Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Biomarker Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Trial Characteristics
3.3. Methodology Quality Appraisal
3.4. Shared Biomarkers Between Sarcopenia and SO
3.4.1. Metabolic Biomarkers in Sarcopenia and SO
3.4.2. Inflammation Biomarkers in Sarcopenia and SO
3.4.3. Hematological Biomarkers in Sarcopenia and SO
3.4.4. Hormonal Biomarkers in Sarcopenia and SO
3.5. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Principal Findings and Comparison with Previous Studies
4.2. Implications of Study and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- da Costa, J.P.; Vitorino, R.; Silva, G.M.; Vogel, C.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. A Synopsis on Aging-Theories, Mechanisms and Future Prospects. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 29, 90–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.S.; Singer, B.D.; Vaughan, D.E. Molecular and Physiological Manifestations and Measurement of Aging in Humans. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Park, S.W.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Nevitt, M.; Schwartz, A.V.; Simonsick, E.M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Visser, M.; Newman, A.B.; et al. The Loss of Skeletal Muscle Strength, Mass, and Quality in Older Adults: The Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.-P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granic, A.; Suetterlin, K.; Shavlakadze, T.; Grounds, M.D.; Sayer, A.A. Hallmarks of Ageing in Human Skeletal Muscle and Implications for Understanding the Pathophysiology of Sarcopenia in Women and Men. Clin. Sci. 2023, 137, 1721–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmer, P.; Jung, T.; Castro, J.P.; Pomatto, L.C.; Sun, P.Y.; Davies, K.J.; Grune, T. Sarcopenia-Molecular Mechanisms and Open Questions. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 65, 101200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzoni, R.; Bischoff, S.C.; Boirie, Y.; Busetto, L.; Cederholm, T.; Dicker, D.; Toplak, H.; Van Gossum, A.; Yumuk, V.; Vettor, R. Sarcopenic Obesity: Time to Meet the Challenge. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37 Pt A, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Chourdakis, M.; Cuerda, C.; Delzenne, N.M.; Deutz, N.E.; Fouque, D.; Genton, L.; Gil, C.; et al. Towards a Multidisciplinary Approach to Understand and Manage Obesity and Related Diseases. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 917–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.M.; Landi, F.; Chew, S.T.; Atherton, P.J.; Molinger, J.; Ruck, T.; Gonzalez, M.C. Advances in Muscle Health and Nutrition: A Toolkit for Healthcare Professionals. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2244–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Sarcopenia: Still in Relative Definition-Penia and Severe Treatment-Penia. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2024, 150, 155717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.V.; Paiva, A.E.G.; Silva, A.C.B.; de Castro, I.C.; Santiago, A.F.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Porto, L.C.J. Prevalence of Sarcopenia According to Ewgsop1 and Ewgsop2 in Older Adults and Their Associations with Unfavorable Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Mei, F.; Shang, Y.; Hu, K.; Chen, F.; Zhao, L.; Ma, B. Global Prevalence of Sarcopenic Obesity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4633–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic Obesity in Older Adults: Aetiology, Epidemiology and Treatment Strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, C.A.; Dekker, L.H.; Navis, G.J. Prevalence of Sarcopenic Obesity and Sarcopenic Overweight in the General Population: The Lifelines Cohort Study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4422–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, J.N.; Ferrucci, L.; Newman, A.B.; Aroda, V.R.; Bahnson, J.L.; Divers, J.; Espeland, M.A.; Marcovina, S.; Pollak, M.N.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; et al. A Framework for Selection of Blood-Based Biomarkers for Geroscience-Guided Clinical Trials: Report from the Tame Biomarkers Workgroup. GeroScience 2018, 40, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvani, R.; Marini, F.; Cesari, M.; Tosato, M.; Anker, S.D.; Von Haehling, S.; Miller, R.R.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F.; Marzetti, E.; et al. Biomarkers for Physical Frailty and Sarcopenia: State of the Science and Future Developments. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2015, 6, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picca, A.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Cesari, M.; Marini, F.; Miccheli, A.; Gervasoni, J.; Bossola, M.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; Marzetti, E.; et al. The Metabolomics Side of Frailty: Toward Personalized Medicine for the Aged. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 126, 110692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, T.E.; McEwen, B.S.; Rowe, J.W.; Singer, B.H. Allostatic Load as a Marker of Cumulative Biological Risk: Macarthur Studies of Successful Aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4770–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, M.D.F.; Moher, D.; Thombs, B.D.; McGrath, T.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Clifford, T.; Cohen, J.F.; Deeks, J.J.; Gatsonis, C.; Hooft, L.; et al. Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies: The Prisma-Dta Statement. JAMA 2018, 319, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated Guidance for Trusted Systematic Reviews: A New Edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, Ed000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, R.J.; Mente, A.; Maroleanu, A.; Cozma, A.I.; Ha, V.; Kishibe, T.; Uleryk, E.; Budylowski, P.; Schünemann, H.; Beyene, J.; et al. Intake of Saturated and Trans Unsaturated Fatty Acids and Risk of All Cause Mortality, Cardiovascular Disease, and Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Laurentius, T.; Fait, Y.; Müller, A.; Mückter, E.; Bollheimer, L.C.; Nourbakhsh, M. Associations of Serum Cxcl12α and Ck Levels with Skeletal Muscle Mass in Older Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-H.; Chang, P.-S.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lin, P.-T. Identification of Coenzyme Q10 and Skeletal Muscle Protein Biomarkers as Potential Factors to Assist in the Diagnosis of Sarcopenia. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.-M.; Zhou, J.-Y. A Combination of Serum Biomarkers in Elderly Patients with Sarcopenia: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 2022, 4026940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.L.; Hau, R.; Taylor, A.; Guerra, M.; Guerra, P.; Darzins, P.; Gilfillan, C. Sarcopenia in Women with Hip Fracture: A Comparison of Hormonal Biomarkers and Their Relationship to Skeletal Muscle Mass and Function. Osteoporos. Sarcopenia 2020, 6, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wumaer, A.; Maimaitiwusiman, Z.; Xiao, W.; Xuekelati, S.; Liu, J.; Musha, T.; Wang, H. Plasma Tumor Necrosis Factor-A Is Associated with Sarcopenia in Elderly Individuals Residing in Agricultural and Pastoral Areas of Xinjiang, China. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 788178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldisi, D.; Abulmeaty, M.M.A.; Alsaawi, T.A.; Alorf, A.S.; Mujlli, G.; Alshahrani, A.M.; Alahmari, R.M.; Alquraishi, M.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Alruwaili, N.W.; et al. Diagnostic Value of Inflammatory Markers in Elderly Arab Women with Sarcopenia. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Deng, M.; Li, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, G. Resistin as a Systemic Inflammation-Related Biomarker for Sarcopenia in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 921399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, B.; Zheng, Z.; Ye, H. Circulating Mir-29b Decrease in Response to Sarcopenia in Patients with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Older Chinese. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1094388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, S.; Singh, S.; Upadhyay, A.D.; Dwivedi, S.N.; Das, C.J.; Mohta, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Dey, A.B.; Chakrawarty, A. Serum Creatinine and Cystatin C-Based Index Can Be a Screening Biomarker for Sarcopenia in Older Population. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 10, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balazs, I.; Stelzer, M.; Traub, J.; Horvath, A.; Feldbacher, N.; Stadlbauer, V. Primary Sarcopenia Is Associated with Elevated Spontaneous Net Formation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1347495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.-F.; Li, S.-T.; Wang, L.-P.; Zhou, N.-L.; Ran, J.-J.; Yang, X.; Tian, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.; Peng, W. Diagnostic Value of Nutritional Risk Index and Other Indices for Predicting Sarcopenia in the Middle-Aged and Elderly Population of China without Cancer: A Roc Curve Analysis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 2527–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, B.; Kara, O.; Kizilarslanoglu, M.C.; Arik, G.; Aycicek, G.S.; Sumer, F.; Civelek, R.; Demirtas, C.; Ulger, Z. Serum Markers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Sarcopenia. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Coelho-Júnior, H.J.; Marini, F.; Landi, F.; Marzetti, E. Circulating Inflammatory, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Senescence-Related Markers in Older Adults with Physical Frailty and Sarcopenia: A Biosphere Exploratory Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Castellano, C.; Martín-Aragón, S.; Bermejo-Bescós, P.; Vaquero-Pinto, N.; Miret-Corchado, C.; de Miguel, A.M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Biomarkers of Sarcopenia in Very Old Patients with Hip Fracture. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ding, F.; Yin, M.; Zhang, H.; Hou, L.; Cui, T.; Xu, J.; Yue, J.; Zheng, Q. High Serum Ast/Alt Ratio and Low Serum Ins*Pa Product Are Risk Factors and Can Diagnose Sarcopenia in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 843610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, Y.; Toyoguchi, T.; Inage, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Orita, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kanamoto, H.; Abe, K.; Norimoto, M.; Umimura, T.; et al. Advanced Glycation End Products Are Associated with Sarcopenia in Older Women: Aging Marker Dynamics. J. Women Aging 2021, 33, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibamoto, A.; Namisaki, T.; Suzuki, J.; Kubo, T.; Iwai, S.; Tomooka, F.; Takeda, S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Enomoto, M.; Murata, K.; et al. Hemoglobin Levels as a Surrogate Marker of Sarcopenia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2023, 53, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsürekci, C.; Ayçiçek, G.Ş.; Çalışkan, H.; Doğrul, R.T.; Neşelioğlu, S.; Özcan, M.; Doğu, B.B.; Cankurtaran, M.; Erel, Ö.; Halil, M.G. Thiol–Disulfide Homeostasis and Ischemia-Modified Albumin as a Marker of Oxidative Stress in Patients with Sarcopenia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2021, 21, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameda, M.; Teruya, T.; Yanagida, M.; Kondoh, H. Reduced Uremic Metabolites Are Prominent Feature of Sarcopenia, Distinct from Antioxidative Markers for Frailty. Aging 2021, 13, 20915–20934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Huang, H.; Hu, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Luo, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, W. Correlation between Sarcopenia and Novel Inflammatory Biomarkers in Elder Adults. Chin. J. Osteoporos. 2024, 30, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Zeng, J.; Ma, H.; Sun, S.; Zhao, Z.; Jing, Y.; Qian, C.; Fei, Z.; Cui, R.; Qu, S.; et al. A New Index Based on Serum Creatinine and Cystatin C Can Predict the Risks of Sarcopenia, Falls and Fractures in Old Patients with Low Bone Mineral Density. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Laurentius, T.; Fait, Y.; Müller, A.; Mückter, E.; Hao, D.; Bollheimer, L.C.; Nourbakhsh, M. Sex-Specific Associations between Serum Il-16 Levels and Sarcopenia in Older Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-J.; Peng, L.-N.; Loh, C.-H.; Chen, L.-K. Sex-Different Associations between Serum Homocysteine, High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Sarcopenia: Results from I-Lan Longitudinal Aging Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 132, 110832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-J.; Lin, C.-M.; Fan, C.-M.; Tang, H.-Y.; Liu, H.-F.; Ho, H.-Y.; Cheng, M.-L. Plasma Acylcarnitine in Elderly Taiwanese: As Biomarkers of Possible Sarcopenia and Sarcopenia. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, A.C.; Boga, J.A.; Millo, C.B.; González, A.R.; Ochoa, Y.P.; Naredo, I.V.; Reig, M.M.; Rizos, L.R.; Jurado, P.M.S.; Solano, J.J.; et al. Potential Early Biomarkers of Sarcopenia Among Independent Older Adults. Maturitas 2017, 104, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-C.; Han, D.-S.; Hsu, C.-C.; Wang, J.-S. Circulating Microrna-486 and Microrna-146a Serve as Potential Biomarkers of Sarcopenia in the Older Adults. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvani, R.; Picca, A.; Marini, F.; Biancolillo, A.; Gervasoni, J.; Persichilli, S.; Primiano, A.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Cesari, M.; Bossola, M.; et al. Identification of Biomarkers for Physical Frailty and Sarcopenia through a New Multi-Marker Approach: Results from the Biosphere Study. Geroscience 2021, 43, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, P.; Wu, C.; Lang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Jin, K.; Chen, L. A Combined Diagnostic Approach Based on Serum Biomarkers for Sarcopenia in Older Patients with Hip Fracture. Australas. J. Ageing 2022, 41, E339–E347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, S.; Nakajima, T.; Nozawa, N.; Katayanagi, S.; Ishizaka, H.; Mizushima, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Nishikawa, K.; Toyama, Y.; Takahashi, R.; et al. Phase Angle as an Indicator of Sarcopenia, Malnutrition, and Cachexia in Inpatients with Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, B.G.; Jung, Y.; Baek, K.; Song, M.; Cho, M. Comparative Analysis of the Association between Various Serum Vitamin D Biomarkers and Sarcopenia. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.E.; Won, C.W.; Kim, M. Metabolomic Profiles to Explore Biomarkers of Severe Sarcopenia in Older Men: A Pilot Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 167, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzetti, E.; Calvani, R.; Lorenzi, M.; Marini, F.; D’Angelo, E.; Martone, A.M.; Celi, M.; Tosato, M.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. Serum Levels of C-Terminal Agrin Fragment (Caf) Are Associated with Sarcopenia in Older Hip Fractured Patients. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 60, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L. Correlation Study of Serum Creatinine/Cystatin C and Sarcopenia. Chin. J. Geriatr. 2023, 42, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Shibamoto, A.; Namisaki, T.; Suzuki, J.; Kubo, T.; Iwai, S.; Tomooka, F.; Takeda, S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Inoue, T.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Hemoglobin and Endotoxin Levels Predict Sarcopenia Occurrence in Patients with Alcoholic Cirrhosis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Cui, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.-C.; Ma, L.-L.; Yang, H.-N.; Wen, F.-M. Circulating Mirna-1-3p as Biomarker of Accelerated Sarcopenia in Patients Diagnosed with Chronic Heart Failure. Rev. Investig. Clin. Clin. Transl. Investig. 2022, 74, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbeni, A.; Natola, L.A.; Garbin, M.; Zoncapè, M.; Cattazzo, F.; Mantovani, A.; Vella, A.; Canè, S.; Kassem, J.; Bevilacqua, M.; et al. Interleukin-6: A New Marker of Advanced-Sarcopenic Hcc Cirrhotic Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Xie, L.; Tan, L.; Hu, X.; Yang, M. Inflammatory Indexes Are Not Associated with Sarcopenia in Chinese Community-Dwelling Older People: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.E.; Won, C.W.; Kim, M. Development of Multiple Biomarker Panels for Prediction of Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2023, 115, 105115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Ding, F.; Hou, L.; Deng, Y.; Cui, T.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. Determination of Skeletal Muscle Mass by Aspartate Aminotransferase / Alanine Aminotransferase Ratio, Insulin and Fsh in Chinese Women with Sarcopenia. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, T.; Yajima, K. Serum Creatinine-to-Cystatin C Ratio as an Indicator of Sarcopenia in Hemodialysis Patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 56, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Kao, T.-W.; Peng, T.-C.; Yang, H.-F.; Chen, W.-L. Cross-Sectional Associations among P3np, Htra, Hsp70, Apelin and Sarcopenia in Taiwanese Population. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, Z.A.; Kul, S.; Türkbeyler, I.H.; Sayıner, Z.A.; Abiyev, A. Is Increased Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio Remarking the Inflammation in Sarcopenia? Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 110, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.; Wang, S.; Chang, C.; Chen, C.; Wen, C.; Chen, G.; Kuo, C.; Tseng, Y.J. Identification of Traumatic Acid as a Potential Plasma Biomarker for Sarcopenia Using a Metabolomics-Based Approach. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Yang, J.-Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.-X.; Zhong, X.-Y. Altered Levels of Circulating Mitochondrial DNA in Elderly People with Sarcopenia: Association with Mitochondrial Impairment. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 163, 111802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Okada, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Takahashi, F.; Okamura, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Nakanishi, N.; Senmaru, T.; Ushigome, E.; Hamaguchi, M.; et al. Leucine and Glutamic Acid as a Biomarker of Sarcopenic Risk in Japanese People with Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, A.; Hawke, P.; Tokuda, S.; Toda, T.; Higashizono, K.; Nagai, E.; Watanabe, M.; Nakatani, E.; Kanemoto, H.; Oba, N. Serum Carnitine as a Biomarker of Sarcopenia and Nutritional Status in Preoperative Gastrointestinal Cancer Patients. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawin, B.; Tylutka, A.; Bielewicz, F.; Zembron-Lacny, A. Diagnostics of Inflammaging in Relation to Sarcopenia. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1162385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Imaoka, M.; Sakai, K.; Kubo, T.; Imai, R.; Hida, M.; Tazaki, F.; Orui, J.; Inoue, T.; Takeda, M. Complement Component C3 Is Associated with Body Composition Parameters and Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in Japan. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-L.; Li, Y.-R.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Li, M.-L.; Jia, K.-Y.; Sun, H.-X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Lu, X.; Gao, W. Serum Retinol Binding Protein 4 as a Potential Biomarker for Sarcopenia in Older Adults. Journals Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 78, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-L.; Chen, D.-M.; Luo, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Huang, C.-Q.; Zhao, K.-X.; Xiao, Q. Fibrinogen, Fibrin Degradation Products and Risk of Sarcopenia. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4830–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jin, C.; Yin, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. Relationship between Serum Bilirubin Concentration and Sarcopenia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 03000605211004226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Levels and Their Correlation of Testosterone, Estradiol and Il-6 in Elderly Men with Different Sarcopenia Stages. Chin. J. Osteoporos. Bone Miner. Res. 2021, 14, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.-S.; Kim, H.C.; Zhang, D.; Yeom, H.; Lim, S.-K. The Novel Myokine Irisin: Clinical Implications and Potential Role as a Biomarker for Sarcopenia in Postmenopausal Women. Endocrine 2019, 64, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, A.; Silay, K.; Balik, A.R.; Avcioğlu, G.; Aydin, A.S. The Relationship between Plasma Interleukin-15 Levels and Sarcopenia in Outpatient Older People. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.A.C.; Soares, L.A.; Parentoni, A.N.; Nobre, J.N.P.; Figueiredo, P.H.S.; Leopoldino, A.A.O.; Avelar, N.C.P.; Mendonça, V.A.; Lacerda, A.C.R. Inflammatory Biomarkers of Osteosarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Woman. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2024, 55, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Ji, E.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, K.; Ji, S.; Baek, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, H.-W.; Jang, I.-Y.; Lee, E.; et al. Circulating Lumican as a Potential Biomarker for Osteosarcopenia in Older Adults. Bone 2024, 179, 116959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Shin, H.E.; Won, C.W.; Kim, M. Comparison of the Serum Creatinine- and Cystatin-C–Based Indices as Screening Biomarkers for Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2023, 115, 105207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cao, X.; Yang, Q. Correlation between Muscle Mass Reduction and Serum Uric Acid and Urinary Albumin in Middle-Aged and Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Men. J. Men’s Health 2023, 19, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-J.; Lee, W.-J.; Peng, L.-N.; Huang, Y.-L.; Tung, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Tsai, T.-F.; Chen, L.-K. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-A Is Potentially Better Than Tumor Necrosis Factor-A as the Biomarker for Sarcopenia: Results from the I-Lan Longitudinal Aging Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 172, 112053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Lorenzi, M.; Martone, A.M.; Tosato, M.; Drey, M.; D’Angelo, E.; Capoluongo, E.; Russo, A.; Bernabei, R.; et al. Serum Levels of C-Terminal Agrin Fragment (Caf) Are Associated with Sarcopenia in Older Multimorbid Community-Dwellers: Results from the Ilsirente Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 79, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciatore, F.; Della-Morte, D.; Basile, C.; Curcio, F.; Liguori, I.; Roselli, M.; Gargiulo, G.; Galizia, G.; Bonaduce, D.; Abete, P. Butyryl-Cholinesterase Is Related to Muscle Mass and Strength. A New Biomarker to Identify Elderly Subjects at Risk of Sarcopenia. Biomarkers Med. 2015, 9, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Karagounis, L.G.; Ng, T.P.; Carre, C.; Narang, V.; Wong, G.; Tan, C.T.Y.; Nyunt, M.S.Z.; Gao, Q.; Abel, B.; et al. Systemic and Metabolic Signature of Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2019, 75, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Bao, Z.; Fan, Y. C-Reactive Protein Level as a Novel Serum Biomarker in Sarcopenia. Mediat. Inflamm. 2024, 2024, 3362336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanat, B.B.; Suzan, V.; Avci, G.U.; Unal, D.; Gedik, T.E.; Erdincler, D.S.; Doventas, A.; Yavuzer, H. Systemic Inflammatory Response Index and Monocyte-to-High Density Lipoprotein Ratio- New Biomarkers Remarking the Inflammation in Primary Sarcopenia: The Simps Study. Bratisl. Med. J. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2024, 125, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Di Ciaula, A.; Jaber, N.; Grandolfo, R.; Fiermonte, F.; Portincasa, P. Multidimensional Assessment of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity in Geriatric Patients: Creatinine/Cystatin C Ratio Performs Better than Sarcopenia Index. Metabolites 2024, 14, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, D.d.C.; Oliveira, S.d.C.; Vieira, D.C.L.; Funghetto, S.S.; Silva, A.O.; Valduga, R.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Prestes, J. The Impact of Sarcopenic Obesity on Inflammation, Lean Body Mass, and Muscle Strength in Elderly Women. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2018, 11, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.C.; Duarte, J.G.; Gomes, G.A.; Costa-Guarisco, L.P.; de Jesus, I.T.; Nascimento, C.M.; Santos-Orlandi, A.A.; Orlandi, F.S.; Vasilceac, F.A.; Zazzetta, M.S.; et al. Associations between Inflammatory Markers and Muscle Strength in Older Adults According to the Presence or Absence of Obesity. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 151, 111409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, S.; Won, Y.J.; Kim, S.H. Clinical Manifestations and Factors Associated with Osteosarcopenic Obesity Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study in Koreans with Obesity. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2019, 105, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, M.T.; Avelar, B.P.; Souza, V.C.; Bottaro, M.; Oliveira, R.J.; Nóbrega, O.T.; Moreno Lima, R. Relationship between Sarcopenic Obesity-Related Phenotypes and Inflammatory Markers in Postmenopausal Women. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2017, 37, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-W.; Li, C.-I.; Li, T.-C.; Liu, C.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Lin, W.-Y.; Lin, C.-C. Association of Sarcopenic Obesity with Higher Serum High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels in Chinese Older Males—A Community-Based Study (Taichung Community Health Study-Elderly, Tchs-E). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendham, A.E.; Goedecke, J.H.; Micklesfield, L.K.; Brooks, N.E.; Faber, M.; Christensen, D.L.; Gallagher, I.J.; Lundin-Olsson, L.; Myburgh, K.H.; Odunitan-Wayas, F.A.; et al. Understanding Factors Associated with Sarcopenic Obesity in Older African Women from a Low-Income Setting: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Peroni, G.; Faliva, M.A.; Bartolo, A.; Naso, M.; Miccono, A.; Rondanelli, M. Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity in Comparison: Prevalence, Metabolic Profile, and Key Differences. A Cross-Sectional Study in Italian Hospitalized Elderly. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, S.; KA, A.S.; VM, V. Trop T, Hand Grip Strength and Waist Circumference as Markers of Sarcopenic Obesity in Postmenopausal Women: An Analytical Cross-Sectional Study. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2024, 68, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantin, F.; Giani, A.; Manzato, G.; Zampieri, A.; Comellato, G.; Urbani, S.; Zoico, E.; Mazzali, G.; Zamboni, M. Sarcopenia, Sarcopenic Obesity, and Arterial Stiffness among Older Adults. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1272854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri-Najafabady, N.; Dabbaghmanesh, M.H.; Nasimi, N.; Sohrabi, Z.; Chatrabnous, N. The Association between Tp53 Rs1625895 Polymorphism and the Risk of Sarcopenic Obesity in Iranian Older Adults: A Case-Control Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Cumming, R.; Naganathan, V.; Blyth, F.; Le Couteur, D.G.; Handelsman, D.J.; Seibel, M.; Waite, L.M.; Hirani, V. Associations of Sarcopenic Obesity with the Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance over Five Years in Older Men: The Concord Health and Ageing in Men Project. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 108, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Spadaccini, D.; Nichetti, M.; Avanzato, I.; Faliva, M.A.; Rondanelli, M. Osteosarcopenic Visceral Obesity and Osteosarcopenic Subcutaneous Obesity, Two New Phenotypes of Sarcopenia: Prevalence, Metabolic Profile, and Risk Factors. J. Aging Res. 2018, 2018, 6147426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, E.P.; Gadelha, A.B.; Safons, M.P.; Nóbrega, O.T.; Oliveira, R.J.; Lima, R.M. Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity Classifications and Cardiometabolic Risks in Older Women. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2014, 59, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-W.; Yang, K.-C.; Chang, H.-H.; Lee, L.-T.; Chen, C.-Y.; Huang, K.-C. Sarcopenic Obesity Is Closely Associated with Metabolic Syndrome. Obes. Res. Clin. Pr. 2013, 7, e301–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hao, Q.; Yue, J.; Hou, L.; Xia, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, M.; Ge, N.; Dong, B. Sarcopenia, Obesity and Sarcopenia Obesity in Comparison: Prevalence, Metabolic Profile, and Key Differences: Results from Wchat Study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picca, A.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Calvani, R.; Marzetti, E.; Vetrano, D.L. Biomarkers Shared by Frailty and Sarcopenia in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 73, 101530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, C.S.; Thang, L.A.; Maier, A.B. Markers of Inflammation and Their Association with Muscle Strength and Mass: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, G.; Trevisan, C.; Carraro, S.; Solmi, M.; Luchini, C.; Stubbs, B.; Manzato, E.; Sergi, G.; Veronese, N. Inflammation and Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Maturitas 2017, 96, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzik, K.P.; Kaczor, J.J. Mechanisms of Vitamin D on Skeletal Muscle Function: Oxidative Stress, Energy Metabolism and Anabolic State. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, C.M.; Brightwell, C.R.; Keeble, A.R.; Munson, B.D.; Thomas, N.T.; Zagzoog, A.M.; Fry, C.S.; Fry, J.L. Vitamin D Promotes Skeletal Muscle Regeneration and Mitochondrial Health. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 660498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. Excess Triglycerides in Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (Vldl) Estimated from Vldl-Cholesterol Could Be a Useful Biomarker of Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2025, 32, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Sathyanarayan, A.; Lopresti, M.; Aghajan, M.; Chen, C.; Mashek, D.G. Lipophagy-Derived Fatty Acids Undergo Extracellular Efflux Via Lysosomal Exocytosis. Autophagy 2021, 17, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, I.; Oguri, Y.; Verkerke, A.R.; Monteiro, L.B.; Knuth, C.M.; Auger, C.; Qiu, Y.; Westcott, G.P.; Cinti, S.; Shinoda, K.; et al. Lipolysis-Derived Linoleic Acid Drives Beige Fat Progenitor Cell Proliferation. Dev. Cell 2022, 57, 2623–2637.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fougerat, A.; Schoiswohl, G.; Polizzi, A.; Régnier, M.; Wagner, C.; Smati, S.; Fougeray, T.; Lippi, Y.; Lasserre, F.; Raho, I.; et al. Atgl-Dependent White Adipose Tissue Lipolysis Controls Hepatocyte Pparα Activity. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahas, P.C.; Rossato, L.T.; de Branco, F.M.; Azeredo, C.M.; Rinaldi, A.E.M.; de Oliveira, E.P. Serum Uric Acid Is Positively Associated with Muscle Strength in Older Men and Women: Findings from Nhanes 1999–2002. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4386–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, C.P.; Wilkens, L.R.; Shvetsov, Y.B.; Maskarinec, G.; Park, S.-Y.; Shepherd, J.A.; Boushey, C.J.; Hebert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Ernst, T.; et al. Associations of the Dietary Inflammatory Index with Total Adiposity and Ectopic Fat through the Gut Microbiota, Lps, and C-Reactive Protein in the Multiethnic Cohort-Adiposity Phenotype Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, K.-A.; Mahurkar, S.; Alderete, T.L.; Hasson, R.E.; Adam, T.C.; Kim, J.S.; Beale, E.; Xie, C.; Greenberg, A.S.; Allayee, H.; et al. Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Macrophage Infiltration Is Associated with Hepatic and Visceral Fat Deposition, Hyperinsulinemia, and Stimulation of Nf-Κb Stress Pathway. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2802–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, S.K.; Voulgaridou, G.; Kondyli, F.S.; Drakaki, M.; Sianidou, K.; Andrianopoulou, R.; Rodopaios, N.; Pritsa, A. Nutritional and Nutrition-Related Biomarkers as Prognostic Factors of Sarcopenia, and Their Role in Disease Progression. Diseases 2022, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Xue, Y.; Hu, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, G.; Shi, Q.; Rui, Y. Irisin Alleviates Obesity-Induced Bone Loss by Inhibiting Interleukin 6 Expression Via Tlr4/Myd88/Nf-Κb Axis in Adipocytes. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 69, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Lynch, G.S.; Murphy, K.T.; Reid, M.B.; Zijdewind, I. Disease-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy and Fatigue. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizário, J.E.; Fontes-Oliveira, C.C.; Borges, J.P.; Kashiabara, J.A.; Vannier, E. Skeletal Muscle Wasting and Renewal: A Pivotal Role of Myokine Il-6. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Parini, P.; Giuliani, C.; Santoro, A. Inflammaging: A New Immune-Metabolic Viewpoint for Age-Related Diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frikke-Schmidt, H.; Zamarron, B.F.; O’Rourke, R.W.; Sandoval, D.A.; Lumeng, C.N.; Seeley, R.J. Weight Loss Independent Changes in Adipose Tissue Macrophage and T Cell Populations after Sleeve Gastrectomy in Mice. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herro, R.; Grimes, H.L. The Diverse Roles of Neutrophils from Protection to Pathogenesis. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockenbrough, A.T.; Dittrich, M.O.; Page, S.T.; Smith, T.; Stivelman, J.C.; Bremner, W.J. Transdermal Androgen Therapy to Augment Epo in the Treatment of Anemia of Chronic Renal Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2006, 47, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, M.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Chen, X.; An, J.; Lu, H. Leptin Promotes the Proliferation and Neuronal Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells through the Cooperative Action of Mapk/Erk1/2, Jak2/Stat3 and Pi3k/Akt Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, M.; Zhang, L.; Halasz, N.A.; Hunter, T.; Chojkier, M. Nuclear Export of Phosphorylated C/Ebpbeta Mediates the Inhibition of Albumin Expression by Tnf-Alpha. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6712–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, J.; Chanet, A.; Guillet, C.; Vaes, A.M.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Rocher, C.; Giraudet, C.; Patrac, V.; Meugnier, E.; Montaurier, C.; et al. Vitamin D Status Modulates Mitochondrial Oxidative Capacities in Skeletal Muscle: Role in Sarcopenia. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, S.P.; Bass, J.J.; Kazi, A.A.; Atherton, P.J.; Philp, A. The Vitamin D Receptor Regulates Mitochondrial Function in C2c12 Myoblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C536–C541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; Kye, S.; Chung, Y.; Lee, O. Association of Serum Vitamin D with Osteosarcopenic Obesity: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2010. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Marwaha, R.K.; Kumar, P.; Narang, A.; Devi, M.M.; Tripathi, R.P.; Khushu, S. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Muscle Energy Phospho-Metabolites: A ³¹p Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy-Based Pilot Study. Endocr. Res. 2014, 39, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusi-Rasi, K.; Patil, R.; Karinkanta, S.; Kannus, P.; Tokola, K.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Sievänen, H. Exercise and Vitamin D in Fall Prevention among Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lim, W.S.; Jin, X.; Nyunt, M.S.Z.; Fulop, T.; Gao, Q.; Lim, S.C.; Larbi, A.; Ng, T.P. Lower Insulin Level Is Associated with Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Frail and Non-Frail Older Adults. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 971622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, I.M.; Gibson, D.S.; McGilligan, V.; McNerlan, S.E.; Alexander, H.D.; Ross, O.A. Age and Age-Related Diseases: Role of Inflammation Triggers and Cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesbertz, P.; Brandl, B.; Volkert, D.; Hauner, H.; Skurk, T. Age-Related Metabolite Profiles and Their Relation to Clinical Outcomes in Young Adults, Middle-Aged Individuals, and Older People. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2023, 37, e22968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjia, J.; Rothman, M.R.; Kiely, D.K.; Shaffer, M.L.; Holmes, H.M.; Sachs, G.A.; Mitchell, S.L. Daily Medication Use in Nursing Home Residents with Advanced Dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, B.; Godos, J.; Varrasi, S.; Roggio, F.; Castellano, S.; Musumeci, G. Physical Activity, Sun Exposure, Vitamin D Intake and Perceived Stress in Italian Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mahendran, R.; Yu, P.; Xu, R.; Yu, W.; Godellawattage, S.; Li, S.; Guo, Y. Health Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Pm(2.5) in Asia-Pacific: A Systematic Review of Cohort Studies. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2022, 9, 130–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Sánchez, M.; Navas-Carrillo, D.; Orenes-Piñero, E. Controversies Surrounding High-Protein Diet Intake: Satiating Effect and Kidney and Bone Health. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gao, X.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Socioeconomic Status, Diet, and Behavioral Factors and Cardiometabolic Diseases and Mortality. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2451837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, A.; Sun, G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Li, G. Relationship between Metabolic Status, Physical Activity and Cardiovascular Disease in Participants with Obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E. Treatment of Sarcopenia: The Road to the Future. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sarcopenia (n = 66) | Sarcopenic Obesity (n = 16) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMD | 95% CI | I2 | SMD | 95% CI | I2 | |
| Metabolic | ||||||
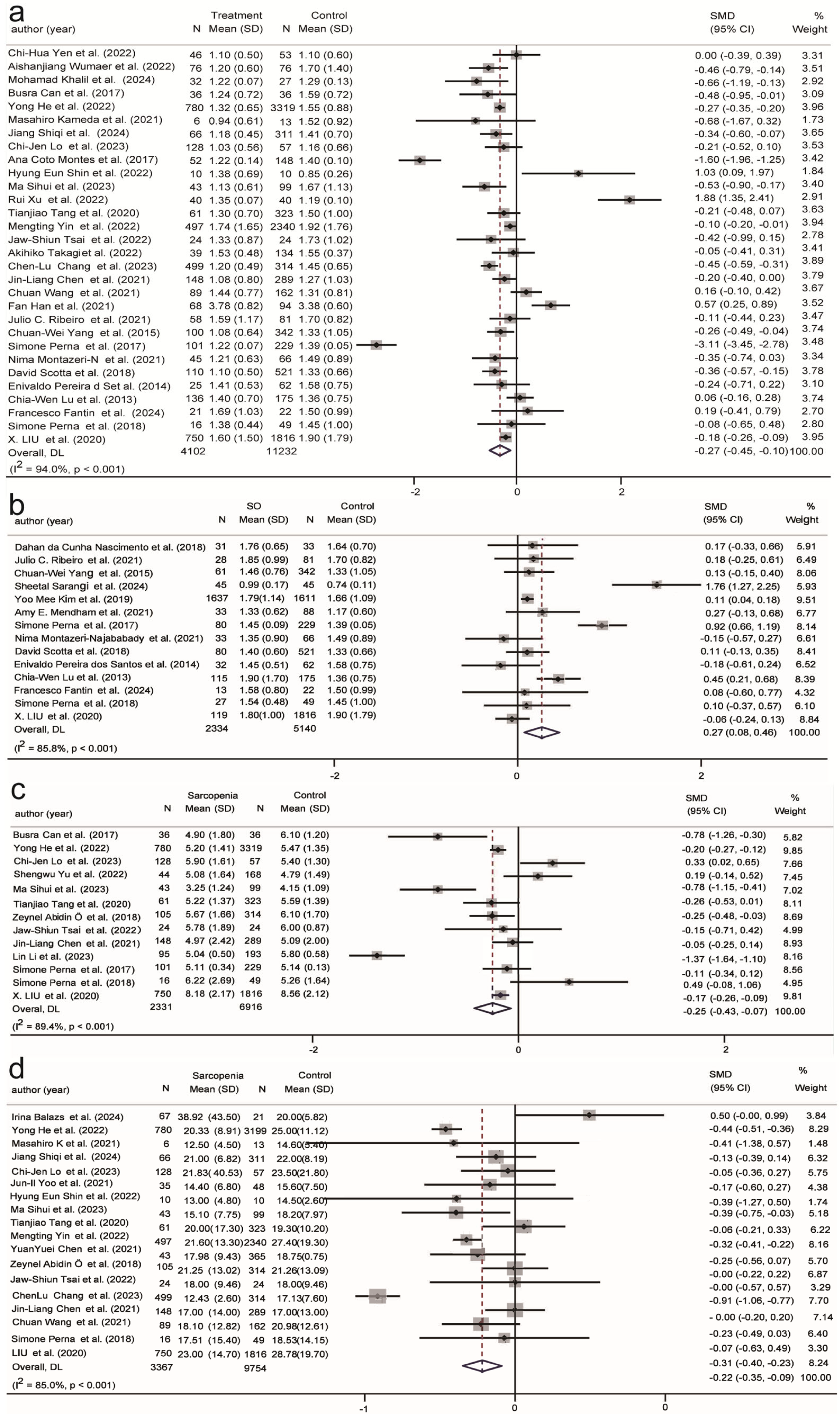
| Glucose (9/11) | −0.10 | −0.25, 0.04 | 87.1% | 0.00 | −0.19, 0.19 | 77.1% |
| Cholesterol (33/12) | −0.13 | −0.32, 0.07 | 95.8% | −0.07 | −0.37, 0.22 | 93.0% |
| Triglycerides (30/14) | −0.27 | −0.45, −0.10 | 94.0% | 0.27 | 0.08, 0.46 | 85.8% |
| HDL (26/12) | 0.15 | −0.03, 0.34 | 94.6% | −0.16 | −0.41, 0.09 | 90.9% |
| LDL (25/9) | 0.14 | −0.02, 0.30 | 91.5% | 0.10 | −0.03, 0.22 | 41.4% |
| Creatinine (26/6) | 0.04 | −0.07, 0.15 | 77.7% | 0.25 | −0.60, 0.11 | 96.6% |
| Uric acid (13/4) | −0.25 | −0.43, −0.07 | 89.4% | 1.14 | −0.35, 2.64 | 98.8% |
| ALT (18/3) | −0.22 | −0.35, −0.09 | 85.0% | −0.02 | −0.15, 0.10 | 38.8% |
| AST (17/3) | 0.02 | −0.04, 0.09 | 36.9% | 0.05 | −0.02, 0.12 | 3.0% |
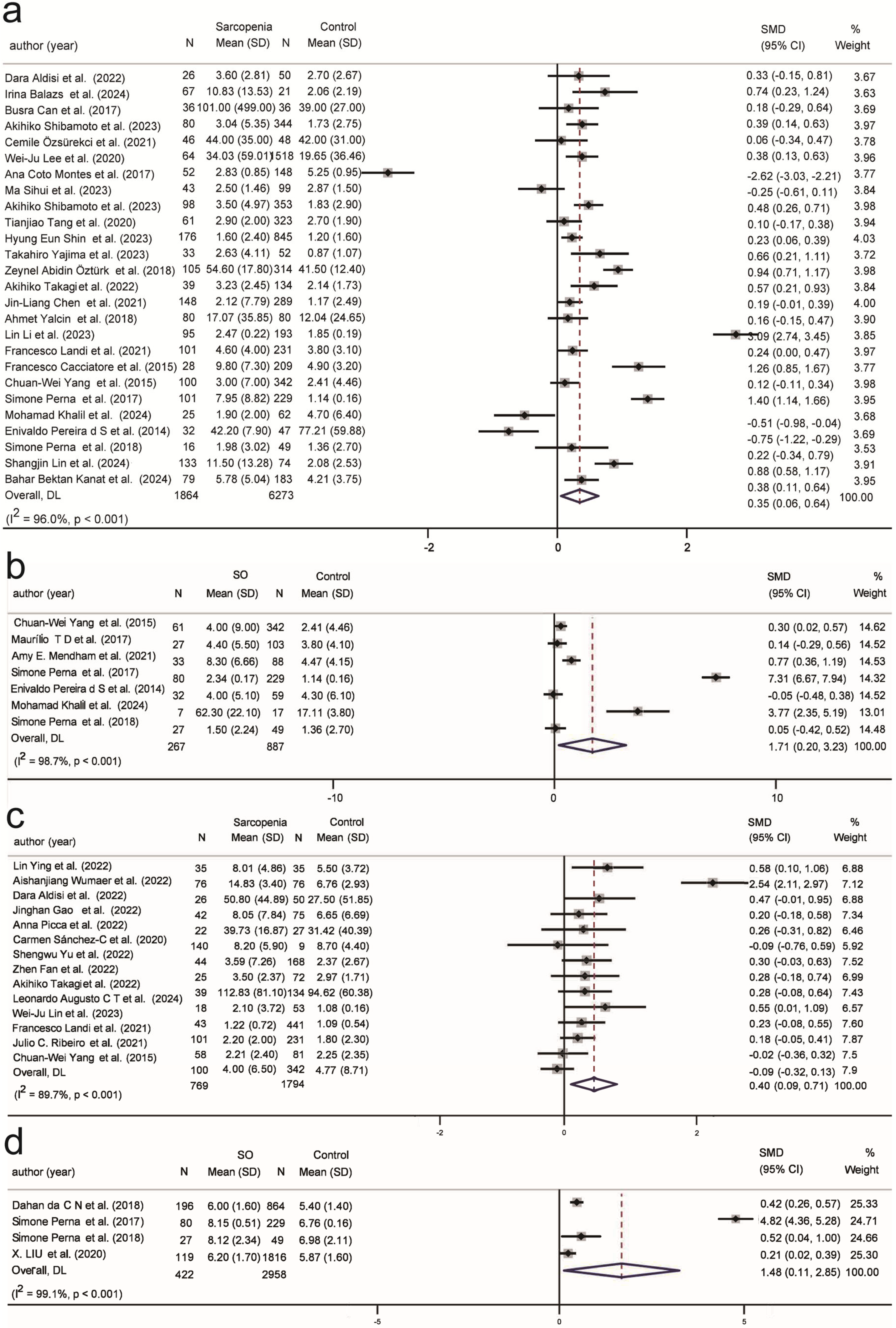
| Inflammatory | ||||||
| IL-6 (17/5) | 0.25 | −0.01, 0.52 | 88.7% | 0.07 | −0.24, 0.38 | 56.9% |
| TNF-α (14/3) | 0.40 | 0.09, 0.71 | 89.7% | −0.10 | −0.30, 0.10 | 0.0% |
| CRP (26/7) | 0.35 | 0.06, 0.64 | 96.0% | 1.71 | 0.20, 3.23 | 98.7% |
| WBC (18/4) | 0.07 | −0.19, 0.32 | 96.2% | 1.48 | 0.11, 2.85 | 99.1% |
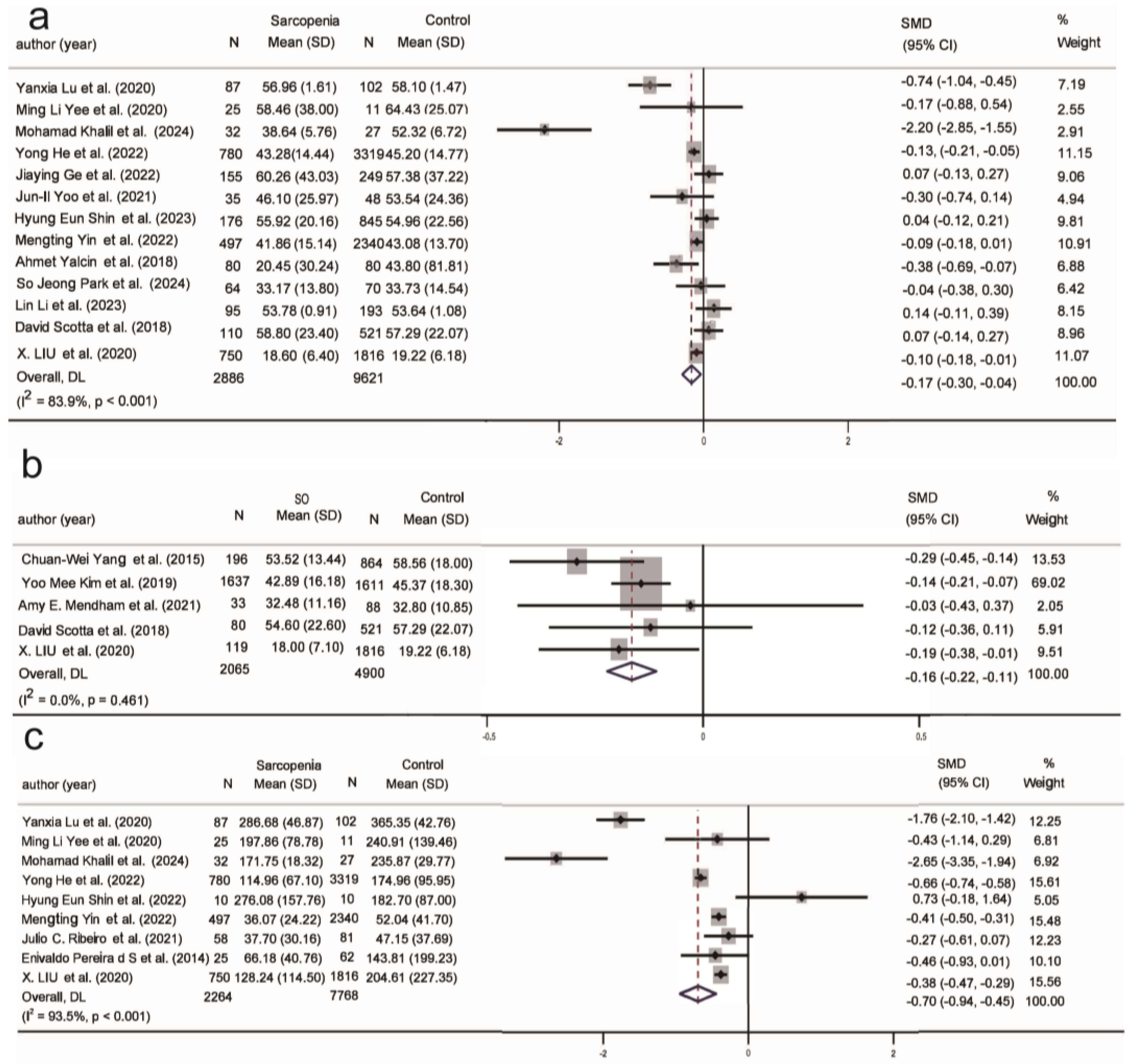
| Hematologic | ||||||
| ALB (36/4) | −0.58 | −0.75, −0.42 | 94.2% | −1.33 | −3.25, 0.60 | 99.1% |
| HB (23/3) | −0.59 | −0.85, −0.33 | 94.4% | 0.09 | −0.09, 0.27 | 32% |
| Hormonal | ||||||
| 25(OH)D (13/5) | −0.17 | −0.30, −0.04 | 83.9% | −0.16 | −0.22, −0.11 | 0.0% |
| Insulin (9/4) | −0.70 | −0.94, −0.45 | 93.5% | 0.09 | −0.14, 0.32 | 75.7% |
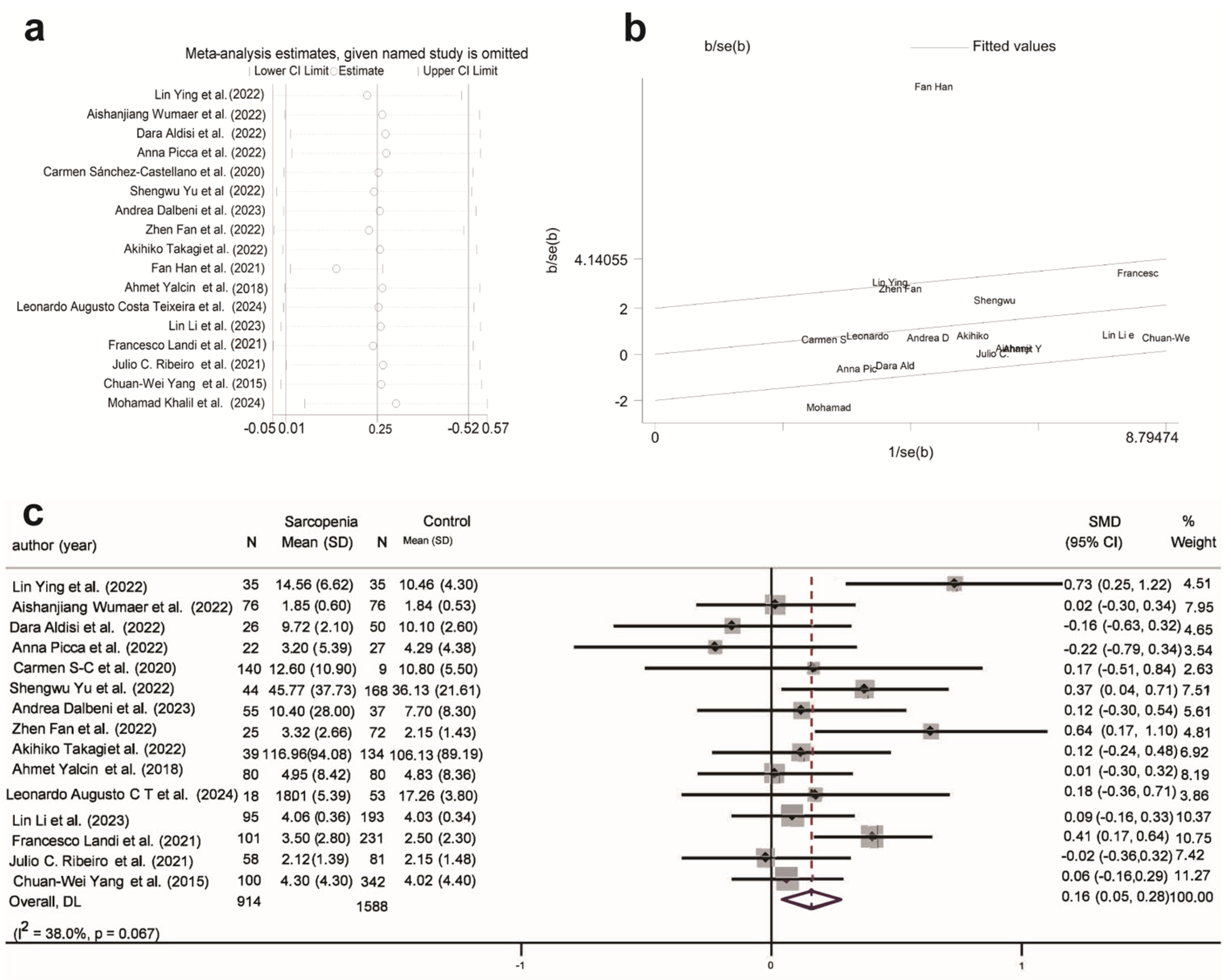
| SMD | 95% CI | I2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 (15) | Overall | 0.16 | 0.05, 0.28 | 38.0% |
| Age | <75 | 0.14 | 0.00, 0.28 | 34.3% |
| >75 | 0.21 | −0.02, 0.43 | 44.4% | |
| Setting | Hospitalized | 0.24 | 0.07, 0.42 | 39.8% |
| Community-dwelling | 0.09 | −0.08, 0.25 | 38.3% | |
| DC/LDC | DC | 0.20 | −0.01, 0.40 | 24.3% |
| LDC | 0.16 | 0.01, 0.30 | 44.8% | |
| Gender (male/female) | <1 | 0.13 | −0.01, 0.27 | 24.7% |
| >1 | 0.26 | 0.02, 0.50 | 61.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Z.; Xia, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, S.; Yang, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, W.; Wang, S.; et al. Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Biomarker Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115113
Feng Z, Xia J, Yu J, Wang J, Yin S, Yang J, Wu T, Zhang Z, Yan W, Wang S, et al. Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Biomarker Evidence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115113
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Zhiyuan, Jiayue Xia, Junhui Yu, Jiongnan Wang, Shiyu Yin, Jingyi Yang, Tianyu Wu, Zhenzhen Zhang, Wei Yan, Shaokang Wang, and et al. 2025. "Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Biomarker Evidence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115113
APA StyleFeng, Z., Xia, J., Yu, J., Wang, J., Yin, S., Yang, J., Wu, T., Zhang, Z., Yan, W., Wang, S., & Sun, G. (2025). Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Biomarker Evidence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115113









