Performance of Plasma Phosphorylated tau-217 in Patients on the Continuum of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Participants Characteristics
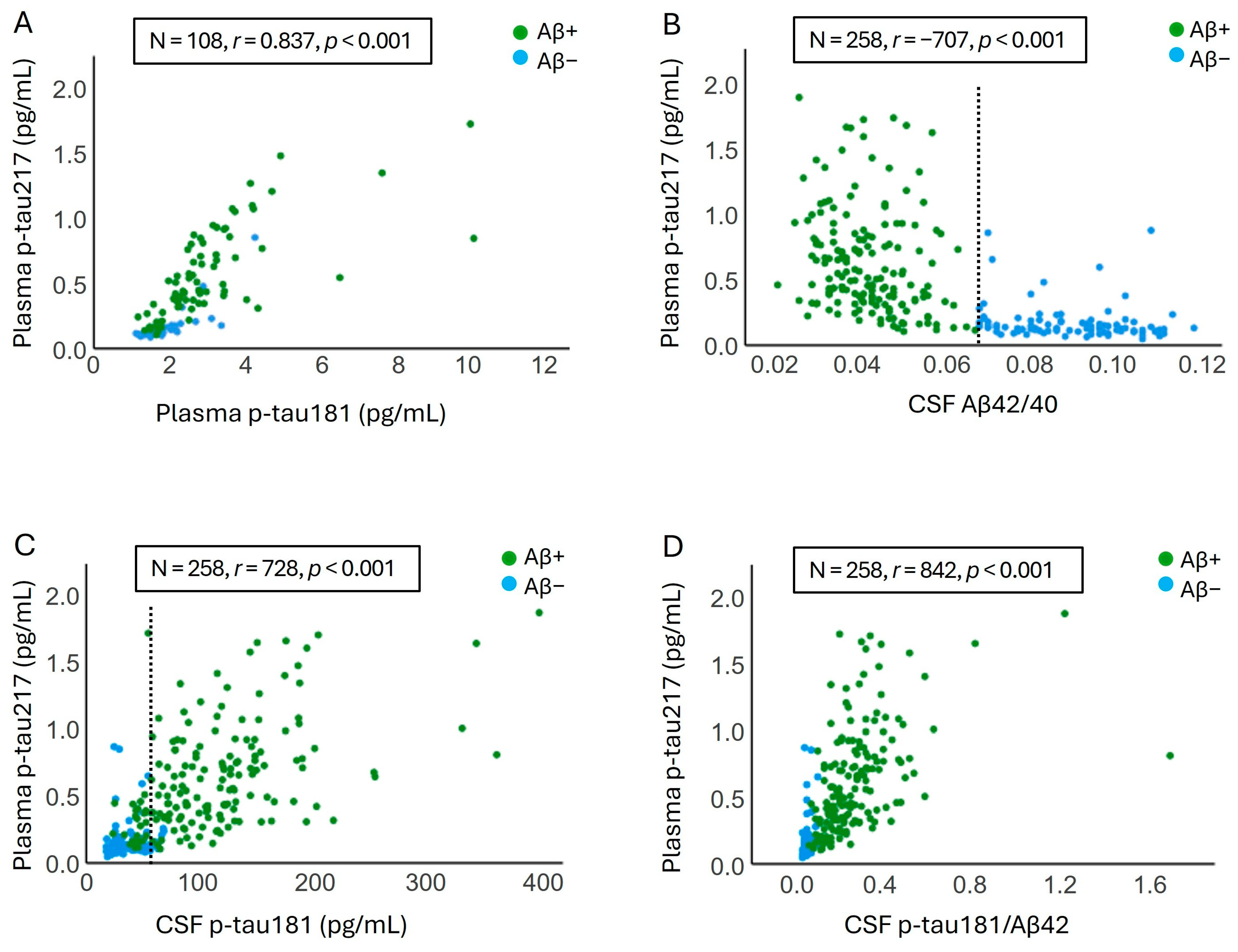
2.2. Correlation Between Plasma Levels of p-tau217 and Other Plasma and CSF AD Biomarkers Levels
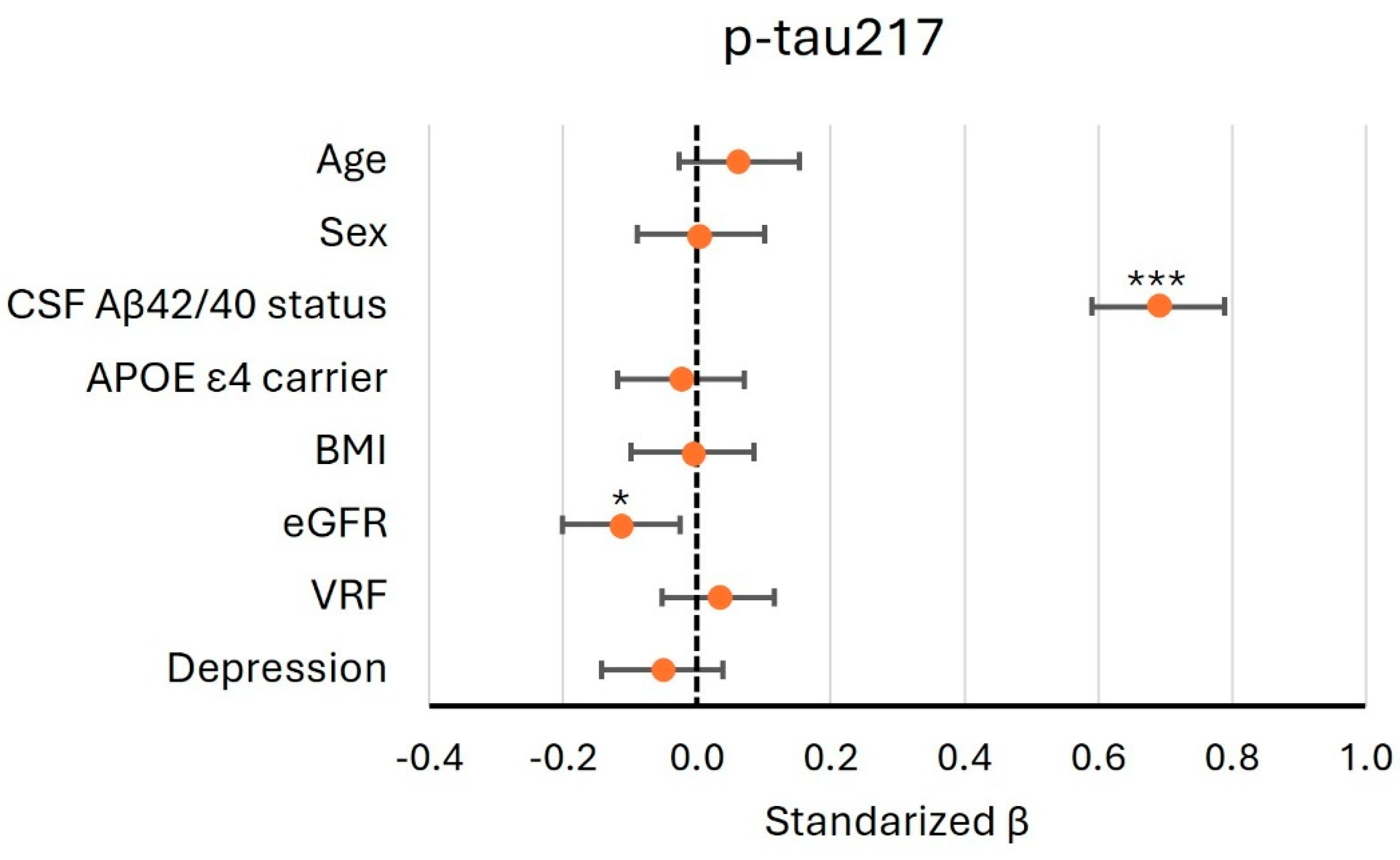
2.3. Identifying the Factors That May Influence Plasma Levels of p-tau217
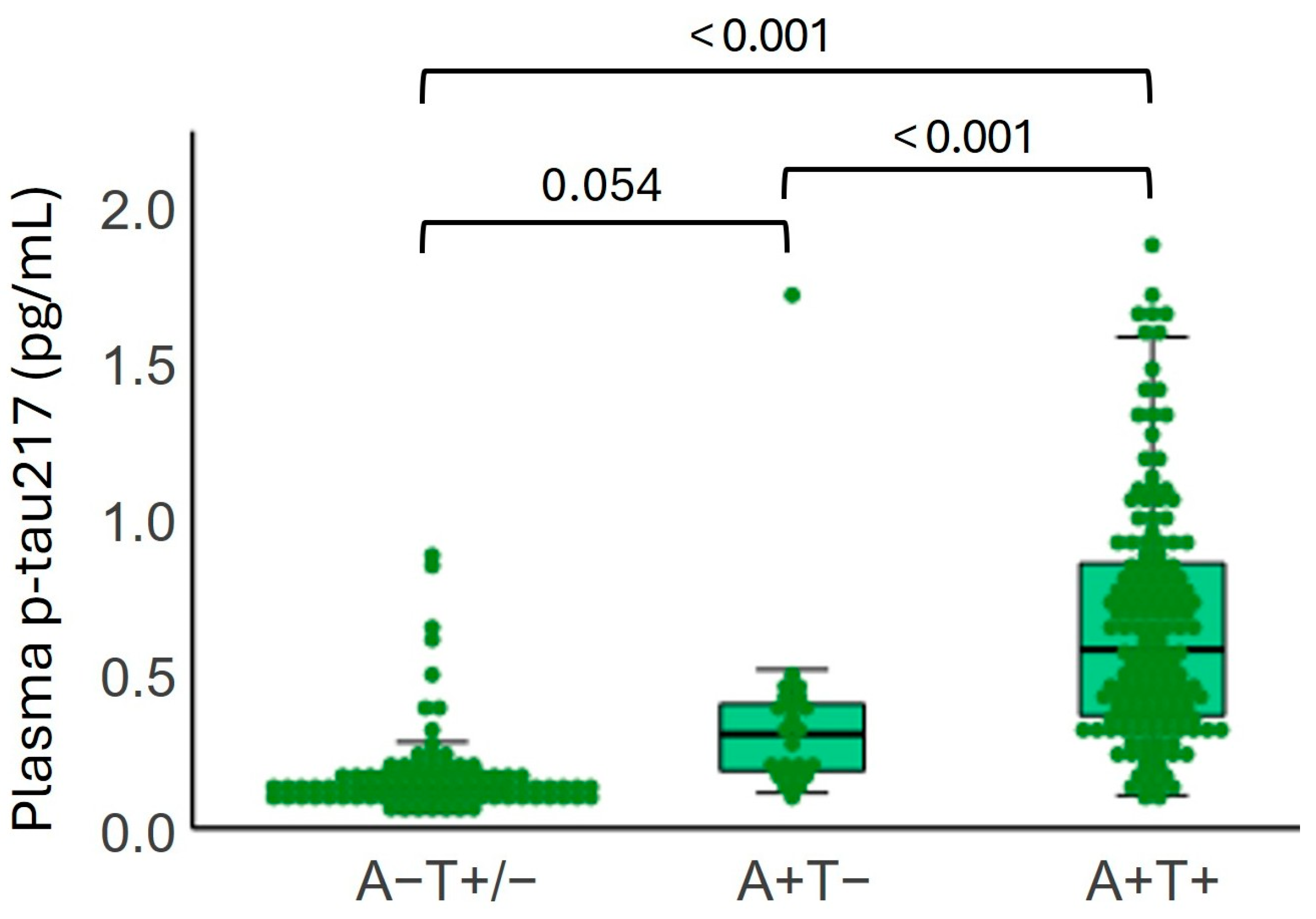
2.4. Plasma p-tau217 Levels by Amyloid and Tau Status in CSF
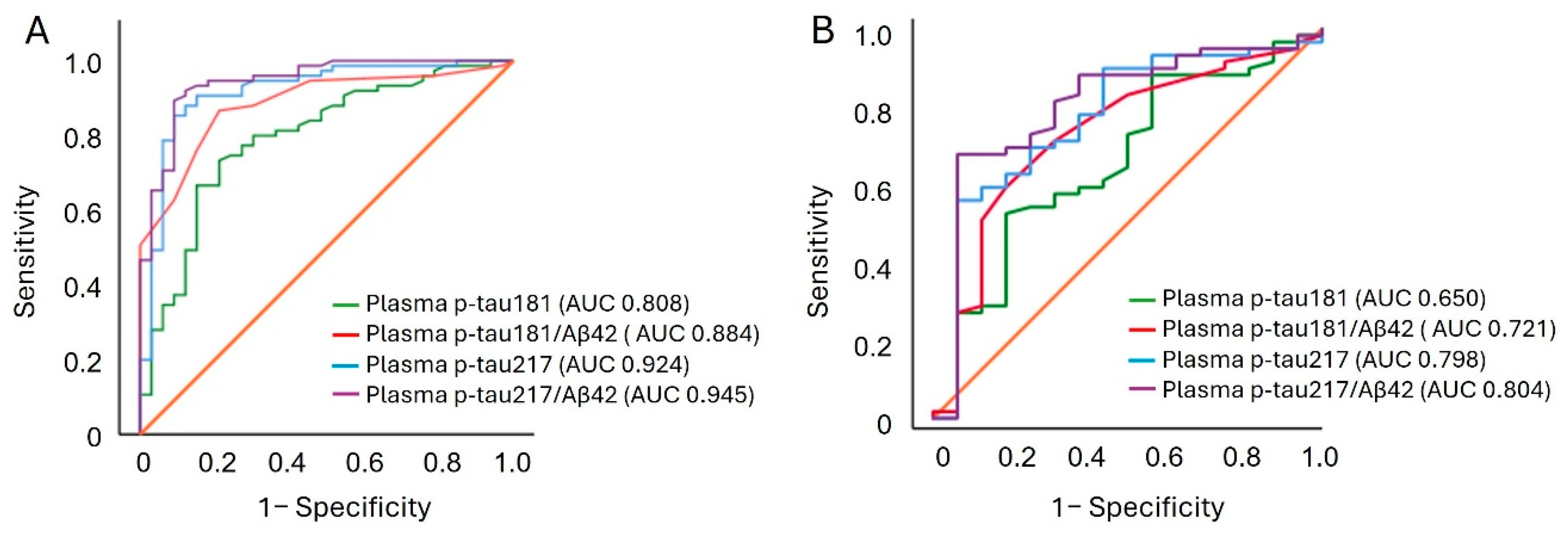
2.5. Accuracy in Discriminating Abnormal Amyloid and Tau Pathologies
2.6. Relationship Between Plasma Levels of p-tau217 and Longitudinal Changes in Cognition
2.7. Determining the Predictive Power of Plasma Biomarkers Regarding MCI to AD Progression
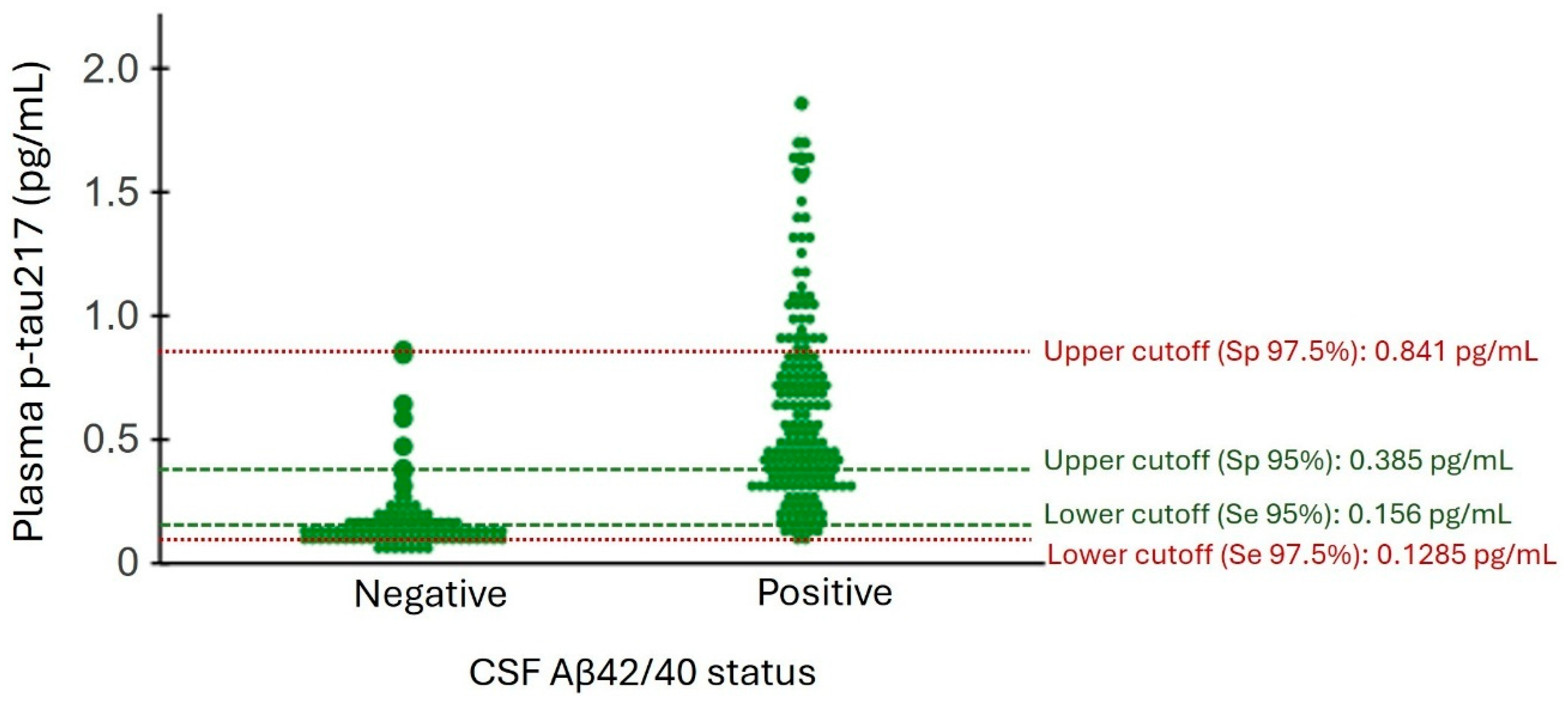
2.8. Reference Ranges for Plasma p-tau217 Based on CSF Aβ42/40 Status
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Sample Collection and Storage
4.3. Sample Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olsson, B.; Lautner, R.; Andreasson, U.; Öhrfelt, A.; Portelius, E.; Bjerke, M.; Hölttä, M.; Rosén, C.; Olsson, C.; Strobel, G.; et al. CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiotis, K.; Saint-Aubert, L.; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E.; Leuzy, A.; Almkvist, O.; Savitcheva, I.; Jonasson, M.; Lubberink, M.; Wall, A.; Antoni, G.; et al. Longitudinal changes of tau PET imaging in relation to hypometabolism in prodromal and Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakterzada, F.; Cipriani, R.; López-Ortega, R.; Arias, A.; Riba-Llena, I.; Ruiz-Julián, M.; Huerto, R.; Tahan, N.; Matute, C.; Capetillo-Zarate, E.; et al. Assessment of the Correlation and Diagnostic Accuracy between Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers: A Comparison of the Lumipulse and Simoa Platforms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simrén, J.; Leuzy, A.; Karikari, T.K.; Hye, A.; Benedet, A.L.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Schöll, M.; Mecocci, P.; Vellas, B.; et al. The diagnostic and prognostic capabilities of plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, X.N.; Wang, H.F.; Chen, S.D.; Zhang, Y.R.; Chen, S.F.; Cui, M.; Cheng, W.; Dong, Q.; Ma, T.; et al. The dynamics of plasma biomarkers across the Alzheimer’s continuum. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, S.; Schaeverbeke, J.M.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Gille, B.; De Schaepdryver, M.; Luckett, E.S.; Gabel, S.; Bruffaerts, R.; Mauroo, K.; Thijssen, E.H.; et al. Comparison of ELISA- and SIMOA-based quantification of plasma Aβ ratios for early detection of cerebral amyloidosis. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, N.C.; Leuzy, A.; Janelidze, S.; Palmqvist, S.; Svenningsson, A.L.; Stomrud, E.; Dage, J.L.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Hansson, O. Plasma biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease improve prediction of cognitive decline in cognitively unimpaired elderly populations. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planche, V.; Bouteloup, V.; Pellegrin, I.; Mangin, J.F.; Dubois, B.; Ousset, P.J.; Pasquier, F.; Blanc, F.; Paquet, C.; Hanon, O.; et al. Validity and Performance of Blood Biomarkers for Alzheimer Disease to Predict Dementia Risk in a Large Clinic-Based Cohort. Neurology 2023, 100, E473–E484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, D.; Stampacchia, S.; Ribaldi, F.; Tomczyk, S.; Chevalier, C.; Poulain, G.; Asadi, S.; Bancila, B.; Marizzoni, M.; Martins, M.; et al. Plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: A field-test in a memory clinic. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, E.R.; Beiser, A.S.; Yang, Q.; Ghosh, S.; DeCarli, C.S.; Himali, J.J.; O’Donnell, A.; Satizabal, C.L.; Johnson, K.A.; Tracy, R.P.; et al. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 predicts early, preclinical brain amyloid deposition. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, e055485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Hagen, C.E.; Xu, J.; Chai, X.; Vemuri, P.; Lowe, V.J.; Airey, D.C.; Knopman, D.S.; Roberts, R.O.; Machulda, M.M.; et al. Plasma phospho-tau181 increases with Alzheimer’s disease clinical severity and is associated with tau- and amyloid-positron emission tomography. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thijssen, E.H.; La Joie, R.; Wolf, A.; Strom, A.; Wang, P.; Iaccarino, L.; Bourakova, V.; Cobigo, Y.; Heuer, H.; Spina, S.; et al. Diagnostic value of plasma phosphorylated tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thijssen, E.H.; La Joie, R.; Strom, A.; Fonseca, C.; Iaccarino, L.; Wolf, A.; Spina, S.; Allen, I.E.; Cobigo, Y.; Heuer, H.; et al. Plasma phosphorylated tau 217 and phosphorylated tau 181 as biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration: A retrospective diagnostic performance study. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Mattsson, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Smith, R.; Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; Chai, X.; Proctor, N.K.; Eichenlaub, U.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: Relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Binette, A.P.; Strandberg, O.; Brum, W.S.; Karikari, T.K.; González-Ortiz, F.; Molfetta, G.D.; Meda, F.J.; et al. Differential roles of Aβ42/40, p-tau231 and p-tau217 for Alzheimer’s trial selection and disease monitoring. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, N.J.; Brum, W.S.; Di Molfetta, G.; Benedet, A.L.; Arslan, B.; Jonaitis, E.; Langhough, R.E.; Cody, K.; Wilson, R.; Carlsson, C.M.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of a Plasma Phosphorylated Tau 217 Immunoassay for Alzheimer Disease Pathology. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 81, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milà-Alomà, M.; Ashton, N.J.; Shekari, M.; Salvadó, G.; Ortiz-Romero, P.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Vanmechelen, E.; et al. Plasma p-tau231 and p-tau217 as state markers of amyloid-β pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Zetterberg, H.; Lopera, F.; Stomrud, E.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Serrano, G.E.; Leuzy, A.; et al. Discriminative Accuracy of Plasma Phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer Disease vs Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. JAMA 2020, 324, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feizpour, A.; Doecke, J.D.; Doré, V.; Krishnadas, N.; Huang, K.; Bourgeat, P.; Lawsd, S.M.; Fowlera, C.; Robertsona, J.; Mackintosh, L.; et al. Detection and staging of Alzheimer’s disease by plasma pTau217 on a high throughput immunoassay platform. eBioMedicine 2024, 109, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R.; Wiste, H.J.; Algeciras-Schimnich, A.; Figdore, D.J.; Schwarz, C.G.; Lowe, V.J.; Ramanan, V.K.; Vemuri, P.; Mielke, M.M.; Knopman, D.S.; et al. Predicting amyloid PET and tau PET stages with plasma biomarkers. Brain 2023, 146, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Salvadó, G.; Ashton, N.J.; Tideman, P.; Stomrud, E.; Zetterberg, H.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Betthauser, T.J.; Cody, K.A.; Jonaitis, E.M.; et al. Prediction of Longitudinal Cognitive Decline in Preclinical Alzheimer Disease Using Plasma Biomarkers. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, A.J.; Ribaldi, F.; Lathuiliere, A.; Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Scheffler, M.; Assal, F.; Garibotto, V.; Blennow, K.; et al. Head-to-head study of diagnostic accuracy of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 versus p-tau181 and p-tau231 in a memory clinic cohort. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 2053–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarto, J.; Esteller-Gauxax, D.; Guillén, N.; Falgàs, N.; Borrego-Écija, S.; Massons, M.; Fernández-Villullas, G.; González, Y.; Tort-Merino, A.; Bosch, B.; et al. Accuracy and clinical applicability of plasma tau 181 and 217 for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis in a memory clinic cohort. J. Neurol. 2025, 272, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arranz, J.; Zhu, N.; Rubio-Guerra, S.; Rodríguez-Baz, Í.; Ferrer, R.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Barroeta, I.; Illán-Gala, I.; Santos-Santos, M.; Fortea, J.; et al. Diagnostic performance of plasma pTau217, pTau181, Aβ1-42 and Aβ1-40 in the LUMIPULSE automated platform for the detection of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, A.H.; Dolphin, H.; O’Connor, A.; Morrison, L.; Sedgwick, G.; Young, C.; Killeen, E.; Gallagher, C.; McFeely, A.; Connolly, E.; et al. Performance of plasma p-tau217 for the detection of amyloid-β positivity in a memory clinic cohort using an electrochemiluminescence immunoassay. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.R.; Hilal, S.; Tan, B.Y.; Venketasubramanian, N.; Schöll, M.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Ashton, N.J.; Chen, C.P.; Lai, M.K.P. Clinical utility of plasma p-tau217 in identifying abnormal brain amyloid burden in an Asian cohort with high prevalence of concomitant cerebrovascular disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2025, 21, e14502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintun, M.A.; Lo, A.C.; Evans, C.D.; Wessels, A.M.; Ardayfio, P.A.; Andersen, S.W.; Ardayfio, P.A.; Andersen, S.W.; Shcherbinin, S.; Sparks, J.; et al. Donanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algeciras-Schimnich, A. Effect of kidney function on plasma pTau217 concentrations using different pTau217 assays. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 20, e088364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Barthélemy, N.R.; He, Y.; Bateman, R.J.; Hansson, O. Mitigating the Associations of Kidney Dysfunction With Blood Biomarkers of Alzheimer Disease by Using Phosphorylated Tau to Total Tau Ratios. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmqvist, S.; Warmenhoven, N.; Anastasi, F.; Pilotto, A.; Janelidze, S.; Tideman, P.; Stomrud, E.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Smith, R.; Ossenkoppele, R.; et al. Plasma phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis in primary and secondary care using a fully automated platform. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.G.; Ghodsi, M.; Stukas, S.; Leach, S.; Brooks-Wilson, A.; Wellington, C.L. APOE ε4 carrier status modifies plasma p-tau181 concentrations in cognitively healthy super-seniors. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 4373–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salami, A.; Adolfsson, R.; Andersson, M.; Blennow, K.; Lundquist, A.; Adolfsson, A.N.; Schöll, M.; Zetterberg, H.; Nyberg, L. Association of APOE ϵ4 and Plasma p-tau181 with Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease and Longitudinal Change in Hippocampus Function. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 85, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiung, G.Y.R.; Kumar, P.; Mousavi, A.; Encarnacion, M.; Frykman, H. The effects of ApoE e4 genotype on plasma p-tau181 concentrations on clinically diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease (AD) compared to controls. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, e080482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S.; Schraen-Maschke, S.; Vidal, J.S.; Delaby, C.; Buee, L.; Blanc, F.; Paquet, C.; Allinquant, B.; Bombois, S.; Gabelle, A.; et al. Clinical value of plasma ALZpath pTau217 immunoassay for assessing mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, S.E.; Galasko, D.; Pereira, A.C.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Salloway, S.; Suárez-Calvet, M.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Mielke, M.M.; Udeh-Momoh, C.; Weiss, J.; et al. Acceptable performance of blood biomarker tests of amyloid pathology—recommendations from the Global CEO Initiative on Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Hillis, A.E.; Weintraub, S.; Kertesz, A.; Mendez, M.; Cappa, S.F.; Ogar, J.M.; Rohrer, J.D.; Black, S.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants. Neurology 2011, 76, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rascovsky, K.; Hodges, J.R.; Knopman, D.; Mendez, M.F.; Kramer, J.H.; Neuhaus, J.; van Swieten, J.C.; Seelaar, H.; Dopper, E.G.P.; Onyike, C.U.; et al. Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain 2011, 134, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| N | All Participants | MCI | AD | Non-AD Dementia | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 276 (100%) | 193 (69.9%) | 56 (20.3%) | 27 (9.8%) | ||
| Demographic data | ||||||
| Age (years) | 276 | 74 (70, 78) | 75 (72, 78) | 74 (70, 77) | 75 (70, 79) | 0.242 |
| Sex (female), n(%) | 276 | 164 (59%) | 116 (60%) | 39 (70%) | 9 (33%) | 0.006 |
| Education (years) | 264 | 9 (8, 12) | 9 (8, 14) | 10 (8, 12) | 8 (6, 10) | 0.047 |
| Family history of cognitive impairment (yes), n (%) | 274 | 113 (41%) | 24 (43%) | 80 (42%) | 9 (33%) | 0.674 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Hypertension, n(%) | 276 | 153 (55%) | 100 (52%) | 39 (70%) | 14 (52%) | 0.057 |
| Diabetes Mellitus, n(%) | 276 | 84 (30%) | 60 (31%) | 17 (30%) | 7 (26%) | 0.861 |
| Dyslipidemia, n(%) | 276 | 148 (54%) | 107 (55%) | 29 (52%) | 12 (44%) | 0.536 |
| Depression, n(%) | 275 | 98 (35%) | 125 (65%) | 35 (63%) | 17 (63%) | 0.926 |
| CSF AD biomarkers | ||||||
| Aβ42 pg/mL | 276 | 546 (410, 799) | 595 (432, 866) | 424 (346, 537) | 784 (508, 988) | <0.001 |
| Aβ40 pg/mL | 276 | 10788 (8335, 13467) | 11121 (8565, 13659) | 10246 (8162, 12222) | 9215 (8092, 13469) | 0.139 |
| Aβ42/40 | 276 | 0.051 (0.04, 0.082) | 0.052 (0.040, 0.085) | 0.041 (0.035, 0.050) | 0.082 (0.063, 0.101) | <0.001 |
| t-tau pg/mL | 276 | 455 (268, 747) | 425 (258, 661) | 653 (432, 897) | 265 (170, 487) | <0.001 |
| p-tau181 pg/mL | 276 | 69 (41, 121) | 65 (41, 118) | 107 (71, 149) | 40 (27, 56) | <0.001 |
| t-tau/Aβ42 | 276 | 0.9 (0.3, 1.57) | 0.79 (0.29, 1.39) | 1.60 (0.99, 1.98) | 0.29 (0.22, 0.90) | <0.001 |
| p-tau181/Aβ42 | 276 | 0.15 (0.04, 0.27) | 0.13 (0.04, 0.24) | 0.27 (0.15, 0.32) | 0.04 (0.03, 0.10) | <0.001 |
| Plasma AD biomarkers | ||||||
| Aβ42 pg/mL | 124 | 24 (21, 27.8) | 24.1 (21.1, 27.2) | 22.5 (20.3, 26.6) | 25.9 (24.1, 29.2) | 0.040 |
| Aβ40 pg/mL | 123 | 303 (276, 359) | 309 (276, 359) | 283 (272, 334) | 320 (282, 371) | 0.211 |
| Aβ42/40 | 123 | 0.08 (0.07, 0.08) | 0.08 (0.07, 0.08) | 0.08 (0.07, 0.08) | 0.08 (0.07, 0.09) | 0.093 |
| p-tau181 pg/mL | 126 | 2.29 (1.69, 3.13) | 2.17 (1.65, 2.85) | 2.86 (2.28, 3.49) | 2.10 (1.62, 3.08) | 0.009 |
| p-tau217 pg/mL | 258 | 0.34 (0.15, 0.69) | 0.31 (0.14, 0.59) | 0.70 (0.39, 0.98) | 0.13 (0.11, 0.30) | <0.001 |
| p-tau181/Aβ42 | 126 | 0.1 (0.07, 0.14) | 0.09 (0.07, 0.12) | 0.13 (0.10, 0.15) | 0.07 (0.06, 0.13) | 0.001 |
| p-tau217/Aβ42 | 123 | 0.015 (0.006, 0.028) | 0.014 (0.005, 0.023) | 0.029 (0.015, 0.038) | 0.005 (0.004, 0.013) | <0.001 |
| Other variables | ||||||
| BMI | 258 | 26.6 (23.89, 29.27) | 26.6 (24.3, 29.1) | 25.5 (23.4, 30.4) | 27.0 (24.6, 28.9) | 0.718 |
| eGFR | 264 | 75 (63, 86) | 73 (62, 86) | 73 (55, 84) | 82 (66, 88) | 0.349 |
| MMSE score | 269 | 25 (21, 27) | 25 (23, 27) | 21 (18, 23) | 25 (18, 27) | <0.001 |
| APOE ε4, n(%) | 272 | 106 (38%) | 72 (38%) | 29 (52%) | 5 (19%) | 0.013 |
| Biomarker | AUC (95% CI) | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPA | NPA | Total% of Predictive Accuracy * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aβ42 | 0.668 (0.568–0.768) | 62.4% | 61.5% | 77.9% | 42.9% | 62.1% |
| Aβ40 | 0.505 (0.391–0.618) | 52.4% | 48.7% | 69.8% | 32.8% | 51.6% |
| Aβ42/40 | 0.796 (0.713–0.879) | 57.1% | 89.7% | 92.6% | 50.0% | 68.3% |
| p-tau181 | 0.808 (0.727–0.890) | 80.2% | 75.0% | 87.3% | 63.8% | 78.6% |
| p-tau181/Aβ42 | 0.884 (0.824–0.944) | 87.1% | 82.1% | 91.5% | 75.0% | 85.7% |
| p-tau217 | 0.924 (0.889–0.960) | 87.3% | 89.1% | 93.5% | 79.6% | 87.9% |
| p-tau217/Aβ42 | 0.945 (0.900–0.990) | 89.3% | 90.9% | 95.7% | 78.9% | 89.8% |
| Biomarker | AUC (95% CI) | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPA | NPA | Total% of Predictive Accuracy * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aβ42 | 0.412 (0.277–0.548) | 81.3% | 18.8% | 75.9% | 9.7% | 51.7% |
| Aβ40 | 0.396 (0.257–0.535) | 66.2% | 18.8% | 77.6% | 11.5% | 57.1% |
| Aβ42/40 | 0.506 (0.355–0.658) | 44.1% | 62.5% | 83.3% | 20.8% | 47.6% |
| p-tau181 | 0.650 (0.498–0.802) | 51.4% | 81.3% | 92.3% | 29.2% | 57.4% |
| p-tau181/Aβ42 | 0.721 (0.580–0.861) | 56.5% | 81.3% | 92.9% | 30.2% | 61.2% |
| p-tau217 | 0.798 (0.701–0.894) | 71.3% | 78.3% | 91.0% | 47.6% | 85.5% |
| p-tau217/Aβ42 | 0.804 (0.675–0.933) | 72.9% | 75.0% | 91.5% | 41.4% | 72.3% |
| Biomarker | AUC (95% CI) | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aβ42 | 0.374 (0.249–0.500) | 46.5% | 31.4% |
| Aβ40 | 0.460 (0.329–0.591) | 41.9% | 42.9% |
| Aβ42/40 | 0.673 (0.553–0.793) | 67.4% | 65.7% |
| p-tau181 | 0.795 (0.692–0.898) | 90.1% | 63.9% |
| p-tau181/Aβ42 | 0.852 (0.762–0.943) | 86.0% | 77.1% |
| p-tau217 | 0.876 (0.787–0.964) | 87.2% | 83.9% |
| p-tau217/Aβ42 | 0.888 (0.803–0.972) | 84.6% | 87.1% |
| Binary Reference Point $ | Three-Range Reference Points | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% * | 97.5% ** | |||
| Characteristics | ≥0.2375 pg/mL | Characteristics | <0.1560 ≥0.3850 pg/mL | <0.1285 ≥0.8410 pg/mL |
| Participants, n | 258 | Participants, n | 258 | 258 |
| Positive for Aβ42/40, n (%) | 177 (68.6) | Positive for Aβ42/40, n (%) | 177 (68.6) | 177 (68.6) |
| Positive for plasma p-tau217, n (%) | 155 (60.1) | Negative for plasma p-tau217, n (%) | 69 (26.7) | 48 (18.6) |
| Intermediate for plasma p-tau217, n (%) | 72 (27.9) | 170 (61.6) | ||
| Positive for plasma p-tau217, n (%) | 117 (45.3) | 40 (15.5) | ||
| Sensitivity, % | 87.3% | Sensitivity of lower reference point, % | 95.2% | 97.6% |
| Specificity, % | 89.1% | Specificity of upper reference point, % | 94.6% | 97.8% |
| PPA, % | 93.5% | PPA, upper reference point, % | 95.7% | 95.0% |
| NPA, % | 79.6% | NPA, lower reference point, % | 88.4% | 91.7% |
| OPA, % | 87.9% | OPA for plasma p-tau217 positive and negative, % | 94.9% | 97.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dakterzada, F.; López-Ortega, R.; Vilella-Figuerola, A.; Montero-Castilla, N.; Riba-Llena, I.; Ruiz-Julián, M.; Arias, A.; Sarto, J.; Tahan, N.; Piñol-Ripoll, G. Performance of Plasma Phosphorylated tau-217 in Patients on the Continuum of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6771. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146771
Dakterzada F, López-Ortega R, Vilella-Figuerola A, Montero-Castilla N, Riba-Llena I, Ruiz-Julián M, Arias A, Sarto J, Tahan N, Piñol-Ripoll G. Performance of Plasma Phosphorylated tau-217 in Patients on the Continuum of Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6771. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146771
Chicago/Turabian StyleDakterzada, Farida, Ricard López-Ortega, Alba Vilella-Figuerola, Nathalia Montero-Castilla, Iolanda Riba-Llena, Maria Ruiz-Julián, Alfonso Arias, Jordi Sarto, Nuria Tahan, and Gerard Piñol-Ripoll. 2025. "Performance of Plasma Phosphorylated tau-217 in Patients on the Continuum of Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6771. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146771
APA StyleDakterzada, F., López-Ortega, R., Vilella-Figuerola, A., Montero-Castilla, N., Riba-Llena, I., Ruiz-Julián, M., Arias, A., Sarto, J., Tahan, N., & Piñol-Ripoll, G. (2025). Performance of Plasma Phosphorylated tau-217 in Patients on the Continuum of Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6771. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146771






