PAI-1 Inhibitor TM5441 Attenuates Emphysema and Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
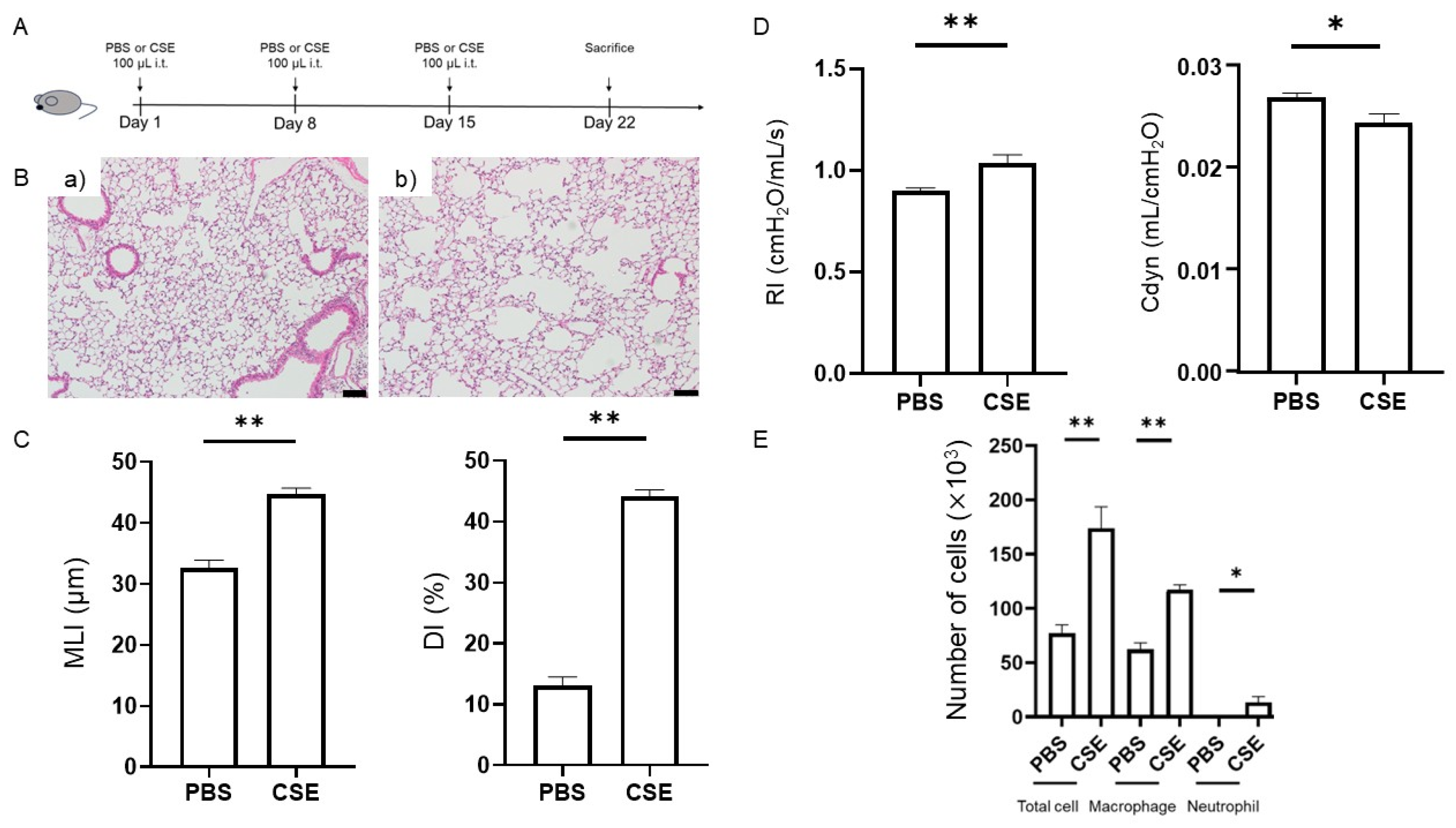
2.1. Effects of Intratracheal Administration of CSE on Emphysema
2.2. CSE-Induced Lung Functional Impairment
2.3. Effects of CSE on Total Cell, Macrophage, and Neutrophil Counts in the Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF)
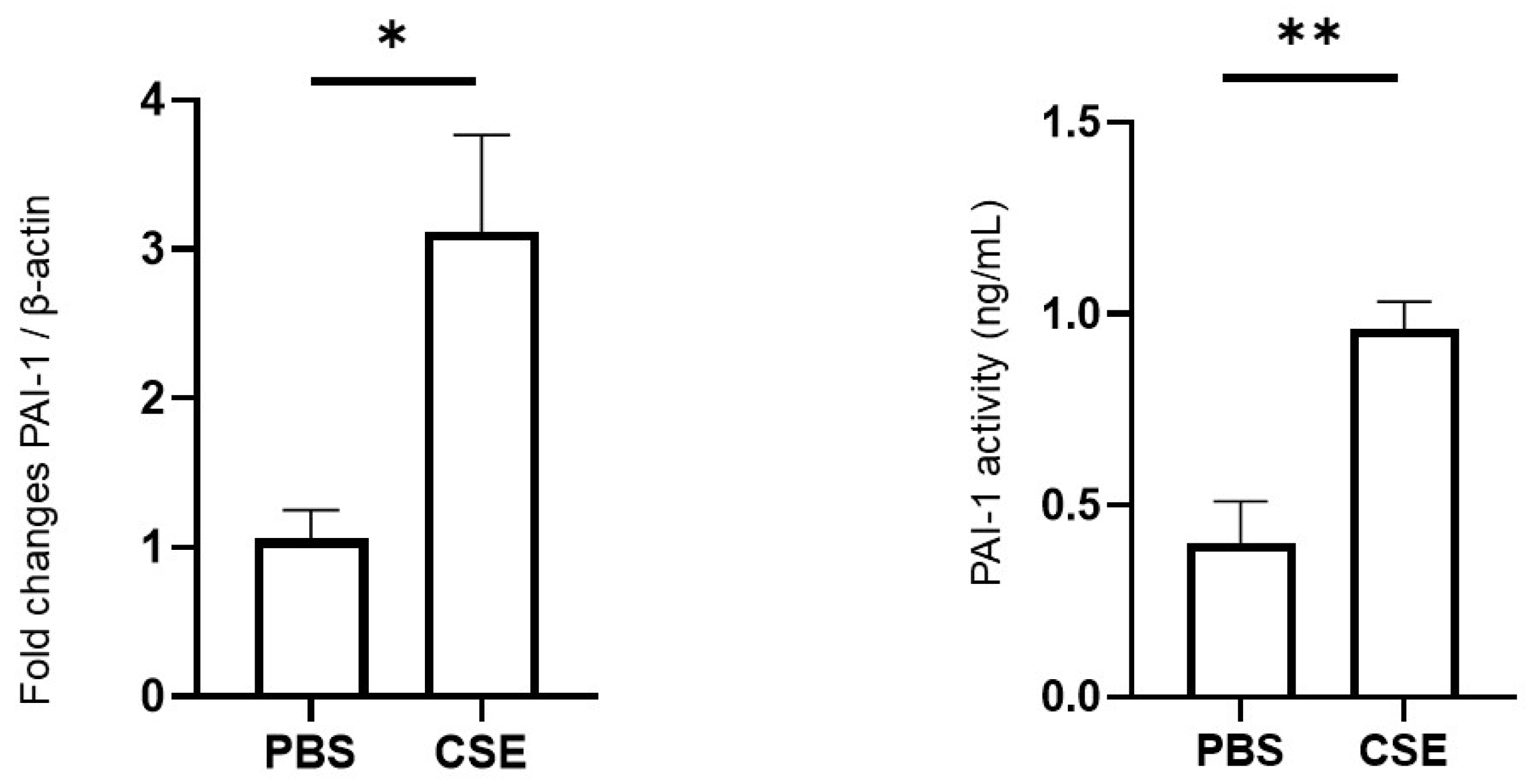
2.4. Effects of CSE on PAI-1 Expression in Lung Tissues and PAI-1 Activity in Plasma
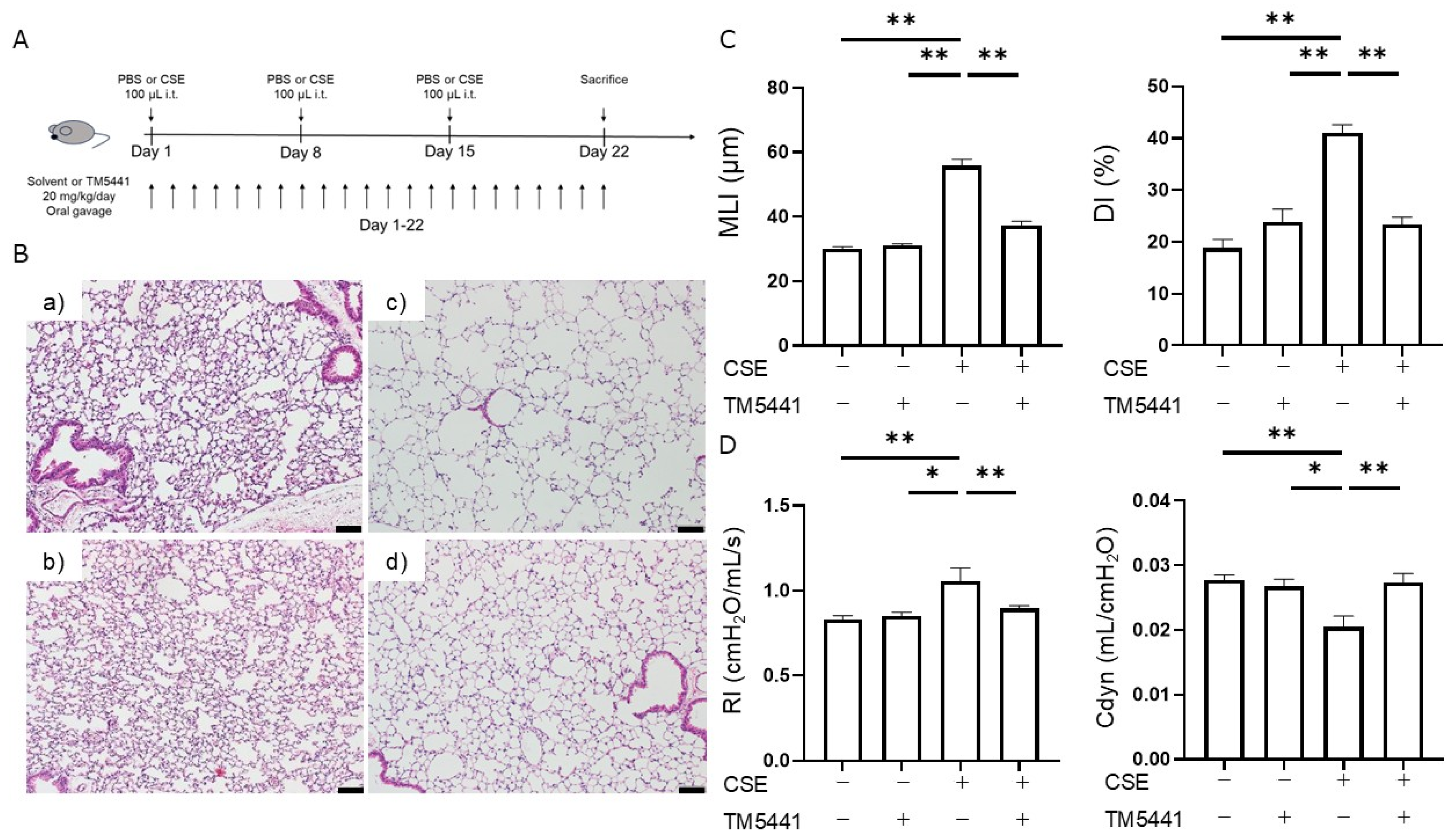
2.5. Effects of TM5441 on CSE-Induced Pulmonary Emphysema
2.6. Effects of TM5441 on CSE-Induced Respiratory Dysfunction
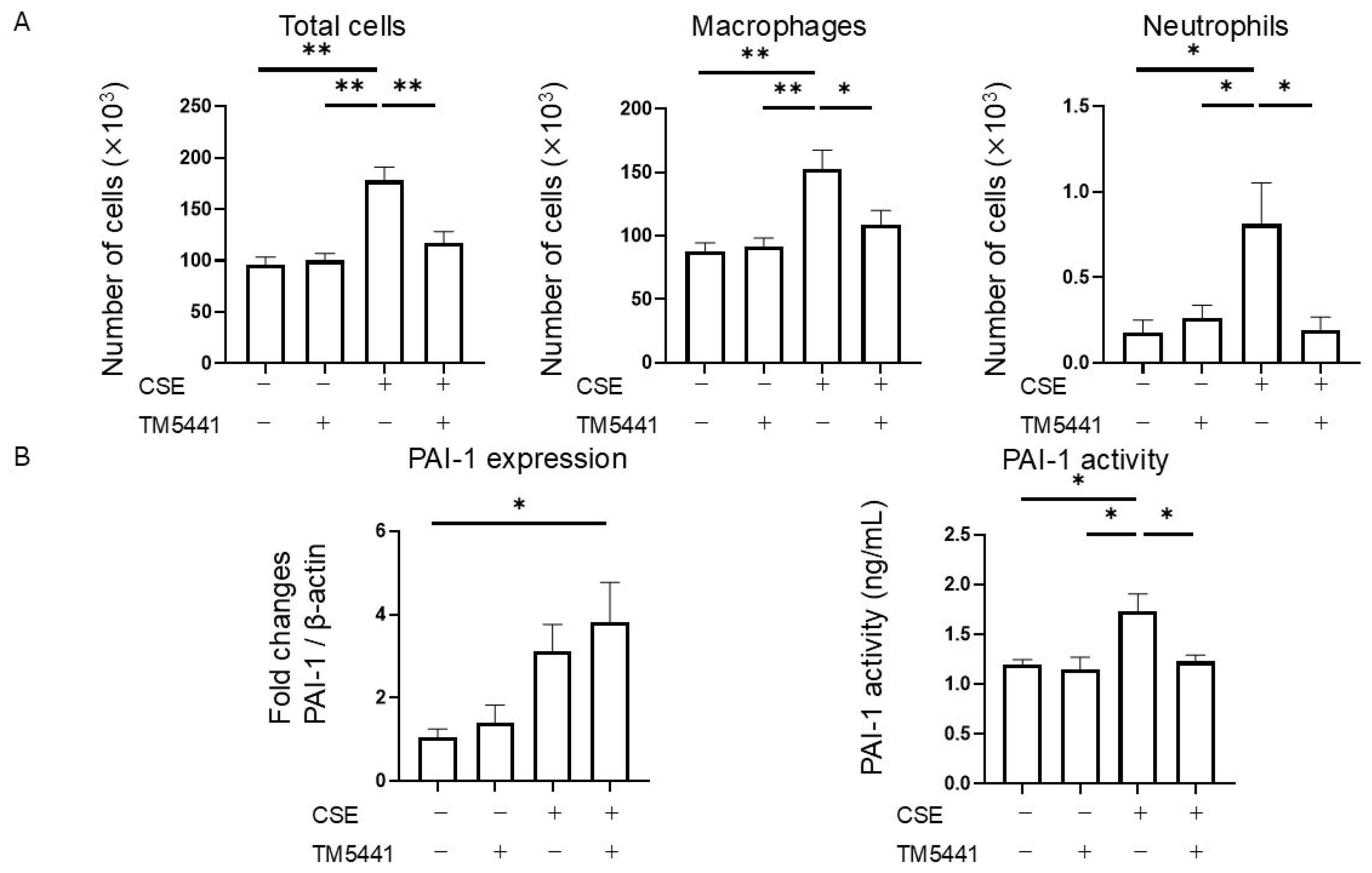
2.7. Effects of TM5441 on CSE-Induced Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in BALF
2.8. Effects of TM5441 on CSE-Induced PAI-1 Expression in Lung Tissue and Plasma PAI-1 Activity
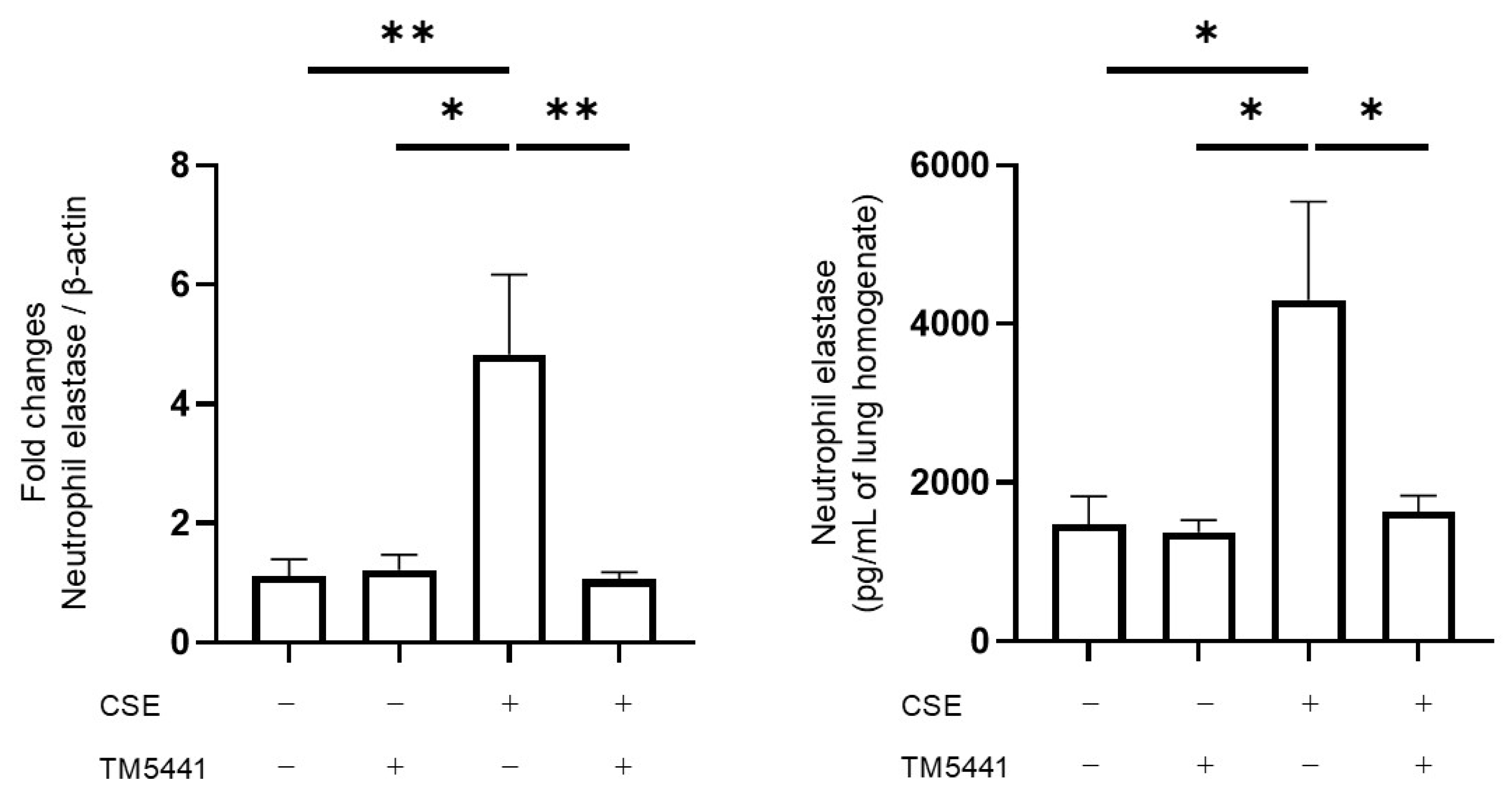
2.9. Effects of TM5441 on CSE-Induced NE mRNA Expression and Protein Levels in Lung Tissue
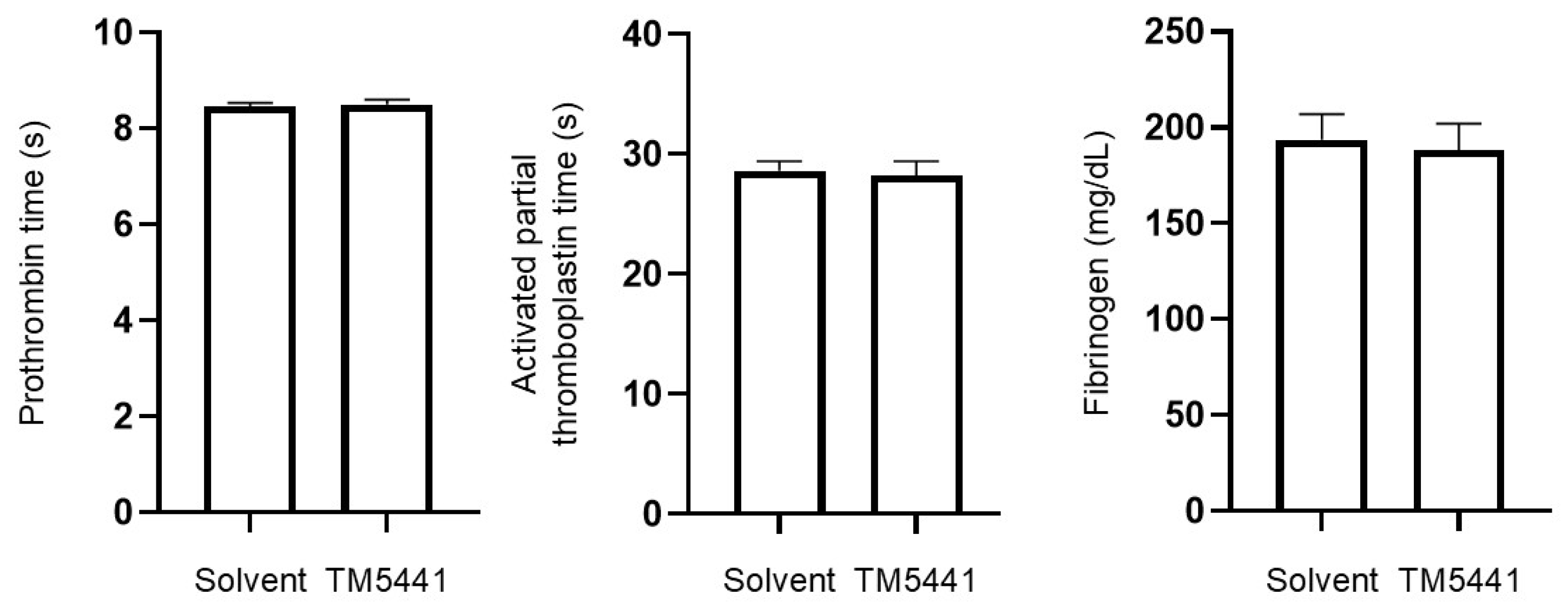
2.10. Effects of TM5441 on Coagulation Parameters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Protocol
4.2. Preparation of CSE
4.3. Intratracheal CSE-Induced COPD Model
4.4. TM5441 Administration
4.5. Histopathological Analysis
4.6. Lung Physiology and BAL
4.7. RT-PCR
4.8. ELISA
4.9. Coagulation Times
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| Cdyn | Dynamic compliance |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CSE | Cigarette smoke extract |
| DI | Destructive index |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| FSC | Forward scatter |
| Gr-1 | Ly-6G/Ly-6C |
| HE | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| L-NAME | Nω-nitro-arginine methyl ester |
| MLI | Mean linear intercept |
| NE | Neutrophil elastase |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| PE | Phycoerythrin |
| RI | Airway resistance |
| SSC | Side scatter |
References
- Global Strategy for Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Copd: 2025 Report. Available online: https://goldcopd.org/2025-gold-report/ (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Adeloye, D.; Song, P.; Zhu, Y.; Campbell, H.; Sheikh, A.; Rudan, I. Global, regional, and national prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in 2019: A systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, E.; Barrett, M.; Su, J.G.; Benjafield, A.V.; Sinha, S.; Kaye, L.; Zar, H.J.; Vuong, V.; Tellez, D.; Gondalia, R.; et al. Global Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Through 2050. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2346598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikichi, M.; Mizumura, K.; Maruoka, S.; Gon, Y. Pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) induced by cigarette smoke. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S2129–S2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, R.T.; Vimalanathan, S. Pathogenesis of COPD. Part I. The role of protease-antiprotease imbalance in emphysema. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2008, 12, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. The cytokine network in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 41, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.D.; Goldstein, N.M.; Houghton, A.M.; Kobayashi, D.K.; Kelley, D.; Belaaouaj, A. Neutrophil elastase contributes to cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 2329–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Yi, M.; Belcastro, R.; Li, J.; Lopez, L.; Kantores, C.; Jankov, R.P.; Tanswell, A.K. Neutrophil elastase-induced elastin degradation mediates macrophage influx and lung injury in 60% O2-exposed neonatal rats. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L53–L62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Vaughan, D.E. PAI-1 in tissue fibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, T.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, C.; Zhang, J.; Ying, B.; Wang, T.; Wen, F. Elevated circulating PAI-1 levels are related to lung function decline, systemic inflammation, and small airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2016, 11, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, N.; Marudamuthu, A.S.; Tsukasaki, Y.; Ikebe, M.; Fu, J.; Shetty, S. p53- and PAI-1-mediated induction of C-X-C chemokines and CXCR2: Importance in pulmonary inflammation due to cigarette smoke exposure. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 310, L496–L506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren, M.; Boe, A.E.; Murphy, S.B.; Place, A.T.; Nagpal, V.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Urich, D.; Quaggin, S.E.; Budinger, G.R.; Mutlu, G.M.; et al. PAI-1-regulated extracellular proteolysis governs senescence and survival in Klotho mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7090–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.M.; Eldridge, S.; Watanabe, N.; Deshane, J.; Kuo, H.C.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Schwiebert, L.; Miyata, T.; et al. Therapeutic potential of an orally effective small molecule inhibitor of plasminogen activator inhibitor for asthma. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 310, L328–L336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.T.; Vayalil, P.K.; Miyata, T.; Hagood, J.; Liu, R.M. Therapeutic value of small molecule inhibitor to plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 for lung fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillen, M.; Declerck, P.J. Targeting PAI-1 in Cardiovascular Disease: Structural Insights Into PAI-1 Functionality and Inhibition. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 622473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.H.; Chen, P.; Chen, Y.; He, S.D.; Ye, J.R.; Zhang, H.L.; Cao, J. Comparison between cigarette smoke-induced emphysema and cigarette smoke extract-induced emphysema. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2015, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, Y.; Xiang, B.; Huang, X.; Guan, W.; Zheng, J. Carbocisteine inhibits the expression of Muc5b in COPD mouse model. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 3259–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzola, M.; Hanania, N.A.; Page, C.P.; Matera, M.G. Novel Anti-Inflammatory Approaches to COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2023, 18, 1333–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, K.M.; Seniukovich, A. Inhaled steroids and risk of pneumonia for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, Cd010115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, M.; Ma, C.; Yan, H. Inhaled Corticosteroids and the Pneumonia Risk in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 691621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjua, S.; Fortescue, R.; Poole, P. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 5, Cd002309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmeier, C.; Aquino, T.O.; O’Brien, C.D.; Perrett, J.; Gunawardena, K.A. A randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-finding study of AZD9668, an oral inhibitor of neutrophil elastase, in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with tiotropium. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2012, 9, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasagi, S.; Seyama, K.; Mori, H.; Souma, S.; Sato, T.; Akiyoshi, T.; Suganuma, H.; Fukuchi, Y. Tomato juice prevents senescence-accelerated mouse P1 strain from developing emphysema induced by chronic exposure to tobacco smoke. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L396–L404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.L.; Cosio, M.; Churg, A. Animal models of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L1–L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, R.; Olivo, C.R.; Lourenço, J.D.; Riane, A.; Cervilha, D.A.B.; Ito, J.T.; Martins, M.A.; Lopes, F. A murine model of elastase- and cigarette smoke-induced emphysema. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2017, 43, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.H.; Wang, X.Q.; He, Q.; Fang, W.F.; Mitra, S.; Bdeir, K.; Ploplis, V.A.; Xu, Z.; Idell, S.; Cines, D.; et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 potentiates LPS-induced neutrophil activation through a JNK-mediated pathway. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 95, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Liu, G.; Lorne, E.F.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Tsuruta, Y.; Zmijewski, J.; Abraham, E. PAI-1 inhibits neutrophil efferocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11784–11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L.J.; Ramdin, L.S.; Brooks, T.; PC, D.P.; Shute, J.K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 supports IL-8-mediated neutrophil transendothelial migration by inhibition of the constitutive shedding of endothelial IL-8/heparan sulfate/syndecan-1 complexes. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waschki, B.; Watz, H.; Holz, O.; Magnussen, H.; Olejnicka, B.; Welte, T.; Rabe, K.F.; Janciauskiene, S. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is elevated in patients with COPD independent of metabolic and cardiovascular function. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, M.; Takagi, D.; Akashi, K.; Kano, I.; Haruki, K.; Barnes, P.J.; Ito, K. Sputum plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 elevation by oxidative stress-dependent nuclear factor-κB activation in COPD. Chest 2013, 144, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Ma, D.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. Levels of components of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator system are related to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease parenchymal destruction and airway remodelling. J. Int. Med. Res. 2012, 40, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuhara, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Nangaku, M.; Takizawa, S.; Ishida, H.; Kurokawa, K.; van Ypersele de Strihou, C.; Hirayama, N.; Miyata, T. Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: Its mechanism and effectiveness on coagulation and fibrosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuhara, Y.; Yamaoka, N.; Kodama, H.; Dan, T.; Takizawa, S.; Hirayama, N.; Meguro, K.; van Ypersele de Strihou, C.; Miyata, T. A novel inhibitor of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 provides antithrombotic benefits devoid of bleeding effect in nonhuman primates. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Sano, H.; Suda, T.; Chida, K.; Dan, T.; Miyata, T.; Urano, T. TM5275 prolongs secreted tissue plasminogen activator retention and enhances fibrinolysis on vascular endothelial cells. Thromb. Res. 2013, 132, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Suzuki, S.; Dan, T.; Yamaki, S.; Sato, Y.; Kiyomoto, H.; Ishii, N.; Okada, K.; Matsuo, O.; et al. A small molecule inhibitor to plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 inhibits macrophage migration. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boe, A.E.; Eren, M.; Murphy, S.B.; Kamide, C.E.; Ichimura, A.; Terry, D.; McAnally, D.; Smith, L.H.; Miyata, T.; Vaughan, D.E. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 antagonist TM5441 attenuates Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester-induced hypertension and vascular senescence. Circulation 2013, 128, 2318–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boe, A.E.; Eren, M.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Murphy, S.B.; Budinger, G.R.; Mutlu, G.M.; Miyata, T.; Vaughan, D.E. Nitric oxide prevents alveolar senescence and emphysema in a mouse model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voynow, J.A.; Shinbashi, M. Neutrophil Elastase and Chronic Lung Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmijewski, J.W.; Bae, H.B.; Deshane, J.S.; Peterson, C.B.; Chaplin, D.D.; Abraham, E. Inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis by PAI-1. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 301, L247–L254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemini, C.; Jaimez, R.; Franco, Y. Gender and inter-species influence on coagulation tests of rats and mice. Thromb. Res. 2007, 120, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.H.; Dukes, J.; Levy, R.E.; Sos, B.; Mason, S.E.; Fong, T.S.; Weiss, E.J. Sex differences in thrombosis in mice are mediated by sex-specific growth hormone secretion patterns. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2969–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Wachami, N.; Guennouni, M.; Iderdar, Y.; Boumendil, K.; Arraji, M.; Mourajid, Y.; Bouchachi, F.Z.; Barkaoui, M.; Louerdi, M.L.; Hilali, A.; et al. Estimating the global prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, Y.; Deguchi, S.; Matsuo, T.; Suzuki, A.; Terashima, G.; Tajima, T.; Shibata, Y.; Sagara, H. Underdiagnosis of COPD: The Japan COPD Real-World Data Epidemiological (CORE) Study. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2024, 19, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placencio, V.R.; Ichimura, A.; Miyata, T.; DeClerck, Y.A. Small Molecule Inhibitors of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Elicit Anti-Tumorigenic and Anti-Angiogenic Activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitzman, D.T.; McCoy, R.D.; Zheng, X.; Fay, W.P.; Shen, T.; Ginsburg, D.; Simon, R.H. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in transgenic mice that either lack or overexpress the murine plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, A.; Quinn, A.M.; Cançado, J.E.D.; Singh, D. The pathology of small airways disease in COPD: Historical aspects and future directions. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, T.; Mazaki, Y.; Miwa, S. Mechanism of cytotoxicity induced by the cigarette smoke extract (CSE) of heated tobacco products in vascular smooth muscle cells: A comparative study of the cytotoxic effects of CSE and the ferroptosis inducer, erastin. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 154, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morichika, D.; Taniguchi, A.; Oda, N.; Fujii, U.; Senoo, S.; Itano, J.; Kanehiro, A.; Kitaguchi, Y.; Yasuo, M.; Hanaoka, M.; et al. Loss of IL-33 enhances elastase-induced and cigarette smoke extract-induced emphysema in mice. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, K.H.; Jang, A.H.; Yoo, C.G. The Impact of Autophagy on the Cigarette Smoke Extract-Induced Apoptosis of Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2017, 80, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, L.; Jung, I.; Huh, J.Y.; Miyata, T.; Ha, H. A novel plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitor, TM5441, protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity and adipocyte injury in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2622–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, C.C.; Hyde, D.M.; Ochs, M.; Weibel, E.R. An official research policy statement of the American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society: Standards for quantitative assessment of lung structure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 394–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetta, M.; Shiner, R.J.; Angus, G.E.; Kim, W.D.; Wang, N.S.; King, M.; Ghezzo, H.; Cosio, M.G. Destructive index: A measurement of lung parenchymal destruction in smokers. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 131, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle-Treger, L.; Suzuki, Y.; Patel, N.; Sankaranarayanan, I.; Aron, J.L.; Maazi, H.; Chen, L.; Akbari, O. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist attenuates ILC2-dependent airway hyperreactivity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Aono, Y.; Akiyama, N.; Horiike, Y.; Naoi, H.; Horiguchi, R.; Shibata, K.; Hozumi, H.; Karayama, M.; Furuhashi, K.; et al. Involvement of autophagy in exacerbation of eosinophilic airway inflammation in a murine model of obese asthma. Autophagy 2022, 18, 2216–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ’EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oishi, K.; Yasui, H.; Inoue, Y.; Hozumi, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Karayama, M.; Furuhashi, K.; Enomoto, N.; Fujisawa, T.; Horinouchi, T.; et al. PAI-1 Inhibitor TM5441 Attenuates Emphysema and Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157086
Oishi K, Yasui H, Inoue Y, Hozumi H, Suzuki Y, Karayama M, Furuhashi K, Enomoto N, Fujisawa T, Horinouchi T, et al. PAI-1 Inhibitor TM5441 Attenuates Emphysema and Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157086
Chicago/Turabian StyleOishi, Kyohei, Hideki Yasui, Yusuke Inoue, Hironao Hozumi, Yuzo Suzuki, Masato Karayama, Kazuki Furuhashi, Noriyuki Enomoto, Tomoyuki Fujisawa, Takahiro Horinouchi, and et al. 2025. "PAI-1 Inhibitor TM5441 Attenuates Emphysema and Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157086
APA StyleOishi, K., Yasui, H., Inoue, Y., Hozumi, H., Suzuki, Y., Karayama, M., Furuhashi, K., Enomoto, N., Fujisawa, T., Horinouchi, T., Iwaki, T., Suzuki, Y., Miyata, T., Inui, N., & Suda, T. (2025). PAI-1 Inhibitor TM5441 Attenuates Emphysema and Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157086





