Autophagy Differentially Influences Toll-like Receptor 9 and B Cell-Receptor-Mediated B Cell Expansion, Expression of Major Histocompatibility Class II Proteins, and Antigenic Peptide Presentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
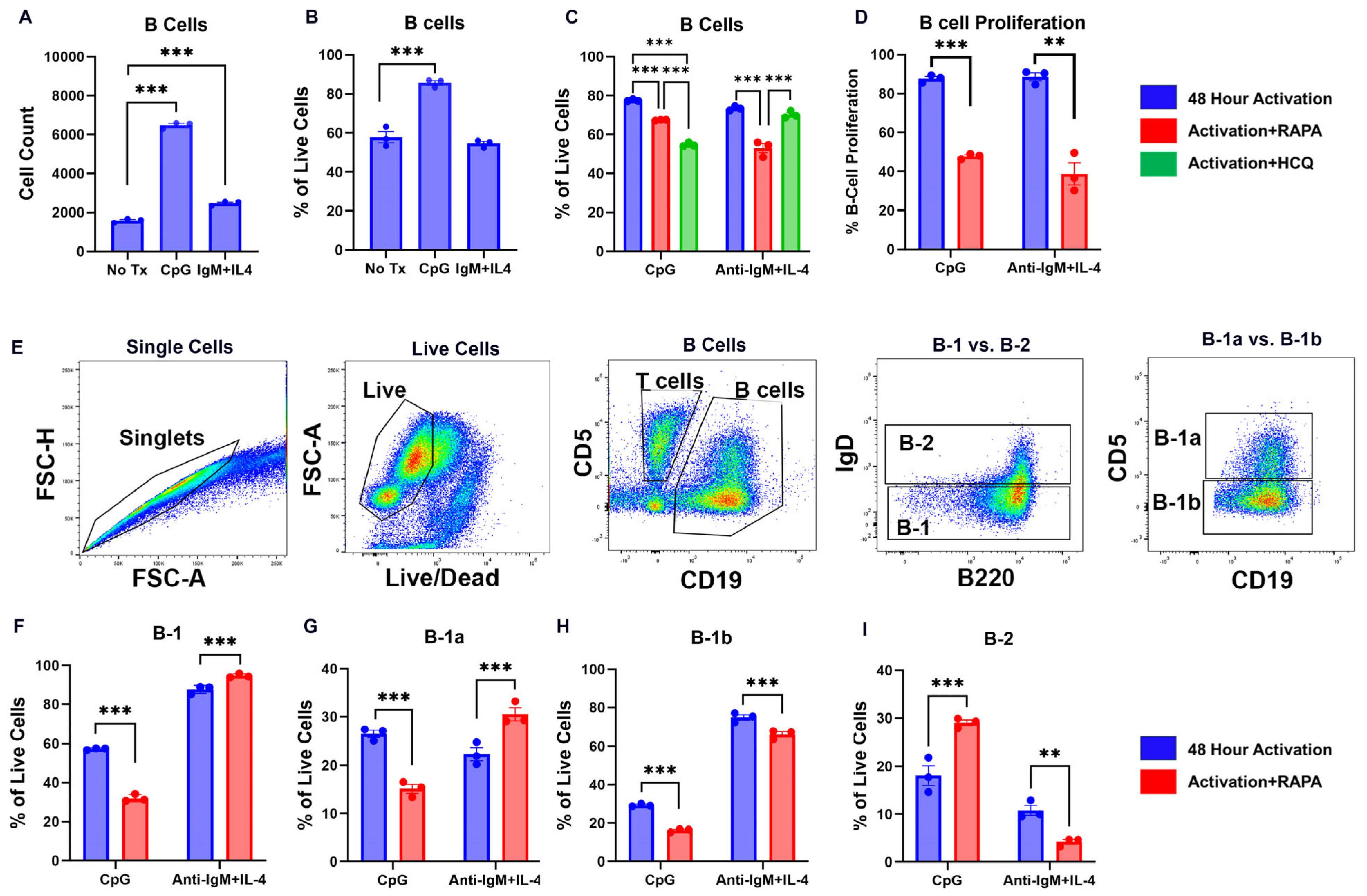
2.1. TLR9 and BCR Activation Drive Opposing B Cell Subsets
2.2. TLR9 and BCR Activation Induce MHC-II and CLIP Expression on B Cells That Are Modified by RAPA and HCQ
2.3. RAPA and HCQ Regulate the Relationship Between CLIP and MHC-II on B Cells
2.4. RAPA and HCQ Regulate Loading of Antigenic Peptide on Activated B Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Mice
3.3. Splenocyte Isolation
3.4. Peritoneal Cavity Lymphocyte Isolation
3.5. Splenocyte Activation and Treatment
3.6. Cell-Surface Staining and Flow Cytometry
3.7. Proliferation Assay
3.8. Competitive Binding Studies
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCR | B cell receptor |
| CAP | CLIP antagonist peptide |
| CD74 | Invariant chain |
| CLIP | Class II-associated invariant peptide |
| CpG | Cytidine monophosphate guanosine oligodeoxynucleotides |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| HCQ | Hydroxychloroquine |
| MHC-II | Major histocompatibility complex II |
| MFI | Mean fluorescent intensity |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
References
- Lee, D.S.W.; Rojas, O.L.; Gommerman, J.L. B cell depletion therapies in autoimmune disease: Advances and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Levine, B. Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.C.; Zhao, Z.; Stephenson, L.M.; Cadwell, K.; Pua, H.H.; Lee, H.K.; Mizushima, N.N.; Iwasaki, A.; He, Y.W.; Swat, W.; et al. The autophagy gene ATG5 plays an essential role in B lymphocyte development. Autophagy 2008, 4, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Martin, N.; Maldonado, P.; Gasparrini, F.; Frederico, B.; Aggarwal, S.; Gaya, M.; Tsui, C.; Burbage, M.; Keppler, S.J.; Montaner, B.; et al. A switch from canonical to noncanonical autophagy shapes B cell responses. Science 2017, 355, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.J.; Riffelmacher, T.; Braas, D.; Cornall, R.J.; Simon, A.K. B1a B cells require autophagy for metabolic homeostasis and self-renewal. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Pruitt, M.; Tran, D.; Du Bois, W.; Zhang, K.; Patel, R.; Hoover, S.; Simpson, R.M.; Simmons, J.; Gary, J.; et al. B cell-specific deficiencies in mTOR limit humoral immune responses. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 1692–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Readinger, J.A.; Du Bois, W.; Janka-Junttila, M.; Robinson, R.; Pruitt, M.; Bliskovsky, V.; Wu, J.Z.; Sakakibara, K.; Patel, J.; et al. Constitutive reductions in mTOR alter cell size, immune cell development, and antibody production. Blood 2011, 117, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.; Murera, D.; Arbogast, F.; Fauny, J.D.; Muller, S.; Gros, F. Autophagy is dispensable for B-cell development but essential for humoral autoimmune responses. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shachar, I.; Flavell, R.A. Requirement for invariant chain in B cell maturation and function. Science 1996, 274, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matza, D.; Kerem, A.; Shachar, I. Invariant chain, a chain of command. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matza, D.; Lantner, F.; Bogoch, Y.; Flaishon, L.; Hershkoviz, R.; Shachar, I. Invariant chain induces B cell maturation in a process that is independent of its chaperonic activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3018–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengjel, J.; Schoor, O.; Fischer, R.; Reich, M.; Kraus, M.; Müller, M.; Kreymborg, K.; Altenberend, F.; Brandenburg, J.; Kalbacher, H.; et al. Autophagy promotes MHC class II presentation of peptides from intracellular source proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7922–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, K.L.; Kuballa, P.; Khor, B.; Zhang, M.; Shi, H.N.; Virgin, H.W.; Xavier, R.J. ATG5 regulates plasma cell differentiation. Autophagy 2013, 9, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Ichinose, S.; Hayashizaki, K.; Tsubata, T. Induction of autophagy by B cell antigen receptor stimulation and its inhibition by costimulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, I.G.A.; Clarke, A.J. B Cell Metabolism and Autophagy in Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 681105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, E.P. Regulation of B-cell responses by Toll-like receptors. Immunology 2012, 136, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Tsubata, T. Autophagy connects antigen receptor signaling to costimulatory signaling in B lymphocytes. Autophagy 2009, 5, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Hou, B. TLR signaling in B-cell development and activation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, E.; Schoenemeyer, A.; Visintin, A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Monks, B.G.; Knetter, C.F.; Lien, E.; Nilsen, N.J.; Espevik, T.; Golenbock, D.T. TLR9 signals after translocating from the ER to CpG DNA in the lysosome. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Nguyen, K.C.T.; Cho, K.A. The role of TLR9 in stress-dependent autophagy formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 481, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, S.; Samson, M.; Pons, C.; Guigonis, J.-M.; Gavelli, A.; Baqueé, P.; Brossette, N.; Pagnotta, S.; Ricci, J.-E.; Pierrefite-Carle, V. Comparative Proteomics Study Reveals that Bacterial CpG Motifs Induce Tumor Cell Autophagy in Vitro and in Vivo. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 2311–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, F.Z.; Zhan, Y.W.; Wang, R.; Mo, B.Y.; Lin, S.D. TLR9 regulates the autophagy-lysosome pathway to promote dendritic cell maturation and activation by activating the TRAF6-cGAS-STING pathway. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.A.; Elmaoued, R.A.; Davis, A.S.; Kyei, G.; Deretic, V. Toll-like receptors control autophagy. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henault, J.; Martinez, J.; Riggs, J.M.; Tian, J.; Mehta, P.; Clarke, L.; Sasai, M.; Latz, E.; Brinkmann, M.M.; Iwasaki, A.; et al. Noncanonical Autophagy is Required for Type I Interferon Secretion in Response to DNA-Immune Complexes. Immunity 2012, 37, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minton, K. LC3 anchors TLR9 signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, L.A. Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for inflammatory and infectious diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2003, 3, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbetter, E.A.; Rifkin, I.R.; Hohlbaum, A.M.; Beaudette, B.C.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Marshak-Rothstein, A. Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and Toll-like receptors. Nature 2002, 416, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, M.K.; Tobin, R.P.; Cabrera, J.H.; Sorensen, M.B.; Huckstep, A.; Villalobos-Menuey, E.M.; Burnett, M.; McCrea, E.; Harvey, C.P.; Buddiga, A.; et al. TLR-mediated B cell activation results in ectopic CLIP expression that promotes B cell-dependent inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, H.; Kodali, S.; Wang, J. Regulation of B cell fate, survival, and function by mitochondria and autophagy. Mitochondrion 2018, 41, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam-Puc, J.C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Toellner, K.M. Role of B-cell receptors for B-cell development and antigen-induced differentiation. F1000Research 2018, 7, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, H.; Yabas, M.; Short, A.; Miosge, L.; Barthel, N.; Teh, C.E.; Roots, C.M.; Bull, K.R.; Jeelall, Y.; Horikawa, K.; et al. B cell survival, surface BCR and BAFFR expression, CD74 metabolism, and CD8-dendritic cells require the intramembrane endopeptidase SPPL2A. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesnut, R.W.; Grey, H.M. Studies on the capacity of B cells to serve as antigen-presenting cells. J. Immunol. 1981, 126, 1075–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phee, H.; Rodgers, W.; Coggeshall, K.M. Visualization of negative signaling in B cells by quantitative confocal microscopy. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 8615–8625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth Control and Disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, J.; Ito, Y.; Iwata, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kawano, Y.; Kanazawa, T.; Siddiquey, M.N.; Kimura, H. mTOR inhibitors induce cell-cycle arrest and inhibit tumor growth in Epstein-Barr virus-associated T and natural killer cell lymphoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5412–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingar, D.C.; Richardson, C.J.; Tee, A.R.; Cheatham, L.; Tsou, C.; Blenis, J. mTOR controls cell cycle progression through its cell growth effectors S6K1 and 4E-BP1/eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Hardy, R.R.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Herzenberg, L.A. Progenitors for Ly-1 B cells are distinct from progenitors for other B cells. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 161, 1554–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgarth, N. The double life of a B-1 cell: Self-reactivity selects for protective effector functions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raybuck, A.L.; Cho, S.H.; Li, J.; Rogers, M.C.; Lee, K.; Williams, C.L.; Shlomchik, M.; Thomas, J.W.; Chen, J.; Williams, J.V.; et al. B Cell-Intrinsic mTORC1 Promotes Germinal Center-Defining Transcription Factor Gene Expression, Somatic Hypermutation, and Memory B Cell Generation in Humoral Immunity. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2627–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersching, J.; Efeyan, A.; Mesin, L.; Jacobsen, J.T.; Pasqual, G.; Grabiner, B.C.; Dominguez-Sola, D.; Sabatini, D.M.; Victora, G.D. Germinal Center Selection and Affinity Maturation Require Dynamic Regulation of mTORC1 Kinase. Immunity 2017, 46, 1045–1058.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, B. The multifaceted roles of the invariant chain CD74–More than just a chaperone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, P.A.; Cresswell, P. Proteolysis of the class II-associated invariant chain generates a peptide binding site in intracellular HLA-DR molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 3150–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Hengeveld, R.; Zechel, M.A.; Lee-Chan, E.; Singh, B. The functional role of class II-associated invariant chain peptide (CLIP) in its ability to variably modulate immune responses. Int. Immunol. 2000, 12, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropshofer, H.; Vogt, A.B.; Hämmerling, G.J. Structural features of the invariant chain fragment CLIP controlling rapid release from HLA-DR molecules and inhibition of peptide binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8313–8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechel, M.A.; Chaturvedi, P.; Lee-Chan, E.C.; Rider, B.J.; Singh, B. Modulation of antigen presentation and class II expression by a class II-associated invariant chain peptide. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 4232–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Chiasson, V.L.; Seerangan, G.; De Guzman, E.; Milad, M.; Bounds, K.R.; Gasheva, O.; Tobin, R.P.; Hatahet, M.; Kopriva, S.; et al. Depletion of MHC class II invariant chain peptide or γ-δ T-cells ameliorates experimental preeclampsia. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2047–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirk, E.L.; Reggiori, F.; Mauthe, M. Hydroxychloroquine in rheumatic autoimmune disorders and beyond. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, M.; Sokolovska, A.; Tam, J.M.; Conway, K.L.; Stefani, C.; Raso, F.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Feliu, M.; Paul, E.; Savill, J.; et al. αv Integrins combine with LC3 and atg5 to regulate Toll-like receptor signalling in B cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peddaboina, C.; Iannucci, J.; Tobin, R.P.; Shapiro, L.A.; Newell Rogers, M.K. Autophagy Differentially Influences Toll-like Receptor 9 and B Cell-Receptor-Mediated B Cell Expansion, Expression of Major Histocompatibility Class II Proteins, and Antigenic Peptide Presentation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136054
Peddaboina C, Iannucci J, Tobin RP, Shapiro LA, Newell Rogers MK. Autophagy Differentially Influences Toll-like Receptor 9 and B Cell-Receptor-Mediated B Cell Expansion, Expression of Major Histocompatibility Class II Proteins, and Antigenic Peptide Presentation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136054
Chicago/Turabian StylePeddaboina, Chander, Jaclyn Iannucci, Richard P. Tobin, Lee A. Shapiro, and M. Karen Newell Rogers. 2025. "Autophagy Differentially Influences Toll-like Receptor 9 and B Cell-Receptor-Mediated B Cell Expansion, Expression of Major Histocompatibility Class II Proteins, and Antigenic Peptide Presentation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136054
APA StylePeddaboina, C., Iannucci, J., Tobin, R. P., Shapiro, L. A., & Newell Rogers, M. K. (2025). Autophagy Differentially Influences Toll-like Receptor 9 and B Cell-Receptor-Mediated B Cell Expansion, Expression of Major Histocompatibility Class II Proteins, and Antigenic Peptide Presentation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136054




