Lifetime Variations in Prolactin Expression in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Hippocampal Prl mRNA Detection via qPCR
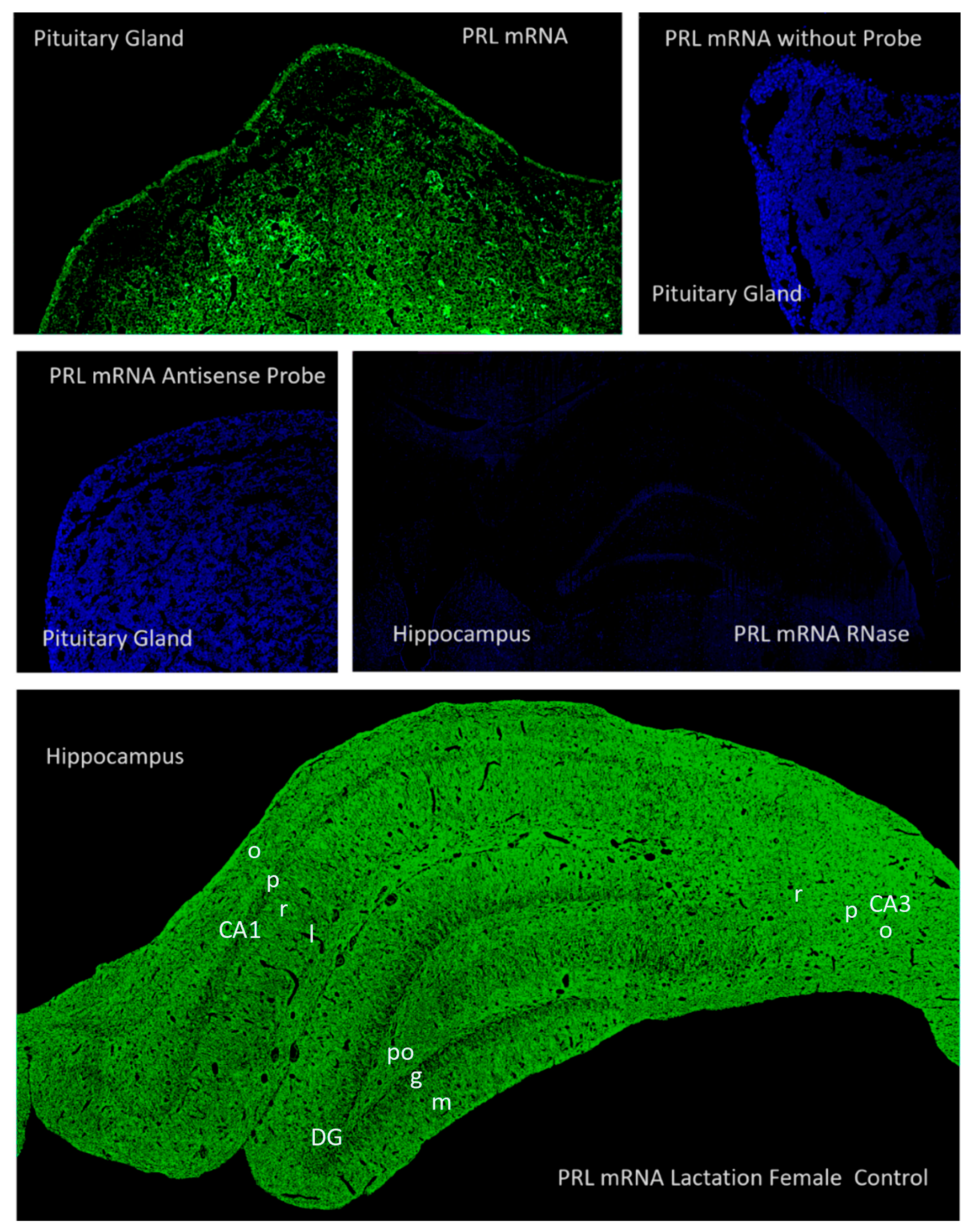
2.2. Hippocampal Prl mRNA Detection via In Situ Hybridization, Densitometric Analysis
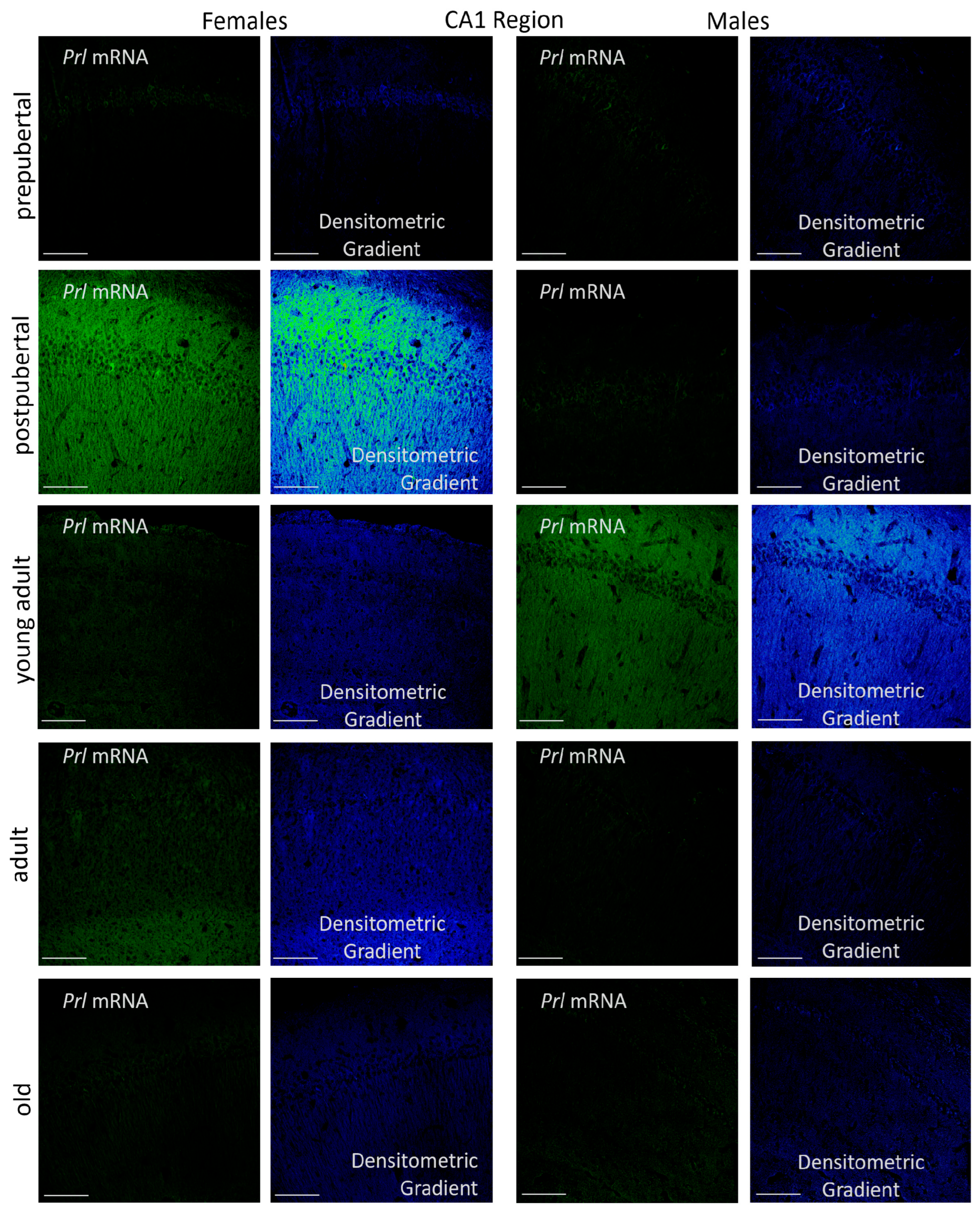
2.3. Prolactin-Synthesizing Cells: Regional Analysis of In Situ Hybridization
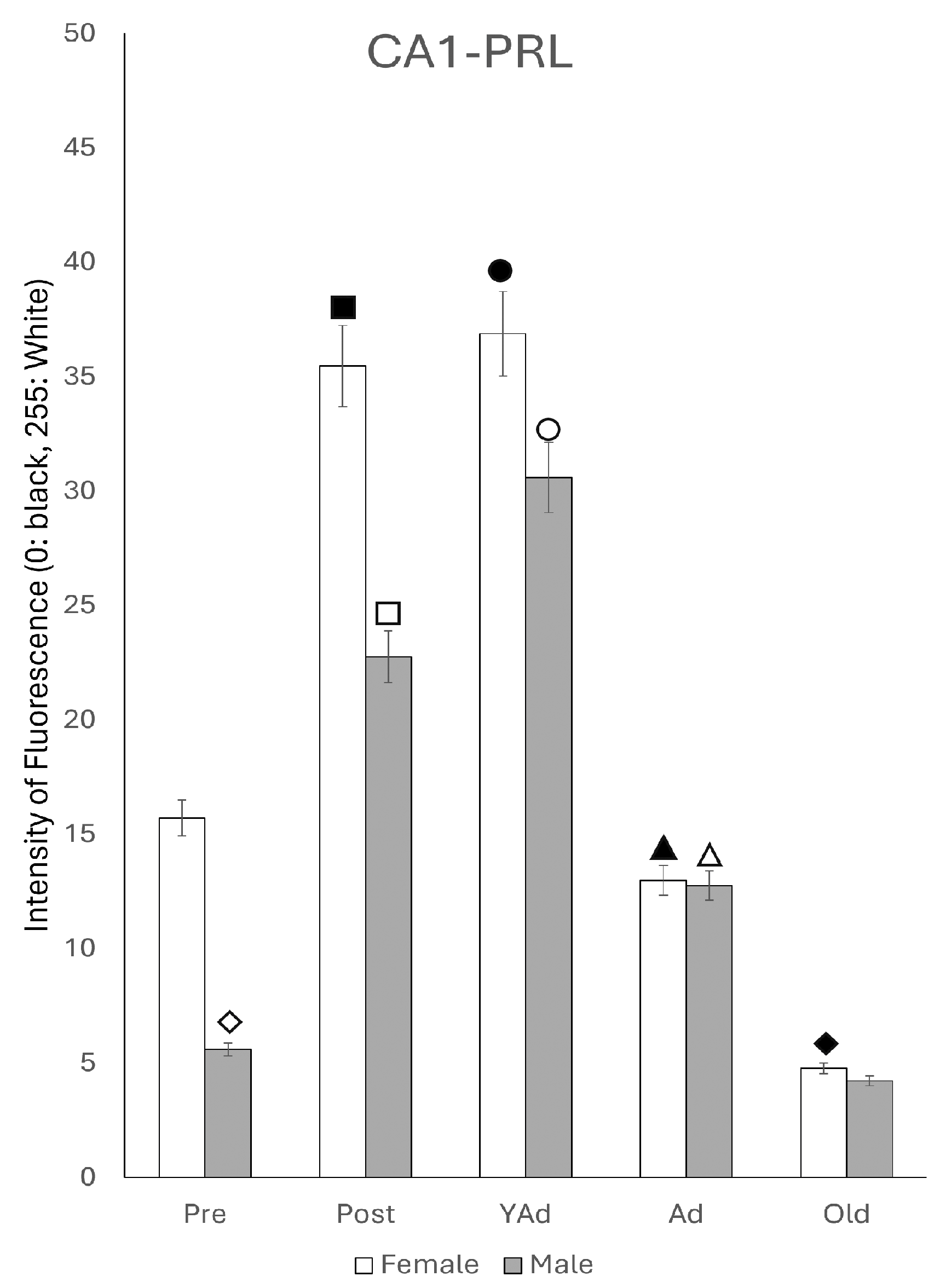
2.3.1. CA1 Region
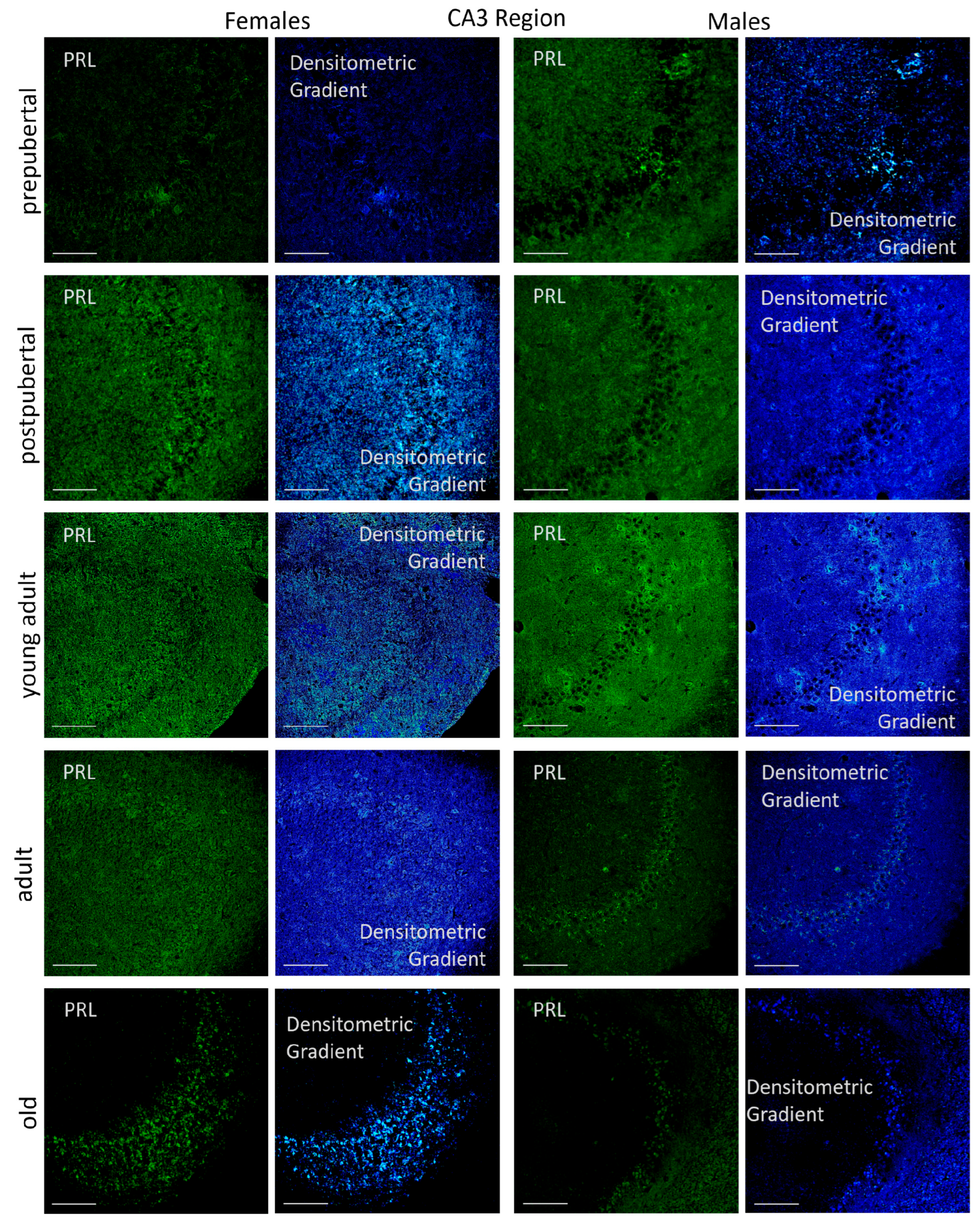
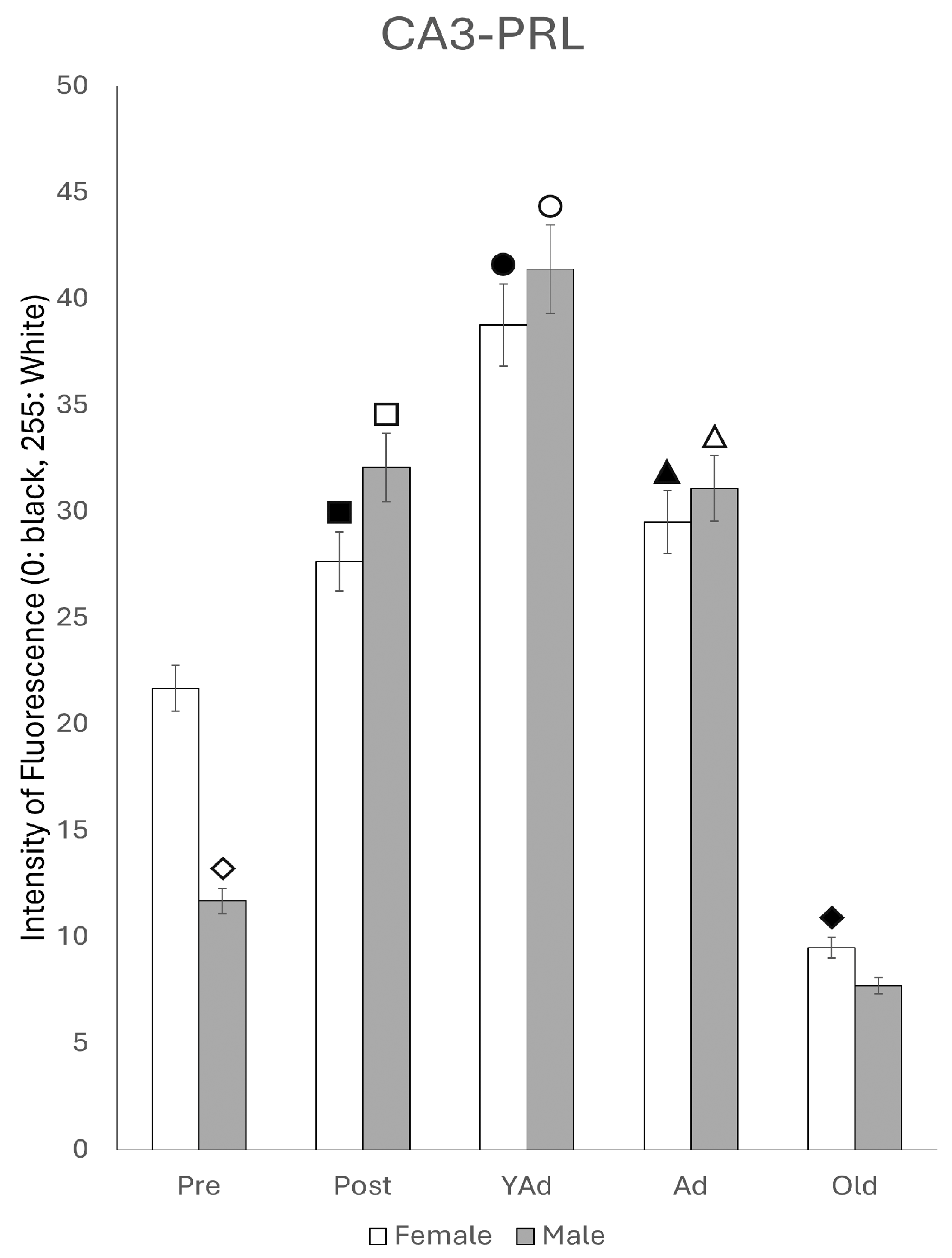
2.3.2. CA3 Region
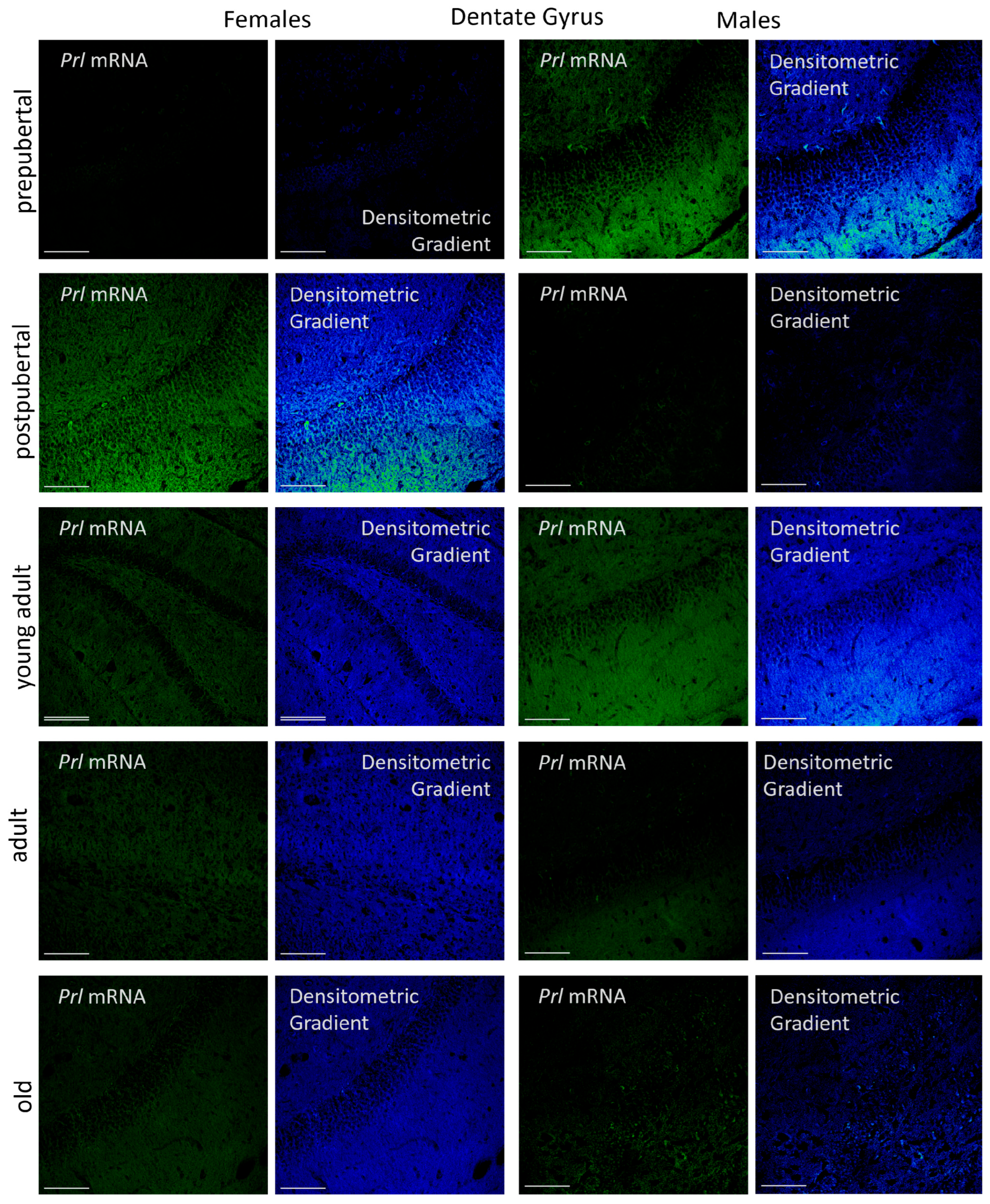
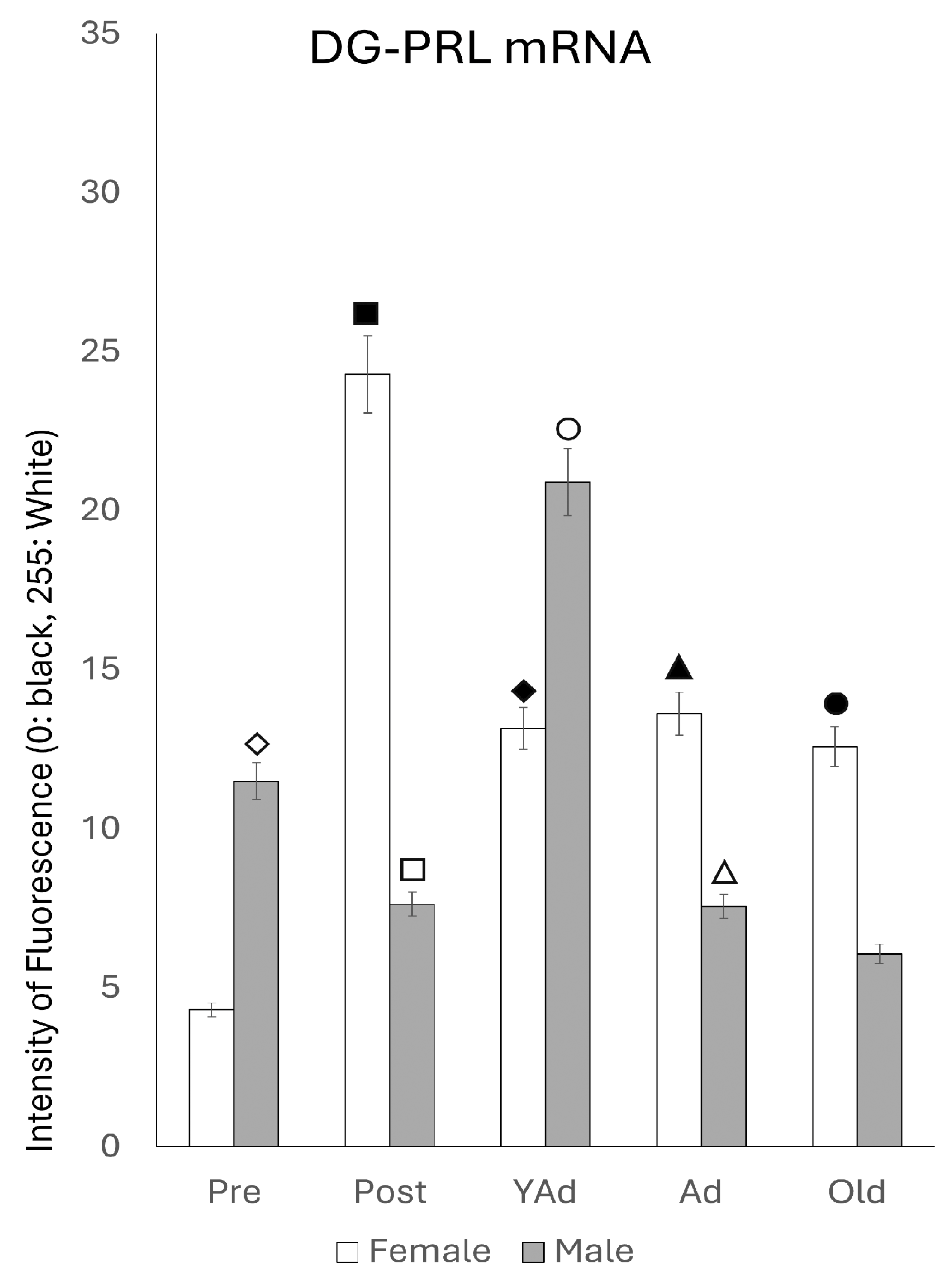
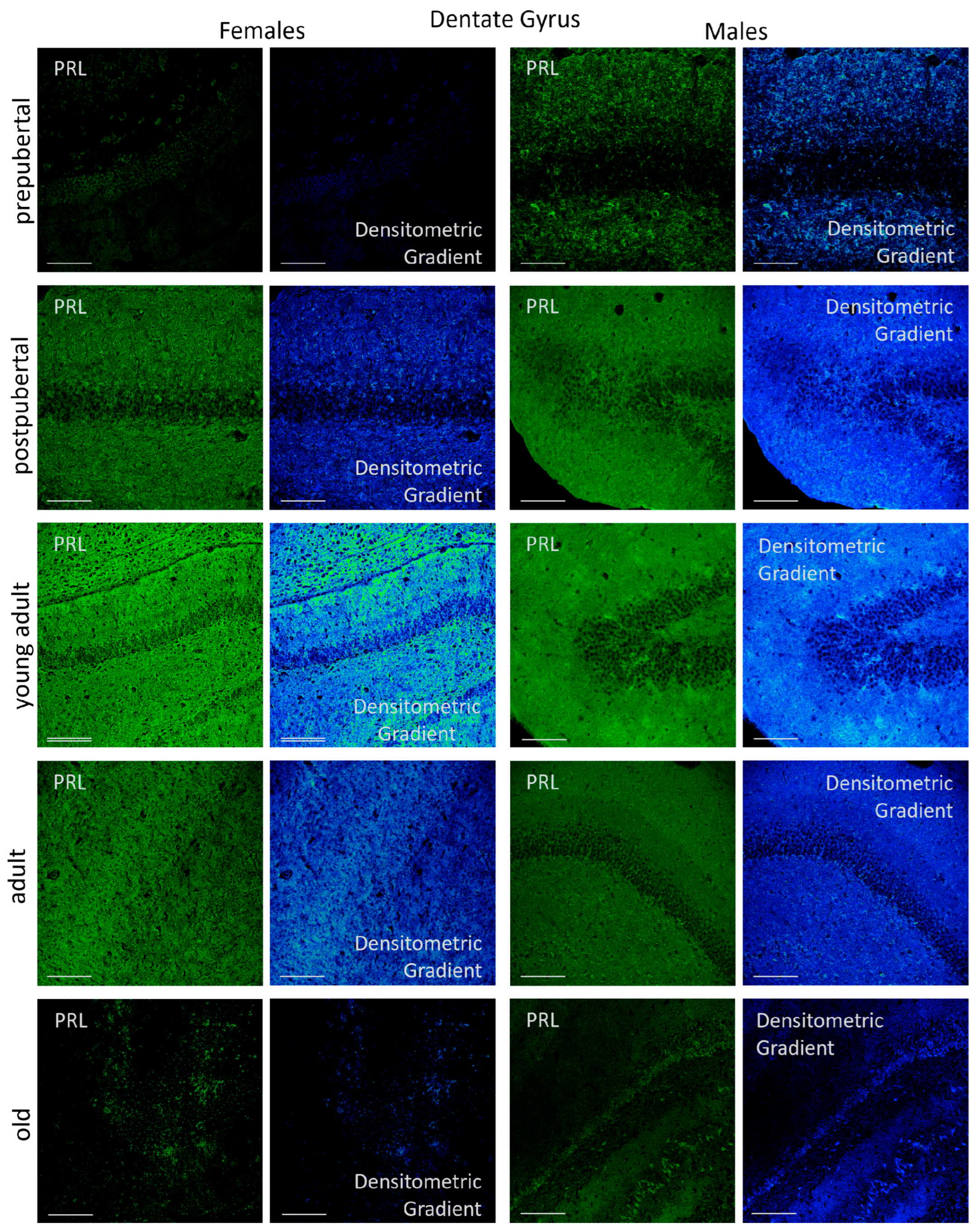
2.3.3. Dentate Gyrus
2.4. Serum and Hippocampal Prolactin Detection via ELISA
2.4.1. Serum Prolactin Levels
2.4.2. Hippocampal Prolactin Levels
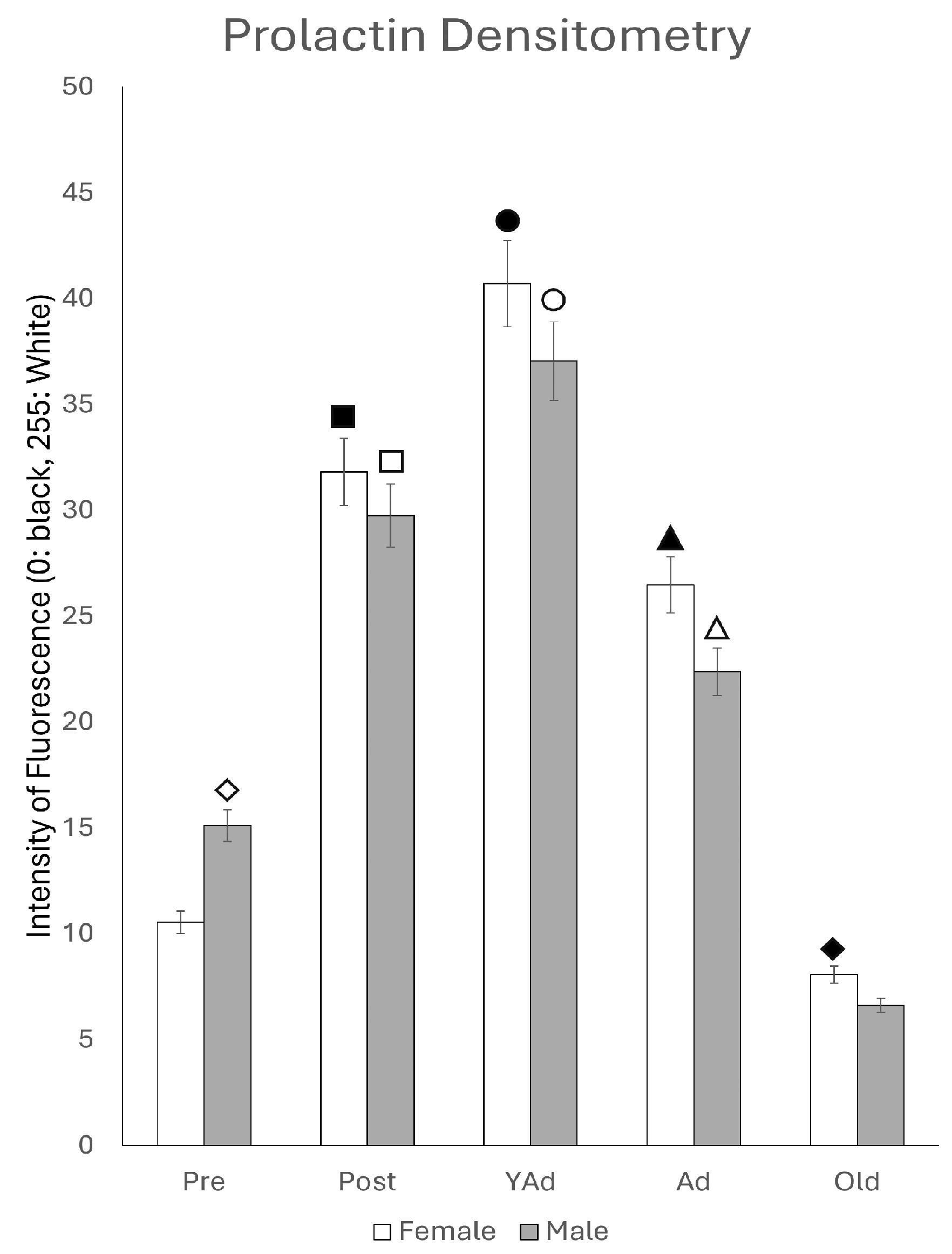
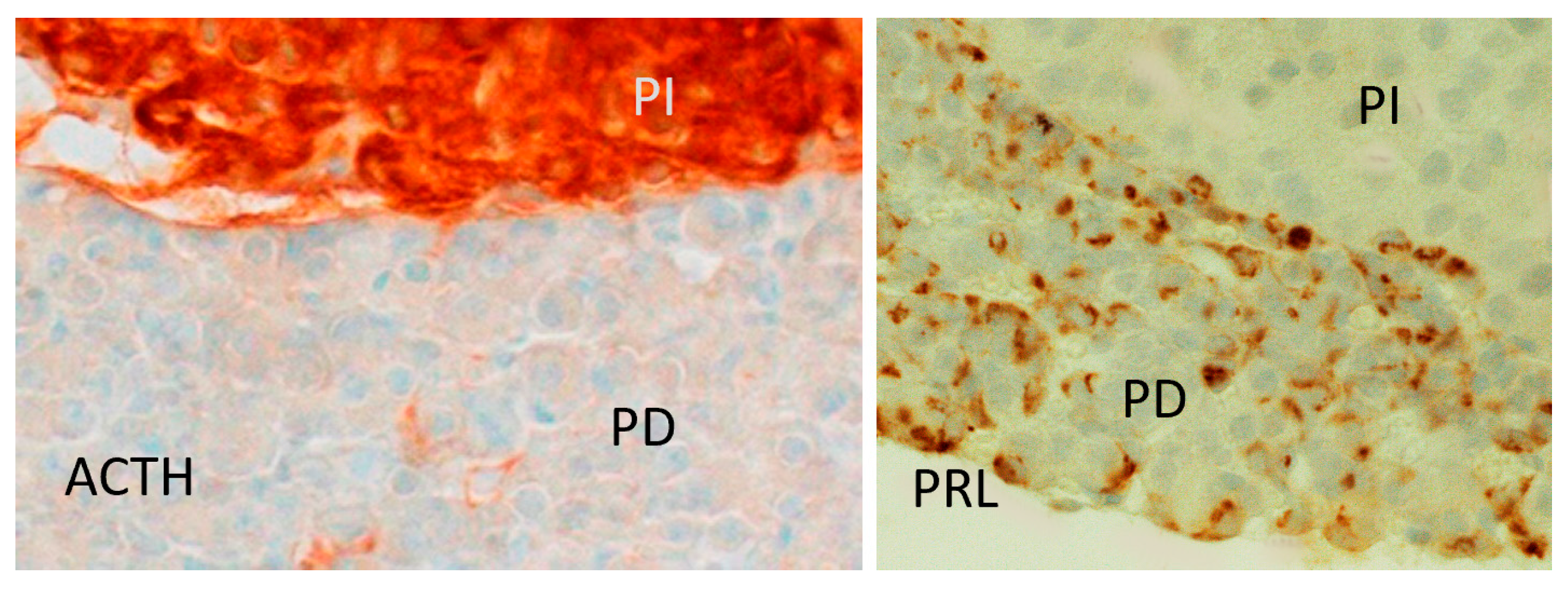
2.5. Prolactin-Positive Cells: Immunohistochemical Study and Densitometric Analysis
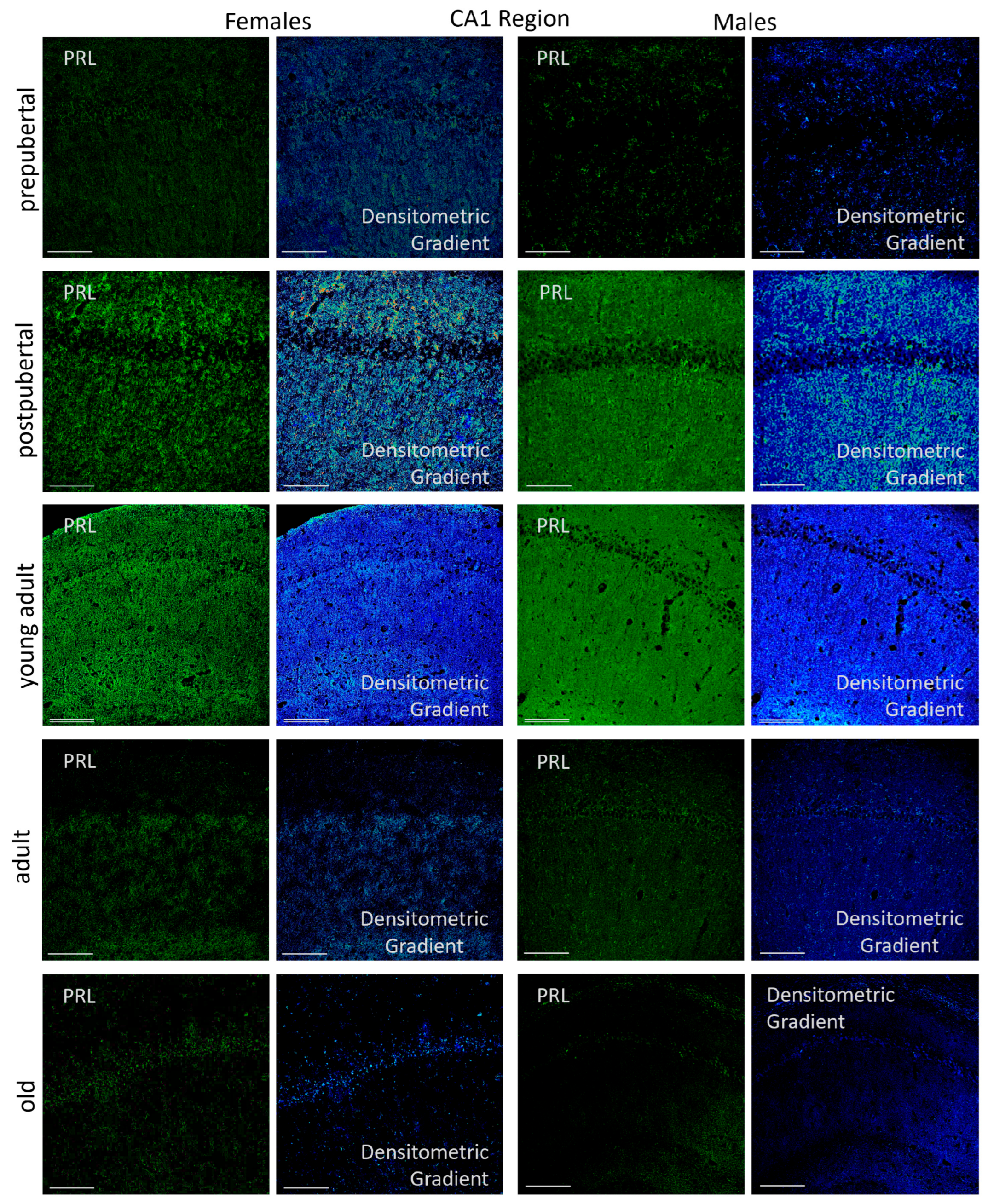
2.6. Prolactin-Positive Cells: Immunohistochemical Study and Regional Analysis
2.6.1. CA1 Region
2.6.2. CA3 Region
2.6.3. Dentate Gyrus
3. Discussion
3.1. Circulating Versus Hippocampal Prolactin: Differential Regulation Across Life Stages
3.2. Evidence for Local Synthesis of Prolactin in the Hippocampus: Technical and Conceptual Validation
3.3. Possible Functional Implications: From Neurogenesis to Hippocampal Regulation
3.4. From Undetected to Demonstrated: How Region-Specific Focus and Multiple Techniques Revealed Hippocampal Prolactin Expression
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Groups to Study
4.2. Animal Sacrifice and Sample Collection
4.3. ELISA Analysis Technique
4.4. Immunostaining for Prolactin
4.5. Immunostaining for Pituitary Prolactin and ACTH (Opiomelanocortin)
4.6. In Situ Hybridization
- Sense probe for Rat PRL: {Btn}CATTACAACTTTCAGCACATGCTTAAGT.
- Antisense probe for Rat PRL: {Btn}GTAATGTTGAAAGTCGTGTACGAATTCA.
4.7. Image Analysis
4.8. Immunofluorescence Gradient Python Script
4.9. q-PCR Technique
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| Ad | Adult animals |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| CA1 | Cornus Amonii (Ammon’s horn) 1 region |
| CA3 | Cornus Amonii (Ammon’s horn) 3 region |
| CA4 | Cornus Amonii (Ammon’s horn) 4 region |
| CaCl2 | Calcium chloride |
| cDNA | Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| DG | Dentate Gyrus |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay |
| HPRT1 | Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase 1, housekeeping gene |
| KCl | Potassium chloride |
| kDa | Kilo Daltons |
| M.W. | Molecular weight |
| MgCl2 | Magnesium chloride |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| NaCl | Sodium chloride |
| NaH2PO4 | Sodium phosphate |
| NaHCO3 | Sodium bicarbonate |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PD | Hypophyseal pars distalis |
| PI | Hypophyseal pars intermedia |
| Post | Postpubertal animals, |
| Pre | Prepubertal animals, |
| PRL | Prolactin hormone |
| Prl mRNA | Mesenger ribonucleic acid for prolactin |
| qPCR | quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RIA | Radio immune assay |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| RNase | Ribonuclease |
| RT-PCR | Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SSC | Sodium citrate solution |
| TB | Tris buffer |
| TBS | Tris buffer saline |
| YAd | Young adult animals |
References
- Larsen, C.M.; Grattan, D.R. Prolactin, neurogenesis, and maternal behaviors. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, J.; Bernichtein, S.; Pisera, D.; Goffin, V. Use of prolactin receptor antagonist to better understand prolactin regulation of pituitary homeostasis. Neuroendocrinology 2013, 98, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.J.; Henry, M.A.; Akopian, A.N. Prolactin receptor in regulation of neuronal excitability and channels. Channels 2014, 8, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanoye-Carlo, A.; Morales, T.; Ramos, E.; Mendoza-Rodríguez, A.; Cerbón, M. Neuroprotective effects of lactation against kainic acid treatment in the dorsal hippocampus of the rat. Horm. Behav. 2008, 53, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, V.; Cantú, D.; Ramos, E.; Vanoye-Carlo, A.; Cerbón, M.; Morales, T. Lactation is a natural model of hippocampus neuroprotection against excitotoxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 461, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejadilla, D.; Cerbón, M.; Morales, T. Prolactin reduces the damaging effects of excitotoxicity in the dorsal hippocampus of the female rat independently of ovarian hormones. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Flores-Soto, E.; García de la Cadena, S.; Coronado-Mares, I.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C.; Ferreira, D.G.; Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Lopes, L.V.; Massieu, L.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin-induced neuroprotection against glutamate excitotoxicity is mediated by the reduction of [Ca2+]i overload and NF-κb activation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, D.; Ramos, E.; Campbell, S.N.; Morales, T.; Rissman, R.A. Reproductive stage and modulation of stress-induced Tau phosphorylation in female rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 27, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holubová, M.; Hrubá, L.; Popelová, A.; Bencze, M.; Pražienková, V.; Gengler, S.; Kratochvílová, H.; Haluzík, M.; Železná, B.; Kuneš, J.; et al. Liraglutide and a lipidized analog of prolactin-releasing peptide show neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of β-amyloid pathology. Neuropharmacology 2019, 144, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.A.; Sawyer, B.D. Identification of prolactin in cerebrospinal fluid. Exp. Brain Res. 1974, 21, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, J.; Nishita, M.; Nakao, N.; Saito, T.R.; Tanaka, M. Regulation of prolactin receptor gene expression in the rat choroid plexus via transcriptional activation of multiple first exons during postnatal development and lactation. Exp. Anim. 2013, 62, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.S.E.; Wyatt, A.K.; Herbison, R.E.; Knowles, P.J.; Ladyman, S.R.; Binart, N.; Banks, W.A.; Grattan, D.R. Prolactin transport into mouse brain is independent of prolactin receptor. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, D.R. The hypothalamo-prolactin axis. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, T101–T122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, N.; Ikeda, T.; Watanabe, M.; Toyomura, J.; Ohyama, A.; Ishikawa, T. Prolactin selectively transported to cerebrospinal fluid from blood under hypoxic/ischemic conditions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVito, W.J. Distribution of immunoreactive prolactin in the male and female rat brain: Effects of hypophysectomy and intraventricular administration of colchicine. Neuroendocrinology 1988, 47, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuele, N.V.; Jurgens, J.K.; Halloran, M.M.; Tentler, J.J.; Lawrence, A.M.; Kelley, M.R. The rat prolactin gene is expressed in brain tissue: Detection of normal and alternatively spliced prolactin messenger RNA. Mol. Endocrinol. 1992, 6, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, K.; Kulig, E.; Lloyd, R.V. Detection of prolactin messenger RNA in mammary and other normal and neoplastic tissues by polymerase chain reaction. Lab. Investig. 1993, 68, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roselli, C.E.; Bocklandt, S.; Stadelman, H.L.; Wadsworth, T.; Vilain, E.; Stormshak, F. Prolactin expression in the sheep brain. Neuroendocrinology 2008, 87, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Vergara-Castañeda, E.; Rivero-Segura, N.; Cerbón, M. Sex differences in prolactin and its receptor expression in pituitary, hypothalamus, and hippocampus of the rat. Rev. Mex. Endocrinol. Metab. Nutr. 2015, 2, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Howie, P.W.; McNeilly, A.S.; Mcardle, T.; Smart, L.; Houston, M. The relationship between suckling-induced prolactin response and lactogenesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1980, 50, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lévy, F.; Gheusi, G.; Keller, M. Plasticity of the parental brain: A case for neurogenesis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2011, 23, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.L.; Vukovic, J.; Koudijs, M.M.; Blackmore, D.G.; Mackay, E.W.; Sykes, A.M.; Overall, R.W.; Hamlin, A.S.; Bartlett, P.F. Prolactin stimulates precursor cells in the adult mouse hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, Y. Effects of ageing on endocrine and neuroendocrine rhythms in humans. Horm. Res. 1995, 43, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Wu, F.C.; Rastrelli, G.; Lee, D.M.; Forti, G.; O’Connor, D.B.; O’Neill, T.W.; Pendleton, N.; Bartfai, G.; Boonen, S.; et al. EMAS Study Group. Low prolactin is associated with sexual dysfunction and psychological or metabolic disturbances in middle-aged and elderly men: The European Male Aging Study (EMAS). J. Sex. Med. 2014, 11, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, T.; Shimamoto, K.; Ishibashi, M.; Kosaka, K.; Orimo, H. Effect of age and sex on circulating and pituitary prolactin levels in human. Acta Endocrinol. 1976, 83, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquifino, A.I.; Cano, P.; Jimenez, V.; Reyes Toso, C.F.; Cardinali, D.P. Changes of prolactin regulatory mechanisms in aging: 24-h rhythms of serum prolactin and median eminence and adenohypophysial concentration of dopamine, serotonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid, taurine and somatostatin in young and aged rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2004, 39, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goya, R.G.; Castro, M.G.; Meites, J. Differential effect of aging on serum levels of prolactin and alpha-melanotropin in rats. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1991, 196, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Putten, L.J.; Van Zwieten, M.J.; Mattheij, J.A.; Van Kemenade, J.A. Studies on prolactin-secreting cells in aging rats of different strains. I. Alterations in pituitary histology and serum prolactin levels as related to aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1988, 42, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duc Nguyen, H.; Hoang, N.M.H.; Jo, W.H.; Ham, J.R.; Lee, M.-K.; Kim, M.S. Associations among the TREM-1 pathway, Tau hyperphosphorylation, prolactin expression, and metformin in diabetes mice. Neuroimmunomodulation 2022, 29, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, J.; Sánchez, F.; Blanco, E.; Riesco, J.M.; Sánchez-Franco, F.; Vázquez, R. Morphofunctional study of mammotropic cells following intraventricular administration of met-enkephalin. Anat. Embryol. 1989, 179, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, J.; Burks, D.J.; Vázquez, G.; Rubio, M.; Hernández, E.; Bodego, P.; Vázquez, R. Expression of aromatase P450 is increased in spontaneous prolactinomas of aged rats. Pituitary 2002, 5, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretero, J.; Blanco, E.J.; Carretero, M.; Carretero-Hernández, M.; García-Barrado, M.J.; Iglesias-Osma, M.C.; Burks, D.J.; Font de Mora, J. The expression of AIB1 correlates with cellular proliferation in human prolactinomas. Ann. Anat. 2013, 195, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Barrado, M.J.; Blanco, E.J.; Iglesias-Osma, M.C.; Carretero-Hernández, M.; Catalano-Iniesta, L.; Sanchez-Robledo, V.; Carretero, M.; Herrero, J.J.; Carrero, S.; Carretero, J. Relation among aromatase P450 and tumoral growth in human prolactinomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A. Brain meets body: The blood-brain barrier as an endocrine interface. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4111–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofi, P. The arcuate nucleus as a circumventricular organ in the mouse. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 487, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsted, E.; Gömüç, B.; Meister, B. Protein components of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in the mediobasal hypothalamus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2008, 36, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Jonathan, N.; Mewrshon, J.L.; Allen, D.L.; Steinmetz, R.W. Extrapituitary prolactin: Distribution, regulation, functions and clinical aspects. Endocr. Rev. 1996, 17, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.E.; Kanyicska, B.; Lerant, A.; Nagy, G. Prolactin: Structure, function, and regulation of secretion. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1523–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, C.; Torner, L.; Gutiérrez-Ospina, G.; Alcántara, E.; López-Gómez, F.J.; Nagano, M.; Kelly, P.A.; Mejía, S.; Morales, M.A.; Martínez de la Escalera, G. The prolactin gene is expressed in the hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal system and the protein is processed into a 14-kDa fragment with activity like 16-kDa prolactin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10384–10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Brito, A.R.; Quintela, T.; Gonçalves, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Costa, A.R.; Arosa, F.A.; Cavaco, J.E.; Lemos, M.C.; Santos, C.R.A. The choroid plexus is an alternative source of prolactin to the rat brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVito, W.J.; Avakian, C.; Stone, S.; Ace, C.I. Estradiol increases prolactin synthesis and prolactin messenger ribonucleic acid in selected brain regions in the hypophysectomized female rat. Endocrinology 1992, 131, 2154–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, S.; Schraut, K.-G.; Schmitt, A.G.; Scholz, C.-J.; Ortega, G.; Steinbusch, H.W.; Lesch, K.-P.; van den Hove, D.L.A. Differential effects of prenatal stress in female 5-HTT-deficient mice: Towards molecular mechanisms of resilience. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torner, L.; Toschi, N.; Nava, G.; Clapp, C.; Neumann, I.D. Increased hypothalamic expression of prolactin in lactation: Involvement in behavioural and neuroendocrine stress responses. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torner, L.; Maloumby, R.; Nava, G.; Aranda, J.; Clapp, C.; Neumann, I.D. In vivo release and gene upregulation of brain prolactin in response to physiological stimuli. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordronneau, P.; Petrusz, P. Immunocytochemical demonstration of anterior pituitary hormones in the pars tuberalis of long-term hypophysectomized rats. Am. J. Anat. 1980, 158, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, K.; Yagi, S.; Ono, K.; Nishiura, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Ishida, M.; Harigaya, T. Prolactin gene expression in mouse spleen helper T cells. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 183, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, D.W. Prolactin production by immune cells. Lupus 2001, 10, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Castañeda, E.; Grattan, D.R.; Pasantes-Morales, H.; Pérez-Domínguez, M.; Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Morales, T.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin mediates neuroprotection against excitotoxicity in primary cell cultures of hippocampal neurons via its receptor. Brain Res. 2016, 1636, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlan, R.E.; Shivers, B.D.; Fox, S.R.; Kaplove, K.A.; Schachter, B.S.; Pfaff, D.W. Distribution and partial characterization of immunoreactive prolactin in the rat brain. Neuroendocrinology 1989, 49, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siaud, P.; Manzoni, O.; Balmefrezol, M.; Barbanel, G.; Assenmacher, I.; Alonso, G. The organization of prolactin-like-immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system. Light- and electron-microscopic immunocytochemical studies. Cell Tissue Res. 1989, 255, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.A.; Ladyman, S.R.; Bouwer, G.T.; Alyousif, Y.; Sapsford, T.J.; Scott, V.; Kokay, I.C.; Grattan, D.R.; Brown, C.H. Prolactin regulation of oxytocin neurone activity in pregnancy and lactation. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 3591–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.S.E.; Aoki, M.; Ladyman, S.R.; Phillipps, H.R.; Wyatt, A.; Boehm, U.; Grattan, D.R. Prolactin action in the medial preoptic area is necessary for postpartum maternal nursing behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10779–10784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, S.; Amano, I.; Takatsuru, Y. High prolactin concentration during lactation period induced disorders of maternal behavioral in offspring. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 88, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairenji, T.J.; Ikezawa, J.; Kaneko, R.; Masuda, S.; Uchida, K.; Takanashi, Y.; Masuda, H.; Sairenji, T.; Amano, I.; Takatsuru, Y.; et al. Maternal prolactin during late pregnancy is important in generating nurturing behavior in the offspring. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13042–13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Su, Q.; Yao, D.; Wang, S.; Dang, S.; Ding, D.; Zhu, Z.; Shao, S.; Li, H. Prolactin, a potential mediator of reduced social interactive behavior in newborn infants following maternal perinatal depressive symptoms. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 215, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingler, E.; Amorim Amato, A.; Zanatta, A.; Brito Vogt, M.F.; da Silva Wanderley, M.; Mariani Neto, C.; Morenom Zaconeta, A. Lactation induction in a commissioned mother by surrogacy: Effects on prolactin levels, milk secretion and mother satisfaction. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obstet. 2017, 39, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, T.; Lorenson, M.; Walker, A.M.; Ramos, E. Both prolactin (prl) and a molecular mimic of phosphorylated prl, s179d-prl, protect the hippocampus of female rats against excitotoxicity. Neuroscience 2014, 258, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Mendoza, J.; Morales, T. Post-treatment with prolactin protects hippocampal CA1 neurons of the ovariectomized female rat against kainic acid-induced neurodegeneration. Neuroscience 2016, 328, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torner, L.; Karg, S.; Blume, A.; Kandasamy, M.; Kuhn, H.G.; Winkler, J.; Aigner, L.; Neumann, I.D. Prolactin prevents chronic stress-induced decrease of adult hippocampal neurogenesis and promotes neuronal fate. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, G.V.E.; Goularte, J.F.; Hoefel, A.L.; de Castro, A.L.; Kucharski, L.C.; da Rosa Araujo, A.S.; Lucion, A.B. Effects of sleep restriction during pregnancy on the mother and fetuses in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 155, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusco, J.; Wittmann, R.; de Azevedo, M.S.; Lucion, A.B.; Franci, C.R.; Giovenardi, M.; Rasia-Filho, A.A. Plasma hormonal profiles and dendritic spine density and morphology in the hippocampal CA1 stratum radiatum, evidenced by light microscopy, of virgin and postpartum female rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 438, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsley, C.H.; Trainer, R.; Stafisso-Sandoz, G.; Quadros, P.; Marcus, L.K.; Hearon, C.; Meyer, E.A.A.; Hester, N.; Morgan, M.; Kozub, F.J. Motherhood and the hormones of pregnancy modify concentrations of hippocampal neuronal dendritic spines. Horm. Behav. 2006, 49, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.M.; Kokay, I.C.; Grattan, D.R. Male pheromones initiate prolactin-induced neurogenesis and advance maternal behavior in female mice. Horm. Behav. 2008, 53, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathipati, P.; Gorba, T.; Scheepens, A.; Goffin, V.; Sun, Y.; Fraser, M. Growth hormone and prolactin regulate human neural stem cell regenerative activity. Neuroscience 2011, 190, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Lehner, B.; Brockhoff, G.; Rivera, F.J.; Blume, A.; Neumann, I.; Aigner, L. Prolactin induces mapk signaling in neural progenitors without alleviating glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of in vitro neurogenesis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 24, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, S.; Moreno-Ruiz, B.; Expósito, S.; Fernández, M.; Martín, E.D. Prolactin reduces hippocampal parvalbumin and GABAA receptor expression in female mice. Neuroendocrinology 2022, 112, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Ruiz, B.; Mellado, S.; Zamora-Moratalla, A.; Albarracín, A.L.; Martín, E.D. Increase in serum prolactin levels in females improves the performance of spatial learning by promoting changes in the circuital dynamics of the hippocampus. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 124, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Moratalla, A.; Martín, E.D. Prolactin enhances hippocampal synaptic plasticity in female mice of reproductive age. Hippocampus 2021, 31, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuxe, K.; Hökfelt, T.; Eneroth, P.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Skett, P. Prolactin-like immunoreactivity: Localization in nerve terminals of rat hypothalamus. Science 1977, 196, 899–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVito, W.J.; Connors, J.M.; Hedge, G.A. Immunoreactive prolactin in the rat hypothalamus: In vitro release and subcellular localization. Neuroendocrinology 1987, 46, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuele, N.V.; Metcalfe, L.; Wallock, L.; Tentler, J.; Hagen, T.C.; Beer, C.T.; Martinson, D.; Gout, P.W.; Kirsteins, L.; Lawrence, A.M. Hypothalamic prolactin: Characterization by radioimmunoassay and bioassay and response to hypophysectomy and restraint stress. Neuroendocrinology 1986, 44, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paut-Pagano, L.; Roky, R.; Valatx, J.L.; Kitahama, K.; Jouvet, M. Anatomical distribution of prolactin-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain. Neuroendocrinology 1993, 58, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivers, B.D.; Harlan, R.E.; Pfaff, D.W. A subset of neurons containing immunoreactive prolactin is a target for estrogen regulation of gene expression in rat hypothalamus. Neuroendocrinology 1989, 49, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Handa, R.J. Estrogen receptor-beta, but not estrogen receptor-alpha, is expressed in prolactin neurons of the female rat paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei: Comparison with other neuropeptides. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 484, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuele, N.V.; Metcalfe, L.; Wallock, L.; Tentler, J.; Hagen, T.C.; Beer, C.T.; Martinson, D.; Gout, P.W.; Kirsteins, L.; Lawrence, A.M. Extrahypothalamic brain prolactin: Characterization and evidence for independence from pituitary prolactin. Brain Res. 1987, 421, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popesco, M.C.; Frostholm, A.; Rejmiak, K.; Rotter, A. Digital transcriptome analysis in the aging cerebellum. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1019, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkley, P.R.; Bobrovskaya, L.; Graham, M.E.; von Nagy-Felsobuki, E.I.; Dickson, P.W. Tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation: Regulation and consequences. J. Neurochem. 2004, 91, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T. The spectrum of prolactin action in teleosts. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1986, 205, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hodson, D.J.; Henderson, H.L.; Townsend, J.; Tortonese, D.J. Photoperiodic modulation of the suppressive actions of prolactin and dopamine on the pituitary gonadotropin responses to gonadotropin-releasing hormone in sheep. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möderscheim, T.A.; Gorba, T.; Pathipati, P.; Kokay, I.C.; Grattan, D.R.; Williams, C.E.; Scheepens, A. Prolactin is involved in glial responses following a focal injury to the juvenile rat brain. Neuroscience 2007, 145, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVito, W.J.; Stone, S.; Avakian, C. Prolactin stimulation of protein kinase c activity in the rat hypothalamus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 176, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVito, W.J.; Okulicz, W.C.; Stone, S.; Avakian, C. Prolactin-stimulated mitogenesis of cultured astrocytes. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 2549–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretero-Hernández, M.; Herráez, E.; Hernández-González, D.; Díez-Castro, D.; Catalano-Iniesta, L.; García-Barrado, J.; Blanco, E.J.; Carretero, J. Lifetime variations of prolactin receptor isoforms mRNA in the hippocampus and dentate gyrus of the rat-effects of aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- García-Barrado, M.J.; Blanco, E.J.; Catalano Iniesta, L.; Sánchez-Robledo, V.; Iglesias-Osma, M.C.; Carretero-Hernandez, M.; Rodríguez-Cobos, J.; Burks, D.J.; Carretero, J. Relevance of pituitary aromatase and estradiol on the maintenance of the population of prolactin-positive cells in male mice. Steroids 2016, 111, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happel, J. If-Grad: Fluorescent Image Gradient Converter (v0.1.2) Free Computer Software. Available online: https://github.com/chaotix1992/IF-Grad (accessed on 17 November 2023).
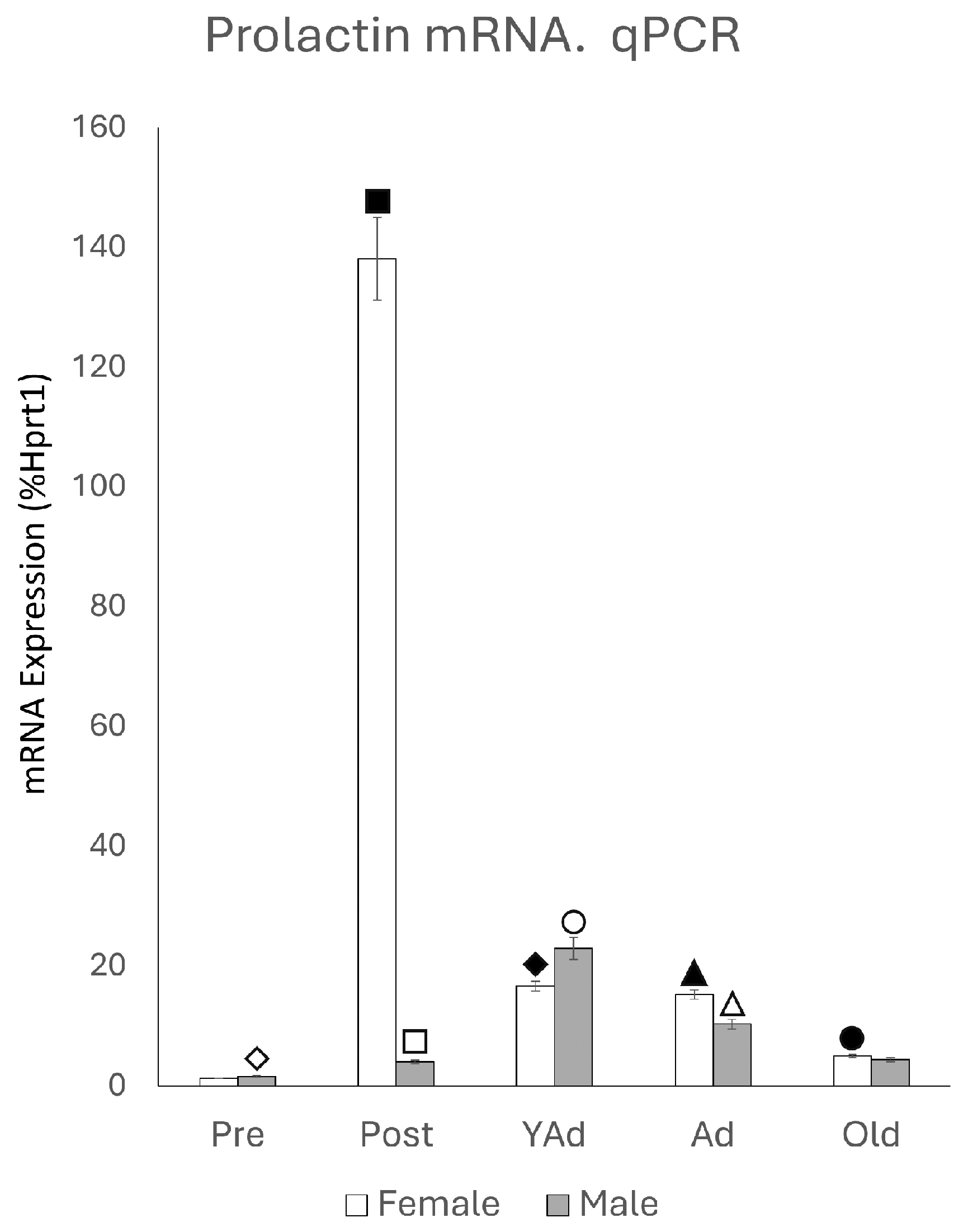
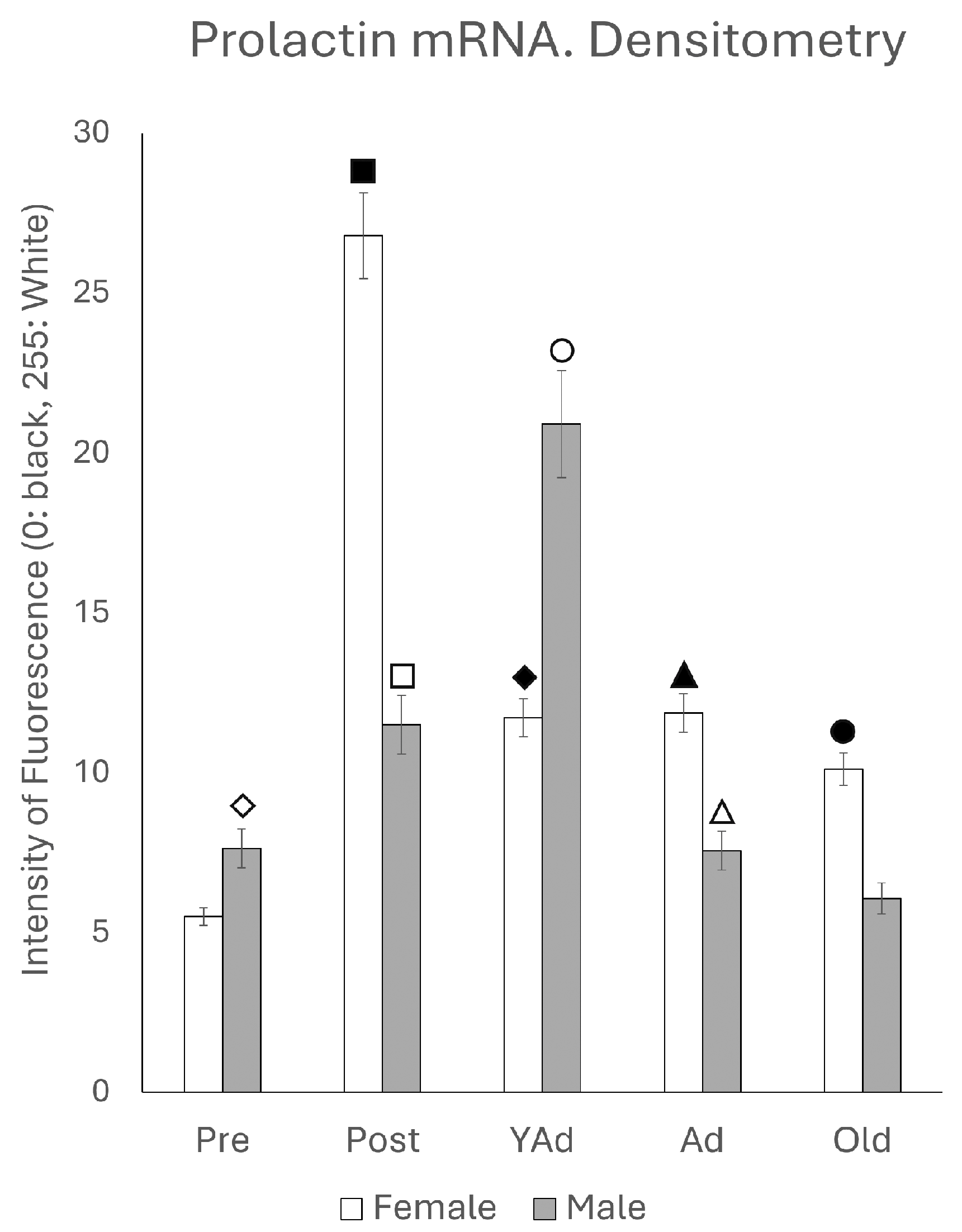
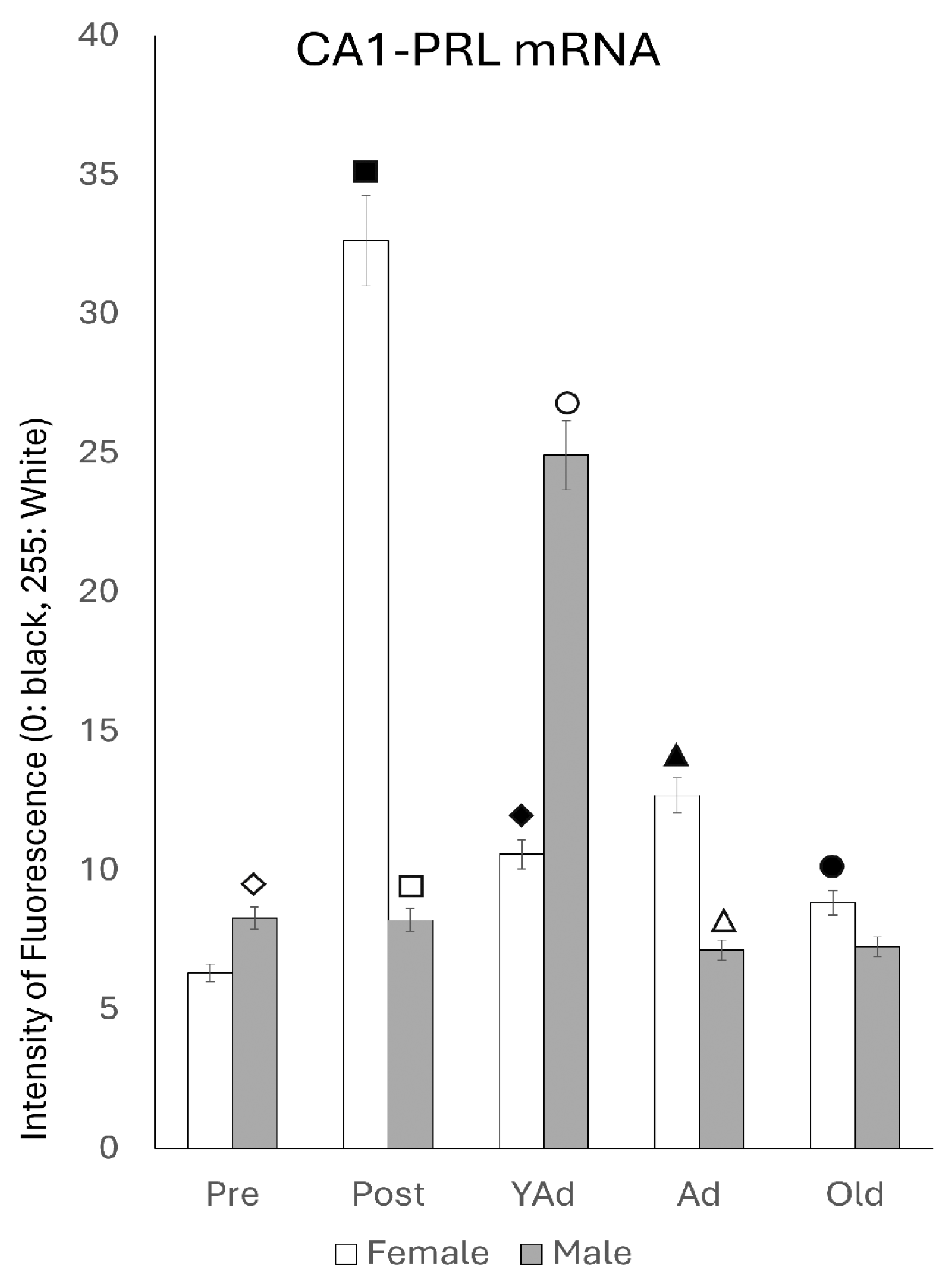
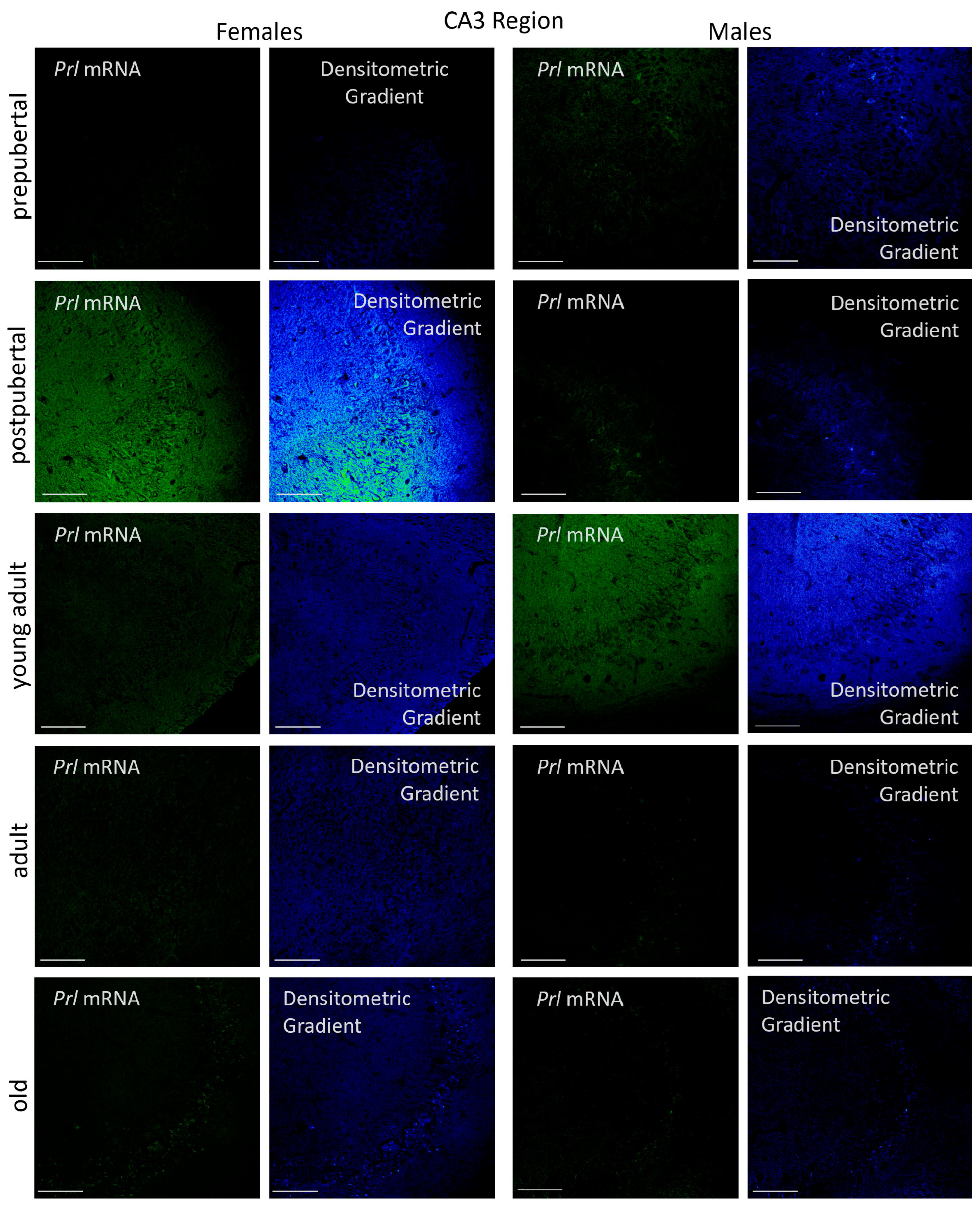
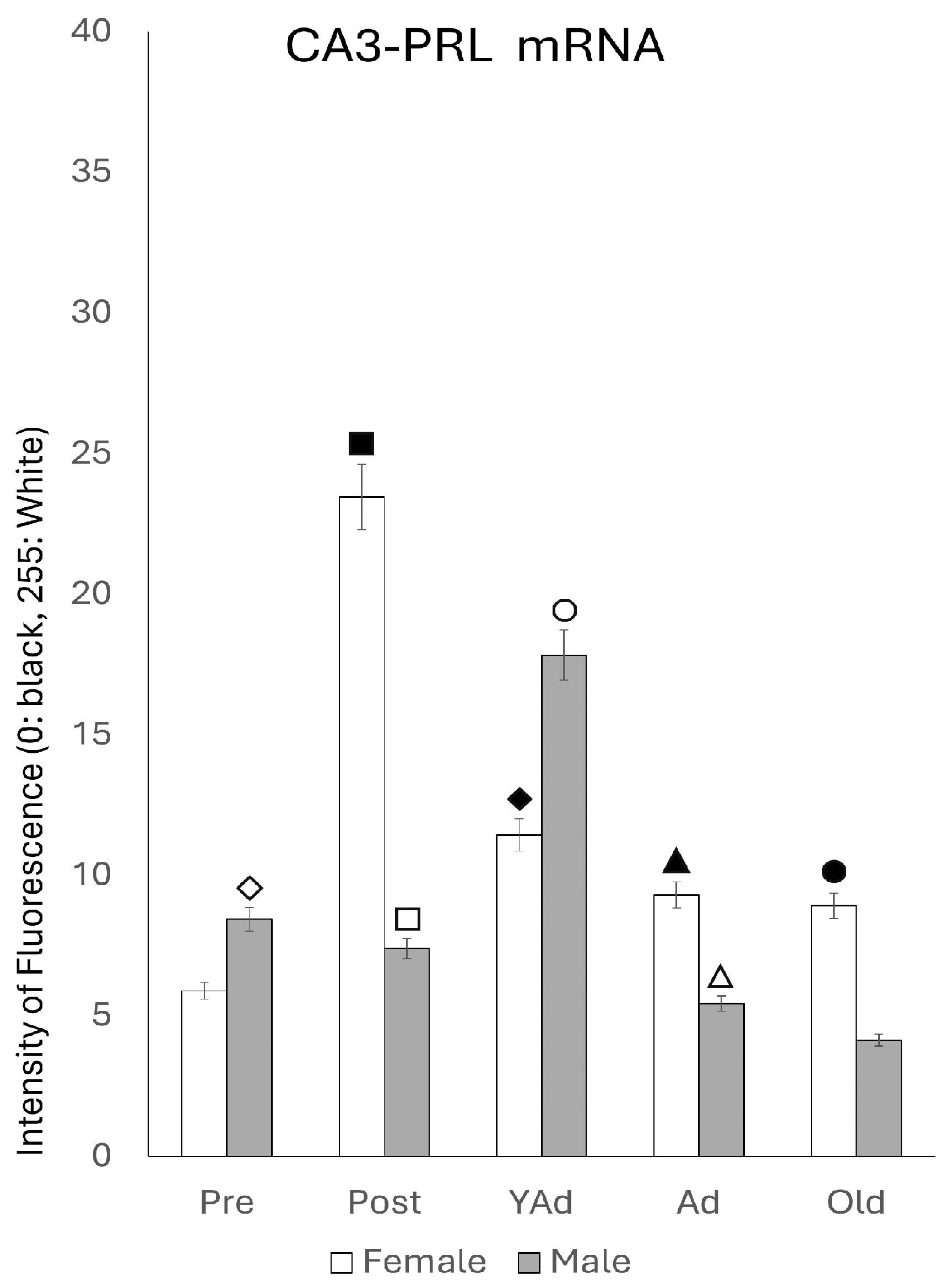
 p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females, ■ p < 0.01 relative to postpubertal males, ☐ p < 0.05 in relation to prepubertal males, ◆ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, ◇ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ▲ p < 0.05 in relation to young adult females, △ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ● p < 0.005 in relation to adult females, p < 0.01 in relation to young adult females and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, and ○ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal, young adult and adult males and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males.
p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females, ■ p < 0.01 relative to postpubertal males, ☐ p < 0.05 in relation to prepubertal males, ◆ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, ◇ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ▲ p < 0.05 in relation to young adult females, △ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ● p < 0.005 in relation to adult females, p < 0.01 in relation to young adult females and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, and ○ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal, young adult and adult males and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males.
 p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females, ■ p < 0.01 relative to postpubertal males, ☐ p < 0.05 in relation to prepubertal males, ◆ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, ◇ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ▲ p < 0.05 in relation to young adult females, △ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ● p < 0.005 in relation to adult females, p < 0.01 in relation to young adult females and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, and ○ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal, young adult and adult males and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males.
p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females, ■ p < 0.01 relative to postpubertal males, ☐ p < 0.05 in relation to prepubertal males, ◆ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, ◇ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ▲ p < 0.05 in relation to young adult females, △ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ● p < 0.005 in relation to adult females, p < 0.01 in relation to young adult females and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, and ○ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal, young adult and adult males and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males.
 p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females, ■ p < 0.01 relative to prepubertal females, ☐ p < 0.01 relative to prepubertal males, ◆ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, ◇ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal male and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ▲ p < 0.01 in relation to young adult females, △ p < 0.01 in relation to young adult males, ● p < 0.05 in relation to adult females and p < 0.01 in relation to old males, and ○ p < 0.01 in relation to adult males old females.
p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females, ■ p < 0.01 relative to prepubertal females, ☐ p < 0.01 relative to prepubertal males, ◆ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, ◇ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal male and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ▲ p < 0.01 in relation to young adult females, △ p < 0.01 in relation to young adult males, ● p < 0.05 in relation to adult females and p < 0.01 in relation to old males, and ○ p < 0.01 in relation to adult males old females.
 p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females, ■ p < 0.01 relative to prepubertal females, ☐ p < 0.01 relative to prepubertal males, ◆ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, ◇ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal male and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ▲ p < 0.01 in relation to young adult females, △ p < 0.01 in relation to young adult males, ● p < 0.05 in relation to adult females and p < 0.01 in relation to old males, and ○ p < 0.01 in relation to adult males old females.
p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal females, ■ p < 0.01 relative to prepubertal females, ☐ p < 0.01 relative to prepubertal males, ◆ p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal females, ◇ p < 0.01 in relation to prepubertal male and p < 0.05 in relation to postpubertal males, ▲ p < 0.01 in relation to young adult females, △ p < 0.01 in relation to young adult males, ● p < 0.05 in relation to adult females and p < 0.01 in relation to old males, and ○ p < 0.01 in relation to adult males old females.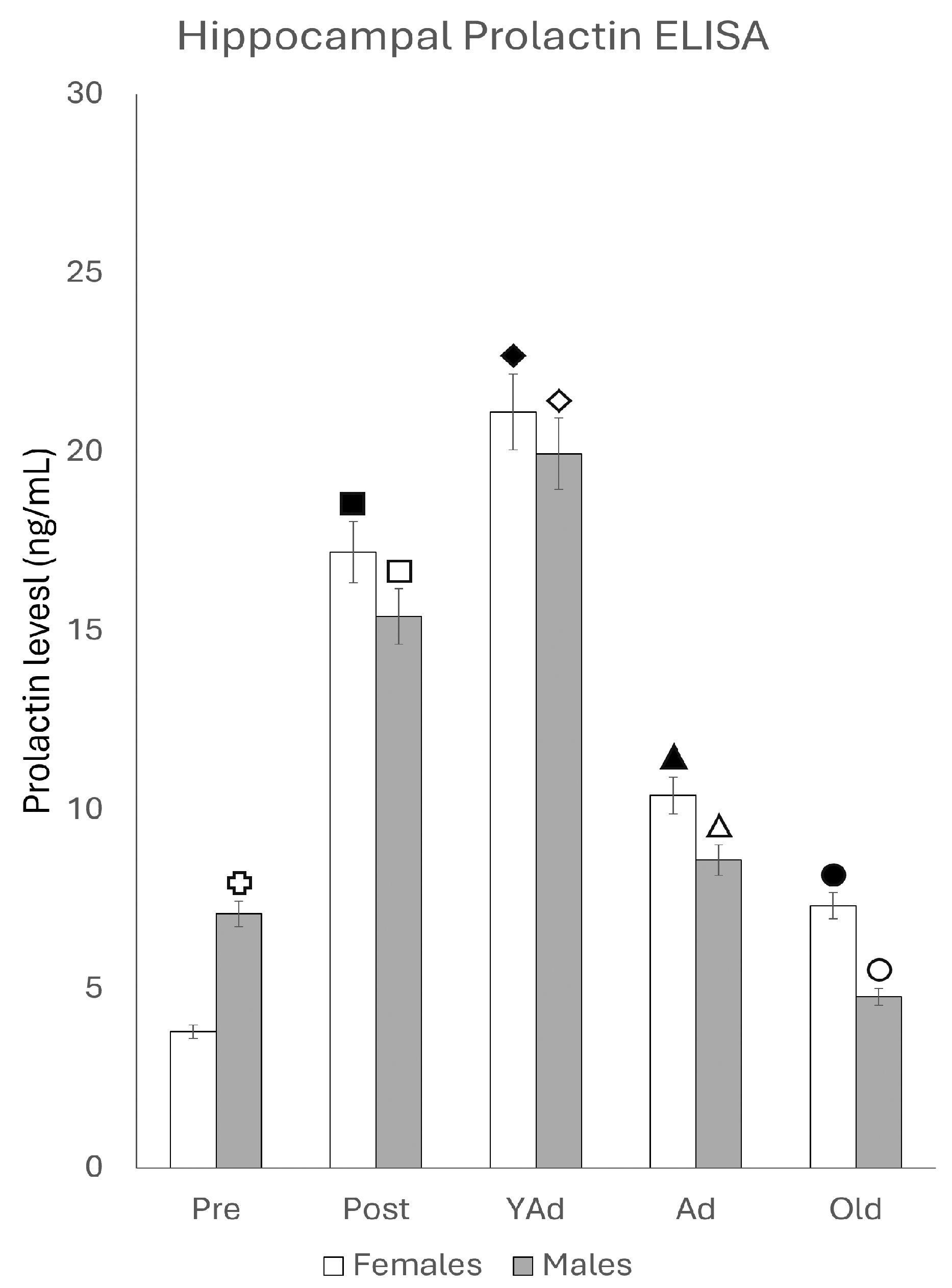

| Pearson r | Males | Females |
|---|---|---|
| r | 0.2402 | −0.09306 |
| 95% confidence interval | −0.8147 to 0.9262 | −0.9013 to 0.8598 |
| R squared | 0.05769 | 0.00888661 |
| p value | ||
| p (two-tailed) | 0.6971 | 0.8817 |
| p value summary | No Significant | No Significant |
| Significant? (alpha = 0.05) | No | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carretero-Hernández, M.; Herráez, E.; Catalano-Iniesta, L.; Hernández-González, D.; Díez-Castro, D.; Rodríguez-Vicente, A.E.; García-Barrado, J.; Vicente-García, T.; Robles-García, M.; Blanco, E.J.; et al. Lifetime Variations in Prolactin Expression in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157299
Carretero-Hernández M, Herráez E, Catalano-Iniesta L, Hernández-González D, Díez-Castro D, Rodríguez-Vicente AE, García-Barrado J, Vicente-García T, Robles-García M, Blanco EJ, et al. Lifetime Variations in Prolactin Expression in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157299
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarretero-Hernández, Marta, Elisa Herráez, Leonardo Catalano-Iniesta, David Hernández-González, David Díez-Castro, Ana E. Rodríguez-Vicente, Josefa García-Barrado, Teresa Vicente-García, Miguel Robles-García, Enrique J. Blanco, and et al. 2025. "Lifetime Variations in Prolactin Expression in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157299
APA StyleCarretero-Hernández, M., Herráez, E., Catalano-Iniesta, L., Hernández-González, D., Díez-Castro, D., Rodríguez-Vicente, A. E., García-Barrado, J., Vicente-García, T., Robles-García, M., Blanco, E. J., & Carretero, J. (2025). Lifetime Variations in Prolactin Expression in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157299






