Polygenic Risk Score for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
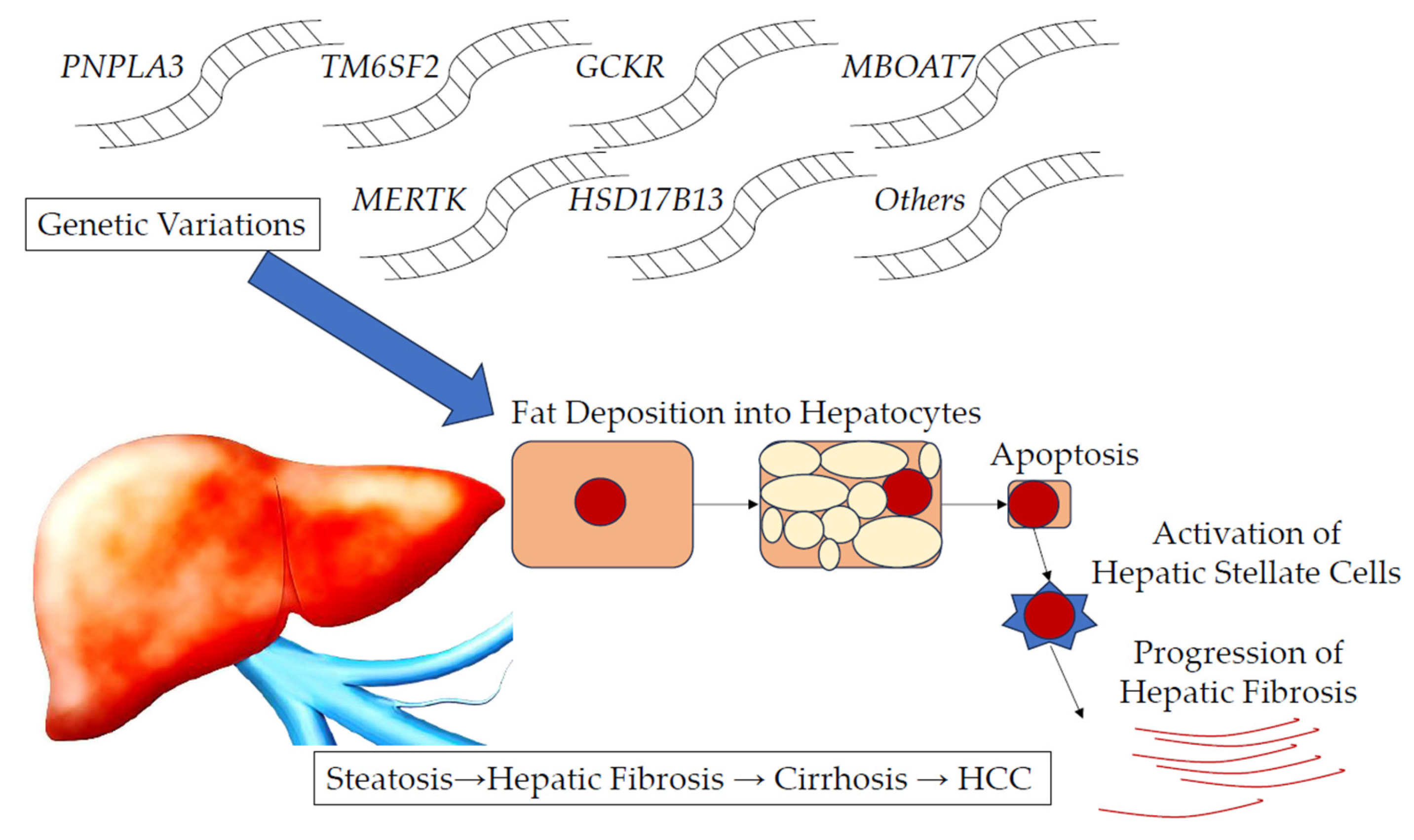
1. Introduction
2. Representative Genetic Variants Involved in the Progression of MASLD/MASH
2.1. Patatin-like Phospholipase Domain-Containing Protein 3 (PNPLA3)
2.1.1. Distribution and Intracellular Localization of PNPLA3
2.1.2. Function of PNPLA3
2.1.3. PNPLA3 Genetic Variants and MASLD, MASH, Cirrhosis, and HCC
2.2. Therapies Targeting Patatin-like Phospholipase Domain-Containing Protein 3 (PNPLA3)
2.3. Transmembrane 6 Superfamily Member 2 (TM6SF2)
2.4. Glucokinase Regulator (GCKR)/Glucokinase Regulatory Protein (GKRP)
2.5. Membrane-Bound O-Acyltransferase Domain-Containing 7 (MBOAT7)
2.6. Myeloid-Epithelial-Reproductive Tyrosine Kinase (MERTK)
2.7. Hydroxysteroid 17-Beta Dehydrogenase 13 (HSD17B13)
2.8. Other Genes
3. Polygenic Risk Score (PRS) for the Progression of MASLD/MASH
3.1. PRS for ALT Elevation, Hepatic Fat Accumulation, and Liver Fibrosis
3.2. PRS for MASLD and MASH
3.3. PRS for Severe Liver Diseases, Such as Cirrhosis and HCC in MASLD MASH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MASLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MASH | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| NAFLD | nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| GWAS | genome-wide association study |
| PRS | polygenic risk score |
| PNPLA3 | patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 |
| TM6SF2 | transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 |
| GCKR | glucokinase regulator |
| MBOAT7 | membrane-bound O-acyltransferase domain-containing 7 |
| MERTK | myeloid–epithelial–reproductive tyrosine kinase |
| HSD17B13 | hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 13 |
| ATGL | adipose triglyceride lipase |
| HSC | hepatic stellate cell |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| SNP | single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| CPN1 | carboxypeptidase N subunit 1 |
| ERLIN1 | endoplasmic reticulum lipid raft-associated 1 |
| CHUK/IKK-α | component of inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase (NF-κß) complex |
| SAMM50 | SAMM50 sorting and assembly machinery component |
| IL | interleukin |
| DAPM | damage-associated molecular pattern |
| ASO | antisense oligonucleotide |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| VLDL | very-low-density lipoprotein |
| HTGC | hepatic triglyceride content |
| DHS | Dallas Heart Study |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| PMBB | Penn Medicine Biobank |
| WES | whole-exome sequence |
| UKB | UK Biobank |
| OR | odds ratio |
| HFHC | high-fat/high-cholesterol |
| GK | glucokinase |
| GKRP | GK regulatory protein |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| ADAM17 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17 (ADAM17) |
| ENPP1 | ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase |
| MTTP/MTP | microsomal triglyceride transfer protein |
| UCP2 | uncoupling protein 2 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| COL13A1 | collagen type XIII alpha 1 chain |
| HOMA-IR | homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance |
| HFC-PRS | PRS for hepatic fat |
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Price, J.K.; Owrangi, S.; Gundu-Rao, N.; Satchi, R.; Paik, J.M. The Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1999–2010.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owrangi, S.; Paik, J.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Hashida, R.; Nader, A.; Paik, A.; Henry, L.; Younossi, Z.M. Meta-Analysis: Global Prevalence and Mortality of Cirrhosis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 61, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; International Consensus Panel. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, F.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Rinella, M.E. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Update and impact of new nomenclature on the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases practice guidance on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2024, 79, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Mejía, M.M.; Jiménez-Gutiérrez, C.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. Breaking new ground: MASLD vs. MAFLD-which holds the key for risk stratification? Hepatol. Int. 2024, 18, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.G.; Xu, X.Y.; Yang, R.X.; Nan, Y.M.; Wei, L.; Jia, J.D.; Zhuang, H.; Shi, J.P.; Li, X.Y.; Sun, C.; et al. Guideline for the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Fatty Liver Disease (Version 2024). J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2024, 12, 955–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Goto, T.; Hirotsu, Y.; Masuzaki, R.; Moriyama, M.; Omata, M. Molecular Mechanisms: Connections between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Steatohepatitis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Fan, J.G.; Yu, M.L.; Wong, V.W.; Cua, I.H.; Liu, C.J.; Tanwandee, T.; Gani, R.; Seto, W.K.; Alam, S.; et al. The Asian Pacific association for the study of the liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2025, 19, 261–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascha, M.S.; Hanouneh, I.A.; Lopez, R.; Tamimi, T.A.; Feldstein, A.F.; Zein, N.N. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertle, J.; Dechêne, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Penndorf, V.; Herzer, K.; Kaiser, G.; Schlaak, J.F.; Gerken, G.; Syn, W.K.; Canbay, A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progresses to hepatocellular carcinoma in the absence of apparent cirrhosis. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederseer, D.; Wernly, B.; Aigner, E.; Stickel, F.; Datz, C. NAFLD and Cardiovascular Diseases: Epidemiological, Mechanistic and Therapeutic Considerations. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakis, N.; Nikolaou, M. From Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome to Cardiovascular-Renal-Hepatic-Metabolic Syndrome: Proposing an Expanded Framework. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Caldwell, S.; Barb, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Loomba, R. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1797–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Nishida, N.; Sugiyama, M.; Kurosaki, M.; Matsuura, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Nakagawa, M.; Korenaga, M.; Hino, K.; Hige, S.; et al. Genome-wide association of IL28B with response to pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppiah, V.; Moldovan, M.; Ahlenstiel, G.; Berg, T.; Weltman, M.; Abate, M.L.; Bassendine, M.; Spengler, U.; Dore, G.J.; Powell, E.; et al. IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.L.; Thio, C.L.; Martin, M.P.; Qi, Y.; Ge, D.; O’Huigin, C.; Kidd, J.; Kidd, K.; Khakoo, S.I.; Alexander, G.; et al. Genetic variation in IL28B and spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus. Nature 2009, 461, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkamani, A.; Wineinger, N.E.; Topol, E.J. The personal and clinical utility of polygenic risk scores. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.M.; Vassos, E. Polygenic risk scores: From research tools to clinical instruments. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingitore, P.; Romeo, S. The role of PNPLA3 in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; He, S.; Li, J.Z.; Seo, Y.K.; Osborne, T.F.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. A feed-forward loop amplifies nutritional regulation of PNPLA3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7892–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirazzi, C.; Valenti, L.; Motta, B.M.; Pingitore, P.; Hedfalk, K.; Mancina, R.M.; Burza, M.A.; Indiveri, C.; Ferro, Y.; Montalcini, T.; et al. PNPLA3 has retinyl-palmitate lipase activity in human hepatic stellate cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 4077–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, P.A.; Gardner, S.D.; Lambie, N.M.; Commans, S.A.; Crowther, D.J. Characterization of the human patatin-like phospholipase family. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.C. PNPLA3-A Potential Therapeutic Target for Personalized Treatment of Chronic Liver Disease. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.M.; Bao, H.; McMahon, C.E.; Chen, Y.; Burr, S.D.; Anderson, A.M.; Madeyski-Bengtson, K.; Lindén, D.; Han, X.; Liu, J. PNPLA3 is a triglyceride lipase that mobilizes polyunsaturated fatty acids to facilitate hepatic secretion of large-sized very low-density lipoprotein. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Dungubat, E.; Kusano, H.; Fukusato, T. Pathology and Pathogenesis of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-Associated Hepatic Tumors. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Waterworth, D.; Perry, J.R.; Lim, N.; Song, K.; Chambers, J.C.; Zhang, W.; Vollenweider, P.; Stirnadel, H.; Johnson, T.; et al. Population-based genome-wide association studies reveal six loci influencing plasma levels of liver enzymes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruschi, F.V.; Tardelli, M.; Claudel, T.; Trauner, M. PNPLA3 expression and its impact on the liver: Current perspectives. Hepat. Med. 2017, 9, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilcher, K.; Dayoub, R.; Kubitza, M.; Riepl, J.; Klein, K.; Buechler, C.; Melter, M.; Weiss, T.S. Saturated Fat-Mediated Upregulation of IL-32 and CCL20 in Hepatocytes Contributes to Higher Expression of These Fibrosis-Driving Molecules in MASLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BasuRay, S.; Wang, Y.; Smagris, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Accumulation of PNPLA3 on lipid droplets is the basis of associated hepatic steatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9521–9526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kory, N.; BasuRay, S.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. PNPLA3, CGI-58, and Inhibition of Hepatic Triglyceride Hydrolysis in Mice. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2427–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bril, F.; Kalavalapalli, S.; Lomonaco, R.; Frye, R.; Godinez Leiva, E.; Cusi, K. Insulin resistance is an integral feature of MASLD even in the presence of PNPLA3 variants. JHEP Rep. 2024, 6, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiorana, F.; Neschuk, M.; Caronia, M.V.; Elizondo, K.; Robledo, M.L.; Schneider, A.; Veron, G.; Zapata, P.D.; Barreyro, F.J. The interplay between Helicobacter pylori infection and rs738409 PNPLA3 in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0310361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanho Martins, M.; Dixon, E.D.; Lupo, G.; Claudel, T.; Trauner, M.; Rombouts, K. Role of PNPLA3 in Hepatic Stellate Cells and Hepatic Cellular Crosstalk. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo, M.; Xie, J.; Alvarez, C.S.; Parisi, D.; Yang, S.; Rivera-Andrade, A.; Kroker-Lobos, M.F.; Groopman, J.D.; Guallar, E.; Ramirez-Zea, M.; et al. Frequency of the PNPLA3 rs738409 polymorphism and other genetic loci for liver disease in a Guatemalan adult population. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 1470–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.M.; Li, D.; Han, Y.; Byun, J.; Hatia, R.I.; Long, E.; Choi, J.; Kelley, R.K.; Cleary, S.P.; Lok, A.S.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies high-impact susceptibility loci for HCC in North America. Hepatology 2024, 80, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlitina, J.; Sookoian, S. Global Epidemiological Impact of PNPLA3 I148M on Liver Disease. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caddeo, A.; Romeo, S. Precision medicine and nucleotide-based therapeutics to treat steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, S76–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armisen, J.; Rauschecker, M.; Sarv, J.; Liljeblad, M.; Wernevik, L.; Niazi, M.; Knöchel, J.; Eklund, O.; Sandell, T.; Sherwood, J.; et al. AZD2693, a PNPLA3 antisense oligonucleotide, for the treatment of MASH in 148M homozygous participants: Two randomized phase I trials. J. Hepatol. 2025, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindén, D.; Tesz, G.; Loomba, R. Targeting PNPLA3 to Treat MASH and MASH Related Fibrosis and Cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Varmazyad, M.; Pla-Palacín, I.; Gavlock, D.C.; DeBiasio, R.; LaRocca, G.; Reese, C.; Florentino, R.M.; Faccioli, L.A.P.; Brown, J.A.; et al. Comparison of wild-type and high-risk PNPLA3 variants in a human biomimetic liver microphysiology system for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease precision therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1423936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlitina, J.; Smagris, E.; Stender, S.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Zhou, H.H.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Vogt, T.F.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Exome-wide association study identifies a TM6SF2 variant that confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdessian, H.; Taxiarchis, A.; Popov, S.; Silveira, A.; Franco-Cereceda, A.; Hamsten, A.; Eriksson, P.; van’t Hooft, F. TM6SF2 is a regulator of liver fat metabolism influencing triglyceride secretion and hepatic lipid droplet content. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8913–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.R.; Vitali, C.; Zhang, D.; Hand, N.J.; Phillips, M.C.; Creasy, K.T.; Scorletti, E.; Park, J.; Regeneron Centre; Schneider, K.M.; et al. Deep metabolic phenotyping of humans with protein-altering variants in TM6SF2 using a genome-first approach. JHEP Rep. 2024, 7, 101243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seko, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shima, T.; Iwaki, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kawanaka, M.; Tanaka, S.; Mitsumoto, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Nakajima, A.; et al. Clinical Utility of Genetic Variants in PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 to Predict Liver-Related Events in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, M.; Wen, J.; Liang, C.; Song, Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Lau, H.C.H.; Cheung, A.H.; et al. Hepatic TM6SF2 activates antitumour immunity to suppress metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma and boosts immunotherapy. Gut 2025, 74, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Shi, M.; Luk, A.O.Y.; Kong, A.P.S.; Ma, R.C.W.; Li, C.; Chen, L.; Chow, E.; Chan, J.C.N. Impaired GK-GKRP interaction rather than direct GK activation worsens lipid profiles and contributes to long-term complications: A Mendelian randomization study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, N.L.; Tribble, N.D.; McCulloch, L.J.; Roos, C.; Johnson, P.R.; Orho-Melander, M.; Gloyn, A.L. The P446L variant in GCKR associated with fasting plasma glucose and triglyceride levels exerts its effect through increased glucokinase activity in liver. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4081–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffeis, C.; Piona, C.; Morandi, A.; Marigliano, M.; Morotti, E.; Mancioppi, V.; Caiazza, E.; Zusi, C.; Emiliani, F.; Mantovani, A.; et al. Glycaemic control metrics and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 5896–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, N.; Caprio, S.; Pierpont, B.; Van Name, M.; Savoye, M.; Parks, E.J. Hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis in Obese Youth Is Modulated by a Common Variant in the GCKR Gene. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1125–E1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, N.; Zhang, C.K.; Zhao, H.; Pakstis, A.J.; Kim, G.; Kursawe, R.; Dykas, D.J.; Bale, A.E.; Giannini, C.; Pierpont, B.; et al. Variant in the glucokinase regulatory protein (GCKR) gene is associated with fatty liver in obese children and adolescents. Hepatology 2012, 55, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernaez, R.; McLean, J.; Lazo, M.; Brancati, F.L.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Borecki, I.B.; Harris, T.B.; Genetics of Obesity-Related Liver Disease (GOLD) Consortium; Nguyen, T.; Kamel, I.R.; et al. Association between variants in or near PNPLA3, GCKR, and PPP1R3B with ultrasound-defined steatosis based on data from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1183–1190.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancina, R.M.; Dongiovanni, P.; Petta, S.; Pingitore, P.; Meroni, M.; Rametta, R.; Borén, J.; Montalcini, T.; Pujia, A.; Wiklund, O.; et al. The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals of European Descent. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1219–1230.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buch, S.; Stickel, F.; Trépo, E.; Way, M.; Herrmann, A.; Nischalke, H.D.; Brosch, M.; Rosendahl, J.; Berg, T.; Ridinger, M.; et al. A genome-wide association study confirms PNPLA3 and identifies TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 as risk loci for alcohol-related cirrhosis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thabet, K.; Asimakopoulos, A.; Shojaei, M.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Mangia, A.; Irving, W.L.; Berg, T.; Dore, G.J.; Grønbæk, H.; Sheridan, D.; et al. MBOAT7 rs641738 increases risk of liver inflammation and transition to fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharthi, J.; Bayoumi, A.; Thabet, K.; Pan, Z.; Gloss, B.S.; Latchoumanin, O.; Lundberg, M.; Twine, N.A.; McLeod, D.; Alenizi, S.; et al. A metabolic associated fatty liver disease risk variant in MBOAT7 regulates toll like receptor induced outcomes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.P.; Wang, X.; Kennelly, J.P.; Shi, H.; Ishino, Y.; Kano, K.; Aoki, J.; Cherubini, A.; Ronzoni, L.; Guo, X.; et al. Low MBOAT7 expression, a genetic risk for MASH, promotes a profibrotic pathway involving hepatocyte TAZ upregulation. Hepatology 2025, 81, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, G.; Zhu, X.; Si, X.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, F.; Lu, J. The correlation between the polymorphism of lysolecithin acyltransferase (MBOAT7) rs641738 and liver fibrosis. Pers. Med. 2025, 22, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petta, S.; Valenti, L.; Marra, F.; Grimaudo, S.; Tripodo, C.; Bugianesi, E.; Cammà, C.; Cappon, A.; Di Marco, V.; Di Maira, G.; et al. MERTK rs4374383 polymorphism affects the severity of fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Dongiovanni, P.; Corey, K.E.; Wang, X.; Shmarakov, I.O.; Zheng, Z.; Kasikara, C.; Davra, V.; Meroni, M.; Chung, R.T.; et al. Macrophage MerTK Promotes Liver Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 406–421.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cai, B. MerTK, a risk factor for NASH fibrosis. Aging 2020, 12, 19832–19833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutusaus, A.; Morales, A.; García de Frutos, P.; Marí, M. GAS6/TAM Axis as Therapeutic Target in Liver Diseases. Semin. Liver Dis. 2024, 44, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grøndal, S.M.; Tutusaus, A.; Boix, L.; Reig, M.; Blø, M.; Hodneland, L.; Gausdal, G.; Jackson, A.; Garcia de Frutos, P.; Lorens, J.B.; et al. Dynamic changes in immune cell populations by AXL kinase targeting diminish liver inflammation and fibrosis in experimental MASH. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1400553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abul-Husn, N.S.; Cheng, X.; Li, A.H.; Xin, Y.; Schurmann, C.; Stevis, P.; Liu, Y.; Kozlitina, J.; Stender, S.; Wood, G.C.; et al. A Protein-Truncating HSD17B13 Variant and Protection from Chronic Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirtas, C.O.; Yilmaz, Y. Decoding 17-Beta-hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase 13: A Multifaceted Perspective on Its Role in Hepatic Steatosis and Associated Disorders. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2024, 12, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, S.; Morrice, N.; Thompson, D.; Milanizadeh, S.; Wilson, S.; Whitfield, P.D.; Mcilroy, G.D.; Rochford, J.J.; Mody, N. Hydroxysteroid 17beta-dehydrogenase 13 (Hsd17b13) knockdown attenuates liver steatosis in high-fat diet obese mice. Exp. Physiol. 2025, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudert, C.A.; Selinski, S.; Rudolph, B.; Bläker, H.; Loddenkemper, C.; Thielhorn, R.; Berndt, N.; Golka, K.; Cadenas, C.; Reinders, J.; et al. Genetic determinants of steatosis and fibrosis progression in paediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z. Enpp1 ameliorates MAFLD by regulating hepatocyte lipid metabolism through the AMPK/PPARα signaling pathway. Cell Biosci. 2025, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uygun, A.; Ozturk, K.; Demirci, H.; Oztuna, A.; Eren, F.; Kozan, S.; Yilmaz, Y.; Kurt, O.; Turker, T.; Vatansever, S.; et al. The association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with genetic polymorphisms: A multicenter study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Lu, L.; An, B.; Jin, W.; Dong, Q.; Xin, Y.; Xuan, S. Association Between LYPLAL1 rs12137855 Polymorphism With Ultrasound-Defined Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Chinese Han Population. Hepat. Mon. 2015, 15, e33155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliba-Gustafsson, P.; Justesen, J.M.; Ranta, A.; Sharma, D.; Bielczyk-Maczynska, E.; Li, J.; Najmi, L.A.; Apodaka, M.; Aspichueta, P.; Björck, H.M.; et al. A functional genomic framework to elucidate novel causal metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease genes. Hepatology 2024, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, R.; Bélanger, É.; Chen, X.; Lefebvre, D.; Uguccioni, S.M.; Pezacki, J.P. LYPLAL1 enzyme activity is linked to hepatic glucose metabolism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 759, 151656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouik, Y.; Di Filippo, M.; Radenne, S.; Dumortier, J.; Moulin, P.; Levrero, M. Combination of heterozygous APOB gene mutation with PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 variants promotes steatotic liver disease, cirrhosis and HCC development. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 1474–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.V.; Hehl, L.; Creasy, K.T.; Vitali, C.; Vell, M.S.; Vujkovic, M.; Park, J.; Scorletti, E.; Seeling, K.S.; Rendel, M.D.; et al. A coding variant in the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein reduces both hepatic steatosis and plasma lipids. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 58, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, M.E.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Friedman, S.N.; Wang, M.; Emdin, C.A.; Ajmera, V.H.; Simon, T.G.; Homburger, J.R.; Guo, X.; Budoff, M.; et al. Machine learning enables new insights into genetic contributions to liver fat accumulation. Cell Genom. 2021, 1, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, L.; Motta, B.M.; Alisi, A.; Sartorelli, R.; Buonaiuto, G.; Dongiovanni, P.; Rametta, R.; Pelusi, S.; Fargion, S.; Nobili, V. LPIN1 rs13412852 polymorphism in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liukkonen, V.; Semenova, M.; Hyvärinen, K.; Lauronen, J.; Partanen, J.; Arola, J.; Nordin, A.; Färkkilä, M.; Åberg, F. Genetic Risk Factors for Steatotic Liver Disease After Liver Transplantation. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e70067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez-Pinto, H.; Zhi Lin, H.; Qi Yang, S.; Odwin Da Costa, S.; Diehl, A.M. Lipids up-regulate uncoupling protein 2 expression in rat hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maamari, D.J.; Abou-Karam, R.; Fahed, A.C. Polygenic Risk Scores in Human Disease. Clin. Chem. 2025, 71, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.W.; Mak, T.S.; O’Reilly, P.F. Tutorial: A guide to performing polygenic risk score analyses. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2759–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, M.; Chambers, J.C. Polygenic risk scores for complex diseases: Where are we now? Singap. Med. J. 2023, 64, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, N.J.; Kottyan, L.C.; Kachulis, C.; Abul-Husn, N.S.; Arias, J.; Belbin, G.; Below, J.E.; Berndt, S.I.; Chung, W.K.; Cimino, J.J.; et al. Selection, optimization and validation of ten chronic disease polygenic risk scores for clinical implementation in diverse US populations. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrieta-Carrasco, E.; Flores, Y.N.; Macías-Kauffer, L.R.; Ramírez-Palacios, P.; Quiterio, M.; Ramírez-Salazar, E.G.; León-Mimila, P.; Rivera-Paredez, B.; Cabrera-Álvarez, G.; Canizales-Quinteros, S.; et al. Genetic variants in COL13A1, ADIPOQ and SAMM50, in addition to the PNPLA3 gene, confer susceptibility to elevated transaminase levels in an admixed Mexican population. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2018, 104, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stender, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Richardson, T.G. Genetic variation and elevated liver enzymes during childhood, adolescence and early adulthood. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2023, 52, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Stender, S.; Pietrelli, A.; Mancina, R.M.; Cespiati, A.; Petta, S.; Pelusi, S.; Pingitore, P.; Badiali, S.; Maggioni, M.; et al. Causal relationship of hepatic fat with liver damage and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 283, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åberg, F.; Saarinen, K.; Jula, A.; Lundqvist, A.; Vihervaara, T.; Erlund, I.; Färkkilä, M. Combined use of the ELF test and CLivD score improves prediction of liver-related outcomes in the general population. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Garske, K.M.; Pan, D.Z.; Koka, A.; Kaminska, D.; Männistö, V.; Sinsheimer, J.S.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Pajukanta, P. Identification of 90 NAFLD GWAS loci and establishment of NAFLD PRS and causal role of NAFLD in coronary artery disease. HGG Adv. 2021, 3, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, C.; Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, M.; Jiang, T.; et al. Behavioural activity pattern, genetic factors, and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study in the UK Biobank. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.; Sun, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhao, J.; Dan, L.; Shi, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Risk Assessment for Gastrointestinal Diseases via Clinical Dimension and Genome-Wide Polygenic Risk Scores of Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Männistö, V.T.; Salomaa, V.; Färkkilä, M.; Jula, A.; Männistö, S.; Erlund, I.; Sundvall, J.; Lundqvist, A.; Perola, M.; Åberg, F. Incidence of liver-related morbidity and mortality in a population cohort of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2590–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardoglou, P.; Gavra, I.; Amanatidou, A.I.; Kalafati, I.P.; Symianakis, P.; Kafyra, M.; Moulos, P.; Dedoussis, G.V. Development of a Polygenic Risk Score for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Prediction in UK Biobank. Genes 2024, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Yoo, H.Y. Sex differences in predicting dyslipidemia using polygenic risk score with fatty liver index and fibrotic nonalcoholic steatohepatitis index. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Zheng, K.I.; Chen, S.D.; Lee, D.H.; Wu, X.X.; Wang, X.D.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Chen, Y.P.; Kim, W.; et al. Individualized Polygenic Risk Score Identifies NASH in the Eastern Asia Region: A Derivation and Validation Study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridi, L.; Agrawal, S.; Tesfai, K.; Madamba, E.; Bettencourt, R.; Richards, L.M.; Khera, A.V.; Loomba, R.; Ajmera, V. The impact of genetic risk on the prevalence of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in prospectively assessed patients with type 2 diabetes. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vincentis, A.; Tavaglione, F.; Jamialahmadi, O.; Picardi, A.; Antonelli Incalzi, R.; Valenti, L.; Romeo, S.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U. A Polygenic Risk Score to Refine Risk Stratification and Prediction for Severe Liver Disease by Clinical Fibrosis Scores. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellert-Kristensen, H.; Richardson, T.G.; Davey Smith, G.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Stender, S. Combined Effect of PNPLA3, TM6SF2, and HSD17B13 Variants on Risk of Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the General Population. Hepatology 2020, 72, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, C.; Jamialahmadi, O.; Pelusi, S.; Baselli, G.; Dongiovanni, P.; Zanoni, I.; Santoro, L.; Maier, S.; Liguori, A.; Meroni, M.; et al. Non-invasive stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma risk in non-alcoholic fatty liver using polygenic risk scores. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.E.; Diergaarde, B.; Kuipers, A.L.; Adibi, J.J.; Luu, H.N.; Chang, X.; Dorajoo, R.; Heng, C.K.; Khor, C.C.; Wang, R.; et al. NAFLD polygenic risk score and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in an East Asian population. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2310–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrift, A.P.; Kanwal, F.; Liu, Y.; Khaderi, S.; Singal, A.G.; Marrero, J.A.; Loo, N.; Asrani, S.K.; Luster, M.; Al-Sarraj, A.; et al. Risk stratification for hepatocellular cancer among patients with cirrhosis using a hepatic fat polygenic risk score. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Li, Y.; Hong, C.; Ma, P.; Zhu, H.; Cui, H.; Zou, X.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; He, J.; et al. Polygenic risk score of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease amplifies the health impact on severe liver disease and metabolism-related outcomes. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, C.J.; Salatino, A.; Quintanilla, M.F.; Castaño, G.O.; Garaycoechea, M.; Sookoian, S. The influence of host genetics on liver microbiome composition in patients with NAFLD. EBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafyra, M.; Kalafati, I.P.; Dimitriou, M.; Grigoriou, E.; Kokkinos, A.; Rallidis, L.; Kolovou, G.; Trovas, G.; Marouli, E.; Deloukas, P.; et al. Robust Bioinformatics Approaches Result in the First Polygenic Risk Score for BMI in Greek Adults. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.H.; Gao, P.Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, Y.; Chi, H.C.; Zhang, Z.H.; Han, S.L.; Han, B.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xu, W.; et al. Liver Diseases and Brain Disorders: Genetic Mechanisms and Biomarker Pathways in a Prospective Cohort Study From the UK Biobank. J. Neurochem. 2025, 169, e70066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccioli, L.A.P.; Cetin, Z.; Kocas-Kilicarslan, Z.N.; Ortiz, K.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Z.; Kurihara, T.; Tafaleng, E.N.; Florentino, R.M.; Wang, Z.; et al. Evaluation of Human Hepatocyte Drug Metabolism Carrying High-Risk or Protection-Associated Liver Disease Genetic Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moonlisarn, K.; Somnark, P.; Boonkaew, B.; Bunchorntavakul, C.; Tangkijvanich, P. Interaction Between PNPLA3 and SIRT5 Genetic Variants in Association with Liver Fibrosis Severity in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Genes 2024, 15, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, E.; Rady, B.; Koshkina, A.; Jeon, J.Y.; Ayyar, V.S.; Gargano, C.; DiProspero, N.; Wendel, S.; Hegge, J.; Hamilton, H.; et al. Phase 1 Trials of PNPLA3 siRNA in I148M Homozygous Patients with MAFLD. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 475–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Iino, C.; Sasada, T.; Furusawa, K.; Yoshida, K.; Sawada, K.; Mikami, T.; Fukuda, S.; Nakaji, S.; Sakuraba, H. A 4-year cohort study of the effects of PNPLA3 rs738409 genotypes on liver fat and fibrosis and gut microbiota in a non-fatty liver population. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2025, 30, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Yamazaki, M.; Shibata, T.; Nirei, K.; Takahashi, H.; Kaneko, T.; Fujisawa, M.; Higuchi, T.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Apoptosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, L.; Pollock, R.F.; Stepanova, M.; Nader, F. Economic evaluation of non-invasive test pathways for high-risk metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in the United Kingdom (UK). Ann. Hepatol. 2025, 30, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Carnicero, J.; Saurí-Ferrer, I.; Redon, J.; Navarro, J.; Fernández, G.; Hurtado, C.; Ferreira, K.; Alvarez-Ortega, C.; Gómez, A.; Martos-Rodríguez, C.J.; et al. Clinical and Economic Burden of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in a Spanish Mediterranean Region: A Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimassa, L.; Chan, S.L.; Sangro, B.; Lau, G.; Kudo, M.; Reig, M.; Breder, V.; Ryu, M.H.; Ostapenko, Y.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; et al. Five-year overall survival update from the HIMALAYA study of tremelimumab plus durvalumab in unresectable HCC. J. Hepatol. 2025, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathurin, P.; de Zélicourt, M.; Laurendeau, C.; Dhaoui, M.; Kelkouli, N.; Blanc, J.F. Treatment patterns, risk factors and outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed hepatocellular carcinoma in France: A retrospective database analysis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2023, 47, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Taub, R.; Neff, G.W.; Lucas, K.J.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Alkhouri, N.; Bashir, M.R. Resmetirom for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.; Al-Sharif, L.; Antunes, V.L.J.; Huang, D.Q.; Loomba, R. Comparison of pharmacological therapies in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis for fibrosis regression and MASH resolution: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Hepatology 2025, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seko, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shima, T.; Tanaka, S.; Shirono, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Kataoka, S.; Moriguchi, M.; Okanoue, T.; et al. Prognostic performance of a two-step method using the Fibro-Scope system for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2024, 55, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seko, Y.; Lin, H.; Wong, V.W.; Okanoue, T. Impact of PNPLA3 in Lean Individuals and in Cryptogenic Steatotic Liver Disease. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Regions | PNPLA3 I148M (%) | MASLD (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 12 | 13.5 |
| Europe | 23 | 25.1–44.4 |
| South Asia | 24–30 | 33.8 |
| East Asia | 35–45 | 28–33.1 |
| Central and South America | ~50% | ~38.4 |
| North America | ~25 | 31.2 |
| Genes/Liver Diseases | Fat Accumulation/ALT Elevation | MASLD | MASH/Liver Fibrosis | Cirrhosis | HCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNPLA3 | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| HSD17B13 | Negative | Negative | |||
| GCKR | Positive | ||||
| TM6SF2 | Positive | Positive | Positive | ||
| MBOAT7 | Positive | Positive | |||
| MERTK | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Authors, Years, Refs. | Number of Patients | Factors of PRS | Target of PRS | p-Values, etc. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT Level | ||||
| Larrieta-Carrasco E, et al., 2018 [84] | Baseline assessment from 2004 to 2006 (wave 1), Mexican Health Worker Cohort Study (MHWCS), n = ~4000; follow-up phase, n = 1855 (74%) | ADIPOQ rs17366743, COL13A1 (rs7101190 and rs1227756), PNPLA3 (rs3810622 and rs738409), SAMM50 rs2143571 | Higher ALT or AST levels | Mean ALT and AST levels significantly increased as a function of the number of risk alleles (quartiles) (p = 1.0 × 10−9 and 7.7 × 10−11, respectively), adjusted for age, sex, BMI, and admixture. PRS: elevated ALT levels, OR: 1.70 (95%CI: 1.41–2.05; p < 0.0001) |
| Stender S, et al., 2023 [85] | 4018 children | Genome-wide ALT-PRS (PNPLA3 rs738409, TM6SF2 rs58542926, and HSD17B13 rs72613567) | Plasma ALT levels | p for interaction between time and PRS on inverse normalized ALT = 1.5 × 10−4 |
| Fat Accumulation and Liver Fibrosis | ||||
| Dongiovanni P, et al., 2018 [86] | Liver biopsy cohort (LBC), n = 1515; Swedish Obese Subjects Study (SOS), n = 3329; Dallas Heart Study (DHS), n = 4570 | PNPLA3 rs738409, TM6SF2 rs58542926, GCKR rs1260326, MBOAT7 rs641738 | Hepatic fat (TG) accumulation | LBC: <10−16; (no PNPLA3), 1.2 × 10−8; LBC obese: 4.5 × 10−6; (no PNPLA3), 0.0059; (no TM6SF2), 0.0001; DHS: <2.2 × 10−16; (no PNPLA3), 5.8 × 10−8 |
| Dongiovanni P, et al., 2018 [86] | Liver biopsy cohort (LBC), n = 1515 | PNPLA3 rs738409, TM6SF2 rs58542926, GCKR rs1260326, MBOAT7 rs641738 | Liver fibrosis | p = 1.3 × 10−14 |
| Åberg F, et al., 2023 [87] | 5795 adults attending the Finnish Health 2000 Survey | PRS-5 based on variations in PNPLA3, TM6SF2, GCKR, MBOAT7, and HSD17B13 | Liver fibrosis | Model 2: HR, 4.11; 95%CI, 1.24–13.64; p = 0.021; Model 3: HR, 5.05; 95%CI, 1.55–16.50; p = 0.007 |
| MASLD/NAFLD | ||||
| Miao Z, et al., 2021 [88] | UK Biobank (UKB), training set (n = 99,823), test set (n = 34,833), and validation set (n = 5059). | PRS models (90 NAFLD GWAS loci) | NAFLD cases had a significantly higher PRS compared to control subjects | T= −7.89, p = 3.69 × 10−15, OR: 2.1 |
| Ge X, et al., 2023 [89] | NAFLD in the UKB (N = 338,087) | PRS (variants in PNPLA3, TM6SF2, MBOAT7, and GCKR) | NAFLD | HR, 1.78 (95% CI, 1.60–1.98) |
| Fu T, et al., 2024 [90] | 374,125 participants free of gastrointestinal disorders at baseline, including 19,719 (5.27%) with type 2 diabetes mellitus | PRS, using genetic variants ascertained to be strongly related to type 2 diabetes mellitus (p < 5 × 10−8) | NAFLD | Intermediate genetic risk: OR, 1.13 (95% CI, 1.02–1.25); high genetic risk: OR, 1.42 (95% CI, 1.26–1.59) |
| Mannisto VT, et al., 2021 [91] | Finnish population-based FINRISK and Health 2000 studies, n = 10,993 with NAFLD | PRS-5 (PNPLA3, TM6SF2, MBOAT7, GCKR, and HSD17B13 genotype) | The 20-year cumulative incidence of liver-related outcomes in NAFLD | 4.3% in the high-PRS-5 group and 1.5% in the low-PRS-5 group (p < 0.001) |
| Giardoglou P, et al., 2024 [92] | 4617 NAFLD/MRI-PDFF values from the UKB | PRS with 75 SNPs | Prediction of MASLD | Incremental R2 = 0.025, p = 0.00145 |
| Kim S, et al., 2025 [93] | 48,263 South Koreans (17,064 men and 31,199 women) | PRS related to dyslipidemia, using the “auto” mode of the PRS-continuous shrinkage method | Fatty liver index (FLI) and fibrotic NASH index (FNI) in men | AUROC [95% confidence intervals]: 0.704 [0.698–0.711] |
| MASH/NASH | ||||
| Gao F, et al., 2021 [94] | 1070 Asian individuals with biopsy-confirmed NAFLD from 2 countries (China and South Korea) | Nomogram, including sex, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, AST ≥ 40 U/L, and PNPLA3 (rs738409) and HSD17B13 (rs72613567) genetic variants | NASH in the Eastern Asia region | High AUROCs (internal validation set: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.72–0.88; external validation cohort: 0.76, 95% CI: 0.72–0.80) |
| Bridi L, et al., 2024 [95] | 382 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus | PRS (the sum of risk alleles in PNPLA3, TM6SF2, and SERPINA1 minus the protective variant in HSD17B13) | Prevalence of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis | Higher PRSs were associated with an increased risk of cirrhosis (p = 0.037) and an increased risk of advanced cirrhosis among those with a fibrosis-4 index < 1.3 (p = 0.036) |
| Severe liver disease, cirrhosis and HCC | ||||
| De Vincentis, et al., 2022 [96] | UKB, n = 266,687 | HFC-PRS (including PNPLA3, TM6SF2, MBOAT7, and GCKR); HFC-PRS (PRS2) (including only PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 variants) | Severe liver disease (SLD), defined as a composite diagnosis of cirrhosis, decompensated liver disease, HCC, and/or liver transplantation | SLD: the HFC-PRS was highly associated with the risk of SLD in the overall population (age–sex-adjusted HR (aHR) for a 1 SD increase: 1.25; 95% CI, 1.16–1.35; p = 8.9 × 10−9) |
| Gellert-Kristensen H, et al., 2020 [97] | Copenhagen studies, n = 110,219; UKB, n = 334,276 | PNPLA3, TM6SF2, and HSD17B13 variants (weighted by ALT effects) | Cirrhosis and HCC in Europeans | GRS 5-6: cirrhosis, OR: 12 (95% CI: 7.7–19); HCC, OR: 29 (95%CI: 17–51) |
| Bianco C, et al., 2021 [98] | NAFLD cohort, n = 2566; general population (UKB), n = 364,048 | PNPLA3-TM6SF2-GCKR-MBOAT7 and hepatic fat PRS (PRS-4), adjusted for HSD17B13 (PRS-5) | HCC | Fatty liver: HFC-PRS, 4.4 × 10−26; PRS-5, 6.0 × 10−27; Fibrosis F3-F4: HFC-PRS, 9.5 × 10−28; PRS-5, 1.1 × 10−30; MASLD-HCC, HFC-PRS, 2.7 × 10−14; PRS-5, 1.6 × 10−14 |
| Thomas CE, et al., 2022 [99] | 24,333 participants of the Singapore Chinese Health Study (SCHS) | PRS for hepatic fat (HFC-PRS, including four SNPs: rs1260326 (GCKR), rs58542926 (TM6SF2), rs641738 (MBOAT7), and rs738409 (PNPLA3)); NAFLD-related PRS (NAFLD-PRS, including 12 SNPs) | Increased risk of HCC | HFC-PRS and NAFLD-PRS: HR of 2.39 (95% CI: 1.51, 3.78) and 1.77 (95% CI: 1.15, 2.73), respectively. |
| Thrift AP, et al., 2023 [100] | 1644 patients with cirrhosis enrolled in two prospective cohort studies in the U.S. | PRS (high-risk variants in PNPLA3-MBOAT7-TM6SF2-GCKR) | HCC | Compared to cirrhosis patients in the lowest tertile of the PRS, those in the highest tertile had 2-fold higher risk of HCC (HR = 2.05; 95% CI, 1.22–3.44) |
| Xiao L, et al., 2024 [101] | 435,306 from the UKB | PRS (16 genes) | Severe liver disease (SLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus | HR, 3.15 (95% confidence interval, 2.54–3.90) for SLD; HR, 2.81 (2.60–3.03) for type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| Others | ||||
| Seko Y, et al., 2025 [46] | 1304 Japanese patients with biopsy-proven MASLD | High-fat-content PRS (HFC-PRS), including PNPLA3, TM6SF2, GCKR, and MBOAT7 genotypes | Prediction of liver-related events (LREs) | HRs for LRE: 10.72 in the high-risk group and 4.80 in the intermediate-risk group; HRs for prognosis: 8.74 in the high-risk group and 5.62 in the intermediate-risk group |
| Pirola CJ, et al., 2022 [102] | Microbial 16S rRNA reads from the livers of 116 individuals, categorized as non-NAFLD patients (n = 19) and patients with NAFLD (n = 44) and NASH (n = 53) | PRS (PNPLA3-rs738409, TM6SF2-rs58542926, MBOAT7-rs641738, HSD17B13-rs72613567, and FGF21-rs838133) | Abundance of the Tyzzerella genus—a member of the Firmicutes phylum and the Clostridia class—showed the strongest association with high PRS values (>4 risk alleles) | 2.64-fold change differential abundance (p = 0.0019, FDR < 0.05) |
| Pirola CJ, et al., 2022 [102] | Microbial 16S rRNA reads from the liver of 116 individuals, categorized as non-NAFLD patients (n = 19) and patients with NAFL (n = 44) and NASH (n = 53) | PRS (PNPLA3-rs738409, TM6SF2-rs58542926, MBOAT7-rs641738, HSD17B13-rs72613567, and FGF21-rs838133) | Lactobacillus genus—a member of the Firmicutes phylum and Bacilli class—exhibited the strongest association with low PRS values (≤4 risk alleles) | 0.89-fold change, p = 0.033, FDR < 0.05 |
| Kafyra M, et al., 2023 [103] | 2083 participants (the case-control Greek NAFLD study, the cross-sectional OSTEOS study, and the case-control THISEAS study) | PRS (16 SNPs) | BMI in Greek adults | R2 = 0.3241 (beta = 1.011, p = 4 × 10−193) |
| Guo HH, et al., 2025 [104] | UKB (N = 492,059) | PRS for UKB participants, using the PRS-CS method | Brain function scores | PRS for NAFLD, associated with declines in hand grip strength (β = −0.094, FDR-Q = 6.18 × 10−5) and usual walking speed (β = −0.136, FDR-Q = 2.80 × 10−5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanda, T.; Sasaki-Tanaka, R.; Abe, H.; Kimura, N.; Yoshida, T.; Hayashi, K.; Sakamaki, A.; Yokoo, T.; Kamimura, H.; Tsuchiya, A.; et al. Polygenic Risk Score for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115164
Kanda T, Sasaki-Tanaka R, Abe H, Kimura N, Yoshida T, Hayashi K, Sakamaki A, Yokoo T, Kamimura H, Tsuchiya A, et al. Polygenic Risk Score for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115164
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanda, Tatsuo, Reina Sasaki-Tanaka, Hiroyuki Abe, Naruhiro Kimura, Tomoaki Yoshida, Kazunao Hayashi, Akira Sakamaki, Takeshi Yokoo, Hiroteru Kamimura, Atsunori Tsuchiya, and et al. 2025. "Polygenic Risk Score for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis: A Narrative Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115164
APA StyleKanda, T., Sasaki-Tanaka, R., Abe, H., Kimura, N., Yoshida, T., Hayashi, K., Sakamaki, A., Yokoo, T., Kamimura, H., Tsuchiya, A., Kamimura, K., & Terai, S. (2025). Polygenic Risk Score for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115164







