Ursolic Acid-Based Nutraceutical Mitigates Muscle Atrophy and Improves Exercise Performance in Mouse Model of Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Determination of Ursolic Acid (UA) Using HPLC-DAD
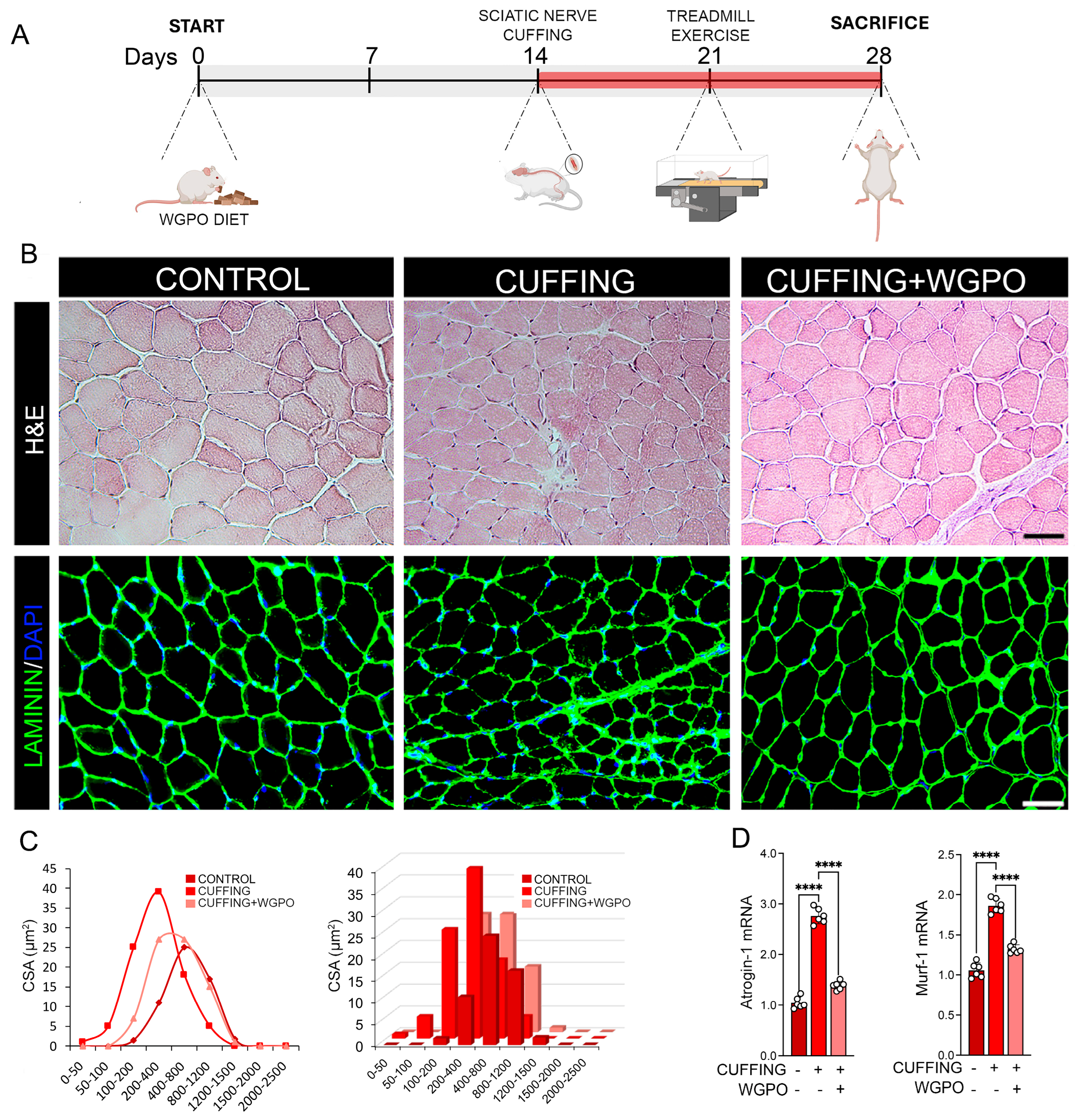
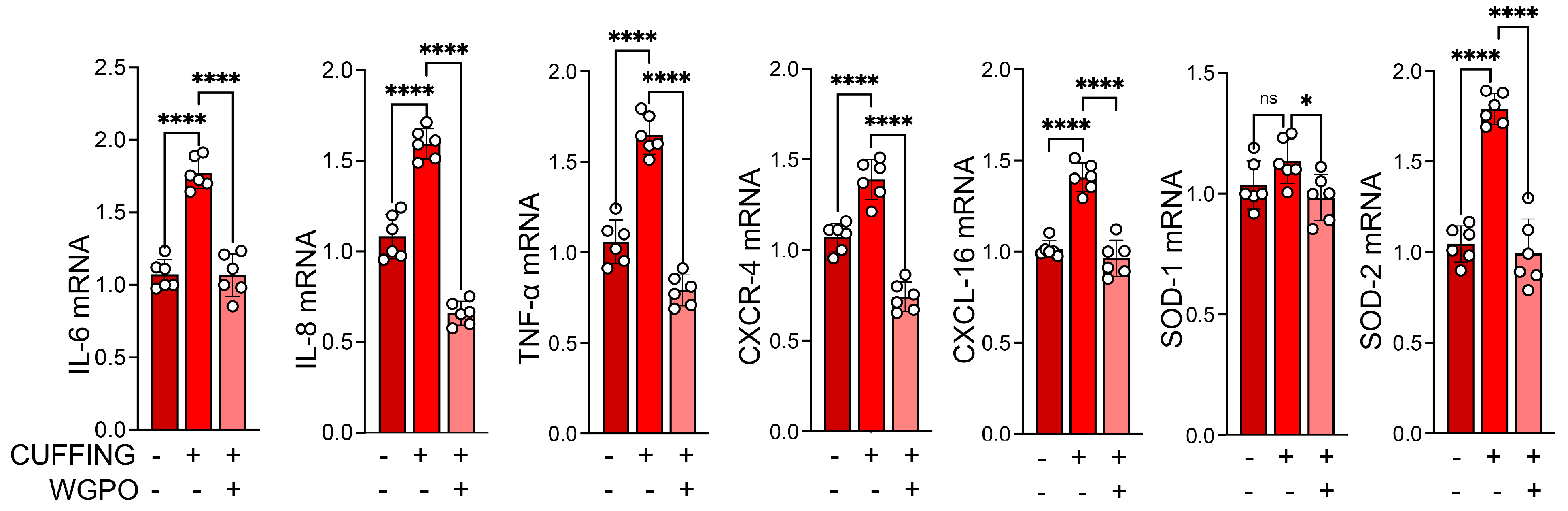
2.2. UA Administration Prevents Muscle Atrophy Following Sciatic Nerve Cuffing
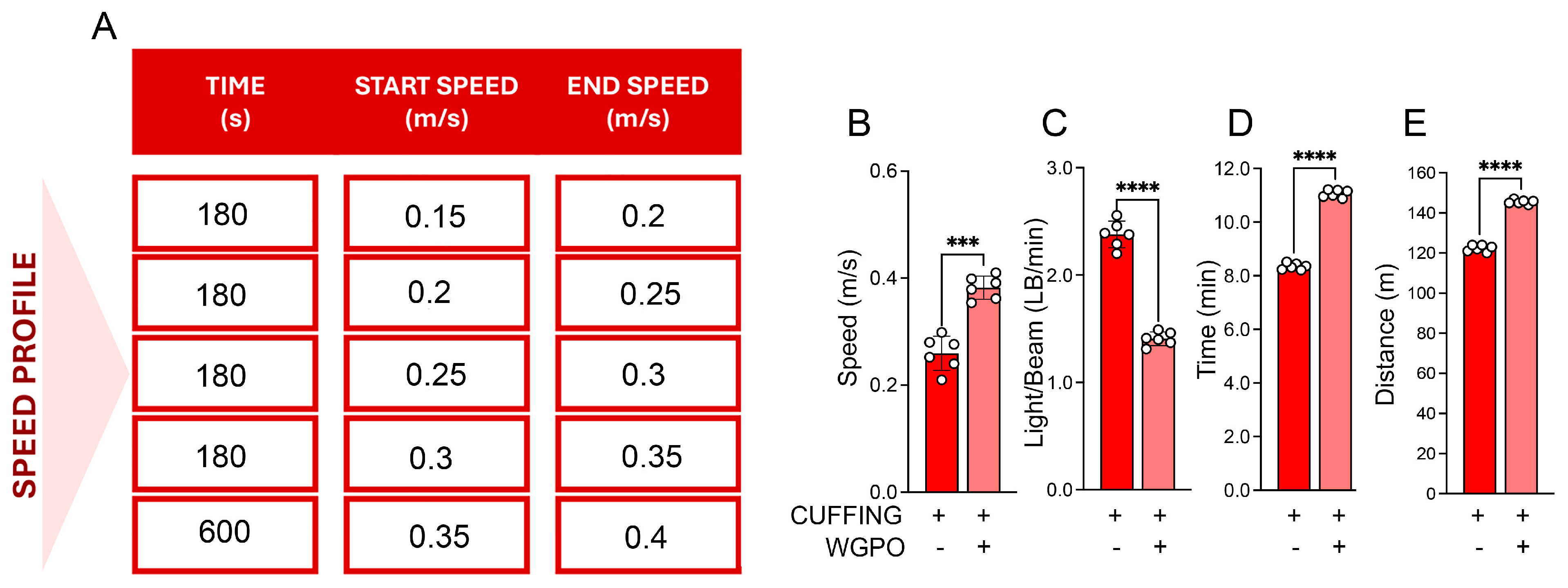
2.3. UA Improves Exercise Performance in Mice Exposed to Sciatic Nerve Cuffing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Oleolyte Preparation Method for In Vivo Animal Experiments
4.3. Ursolic Acid (UA) Extraction Method for HPLC-DAD Analysis
4.3.1. Oil Deacidification Process
4.3.2. Sample Extraction and Quantitative Analysis Method Using HPLC-DAD
4.4. In Vivo Experimental Protocols
4.4.1. Mouse Strains
4.4.2. Real-Time qRT-PCR
4.4.3. Muscle Tissue Histology and Fiber Morphometry
4.4.4. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Muscle Cryosections
4.4.5. Treadmill Exercise Running
4.4.6. Surgical Procedures
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopes, B.; Sousa, P.; Alvites, R.; Branquinho, M.; Sousa, A.C.; Mendonça, C.; Atayde, L.M.; Luís, A.L.; Varejão, A.S.P.; Maurício, A.C. Peripheral Nerve Injury Treatments and Advances: One Health Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.L.; Rivlin, M.; Graham, J.G.; Beredjiklian, P.K. Peripheral Nerve Injury, Scarring, and Recovery. Connect. Tissue Res. 2019, 60, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinsell, D.; Keating, C.P. Peripheral Nerve Reconstruction after Injury: A Review of Clinical and Experimental Therapies. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 698256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, A.L.; West, J.M.; Saffari, T.M.; Nguyen, M.; Moore, A.M. Promoting Nerve Regeneration: Electrical Stimulation, Gene Therapy, and Beyond. Physiology 2022, 37, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostacci, B.; Liguori, R.; Cicero, A.F. Nutraceutical Approach to Peripheral Neuropathies: Evidence from Clinical Trials. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, L.; Fregnan, F.; Maurina, M.; Haastert-Talini, K.; Ronchi, G. The Potential Benefits of Dietary Polyphenols for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannuzzo, F.; Cicatiello, A.G.; Sagliocchi, S.; Schiano, E.; Nappi, A.; Miro, C.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Mollica, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Dentice, M.; et al. Therapeutic Effect of an Ursolic Acid-Based Nutraceutical on Neuronal Regeneration after Sciatic Nerve Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Xu, Z.; Chen, J. Ursolic Acid Induces Neural Regeneration after Sciatic Nerve Injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Chein, Y.-C.; Wang, J.-Y.; Fu, Y.-S. Ursolic Acid Protects Hippocampal Neurons against Kainate-Induced Excitotoxicity in Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 362, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, S.D.; Suneja, M.; Ebert, S.M.; Bongers, K.S.; Fox, D.K.; Malmberg, S.E.; Alipour, F.; Shields, R.K.; Adams, C.M. mRNA Expression Signatures of Human Skeletal Muscle Atrophy Identify a Natural Compound That Increases Muscle Mass. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Raigond, P.; Singh, Y.; Mishra, T.; Singh, B.; Lal, M.K.; Dutt, S. Recent Updates on Bioaccessibility of Phytonutrients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Serna, I.E.; Rocha-Guzmán, N.E.; Gallegos-Infante, J.A.; Cháirez-Ramírez, M.H.; Rosas-Flores, W.; Pérez-Martínez, J.D.; Moreno-Jiménez, M.R.; González-Laredo, R.F. Water-in-Oil Organogel Based Emulsions as a Tool for Increasing Bioaccessibility and Cell Permeability of Poorly Water-Soluble Nutraceuticals. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L. Editorial: Signaling Crosstalk in Obesity and Adipose Tissue-Derived Metabolic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1233284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Ahmad, M.; Ying, R.; Wang, Y.; Tan, C. Fabrication of Pickering High Internal Phase Emulsions Stabilized by Pecan Protein/Xanthan Gum for Enhanced Stability and Bioaccessibility of Quercetin. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbouzid, M.; Pallage, V.; Rajalu, M.; Waltisperger, E.; Doridot, S.; Poisbeau, P.; Freund-Mercier, M.J.; Barrot, M. Sciatic Nerve Cuffing in Mice: A Model of Sustained Neuropathic Pain. Eur. J. Pain 2008, 12, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisto, M.; Piccolo, V.; Novellino, E.; Schiano, E.; Iannuzzo, F.; Ciampaglia, R.; Summa, V.; Tenore, G.C. Optimization of Ursolic Acid Extraction in Oil from Annurca Apple to Obtain Oleolytes with Potential Cosmeceutical Application. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Wu, F.; Tang, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, B. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity of Ursolic Acid: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1256946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, A.L.; Mackinnon, S.E. Chronic Nerve Compression Model for the Double Crush Hypothesis. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1991, 26, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, Ł.; Skąpska, S.; Marszałek, K. Ursolic Acid—A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid with a Wide Spectrum of Pharmacological Activities. Molecules 2015, 20, 20614–20641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulnangai, R.; Asia Thabassoom, H.; Vajiha Banu, H.; Thirugnanasambandham, K.; Ganesamoorthy, R. Recent Developments on Ursolic Acid and Its Potential Biological Applications. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 101900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigford, G.E.; Darr, A.J.; Bracchi-Ricard, V.C.; Gao, H.; Nash, M.S.; Bethea, J.R. Effects of Ursolic Acid on Sub-Lesional Muscle Pathology in a Contusion Model of Spinal Cord Injury. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, R.; Leff, A.; Sinha, N.; Turner, C.; Bays, P.; Draganski, B.; Husain, M. Dopamine Reverses Reward Insensitivity in Apathy Following Globus Pallidus Lesions. Cortex 2013, 49, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanth Kumar, P.K.; Gopala Krishna, A.G. Impact of Different Deacidification Methods on Quality Characteristics and Composition of Olein and Stearin in Crude Red Palm Oil. J. Oleo Sci. 2014, 63, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2016/1227 of 27 July 2016 Amending Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91 on the Characteristics of Olive Oil and Olive-Residue Oil and on the Relevant Methods of Analysis. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2016/1227/oj (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Cicatiello, A.G.; Sagliocchi, S.; Nappi, A.; Di Cicco, E.; Miro, C.; Murolo, M.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Dentice, M. Thyroid Hormone Regulates Glutamine Metabolism and Anaplerotic Fluxes by Inducing Mitochondrial Glutamate Aminotransferase GPT2. Cell Rep 2022, 38, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miro, C.; Nappi, A.; Sagliocchi, S.; Di Cicco, E.; Murolo, M.; Torabinejad, S.; Acampora, L.; Pastore, A.; Luciano, P.; La Civita, E.; et al. Thyroid Hormone Regulates the Lipid Content of Muscle Fibers, Thus Affecting Physical Exercise Performance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miro, C.; Iannuzzo, F.; Acampora, L.; Cicatiello, A.G.; Sagliocchi, S.; Schiano, E.; Nappi, A.; Restolfer, F.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Tenore, G.C.; et al. Ursolic Acid-Based Nutraceutical Mitigates Muscle Atrophy and Improves Exercise Performance in Mouse Model of Peripheral Neuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115418
Miro C, Iannuzzo F, Acampora L, Cicatiello AG, Sagliocchi S, Schiano E, Nappi A, Restolfer F, Stornaiuolo M, Tenore GC, et al. Ursolic Acid-Based Nutraceutical Mitigates Muscle Atrophy and Improves Exercise Performance in Mouse Model of Peripheral Neuropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115418
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiro, Caterina, Fortuna Iannuzzo, Lucia Acampora, Annunziata Gaetana Cicatiello, Serena Sagliocchi, Elisabetta Schiano, Annarita Nappi, Federica Restolfer, Mariano Stornaiuolo, Gian Carlo Tenore, and et al. 2025. "Ursolic Acid-Based Nutraceutical Mitigates Muscle Atrophy and Improves Exercise Performance in Mouse Model of Peripheral Neuropathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115418
APA StyleMiro, C., Iannuzzo, F., Acampora, L., Cicatiello, A. G., Sagliocchi, S., Schiano, E., Nappi, A., Restolfer, F., Stornaiuolo, M., Tenore, G. C., Dentice, M., & Novellino, E. (2025). Ursolic Acid-Based Nutraceutical Mitigates Muscle Atrophy and Improves Exercise Performance in Mouse Model of Peripheral Neuropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115418











