Phenolic Profiling and Bioactive Properties of Arthrospira platensis Extract in Alleviating Acute and Sub-Chronic Colitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
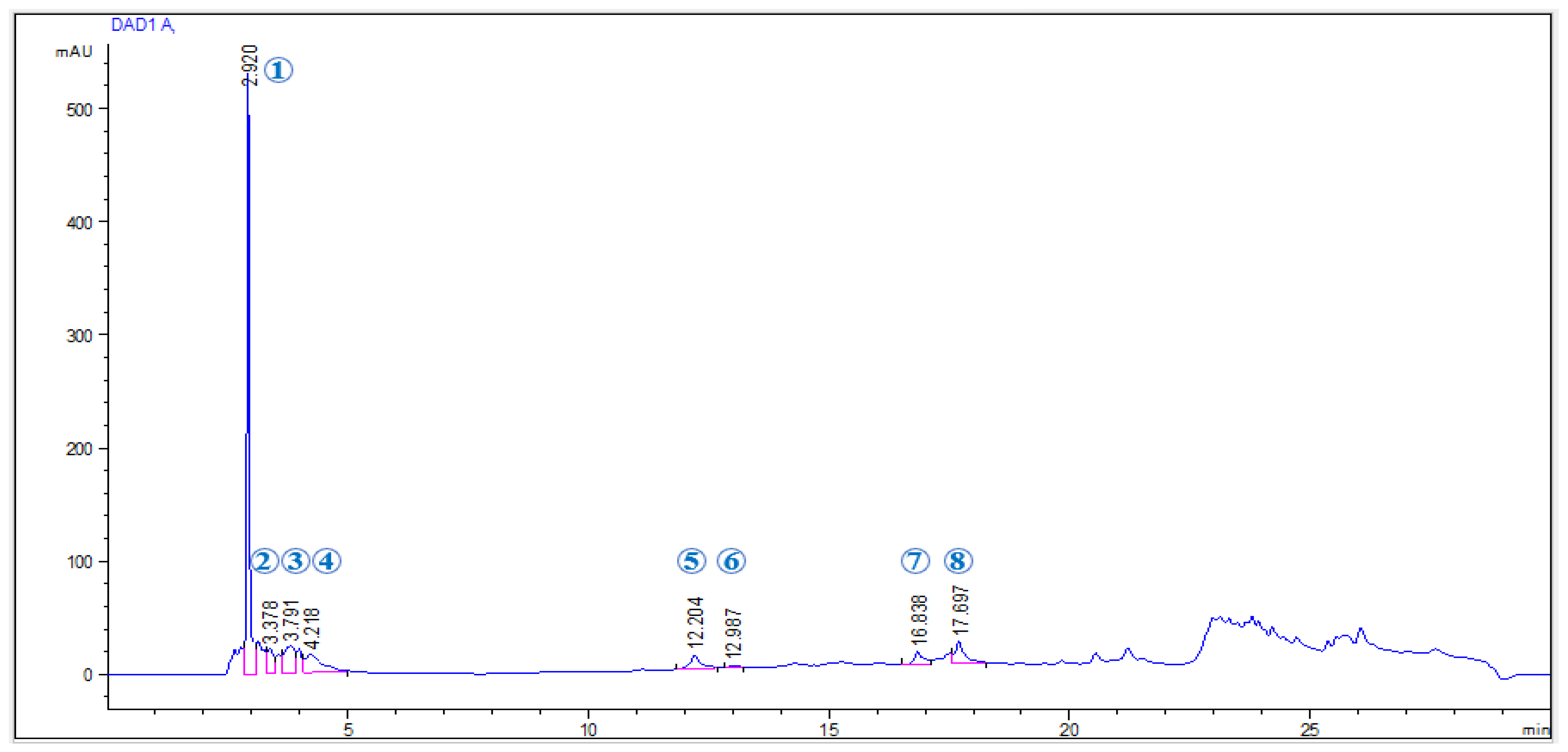
2.1. Phenolic Profile of EAP Extract
2.2. Effect of EAP on Acute Colitis
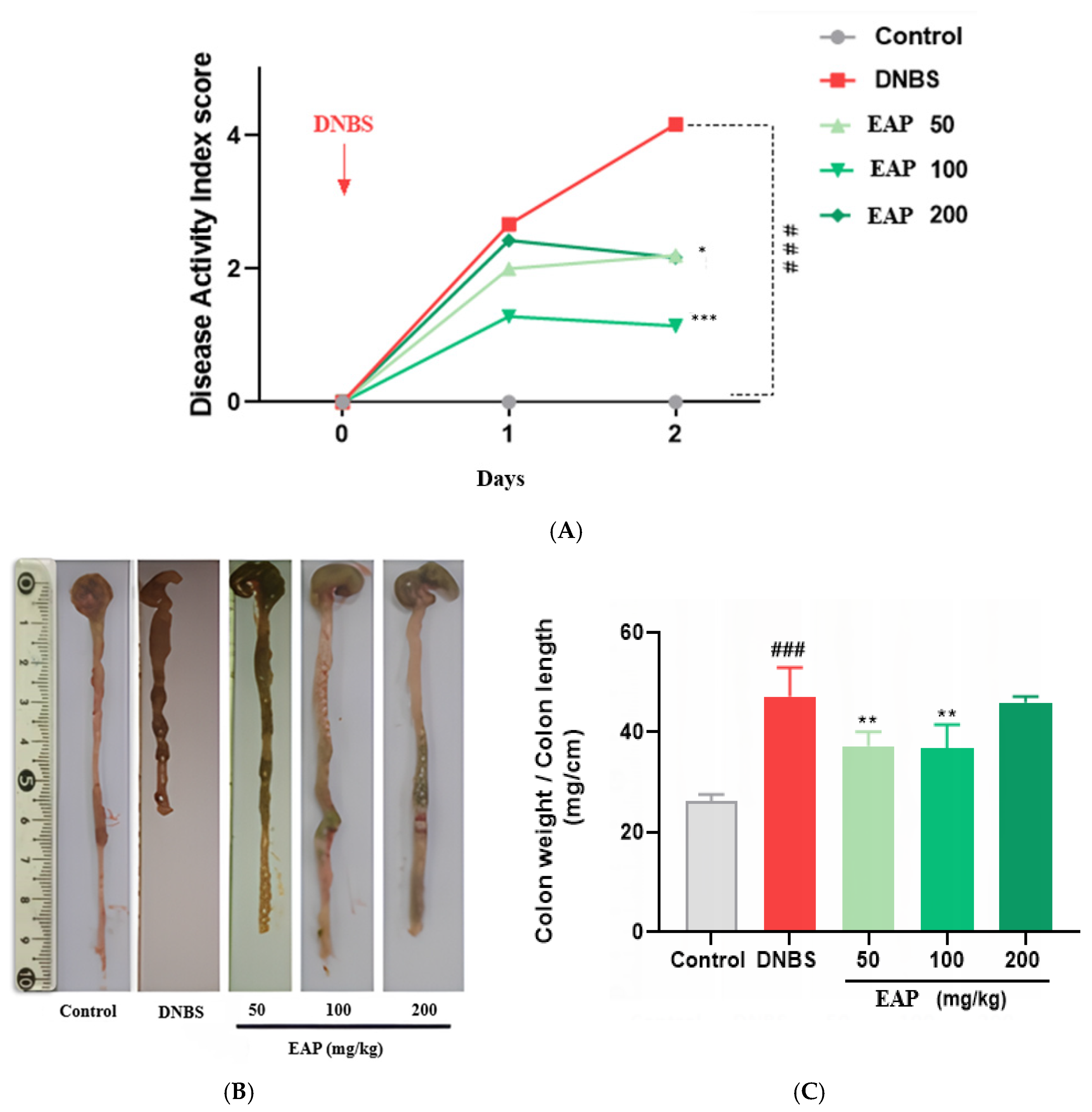
2.2.1. Clinical and Morphological Parameters
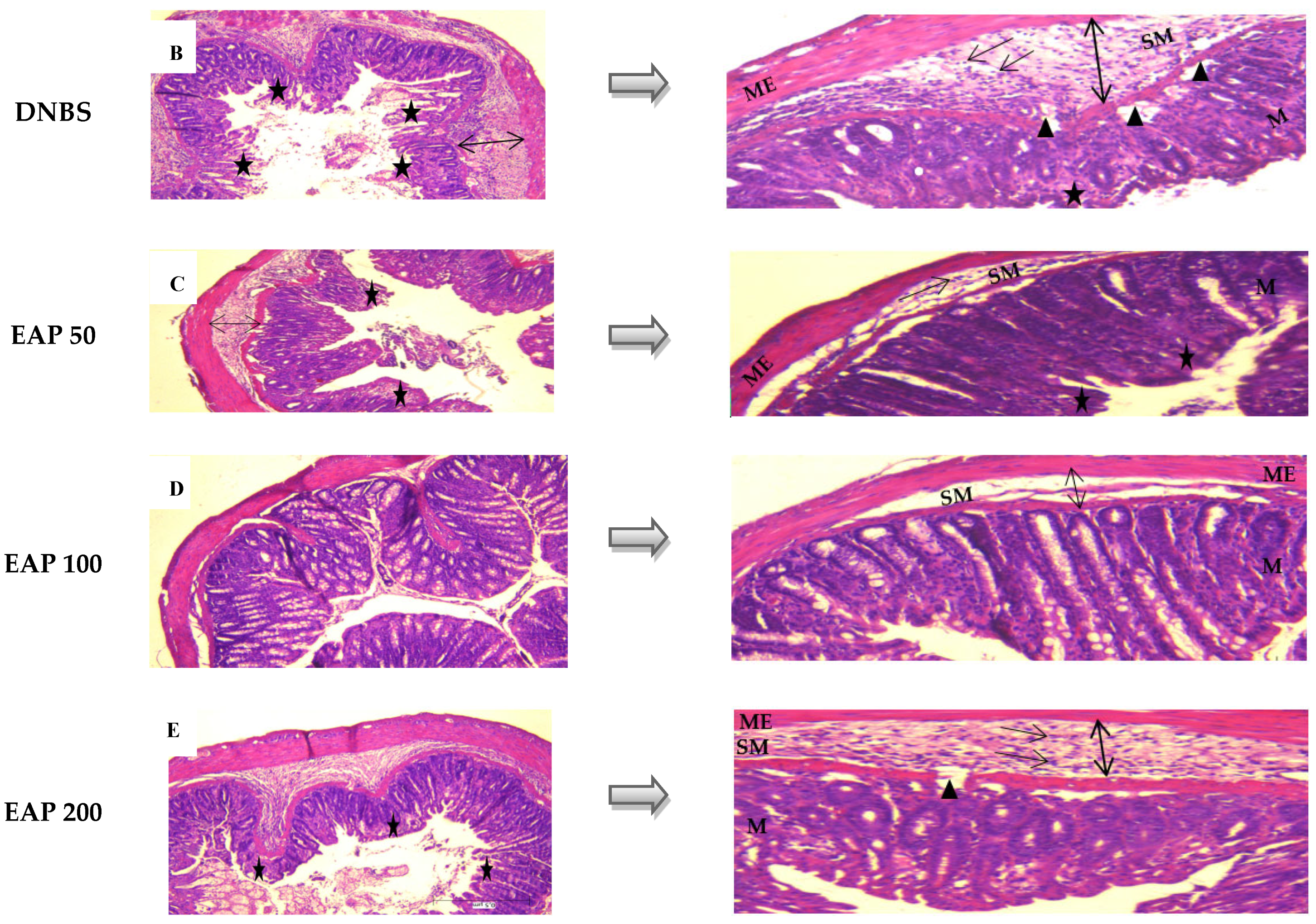
2.2.2. Histological Evaluation
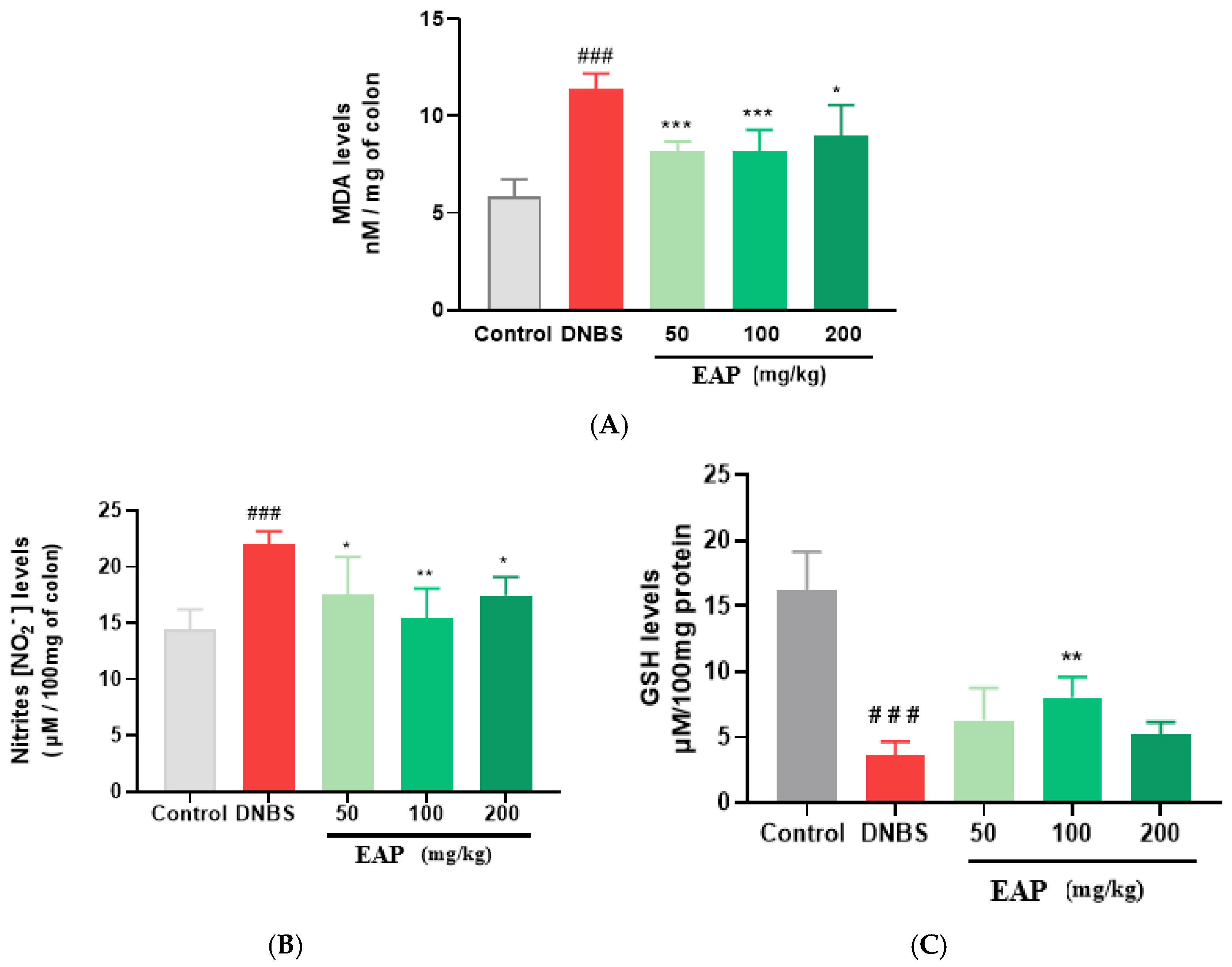
2.2.3. Biochemical Markers
2.3. Effect of EAP on Sub-Chronic Colitis
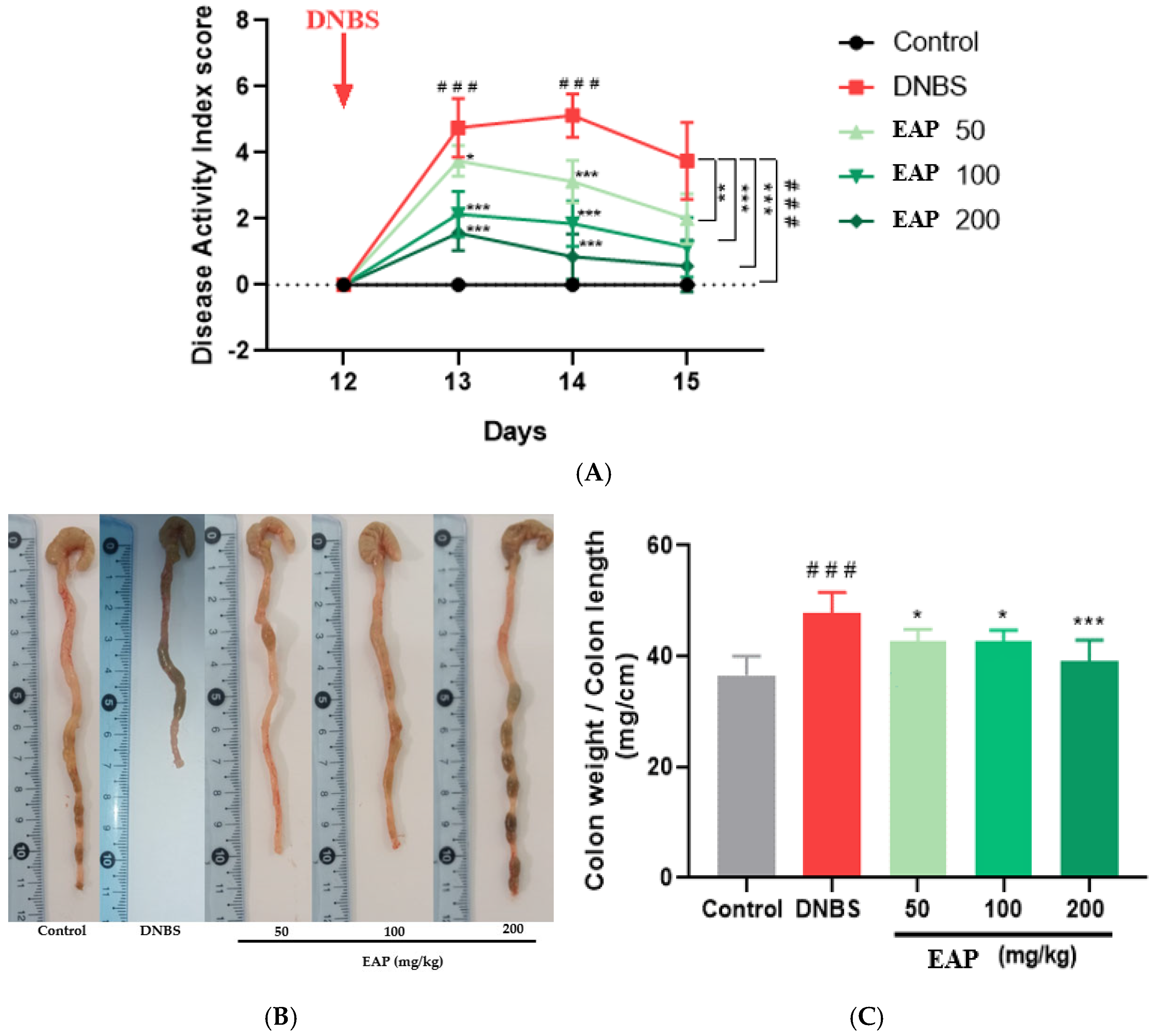
2.3.1. Clinical and Morphological Parameters
2.3.2. Histological Evaluation
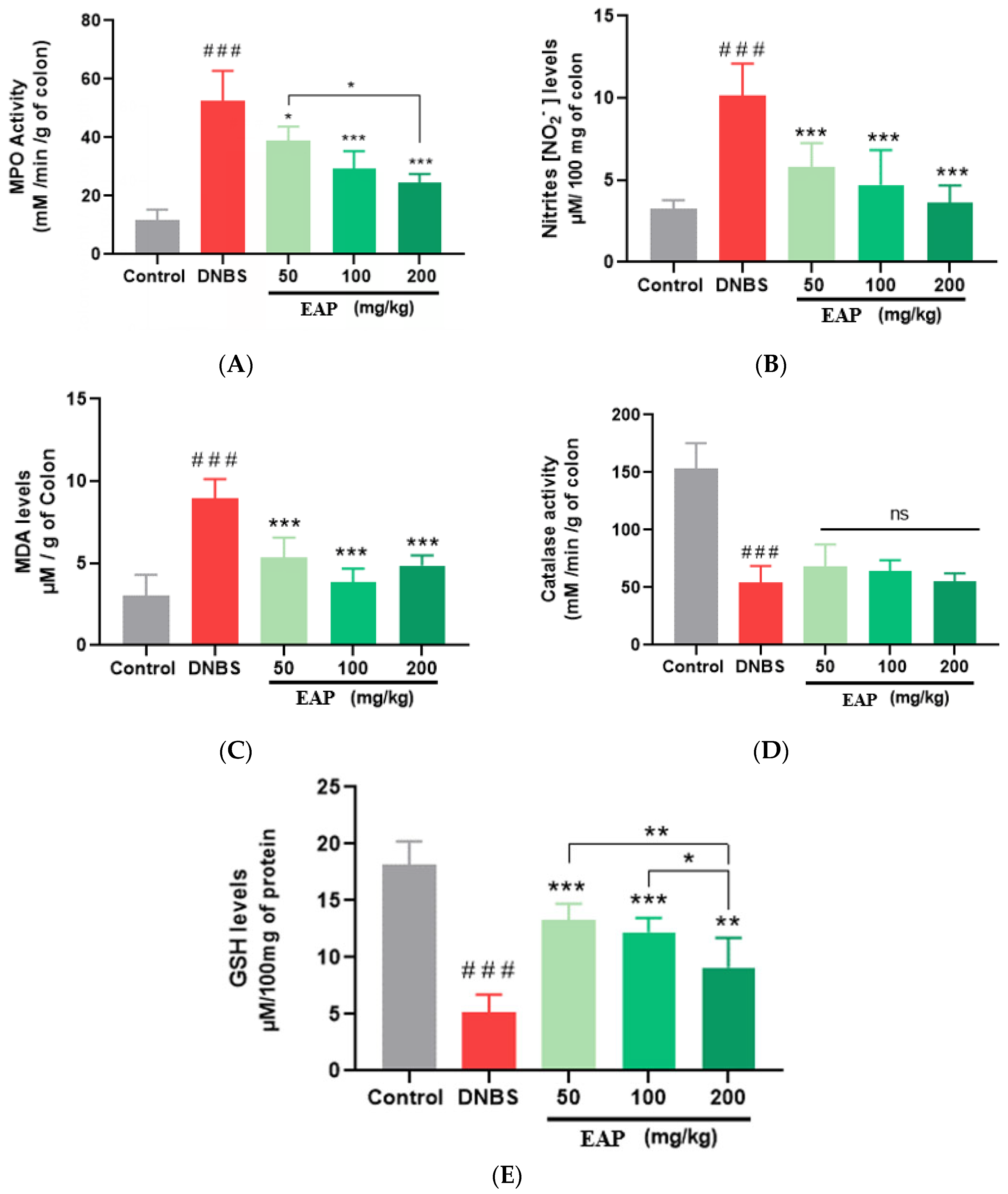
2.3.3. Biochemical Markers
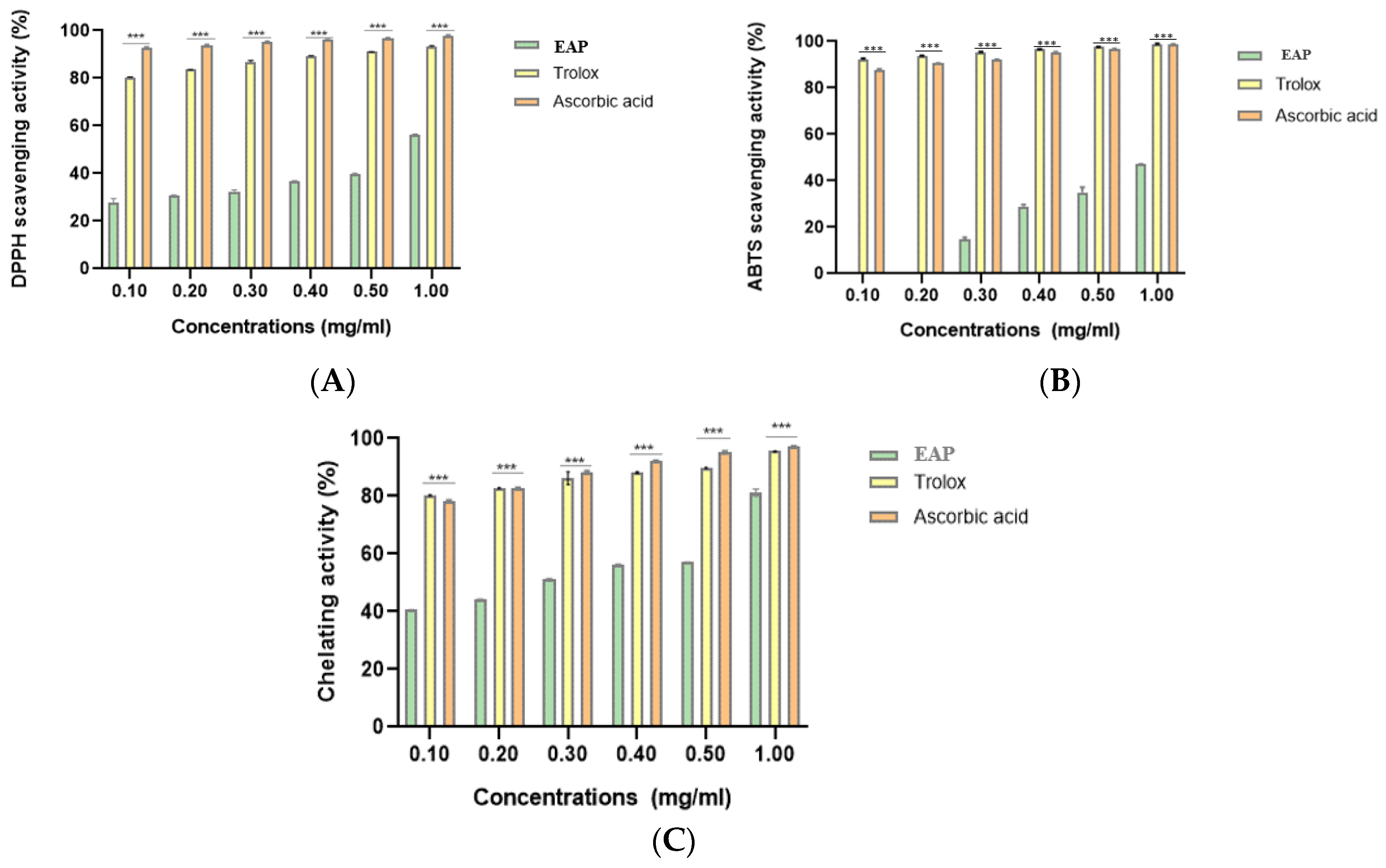
2.4. Antioxidant Activities
2.5. Antifungal Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Material and Reagents
4.2. Ethanolic Extraction Process
4.3. Phenolic Profiling of EAP Extract Using HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS
4.4. Animals and Grouping
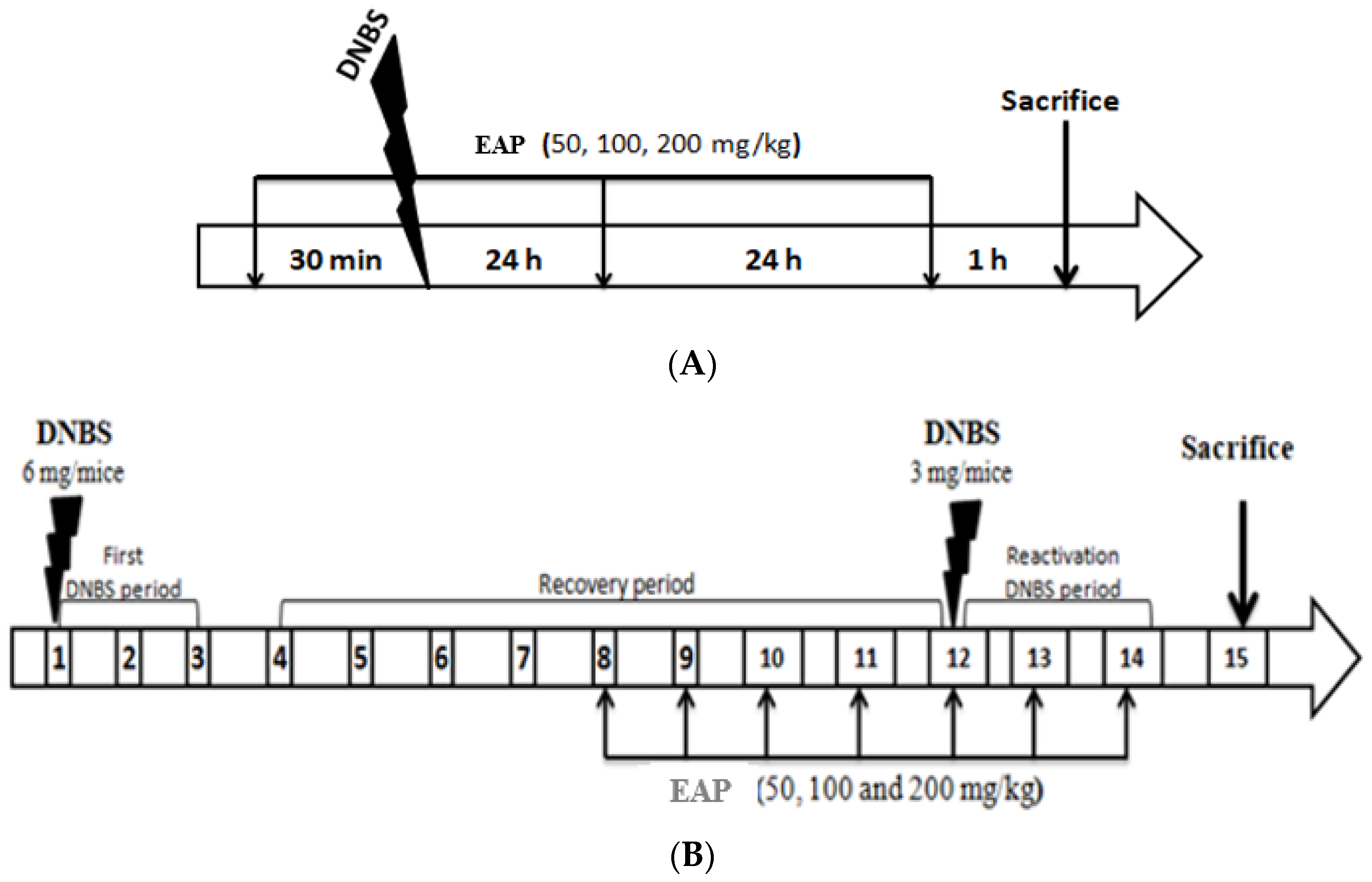
4.4.1. Induction of Acute Colitis
4.4.2. Induction of Sub-Chronic Colitis
4.5. Colitis Severity Scoring and Histopathological Assessment
4.6. Evaluation of Biochemical Parameters
4.6.1. Myeloperoxidase Activity
4.6.2. Nitric Oxide Level
4.6.3. Malondialdehyde Level
4.6.4. Catalase Activity
4.6.5. GSH Level
4.7. In Vitro Antioxidant Activities
4.7.1. DPPH Scavenging Assay
4.7.2. ABTS Scavenging Assay
4.7.3. Ferrous Ion-Chelating Assay
4.8. Antifungal Activity
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) |
| CD | Crohn’s Disease |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| DAI | Disease Activity Index |
| DNBS | Dinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid |
| DPPH | 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl |
| EAP | Ethanolic extract of Arthrospira platensis |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| GSH | Reduced Glutathion |
| HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array Detection coupled to Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry |
| HTAB | Hexadecyl-Trimethyl-Ammonium Bromide |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MPO | Myeloperoxydase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| Nrf2/ARE | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/antioxidant response element |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PMS | Post-Mitochondrial Supernatant |
| RNS | Reactive Nitrogen Species |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
References
- Kaser, A.; Zeissig, S.; Blumberg, R.S. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 573–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szigethy, E.; McLafferty, L.; Goyal, A. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 19, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, C.; Farooq, U.; Haseeb, M. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Sandborn, W.J. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical Aspects and Established and Evolving Therapies. Lancet 2007, 369, 1641–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bribi, N.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Vezza, T.; Algieri, F.; Rodriguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Gálvez, J. Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Total Alkaloid Fraction from Fumaria capreolata in the DSS Model of Colitis in Mice. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedian, S.S.; Nokhostin, F.; Malamir, M.D. A Review of the Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment Methods of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Med. Life 2019, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Jin, Y.; Shao, X.; Xu, Y.; Ma, G.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, D. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, 1990–2021: Insights from the Global Burden of Disease 2021. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2024, 39, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammil, M.A.; Fariha, F.; Patel, T.; Sohail, R.; Kumar, M.; Khan, E.; Khanam, B.; Kumar, S.; Khatri, M.; Varrassi, G.; et al. Advancements in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Narrative Review of Diagnostics, Management, Epidemiology, Prevalence, Patient Outcomes, Quality of Life, and Clinical Presentation. Cureus 2023, 15, e41120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide Incidence and Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the 21st Century: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Zheng, H.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, J. Analysis of Global Prevalence, DALY and Trends of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Their Correlations with Sociodemographic Index: Data from 1990 to 2019. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bribi, N.; Algieri, F.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Vezza, T.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Utrilla, M.P.; del Mar Contreras, M.; Maiza, F.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Rodriguez-Cabezas, M.E.; et al. Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Total Alkaloid Extract from Fumaria capreolata in the DNBS Model of Mice Colitis and Intestinal Epithelial CMT93 Cells. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, S.; Zielińska, M.; Sokal, A.; Filip, R. Genetic and Epigenetic Etiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Update. Genes 2022, 13, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemany-Cosme, E.; Sáez-González, E.; Moret, I.; Mateos, B.; Iborra, M.; Nos, P.; Sandoval, J.; Beltrán, B. Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Crohn’s Disease and the Interconnection with Immunological Response, Microbiota, External Environmental Factors, and Epigenetics. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales-Campos, H.; Basso, P.J.; Alves, V.B.F.; Fonseca, M.T.C.; Bonfá, G.; Nardini, V.; Cardoso, C.R.B. Classical and Recent Advances in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2014, 48, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damião, A.O.M.C.; de Azevedo, M.F.C.; de Sousa Carlos, A.; Wada, M.Y.; Silva, T.V.M.; de Castro Feitosa, F. Conventional Therapy for Moderate to Severe Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Literature Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Veeraperumal, S.; Teng, B.; Li, R.; Qian, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhong, S.; Cheong, K.-L. Antioxidative and Protective Effect of Morchella esculenta against Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Alterations in Liver. Foods 2023, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddine, B. Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Paeonia mascula Extract. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2018, 6, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bribi, N.; Mohamed Sofiane, M.; Ouahmed-Boudaoud, H. Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Linum Usitatissimum Alkaloid on Experimental Ulcerative Colitis in BALB/c Mice. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2023, 19, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutadilok-Towatana, N.; Reanmongkol, W.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Evaluation of the Toxicity of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis Extract. J. Appl. Phycol. 2010, 22, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukavský, J.; Vonshak, A. (Eds.) Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira). Physiology, Cell Biology and Biotechnology. Photosynthetica 2000, 38, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentscheva, G.; Nikolova, K.; Panayotova, V.; Peycheva, K.; Makedonski, L.; Slavov, P.; Radusheva, P.; Petrova, P.; Yotkovska, I. Application of Arthrospira platensis for Medicinal Purposes and the Food Industry: A Review of the Literature. Life 2023, 13, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulqader, G.; Barsanti, L.; Tredici, M.R. Harvest of Arthrospira platensis from Lake Kossorom (Chad) and Its Household Usage among the Kanembu. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcea, M.; Sorto, M.; Batello, C.; Narducci, V.; Aguzzi, A.; Azzini, E.; Fantauzzi, P.; Finotti, E.; Gabrielli, P.; Galli, V.; et al. Nutritional Characterization of Traditional and Improved Dihé, Alimentary Blue-Green Algae from the Lake Chad Region in Africa. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, J.C.; Phuc, A.P.; Dubacq, J.P. Nutritional Value of the Alga Spirulina. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1995, 77, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkos, P.D.; Leong, S.C.; Karkos, C.D.; Sivaji, N.; Assimakopoulos, D.A. Spirulina in Clinical Practice: Evidence-Based Human Applications. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 531053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, K.; Wal, A.; Parveen, A.; Singh, P.; Mishra, P.; Wal, P.; Mishra, N. Exploring the Nutritional and Medicinal Potential of Spirulina. Nat. Resour. Hum. Health 2024, 4, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.; Chamorro, G.A.; Salazar, S.; Steele, C.E. Effect of Spirulina Maxima Consumption on Reproduction and Peri- and Postnatal Development in Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 1996, 34, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.; Martínez, E.; Madrigal, E.; Ruiz, L.E.; Chamorro, G.A. Subchronic Toxicity Study in Mice Fed Spirulina Maxima. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1998, 62, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, D.G.; Maciel, G.M.; de Fernandes, I.A.A.; Pedro, A.C.; Rubio, F.T.V.; Branco, I.G.; Haminiuk, C.W.I. Functional Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Spirulina Spp.: Current Status and Future Trends. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2022, 5, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarga, T.; Sanchez Zurano, A.; Villaró, S.; Morillas-España, A.; Acien, G. Industrial Production of Spirulina as a Protein Source for Bioactive Peptide Generation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanović, B.; Benković, M.; Jurina, T.; Sokač Cvetnić, T.; Valinger, D.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J.; Jurinjak Tušek, A. Bioactive Compounds from Spirulina Spp.—Nutritional Value, Extraction, and Application in Food Industry. Separations 2024, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Chow, T.-J. Hypolipidemic, Antioxidant and Antiinflammatory Activities of Microalgae Spirulina. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 28, e33–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khafaga, A.F.; El-Sayed, Y.S. Spirulina Ameliorates Methotrexate Hepatotoxicity via Antioxidant, Immune Stimulation, and Proinflammatory Cytokines and Apoptotic Proteins Modulation. Life Sci. 2018, 196, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agustina, S.; Aidha, N.N.; Oktarina, E.; Kurniati, N.F. Evaluation of Antioxidant and Wound Healing Activities of Spirulina Sp. Extract. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 64, 4601–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, Y.I.; Abd El-Ghffar, E.A. Spirulina Ameliorates Aspirin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Albino Mice by Alleviating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.A.; Gupta, S.; Nair, A.B.; Venugopala, K.N.; Greish, K.; El-Daly, M. Protective Effect of Spirulina platensis Extract against Dextran-Sulfate-Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Garcia, F.A.; Sales-Campos, H.; Yuen, V.G.; Machado, J.R.; de Barros Viana, G.S.; Oliveira, C.J.F.; McNeill, J.H. Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis Attenuates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice by Suppressing Key Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 76, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Farouk, S.M.; Madkour, F.F.; Azab, S.S. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Spirulina platensis in Comparison to Dunaliella salina in Acetic Acid-Induced Rat Experimental Colitis. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2015, 37, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Chain, F.; Sokol, H.; Brigidi, P.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Langella, P.; Martín, R. A Versatile New Model of Chemically Induced Chronic Colitis Using an Outbred Murine Strain. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- te Anje, A.V.; Marleen, I.V.; Daniel, H. Critical Appraisal of the Current Practice in Murine TNBS-Induced Colitis Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/ibdjournal/article/12/10/995/4682862?login=true (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Martín, R.; Chain, F.; Miquel, S.; Lu, J.; Gratadoux, J.-J.; Sokol, H.; Verdu, E.F.; Bercik, P.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Langella, P. The Commensal Bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Is Protective in DNBS-Induced Chronic Moderate and Severe Colitis Models. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziez, M.; Bribi, N.; Mohamed Sofiane, M.; Riad, F.; Affenai, S. Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Potential of Arthrospira platensis Aqueous Extract on DNBS-Induced Colitis in BALB/c Mice. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2024, 18, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morampudi, V.; Bhinder, G.; Wu, X.; Dai, C.; Sham, H.P.; Vallance, B.A.; Jacobson, K. DNBS/TNBS Colitis Models: Providing Insights Into Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Effects of Dietary Fat. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2014, 84, 51297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, E.; Margonis, G.A.; Angelou, A.; Pikouli, A.; Argiri, P.; Karavokyros, I.; Papalois, A.; Pikoulis, E. The TNBS-Induced Colitis Animal Model: An Overview. Ann. Med. Surg. 2016, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Choi, H.-S.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Kim, S.-B.; Shin, M.-S.; Lee, S.; Hwang, G.S.; Koo, B.A.; Kang, K.S. Preparation of Herbal Formulation for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Based on In Vitro Screening and In Vivo Evaluation in a Mouse Model of Experimental Colitis. Molecules 2019, 24, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.P.; Trivedi, N.D. Effect of Karanjin on 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzenesulfonic Acid-Induced Colitis in Balb/c Mice. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2017, 49, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marius, M.; Amadou, D.; Donatien, A.A.; Gilbert, A.; William, Y.N.; Rauf, K.; Arif, M.; Adeline, F.Y.S.; Saint, N.I.; Dar, H.; et al. In Vitro Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and In Vivo Anticolitis Effects of Combretin A and Combretin B on Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 4253174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Wang, C.; Zeng, Z.; Ren, Y.; Li, D.; Song, J.-L. Ameliorative Effect of Sinapic Acid on Dextran Sodium Sulfate- (DSS-) Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Kunming (KM) Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8393504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuno, K.; Akasako, T.; Sugihara, N. The Contribution of the Pyrogallol Moiety to the Superoxide Radical Scavenging Activity of Flavonoids. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Rui, Y.; Guo, S.; Luan, F.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Its Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Derivatives. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xie, M.; He, L.; Song, X.; Cao, T. Chlorogenic Acid: A Review on Its Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammation, Disease Treatment, and Related Delivery Systems. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1218015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzlasir, T.; Selli, S.; Kelebek, H. Effect of Salt Stress on the Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Capacity, Microbial Load, and In Vitro Bioaccessibility of Two Microalgae Species (Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Spirulina platensis). Foods 2023, 12, 3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, R.A.; Sudhakar, K.; Rana, R.S. Comparative Study on the Growth Performance of Spirulina platensis on Modifying Culture Media. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stunda-Zujeva, A.; Berele, M.; Lece, A.; Šķesters, A. Comparison of Antioxidant Activity in Various Spirulina Containing Products and Factors Affecting It. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlFadhly, N.K.Z.; Alhelfi, N.; Altemimi, A.B.; Verma, D.K.; Cacciola, F. Tendencies Affecting the Growth and Cultivation of Genus Spirulina: An Investigative Review on Current Trends. Plants 2022, 11, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoghaibi, M.A. Concepts of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense in Crohn’s Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2013, 19, 6540–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Myeloperoxidase as an Active Disease Biomarker: Recent Biochemical and Pathological Perspectives. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo-Téllez, S.A.; Sekheri, M.; Filep, J.G. Myeloperoxidase: Regulation of Neutrophil Function and Target for Therapy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Rustamov, N.; Roh, Y.-S. The Roles of NFR2-Regulated Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Quality Control in Chronic Liver Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterji, A.; Banerjee, D.; Billiar, T.R.; Sengupta, R. Understanding the Role of S-Nitrosylation/Nitrosative Stress in Inflammation and the Role of Cellular Denitrosylases in Inflammation Modulation: Implications in Health and Diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 604–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, Z.K.; Kerem, M.; Gurbuz, N.; Omeroglu, S.; Pasaoglu, H.; Demirtas, C.; Lortlar, N.; Salman, B.; Pasaoglu, O.T.; Turgut, H.B. The Study of Biochemical and Histopathological Effects of Spirulina in Rats with TNBS-Induced Colitis. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2011, 112, 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Chantarasakha, K.; Asawapanumas, T.; Suntivich, R.; Panya, A.; Phonsatta, N.; Thiennimitr, P.; Laoteng, K.; Tepaamorndech, S. Hatakabb, a Herbal Extract, Contains Pyrogallol as the Novel Mediator Inhibiting LPS-Induced TNF-α Production by NF-κB Inactivation and HMOX-1 Upregulation. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 90, 104992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.S.; Satti, N.K.; Sharma, V.K.; Dutt, P.; Suri, K.A.; Bani, S. Amelioration of Inflammatory Responses by Chlorogenic Acid via Suppression of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Conforti, F.; Menichini, F. Phenolic Compounds from Plants as Nitric Oxide Production Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdag, E. Investigation of Some Phenolic Compounds as iNOS Inhibitors: An in Silico Approach. Chem. Methodol. 2023, 7, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Burgos, E.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Effect of Phenolic Compounds on Human Health. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, J.; Aboul-Enein, B.H.; Duchnik, E.; Marchlewicz, M. Antioxidative Properties of Phenolic Compounds and Their Effect on Oxidative Stress Induced by Severe Physical Exercise. J. Physiol. Sci. 2022, 72, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive Oxygen Species in Inflammation and Tissue Injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Abdul Manap, A.S.; Attiq, A.; Albokhadaim, I.; Kandeel, M.; Alhojaily, S.M. From Imbalance to Impairment: The Central Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Oxidative Stress-Induced Disorders and Therapeutic Exploration. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1269581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, G.; Ulku Karabay, N.; Dalay, M.C.; Pazarbasi, B. Antibacterial Activity of Volatile Component and Various Extracts of Spirulina platensis. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usharani, G.; Srinivasan, G.; Sivasakthi, S.; Saranraj, P. Antimicrobial Activity of Spirulina platensis Solvent Extracts Against Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi. Biol. Res. 2015, 9, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shehata, A.M.; Saad, A.M.; Aldhumri, S.A.; Ouda, S.M.; Mesalam, N.M. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Spirulina platensis Extracts and Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles against Selected Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerard, R.; Sendid, B.; Colombel, J.-F.; Poulain, D.; Jouault, T. An Immunological Link between Candida albicans Colonization and Crohn’s Disease. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sb, D. Phytochemical Screening and Antibacterial Activity of Crude Extracts of Spirulina Species Isolated from Lonar Lake. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 3, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Călinoiu, L.F.; Vodnar, D.C. Thermal Processing for the Release of Phenolic Compounds from Wheat and Oat Bran. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, A.; Upmanyu, N. Formulation, Development and Evaluation of Budesonide Oral Nano-Sponges Using DOE Approach: In Vivo Evidences. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 11, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.N.; Rehman, N.U.; Karim, A.; Soliman, G.A.; Ganaie, M.A.; Raish, M.; Hamad, A.M. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) in Acetic Acid-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats: Ameliorated by Otostegia fruticosa. Life 2021, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merakeb, M.S.; Bribi, N.; Ferhat, R.; Aziez, M.; Yanat, B. Alkaloids Extract from Linum Usitatissimum Attenuates 12-OTetradecanoylphorbol- 13-Acetate (TPA)-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Mouse Skin. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2023, 21, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, M.S. Antioxidant Determinations by the Use of a Stable Free Radical. Nature 1958, 181, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.; Chiu, F.; Ng, K. Identification and Quantification of Antioxidants in Fructus lycii. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.H.; Grange, J.M.; Lyne, P.M. Collins and Lyne’s Microbiological Methods, 6th ed.; Butterworths: London, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 1989; ISBN 978-0-407-00885-4. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ghanayem, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Spirulina platensis Extracts against Certain Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi. Adv. Biores. 2017, 8, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
 ) submucosal edema; (
) submucosal edema; ( ) infiltration of mononuclear cells in the submucosa; (
) infiltration of mononuclear cells in the submucosa; ( ) disruption of crypt integrity; (
) disruption of crypt integrity; ( ) necrotic areas. M: mucosa. SM: submucosa. ME: muscularis externa.
) necrotic areas. M: mucosa. SM: submucosa. ME: muscularis externa.
 ) submucosal edema; (
) submucosal edema; ( ) infiltration of mononuclear cells in the submucosa; (
) infiltration of mononuclear cells in the submucosa; ( ) disruption of crypt integrity; (
) disruption of crypt integrity; ( ) necrotic areas. M: mucosa. SM: submucosa. ME: muscularis externa.
) necrotic areas. M: mucosa. SM: submucosa. ME: muscularis externa.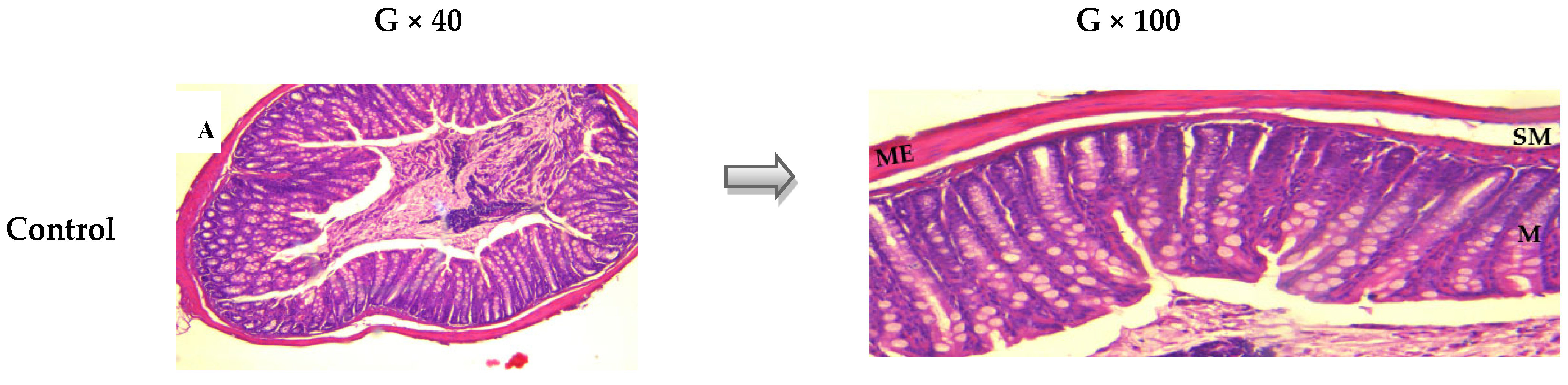
 ) submucosal edema; (
) submucosal edema; ( ) infiltration of mononuclear cells in the submucosa; (
) infiltration of mononuclear cells in the submucosa; ( ) disruption of crypt integrity; (
) disruption of crypt integrity; ( ) granulomas. M: mucosa. SM: submucosa. ME: muscularis externa.
) granulomas. M: mucosa. SM: submucosa. ME: muscularis externa.
 ) submucosal edema; (
) submucosal edema; ( ) infiltration of mononuclear cells in the submucosa; (
) infiltration of mononuclear cells in the submucosa; ( ) disruption of crypt integrity; (
) disruption of crypt integrity; ( ) granulomas. M: mucosa. SM: submucosa. ME: muscularis externa.
) granulomas. M: mucosa. SM: submucosa. ME: muscularis externa.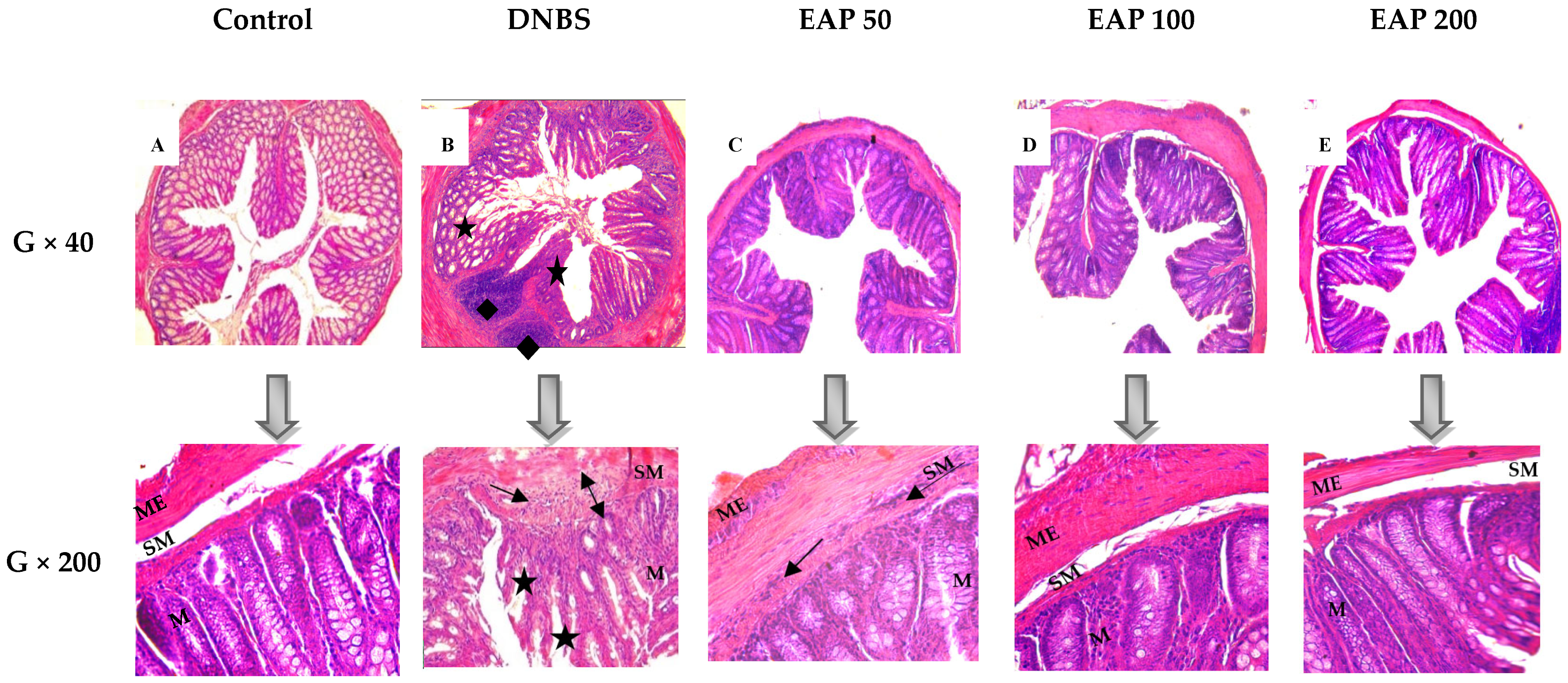
| Phenolic Compounds | Rt (min) | λmax (nm) | [M + H] (m/z) | Concentration (mg g−1 Extract) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pyrogallol | 2.92 | 270 | 127 | 3.142 |
| 2 | 3-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 3.37 | 270 | 139 | 0.284 |
| 3 | 2,4 Dihydroxybenzoic acid | 3.79 | 270 | 155 | 0.581 |
| 4 | 3,5 Dihydroxybenzoic acid | 4.21 | 270 | 155 | 0.597 |
| 5 | Chlorogenic acid | 12.20 | 330 | 355 | 0.703 |
| 6 | Vanilic acid | 12.98 | 280 | 169 | 0.002 |
| 7 | p-Coumaric acid | 16.83 | 331 | 165 | 0.444 |
| 8 | Ferulic acid | 17.69 | 331 | 195 | 1.024 |
| Total phenolics | 6.777 | ||||
| IC50 (mg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| EAP | Trolox | Ascorbic Acid | |
| DPPH• scavenging activity | 0.871 ± 0.012 | 0.081 ± 0.001 | 0.067 ± 0.00004 |
| ABTS•+ scavenging activity | 0.675 ± 0.026 | 0.068 ± 0.00009 | 0.072 ± 0.0001 |
| Ferrous ion-chelating activity | 0.213 ± 0.001 | 0.081 ± 0.001 | 0.083 ± 0.00003 |
| Microorganisms | Inhibition Zone (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EAP (mg.mL−1) | Ketoconazole (µg/disc) | ||
| 50 | 100 | 10 | |
| Candida albicans | 15 ± 0.2 | 20 ± 0.1 | 30 ± 0.05 |
| Aspergillus flavus | 12 ± 0.3 | 15 ± 0.1 | 20 ± 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aziez, M.; Suharoschi, R.; Merakeb, M.S.; Pop, O.L.; Ciont, C.; Ranga, F.; Ferhat, R.; Affenai, S.; Vodnar, D.C.; Cozma, A.; et al. Phenolic Profiling and Bioactive Properties of Arthrospira platensis Extract in Alleviating Acute and Sub-Chronic Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125692
Aziez M, Suharoschi R, Merakeb MS, Pop OL, Ciont C, Ranga F, Ferhat R, Affenai S, Vodnar DC, Cozma A, et al. Phenolic Profiling and Bioactive Properties of Arthrospira platensis Extract in Alleviating Acute and Sub-Chronic Colitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125692
Chicago/Turabian StyleAziez, Meriem, Ramona Suharoschi, Mohamed Sofiane Merakeb, Oana Lelia Pop, Călina Ciont, Floricuța Ranga, Riad Ferhat, Safia Affenai, Dan C. Vodnar, Angela Cozma, and et al. 2025. "Phenolic Profiling and Bioactive Properties of Arthrospira platensis Extract in Alleviating Acute and Sub-Chronic Colitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125692
APA StyleAziez, M., Suharoschi, R., Merakeb, M. S., Pop, O. L., Ciont, C., Ranga, F., Ferhat, R., Affenai, S., Vodnar, D. C., Cozma, A., Fodor, A., Mansouri, E., Smati, D., & Bribi, N. (2025). Phenolic Profiling and Bioactive Properties of Arthrospira platensis Extract in Alleviating Acute and Sub-Chronic Colitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125692











