Development of Efficient Expression Systems for Bacteriolytic Proteases L1 and L5 of Lysobacter capsici XL1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
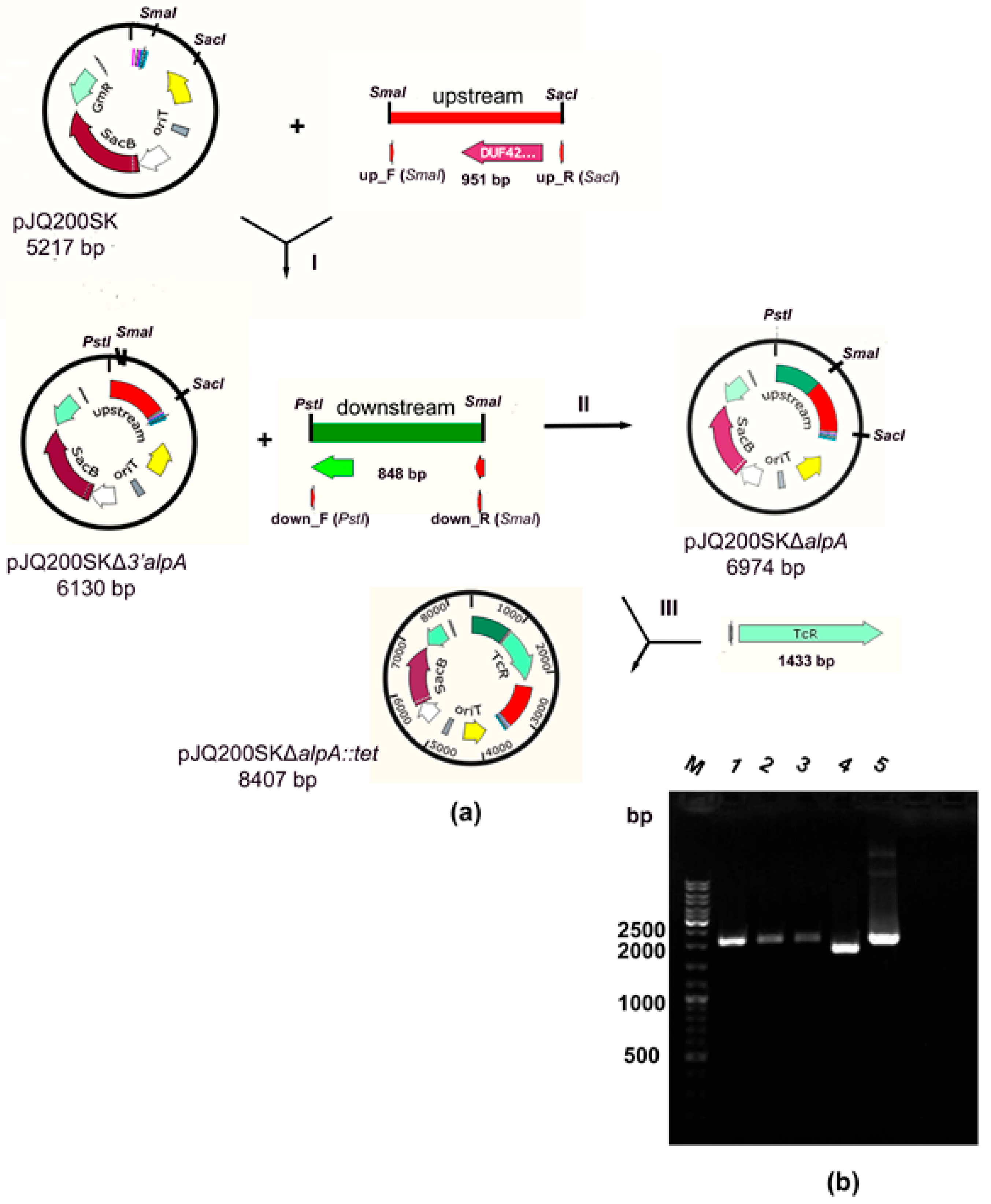
2.1. Production of a Strain with a Deletion of the alpA Gene
2.2. Production of Expression Strains L. capsici PT5–alpB and L. capsici PT5–alpA
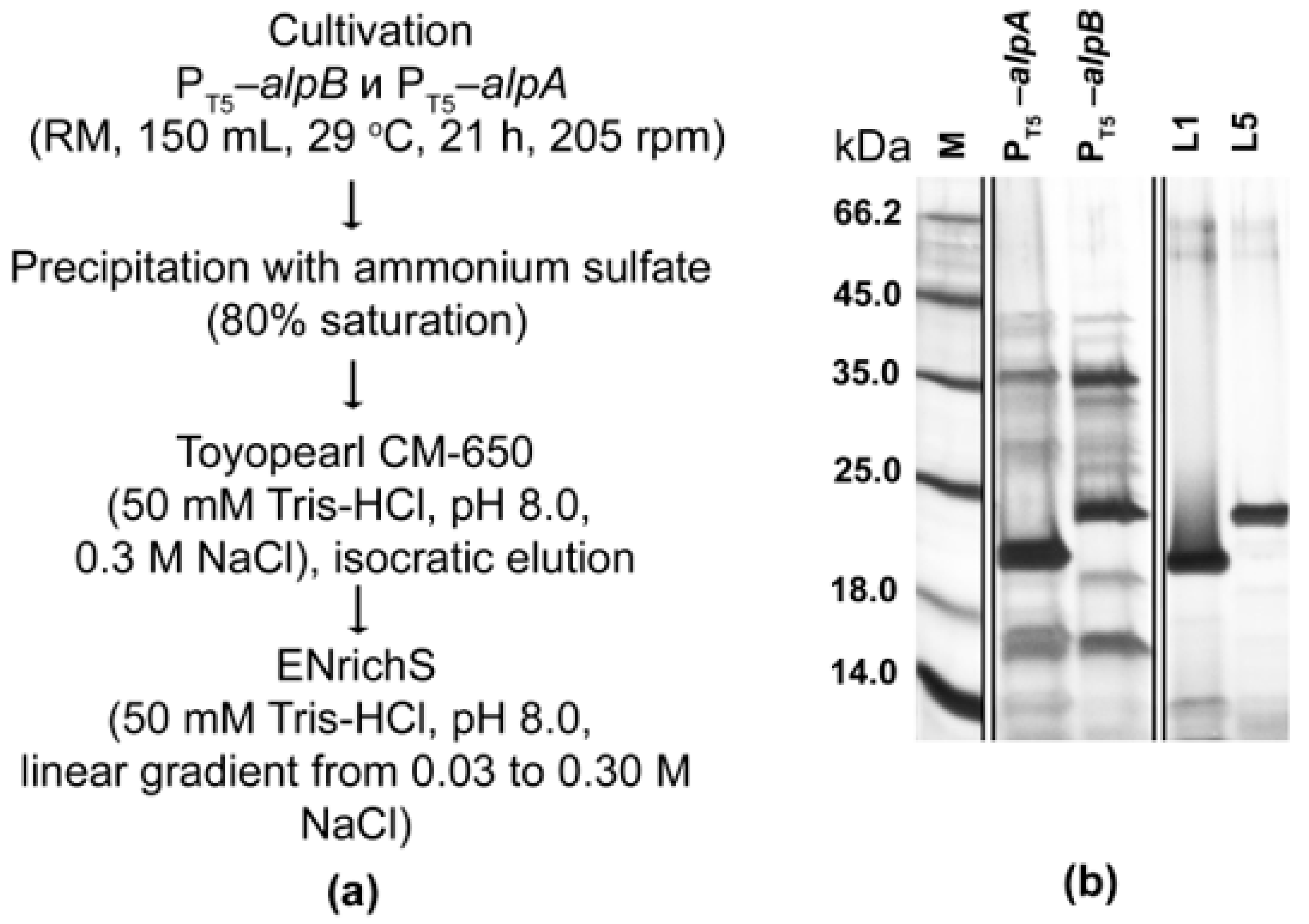
2.3. Expression and Purification of Bacteriolytic Proteases
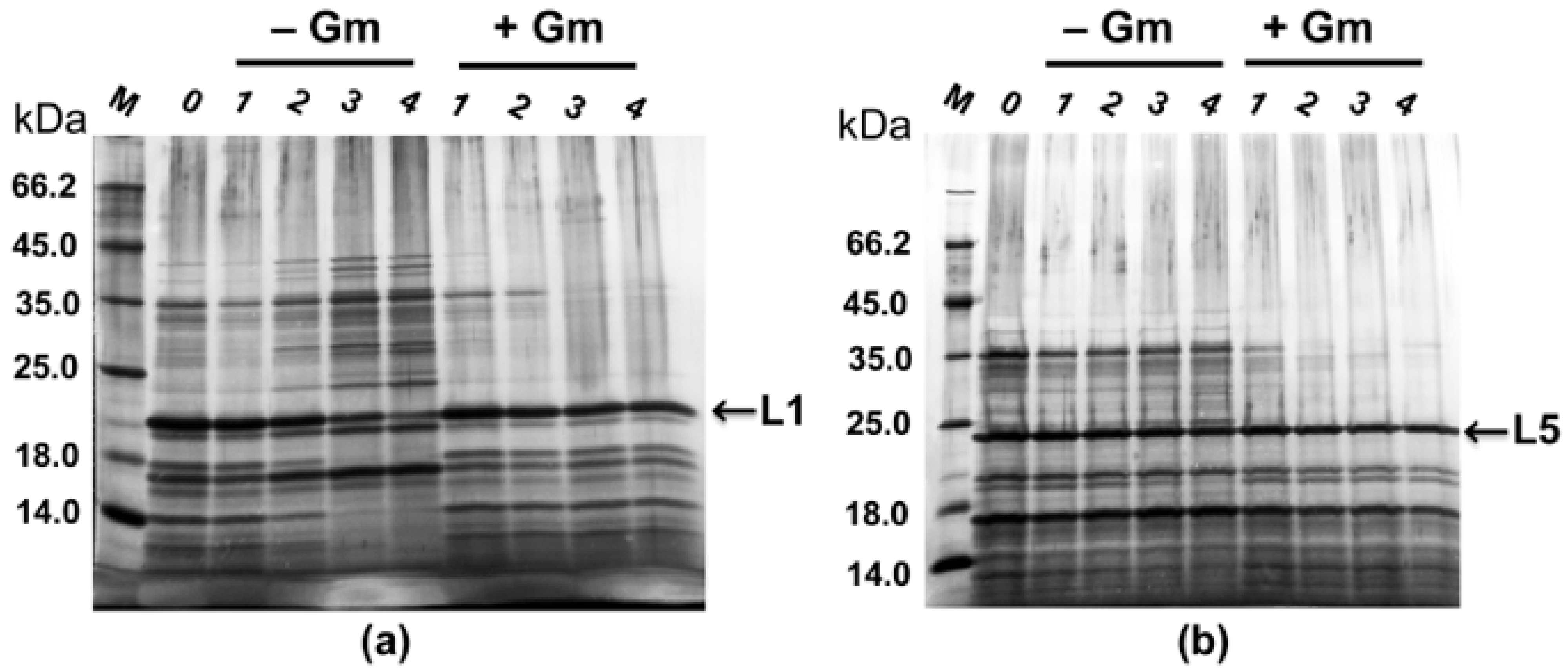
2.4. Maintenance of Recombinant Plasmids by Expression Strains PT5–alpA and PT5–alpB
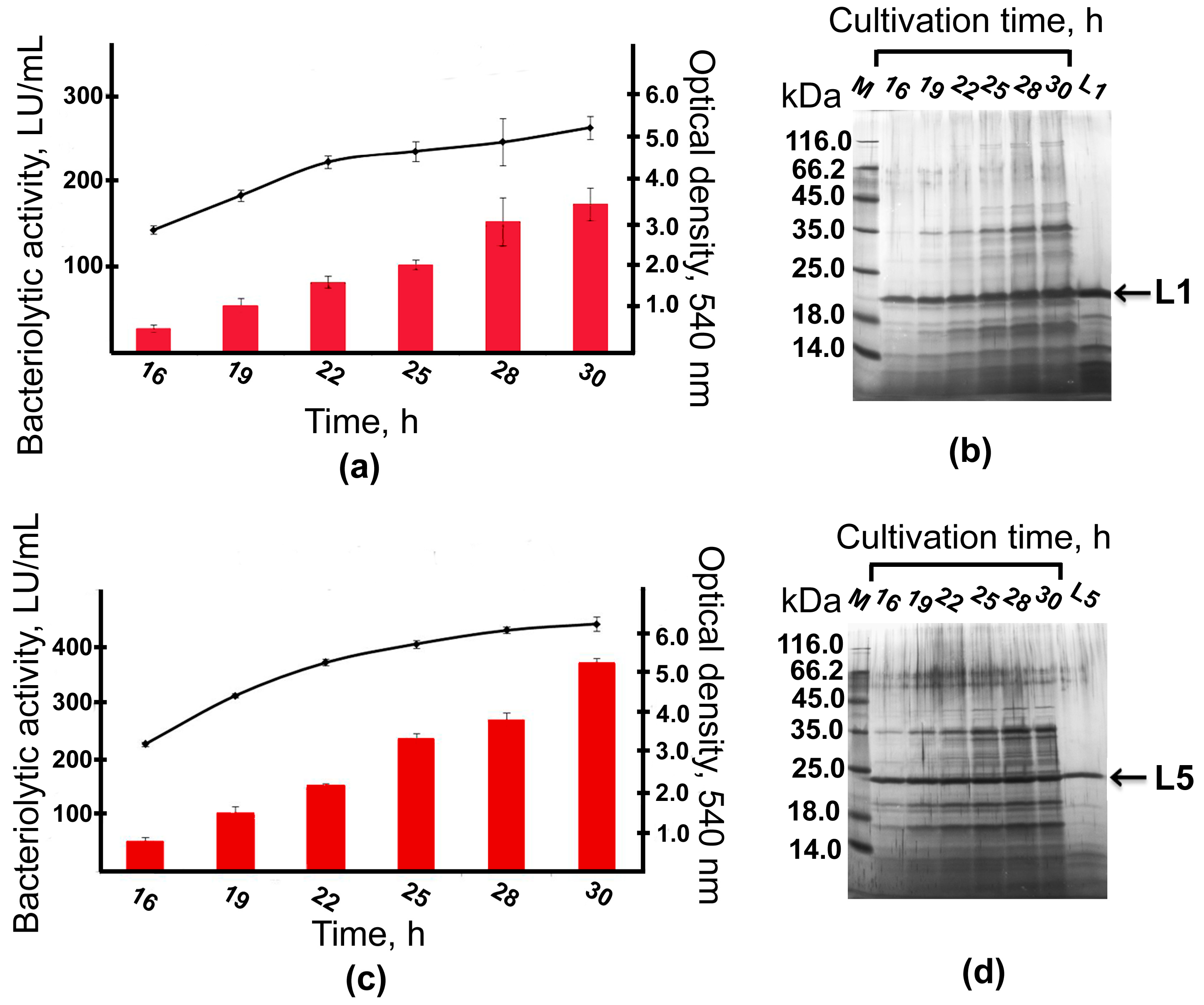
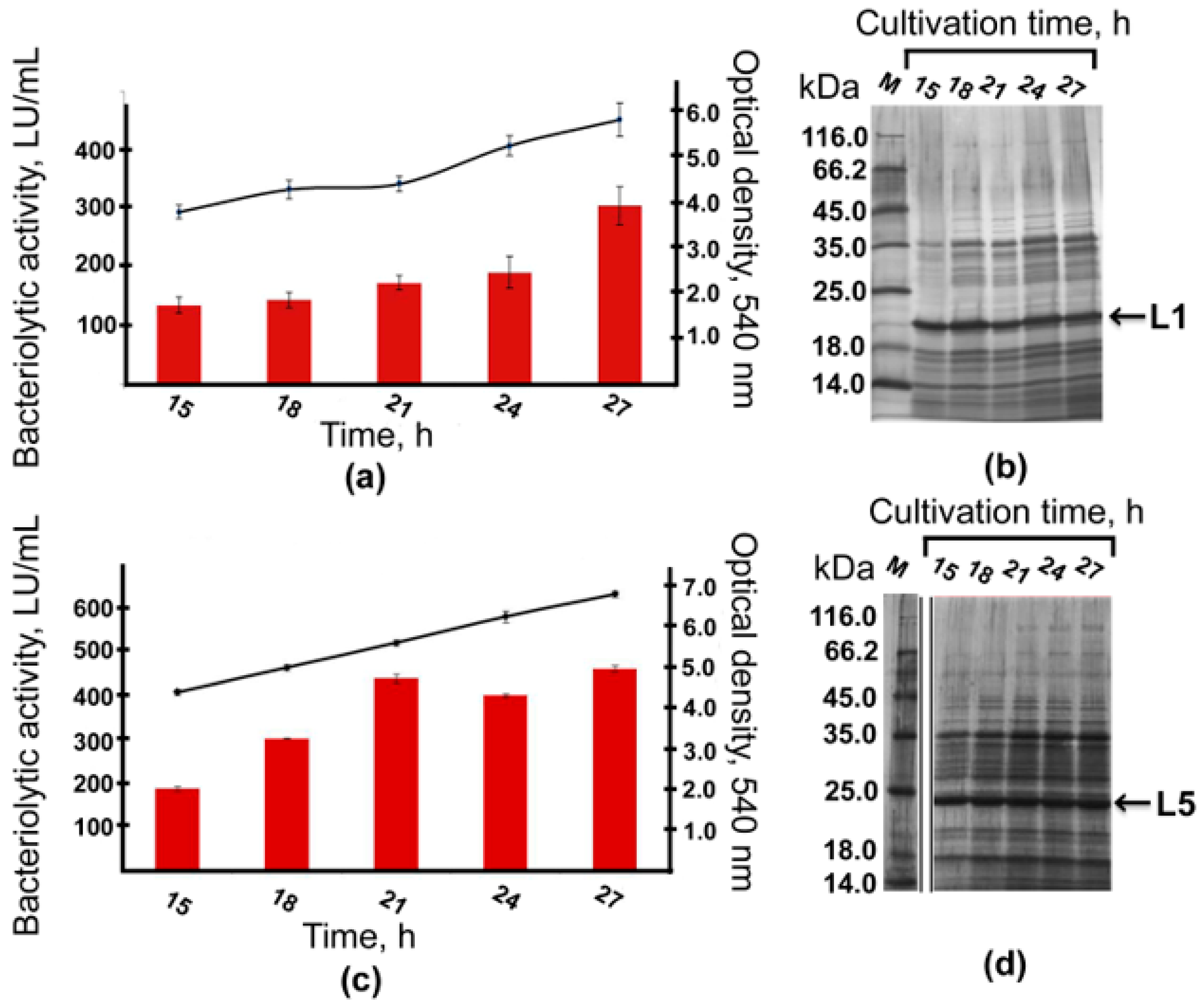
2.5. Bioreactor Cultivation
3. Discussion
| Enzyme/Producing Strain | Expression Strain | Yield of Protein, mg/L | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-Lytic protease/ Lysobacter enzymogenes | Escherichia coli DG98 | 6.0 | [9] |
| E. coli TG1, JM109 | 77.0 | [10] | |
| Bacillus subtilis DB104 | 14.0 | [11] | |
| Lysostaphin/ Staphylococcus simulans biovar staphylolyticus | E. coli TOP10 | 200.0 | [18] |
| E. coli BL21 | 55.0–70.0 | [19] | |
| Brevibacillus choshinensis | 90.0 | [20] | |
| B. subtilis DSM402, Lactobacillus casei 102S | Not detected | [21] | |
| Pichia pastoris GS115 | 250.0 | [22] | |
| Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris NZ3900 | 300.0 | [23] | |
| Staphylolysin/ Pseudomonas aeruginosa | E. coli JM109, P. aeruginosa FRD2128 | Not detected | [12] |
| Enterolysin A/ Enterococcus faecalis II/1 | E. coli SG13009 | 20.0 | [24] |
| Zoocin A/ Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus 4881 | E. coli M15 | 30.0 | [25] |
| Pseudoalterin /Pseudoalteromonas sp. CF6-2 | Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM20429 | 1.2 | [13] |
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Plasmids, and Cultivation Conditions
| Plasmids | Characteristics | Refs |
|---|---|---|
| Plasmids | ||
| pJQ200SK | Suicide vector with the sacB gene, GmR | [30] |
| pBR322 | Origin of TcR | [31] |
| pJQ200SKΔ3′alpA | pJQ200SK with the 5′ fragment of the alpA gene and the adjacent upstream region (951 bp) | This work |
| pJQ200SKΔalpA | pJQ200SK with deletion in the alpA gene (1134 bp) | This work |
| pJQ200SKΔalpA::tet | pJQ200SK with deletion in the alpA gene, marked by the TcR gene cassette | This work |
| pBBR1-MCS5 PT5–gfp | pBBR1-MCS5 with the gfp gene under control of bacteriophage T5 promoter | [16] |
| pBBR1-MCS5 PT5–alpB | pBBR1-MCS5 with the alpB gene under control of bacteriophage T5 promoter | This work |
| pBBR1-MCS5 PT5–alpA | pBBR1-MCS5 with the alpA gene under control of bacteriophage T5 promoter | This work |
| Strains | ||
| L. capsici XL1 | Wild-type | [32] |
| L. capsici XL1ΔalpA | Strain L. capsici XL1 with deletion in the alpA gene (1134 bp) and replacement of the corresponding segment by the TcR gene cassette | This work |
| L. capsici XL1ΔalpB | Strain L. capsici XL1 with deletion in the alpB gene (880 bp) and replacement of the corresponding segment by the TcR gene cassette | [17] |
| L. capsici PT5–alpB | Strain L. capsici XL1ΔalpB containing the plasmid pBBR1-MCS5 PT5–alpB | This work |
| L. capsici PT5–alpA | Strain L. capsici XL1ΔalpA containing the plasmid pBBR1-MCS5 PT5–alpA | This work |
| Escherichia coli XL1–Blue | recA1 endA1 gyrA96 thi hsdR17 supE44 relA1 lac/[F’::Tn10 proAB + lacIq lacZDM15 traD36] | [33] |
4.2. Molecular–Genetic Manipulations
| Oligonucleotides | Sequence | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| L5_BamHI (for) | GGATCCATGTCCGTATCGAAGTCGAATCTGC | To amplify the alpB gene (1200 bp) with DNA of L. capsici XL1 |
| L5_HindIII (rev) | AAGCTTTCAACTCGTGACCAGGGCC | |
| L1_BamHI (for) | GGATCCATGTCCGTATCGAAGTCCAATGCG | To amplify the alpA gene (1197 bp) with DNA of L. capsici XL1 |
| L1_HindIII (rev) | AAGCTTTCACGAGGTGACCAGGCTCAG | |
| T5_KpnI (for) | GGTACCGTGCCACCTGACGTCTAAG | To confirm the absence of mutations and the correct assembly of constructs |
| T5_XbaI (rev) | TCTAGACTGAAAATCTCGCCAAGCTAGC | |
| up_F (SmaI) | CCCGGGACTTCGATACTGACATGCG | To amplify the 951 bp fragment (of the 5′ end of the alpA gene and its upstream region) with DNA of L. capsici XL1 |
| up_R (SacI) | GAGCTCGATTTCCGCCGCGATGG | |
| down_F (PstI) | CTGCAGCGCGGCTTCCTGG | To amplify the 848 bp fragment (of the 3′ end of the alpA gene and its downstream region) with DNA of L. capsici XL1 |
| down_R (SmaI) | CCCGGGCCGATCCTGAGCC | |
| Tc (for) | GAATTCTCATGTTTGACAGCTTATCATCGA | To amplify the 1433 bp fragment of the Tc cassette from the plasmid pBR322 |
| Tc (rev) | CCCGAGATGCGCCG | |
| check_F | CTCGATAAAGGCCACATC | To amplify the 2056 bp fragment from the plasmid pJQ200SKΔalpA::tet and clones with deletion in the alpA geneAmplification of a 1756 bp fragment with DNA of L. capsici XL1 |
| check_R | ACGGTTCATGTCCTTATG |
4.3. Purification of Bacteriolytic Proteases L1 and L5
4.4. Measurement of Bacteriolytic Activity by Turbidimetric Method
4.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
4.6. Protein Concentration Assay
4.7. Fermentation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fleming, A. On a remarkable bacteriolytic element found in tissues and secretions. Proc. R. Soc. 1922, 93, 306–317. [Google Scholar]
- Afoshin, A.S.; Kudryakova, I.V.; Borovikova, A.O.; Suzina, N.E.; Toropygin, I.Y.; Shishkova, N.A.; Vasilyeva, N.V. Lytic potential of Lysobacter capsici VKM B-2533T: Bacteriolytic enzymes and outer membrane vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afoshin, A.; Kudryakova, I.; Tarlachkov, S.; Leontyevskaya, E.; Zelenov, D.; Rudenko, P.; Leontyevskaya (Vasilyeva), N. Transcriptomic analysis followed by the isolation of extracellular bacteriolytic proteases from Lysobacter capsici VKM B-2533T. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J.; Thomas, P.D.; Huang, X.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database. Nucl. Acids Res. 2018, 46, D624–D632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tishchenko, S.; Gabdulkhakov, A.; Melnik, B.; Kudryakova, I.; Latypov, O.; Vasilyeva, N.; Leontievsky, A. Structural studies of component of lysoamidase bacteriolytic complex from Lysobacter sp. XL1. Protein J. 2016, 35, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryakova, I.V.; Gabdulkhakov, A.G.; Tishchenko, S.V.; Lysanskaya, V.Y.; Suzina, N.E.; Tsfasman, I.M.; Afoshin, A.S.; Vasilyeva, N.V. Structural and functional properties of antimicrobial protein L5 of Lysobacter sp. XL1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 10043–10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepnaya, O.A.; Begunova, E.A.; Tsfasman, I.M.; Kulaev, I.S. Bacteriolytic enzyme preparation lysoamidase. Purification and some properties of bacteriolytic peptidase L1. Biokhimiya 1996, 61, 656–663. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vasilyeva, N.V.; Shishkova, N.A.; Marinin, L.I.; Ledova, L.A.; Tsfasman, I.M.; Muranova, T.A.; Stepnaya, O.A.; Kulaev, I.S. Lytic peptidase L5 of Lysobacter sp. XL1 with broad antimicrobial spectrum. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silen, J.L.; Frank, D.; Fujishige, A.; Bone, R.; Agard, D.A. Analysis of prepro-alpha-lytic protease expression in Escherichia coli reveals that the pro region is required for activity. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggett, K.D.; Graham, L.D.; Wright, D.S.; Whittaker, R.G. Over-expression of α-lytic protease and its mutants by recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Lett. 1994, 16, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambot, S.B.; Russell, A.J. Expression of α-lytic protease in Bacillus subtilis. Biocatalysis 1994, 11, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, J.K.; Kessler, E.; Ohman, D.E. A substitution at His-120 in the LasA protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa blocks enzymatic activity without affecting propeptide processing or extracellular secretion. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 6608–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.C.; Tang, B.L.; Zhao, D.L.; Pang, X.; Qin, Q.L.; Zhou, B.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Z. Development of a cold-adapted Pseudoalteromonas expression system for the Pseudoalteromonas proteins intractable for the Escherichia coli system. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovsky, I.E.; Kalinin, A.E.; Lapteva, Y.S.; Latypov, O.R.; Vasilyeva, N.V.; Tsfasman, I.M.; Stepnaya, O.A.; Kulaev, I.S.; Muranova, T.A.; Krasovskaya, L.A. Alpa lytic protease of Lysobacter sp. XL1 bacteria, DNA fragment coding Alpa lytic protease of Lysobacter sp. XL1 bacteria, and method of obtaining AlpA lytic protease of Lysobacter sp. XL1 bacteria. RF Patent No 2407782, 27 December 2010. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Granovsky, I.E.; Kalinin, A.E.; Lapteva, Y.S.; Latypov, O.R.; Vasilyeva, N.V.; Tsfasman, I.M.; Stepnaya, O.A.; Kulaev, I.S.; Muranova, T.A.; Krasovskaya, L.A. Lytic protease AlpB of bacterium Lysobacter sp. XL1, DNA fragment, coding lytic protease AlpB of bacterium Lysobacter sp. XL1, and method for production of lytic protease AlpB of bacterium Lysobacter sp. XL1. RF Patent No 2408725, 10 January 2011. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Kudryakova, I.; Afoshin, A.; Leontyevskaya, E.; Leontyevskaya (Vasilyeva), N. The first homologous expression system for the β-lytic protease of Lysobacter capsici VKM B-2533T, a promising antimicrobial agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryakova, I.V.; Afoshin, A.S.; Ivashina, T.V.; Suzina, N.E.; Leontyevskaya, E.A.; Leontyevskaya (Vasilyeva), N.V. Deletion of alpB gene influences outer membrane vesicles biogenesis of Lysobacter sp. XL1. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 715802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, Z.E.; Ünlü, A.; Çakar, M.M.; Ünal, H.; Binay, B. Enhanced production of recombinant Staphylococcus simulans lysostaphin using medium engineering. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boksha, I.S.; Lavrova, N.V.; Grishin, A.V.; Demidenko, A.V.; Lyashchuk, A.M.; Galushkina, Z.M.; Ovchinnikov, R.S.; Umyarov, A.M.; Avetisian, L.R.; Chernukha, M.I.; et al. Staphylococcus simulans recombinant lysostaphin: Production, purification, and determination of antistaphylococcal activity. Biochemistry 2016, 81, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfertsev, E.A.; Baranova, E.V.; Levchuk, V.V.; Reshetnyak, T.V.; Soloviev, P.V.; Shishkova, N.A.; Fedorov, T.V.; Voloshin, A.G.; Biketov, S.F. Obtaining and purification of lysostaphin secreted in the culture liquid by Brevibacillus choshinensis/pNCMO2/lsf12 recombinant strain. Biotechnology 2020, 36, 7–15. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gaier, W.; Vogel, R.F.; Hammes, W.P. Cloning and expression of the lysostaphin gene in Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus casei. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1992, 14, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Blazanovic, K.; Choi, Y.; Bailey-Kellogg, C.; Griswold, K.E. Gene and protein sequence optimization for high-level production of fully active and aglycosylated lysostaphin in Pichia pastoris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2746–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierau, I.; Olieman, K.; Mond, J.; Smid, E.J. Optimization of the Lactococcus lactis nisin-controlled gene expression system NICE for industrial applications. Microb. Cell Fact. 2005, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigutová, K.; Serencová, L.; Piknová, M.; Javorský, P.; Pristas, P. Heterologous expression of functionally active enterolysin A, class III bacteriocin from Enterococcus faecalis, in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 60, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, A.C.; Tran, S.; Simmonds, R.S. Functional characterization of domains found within a lytic enzyme produced by Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 215, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsfasman, I.M.; Lapteva, Y.S.; Krasovskaya, L.A.; Kudryakova, I.V.; Vasilyeva, N.V.; Granovsky, I.E.; Stepnaya, O.A. Gene expression of lytic endopeptidases AlpA and AlpB from Lysobacter sp. XL1 in Pseudomonads. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Qian, G.; Liu, F. LetR is a TetR family transcription factor from Lysobacter controlling antifungal antibiotic biosynthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3273–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, T.; Li, H.; Yu, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.H. A novel heterologous expression strategy for the quorum-quenching enzyme MomL in Lysobacter enzymogenes to the inhibit pathogenicity of Pectobacterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8889–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Su, W.; Fey, P.D.; Liu, F.; Du, L. Yield improvement of the anti-MRSA antibiotics WAP-8294A by CRISPR/dCas9 combined with refactoring self-protection genes in Lysobacter enzymogenes OH11. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quandt, J.; Hynes, M.F. Versatile suicide vectors which allow direct selection for gene replacement in gram-negative bacteria. Gene 1993, 127, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbás, P.; Soberón, X.; Merino, E.; Zurita, M.; Lomeli, H.; Valle, F.; Flores, N.; Bolivar, F. Plasmid vector pBR322 and its special-purpose derivatives—A review. Gene 1986, 50, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaev, I.S.; Stepnaya, O.A.; Tsfasman, I.M.; Tchermenskaja, T.S.; Ledova, L.A.; Zubrizkaja, L.G.; Akimenko, V.K. Bacteriolytic complex, method for producing said complex and strain for carrying out said method. RF Patent No 2193063, 20 December 2002. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, W.O.; Fernandez, J.M.; Short, J.M. XL1-Blue: A high efficiency plasmid transforming recA Escherichia coli strain with β-galactosidase selection. BioTechniques 1987, 5, 376–378. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J. Mol. Biol. 1983, 166, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; McBride, M.J. Development of techniques for the genetic manipulation of the gliding bacteria Lysobacter enzymogenes and Lysobacter brunescens. Can. J. Microbiol. 1996, 42, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Patron, C.; Castellanos-Serra, L.; Rodriguez, P. Reverse staining of sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels by imidazole-zinc salts: Sensitive detection of unmodified proteins. Biotechniques 1992, 12, 564–573. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kudryakova, I.; Afoshin, A.; Leontyevskaya, E.; Leontyevskaya, N. Development of Efficient Expression Systems for Bacteriolytic Proteases L1 and L5 of Lysobacter capsici XL1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136056
Kudryakova I, Afoshin A, Leontyevskaya E, Leontyevskaya N. Development of Efficient Expression Systems for Bacteriolytic Proteases L1 and L5 of Lysobacter capsici XL1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136056
Chicago/Turabian StyleKudryakova, Irina, Alexey Afoshin, Elena Leontyevskaya, and Natalia Leontyevskaya. 2025. "Development of Efficient Expression Systems for Bacteriolytic Proteases L1 and L5 of Lysobacter capsici XL1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136056
APA StyleKudryakova, I., Afoshin, A., Leontyevskaya, E., & Leontyevskaya, N. (2025). Development of Efficient Expression Systems for Bacteriolytic Proteases L1 and L5 of Lysobacter capsici XL1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136056






