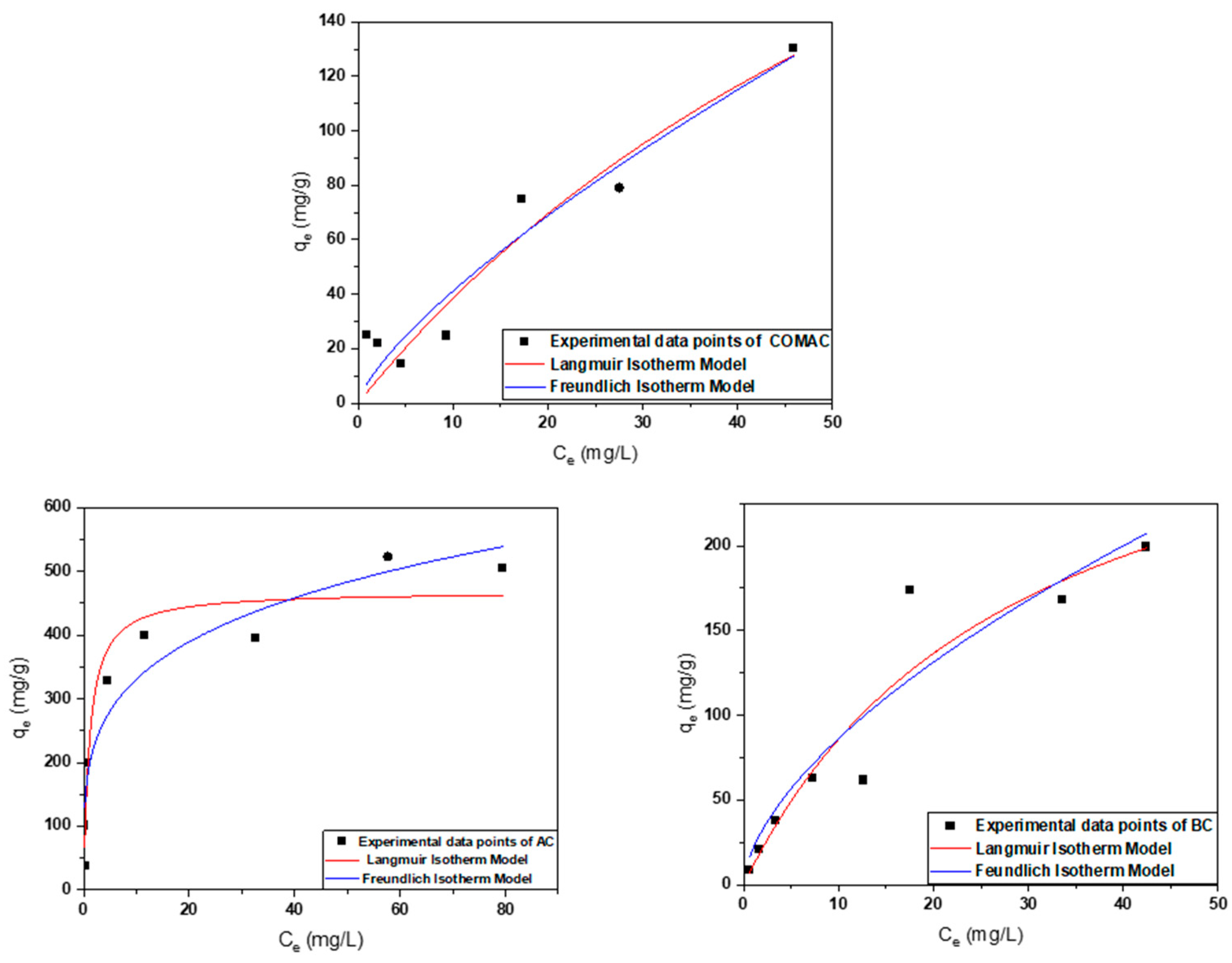
2.2.2. Effect of Initial Cobalt Concentration and Adsorption Isotherm Investigation
2.2.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Characterization of Carbonaceous Material
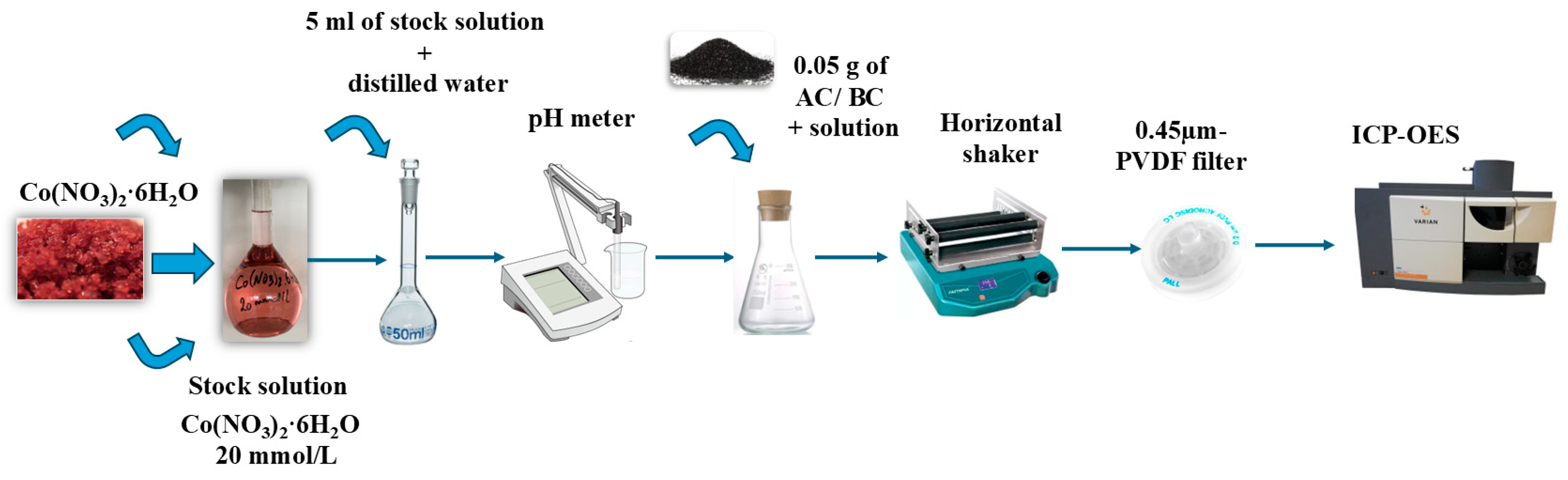
3.3. Adsorption Studies
3.3.1. Effect of pH Solution
3.3.2. Effect of the Initial Metal Concentration
3.3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
- The Langmuir isotherm model
- The Freundlich isotherm model
3.3.4. Effect of AC/BC Dose
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Activated Carbon |
| BC | Biochar |
| COMAC | Commercial Activated Carbon |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller Isotherm |
| ICP-OES | Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer |
| pHpzc | pH at the point of zero charge |
| Ce | equilibrium metal concentration |
| Ci | initial metal concentration |
| KL | Langmuir equilibrium constant |
| qm | Maximum monolayer adsorption capacity |
| Kf | Freundlich constant |
| n | heterogeneity factor |
References
- Lichtfouse, E.; Schwarzbauer, J.; Robert, D. Environmental Chemistry: Green Chemistry and Pollutants in Ecosystems; Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, I.R.; Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Ahmed, A. Removal of Lead Ions (Pb2+) from Water and Wastewater: A Review on the Low-Cost Adsorbents. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K. A Review on the Adsorption of Heavy Metals by Clay Minerals, with Special Focus on the Past Decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, D.; Palet, C.; Costas, A.; Cristóbal, A. Agro-Industrial Waste as Potential Heavy Metal Adsorbents and Subsequent Safe Disposal of Spent Adsorbents. Water 2022, 14, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkanen, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A Review on Modification Methods to Cellulose-Based Adsorbents to Improve Adsorption Capacity. Water Res. 2016, 91, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mishra, S.; Sahu, H. A Review of Activated Carbon to Counteract the Effect of Iron Toxicity on the Environment. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 5, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; Khaled, A.; Abdelwahab, O.; El-Sikaily, A. Treatment of Wastewater Containing Toxic Chromium Using New Activated Carbon Developed from Date Palm Seed. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, N.K.; Moustafa, A.F. Industrial Solid Waste for Heavy Metals Adsorption Features and Challenges; a Review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10235–10253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, Z.; Karim, A.; Karam, A.; Khalloufi, S. Adsorption of Heavy Metals: Mechanisms, Kinetics, and Applications of Various Adsorbents in Wastewater Remediation—A Review. Waste 2023, 1, 775–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hossain, M.F.; Duan, C.; Lu, J.; Tsang, Y.F.; Islam, M.S.; Zhou, Y. Isotherm Models for Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Water—A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, I.; Ismail, A.A.; Al Sayed, F.; Almedolab, A.; Aboelghait, K.M. Biosorption of Heavy Metals Ions in Real Industrial Wastewater Using Peanut Husk as Efficient and Cost Effective Adsorbent. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 6, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Investigation of Adsorption Kinetics and the Isotherm Mechanism of Manganese by Modified Diatomite. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 16402–16409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Upadhyay, U.; Sreedhar, I.; Singh, S.A.; Patel, C.M. A Review on Valorization of Biomass in Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 38, 101602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.K.; Kim, W.H.; Park, J.; Cho, J.; Jeong, T.Y.; Park, P.K. Application of Langmuir and Freundlich Isotherms to Predict Adsorbate Removal Efficiency or Required Amount of Adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radenović, A.; Malina, J. Adsorption Ability of Carbon Black for Nickel Ions Uptake from Aqueous Solution. Hem. Ind. 2013, 67, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnib, M.; Kabbani, A.; Holail, H.; Olama, Z. Heavy Metals Removal Using Activated Carbon, Silica and Silica Activated Carbon Composite. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarinejad, Z.; Dehghani, M.H.; Heidari, M.; Javedan, G.; Ali, I.; Sillanpää, M. Methods for Preparation and Activation of Activated Carbon: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 393–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francoeur, M.; Ferino-Pérez, A.; Yacou, C.; Jean-Marius, C.; Emmanuel, E.; Chérémond, Y.; Jauregui-Haza, U.; Gaspard, S. Activated Carbon Synthetized from Sargassum (sp.) for Adsorption of Caffeine: Understanding the Adsorption Mechanism Using Molecular Modeling. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranguin, R.; Delannoy, M.; Yacou, C.; Jean-Marius, C.; Feidt, C.; Rychen, G.; Gaspard, S. Biochar and Activated Carbons Preparation from Invasive Algae Sargassum spp. For Chlordecone Availability Reduction in Contaminated Soils. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louime, C.; Fortune, J.; Gervais, G. Sargassum Invasion of Coastal Environments: A Growing Concern. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 13, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, S.; Yacou, C.; Jean Marius, C.; Ranguin, R.; Francoeur, M.; Taberna, P.L.; Passe-Coutrin, N.; Gaspard, S. Carbon Materials Prepared from Invading Pelagic Sargassum for Supercapacitors’ Electrodes. Molecules 2023, 28, 5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Teo, T.T.; Balasubramanian, R.; Joshi, U.M. Application of Sargassum Biomass to Remove Heavy Metal Ions from Synthetic Multi-Metal Solutions and Urban Storm Water Runoff. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, R.; Zhao, J.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q. Characterization of H3PO4-Treated Rice Husk Adsorbent and Adsorption of Copper(II) from Aqueous Solution. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 496878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Kaddour, S.; Trari, M. Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Cobalt Adsorption on Apricot Stone Activated Carbon. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; Yu, Q.J.; El Hanandeh, A. Investigation of the Kinetics and Mechanisms of Nickel and Copper Ions Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions by Date Seed Derived Biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.J.; Li, J.Y.; Yuan, J.H.; Xu, R.K. Adsorption of Cu(II) by Biochars Generated from Three Crop Straws. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, V.; Mohanasundaram, S.; Ramaraju, P.; Jeyanthi, J.; Periyasamy, S. Study on the Production, Characterization, and Application of Coconut Fiber Biochar for Effective Removal of Co(II) Ions from Synthetic Wastewater. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 13677–13693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iáñez-Rodríguez, I.; Calero, M.; Blázquez, G.; Martín-Lara, M.Á. Greenhouse Crop Residue and Its Derived Biochar: Potential as Adsorbent of Cobalt from Aqueous Solutions. Water 2020, 12, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallouhi, J.; Varga, M.; Sikora, E.; Gráczer, K.; Bánhidi, O.; Gaspard, S.; Goudou, F.; Viskolcz, B.; Szőri-Dorogházi, E.; Fiser, B. Activated Carbon and Biochar Derived from Sargassum sp. Applied in Polyurethane-Based Materials Development. Polymers 2024, 16, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Matis, K.A. Activated Carbons Produced by Pyrolysis of Waste Potato Peels: Cobaltions Removal by Adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 490, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, E.; Dizge, N.; Sulak, M.T.; Kobya, M. Adsorption Kinetics and Equilibrium of Copper from Aqueous Solutions Using Hazelnut Shell Activated Carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 148, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Galvan, Y.; Minofar, B.; Futera, Z.; Francoeur, M.; Jean-Marius, C.; Brehm, N.; Yacou, C.; Jauregui-Haza, U.J.; Gaspard, S. Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium Using Activated Carbon Produced from Sargassum ssp.: Comparison between Lab Experiments and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Molecules 2022, 27, 6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Shuaib, D.T.; Ndamitso, M.M.; Etsuyankpa, M.B.; Sumaila, A.; Mohammed, U.M.; Nasirudeen, M.B. Adsorption Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies for the Removal of Pb(II), Cd(II), Zn(II) and Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Albizia Lebbeck Pods. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.K. Agricultural Solid Wastes Based Adsorbent Materials in the Remediation of Heavy Metal Ions from Water and Wastewater by Adsorption: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerçel, Ö.; Gerçel, H.F. Adsorption of Lead(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Activated Carbon Prepared from Biomass Plant Material of Euphorbia rigida. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 132, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; Hanandeh, A.E.; Yu, Q. Influence of Pyrolysis Conditions on Surface Characteristics and Methylene Blue Adsorption of Biochar Derived from Date Seed Biomass. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Hao, P.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, L. Effect of Oxidation-Induced Aging on the Adsorption and Co-Adsorption of Tetracycline and Cu2+ onto Biochar. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 673, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, A.; Pagnanelli, F.; Lodi, A.; Solisio, C.; Veglio, F. Biosorption of heavy metals by Sphaerotilus natans: An equilibrium study at different pH and biomass concentrations. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 60, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momčilović, M.; Purenović, M.; Bojić, A.; Zarubica, A.; Randelovid, M. Removal of Lead(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Pine Cone Activated Carbon. Desalination 2011, 276, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olupot, P.W.; Wakatuntu, J.; Turyasingura, M.; Jjagwe, J.; Menya, E.; Okure, M. Optimization of Heavy Metal Removal by Activated Carbon Obtained as a Co-Product from Fast Pyrolysis of Rice Husks. Results Mater. 2024, 21, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Huang, D.L.; Liu, Y.G.; Zhang, C.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.M.; Cheng, M.; Gong, X.M.; Wan, J.; Luo, H. Investigating the Adsorption Behavior and the Relative Distribution of Cd2+ Sorption Mechanisms on Biochars by Different Feedstock. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, Y.; Xing, B.; Qin, X.; Zhang, C.; Xia, H. Lead and Cadmium Clean Removal from Wastewater by Sustainable Biochar Derived from Poplar Saw Dust. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Huang, S.; Laird, D.A.; Wang, X.; Meng, Z. Adsorption Behaviour and Mechanisms of Cadmium and Nickel on Rice Straw Biochars in Single- and Binary-Metal Systems. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Dang, J.; Jin, R.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y. Wheat Straws and Corn Straws as Adsorbents for the Removal of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) from Aqueous Solution: Kinetics, Isotherm, and Mechanism. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6003–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.E.; Park, J.H.; Chung, J.W. Comparison of the Lead and Copper Adsorption Capacities of Plant Source Materials and Their Biochars. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Gao, B.; Mosa, A.; Yu, H.; Yin, X.; Bashir, A.; Ghoveisi, H.; Wang, S. Removal of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Biochars Derived from Potassium-Rich Biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thuan, T.; Quynh, B.T.P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Ho, V.T.T.; Bach, L.G. Response Surface Methodology Approach for Optimization of Cu2+, Ni2+ and Pb2+ Adsorption Using KOH-Activated Carbon from Banana Peel. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, P.; Gaspard, S.; Dulormne, M.; Francoeur, M.; Melyon, S.; Hartmeyer, P.; Rychen, G.; Delannoy, M. Antillean Contaminated Soils Amendment with Microwave Prepared Sargassum Biochar: A Promising Solution to Reduce Chlordecone Transfer to Laying Hens and Piglets? Chemosphere 2024, 359, 142282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Galil, E.A.; Rizk, H.E.; Mostafa, A.Z. Production and Characterization of Activated Carbon from Leucaena Plant Wastes for Removal of Some Toxic Metal Ions from Waste Solutions. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 17880–17891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, S.; Salari, M.; Shahrashoub, M.; Zeidabadinejad, A.; Sharma, G.; Sillanpää, M. A Comprehensive Review on Green and Eco-Friendly Nano-Adsorbents for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions: Synthesis, Adsorption Mechanisms, and Applications. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2024, 10, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, P.T.; Chung, P.Y.; Tsang, H.C.; Cheuk-On Tang, J.; Yin-Ming Cheng, G.; Gambari, R.; Chui, C.H.; Lam, K.H. Preparation and Characterization of Bio-Safe Activated Charcoal Derived from Coffee Waste Residue and Its Application for Removal of Lead and Copper Ions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 38839–38847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Isotherm Models: Classification, Physical Meaning, Application and Solving Method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaimee, M.Z.A.; Sarjadi, M.S.; Rahman, M.L. Heavy Metals Removal from Water by Efficient Adsorbents. Water 2021, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic of the Samples | Carbonaceous Materials | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| COMAC | AC | BC | |
| Surface area (m2/g) | 1120 ± 4.5 | 1695 ± 7 | 854 ± 4 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −13.21 ± 0.43 | −20.07 ± 1.71 | −22.80 ± 0.28 |
| FTIR | Functional group | ||
| For all samples (-CH, C-O, C=O, O=C=O, C-H, -OH) | |||
| pH | Adsorbed Amount mg/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| COMAC | AC | BC | |
| 2.8 | 9.1 | 13.2 | 5.7 |
| 3.6 | 9.7 | 16.6 | 8.6 |
| 4.4 | 9.8 | 20.0 | 9.1 |
| 5.2 | 7.8 | 21.1 | 6.1 |
| 6.0 | 9.2 | 21.1 | 5.5 |
| 6.8 | 10.8 | 26.5 | 7.7 |
| 7.6 | 5.8 | 27.6 | 10.5 |
| 8.4 | 15.0 | 31.7 | 22.7 |
| Adsorbent | Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||||
| qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | KF (mg/g) | n | 1/n | R2 | |
| COMAC | 361.23 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 7.45 | 1.35 | 0.74 | 0.91 |
| AC | 468.97 | 0.9 | 0.91 | 192.53 | 4.24 | 0.23 | 0.90 |
| BC | 334.36 | 0.03 | 0.90 | 21.30 | 1.66 | 0.60 | 0.99 |
| Adsorbent | Toxic Metals | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC/Commercial | Co(II) | 361.23 | * |
| AC/Sargassum sp. | Co(II) | 468.97 | * |
| BC/Sargassum sp. | Co(II) | 334.36 | * |
| BC/coconut fiber | Co(II) | 106.8 | [28] |
| BC/Greenhouse Crop Residue | Co(II) | 30.98 | [29] |
| AC/Pine cone | Pb(II) | 27.5 | [40] |
| AC/Rice Husk | Pb(II) | 172.7 | [41] |
| BC/Bamboo | Cd(II) | 73.4 | [42] |
| BC/poplar sawdust | Cd(II) | 49.3 | [43] |
| BC/Rice straw | Cd(II) | 65.4 | [44] |
| AC//Rice Husk | Zn(II) | 128.7 | [41] |
| AC/Wheat Straw | Cr(VI) | 125.6 | [45] |
| BC/Gingko leaf | Cu (II) | 59.9 | [46] |
| BC/cauliflower leaves | Cu (II) | 75.9 | [47] |
| AC/Banana Peels | Ni(II) | 27.4 | [48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mallouhi, J.; Sikora, E.; Gráczer, K.; Bánhidi, O.; Gaspard, S.; Francoeur, M.; Alvarez-Galvan, Y.; Goudou, F.; Viskolcz, B.; Szőri-Dorogházi, E.; et al. Cobalt Ion Removal by Activated Carbon and Biochar Derived from Sargassum sp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167666
Mallouhi J, Sikora E, Gráczer K, Bánhidi O, Gaspard S, Francoeur M, Alvarez-Galvan Y, Goudou F, Viskolcz B, Szőri-Dorogházi E, et al. Cobalt Ion Removal by Activated Carbon and Biochar Derived from Sargassum sp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167666
Chicago/Turabian StyleMallouhi, Julie, Emőke Sikora, Kitti Gráczer, Olivér Bánhidi, Sarra Gaspard, Marckens Francoeur, Yeray Alvarez-Galvan, Francesca Goudou, Béla Viskolcz, Emma Szőri-Dorogházi, and et al. 2025. "Cobalt Ion Removal by Activated Carbon and Biochar Derived from Sargassum sp." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167666
APA StyleMallouhi, J., Sikora, E., Gráczer, K., Bánhidi, O., Gaspard, S., Francoeur, M., Alvarez-Galvan, Y., Goudou, F., Viskolcz, B., Szőri-Dorogházi, E., & Fiser, B. (2025). Cobalt Ion Removal by Activated Carbon and Biochar Derived from Sargassum sp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167666








