TL1A as a Target in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Exploring Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
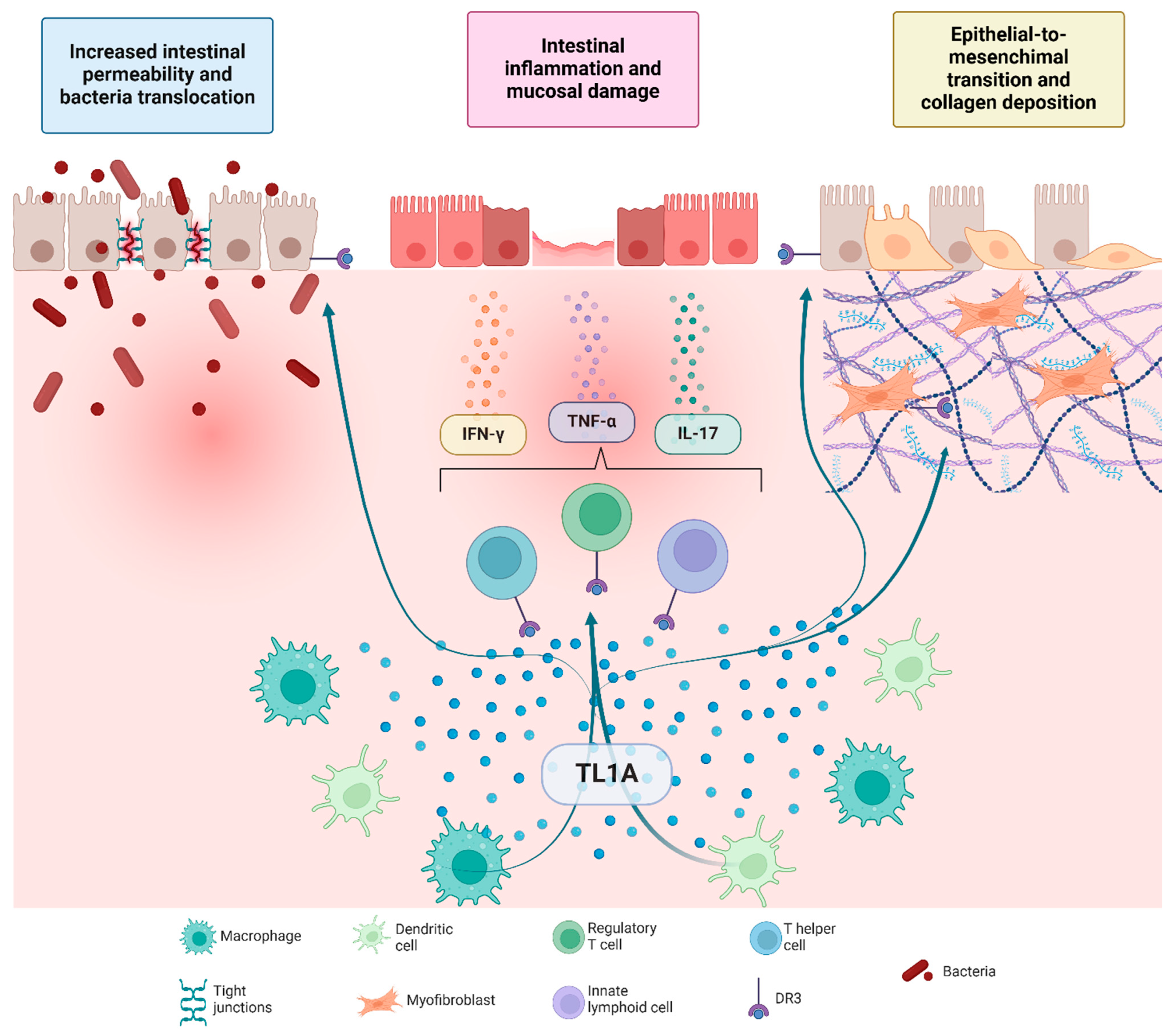
2. TL1A/DR3 Signaling in Mucosal Inflammation
3. TL1A/DR3-Driven Fibrotic Remodeling
4. Evidence from Clinical Trials on the Use of Anti-TL1A Drugs in IBD
5. TL1A as a Potential Target in the Gut–Synovium–Skin Axis
6. TL1A as a Mediator in Other Diseases
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neurath, M.F. Targeting Immune Cell Circuits and Trafficking in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessio, S.; Ungaro, F.; Noviello, D.; Lovisa, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Revisiting Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: The Gut Thickens. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Wallis, A.M.; Bishop, G.A. Roles of TRAF3 in T Cells: Many Surprises. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, H.T.; Naismith, J.H. TNFα and the TNF Receptor Superfamily: Structure-Function Relationship(s). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 50, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, M.; Benedict, C.A.; Ware, C.F. Clinical Targeting of the TNF and TNFR Superfamilies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Yan, Q.; Patskovsky, Y.; Li, Z.; Toro, R.; Meyer, A.; Cheng, H.; Brenowitz, M.; Nathenson, S.G.; Almo, S.C. Biochemical and Structural Characterization of the Human TL1A Ectodomain, Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7636–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, A.C.; Ferdinand, J.R.; Meylan, F.; Hayes, E.T.; Gabay, O.; Siegel, R.M. The TNF-Family Cytokine TL1A: From Lymphocyte Costimulator to Disease Co-Conspirator. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.; Viney, J.L. The Tale of TL1A in Inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valatas, V.; Kolios, G.; Bamias, G. TL1A (TNFSF15) and DR3 (TNFRSF25): A Co-Stimulatory System of Cytokines with Diverse Functions in Gut Mucosal Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, F.; Davidson, T.S.; Kahle, E.; Kinder, M.; Acharya, K.; Jankovic, D.; Bundoc, V.; Hodges, M.; Shevach, E.M.; Keane-Myers, A.; et al. The TNF-Family Receptor DR3 Is Essential for Diverse T Cell-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Immunity 2008, 29, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takedatsu, H.; Michelsen, K.S.; Wei, B.; Landers, C.J.; Thomas, L.S.; Dhall, D.; Braun, J.; Targan, S.R. TL1A (TNFSF15) Regulates the Development of Chronic Colitis by Modulating Both T-Helper 1 and T-Helper 17 Activation. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 552–567.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, K.; McGovern, D.; Ragoussis, J.; Paolucci, M.; Butler, H.; Jewell, D.; Cardon, L.; Takazoe, M.; Tanaka, T.; Ichimori, T.; et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in TNFSF15 Confer Susceptibility to Crohn’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 3499–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picornell, Y.; Mei, L.; Taylor, K.; Yang, H.; Targan, S.R.; Rotter, J.I. TNFSF15 Is an Ethnic-Specific IBD Gene. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.D.; Choi, H.; Hong, M.; Yun, W.J.; Low, H.-Q.; Haritunians, T.; Kim, K.-J.; Park, S.H.; Lee, I.; Bang, S.-Y.; et al. Identification of Ten Additional Susceptibility Loci for Ulcerative Colitis Through Immunochip Analysis in Koreans. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiébaut, R.; Kotti, S.; Jung, C.; Merlin, F.; Colombel, J.F.; Lemann, M.; Almer, S.; Tysk, C.; O’Morain, M.; Gassull, M.; et al. TNFSF15 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Susceptibility to Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a New European Cohort. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Gao, H.; Jung, S.; Gao, X.; Sun, R.; Liu, X.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Kawai, Y.; et al. Genetic Architecture of the Inflammatory Bowel Diseases across East Asian and European Ancestries. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.N.; Park, C.; Park, S.J.; Lee, C.K.; Ye, B.D.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Chae, J.; Kim, J.-I.; Kim, Y.-H.; et al. Deep Resequencing of 131 Crohn’s Disease Associated Genes in Pooled DNA Confirmed Three Reported Variants and Identified Eight Novel Variants. Gut 2016, 65, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, R.Y.; Cordero, J.B.; Stiemke, A.B.; Datta, L.W.; Buyske, S.; Kugathasan, S.; McGovern, D.P.B.; Brant, S.R.; Simpson, C.L. Trans-Ancestry, Bayesian Meta-Analysis Discovers 20 Novel Risk Loci for Inflammatory Bowel Disease in an African American, East Asian and European Cohort. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2023, 32, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamias, G.; Filidou, E.; Goukos, D.; Valatas, V.; Arvanitidis, K.; Panagopoulou, M.; Kouklakis, G.; Daikos, G.L.; Ladas, S.D.; Kolios, G. Crohn’s Disease-Associated Mucosal Factors Regulate the Expression of TNF-like Cytokine 1A and Its Receptors in Primary Subepithelial Intestinal Myofibroblasts and Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Transl. Res. 2017, 180, 118–130.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migone, T.-S.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhuang, L.; Chen, C.; Hu, B.; Hong, J.S.; Perry, J.W.; Chen, S.-F.; Zhou, J.X.H.; et al. TL1A Is a TNF-like Ligand for DR3 and TR6/DcR3 and Functions as a T Cell Costimulator. Immunity 2002, 16, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamias, G.; Martin, C.; Marini, M.; Hoang, S.; Mishina, M.; Ross, W.G.; Sachedina, M.A.; Friel, C.M.; Mize, J.; Bickston, S.J.; et al. Expression, Localization, and Functional Activity of TL1A, a Novel Th1-Polarizing Cytokine in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 4868–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prehn, J.L.; Mehdizadeh, S.; Landers, C.J.; Luo, X.; Cha, S.C.; Wei, P.; Targan, S.R. Potential Role for TL1A, the New TNF-Family Member and Potent Costimulator of IFN-γ, in Mucosal Inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 112, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, Y.-C.; Weng, L.-T.; Wei, S.-C.; Wu, L.-L.; Shih, D.Q.; Targan, S.R.; Turner, J.R.; Yu, L.C.-H. Gut Microbial Transcytosis Induced by Tumour Necrosis Factor-like 1A-Dependent Activation of a Myosin Light Chain Kinase Splice Variant Contributes to Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2021, 15, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamias, G.; Mishina, M.; Nyce, M.; Ross, W.G.; Kollias, G.; Rivera-Nieves, J.; Pizarro, T.T.; Cominelli, F. Role of TL1A and Its Receptor DR3 in Two Models of Chronic Murine Ileitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8441–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prehn, J.L.; Thomas, L.S.; Landers, C.J.; Yu, Q.T.; Michelsen, K.S.; Targan, S.R. The T Cell Costimulator TL1A Is Induced by FcγR Signaling in Human Monocytes and Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4033–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamias, G.; Menghini, P.; Pizarro, T.T.; Cominelli, F. Targeting TL1A and DR3: The New Frontier of Anti-Cytokine Therapy in IBD. Gut 2025, 74, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślebioda, T.J.; Bojarska-Junak, A.; Stanisławowski, M.; Cyman, M.; Wierzbicki, P.M.; Roliński, J.; Celiński, K.; Kmieć, Z. TL 1A as a Potential Local Inducer of IL 17A Expression in Colon Mucosa of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. Scand. J. Immunol. 2015, 82, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, N.; Hisamatsu, T.; Honda, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Chinen, H.; Takayama, T.; Kitazume, M.T.; Okamoto, S.; Koganei, K.; Sugita, A.; et al. TL1A Produced by Lamina Propria Macrophages Induces Th1 and Th17 Immune Responses in Cooperation with IL-23 in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnaiyan, A.M.; O’Rourke, K.; Yu, G.-L.; Lyons, R.H.; Garg, M.; Duan, D.R.; Xing, L.; Gentz, R.; Ni, J.; Dixit, V.M. Signal Transduction by DR3, a Death Domain-Containing Receptor Related to TNFR-1 and CD95. Science 1996, 274, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhuang, L.; Luo, X.; Wei, P. TL1A-Induced NF-κB Activation and c-IAP2 Production Prevent DR3-Mediated Apoptosis in TF-1 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39251–39258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, D.Q.; Kwan, L.Y.; Chavez, V.; Cohavy, O.; Gonsky, R.; Chang, E.Y.; Chang, C.; Elson, C.O.; Targan, S.R. Microbial Induction of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Associated Gene TL1A (TNFSF15) in Antigen Presenting Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 3239–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, S.; Knoll, G.; Ehrenschwender, M. Death Receptor 3 Signaling Enhances Proliferation of Human Regulatory T Cells. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu-Varma, M.; Shih, D.Q.; Targan, S.R. Differential Levels of Tl1a Affect the Expansion and Function of Regulatory T Cells in Modulating Murine Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, Y.; More, S.K.; Hamade, H.; Blackwood, A.Y.; Abraham, J.P.; Thomas, L.S.; Miller, J.H.; Stamps, D.T.; Castanon, S.L.; Jacob, N.; et al. DR3 Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Homeostasis and Regeneration After Intestinal Barrier Injury. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Hedl, M.; Abraham, C. TNFSF15 Promotes Antimicrobial Pathways in Human Macrophages and These Are Modulated by TNFSF15 Disease-Risk Variants. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, F.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Massey, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Fiocchi, C. Fibrosis in IBD: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Targets. Gut 2024, 73, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, R.; Zhang, X.; Koon, H.W.; Vu, M.; Chang, J.-Y.; Yeager, N.; Nguyen, M.A.; Michelsen, K.S.; Berel, D.; Pothoulakis, C.; et al. Constitutive TL1A Expression under Colitogenic Conditions Modulates the Severity and Location of Gut Mucosal Inflammation and Induces Fibrostenosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Ichikawa, R.; Wallace, K.; Pothoulakis, C.; Koon, H.W.; Targan, S.R.; Shih, D.Q. Sustained TL1A (TNFSF15) Expression on Both Lymphoid and Myeloid Cells Leads to Mild Spontaneous Intestinal Inflammation and Fibrosis. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, N.; Kumagai, K.; Abraham, J.P.; Shimodaira, Y.; Ye, Y.; Luu, J.; Blackwood, A.Y.; Castanon, S.L.; Stamps, D.T.; Thomas, L.S.; et al. Direct Signaling of TL1A-DR3 on Fibroblasts Induces Intestinal Fibrosis in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, D.Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Kanazawa, Y.; Ichikawa, R.; Wallace, K.L.; Chen, J.; Pothoulakis, C.; Koon, H.W.; et al. Inhibition of a Novel Fibrogenic Factor Tl1a Reverses Established Colonic Fibrosis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 1492–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenxiu, J.; Mingyue, Y.; Fei, H.; Yuxin, L.; Mengyao, W.; Chenyang, L.; Jia, S.; Hong, Z.; Shih, D.Q.; Targan, S.R.; et al. Effect and Mechanism of TL1A Expression on Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition during Chronic Colitis-Related Intestinal Fibrosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 5927064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, N.; Jacobs, J.P.; Kumagai, K.; Ha, C.W.Y.; Kanazawa, Y.; Lagishetty, V.; Altmayer, K.; Hamill, A.M.; Von Arx, A.; Sartor, R.B.; et al. Inflammation-Independent TL1A-Mediated Intestinal Fibrosis Is Dependent on the Gut Microbiome. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banfield, C.; Rudin, D.; Bhattacharya, I.; Goteti, K.; Li, G.; Hassan-Zahraee, M.; Brown, L.S.; Hung, K.E.; Pawlak, S.; Lepsy, C. First-in-human, Randomized Dose-escalation Study of the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Immunogenicity of PF-06480605 in Healthy Subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S.; Klopocka, M.; Scherl, E.J.; Romatowski, J.; Allegretti, J.R.; Peeva, E.; Vincent, M.S.; Schoenbeck, U.; Ye, Z.; Hassan-Zahraee, M.; et al. Anti-TL1A Antibody PF-06480605 Safety and Efficacy for Ulcerative Colitis: A Phase 2a Single-Arm Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2324–2332.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, B.E.; Feagan, B.G.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S.; Rubin, D.T.; Laurent, O.; Luo, A.; Nguyen, D.D.; Lu, J.; Yen, M.; et al. Phase 2 Trial of Anti-TL1A Monoclonal Antibody Tulisokibart for Ulcerative Colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, S.S.; Sands, B.E.; Feagan, B.G.; Yen, M.; Dong, B.; Zhou, W.; Danese, S. P0580 Efficacy and Safety Results of Tulisokibart Re-Induction Treatment in Participants with Ulcerative Colitis in the Phase 2 ARTEMIS-UC Clinical Trial. J. Crohns Colitis 2025, 19, i1158–i1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, J.R.; Yarur, A.; Feagan, B.; Danese, S.; Schreiber, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Ha, C.; Kierkus, J.; Leong, R.W.; Vincent, M.S.; et al. DOP061 RO7790121 Shows Early and Rapid Symptomatic Remission in the Treatment of Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis—Findings from the Phase IIb TUSCANY-2 Trial. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2025, 19, i204–i205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jairath, V.; Allegretti, J.R.; Yarur, A.; Danese, S.; Schreiber, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Kierkus, J.; Leong, R.W.; Vincent, M.S.; Banerjee, A.; et al. OP39 Treatment with RO7790121 Induces and Maintains Histologic and Histologic-Endoscopic Improvement and Remission in Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis—Results from TUSCANY-2. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2025, 19, i75–i76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, W.; Stepek, D.; Kempinski, R.; Danese, S.; Sands, B.E.; Ratiu-Duma, B.; Singh, R.; Barkay, H.; Raphael, G.; Jairath, V. OP41 Duvakitug (TEV-48574), an Anti-TL1a Monoclonal Antibody, Demonstrates Efficacy and Favourable Safety as an Induction Treatment in Adults with Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results from a Phase 2b, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Ranging, Basket Trial (RELIEVE UCCD). J. Crohn’s Colitis 2025, 19, i79–i80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jairath, V.; Kierkus, J.; Duvall, G.A.; Danese, S.; Sands, B.E.; Ratiu-Duma, B.; Singh, R.; Barkay, H.; Raphael, G.; Reinisch, W. OP40 Duvakitug (TEV-48574), an Anti-TL1a Monoclonal Antibody, Demonstrates Efficacy and Favourable Safety as an Induction Treatment in Adults with Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease: Results from a Phase 2b, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Dose-Ranging, Basket Trial (RELIEVE UCCD). J. Crohn’s Colitis 2025, 19, i77–i78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siakavellas, S.I.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Bamias, G. The TL1A/DR3/DcR3 Pathway in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, R.; Su, D.; Feng, X.; Li, X. TL1A Increased the Differentiation of Peripheral Th17 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cytokine 2014, 69, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, M.; Sun, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, F.; Li, X. TL1A Increased IL-6 Production on Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Preferentially Activating TNF Receptor 2 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cytokine 2016, 83, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.-J.; Choi, I.A.; Meylan, F.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Farley, T.; Richard, A.C.; Hawley, E.; Botson, J.; Hong, Y.J.; Lee, E.Y.; et al. Circulating TNF-like Protein 1A (TL1A) Is Elevated Early in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Depends on TNF. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsta, M.; Bamias, G.; Tektonidou, M.G.; Christopoulos, P.; Iliopoulos, A.; Sfikakis, P.P. Increased Levels of Soluble TNF-like Cytokine 1A in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassatella, M.A.; Da Silva, G.P.; Tinazzi, I.; Facchetti, F.; Scapini, P.; Calzetti, F.; Tamassia, N.; Wei, P.; Nardelli, B.; Roschke, V.; et al. Soluble TNF-Like Cytokine (TL1A) Production by Immune Complexes Stimulated Monocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7325–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamias, G.; Evangelou, K.; Vergou, T.; Tsimaratou, K.; Kaltsa, G.; Antoniou, C.; Kotsinas, A.; Kim, S.; Gorgoulis, V.; Stratigos, A.J.; et al. Upregulation and Nuclear Localization of TNF-like Cytokine 1A (TL1A) and Its Receptors DR3 and DcR3 in Psoriatic Skin Lesions. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteleone, G.; Moscardelli, A.; Colella, A.; Marafini, I.; Salvatori, S. Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases: Common and Different Pathogenic and Clinical Features. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.E.; Schmidt, E.G.W.; Sørensen, J.F.; Faber, C.; Nielsen, B.S.; Holmstrøm, K.; Omland, S.H.; Tougaard, P.; Skov, S.; Bang, B. Secretion, Blood Levels and Cutaneous Expression of TL 1A in Psoriasis Patients. APMIS 2015, 123, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fu, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, F.; Chen, T. TNF-like Ligand 1A Is Associated with the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Contributes to IL-17 Production in PBMCs. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T. Upregulation of DR3 Expression in CD4+ T Cells Promotes Secretion of IL-17 in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.-G.; Bamias, G.; Arseneau, K.O.; Burkly, L.C.; Wang, E.C.Y.; Gruszka, D.; Pizarro, T.T.; Cominelli, F. A Novel Role for TL1A/DR3 in Protection against Intestinal Injury and Infection. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, W.; Liu, Q.; Huo, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. TL1A Promotes Metastasis and EMT Process of Colorectal Cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maixner, N.; Pecht, T.; Haim, Y.; Chalifa-Caspi, V.; Goldstein, N.; Tarnovscki, T.; Liberty, I.F.; Kirshtein, B.; Golan, R.; Berner, O.; et al. A TRAIL-TL1A Paracrine Network Involving Adipocytes, Macrophages, and Lymphocytes Induces Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Downstream of E2F1 in Human Obesity. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Chen, Q.-Z.; Jiang, F.; Townsend, T.A.; Mao, C.-J.; You, C.-Y.; Yang, W.-H.; Sun, Z.-Y.; Yu, J.-G.; Yan, H. Changes in TL1A Levels and Associated Cytokines during Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, R.; Jiang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liao, M.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor Ligand-related Molecule 1A Maintains Blood–Retinal Barrier via Modulating SHP-1-Src-VE-cadherin Signaling in Diabetic Retinopathy. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e22008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatelopoulos, K.; Georgiou, S.; Kanakakis, I.; Papamichael, C.; Oikonomidis, N.; Mantzou, A.; Samouilidou, E.; Loizos, S.; Zakopoulos, N.; Sfikakis, P.P. Circulating Levels of TNF-like Cytokine 1A Correlate with Reflected Waves and Atherosclerosis Extent and May Predict Cardiac Death in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Cytokine 2015, 72, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamias, G.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Zampeli, E.; Protogerou, A.; Sigala, F.; Papamichael, C.; Christopoulos, P.; Kitas, G.D.; Sfikakis, P.P. Circulating Levels of TNF-like Cytokine 1A Correlate with the Progression of Atheromatous Lesions in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 147, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, K.; Aw, M.; Salter, B.M.A.; Ju, X.; Mukherjee, M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Nair, P.; Sehmi, R. The Role of the TL1A/DR3 Axis in the Activation of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Subjects with Eosinophilic Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Pan, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Qiao, X.; Cui, W.; Dong, L. The TL1A-DR3 Axis in Asthma: Membrane-Bound and Secreted TL1A Co-Determined the Development of Airway Remodeling. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2022, 14, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial ID/Name | Design | Intervention | Comparator | Patient Cohort | Primary Outcome | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01989143 | Phase 1 | PF-06480605 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300, 600, or 800 mg i.v., or MAD, PF-06480605 3 × 500 mg i.v., or 3 × 30 mg, 3 × 100 mg, or 3 × 300 mg s.c. Q2W for 3 doses | Placebo | Healthy subject | Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of SAD and MAD | Completed |
| NCT02840721 TUSCANY | Phase 2a, single-arm study | PF-06480605 500 mg i.v. Q2W, 7 doses total | / | Moderate-to-severe UC | Safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy (endoscopic improvement at week 14) | Completed |
| NCT04996797 Artemis-UC | Phase 2a | Tulisokibart 1000 mg i.v. on day 1, followed by 500 mg i.v. at weeks 2, 6, and 10 | Placebo | Moderate-to-severe UC | Clinical remission at week 12 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT04090411 TUSCANY-2 | Phase 2b | PF-06480605 50 mg s.c. Q4W or 100 mg s.c. Q4W or 150 mg s.c. Q4W | Placebo | Moderate-to-severe UC | Safety, tolerability, and clinical remission at week 14 | Completed |
| NCT05499130 RELIEVE UCCD | Phase 2b | Initial 2250 mg s.c. loading dose of duvakitug (TEV-48574), followed by 450 mg s.c. Q2W or 900 mg s.c. Q2W | Placebo | Moderate-to-severe UC and CD | Safety, tolerability, clinical remission (UC) and endoscopic response (CD) at week 14 | Completed |
| NCT05668013 RELIEVE UCCD LTE | Phase 2b LTE | Drug: TEV-48574 dose regimen A Drug: TEV-48574 dose regimen B | / | Moderate-to-severe UC and CD | Clinical remission (UC) and endoscopic response (CD) at week 24 | Active, not recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tettoni, E.; Gabbiadini, R.; Dal Buono, A.; Privitera, G.; Vadalà, V.; Migliorisi, G.; Bertoli, P.; Quadarella, A.; Bezzio, C.; Armuzzi, A. TL1A as a Target in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Exploring Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115017
Tettoni E, Gabbiadini R, Dal Buono A, Privitera G, Vadalà V, Migliorisi G, Bertoli P, Quadarella A, Bezzio C, Armuzzi A. TL1A as a Target in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Exploring Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115017
Chicago/Turabian StyleTettoni, Enrico, Roberto Gabbiadini, Arianna Dal Buono, Giuseppe Privitera, Vincenzo Vadalà, Giulia Migliorisi, Peter Bertoli, Alessandro Quadarella, Cristina Bezzio, and Alessandro Armuzzi. 2025. "TL1A as a Target in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Exploring Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115017
APA StyleTettoni, E., Gabbiadini, R., Dal Buono, A., Privitera, G., Vadalà, V., Migliorisi, G., Bertoli, P., Quadarella, A., Bezzio, C., & Armuzzi, A. (2025). TL1A as a Target in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Exploring Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115017







