Detection of Feline Coronavirus Membrane Gene Based on Conventional Revere Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, Nested Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
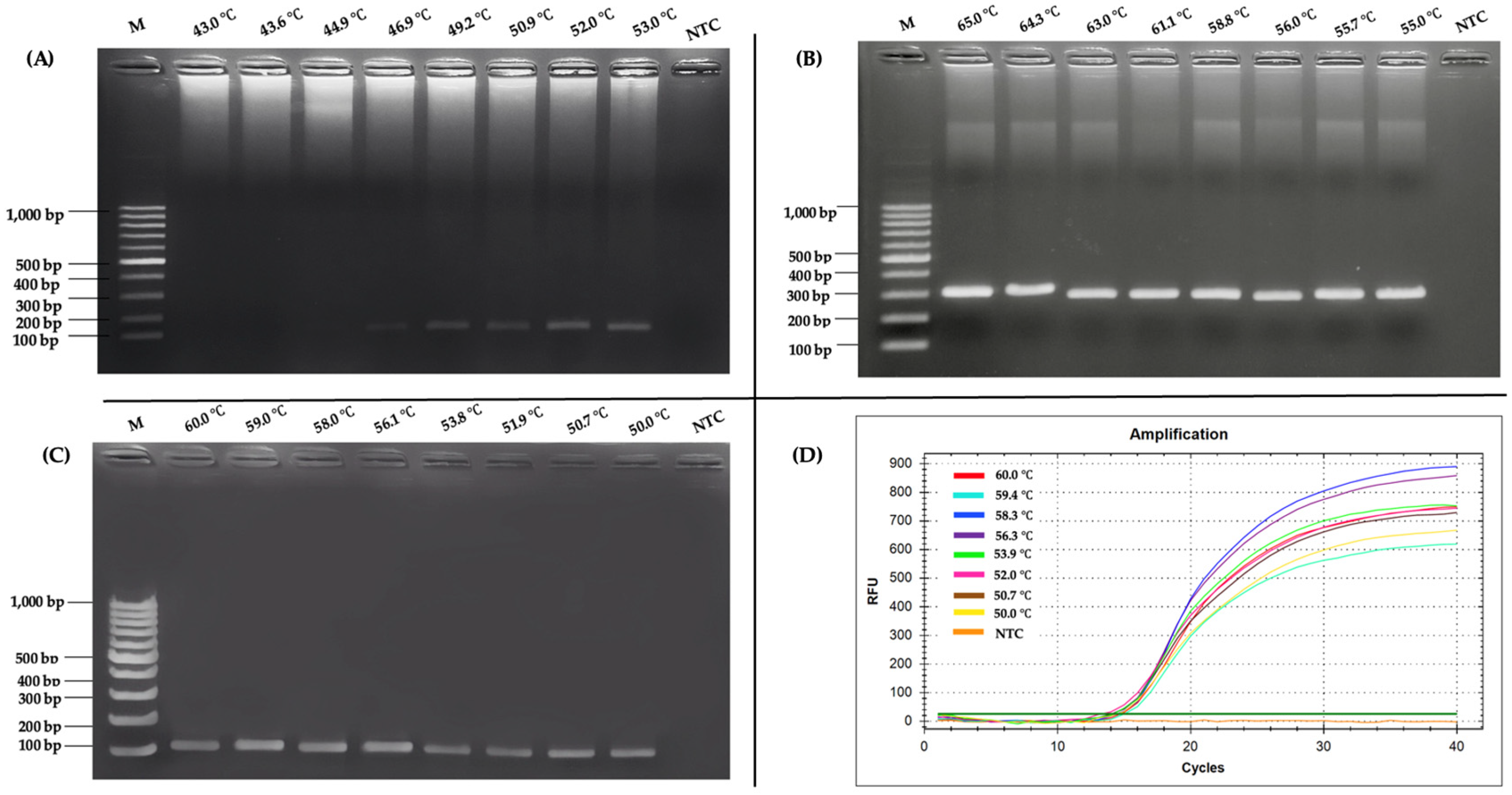
2.1. Optimization of RT-PCR and Nested RT-PCR Assay
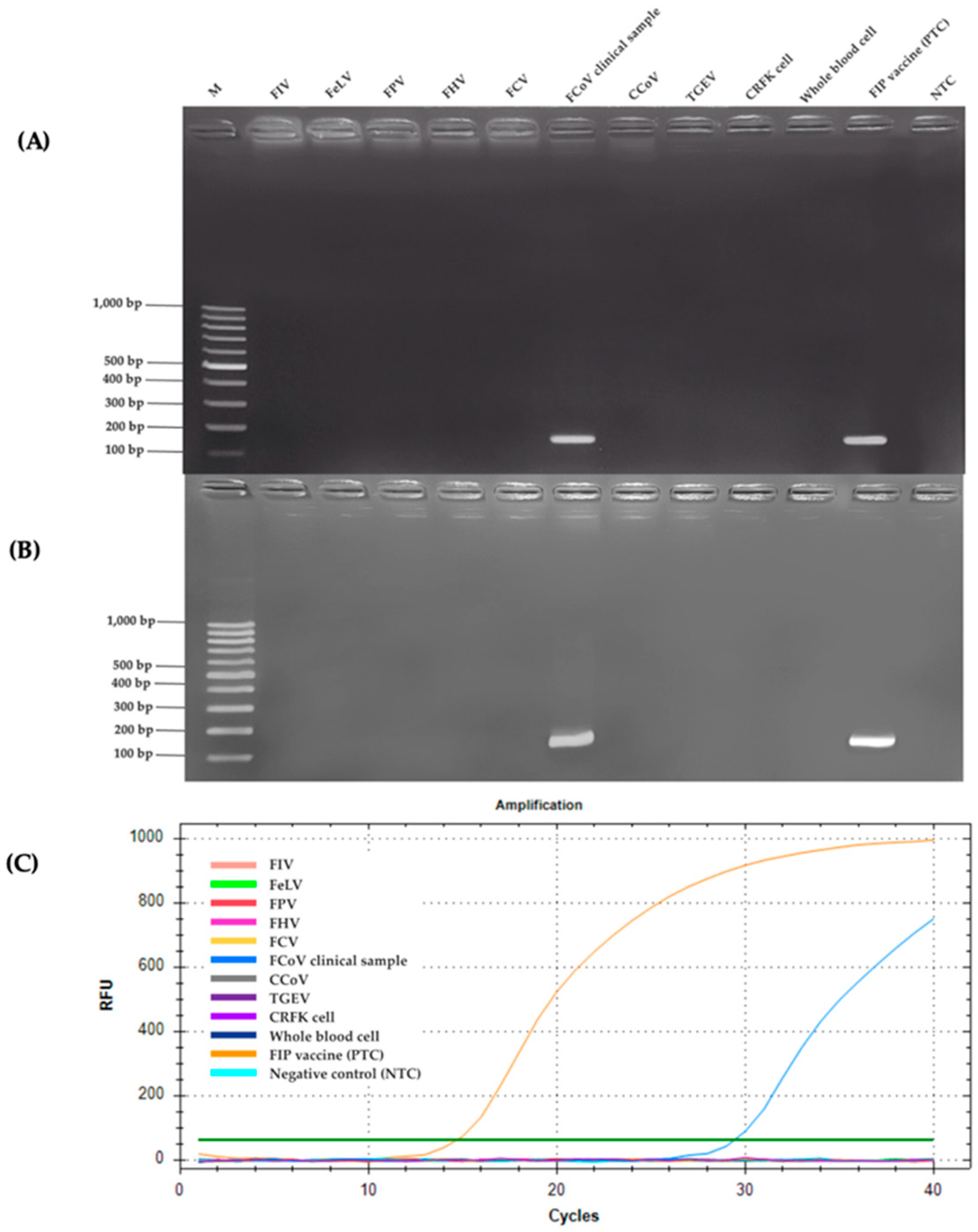
2.2. Specificity Analysis
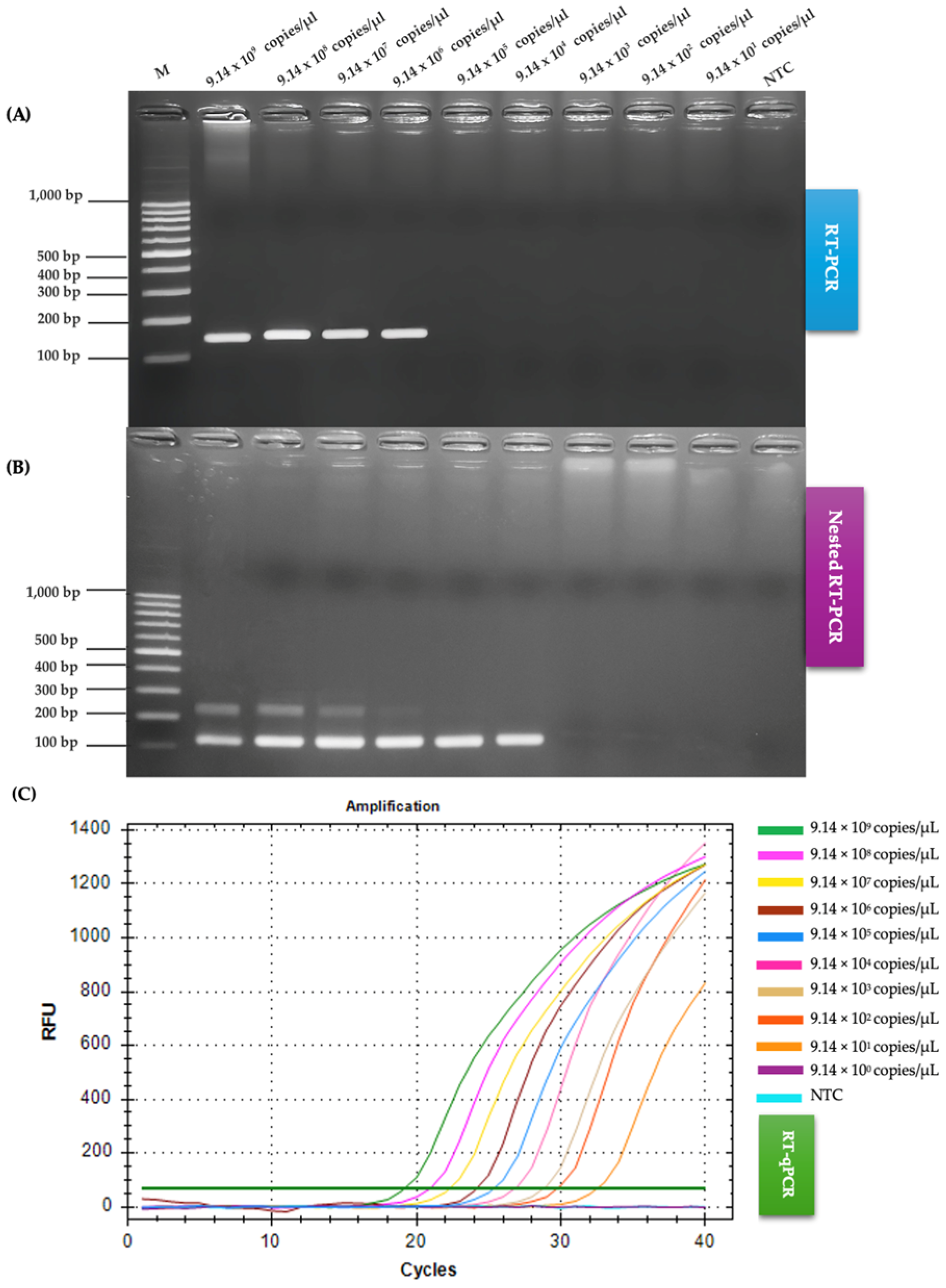
2.3. Comparison of RT-PCR, Nested RT-PCR and RT-qPCR Regarding Sensitivity
2.4. Comparison of RT-PCR, Nested RT-PCR, and RT-qPCR on Clinical Samples for FCoV Detection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Collection of Clinical Samples
4.3. RNA Extraction
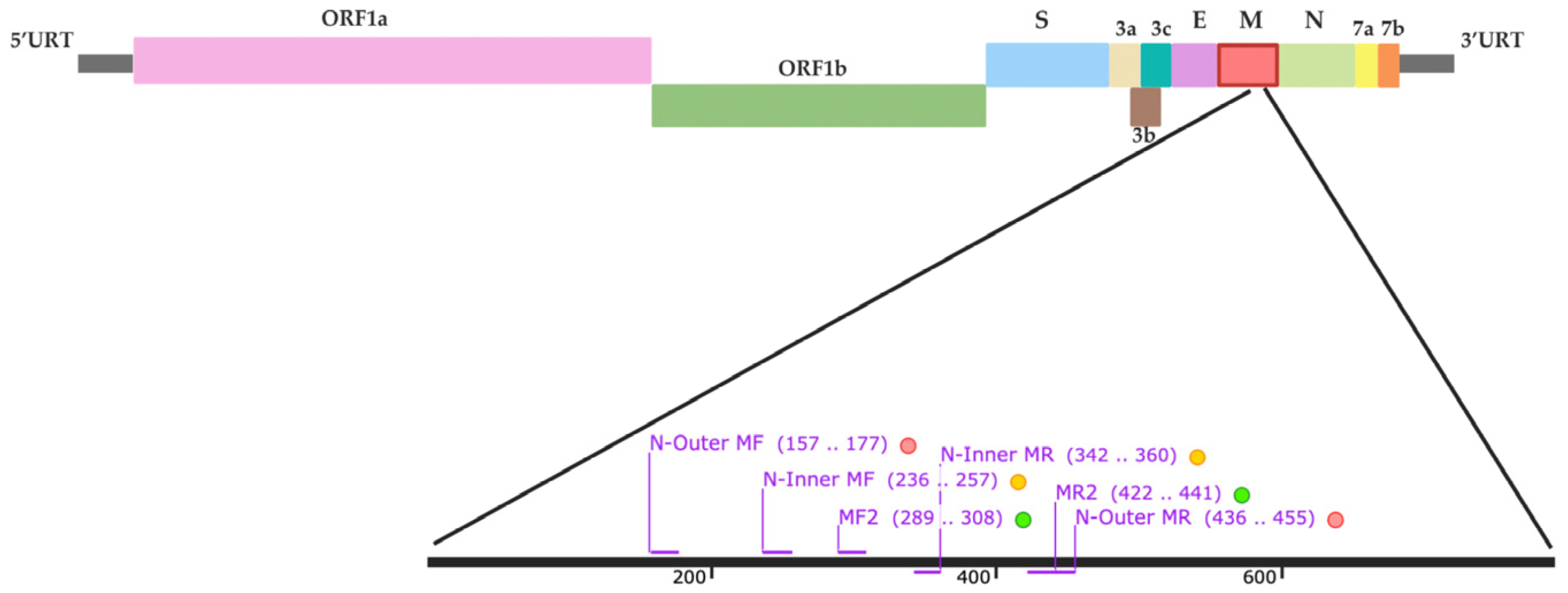
4.4. RT-PCR and Nested RT-PCR Primer Design
4.5. RT-PCR, Nested RT-PCR, and Optimization
4.6. Specificity Analysis
4.7. Comparison of RT-PCR, Nested RT-PCR, and RT-qPCR on Sensitivity for FCoV Detection
4.8. Detection of FCoV in Clinical Samples Using RT- PCR Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barker, E.N.; Tasker, S. Advances in Molecular Diagnostics and Treatment of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Adv. Small Anim. Care 2020, 1, 161–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipar, A.; Meli, M.L. Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licitra, B.N.; Millet, J.K.; Regan, A.D.; Hamilton, B.S.; Rinaldi, V.D.; Duhamel, G.E.; Whittaker, G.R. Mutation in Spike Protein Cleavage Site and Pathogenesis of Feline Coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennema, H.; Godeke, G.J.; Rossen, J.W.; Voorhout, W.F.; Horzinek, M.C.; Opstelten, D.J.; Rottier, P.J. Nucleocapsid-Independent Assembly of Coronavirus-like Particles by Co-Expression of Viral Envelope Protein Genes. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, C.; Temperton, N.; Siddell, S.G. Type I Feline Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein Fails to Recognize Aminopeptidase N as a Functional Receptor on Feline Cell Lines. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekes, G.; Spies, D.; Bank-Wolf, B.; Thiel, V.; Thiel, H.-J. A Reverse Genetics Approach To Study Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6994–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, K.; Maeda, A.; Maeda, J.; Makino, S. Characterization of the Coronavirus M Protein and Nucleocapsid Interaction in Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8127–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedeurwaerder, A.; Olyslaegers, D.A.J.; Desmarets, L.M.B.; Roukaerts, I.D.M.; Theuns, S.; Nauwynck, H.J. ORF7-Encoded Accessory Protein 7a of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus as a Counteragent against IFN-α-Induced Antiviral Response. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedeurwaerder, A.; Desmarets, L.M.; Olyslaegers, D.A.J.; Vermeulen, B.L.; Dewerchin, H.L.; Nauwynck, H.J. The Role of Accessory Proteins in the Replication of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus in Peripheral Blood Monocytes. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Haan, C.A.M.; Vennema, H.; Rottier, P.J.M. Assembly of the Coronavirus Envelope: Homotypic Interactions between the M Proteins. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4967–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.-W.; de Groot, R.J.; Egberink, H.F.; Rottier, P.J.M. Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Insights into Feline Coronavirus Pathobiogenesis and Epidemiology Based on Genetic Analysis of the Viral 3c Gene. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.E.; Hilt, D.A.; Jackwood, M.W. Comparative Sequence Analysis of Full-Length Genome of FIPV at Different Tissue Passage Levels. Virus Genes. 2013, 47, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekes, G.; Thiel, H.J. Feline Coronaviruses. In Coronaviruses; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2016; pp. 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, A.; Siti-Suri, A.; Mohd, H.B.; Abdul-Rahman, O.; Tengku-Azmi, T.I.; Faruku, B.; Ajwad, A. Molecular and Pathological Identification of Feline Coronavirus Type I. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Troyer, J.L.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Roelke, M.E.; O’Brien, S.J. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gut, M.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Huder, J.B.; Pedersen, N.C.; Lutz, H. One-Tube Fluorogenic Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Quantitation of Feline Coronaviruses. J. Virol. Methods 1999, 77, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, C.; Siddell, S.G. Genomic RNA Sequence of Feline Coronavirus Strain FCoV C1Je. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2007, 9, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, P.M.; Elbe, A.; Lynch, B.M.; Lashnits, E.; Kirchdoerfer, R.N. Detection of Feline Coronavirus RNA in Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis and Their Housemates. Viruses 2025, 17, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C. An Update on Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, C.; Helps, C.R.; Siddell, S.G. Evaluation of Real-Time RT-PCR for the Quantification of FCoV Shedding in the Faeces of Domestic Cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Poder, S. Feline and Canine Coronaviruses: Common Genetic and Pathobiological Features. Adv. Virol. 2011, 2011, 609465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.S.; Porter, E.; Matthews, D.; Kipar, A.; Tasker, S.; Helps, C.R.; Siddell, S.G. Genotyping Coronaviruses Associated with Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiba, N.; Maeda, K.; Kato, H.; Mochizuki, M.; Iwata, H. Differentiation of Feline Coronavirus Type I and II Infections by Virus Neutralization Test. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solikhah, T.I.; Agustin, Q.A.D.; Damaratri, R.A.; Siwi, D.A.F.; Rafi’uttaqi, G.N.; Hartadi, V.A.; Solikhah, G.P. A Review of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Infection. Vet. World 2024, 17, 2417–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrewegh, A.A.; de Groot, R.J.; Cepica, A.; Egberink, H.F.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J. Detection of Feline Coronavirus RNA in Feces, Tissues, and Body Fluids of Naturally Infected Cats by Reverse Transcriptase PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C. A Review of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Infection: 1963–2008. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, K.; Binder, C.; Hirschberger, J.; Cole, D.; Reinacher, M.; Schroo, S.; Frost, J.; Egberink, H.; Lutz, H.; Hermanns, W. Comparison of Different Tests to Diagnose Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2003, 17, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stranieri, A.; Paltrinieri, S.; Giudice, C.; Cannito, V.; Lauzi, S.G.A. Comparison of the Performance of Laboratory Tests in the Diagnosis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, D.A.; Lobbiani, A.; Gramegna, M.; Moore, L.E.; Colucci, G. Development of a Nested PCR Assay for Detection of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus in Clinical Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paltrinieri, S.; Parodi, M.C.; Cammarata, G. In Vivo Diagnosis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis by Comparison of Protein Content, Cytology, and Direct Immunofluorescence Test on Peritoneal and Pleural Effusions. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1999, 11, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, M.C.; Cammarata, G.; Paltrinieri, S.; Lavazza, A.; Ape, F. Using Direct Immunofluorescence to Detect Coronaviruses in Peritoneal in Peritoneal and Pleural Effusions. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1993, 34, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, S.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Balzer, H.-J.; Pantchev, N.; Matiasek, K.; Wess, G.; Egberink, H.; Hartmann, K. Sensitivity and Specificity of a Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction Detecting Feline Coronavirus Mutations in Effusion and Serum/Plasma of Cats to Diagnose Feline Infectious Peritonitis. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, F.A.; Vennema, H.; Rofina, J.E.; Pol, J.M.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J.M.; Egberink, H.F. A MRNA PCR for the Diagnosis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 124, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapichai, W.; Saejung, W.; Khumtong, K.; Boonkaewwan, C.; Tuanthap, S.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Choowongkomon, K.; Rattanasrisomporn, J. Development of Colorimetric Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Detecting Feline Coronavirus. Animals 2022, 12, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khumtong, K.; Rapichai, W.; Saejung, W.; Khamsingnok, P.; Meecharoen, N.; Ratanabunyong, S.; Van Dong, H.; Tuanthap, S.; Rattanasrisomporn, A.; Choowongkomon, K.; et al. Colorimetric Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Xylenol Orange Targeting Nucleocapsid Gene for Detection of Feline Coronavirus Infection. Viruses 2025, 17, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felten, S.; Weider, K.; Doenges, S.; Gruendl, S.; Matiasek, K.; Hermanns, W.; Mueller, E.; Matiasek, L.; Fischer, A.; Weber, K.; et al. Detection of Feline Coronavirus Spike Gene Mutations as a Tool to Diagnose Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 19, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamsingnok, P.; Rapichai, W.; Rattanasrisomporn, A.; Rungsuriyawiboon, O.; Choowongkomon, K.; Rattanasrisomporn, J. Comparison of PCR, Nested PCR, and RT-LAMP for Rapid Detection of Feline Calicivirus Infection in Clinical Samples. Animals 2024, 14, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saejung, W.; Khumtong, K.; Rapichai, W.; Ratanabunyong, S.; Rattanasrisomporn, A.; Choowongkomon, K.; Rungsuriyawiboon, O.; Rattanasrisomporn, J. Detection of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus by Neutral Red-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay. Vet. World 2024, 17, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toohey-Kurth, K.; Reising, M.M.; Tallmadge, R.L.; Goodman, L.B.; Bai, J.; Bolin, S.R.; Pedersen, J.C.; Bounpheng, M.A.; Pogranichniy, R.M.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; et al. Suggested Guidelines for Validation of Real-Time PCR Assays in Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratories. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaro, N.; Lorusso, A. Novel Human Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A Lesson from Animal Coronaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addie, D.D.; Schaap, I.A.T.; Nicolson, L.; Jarrett, O. Persistence and Transmission of Natural Type I Feline Coronavirus Infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2735–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalendar, R.; Shevtsov, A.; Otarbay, Z.; Ismailova, A. In Silico PCR Analysis: A Comprehensive Bioinformatics Tool for Enhancing Nucleic Acid Amplification Assays. Front. Bioinform. 2024, 4, 1464197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Chordia, N. Silico PCR Primer Designing and Validation; Human Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, S. Diagnosis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Update on Evidence Supporting Available Tests. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engstrom-Melnyk, J.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Peraud, O.; Hein, R.C. Clinical Applications of Quantitative Real-Time PCR in Virology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 161–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-I.; Kang, S.-Y.; Yoon, K.-J.; Na, K.-J. Nucleic Acid-Based Differential Diagnostic Assays for Feline Coronavirus. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 208, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuanthap, S.; Chiteafea, N.; Rattanasrisomporn, J.; Choowongkomon, K. Comparative Sequence Analysis of the Accessory and Nucleocapsid Genes of Feline Coronavirus Strains Isolated from Cats Diagnosed with Effusive Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, S.; Sarkar, S.; Chenoweth, K.; Johnson, C.; Delmain, D.; Wang, C. Insights on Feline Infectious Peritonitis Risk Factors and Sampling Strategies from Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of Feline Coronavirus in Large-Scale Nationwide Submissions. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2025, 263, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Feng, S.; Shi, K.; Shi, Y.; Long, F.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z. One-Step Triplex TaqMan Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Detection of Feline Coronavirus, Feline Panleukopenia Virus, and Feline Leukemia Virus. Vet. World 2024, 17, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic-Rustempasic, S.; Esona, M.D.; Williams, A.L.; Bowen, M.D. Sensitive and Specific Nested PCR Assay for Detection of Rotavirus A in Samples with a Low Viral Load. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 236, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-H.; Chung, Y.-S.; Kim, K.-S.; Lee, W.-J.; Chung, I.Y.; Oh, H.-B.; Kang, C. Development of Real-Time PCR Assays for Detection and Quantification of Human Bocavirus. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 42, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thieulent, C.J.; Carossino, M.; Peak, L.; Wolfson, W.; Balasuriya, U.B.R. Multiplex One-Step RT-QPCR Assays for Simultaneous Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Enteric Viruses of Dogs and Cats. Viruses 2023, 15, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panei, C.J.; Fuentealba, N.A.; Bravi, M.E.; Moré, G.; Brasso, N. Nested PCR Effective to Detect Low Viral Loads of SARS-CoV-2 in Animal Samples. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 231, 106303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.-Y.; Li, A.-Q.; Guo, X.-M.; Wang, M.; Guan, X.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Huang, J. Optimizing the Nested PCR Method for Decapod Iridescent Virus 1 (DIV1) Targeting ATPase Gene by Reselecting the Inner Primers. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2024, 207, 108212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jian, Y.; Li, Z.; Duo, H.; Guo, Z.; Fu, Y. Optimization of Single-Tube Nested PCR for the Detection of Echinococcus Spp. Exp. Parasitol. 2023, 247, 108494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Song, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H. Analytical Sensitivity Comparison of 14 Conventional and Three Rapid RT-PCR Assays for SARS-CoV-2 Detection. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 293, 114144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangl, L.; Felten, S.; Matiasek, K.; Dörfelt, S.; Bergmann, M.; Balzer, H.-J.; Pantchev, N.; Leutenegger, C.; Hartmann, K. Detection of Feline Coronavirus RNA, Spike Gene Mutations, and Feline Coronavirus Antigen in Macrophages in Aqueous Humor of Cats in the Diagnosis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Detection Method | Positive | Negative | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| RT-PCR | 49 | 31 | 80 |
| Nested RT-PCR | 70 | 10 | 80 |
| RT-qPCR | 75 | 5 | 80 |
| Method | Target Gene | Sample Type | Detection Limit (copies/µL) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-qPCR | 3c | Effusion, serum/plasma | ~102–103 | 90 | 96 | [33] |
| RT-qPCR | M | Effusion, feces | ~103 | 85 | 100 | [36] |
| Nested RT-PCR | 7b | Effusion, tissue | ~105 | 80 | 100 | [29] |
| RT-LAMP | ORF1a/1b | Effusion | 1.5 × 105 | 100 | 100 | [34] |
| RT-LAMP-XO | N | Effusion | 1.7 × 101 | 100 | 100 | [35] |
| RT-qPCR | M | Effusion | 9.14 × 101 | 93.75 | 100 | This study |
| Nested RT-PCR | M | Effusion | 9.14 × 104 | 87.50 | 100 | This study |
| RT-PCR | M | Effusion | 9.14 × 109 | 61.25 | 100 | This study |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′→3′) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| MF2 a | GCDCTTACGATTTTTAATGC | The current study |
| MR2 a | CCACMAWGABTTRGTHCTTC | |
| N-Inner MF b,c | TCGTTKATGGCATTAAAATGC | |
| N-Inner MR b,c | TGCAACACTAAAGCCGAAC | |
| N-Outer MF b | AACTGGAACTTCAGCTGGTCT | |
| N-Outer MR b | TCAGGRTTRAAAGACCACCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopduang, C.; Rapichai, W.; Leangcharoenpong, C.; Khamsingnok, P.; Puangmalee, T.; Ratanabunyong, S.; Rattanasrisomporn, A.; Khaoiam, T.; Dong, H.V.; Choowongkomol, K.; et al. Detection of Feline Coronavirus Membrane Gene Based on Conventional Revere Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, Nested Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146861
Kopduang C, Rapichai W, Leangcharoenpong C, Khamsingnok P, Puangmalee T, Ratanabunyong S, Rattanasrisomporn A, Khaoiam T, Dong HV, Choowongkomol K, et al. Detection of Feline Coronavirus Membrane Gene Based on Conventional Revere Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, Nested Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Comparative Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146861
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopduang, Chiraphat, Witsanu Rapichai, Chalandhorn Leangcharoenpong, Piyamat Khamsingnok, Thanapol Puangmalee, Siriluk Ratanabunyong, Amonpun Rattanasrisomporn, Thanawat Khaoiam, Hieu Van Dong, Kiattawee Choowongkomol, and et al. 2025. "Detection of Feline Coronavirus Membrane Gene Based on Conventional Revere Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, Nested Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Comparative Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146861
APA StyleKopduang, C., Rapichai, W., Leangcharoenpong, C., Khamsingnok, P., Puangmalee, T., Ratanabunyong, S., Rattanasrisomporn, A., Khaoiam, T., Dong, H. V., Choowongkomol, K., & Rattanasrisomporn, J. (2025). Detection of Feline Coronavirus Membrane Gene Based on Conventional Revere Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, Nested Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Comparative Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146861









