Abstract
Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) inhibitors have gained regulatory approval for treating various human diseases. While the JAK2/signal tranducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway plays a role in tumorigenesis, JAK2/STAT3 inhibitors have shown limited therapeutic efficacy in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). In this study, we assessed the antiproliferative effects of clinically approved JAK2 inhibitors in TNBC cell lines (MDA-MB-231 and HS578T) using the MTT assay. Among the four JAK2 inhibitors evaluated (fedratinib, cerdulatinib, peficitinib, and filgotinib), fedratinib significantly inhibited the proliferation of TNBC cells with IC50 values below 2 μM. Fedratinib also demonstrated superior efficacy in inhibiting long-term colony formation compared to other JAK2 inhibitors. Western blot analyses showed that fedratinib uniquely inhibits the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway and moderately affects the MAP kinase/ERK kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, in addition to targeting JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Moreover, fedratinib distinctly decreased MYC and cyclin D1 protein levels while inducing poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage and apoptotic cell death more effectively than other JAK2 inhibitors. We next investigated the effects of simultaneously inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 together with the MEK/ERK or PI3K/AKT pathways, as well as the impact of triple pathway inhibition. Notably, combining ceduratinib with either cobimetinib (MEK inhibitor) and ipatasertib (AKT inhibitor) or trametinib (MEK inhibitor) and alpelisib (PI3K inhibitor) mimicked the effects of fedratinib on the cell proliferation, MYC and cyclin D1 suppression, and pro-apoptotic protein induction. These finding suggest that JAK2 inhibition enhances the anticancer effects of concurrent MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathway inhibition, while JAK2 inhibition alone shows minimal efficacy in TNBC cells.
1. Introduction
TNBC is the most aggressive type of breast cancer, characterized by the absence of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) expression, and lack of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) amplification [1,2,3,4]. Representing 15–20% of breast cancer cases, TNBC exhibits intrinsic resistant against targeted therapeutics for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and MET, despite their frequent amplification in TNBC [1,2,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. Currently, five targeted therapies have received the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval: two poly [adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1) inhibitors (olaparib and talazoparib); a programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor atezolizumab, an antibody targeting programmed cell death 1 (PD1) pembrolizumab, and an antibody drug conjugate (ADC) sacituzumab govitecan [3,13]. However, due to limited clinical responses, alternative therapeutic strategies remain crucial for effective management of TNBC [3,13].
STAT3 functions as a transcriptional regulator responding to various cytokines [14]. The activation of STAT3 occurs through phosphorylation at 705 tyrosine residue (Y705), primarily mediated by JAK2, one of four JAK kinase family members [JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2)] [15]. The JAK2/STAT3 pathway plays significant roles in tumorigenesis and tumor progression across multiple cancer types [16,17,18,19,20]. Currently, eleven small-molecular JAK inhibitors (JAKis) have received global regulatory approval for various conditions, including myelofibrosis, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), polycythemia vera, alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and ulcerative colitis [21,22]. Although the JAK2/STAT3 pathway has been suggested as a potential therapeutic target for treatment of TNBC, clinical application of JAK2/STAT3 inhibitors has not been fully successful [23]. Our previous research demonstrated that the inhibition of JAK1/2 by CP690550 [24] is not sufficient to inhibit the proliferation of TNBC cells [25]. Rather, the inhibition of acetylation of STAT3 at lysine 685 is necessary for anticancer effects of a small molecule inhibitor SH-I-14 though disruption of STAT3-DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) interaction, leading to the induction of re-expression of tumor suppressor gene products such as von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor (VHL) and PDZ and LIM domain protein 4 (PDLIM4) [23].
Here, we report the contribution of JAK2 inhibitor (JAK2i) to augment the MEK/ ERK and PI3K/AKT pathway inhibition in TNBC cells. We found that the inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway alone is not sufficient to reduce the proliferation of TNBC cells, whereas JAK2i is required for the enhancement of anticancer effects by co-inhibition of MEK and AKT or co-inhibition of MEK and PI3K via downregulating levels of MYC and cyclin D1 proteins and inducing apoptosis in TNBC cells. Our data suggest that the inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway provides additional therapeutic benefit for the combination of MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT inhibition.
2. Results
2.1. Fedratinib Inhibits the Proliferation of TNBC Cells
During the course of screening of the US FDA-approved protein kinase inhibitor (PKI) library using MTT assay in TNBC cells [4,5,6,26,27,28,29,30], we observed notable effects of JAK2is. In agreement with our previous findings [25], three JAK2is (cerdulatinib, peficitinib, and filgotinib) showed minimal effects on the proliferation of two TNBC cell lines (Table 1 and Figure 1A). However, fedratinib distinctly reduced the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells with IC50 values of 1.38 ± 0.06 and 1.23 ± 0.19 μM, respectively (Table 1 and Figure 1A). While all these small molecules target JAK2 [31,32,33,34,35], fedratinib specifically inhibits JAK2 with limited activity against other JAK family members [31]. Additionally, fedratinib targets FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) and rearranged during transfection (RET), albeit with lower potency than its JAK2 inhibition [31]. In contrast, cerdulatinib was developed as a dual inhibitor of spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) and JAKs, with IC50 values below 40 nM [32]. Filgotinib demonstrates potent inhibitory activity against both JAK1 and JAK2 [33], while peficitinib inhibits all JAK family members in nanomolar ranges [34,35]. As demonstrated in Table 1 and Figure 1A, fedratinib uniquely suppressed the proliferation of HS578T and MDA-MB-231 cells with IC50 values below 2 μM, whereas the other inhibitors showed only marginal effects with IC50 values exceeding 8 μM. In colony formation assay, fedratinib effectively reduced the long-term survival of both TNBC cell lines, with IC50 values of 2.72 ± 0.46 μM (MDA-MB-231) and 1.26 ± 0.27 μM (HS578T) (Figure 1B). Notably, at 5 μM concentration, cerdulatinib showed comparable effects to fedratinib on long-term survival, while peficitinib did not (Figure 1C).

Table 1.
Information on the clinically approved JAK2is used in this study.
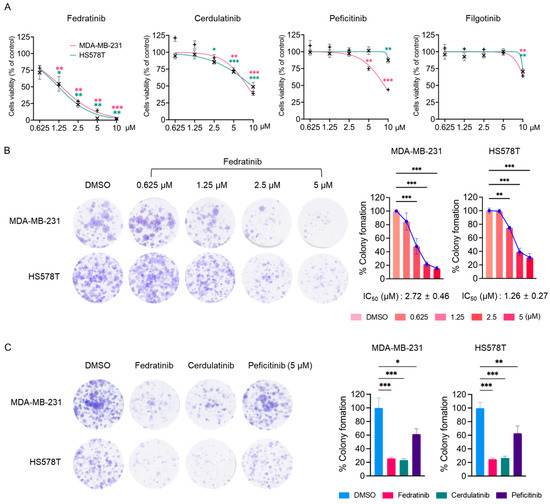
Figure 1.
JAK2is reduces the viability and colony formation in TNBC cells. (A) Cell viability of MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells following 72 h treatment with indicated JAK2is, assessed by MTT assay. (B) Colony formation of MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells (1 × 103 cells/well) treated with fedratinib at indicated concentration for 24 h, followed by 10–14 days of growth in inhibitor-free medium. Representative images and quantification of crystal violet-stained colonies are shown. (C) Clonogenic survival of TNBC cells treated with fedratinib, cerdulatinib, or peficitinib (5 μM) for 24 h. followed by growth in inhibitor-free medium. Data present means ± SEMs from three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.005.
2.2. Fedratinib Inhibits the PI3K/AKT Pathway and Marginally Modulates the MEK/ERK Pathway in TNBC Cells
We further characterized three JAK2is—fedratinib, cerdulatinib, and peficitinib—using western blot analyses. As expected, all these JAK2is reduced the levels of phosphorylation of STAT3 at tyrosine 705 (Y705), a modification catalyzed by JAK2 [36], in TNBC cell lines (Figure 2A; Original WB images are available as Supplementary Materials, File S1: Original WB images). Our previous research demonstrated that the inhibition of phospho (p)-STAT3 (Y705) alone is insufficient to reduce the proliferation of TNBC cells [25]. Given that fedratinib also targets two receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), FLT3 and RET (Table 1), we examined two major downstream pathways of RTK, the PI3K/AKT and MEK/ ERK pathways, in TNBC cell lines. As shown in Figure 2B, fedratinib decreased the levels of p-ribosomal protein S6 (p-RPS6) (S235/236), a downstream target of AKT [37], in both HS578T and MDA-MB-231 cells. While peficitinib also reduced the level of p-RPS6 (S235/236), this reduction did not reach statistical significance in MDA-MB-231 cells. In contrast, cerdulatinib increased p-RPS6 (S235/236) levels in both cell lines. Interestingly, phosphorylation of proline-rich AKT1 substrate 40 (PRAS40) at T248, a direct substrate of AKT [38], remained unchanged by JAK2is. This maintenance of p-PRAS40 (T246) levels might result from compensatory phosphorylation by other kinases, particularly PIM1 [39], which has emerged as a promising therapeutic target for TNBC treatment [40,41,42,43].
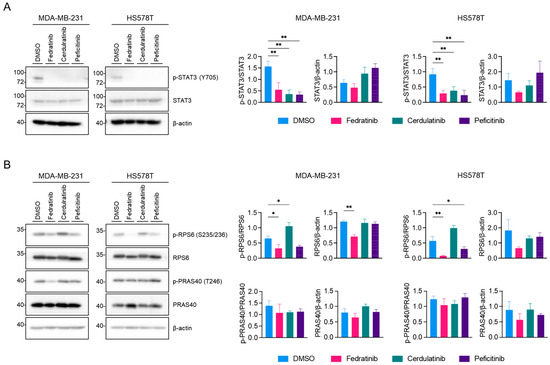
Figure 2.
Fedratinib inhibits JAK2/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling in TNBC cells. (A,B) Western blot analysis of signaling proteins in TNBC cells treated with fedratinib, cerdulatinib, or peficitinib (5 μM, 24 h). Representative images from three independent experiments were shown with densitometric quantification (mean ± SEM). * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.
We further evaluated the effects of fedratinib on key signaling pathways. As anticipated, fedratinib dose-dependently reduced the levels of p-STAT3 (T705), with IC50 values of 2.69 ± 3.44 μM for MDA-MB-231 and 2.69 ± 1.23 μM for HS578T cells (Figure 3A). Under these experimental conditions, fedratinib showed differential effects on p-ERK1/2 (T202/Y204), the sole known substrate for MEK1/2 [44]: modest dose-dependent reduction in MDA-MB-231 cells and a slight, statistically insignificance increase in HS578T cells (Figure 3B).
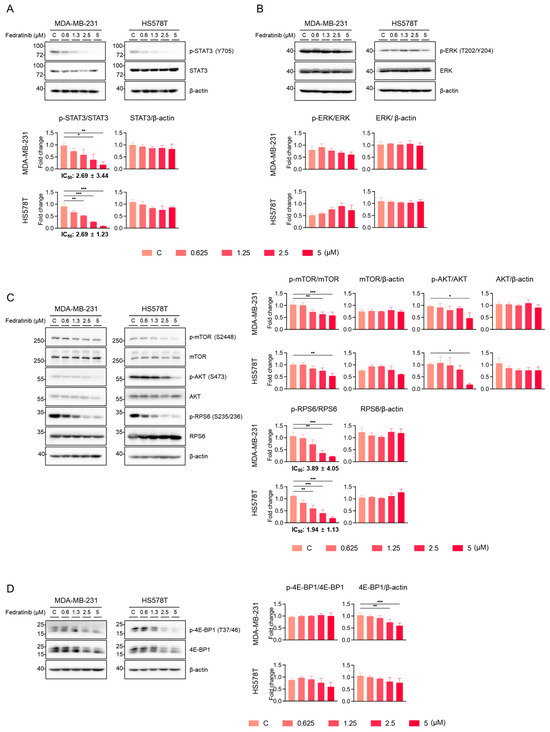
Figure 3.
Fedratinib inhibits multiple signaling pathways in TNBC cells. MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells were treated with increasing concentrations of fedratinib for 24 h. (A) STAT3 phosphorylation (Y705), (B) ERK phosphorylation (T202/Y204), (C) PI3K/AKT pathway proteins [p-mTOR (S2448), p-AKT (S473), and p-RPS6 (S235/236)], and (D) 4E-BP1 levels were analyzed by Western blot, with β-actin as loading control. Representative blot images from three independent experiments are shown with densitometric quantification (mean ± SEM). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.005.
The inhibitory effects of fedratinib on the levels of p-mammalian target of rapamycin (p-mTOR) (S2448), p-AKT (S473), and p-RPS6 (S235/236) became apparent at 2.5 or 5 μM in TNBC cells (Figure 3C). Since S2448 of mTOR is a substrate for AKT1 [also known as protein kinase B (PKB)] [45], the reduction in p-mTOR (S2448) indicates that fedratinib inhibits AKT activity, likely through indirect inhibition of upstream RTKs such as FLT3 or RET. Moreover, as mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2) mediates AKT S473 phosphorylation for full activation [46], the decreased p-AKT (S473) levels further confirm the inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway by fedratinib. The levels of p-RPS6 (S235/236) were dose-dependently reduced by fedratinib with IC50 values of 3.89 ± 4.05 μM for MDA-MB-231 and 1.94 ± 1.33 μM for HS578T cells (Figure 3C). eIF4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1), an oncogenic convergent target integrating the MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways [47], showed reduced phosphorylation at T37/46 upon fedratinib treatment in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 3D). Notably, densitometric analyses revealed a significant reduction in the total 4E-BP1 levels in MDA-MB-231 cells and a marginal reduction in HS578T cells, previously unreported drug effect in cancer cells.
2.3. Fedratinib Inhibited the MEK/ERK Pathway in TNBC Cells in a Time- and Cell Line-Dependent Manners
To clarify the effects of fedratinib on the MEK/ERK pathway, we conducted time-course analyses in TNBC cells. Treatment with 5 μM fedratinib reduced p-STAT3 (Y705) levels to near undetectable levels as early as 2 h post-treatment, maintaining suppression for 24 h, while the control (DMSO-treated) cells showed increasing p-STAT3 (Y705) levels over time (Figure 4A). Similarly, 5 μM peficitinib and cerdulatinib suppressed p-STAT3 (Y705) levels at 24 h post-treatment (Figure 4A). The effects on p-mTOR (S2448) and p-AKT (S473) showed cell line specificity (Figure 4B): In MDA-MB-231 cells, the levels of p-mTOR (S2448) were decreased by fedratinib significantly at as early as 4 h post-treatment, though sustained suppression lacked statistical significance. In HS578T cells, a significant decrease in p-mTOR (S2448) was observed at 8 h post-treatment and persisted through 24 h. p-ATK (S473) inhibition paralleled p-STAT3 (Y705) patterns in MDA-MB-231 cells, showing sustained suppression from 2 h onward, while HS578T cells exhibited significant suppression only at 2 and 24 h post-treatment.
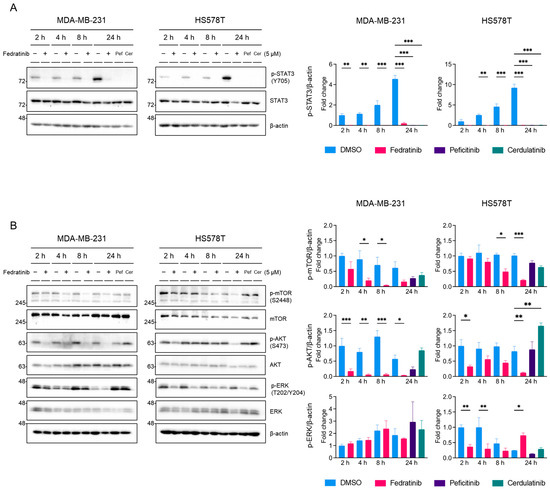
Figure 4.
Time-dependent inhibition of signaling pathways by fedratinib in TNBC cells. MDA-MB-231 and HS578T were treated with DMSO or fedratinib (5 μM) for indicated times, or cerdulatinib (5 μM) and peficitinib (5 μM) 24 h. (A) STAT3 phosphorylation (Y705) and (B) phosphorylation status of PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathway proteins were analyzed by Western blot, with β-actin as a loading control. Data present mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.005.
Peficitinib and cerdulatinib showed inconsistent effects between cell lines: peficitinib reduced p-mTOR (S2448) and p-AKT (S473) levels in MDA-MB-231 cells without statistical significance, while cerdulatinib showed minimal effect on p-mTOR (S2448) levels in both cell lines and increased p-AKT (S473) levels in HS58T cells (Figure 4B). Fedratinib weakly decreased p-ERK (T202/Y204) levels at 24 h post-treatment in MDA-MB-231 (not statistically significant) and at 2 and 4 h post-treatment in HS578T cells (Figure 4B), but markedly increased the levels of p-ERK (T202/Y204) at 24 h in HS578T cells. Peficitinib and cerdulatinib showed minimal effects on ERK phosphorylation. These findings indicate that fedratinib consistently inhibits the PI3K/AKT pathway, while affecting the MEK/ERK pathway in time- and cell line- dependent manners [48,49,50]. Notably, p-ERK (T202/Y204) levels fluctuated in the control cells, as previously reported in normal mammary epithelial cells [51], which may influence TNBC proliferation.
Proto-oncogene MYC and cyclin D1 are common downstream targets of the JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/AKT, and MEK/ERK pathways [48,49,50]. Western blot analyses revealed that fedratinib, but not peficitinib or cerdulatinib, suppressed MYC protein levels in both TNBC cell lines (Figure 5A). This reduction of MYC protein levels became apparent by 8 h and persisted through 24 h post-treatment in both TNBC cell lines. Similarly, fedratinib decreased cyclin D1 levels in both cell lines (Figure 5B), while peficitinib-induced downregulation of cyclin D1 was observed only in HS578T cells.
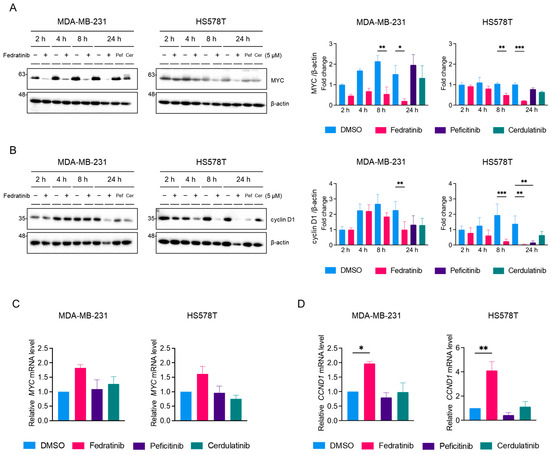
Figure 5.
Fedratinib downregulates MYC and cyclin D1 expressions in TNBC cells. MDA-MB-231 and HS578T were treated with fedratinib (5 μM) for indicated times, or peficitinib and cerdulatinib (5 μM) for 24 h. Western blot analysis of (A) MYC and (B) cyclin D1 (B) protein levels, with β-actin as a loading control. (C) Relative MYC and (D) CCND1 mRNA levels measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.005.
To determine whether these protein level changes resulted from transcriptional regulation, we performed quantitative real-time PCR (RT-PCR) analyses. Interestingly, fedratinib treatment increased MYC mRNA levels in both cell lines (Figure 5D). Similarly, CCND1 (the gene encoding cyclin D1) mRNA levels were also elevated by fedratinib in both cell lines (Figure 5D). Treatment with peficitinib or cerdulatinib showed minimal significant effects.
2.4. Fedratinib Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in TNBC Cells
To investigate whether fedratinib’s antiproliferative effect occur through apoptotic cell death, we conducted western blot analysis as shown in Figure 6. PARP cleavage was prominently detected in both MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells treated with fedratinib, but not with cerdulatinib or peficitinib. Furthermore, fedratinib modestly reduced X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) levels in both TNBC cells lines, though this reduction did not reach statistical significance. Fluorescence cytometric analysis confirmed that only fedratinib, among tested JAK2is, induced apoptotic cell death under these conditions (Figure 6B), with marked increases in both early and late apoptotic cell populations in MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells. Additionally, fedratinib increased the population of necrotic cells specifically in HS578T cells.
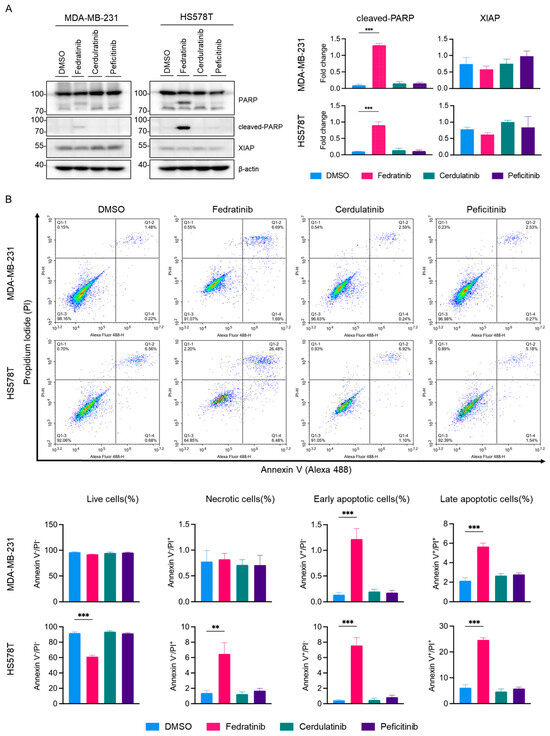
Figure 6.
Selective induction of apoptosis by fedratinib in TNBC cells. MDA-MB-231 and HS578T were treated with 5 μM of JAK2is for 24 h. (A) Western blot analysis of apoptotic markers with densitometric quantification. β-actin serves as a loading control. (B) Fluorescence cytometric analyses using Annexin V-Alexa 488 and propidium iodide (PI) staining. Representative images, histograms, and quantification from three independent experiments are shown. Data represent mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.005.
2.5. Inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Enhances the Effects of Blocking the PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK Pathways in TNBC Cells
Based on our current and previous [25] findings, we hypothesized that while JAK2/STAT3 pathway inhibition alone may be insufficient for treatment, it could enhance the anticancer effects of the PI3K/ATK pathway, MEK/ERK pathway, or their combination in TNBC cells. Given fedratinib’s limited and cell-type-specific effects on the MEK/ERK pathway, we reasoned that more potent MEK inhibitors (MEKis) combined with JAK2is might produce enhanced therapeutic effects. To test this hypothesis, we conducted MTT cell viability assays using cerdulatinib, a JAK2i less potent than fedratinib (Figure 1), alone or in combination with either MEKi (cobimetinib [52] or trametinib [53]), and AKT inhibitor (AKTi) ipatasertib [54] or PI3K inhibitor (PI3Ki) alpelisib [55].
In MDA-MB-231 cells, individual agents showed less potency than fedratinib (Figure 7A). The dual combination of cerdulatinib (Cer) with ipatasertib (Ipa), Cer with cobimetinib (Cobi), or Ipa with Cobi did not produce synergistic antiproliferative effects (Figure 7A,B). However, the triple combination demonstrated modest synergy with a combination index (CI) value of 0.99 (Figure 7B). HS578T cells showed more pronounced responses to combination treatments (Figure 7C,D), with dual or triple combinations achieving synergistic effects (CI values < 0.6). The triple combination exhibited particularly strong synergism in HS578T cells (Figure 7D). Similar enhanced antiproliferative effects were observed when combining cerdulatinib with alpelisib (PI3Ki) and trametinib (MEKi) (Figure 7E–H) [4]. These results indicate that the addition of JAK2i cerdulatinib further enhanced the reduction in cell viability of TNBC cells induced by combination treatment (MEKi + AKTi or MEKi + PI3Ki).
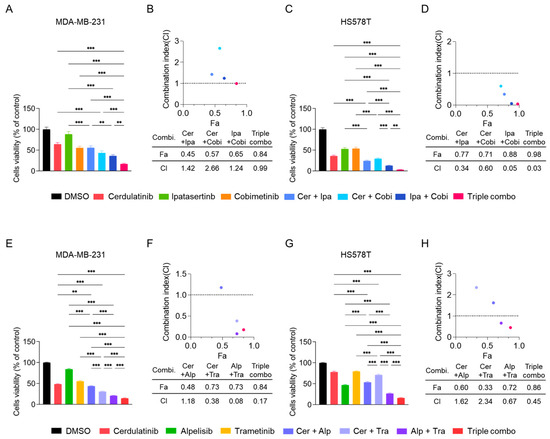
Figure 7.
Combined inhibition of JAK, AKT/PI3K, and MEK pathways synergistically reduces TNBC cell viability. (A–D) Cell viability of TNBC cells treated with cerdulatinib (JAKi, 10 μM), ipatasertib (AKTI, 5 μM), and cobimetinib (MEKi, 5 μM) alone or in combination 72 h. (E,F) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with cerdulatinib (5 μM), alpelisib (PI3Ki, 10 μM), and trametinib (MEKi, 10 μM) alone or in combination for 72 h. (G,H) HS578T cells were treated with cerdulatinib (10 μM), alpelisib (2.5 μM), and trametinib (10 μM) alone or in combination for 72 h. Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.005.
Western blot analyses were performed to examine the effects of combination treatments on the JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/AKT, and MEK/ERK pathways. As shown in Figure 8A, cerdulatinib consistently suppressed p-STAT3 (Y705) levels in both TNBC cell lines, while ipatasertib showed modest reduction. Interestingly, cobimetinib (MEKi) treatment induced p-STAT3 (Y705) levels in both cell lines; however, this increase was abolished by cerdulatinib co-treatment. Ipatasertib treatment elevated p-AKT (S473) levels, a previously documented effect resulting from AKT kinase inhibition [56]. This ipatasertib-induced increase in p-AKT (S473) levels remained unaffected by individual treatment with neither cerdulatinib nor cobimetinib but was reduced by combined ipatasertib and cobimetinib treatment. To further assess the PI3K/AKT pathway inhibition, we monitored p-RPS6 (S235/236) levels. Ipatasertib decreased p-RPS6 (S235/236) levels, with further reduction observed upon cobimetinib co-treatment (Figure 8B). Additionally, cobimetinib treatment completely suppressed p-ERK (T202/Y204) expression in TNBC cells (Figure 8B). These results confirmed that each selected PKIs sufficiently targets its respective pathway as intended.
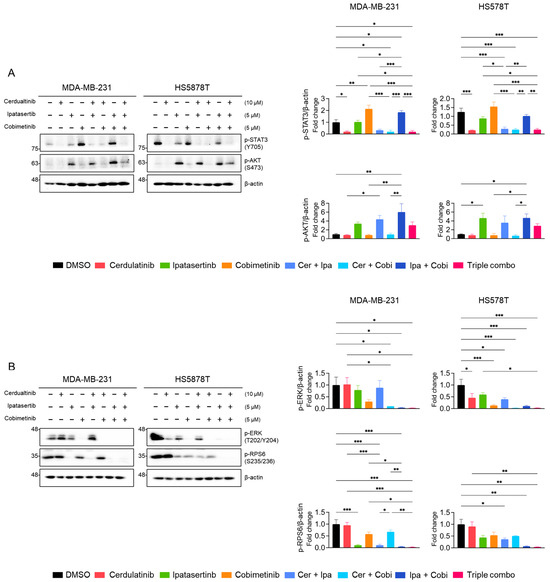
Figure 8.
Effects of single and combined pathway inhibition on JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/AKT, and MEK/ERK signalings in TNBC cells. (A,B) Western blot analysis of signaling proteins in cells treated with the indicated PKIs for 24 h. Representative images with β-actin as a loading control and densitometric quantification from three independent experiments are shown. Data present mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.005.
The effects of selected JAK2i, AKTi, MEKi, and their combinations on the expression of MYC and cyclin D1 were further evaluated using western blot and quantitative RT-PCR analysis. Among single agents, only cobimetinib modestly reduced MYC and cyclin D1 protein levels (Figure 9A). Notably, this cobimetinib-mediated protein reduction was enhanced when combined with JAK2i and AKTi. The triple combination of JAK2i, AKTi, and MEKi produced the most pronounced reduction in MYC and cyclin D1 protein levels. Unlike fedratinib, cerdulatinib did not affect the expression of mRNAs for MYC and CCND1 (Figure 9B,C). Cobimetinib consistently suppressed MYC and CCND1 mRNA levels in TNBC cells, though enhanced suppression through the addition of AKTi or JAK2i was observed exclusively in HS578T cells. These results indicate that JAK2 inhibition augments the suppressive effects of combined AKT and MEK inhibition on MYC and cyclin D1 primarily at the protein levels.

Figure 9.
Effects of combined pathway inhibitions on MYC and cyclin D1 expression in TNBC cells. (A) Western blot analysis of PARP, XIAP, and caspase-3 protein levels in cells treated with indicated inhibitor combinations for 24 h, β-actin as a loading control. Representative images from three independent experiments were shown. (B,C) Relative MYC and CCND1 mRNA levels measured by quantitative RT-PCR following 24 h treatment. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.005.
Neither cerdulatinib nor ipatasertib triggered PARP cleavage or caspase-3 activation (Figure 10), while cobimetinib (MEKi) induced modest PARP cleavage. Notably, the dual combination of JAK2i with either MEKi (Cer + Cobi) or AKTi (Cer + Ipa) substantially enhanced PARP and caspase-3 cleavage. Consistent with MTT assay results, the tiple combination of all PKIs further augmented PARP and caspase-3 cleavage and modestly reduced XIAP levels in both MDA-MB-213 and HS578T cells. These findings suggests that while the inhibition of JAK2 alone insufficiently induces apoptotic cell death in TNBC cells, it significantly enhances the antiproliferative effects of MEKi and AKTi in TNBC cells.
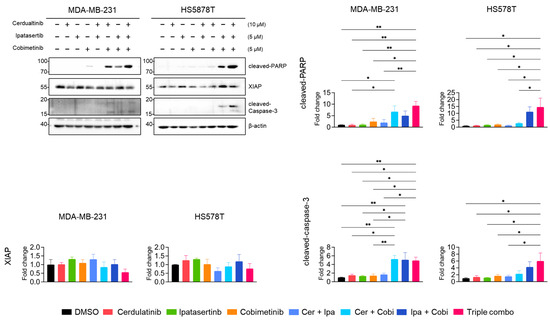
Figure 10.
Combined pathway inhibition induced apoptotic protein expression in TNBC cells. Western blot analysis of PARP, XIAP, and caspase-3 protein levels in cells treated with indicated inhibitor combinations for 24 h, β-actin as a loading control. Representative images from three independent experiments were shown. Representative images from three independent experiments were shown. Data present mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.
3. Discussion
Combination chemotherapy has emerged as a widely adopted strategy for treating various cancers, aiming to achieve synergistic or additive anticancer efficacy by targeting multiple key pathways involved in cancer development [57,58,59]. For TNBC, the development of specific therapies has primarily focused on combination approach due to the molecular heterogeneity of tumor cells and intrinsic or acquired resistance of tumors to existing drugs [1,60,61,62,63]. For instance, the expression of multidrug-resistance (MDR) genes, such as ATP-binding cassette superfamily G member 2 (ABCG2), contributes to chemoresistance in TNBC [64]. Additionally, novel therapeutic entities may offer alternative approaches to conventional treatment options for TNBC [65,66,67]. In this study, we demonstrated that the JAK2/STAT3 pathway represents a potential target for enhancing the antiproliferative effects of the combined PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathway inhibition.
Our analysis of TNBC cell viability using clinically approved JAKis revealed notable antiproliferative effects of fedratinib, a JAK2i. While fedratinib recently received the US FDA approval for treating myeloproliferative neoplasm-associated myelofibrosis [68], its anticancer efficacy remains largely unexplored across various human cancers, including TNBC. Given the distinct antiproliferative efficacy of fedratinib in TNBC cells compared to other JAK2is, further investigation of its effects on malignancy, metastasis, and drug resistance may provide new treatment strategies for TNBC, either as monotherapy or through synthetic lethality approaches.
Growing evidence indicates that dysregulation of the JAK/STAT pathway is implicated in multiple human cancers, including breast, gastric, lung, and ovarian cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [69,70,71,72,73,74,75]. This pathway particularly influences tumorigenesis and chemotherapy sensitivity in TNBC [20]. Studies have shown that JAK2 genomic amplification and increased expression occur specifically in TNBC, but not ER+ and HER2+ breast tumors, correlating with poor clinical outcomes such as progression-free survival and overall survival [76]. Moreover, elevated JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation in TNBC associates with resistance to targeted therapies and promotes more invasive tumor characteristics [77,78]. The interleukin 6 (IL6)/JAK2/STAT3 pathway has also been identified as a key mediator of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis in TNBC [79]. However, a clinical trial of ruxolitinib, a well-tolerated JAK1/2 inhibitor, in metastatic TNBC patients was discontinued due to poor clinical outcomes [80].
In this study, we demonstrated the antiproliferative effect of fedratinib on TNBC cell lines, building on our previous observation from PKI screening [4,5,6,26,27,28,29,30] (Figure 1A). Notably, while cerdulatinib and peficitinib, like fedratinib, completely abolished p-STAT3 (Y705) levels in MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells (Figure 2A), their antiproliferative effects were less potent. These JAK2is differ in their targeting specificity: fedratinib selectively binds to the ATP-binding site of JAK2 [31]; cerdulatinib nonselectively targets JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2 [32]; filgotinib selectively binds to the ATP-binding site of JAK1 [33]; and peficitinib acts as a pan-JAKi with moderate selectivity for JAK3 [34,35]. This comprehensive analysis of inhibitor selectivity suggests the crucial role of JAK2 in TNBC cell proliferation.
Substantial literature supports the JAK2/STAT3 pathway as a therapeutic target for TNBC [23,81]. JAK2/9p24-amplified tumors frequently occur in TNBC treated with chemotherapy, and JAK2-specific inhibitors have been reported to be more effective than dual JAK1/2 inhibitors [82]. Studies demonstrated that targeted inhibition or knockdown of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway efficiently suppressed TNBC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion [83,84,85,86]. The JAK2 pathway has been implicated in the resistance to chemotherapeutic agents such as tamoxifen and paclitaxel [23,87,88]. However, our previous research showed that CP690550-mediated inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation at Y705 alone insufficiently reduces TNBC cell proliferation [21]. CP690550, aka tofacitinib, is an approved drug which specifically target JAK3, JAK2, and JAK1 with IC50 value of 1, 20, and 112 nM, respectively [24,89]. In contrast, SH-I-14, a carbazole compound that inhibits p-STAT3 (Y705), demonstrated anticancer activity in TNBC cells and TNBC tumors in xenograft mouse models [90]. Further investigation revealed that CP690550 did not inhibit the proliferation of TNBC cells in MTT assays, while SH-I-14 dose-dependently reduced the TNBC cells’ proliferation through blocking STAT3 acetylation at K685 residue, disrupting the interaction between STAT3 and DNMT1, and resulting in re-repression of tumor suppressor gene expression [25]. However, since the acetylation of STAT3 (K685) is mediated by histone acetyltransferase P300 [91,92] and the mutation of K685 did not affect Y705 phosphorylation [93], we cannot directly link fedratinib to STAT3 acetylation, suggesting that phosphorylation of STAT3 Y705 may have independent roles in tumorigenesis or tumor progression.
A distinct feature of fedratinib, compared to other JAK2is used in this study, is its additionally targeting of two receptor tyrosine kinases FLT3 and RET (Table 1). This broader targeting profile aligns with our observation that only fedratinib inhibited the PI3K/AKT pathway, while cerdulatinib and peficitinib did not (Figure 2 and Figure 4). Although fedratinib also affected the MEK/ERK pathway, its efficacy showed temporal and cell-type specific limitations. Based on our previous and current findings, we hypothesized that the inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway could provide additional therapeutic benefits when combined with PI3K/AKT and/or MEK/ERK pathway inhibition. Our investigation revealed that while cerdulatinib alone minimally affected TNBC cell proliferation, its combination with MEKi or AKTi, or MEKi or PI3Ki further enhanced antiproliferative effects (Figure 7). The triple combination of JAK2i, MEKi, and AKTi or PI3Ki significantly reduced cell proliferation, markedly increased in the levels of cleaved PARP and caspase-3, and downregulated XIAP expression. This combination also reduced the expression of MYC and cyclin D1 in TNBC cells, primarily at the protein levels, warranting further investigation into the underlying molecular mechanisms.
Collectively, our findings indicate that while JAK2 inhibition alone showed limited efficacy against TNBC cell proliferation, it might potentiate the effects of combined MEK and AKT inhibition through enhanced apoptosis. However, one limitation of the current study lies in the potential adverse effects of simultaneous inhibiting these essential pathways at the systemic levels. Further preclinical and clinical validation of concurrent JAK2/STAT3, MEK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathway inhibition may reveal additional therapeutic advantages for treating TNBC, though careful consideration of the risk–benefit ratio will be crucial.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
The TNBC cell lines HS578T and MDA-MB-231 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA). Cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 1% Antibiotic-Antimycotic (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and 5 μg/mL anti-mycoplasma (GenDEPTO, Baker, TX, USA) at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Cell viability and counting were assessed using the trypan blue (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) exclusion method and a LUNA II Automated Cell Counter (Logos Biosystems, Anyang-si, Gyeonggi-Do, Korea) as described previously [94]. JAK2is (fedratinib, ceduratinib, peficitinib, and filgotinib), MEKis (cobimetinib and trametinib), an AKTi (ipatasertib), and a PI3Ki (alpelisib) were purchased from Selleck Chemicals (Houston, TX, USA). Compounds were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Duchefa Biochemie, Haarlem, The Netherlands) and stored at −20 °C in small aliquots.
4.2. MTT Assay
For cell viability assays, TNBC cells were seeded at 2 × 103 cells per well in 96-well plates and allowed to adhere overnight before treatment. Cells were treated with increasing concentrations of the indicated compounds for 72 h. MTT reagent (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide) was added to a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL and viable cells to measure cell viability as previously described [26,95,96]. The cells were incubated at 37 °C for 4 h, culture medium was removed, and the formazan crystals were dissolved in DMSO. Absorbance was measured at 560 nm using an iMARK Microplate Absorbance Reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). All experiments were performed in triplicate and independently repeated at least three times.
4.3. Clonogenic Survival Assay
For colony formation assays, TNBC cells were at 1 × 103 cells per well in 6-well plates. At the next day, cells were treated with increasing concentrations of fedratinib or 5 μM of fedratinib, cerdulatinib, or peficitinib for 24 h. Following treatment, cells were washed and cultured in fresh normal growth medium for an additional 10–14 days to allow colony formation. Colonies were fixed and stained with crystal violet solution, and then washed and air dried at room temperature. Stained colonies were imaged with a flatbed scanner. For quantification, crystal violet was solubilized in a 1:1 mixture (v/v) of 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH4.5) and ethanol, and absorbance was measure as previously described [4,5,6].
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
Western blot analyses were performed as previously described [30]. In brief, TNBC cells were treated with the indicated compounds under specified conditions, harvested, and lysed on ice using RIPA buffer supplemented with protease and phosphatase inhibitors (ThermoFisher Scientific). Protein concentrations were determined using the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Equal amounts of proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (Sigma-Aldrich). The following antibodies were used in this study (Table 2).

Table 2.
Antibodies used in this study.
4.5. Fluorescence Cell Flow Cytometry
MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells (5 × 105 cells per 60 mm dish) were seeded and incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 for 24 h. Subsequently, the medium was replaced with fresh medium containing 5 µM of fedratinib, cerdulatinib and peficitinib, and cells were incubated for an additional 24 h. Following treatment, cells were harvested using TrypLE™ Express (Thermo Fisher Scientific), washed twice with cold Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline (DPBS), and centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 5 min. Cell pellets were resuspended in 100 µL of 1× Annexin V buffer (Cell Signaling Technology), 5 µL of Annexin V-Alexa 488 (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and 12.5 µL of PI (Cell Signaling Technology) were added to each sample, followed by incubation on ice in the dark for 15 min. Apoptotic and necrotic cells were quantified using a BD FACS Calibur™(Becton Dickinson sciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) system and CellQuest™ Pro software (BD, version 4.0.2) or NovoCyte Flow Cytometer System (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA).
4.6. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from cultured TNBC cells using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Cat. No. 74124, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. RNA concentration and purity were measured using a BioSpectrometer (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). For cDNA synthesis, 1 μg of total RNA was reverse-transcribed in a 20 μL reaction volume using the ReverTra Ace™ qPCR RT Kit & Master Mix (Cat. No. FSQ-101, TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan), containing 250 ng of random primers. The synthesized cDNA was diluted 1:50 with nuclease-free water and stored at –20 °C until further use.
Quantitative RT-qPCR was performed using the iTaq™ Universal SYBR® Green Supermix (Cat. No. 1725121, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) on an Applied Biosystems StepOne™ Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Each 10 μL PCR reaction mixture consisted of 5 μL SYBR Green Supermix, 1 μL diluted cDNA, 0.4 μM of each gene-specific forward and reverse primer, and nuclease-free water to a final volume of 10 μL. The thermal cycling conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 30 s. A melting curve analysis was included to confirm the specificity of the PCR products. The following primers were used in this study: CCND1 (Cyclin D1, Gene ID: 595), forward: 5′-AGCTCCTGTGCTGCGAAGTGGAAAC-3′ and reverse: 5′-AGTGTTCAATGAAATCGTGCGGGGT-3′; MYC (Gene ID: 4609), forward: 5′-GGCTCCTGGCAAAAGGTCA-3′ and reverse: 5′-CTGCGTAGTTGTGCTGATGT-3′; and ACTB (β-actin, internal control), forward: 5′-CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC-3′ and reverse: 5′-AGGTCTTTGCGGATCTCCACGT-3′. Relative gene expression was calculated using the 2^–ΔΔCt method with ACTB as the reference gene. All qPCR reactions were performed in triplicate for each sample to ensure reproducibility.
4.7. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were performed at least thrice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to check the suitability of parametric methods. After confirming, one-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to calculate p-values. Dunnett’s test was used as a post hoc test to compare data between groups. All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism Ver 10.3.1 (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA). Statistically significant differences are indicated as follows: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.005.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26136139/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.S.Y. and Y.W.Y.; methodology, K.S.Y., T.-S.K., J.-S.P., D.J.K. and Y.W.Y.; investigation, K.S.Y., T.-S.K. and S.M.B.; resources, Y.-S.S. and Y.W.Y.; data curation, K.S.Y., J.-S.P. and Y.W.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, K.S.Y., T.-S.K. and Y.W.Y.; writing—review and editing, K.S.Y., T.-S.K., J.-S.P., K.L., Y.-S.S., D.J.K. and Y.W.Y.; visualization, K.S.Y. and Y.W.Y.; supervision, D.J.K. and Y.W.Y.; project administration, Y.W.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.-S.S., D.J.K. and Y.W.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government NRF-2021R1A6A3A01086886 (K.S.Y.), NRF-2022R1F1A1064121 (Y.-S.S.), RS-2023-00237259 (D.J.K.), and RS-2022-NR074902 (Y.W.Y.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data and materials in the present study may be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable requests.
Acknowledgments
We appreciated Mi Joo Park (Department of Crop Science and Biotechnology, Dankook University), Sua Lim, and Hye Ryeong Kim (Department of Biomedical Engineering, Dankook University) for their technical support during the training course for undergraduate research students.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ADC | antibody drug conjugate |
| AKTi | AKT inhibitor |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DNMT1 | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ER | estrogen receptor |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FLT3 | FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 |
| GvHD | graft-versus-host disease |
| HER2 | human epidermal growth factor 2 |
| IL6 | interleukin 6 |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| JAK2i | JAK2 inhibitor |
| MEK | MAP kinase/ERK kinase |
| MEKi | MEK inhibitor |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide |
| PARP1 | poly [adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose] polymerase 1 |
| PD-L1 | programmed cell death ligand 1 |
| PDLIM4 | PDZ and LIM domain protein 4 |
| PKI | protein kinase inhibitor |
| PR | progesterone receptor |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene difluoride |
| RET | rearranged during transfection |
| RTK | receptor tyrosine kinase |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| SYK | spleen tyrosine kinase |
| TNBC | triple-negative breast cancer |
| TYK2 | tyrosine kinase 2 |
| VHL | von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor |
| XIAP | X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein |
References
- You, K.S.; Yi, Y.W.; Cho, J.; Park, J.-S.; Seong, Y.-S. Potentiating Therapeutic Effects of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, L.K.; Cryns, V.L.; Symmans, W.F.; Sneige, N. Triple Negative Breast Carcinoma and the Basal Phenotype: From Expression Profiling to Clinical Practice. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2007, 14, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.; Pambid, M.R.; Jayanthan, A.; Dorr, A.; Los, G.; Dunn, S.E. The Dawn of Targeted Therapies for Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Snapshot of Investigational Drugs in Phase I and II Trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.S.; Yi, Y.W.; Cho, J.; Seong, Y.-S. Dual Inhibition of AKT and MEK Pathways Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Gefitinib in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YI, Y.W.; YOU, K.; BAE, E.J.; KWAK, S.-J.; SEONG, Y.-S.; BAE, I. Dual Inhibition of EGFR and MET Induces Synthetic Lethality in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells through Downregulation of Ribosomal Protein S6. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, K.S.; Yi, Y.W.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Inhibition of RPTOR Overcomes Resistance to EGFR Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DUONG, H.-Q.; YI, Y.W.; KANG, H.J.; HONG, Y.B.; TANG, W.; WANG, A.; SEONG, Y.-S.; BAE, I. Inhibition of NRF2 by PIK-75 Augments Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 44, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, S.A. The Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/Erb-B/HER Family in Normal and Malignant Breast Biology. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarden, Y.; Pines, G. The ERBB Network: At Last, Cancer Therapy Meets Systems Biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, K.; Hung, M.-C.; Yamaguchi, H. A Perspective on Anti-EGFR Therapies Targeting Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga, C.L.; Truica, C.I. Challenges in the Development of Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Therapies in Breast Cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; He, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, R.; Shi, Y.; Teng, X.; Qin, T. EGFR Expression Correlates with Decreased Disease-Free Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis Based on a Tissue Microarray. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapati, A.; Lukong, K.E. Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Approved Treatment Options and Their Mechanisms of Action. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 3701–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromberg, J.; Darnell, J.E. The Role of STATs in Transcriptional Control and Their Impact on Cellular Function. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2468–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, K.; Saharinen, P.; Pesu, M.; Holt, V.E.; Silvennoinen, O.; O’Shea, J.J. The Janus Kinases (Jaks). Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in Cancer Inflammation and Immunity: A Leading Role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankan, A.K.; Greten, F.R. Inhibiting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3: Rationality and Rationale Design of Inhibitors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, B.; Xu, S.; Neamati, N. Small Molecule Inhibitors of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (Stat3) Protein. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6645–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, A.; Oya, M.; Shimada, T.; Uchida, A.; Marumo, K.; Murai, M. Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Study of Incidence and Its Association With Pathological Features and Clinical Outcome. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, S.; Ushijima, K.; Kawano, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Terada, A.; Fujiyoshi, N.; Nishio, S.; Tsuda, N.; Ijichi, M.; Kakuma, T.; et al. Expression of Activated Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-3 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Cervical Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.A. Which JAK Inhibitors Are Approved in the U.S? Available online: https://www.drugs.com/medical-answers/jak-inhibitors-approved-3575793/ (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Shawky, A.M.; Almalki, F.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Abdelazeem, A.H.; Gouda, A.M. A Comprehensive Overview of Globally Approved JAK Inhibitors. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Fei, X.; Chen, L.; Yao, L.; Lei, X. Potential Therapeutic Targets of the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1381251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, M.E.; Blumenkopf, T.A.; Brissette, W.H.; Brown, M.F.; Casavant, J.M.; Shang-Poa, C.; Doty, J.L.; Elliott, E.A.; Fisher, M.B.; Hines, M.; et al. Discovery of CP-690,550: A Potent and Selective Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases and Organ Transplant Rejection. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8468–8484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Yi, Y.W.; Hou, S.-J.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Bae, I.; Brown, M.L. Disruption of STAT3-DNMT1 Interaction by SH-I-14 Induces Re-Expression of Tumor Suppressor Genes and Inhibits Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Tumor. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 83457–83468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.W.; Hong, W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, A.; Seong, Y.; Bae, I. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT Pathway Potentiates Cytotoxicity of EGFR Kinase Inhibitors in Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Wang, A.; Bae, I. Inhibition of Constitutively Activated Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT Pathway Enhances Antitumor Activity of Chemotherapeutic Agents in Breast Cancer Susceptibility Gene 1-defective Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Bae, E.J.; Oh, S.; Seong, Y.-S.; Bae, I. β-TrCP1 Degradation Is a Novel Action Mechanism of PI3K/MTOR Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Exp. Mol. Medicine 2015, 47, e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.W.; Park, J.-S.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Co-Treatment with BEZ235 Enhances Sensitivity of BRCA1-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Olaparib. Anticancer. Res. 2015, 35, 3829–3838. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.W.; You, K.S.; Han, S.; Ha, I.J.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, S.-G.; Seong, Y.-S. Inhibition of IκB Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Circumvent Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernig, G.; Kharas, M.G.; Okabe, R.; Moore, S.A.; Leeman, D.S.; Cullen, D.E.; Gozo, M.; McDowell, E.P.; Levine, R.L.; Doukas, J.; et al. Efficacy of TG101348, a Selective JAK2 Inhibitor, in Treatment of a Murine Model of JAK2V617F-Induced Polycythemia Vera. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, G.; Betz, A.; DeGuzman, F.; Pak, Y.; Inagaki, M.; Baker, D.C.; Hollenbach, S.J.; Pandey, A.; Sinha, U. The Novel Kinase Inhibitor PRT062070 (Cerdulatinib) Demonstrates Efficacy in Models of Autoimmunity and B-Cell Cancer. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 351, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompaey, L.V.; Galien, R.; van der Aar, E.M.; Clement-Lacroix, P.; Nelles, L.; Smets, B.; Lepescheux, L.; Christophe, T.; Conrath, K.; Vandeghinste, N.; et al. Preclinical Characterization of GLPG0634, a Selective Inhibitor of JAK1, for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3568–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Yamagami, K.; Kuno, M.; Morita, Y.; Okuma, K.; Nakamura, K.; Chida, N.; Inami, M.; Inoue, T.; et al. A Novel JAK Inhibitor, Peficitinib, Demonstrates Potent Efficacy in a Rat Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis Model. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 133, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, H.; Amano, Y.; Moritomo, A.; Shirakami, S.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakai, K.; Nomura, N.; Ito, M.; Higashi, Y.; Inoue, T. Discovery and Structural Characterization of Peficitinib (ASP015K) as a Novel and Potent JAK Inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4971–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Hutzen, B.; Zuo, M.; Ball, S.; Deangelis, S.; Foust, E.; Pandit, B.; Ihnat, M.A.; Shenoy, S.S.; Kulp, S.; et al. Novel STAT3 Phosphorylation Inhibitors Exhibit Potent Growth-Suppressive Activity in Pancreatic and Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.W.; You, K.S.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, S.-G.; Seong, Y.-S. Ribosomal Protein S6: A Potential Therapeutic Target against Cancer? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacina, K.S.; Park, G.Y.; Bae, S.S.; Guzzetta, A.W.; Schaefer, E.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Roth, R.A. Identification of a Proline-Rich Akt Substrate as a 14-3-3 Binding Partner*. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10189–10194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbannayya, T.; Leal-Rojas, P.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Ozerov, I.V.; Korzinkin, M.; Babu, N.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Chavan, S.; Raja, R.; Pinto, S.M.; et al. PIM1 Kinase Promotes Gallbladder Cancer Cell Proliferation via Inhibition of Proline-Rich Akt Substrate of 40 KDa (PRAS40). J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 13, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasó-Maristany, F.; Filosto, S.; Catchpole, S.; Marlow, R.; Quist, J.; Francesch-Domenech, E.; Plumb, D.A.; Zakka, L.; Gazinska, P.; Liccardi, G.; et al. PIM1 Kinase Regulates Cell Death, Tumor Growth and Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, D.; Camarda, R.; Zhou, A.Y.; Yau, C.; Momcilovic, O.; Balakrishnan, S.; Corella, A.N.; Eyob, H.; Kessenbrock, K.; Lawson, D.A.; et al. PIM1 Kinase Inhibition as a Targeted Therapy against Triple-Negative Breast Tumors with Elevated MYC Expression. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunder, R.; Velyunskiy, M.; Dunne, S.F.; Cho, B.-K.; Kanojia, D.; Begg, L.; Orriols, A.M.; Fleming-Trujillo, E.; Vadlamani, P.; Vialichka, A.; et al. Synergistic PIM Kinase and Proteasome Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy for MYC-Overexpressing Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cell Chem. Biol. 2022, 29, 358–372.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tang, G. PIM-1 Kinase: A Potential Biomarker of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 6267–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaul, Y.D.; Seger, R. The MEK/ERK Cascade: From Signaling Specificity to Diverse Functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navé, B.T.; Ouwens, D.M.; Withers, D.J.; Alessi, D.R.; Shepherd, P.R. Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Is a Direct Target for Protein Kinase B: Identification of a Convergence Point for Opposing Effects of Insulin and Amino-Acid Deficiency on Protein Translation. Biochem. J. 1999, 344, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Guertin, D.A.; Ali, S.M.; Sabatini, D.M. Phosphorylation and Regulation of Akt/PKB by the Rictor-MTOR Complex. Science 2005, 307, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.-B.; Halilovic, E.; Ye, Q.; Zhen, W.; Shirasawa, S.; Sasazuki, T.; Solit, D.B.; Rosen, N. 4E-BP1 Is a Key Effector of the Oncogenic Activation of the AKT and ERK Signaling Pathways That Integrates Their Function in Tumors. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayele, T.M.; Muche, Z.T.; Teklemariam, A.B.; Kassie, A.B.; Abebe, E.C. Role of JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in the Tumorigenesis, Chemotherapy Resistance, and Treatment of Solid Tumors: A Systemic Review. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 1349–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gera, J.F.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Shi, Y.; Rettig, M.B.; Tran, C.; Hsu, J.; Sawyers, C.L.; Lichtenstein, A.K. AKT Activity Determines Sensitivity to Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) Inhibitors by Regulating Cyclin D1 and c-Myc Expression*. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2737–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Steelman, L.S.; Lee, J.T.; Shelton, J.G.; Navolanic, P.M.; Blalock, W.L.; Franklin, R.A.; McCubrey, J.A. Signal Transduction Mediated by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK Pathway from Cytokine Receptors to Transcription Factors: Potential Targeting for Therapeutic Intervention. Leukemia 2003, 17, 1263–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benary, M.; Bohn, S.; Lüthen, M.; Nolis, I.K.; Blüthgen, N.; Loewer, A. Disentangling Pro-Mitotic Signaling during Cell Cycle Progression Using Time-Resolved Single-Cell Imaging. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeflich, K.P.; Merchant, M.; Orr, C.; Chan, J.; Otter, D.D.; Berry, L.; Kasman, I.; Koeppen, H.; Rice, K.; Yang, N.-Y.; et al. Intermittent Administration of MEK Inhibitor GDC-0973 plus PI3K Inhibitor GDC-0941 Triggers Robust Apoptosis and Tumor Growth Inhibition. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Kakefuda, R.; Tajima, N.; Sowa, Y.; Sakai, T. Antitumor Activities of JTP-74057 (GSK1120212), a Novel MEK1/2 Inhibitor, on Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines in Vitro and in Vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, J.F.; Xu, R.; Bencsik, J.R.; Xiao, D.; Kallan, N.C.; Schlachter, S.; Mitchell, I.S.; Spencer, K.L.; Banka, A.L.; Wallace, E.M.; et al. Discovery and Preclinical Pharmacology of a Selective ATP-Competitive Akt Inhibitor (GDC-0068) for the Treatment of Human Tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8110–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furet, P.; Guagnano, V.; Fairhurst, R.A.; Imbach-Weese, P.; Bruce, I.; Knapp, M.; Fritsch, C.; Blasco, F.; Blanz, J.; Aichholz, R.; et al. Discovery of NVP-BYL719 a Potent and Selective Phosphatidylinositol-3 Kinase Alpha Inhibitor Selected for Clinical Evaluation. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3741–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.K.-H.; Leverson, J.D.; McGonigal, T.; Shah, O.J.; Woods, K.W.; Hunter, T.; Giranda, V.L.; Luo, Y. Akt Inhibitor A-443654 Induces Rapid Akt Ser-473 Phosphorylation Independent of MTORC1 Inhibition. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5655–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination Therapy in Combating Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.A.; Omlin, A.; Bono, J.S. de Development of Therapeutic Combinations Targeting Major Cancer Signaling Pathways. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1592–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Lei, Q.; Zhang, A.-Q.; Zhang, X.-Z. Combinational Strategy for High-Performance Cancer Chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 171, 178–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; He, G.; Yan, S.; Chen, C.; Song, L.; Rosol, T.J.; Deng, X. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Is There a Treatment on the Horizon? Oncotarget 2016, 8, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljković, M.; Damjanović, A. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—How We Can Rise to the Challenge. Cells 2019, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalakur-Ramireddy, N.K.R.; Pakala, S.B. Combined Drug Therapeutic Strategies for the Effective Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.W. Therapeutic Implications of the Drug Resistance Conferred by Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, K.M.; Eyre, R.; Harvey, I.J.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Browell, D.; Lennard, T.W.J.; Meeson, A.P. Breast Cancer, Side Population Cells and ABCG2 Expression. Cancer Lett. 2012, 323, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, E.; Luca, F.D.; Locatelli, C.A.; Ratto, D.; Iorio, C.D.; Savino, E.; Bottone, M.G.; Rossi, P. From a Medicinal Mushroom Blend a Direct Anticancer Effect on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Preclinical Study on Lung Metastases. Molecules 2020, 25, 5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, E.; Luca, F.D.; Iorio, C.D.; Ratto, D.; Siciliani, S.; Ferrari, B.; Cobelli, F.; Borsci, G.; Priori, E.C.; Chinosi, S.; et al. Novel Medicinal Mushroom Blend as a Promising Supplement in Integrative Oncology: A Multi-Tiered Study Using 4T1 Triple-Negative Mouse Breast Cancer Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, F.D.; Roda, E.; Rossi, P.; Bottone, M.G. Medicinal Mushrooms in Metastatic Breast Cancer: What Is Their Therapeutic Potential as Adjuvant in Clinical Settings? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 7577–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpaz, M.; Kiladjian, J.-J. Fedratinib, a Newly Approved Treatment for Patients with Myeloproliferative Neoplasm-Associated Myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rah, B.; Rather, R.A.; Bhat, G.R.; Baba, A.B.; Mushtaq, I.; Farooq, M.; Yousuf, T.; Dar, S.B.; Parveen, S.; Hassan, R.; et al. JAK/STAT Signaling: Molecular Targets, Therapeutic Opportunities, and Limitations of Targeted Inhibitions in Solid Malignancies. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 821344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Low, J.T.; Silke, J.; O’Reilly, L.A. Digesting the Role of JAK-STAT and Cytokine Signaling in Oral and Gastric Cancers. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 835997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.J.H.; Thng, D.K.H.; Lim, J.J.; Toh, T.B. JAK/STAT Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatic Oncol. 2020, 7, HEP18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Moon, H.; Ro, S.W. Exploring the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Unraveling Signaling Complexity and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.Y.; Johnson, F.M. Defining the Role of the JAK-STAT Pathway in Head and Neck and Thoracic Malignancies: Implications for Future Therapeutic Approaches. Drug Resist. Updates 2010, 13, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, S.; Abbasi, R.; Ahmad, N.; Farooqi, A.A. Breast Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance, Challenges and Progress. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1152, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standing, D.; Feess, E.; Kodiyalam, S.; Kuehn, M.; Hamel, Z.; Johnson, J.; Thomas, S.M.; Anant, S. The Role of STATs in Ovarian Cancer: Exploring Their Potential for Therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, M.T.; Anderson, K.S.; Lenkiewicz, E.; Andreozzi, M.; Cunliffe, H.E.; Klassen, C.L.; Dueck, A.C.; McCullough, A.E.; Reddy, S.K.; Ramanathan, R.K.; et al. Genomic Amplification of 9p24.1 Targeting JAK2, PD-L1, and PD-L2 Is Enriched in High-Risk Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26483–26493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marotta, L.L.C.; Almendro, V.; Marusyk, A.; Shipitsin, M.; Schemme, J.; Walker, S.R.; Bloushtain-Qimron, N.; Kim, J.J.; Choudhury, S.A.; Maruyama, R.; et al. The JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway Is Required for Growth of CD44+CD24– Stem Cell–like Breast Cancer Cells in Human Tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britschgi, A.; Andraos, R.; Brinkhaus, H.; Klebba, I.; Romanet, V.; Müller, U.; Murakami, M.; Radimerski, T.; Bentires-Alj, M. JAK2/STAT5 Inhibition Circumvents Resistance to PI3K/MTOR Blockade: A Rationale for Cotargeting These Pathways in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 796–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.-S.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-A.; Shen, P.-C.; Haq, A.T.A.; Chen, L.-M.; Tung, Y.-C.; Hsu, H.-L. MCT-1/MiR-34a/IL-6/IL-6R Signaling Axis Promotes EMT Progression, Cancer Stemness and M2 Macrophage Polarization in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stover, D.G.; Alcazar, C.R.G.D.; Brock, J.; Guo, H.; Overmoyer, B.; Balko, J.; Xu, Q.; Bardia, A.; Tolaney, S.M.; Gelman, R.; et al. Phase II Study of Ruxolitinib, a Selective JAK1/2 Inhibitor, in Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. npj Breast Cancer 2018, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W. Role of JAK/STAT3 Signaling in the Regulation of Metastasis, the Transition of Cancer Stem Cells, and Chemoresistance of Cancer by Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Cells 2020, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balko, J.M.; Schwarz, L.J.; Luo, N.; Estrada, M.V.; Giltnane, J.M.; Dávila-González, D.; Wang, K.; Sánchez, V.; Dean, P.T.; Combs, S.E.; et al. Triple-Negative Breast Cancers with Amplification of JAK2 at the 9p24 Locus Demonstrate JAK2-Specific Dependence. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 334ra53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.; Song, L.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dai, C.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, W.; Zhan, X.; et al. Loss of Wwox Drives Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by JAK2/STAT3 Axis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, J.; Lai, M.; Liu, L.; Zuo, M.; Dang, L. Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Protein (FTO) Mediates Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3)-Drived Resistance of Breast Cancer to Doxorubicin. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 1874–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.-S.; Wang, S.; Deng, A.; Liu, B.; Edgerton, S.M.; Lind, S.E.; Wahdan-Alaswad, R.; Thor, A.D. Metformin Targets Stat3 to Inhibit Cell Growth and Induce Apoptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regua, A.T.; Bindal, S.; Najjar, M.K.; Zhuang, C.; Khan, M.; Arrigo, A.B.J.; Gonzalez, A.O.; Zhang, X.R.; Zhu, J.-J.; Watabe, K.; et al. Dual Inhibition of the TrkA and JAK2 Pathways Using Entrectinib and Pacritinib Suppresses the Growth and Metastasis of HER2-Positive and Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. Cancer Lett. 2024, 597, 217023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y.; Qin, X.; Miao, R.; Nan, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, X.; et al. Loss of ZIP Facilitates JAK2-STAT3 Activation in Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15047–15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Yun, J.; Quan, M.; Kang, W.; Jung, J.-G.; Heo, W.; Li, S.; Lee, K.J.; Son, H.-Y.; Kim, J.H.; et al. JAK2 Regulates Paclitaxel Resistance in Triple Negative Breast Cancers. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changelian, P.S.; Flanagan, M.E.; Ball, D.J.; Kent, C.R.; Magnuson, K.S.; Martin, W.H.; Rizzuti, B.J.; Sawyer, P.S.; Perry, B.D.; Brissette, W.H.; et al. Prevention of Organ Allograft Rejection by a Specific Janus Kinase 3 Inhibitor. Science 2003, 302, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Kong, H.-S.; Grindrod, S.; et al. Novel Carbazole Inhibits Phospho-STAT3 through Induction of Protein–Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPN6. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6342–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Cherukuri, P.; Luo, J. Activation of Stat3 Sequence-Specific DNA Binding and Transcription by P300/CREB-Binding Protein-Mediated Acetylation*. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11528–11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadiminty, N.; Lou, W.; Lee, S.O.; Lin, X.; Trump, D.L.; Gao, A.C. Stat3 Activation of NF-ΚB P100 Processing Involves CBP/P300-Mediated Acetylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7264–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, M.; Unal, H.; Willard, B.; Yang, J.; Karnik, S.S.; Stark, G.R. Critical Role for Lysine 685 in Gene Expression Mediated by Transcription Factor Unphosphorylated STAT3*. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 30763–30771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, K.; Hong, D.; Lim, H.; Cho, K.; Jung, N.; Yi, Y.W. Application of a Non-Hazardous Vital Dye for Cell Counting with Automated Cell Counters. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 492, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Brown, M.M.; Bae, I. Targeting Mutant P53 by a SIRT1 Activator YK-3-237 Inhibits the Proliferation of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.-Q.; You, K.; Oh, S.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Silencing of NRF2 Reduces the Expression of ALDH1A1 and ALDH3A1 and Sensitizes to 5-FU in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).