Pregnancy and Neonatal Outcomes in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
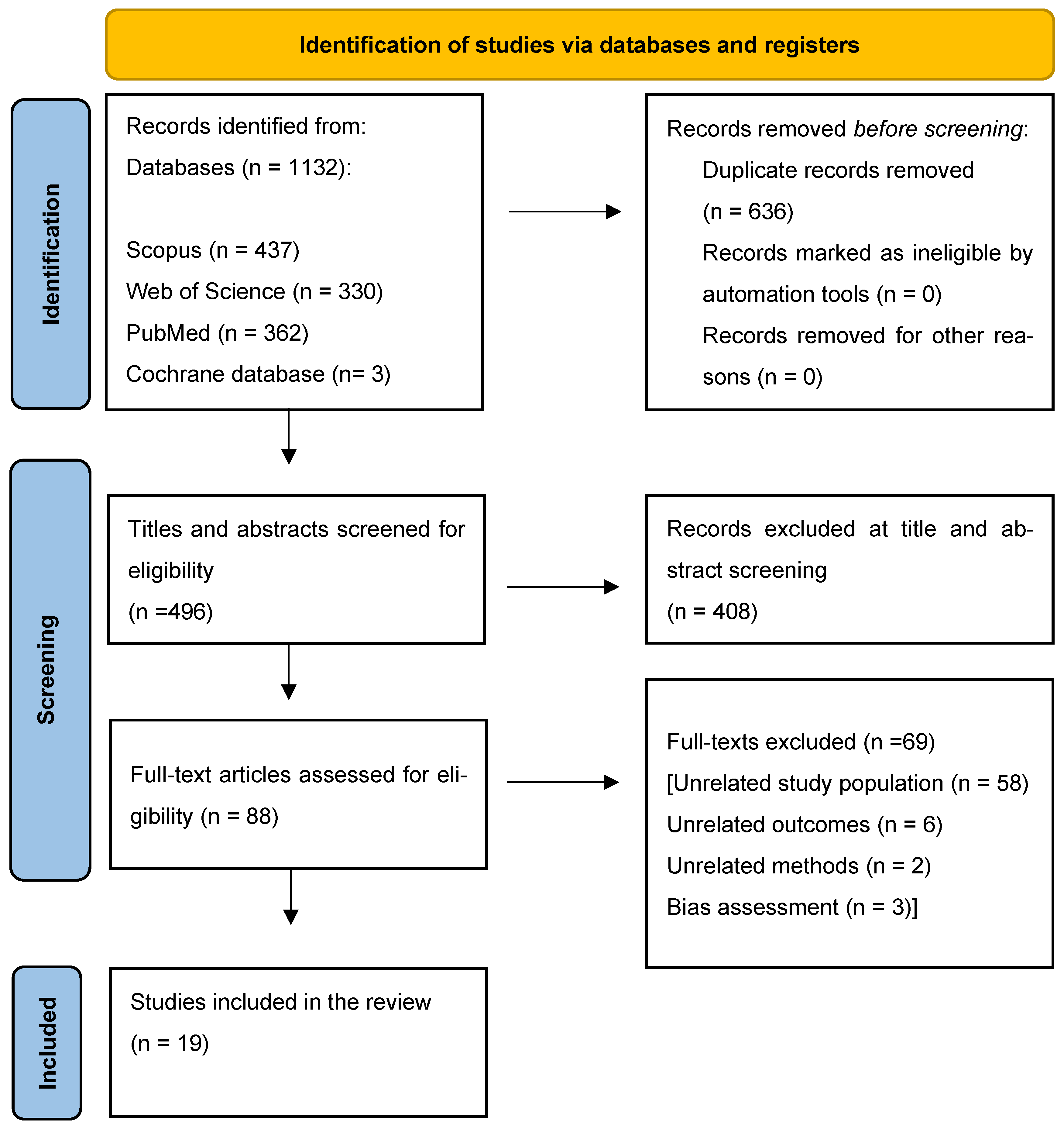
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction and Analysis
2.3. Outcomes
3. Results
3.1. Gestational Age at Delivery
3.2. Fetal Birthweight
3.3. Fetal Macrosomia or Large-for-Gestational-Age Infant
3.4. Small-for-Gestational-Age Infant
3.5. Neonatal Hypoglycemia
3.6. Shoulder Dystocia
3.7. Mode of Delivery
3.8. Insulin Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dickens, L.T.; Naylor, R.N. Clinical Management of Women with Monogenic Diabetes During Pregnancy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, R.; Ellard, S.; Hattersley, A.T. Clinical Implications of a Molecular Genetic Classification of Monogenic Beta-Cell Diabetes. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 4, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarthy, R.; Aston-Mourney, K.; Mikocka-Walus, A.; Radha, V.; Amutha, A.; Anjana, R.M.; Unnikrishnan, R.; Mohan, V. Clinical Features, Complications and Treatment of Rarer Forms of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)—A Review. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colom, C.; Corcoy, R. Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young and Pregnancy. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 24, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaxillaire, M.; Froguel, P. Monogenic Diabetes in the Young, Pharmacogenetics and Relevance to Multifactorial Forms of Type 2 Diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayling, T.M.; Evans, J.C.; Bulman, M.P.; Pearson, E.; Allen, L.; Owen, K.; Bingham, C.; Hannemann, M.; Shepherd, M.; Ellard, S.; et al. Beta-Cell Genes and Diabetes: Molecular and Clinical Characterization of Mutations in Transcription Factors. Diabetes 2001, 50 (Suppl. 1), S94–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, N.H.J.; Ghosh, S.; Bok, C.M.; Ching, C.; Low, B.S.J.; Chen, J.T.; Lim, E.; Miserendino, M.C.; Tan, Y.S.; Hoon, S.; et al. HNF4A and HNF1A Exhibit Tissue Specific Target Gene Regulation in Pancreatic Beta Cells and Hepatocytes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagata, K. Regulation of Pancreatic B-Cell Function by the HNF Transcription Network: Lessons from Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY). Endocr. J. 2003, 50, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love-Gregory, L.; Permutt, M.A. HNF4A genetic variants: Role in diabetes. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007, 10, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boj, S.F.; Párrizas, M.; Maestro, M.A.; Ferrer, J. A Transcription Factor Regulatory Circuit in Differentiated Pancreatic Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14481–14486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.J.; Conley, P.B.; Chen, L.; Sladek, F.M.; Darnell, J.E.; Crabtree, G.R. A Transcriptional Hierarchy Involved in Mammalian Cell-Type Specification. Nature 1992, 355, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ning, G.; Duncan, S.A. Mammalian Hepatocyte Differentiation Requires the Transcription Factor HNF-4α. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, M.M.; Sturis, J.; Clément, K.; Vionnet, N.; Pueyo, M.E.; Stoffel, M.; Takeda, J.; Passa, P.; Cohen, D.; Bell, G.I.; et al. Insulin Secretory Abnormalities in Subjects with Hyperglycemia Due to Glucokinase Mutations. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewska, A.; Stanirowski, P.; Wielgoś, M.; Bomba-Opoń, D. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) in Pregnancy: A Review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2022, 19, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Las Heras, J.; Martínez, R.; Rica, I.; De Nanclares, G.P.; Vela, A.; Castaño, L. Heterozygous Glucokinase Mutations and Birth Weight in Spanish Children. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitterman, O.; Tinto, N.; Franzese, A.; Iafusco, F.; Festa, C.; Mozzillo, E.; Napoli, A.; Iafusco, D. Glucokinase Deficit and Birthweight: Does Maternal Hyperglycemia Always Meet Fetal Needs? Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, S.; Schmid, J.; McCarthy, A.; Edwards, J.; Fleming, A.; Kinsley, B.; Firth, R.; Byrne, B.; Gavin, C.; Byrne, M.M. The Clinical Management of Hyperglycemia in Pregnancy Complicated by Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 213, 236.e1–236.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsonego, S.; Clark, H.; Karovitch, A.; O’Meara, P.; Shaw, T.; Malcolm, J. Management and Outcomes of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young in Pregnancy. Can. J. Diabetes 2019, 43, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudland, V.L. Diagnosis and Management of Glucokinase Monogenic Diabetes in Pregnancy: Current Perspectives. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modified Downs and Black Checklist for Assessment of Methodological Quality. PLoS ONE 2020. [CrossRef]
- Ciangura, C.; Seco, A.; Saint-Martin, C.; Ancel, P.Y.; Bouvet, D.; Jacqueminet, S.; Hartemann, A.; Lepercq, J.; Nizard, J.; Timsit, J.; et al. Pregnancy and Neonatal Outcomes in Women with GCK-MODY: An Observational Study Based on Standardised Insulin Modalities. Diabetologia 2025, 68, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spyer, G.; Macleod, K.M.; Shepherd, M.; Ellard, S.; Hattersley, A.T. Pregnancy Outcome in Patients with Raised Blood Glucose Due to a Heterozygous Glucokinase Gene Mutation. Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, Y.; Higuchi, S.; Kawakita, R.; Hata, I.; Urakami, T.; Isojima, T.; Takasawa, K.; Matsubara, Y.; Mizuno, H.; Maruo, Y.; et al. Pregnancy Outcome of Japanese Patients with Glucokinase–Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 1586–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickens, L.T.; Letourneau, L.R.; Sanyoura, M.; Greeley, S.A.W.; Philipson, L.H.; Naylor, R.N. Management and Pregnancy Outcomes of Women with GCK-MODY Enrolled in the US Monogenic Diabetes Registry. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 56, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Xiao, X. Birthweight Correlates with Later Metabolic Abnormalities in Chinese Patients with Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young Type 2. Endocrine 2019, 65, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Tinoco, C.; Sánchez Lechuga, B.; Bacon, S.; Colclough, K.; Ng, N.; Wong, E.; Goulden, E.L.; Edwards, J.; Fleming, A.; Byrne, B.; et al. Evaluation of Pregnancy Outcomes in Women with GCK-MODY. Diabet. Med. 2021, 38, e14488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopacz-Petranyuk, K.; Brandt-Varma, A.; Buraczewska, M.; Wołoszyn-Durkiewicz, A.; Peczyńska, J.; Preis, K.; Jarosz-Chobot, P.; Szadkowska, A.; Młynarski, W.; Myśliwiec, M. Neonatal Outcome and Diabetes Course in Children with GCK-MODY Born from Women with GCK-MODY. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2018, 24, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Li, M.; Wu, Q.; Xu, C.; Zhang, R.; Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Identification and Management of GCK-MODY Complicating Pregnancy in Chinese Patients with Gestational Diabetes. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2022, 477, 1629–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, T.T.L.; Yu, S.C.Y.; Cheng, J.Y.-K.; Kwok, J.S.S.; Ma, R.C.W. GCK-MODY in Pregnancy: A Pregnant Woman with Diabetes and a Small-for-Gestational-Age Fetus. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udler, M.S.; Powe, C.E.; Austin-Tse, C.A.; Petersen, M.C. Case 6–2020: A 34-Year-Old Woman with Hyperglycemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyer, G.; Hattersley, A.T.; Sykes, J.E.; Sturley, R.H.; MacLeod, K.M. Influence of Maternal and Fetal Glucokinase Mutations in Gestational Diabetes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 185, 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitterman, O.; Iafusco, D.; Torcia, F.; Tinto, N.; Napoli, A. A Dizygotic Twin Pregnancy in a MODY 3-Affected Woman. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikuscheva, A.; Mekhail, A.; Wheeler, B.J. Pregnancy Complicated by Maternal MODY 3 and Paternal MODY 2 Diabetes and Subsequent Rapidly Falling Insulin Requirement. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 2018, 9451061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, A.; Li, L.; Wilson, C. Pregnancy Outcome with Maternal HNF1B Gene Mutations and 17q12 Deletions. Obstet. Med. 2022, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikuscheva, A.; McKenzie, E.; Mekhail, A. 21-Year-Old Pregnant Woman with MODY-5 Diabetes. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 2017, 6431531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Ping, F. Maturity-onset Diabetes of the Young Type 5 Uncovered during Pregnancy with a Long-term Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Han, X.; Ji, L. Maternal and Infant Outcomes in GCK-MODY Complicated by Pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 2739–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirzhner, A.; Barak, O.; Vaisbuch, E.; Zornitzki, T.; Schiller, T. The Challenges of Treating Glucokinase MODY during Pregnancy: A Review of Maternal and Fetal Outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanescu, D.E.; Hughes, N.; Kaplan, B.; Stanley, C.A.; De León, D.D. Novel Presentations of Congenital Hyperinsulinism Due to Mutations in the MODY Genes: HNF1A and HNF4A. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E2026–E2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year and Country | Study Type | MODY Variant | Number of Patients | Number of Offspring | Number of MODY(+) Offspring | Number of MODY(+) Offspring Born to Women Treated with Insulin | Number of MODY(-) Offspring | Number of MODY(-) Offspring Born to Women Not Treated with Insulin | Analyzed Outcomes | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ciangura et al., 2025, France [21] | Prospective observational | GCK-MODY | 45 | 45 | 18 | 15 | 25 and 2 with an undetermined status | 2 | FBW, GA, LGA, SGA, NH, SD, mode of delivery |
|
| Spyer et al., 2009, United Kingdom [22] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY | 42 | 82 | 44 | 14 | 38 | 19 | FBW, GA, fetal macrosomia, SD, mode of delivery, insulin administration |
|
| Hosokawa et al., 2019, Japan [23] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY | 23 | 40 | 28 | 9 | 12 | 3 | FBW, GA, fetal macrosomia, SGA, insulin administration |
|
| Bacon et al., 2015, Ireland [17] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY, HNF1A-MODY | 37 (12 GCK-MODY, 25 HNF1A-MODY) | 132 (106 live births—41 in the GCK-MODY group and 65 in the HNF1A-MODY group) * * Genetic testing performed in 23 neonates of GCK-affected mothers. | 13 with GCK-MODY, no data available for HNF1A-MODY | 3 with GCK-MODY, no data available for HNF1A-MODY | 10 with GCK-MODY, no data available for HNF1A-MODY | 7 with GCK-MODY, no data available for HNF1A-MODY | FBW, GA, fetal macrosomia, NH, mode of delivery, insulin administration, SD, SGA |
|
| Dickens et al., 2019, United States [24] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY | 54 | 128 ** ** Genetic testing performed in 37 neonates, out of whom, in 35 a mutation was confirmed. | 23 | 8 | 12 | 4 | FBW, GA, LGA, mode of delivery, insulin administration, NH |
|
| Fu et al., 2019, China [25] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY | n/a | n/a | 28 | 7 | n/a | n/a | FBW, insulin administration | The mean FBW of neonates born to GCK-MODY women was 3110 ± 440 g. Neonates whose mothers were treated with insulin had significantly lower birthweight (2830 ± 390 vs. 3370 ± 390, p = 0.003). |
| López Tinoco et al., 2021, Spain [26] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY | 34 | 119 (99 live births) | 39 | 11 | 23 | 11 | FBW, GA, LGA, SGA, mode of delivery, insulin administration, SD, NH |
|
| Kopacz-Petranyuk et al., 2018, Poland [27] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY | n/a | 50 | 32 | n/a | n/a | n/a | FBW, fetal macrosomia, NH |
|
| Jiang et al., 2022, China [28] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY | 41 | 41 | 32 | 6 | 9 | 5 | FBW, fetal macrosomia, SGA, insulin administration |
|
| De las Heras et al., 2010, Spain [15] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY | 31 | 67 | 45 | 10 | 22 | 8 | FBW, GA, fetal macrosomia, mode of delivery |
|
| Bitterman et al., 2018, Italy [16] | Retrospective observational | GCK-MODY | n/a | 20 | 20 | 0 | n/a | n/a | FBW, SGA, LGA | Mean FBW was 3130 g (2910–3500). LGA occurred in 3 cases (15%), whereas SGA occurred in 2 (10%). |
| Yau et al., 2022, China [29] | Case report | GCK-MODY | 1 | 1 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | FBW, GA, mode of delivery, SGA | Emergency CS at 33 weeks of gestation due to PPROM. FBW of 1815 g (<3rd percentile). |
| Udler et al., 2020, United States [30] | Case report | GCK-MODY | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | FBW, GA, NH. mode of delivery | Labors occurred between 38 and 39 + 3 weeks of gestation; children weighed between 2600 and 3900 g. NH occurred in 2 (50%) of infants. |
| Spyer et al., 2001, United Kingdom [31] | Case report | GCK-MODY | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | FBW, GA, mode of delivery, SGA | Induced VD at 36 weeks of gestation. FBW of 1610 g (0 percentile). Second labor induced at 37 weeks. FBW of 2630 g (30th percentile). |
| Bitterman et al., 2016, Italy [32] | Case report | HNF1A-MODY | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | FBW, GA, NH, mode of delivery | Elective CS at 37 weeks of gestation. Two neonates were born. FBW of 2600 g (no mutation) and 2660 g (mutation carrier). Transient NH occurred in the mutation-carrying newborn. |
| Mikuscheva et al., 2018, Czech Republic [33] | Case report | HNF1A-MODY | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FBW, GA, mode of delivery | VD at 35 weeks of gestation. FBW of 2220 g. |
| Morton et al., 2022, United Kingdom [34] | Case report | HNF1B-MODY | 3 | 4 | 1 (confirmed) | 1 | 2 | 0 | FBW, GA, fetal macrosomia, LGA, NH, mode of delivery, SGA | Case 1: Emergency CS at 37 weeks of gestation due to preeclampsia. FBW of 3400 g (97th percentile). Elective repeat CS at 37 weeks of gestation. FBW of 4413 g (100th percentile). Case 2: Induced VD at 37 weeks of gestation. FBW of 3206 g (90th percentile). Neonatal course was complicated by hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia requiring intravenous glucose. Case 3: Emergency CS at 25 + 4 weeks of gestation due to placental abruption FBW of 602 g (5th percentile). |
| Mikuscheva et al., 2017, Czech Republic [35] | Case report | HNF1B-MODY | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | FBW, GA, mode of delivery | PPROM and spontaneous VD at 33 weeks of gestation. FBW of 2105 g. |
| Deng et al., 2019, China [36] | Case report | HNF1B-MODY | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | FBW, GA, mode of delivery | Spontaneous VD occurred at 39 + 5 weeks of gestation. FBW of 2900 g. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ługowski, F.; Babińska, J.; Makowska, K.; Ludwin, A.; Stanirowski, P.J. Pregnancy and Neonatal Outcomes in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136057
Ługowski F, Babińska J, Makowska K, Ludwin A, Stanirowski PJ. Pregnancy and Neonatal Outcomes in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136057
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁugowski, Franciszek, Julia Babińska, Katarzyna Makowska, Artur Ludwin, and Paweł Jan Stanirowski. 2025. "Pregnancy and Neonatal Outcomes in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136057
APA StyleŁugowski, F., Babińska, J., Makowska, K., Ludwin, A., & Stanirowski, P. J. (2025). Pregnancy and Neonatal Outcomes in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136057






