Nano-Titanium Dioxide Induces Ovarian Function Damage in Mice by Mediating Granulosa Cell Apoptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
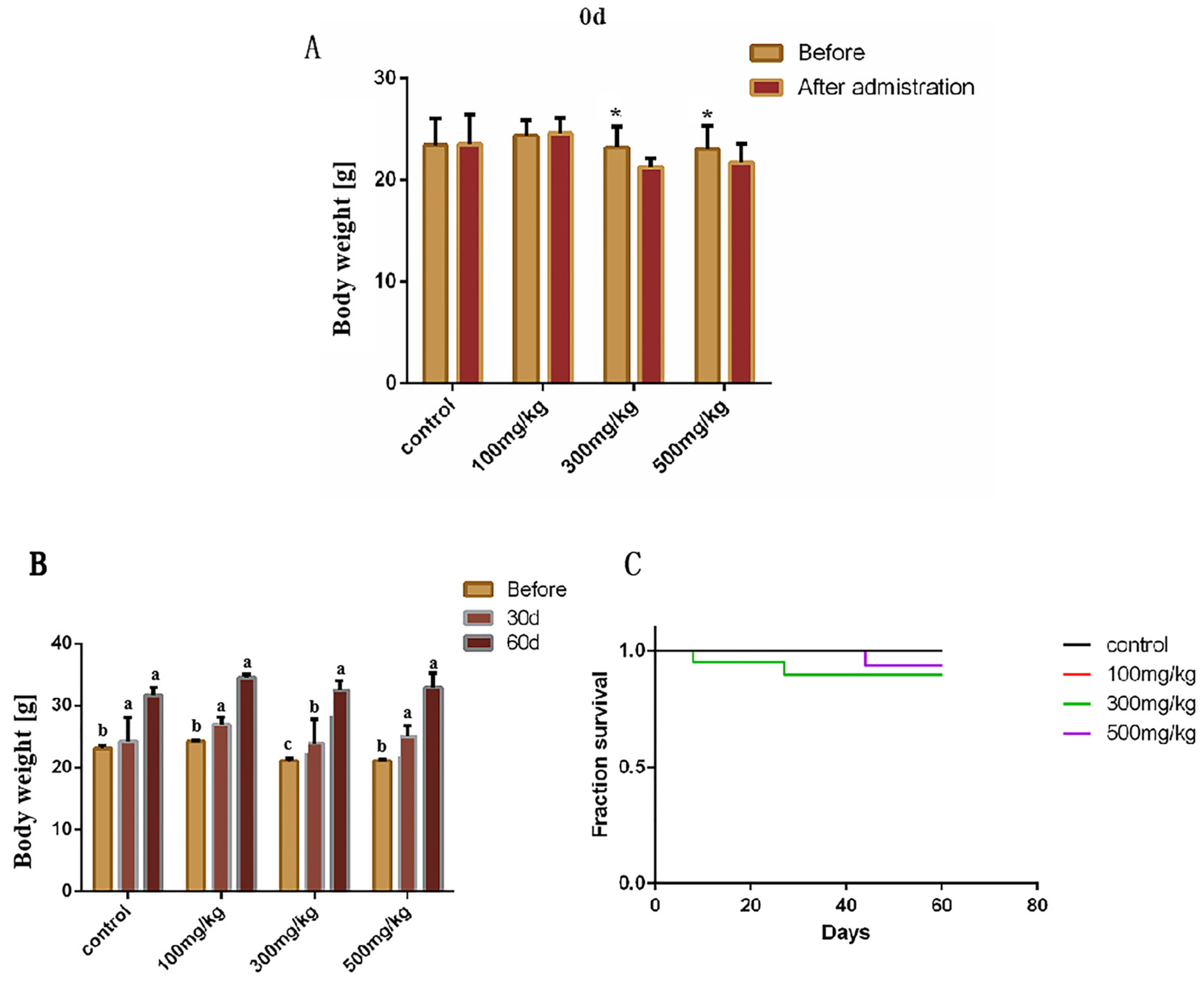
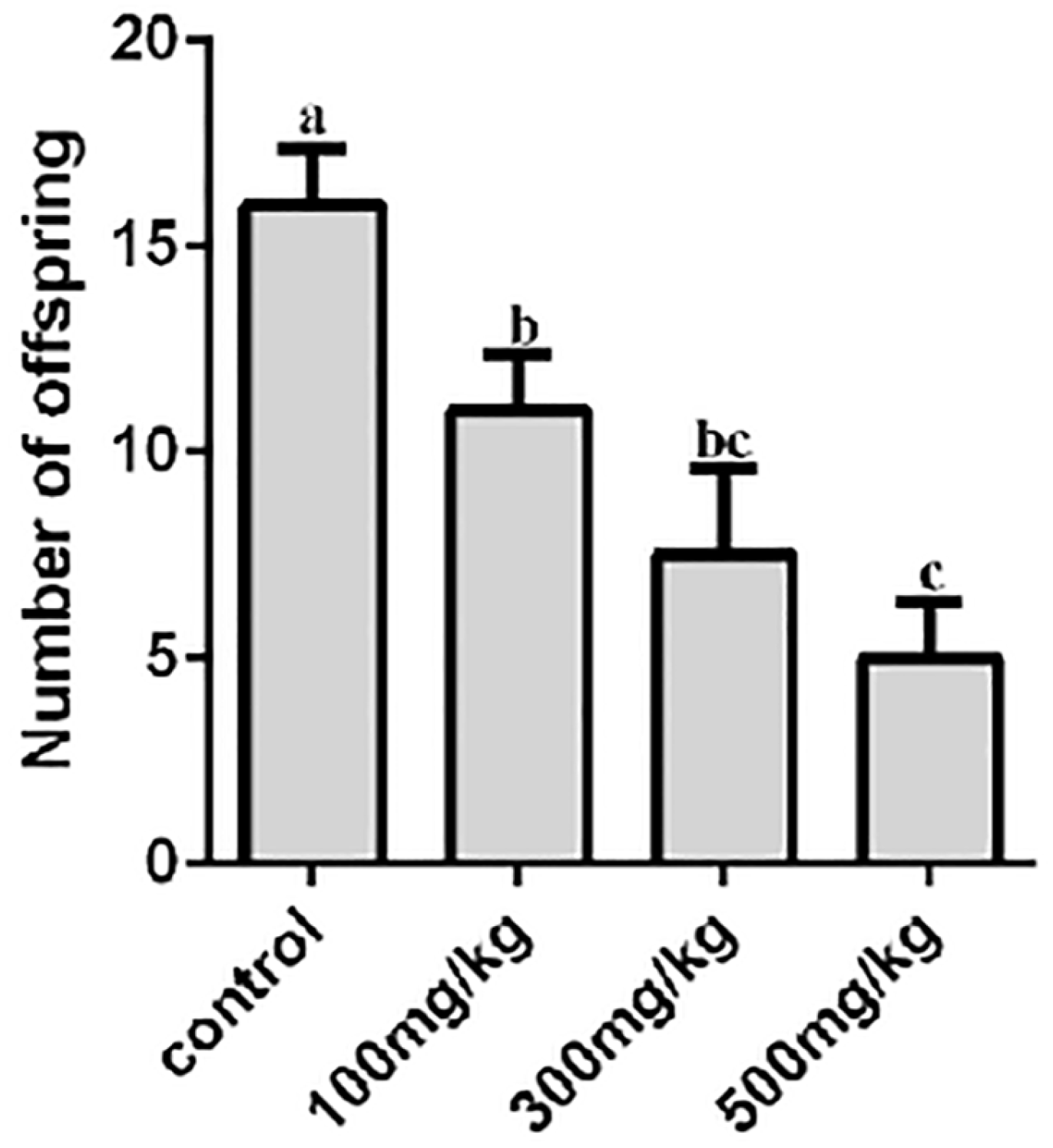
2.1. The Effects of Nano-TiO2 on the Growth and Birth Rate in Mice
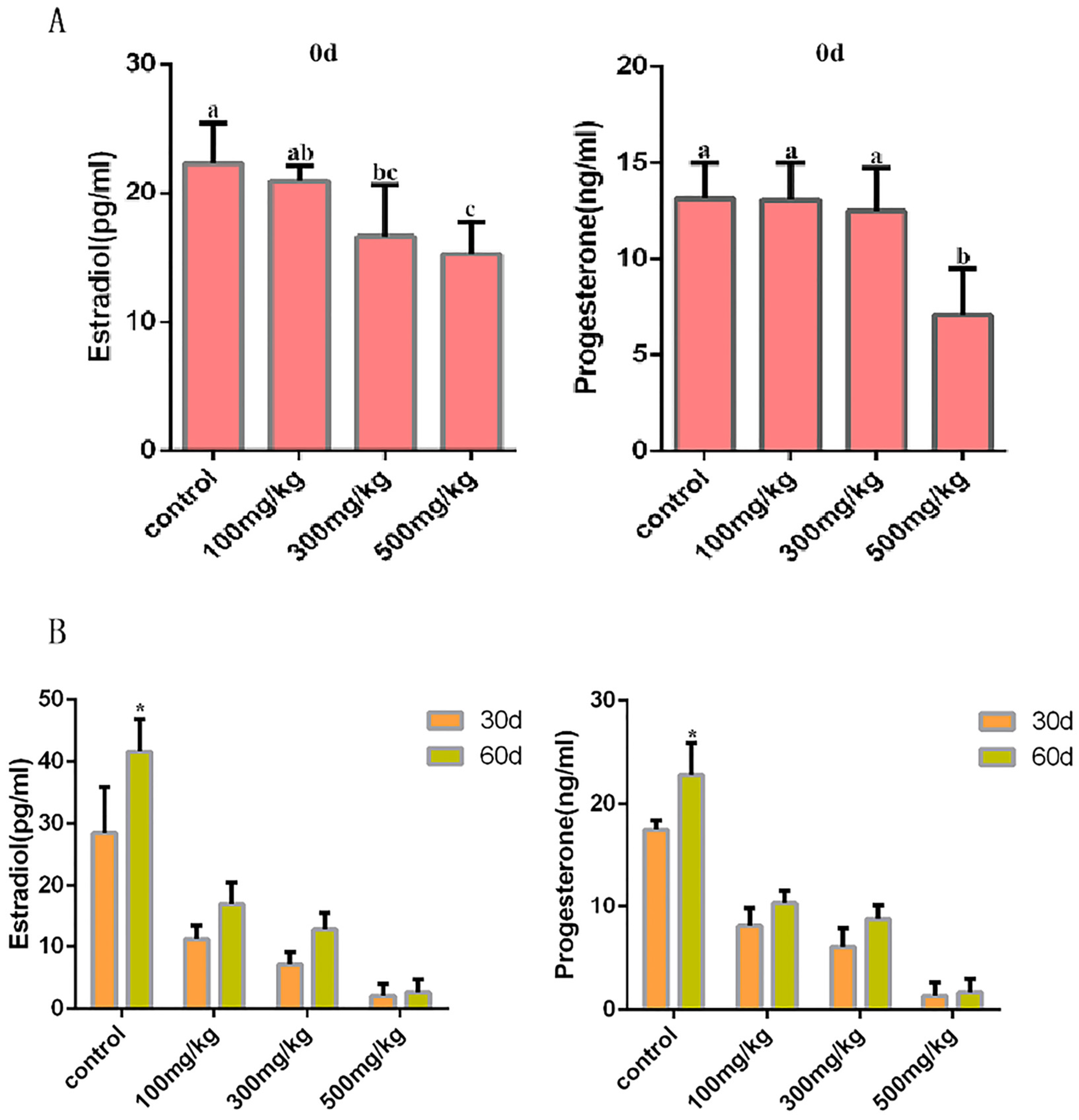
2.2. The Effects of Nano-TiO2 on the Reproductive Endocrine System of Mice
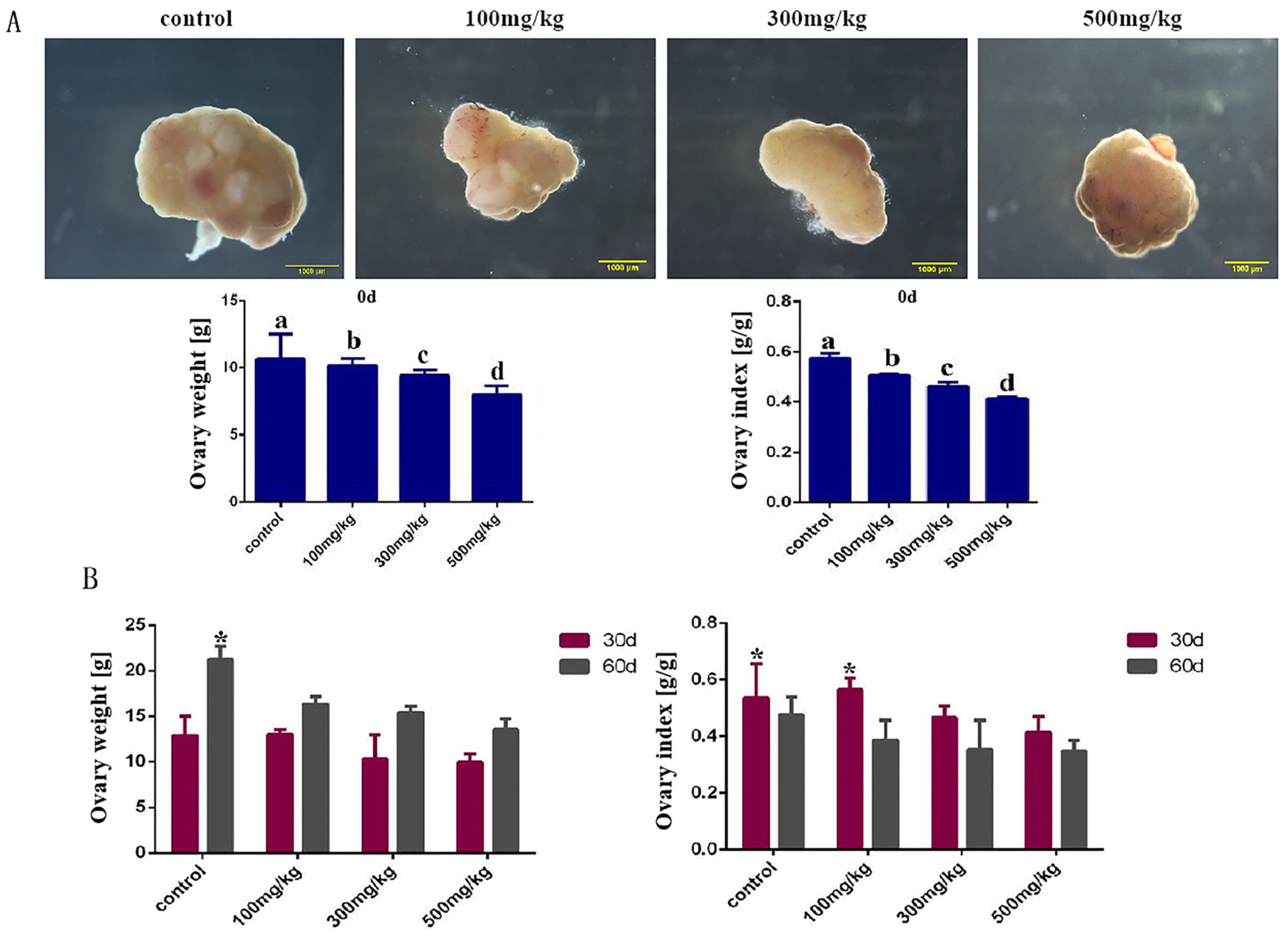
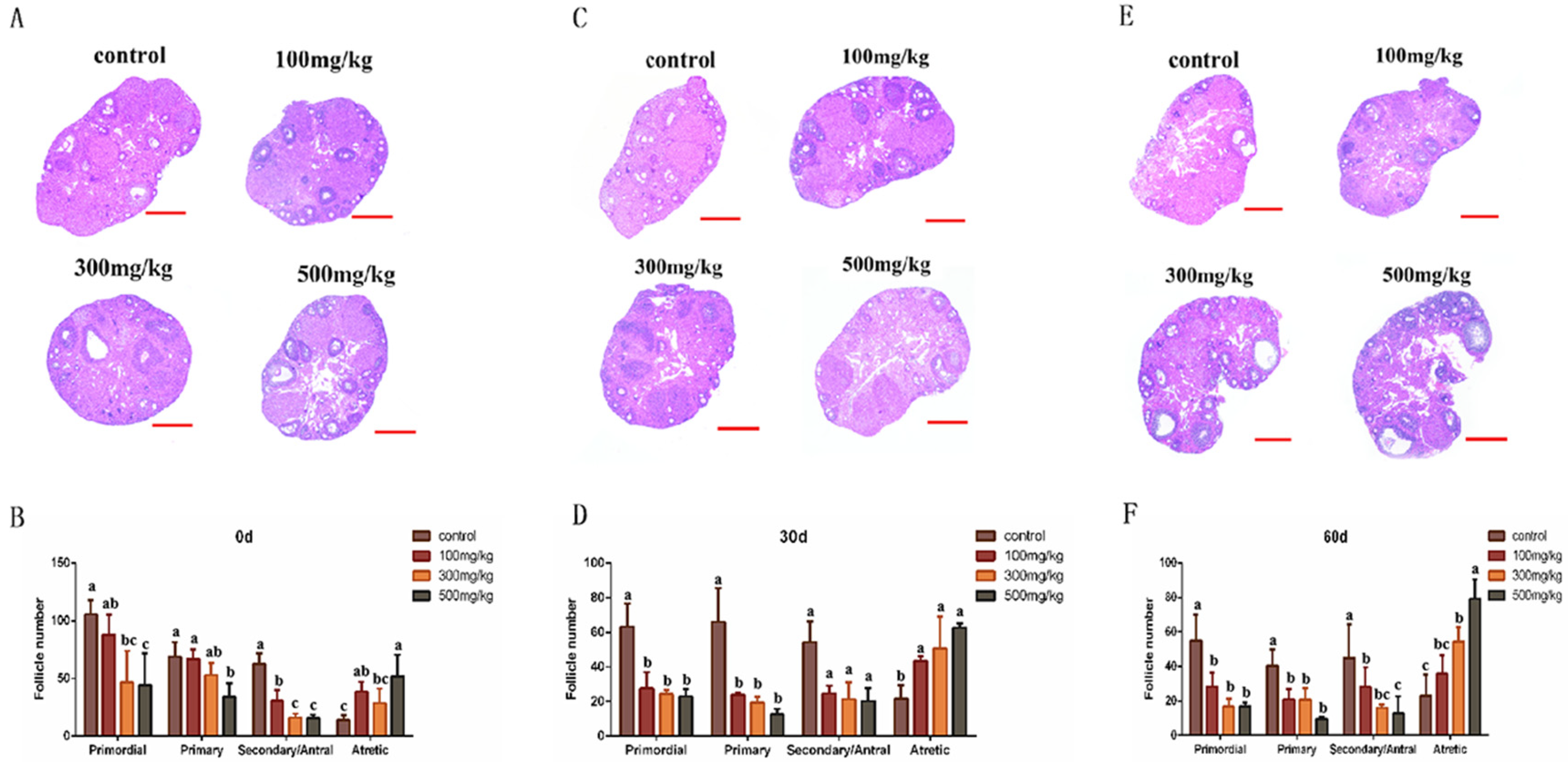
2.3. Histological Changes in Mouse Ovarian After Infusion of Nano-TiO2
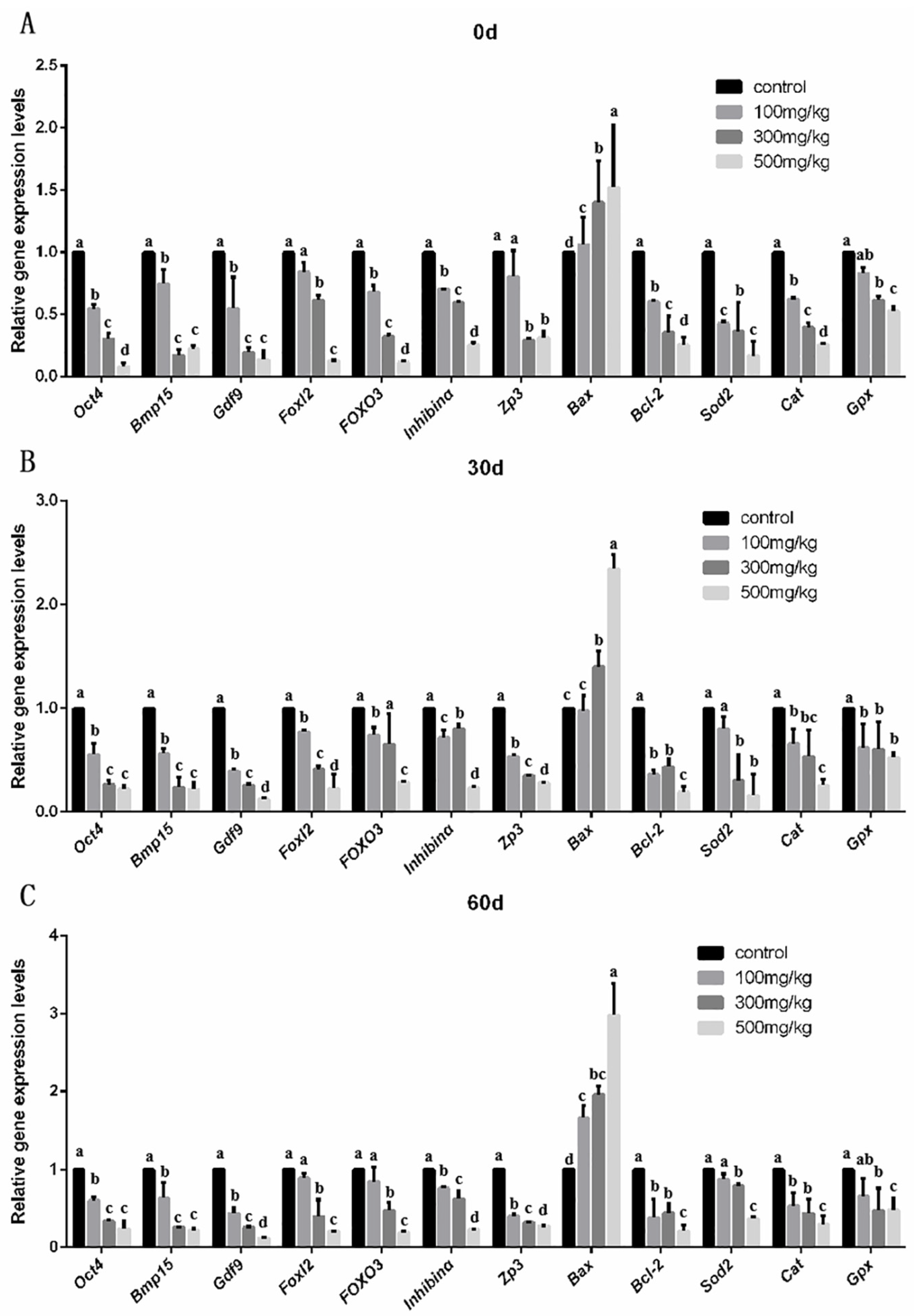
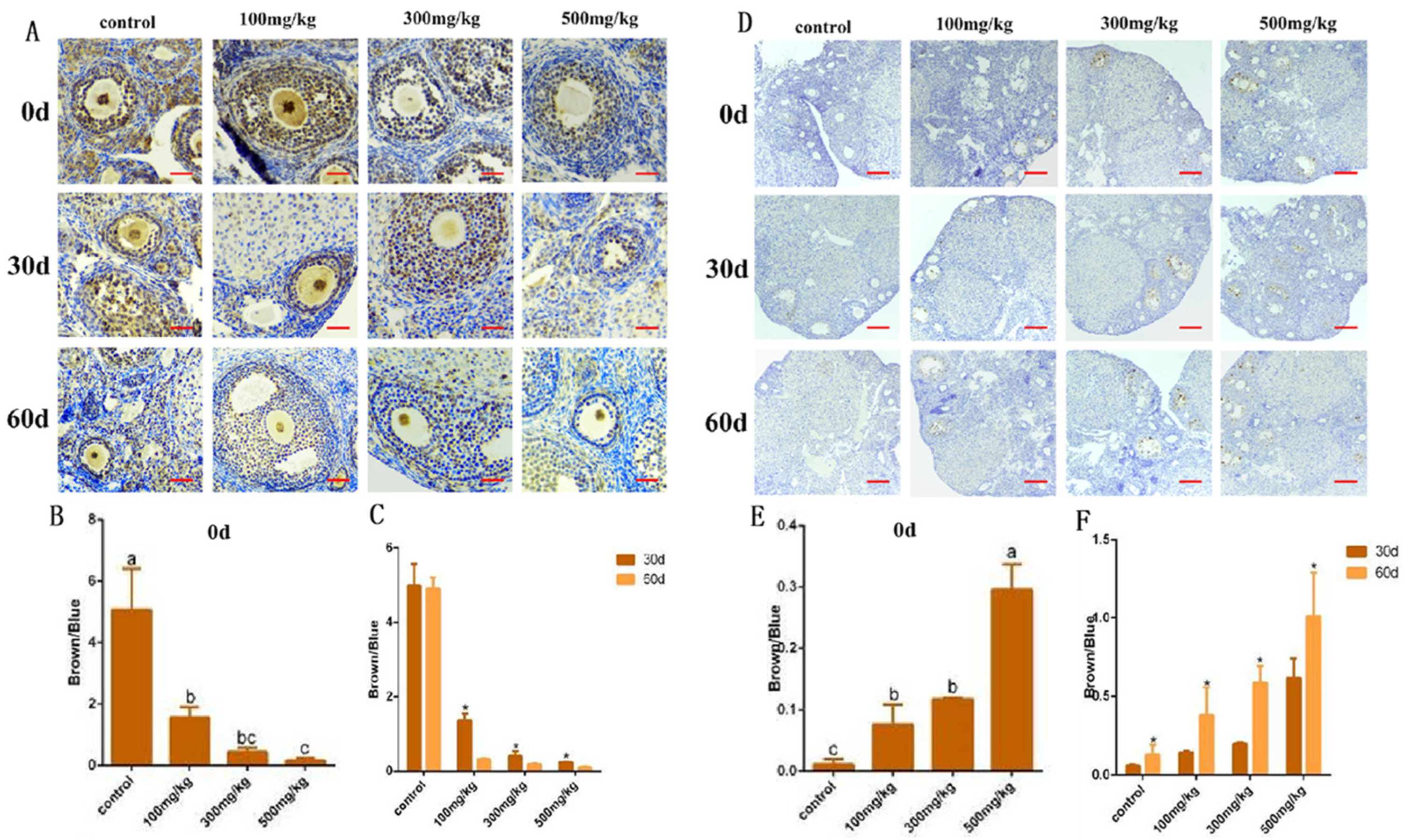
2.4. An Analysis of mRAN Levels in Ovarian Tissue After Nano-TiO2 Infusion and the Detection of Apoptotic Execution Proteins and Their Localization
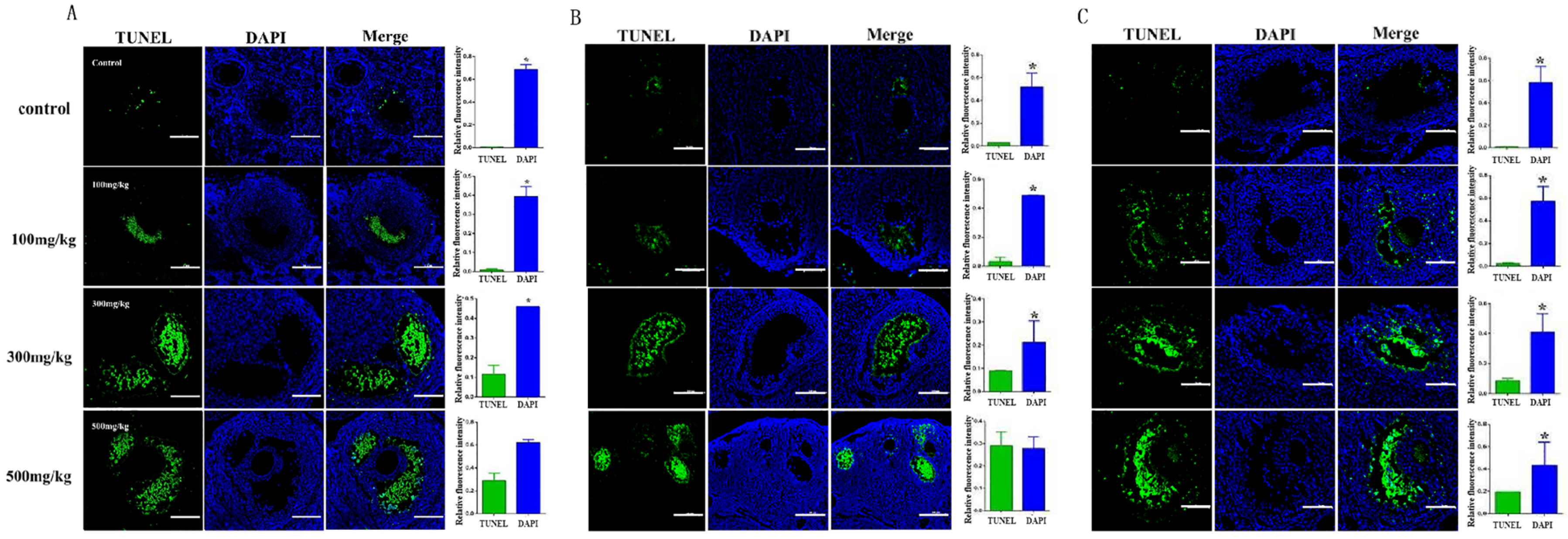
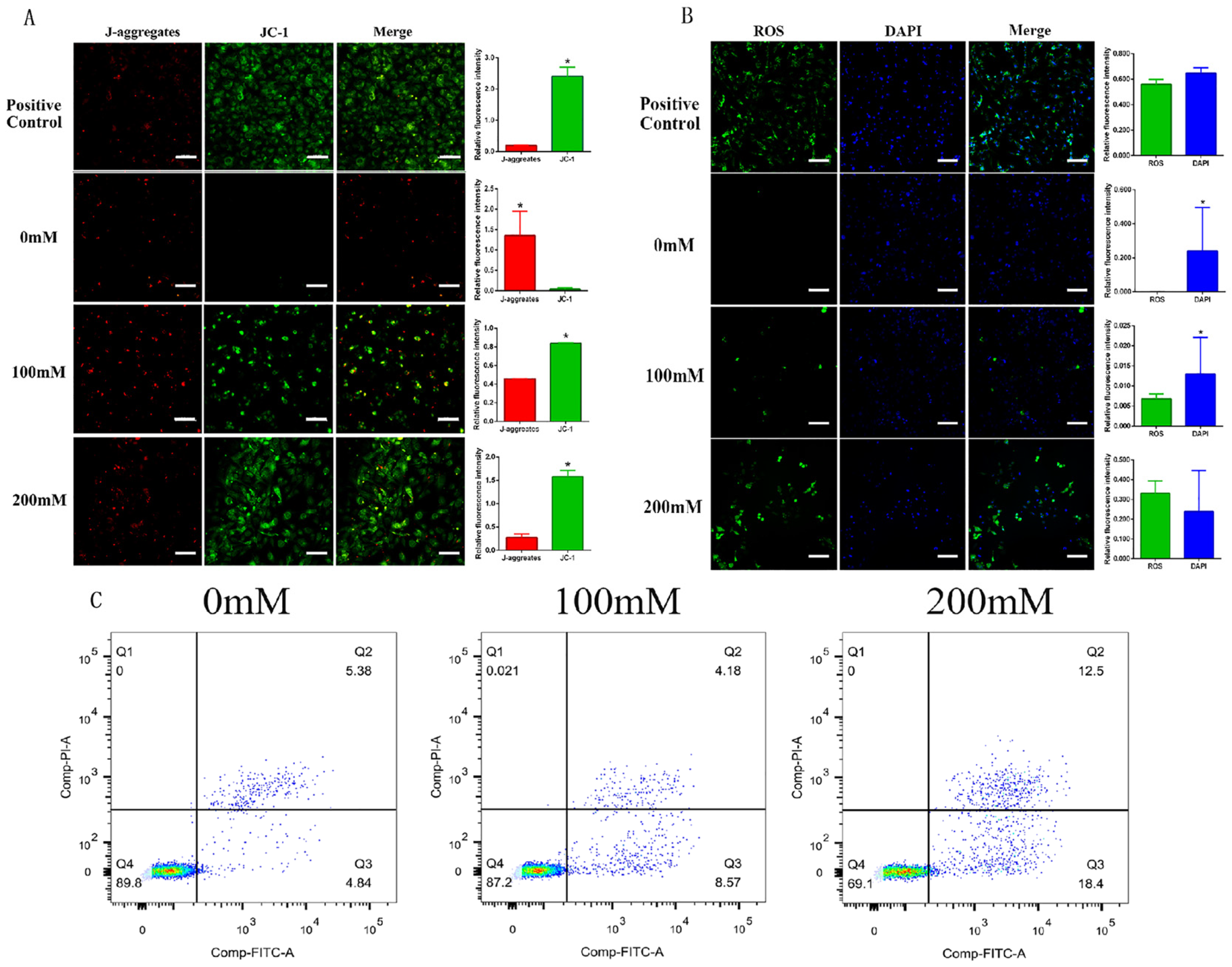
2.5. Determining the Effect of Nano-TiO2 on Promoting the Apoptosis of Granulosa Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation and Infusion of Nano-TiO2
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Hormone Testing in Mice After Nano-TiO2 Infusion
4.4. Detection of Ovarian Indices and Birth Rates in Mice
4.5. Hematoxylin–Eosin Staining of Mouse Ovaries and Follicle Count
4.6. Immunohistochemical Detection
4.7. Apoptosis Detection of Ovarian Granulosa Cells
4.8. RT-qPCR
4.9. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Detection (JC-1)
4.10. Mitochondrial ROS Detection
4.11. Flow Cytometry (FCM) of FITC-PI Apoptotic Cell Detection
4.12. Data Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brumfiel, G. Nanotechnology: A little knowledge. Nature 2003, 424, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colvin, V.L. The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1166–1170, Erratum in Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Gao, S.; Qiao, L. Nanomaterials as novel matrices to improve biomedical applications of MALDI-TOF/MS. Talanta 2025, 293, 128092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Stilwell, J.; Zhang, T.; Elboudwarej, O.; Jiang, H.; Selegue, J.P.; Cooke, P.A.; Gray, J.W.; Chen, F.F. Molecular characterization of the cytotoxic mechanism of multiwall carbon nanotubes and nano-onions on human skin fibroblast. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2448–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, T.; Stilwell, J.L.; Gerion, D.; Ding, L.; Elboudwarej, O.; Cooke, P.A.; Gray, J.W.; Alivisatos, A.P.; Chen, F.F. Cellular effect of high doses of silica-coated quantum dot profiled with high throughput gene expression analysis and high content cellomics measurements. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koivisto, A.J.; Burrueco-Subirà, D.; Candalija, A.; Vázquez-Campos, S.; Nicosia, A.; Ravegnani, F.; Furxhi, I.; Brigliadori, A.; Zanoni, I.; Blosi, M.; et al. Exposure assessment and risks associated with wearing silver nanoparticle-coated textiles. Open Res. Eur. 2024, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shakeel, M.; Jabeen, F.; Qureshi, N.A.; Fakhr-E-Alam, M. Toxic Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Titanium Dioxide Bulk Salt in the Liver and Blood of Male Sprague-Dawley Rats Assessed by Different Assays. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 173, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, R.; Raza, S.; Yadav, A.; Kushwaha, P.; Flora, S.J. Effects of sub-acute exposure to TiO2, ZnO and Al2O3 nanoparticles on oxidative stress and histological changes in mouse liver and brain. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 37, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.S.; Ootsuyama, Y.; Kawasaki, Y.; Morimoto, Y.; Higashi, T.; Kawai, K. Oxidative DNA damage in the rat lung induced by intratracheal instillation and inhalation of nanoparticles. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2018, 62, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, F.; Li, W.; Lao, F.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Ge, C.; Zhou, G.; et al. Potential neurological lesion after nasal instillation of TiO(2) nanoparticles in the anatase and rutile crystal phases. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 183, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churg, A.; Stevens, B.; Wright, J.L. Comparison of the uptake of fine and ultrafine TiO2 in a tracheal explant system. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, L81–L86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimipour, M.; Zirak Javanmard, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Jafari, A. Oral administration of titanium dioxide nanoparticle through ovarian tissue alterations impairs mice embryonic development. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2018, 16, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sakai, H.; Ito, E.; Cai, R.X.; Yoshioka, T.; Kubota, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A. Intracellular Ca2+ concentration change of T24 cell under irradiation in the presence of TiO2 ultrafine particles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1201, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.K.; Sharma, V.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, S.; Sultana, S.; Dhawan, A. ROS-mediated genotoxicity induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human epidermal cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rancan, F.; Nazemi, B.; Rautenberg, S.; Ryll, M.; Hadam, S.; Gao, Q.; Hackbarth, S.; Haag, S.F.; Graf, C.; Rühl, E.; et al. Ultraviolet radiation and nanoparticle induced intracellular free radicals generation measured in human keratinocytes by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Ski. Res. Technol. 2014, 20, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, Y.; Steller, H. Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell 2011, 147, 742–758, Erratum in Cell 2011, 147, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ziental, D.; Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Glowacka-Sobotta, A.; Stanisz, B.; Goslinski, T.; Sobotta, L. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Prospects and Applications in Medicine. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, H.; Chu, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Q.; et al. Titanium Dioxide Promotes New Particle Formation: A Smog Chamber Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, J.; Samali, A.; Orrenius, S. Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamplona, R.; Barja, G. Highly resistant macromolecular components and low rate of generation of endogenous damage: Two key traits of longevity. Ageing Res. Rev. 2007, 6, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, M.J.; Dubey, A.; Dawson, K.M.; Stutts, W.A.; Lal, H.; Sohal, R.S. Age-related losses of cognitive function and motor skills in mice are associated with oxidative protein damage in the brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4765–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rera, M.; Clark, R.I.; Walker, D.W. Intestinal barrier dysfunction links metabolic and inflammatory markers of aging to death in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21528–21533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsai-Turton, M.; Luderer, U. Opposing effects of glutathione depletion and follicle-stimulating hormone on reactive oxygen species and apoptosis in cultured preovulatory rat follicles. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, R.Y.; Youn, S.M.; Choi, S.J. Oral Excretion Kinetics of Food-Additive Silicon Dioxides and Their Effect on In Vivo Macrophage Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wei, S.; Sun, B.; Liu, C.; Sokolova, I.; Waiho, K.; Fang, J.K.H.; Song, H.; Shi, J.; Shang, Y.; Xie, Z.; et al. Nano-TiO2 aggravates the adverse effect of pentachlorophenol on antioxidant and immune response in anti-predatory mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Amouri, R.; Tu, Z.; Abo-Raya, M.H.; Pang, X.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Nano-TiO2 impairs the health of crabs Charybdis japonica under warming conditions through waterborne and dietary exposures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayes, C.M.; Wahi, R.; Kurian, P.A.; Liu, Y.; West, J.L.; Ausman, K.D.; Warheit, D.B.; Colvin, V.L. Correlating nanoscale titania structure with toxicity: A cytotoxicity and inflammatory response study with human dermal fibroblasts and human lung epithelial cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Wang, J.; Jie, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Hou, X. MnO2 nanoparticles enhance the activity of the Zr-MOF matrix electrochemical sensor for efficiently identifying ultra-trace tetracycline residues in food. Mikrochim. Acta 2024, 192, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warheit, D.B.; Webb, T.R.; Reed, K.L.; Frerichs, S.; Sayes, C.M. Pulmonary toxicity study in rats with three forms of ultrafine-TiO2 particles: Differential responses related to surface properties. Toxicology 2007, 230, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.O.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, W.I.; Pak, S.W.; Moon, C.; Shin, I.S.; Heo, J.D.; Ko, J.W.; Kim, J.C. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Exacerbate Allergic Airway Inflammation via TXNIP Upregulation in a Mouse Model of Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rede, D.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Ramos, S.; Oliva-Teles, F.; Antão, C.; Sousa, S.R.; Delerue-Matos, C. Individual and mixture toxicity evaluation of three pharmaceuticals to the germination and growth of Lactuca sativa seeds. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 673, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Brito, W.A.; Mutter, F.; Wende, K.; Cecchini, A.L.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S. Consequences of nano and microplastic exposure in rodent models: The known and unknown. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Long, H.; Zhang, L.; Yin, S.; Li, S.; Zhu, F.; Xie, H. Effectiveness of microwave-assisted thermal treatment in the extraction of gold in cyanide tailings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Jiao, S.; Zhang, X. Astragaloside IV reduces neuronal apoptosis and parthanatos in ischemic injury by preserving mitochondrial hexokinase-II. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 131, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, P.; Dong, R.; Sun, C.; Song, G.; Wang, Y. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis through ROS-Ca2+-p38/AKT/mTOR pathway in TM4 cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyeman, P.C.; Kebonye, N.M.; John, K.; Haghnazar, H.; Borůvka, L.; Vašát, R. Compositional mapping, uncertainty assessment, and source apportionment via pollution assessment-based receptor models in urban and peri-urban agricultural soils. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 1451–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Pandey, V.; Sahu, A.N.; Singh, A.K.; Dubey, P.K. Encircling granulosa cells protects against di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate-induced apoptosis in rat oocytes cultured in vitro. Zygote 2019, 27, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostuni, A.; Faruolo, M.P.; Sileo, C.; Petillo, A.; Boni, R. Effect of follicle size and atresia grade on mitochondrial membrane potential and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression in bovine granulosa cells. Zygote 2018, 26, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márquez-Ramírez, S.G.; Delgado-Buenrostro, N.L.; Chirino, Y.I.; Iglesias, G.G.; López-Marure, R. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles inhibit proliferation and induce morphological changes and apoptosis in glial cells. Toxicology 2012, 302, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, W.; Yunqi, Z.; Zimeng, L.; Kangning, X.; Deji, L.; Chen, Q.; Yong, Z.; Fusheng, Q. Large extracellular vesicles in bovine follicular fluid inhibit the apoptosis of granulosa cell and stimulate the production of steroid hormones. Theriogenology 2023, 195, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. TGF-β1 activates NOX4/ROS pathway to promote the invasion and migration of cervical cancer cells. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019, 35, 121–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lou, Y.; Li, B. Exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles disrupts the BTB by interfering with the assembly of stress granules in germ cells. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, A.; Cruces, J.; Ceprián, N.; Vara, E.; de la Fuente, M. Oxidative-Inflammatory Stress in Immune Cells from Adult Mice with Premature Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomellini, V.; Gomez, C.R.; Kovacs, E.J. Aging and impairment of innate immunity. Contrib. Microbiol. 2008, 15, 188–205. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.S.; Luo, K.L.; Shi, L. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Interacts With Inflammation in Human Diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence | Product Size (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F: AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG R: TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA | 123 | 58 |
| Oct4 | F: GATGCTGTGAGCCAAGGCAAG R: GGCTCCTGATCAACAGCATCAC | 145 | 58 |
| Bmp15 | F: TCCTTGCTGACGACCCTACAT R: TACCTCAGGGGATAGCCTTGG | 100 | 55 |
| Gdf9 | F:TCTTAGTAGCCTTAGCTCTCAGG R: TGTCAGTCCCATCTACAGGCA | 116 | 55 |
| Foxl2 | F:ACAACACCGGAGAAACCAGAC R: CGTAGAACGGGAACTTGGCTA | 145 | 55 |
| Foxo3 | F: CTGGGGGAACCTGTCCTATG R: TCATTCTGAACGCGCATGAAG | 210 | 55 |
| Inhibinα | F: GCACAGGACCTCTGAACCAG R: GGGATGGCCGGAATACATAAG | 101 | 60 |
| Zp3 | F: ATGGCGTCAAGCTATTTCCTC R: CGTGCCAAAAAGGTCTCTACT | 186 | 55 |
| Bax | F: TGAAGACAGGGGCCTTTTTG R: AATTCGCCGGAGACACTCG | 140 | 60 |
| Bcl-2 | F:ATGCCTTTGTGGAACTATATGGC R: GGTATGCACCCAGAGTGATGC | 120 | 55 |
| Sod2 | F: ATGGTGGGGGACATATT R: GAACCTTGGACTCCCACAGA | 167 | 55 |
| Cat | F: CCTCGTTCAGGATGTGGTTT R: TCTGGTGATATCGTGGGTGA | 130 | 57 |
| Gpx | F: GTCCACCGTGTATGCCTTCT R: TCTGCAGATCGTTCATCTCG | 152 | 57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Ren, J.; You, X.; Dai, Y. Nano-Titanium Dioxide Induces Ovarian Function Damage in Mice by Mediating Granulosa Cell Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146981
Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wu C, Ren J, You X, Dai Y. Nano-Titanium Dioxide Induces Ovarian Function Damage in Mice by Mediating Granulosa Cell Apoptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146981
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jie, Yaxuan Zhang, Shengbo Zhang, Changbao Wu, Jingyu Ren, Xiaoxiao You, and Yanfeng Dai. 2025. "Nano-Titanium Dioxide Induces Ovarian Function Damage in Mice by Mediating Granulosa Cell Apoptosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146981
APA StyleChen, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, S., Wu, C., Ren, J., You, X., & Dai, Y. (2025). Nano-Titanium Dioxide Induces Ovarian Function Damage in Mice by Mediating Granulosa Cell Apoptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146981





