Circulating N-Acetylaspartate Levels Associate with Measures of Peripheral and Tissue-Specific Insulin Sensitivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
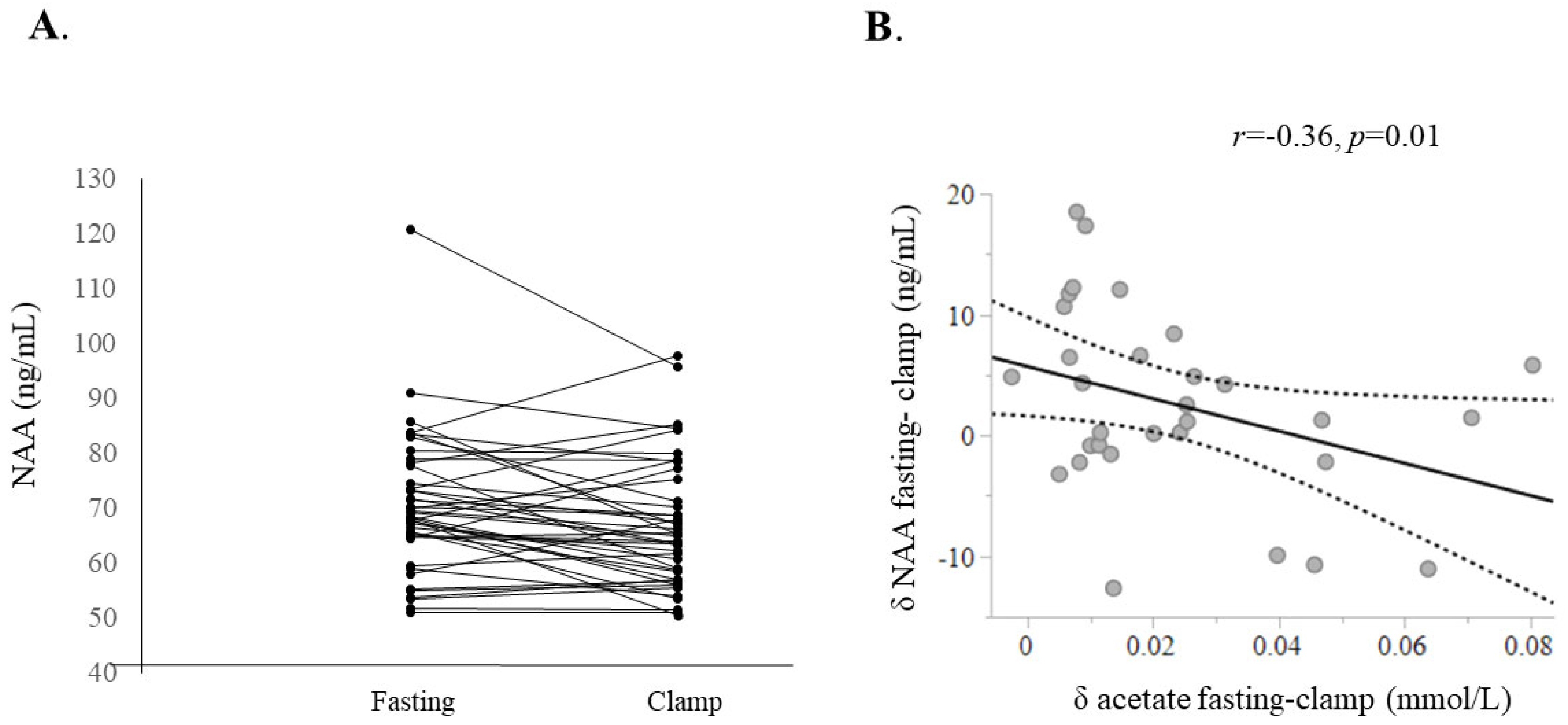
2.1. Fasting vs. Insulin Clamp Experiments
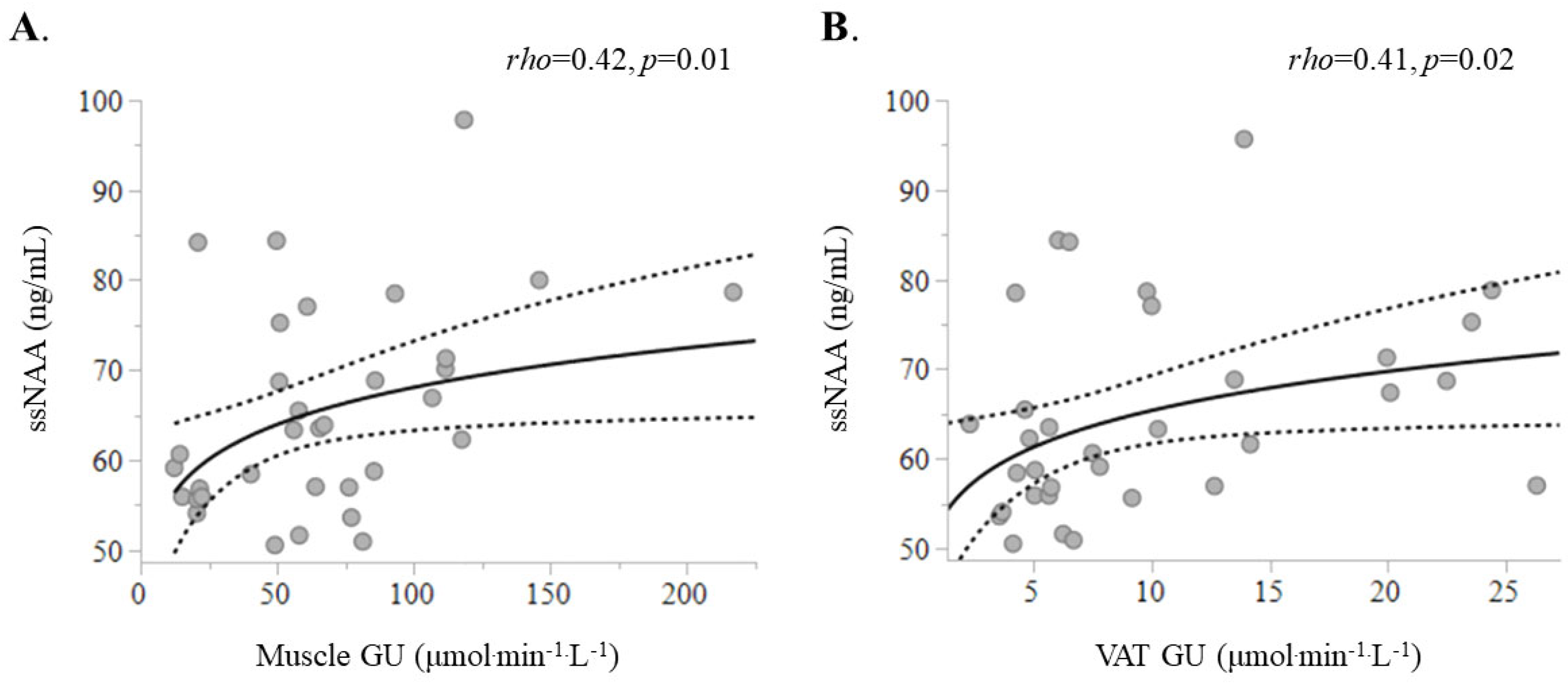
2.2. Associations Between ssNAA Levels with Metabolic Markers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baslow, M.H. N-Acetylaspartate and N-Acetylaspartylglutamate in Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology, 3rd ed.; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baslow, M.H. N-acetylaspartate in the vertebrate brain: Metabolism and function. Neurochem. Res. 2003, 28, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Schuff, N.; Kornak, J.; Soher, B.; Yaffe, K.; Kramer, J.H.; Ezekiel, F.B.; Miller, B.L.; Jagust, W.J.; Weiner, M.W. Effects of Alzheimer disease on fronto-parietal brain N-acetyl aspartate and myo-inositol using magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2006, 20, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.; Atiya, S.; Fogarty, J.; Montero-Odasso, M.; Pasternak, S.H.; Brymer, C.; Borrie, M.J.; Bartha, R. Reduced Hippocampal Glutamate and Posterior Cingulate N-Acetyl Aspartate in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease Is Associated with Episodic Memory Performance and White Matter Integrity in the Cingulum: A Pilot Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 73, 1385–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.; Song, X.; Zhu, C.; Patrick, R.; Skurla, M.; Santangelo, I.; Green, M.; Harper, D.; Ren, B.; Forester, B.P.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and metabolic alterations in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 72, 101503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Iacobaeus, E.; Khademi, M.; Brundin, L.; Norgren, N.; Koel-Simmelink, M.J.A.; Schepens, M.; Bouwman, F.; Twaalfhoven, H.A.; Blom, H.J.; et al. Combination of CSF N-acetylaspartate and neurofilaments in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2009, 72, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardini, M.; Botzkowski, D.; Müller, S.; Vehoff, J.; Kuhle, J.; Ruberte, E.; Würfel, J.; Gass, A.; Valmaggia, C.; Tettenborn, B.; et al. The association between retinal nerve fibre layer thickness and N-acetyl aspartate levels in multiple sclerosis brain normal-appearing white matter: A longitudinal study using magnetic resonance spectroscopy and optical coherence tomography. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 1769–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, L.M.; Reynolds, G.P. Differential regional N-acetylaspartate deficits in postmortem brain in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croarkin, P.E.; Thomas, M.A.; Port, J.D.; Baruth, J.M.; Choi, D.-S.; Abulseoud, O.A.; Frye, M.A. N-acetylaspartate normalization in bipolar depression after lamotrigine treatment. Bipolar Disord. 2015, 17, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, G.; Campi, B.; Saba, A.; Codini, S.; Ciccarone, A.; Giusti, L.; Del Prato, S.; Esterline, R.L.; Ferrannini, E. Plasma N-Acetylaspartate Is Related to Age, Obesity, and Glucose Metabolism: Effects of Antidiabetic Treatment and Bariatric Surgery. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dirbashi, O.Y.; Rashed, M.S.; Al-Qahtani, K.; Al-Mokhadab, M.A.; Kurdi, W.; Al-Sayed, M.A.A. Quantification of N-acetylaspartic acid in urine by LC-MS/MS for the diagnosis of Canavan disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner-Strauss, J.G. N-Acetylaspartate Metabolism Outside the Brain: Lipogenesis, Histone Acetylation, and Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelos, E.; Latva-Rasku, A.; Koskensalo, K.; Pekkarinen, L.; Saukko, E.; Ihalainen, J.; Honka, M.-J.; Tuisku, J.; Bucci, M.; Laurila, S.; et al. Insulin-stimulated brain glucose uptake correlates with brain metabolites in severe obesity: A combined neuroimaging study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2024, 44, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelos, E.; Daniele, G.; Campi, B.; Saba, A.; Koskensalo, K.; Ihalainen, J.; Saukko, E.; Nuutila, P.; Backes, W.H.; Jansen, J.F.A.; et al. Circulating N-Acetylaspartate does not track brain NAA concentrations, cognitive function or features of small vessel disease in humans. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlinguet, L.; Laliberté, M. Metabolism of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid in mice. Can. J. Biochem. 1966, 44, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Eichler, F.; Bley, A.; Bredow, J.; Fay, A.; Townsend, E.L.; Leiro, B.; Shaywitz, A.; Laforet, G.; Crippen-Harmon, D.; et al. Urine N-Acetylaspartate Distinguishes Phenotypes in Canavan Disease. Hum. Gene Ther. 2024, 36, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessentheiner, A.R.; Pelzmann, H.J.; Walenta, E.; Schweiger, M.; Groschner, L.N.; Graier, W.F.; Kolb, D.; Uno, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Nitta, A.; et al. NAT8L (N-acetyltransferase 8-like) accelerates lipid turnover and increases energy expenditure in brown adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 36040–36051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hession, A.O.; Esrey, E.G.; Croes, R.A.; Maxwell, C.A. N-acetylglutamate and N-acetylaspartate in soybeans (Glycine max L.), maize (Zea mays L.), and other foodstuffs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9121–9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, S.; Matalon, R.; Tyring, S.K. Upregulation of aspartoacylase activity in the duodenum of obesity induced diabetes mouse: Implications on diabetic neuropathy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 345, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyannur, P.S.; Moffett, J.R.; Manickam, P.; Pattabiraman, N.; Arun, P.; Nitta, A.; Nabeshima, T.; Madhavarao, C.N.; Namboodiri, A.M. Methamphetamine-induced neuronal protein NAT8L is the NAA biosynthetic enzyme: Implications for specialized acetyl coenzyme A metabolism in the CNS. Brain Res. 2010, 1335, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokesch, A.; Pelzmann, H.J.; Pessentheiner, A.R.; Huber, K.; Madreiter-Sokolowski, C.T.; Drougard, A.; Schittmayer, M.; Kolb, D.; Magnes, C.; Trausinger, G.; et al. N-acetylaspartate catabolism determines cytosolic acetyl-CoA levels and histone acetylation in brown adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadson, P.; Landini, L.; Helmiö, M.; Hannukainen, J.C.; Immonen, H.; Honka, M.J.; Bucci, M.; Savisto, N.; Soinio, M.; Salminen, P.; et al. Effect of bariatric surgery on adipose tissue glucose metabolism in different depots in patients with or without type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, K.A.; Lönnroth, P.; Parkkola, R.; Peltoniemi, P.; Asola, M.; Viljanen, T.; Tolvanen, T.; Knuuti, J.; Rönnemaa, T.; Huupponen, R.; et al. Glucose uptake and perfusion in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue during insulin stimulation in nonobese and obese humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3902–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, J.B.; Saha, P.K.; de Groot, E.; Tan, L.; Sharp, R.; Anaya, E.S.; Li, Y.; Quang, H.; Saidi, N.; Abushamat, L.; et al. N-acetylaspartate from fat cells regulates postprandial body temperature. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campi, B.; Codini, S.; Daniele, G.; Marvelli, A.; Ceccarini, G.; Santini, F.; Zucchi, R.; Ferrannini, E.; Saba, A. Plasma N-acetylaspartate: Development and validation of a quantitative assay based on HPLC-MS-MS and sample derivatization. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 508, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelos, E.; Mari, A.; Honka, M.-J.; Pekkarinen, L.; Latva-Rasku, A.; Laurila, S.; Rajander, J.; Salminen, P.; Iida, H.; Ferrannini, E.; et al. Renal cortical glucose uptake is decreased in insulin resistance and correlates inversely with serum free-fatty acids. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 109, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S13–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelos, E.; Honka, M.-J. PREDIM index: A useful tool for the application of the euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 44, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelos, E.; Immonen, H.; Bucci, M.; Hannukainen, J.C.; Nummenmaa, L.; Honka, M.-J.; Soinio, M.; Salminen, P.; Ferrannini, E.; Iozzo, P.; et al. Brain glucose uptake is associated with endogenous glucose production in obese patients before and after bariatric surgery and predicts metabolic outcome at follow-up. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelos, E.; Mari, A.; Bucci, M.; Honka, M.-J.; Hannukainen, J.C.; Virtanen, K.A.; Hirvonen, J.; Nummenmaa, L.; Heni, M.; Iozzo, P.; et al. Brain substrate metabolism and ß-cell function in humans: A positron emission tomography study. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 3, e00136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Tobin, J.D.; Andres, R. Glucose clamp technique: A method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am. J. Physiol. 1979, 237, E214-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, P.; Kangas, A.J.; Würtz, P.; Suna, T.; Ala-Korpela, M. Quantitative serum nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics in cardiovascular epidemiology and genetics. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2015, 8, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patients with Obesity | Lean Controls | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M/F | 5/19 | 5/14 | 0.9 |
| Age (years) | 46 [40–55] | 48 [34–53] | 0.7 |
| NGT/IFG&IGT/T2D | 10/10/4 | 16/3/0 | 0.02 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 39.5 [37.1–43.6] | 22.9 [21.5–24.5] | <0.0001 |
| W/H | 0.91 [0.87–1.04] | 0.83 [0.76–0.87] | 0.0002 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.4 ± 0.8 | 4.4 ± 0.9 | >0.9 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 0.0006 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.2 [1.1–1.6] | 0.8 [0.6–1.0] | 0.0002 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 36 [33–39] | 34 [32–36] | 0.04 |
| M value (μmol·min−1·kg−1) | 15.4 [9.9–21.4] | 46.5 [34.4–53.6] | <0.0001 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 3.1 [2.0–4.8] | 0.4 [0.2–0.8] | <0.0001 |
| Serum adiponectin (ng/mL) | 51.1 [35.6–65.5] | 55.2 [28.5–92.2] | 0.8 |
| Fasting NAA (ng/mL) | 67.6 [60.3–73.4] | 71.6 [66.8–83.5] | 0.05 |
| ssNAA (ng/mL) | 62.0 [55.9–74.8] | 67.3 [62.3–75.3] | 0.07 |
| Brain GU * (μmol·min−1·100mL−1) | 30.2 [23.3–35.2] | 28.3 [16.7–33.8] | 0.1 |
| Muscle GU * (μmol·min−1·L−1) | 41.0 [17.4–64.3] | 67.6 [48.0–94.4] | 0.005 |
| SAT GU * (μmol·min−1·L−1) | 4.2 [3.1–5.7] | 9.4 [6.5–13.2] | <0.0001 |
| VAT GU * (μmol·min−1·L−1) | 5.7 [4.2–7.5] | 14.1 [9.3–22.8] | 0.0001 |
| Fasting NAA | ssNAA | |
|---|---|---|
| BMI | −0.24 | −0.23 |
| W/H | −0.37 | −0.54 |
| M value | 0.22 | 0.34 |
| ssFFA | −0.36 | −0.44 |
| HDL cholesterol | 0.36 | 0.54 |
| Adiponectin | 0.40 | 0.48 |
| Skel. muscle GU | 0.31 | 0.42 |
| VAT GU | 0.21 | 0.41 |
| SAT GU | 0.03 | 0.20 |
| Brain GU | −0.07 | −0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebelos, E.; Honka, M.-J.; Latva-Rasku, A.; Rajander, J.; Salminen, P.; Anastasiou, I.A.; Kounatidis, D.; Tentolouris, N.; Campi, B.; Dardano, A.; et al. Circulating N-Acetylaspartate Levels Associate with Measures of Peripheral and Tissue-Specific Insulin Sensitivity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115107
Rebelos E, Honka M-J, Latva-Rasku A, Rajander J, Salminen P, Anastasiou IA, Kounatidis D, Tentolouris N, Campi B, Dardano A, et al. Circulating N-Acetylaspartate Levels Associate with Measures of Peripheral and Tissue-Specific Insulin Sensitivity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115107
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebelos, Eleni, Miikka-Juhani Honka, Aino Latva-Rasku, Johan Rajander, Paulina Salminen, Ioanna A. Anastasiou, Dimitris Kounatidis, Nikolaos Tentolouris, Beatrice Campi, Angela Dardano, and et al. 2025. "Circulating N-Acetylaspartate Levels Associate with Measures of Peripheral and Tissue-Specific Insulin Sensitivity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115107
APA StyleRebelos, E., Honka, M.-J., Latva-Rasku, A., Rajander, J., Salminen, P., Anastasiou, I. A., Kounatidis, D., Tentolouris, N., Campi, B., Dardano, A., Daniele, G., Saba, A., Ferrannini, E., & Nuutila, P. (2025). Circulating N-Acetylaspartate Levels Associate with Measures of Peripheral and Tissue-Specific Insulin Sensitivity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115107








