Keratin Expression in Podocytopathies, ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
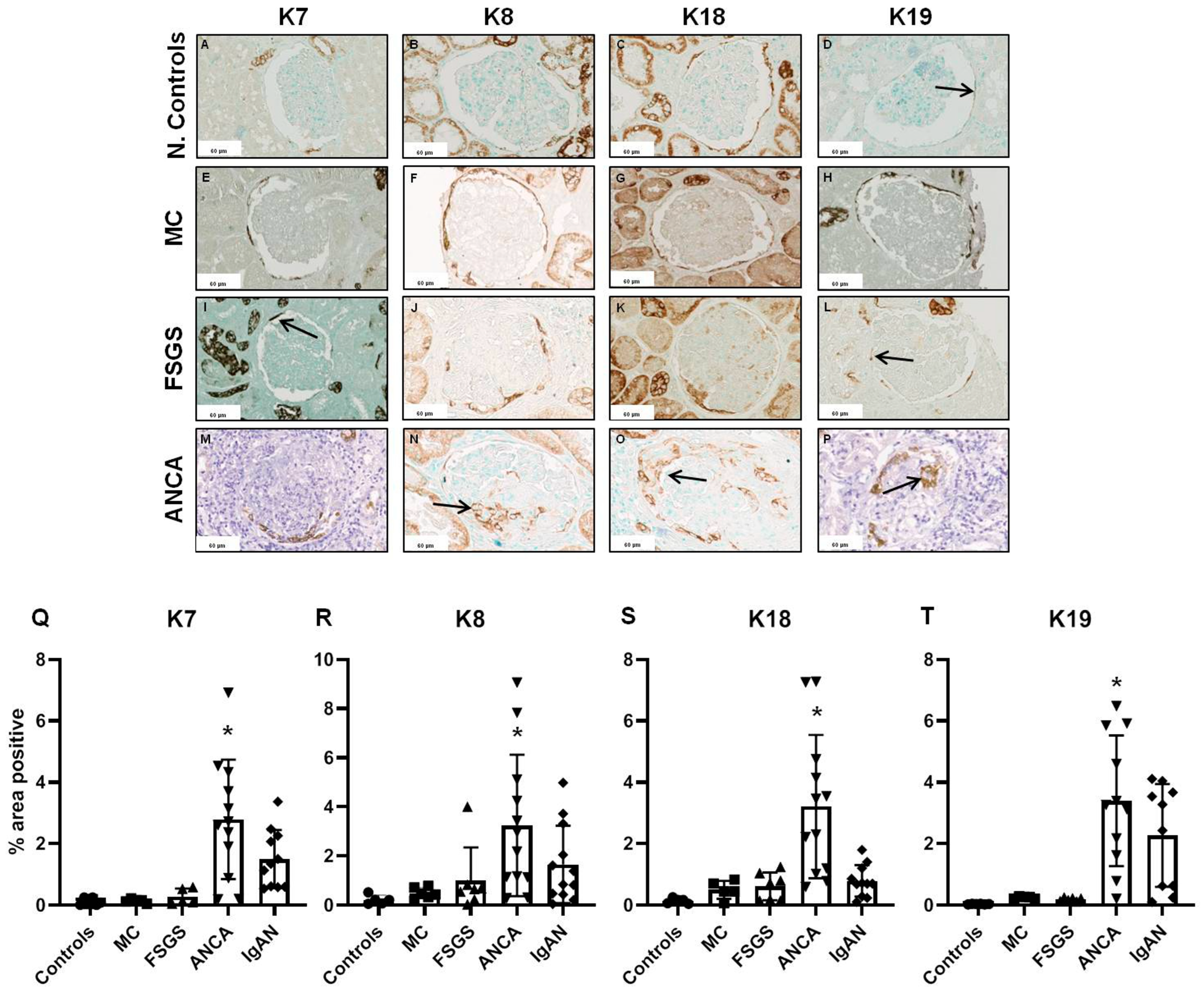
2.1. Glomerular Expression of Keratins
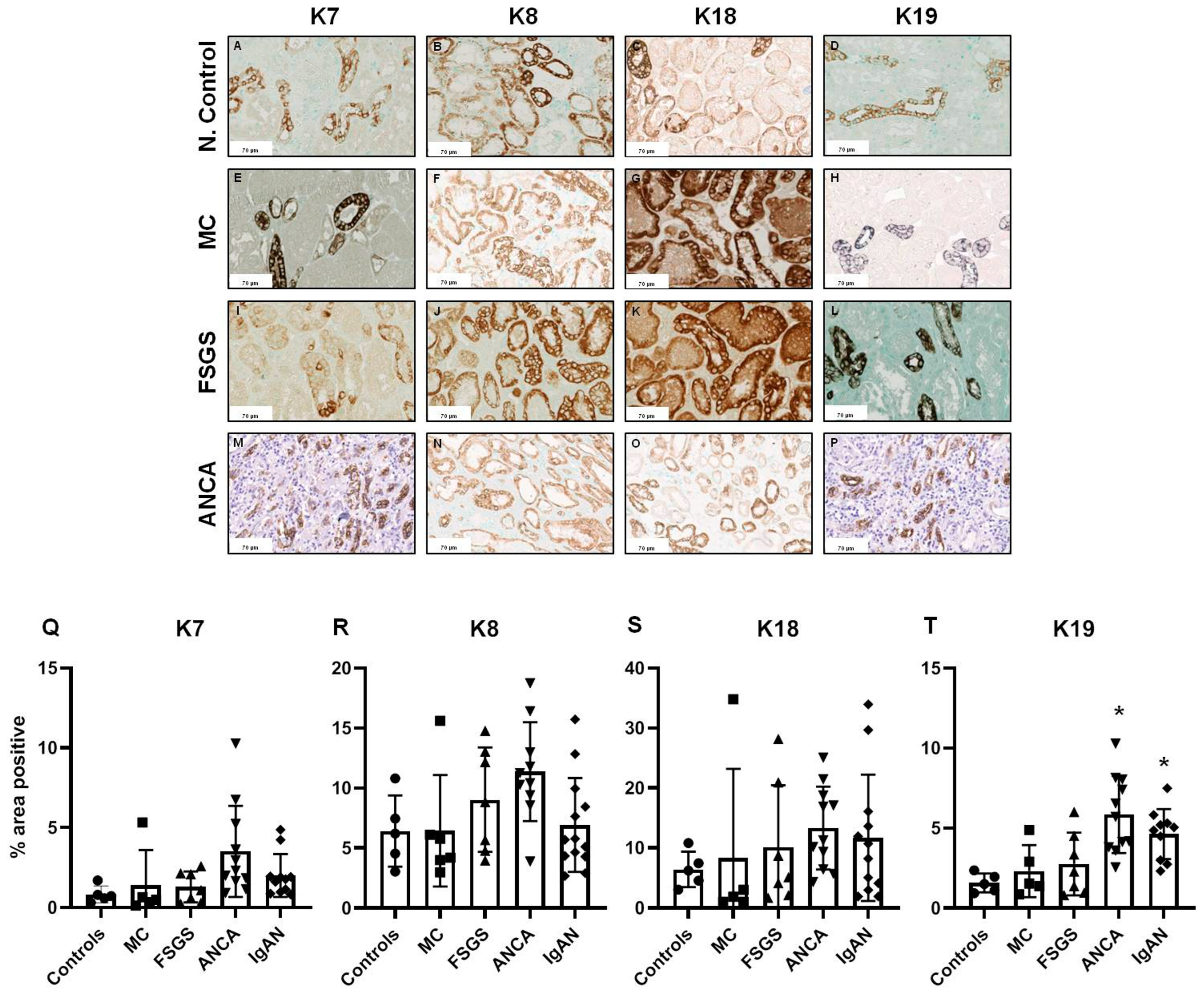
2.2. Tubulointerstitial Expression of Keratins
2.3. Keratin Expression in Comparison to Basic Histopathological Features
2.4. Prognostic Value of Keratin Expression
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Histology, Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence
4.2. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavanaugh, C.; Okusa, M.D. The Evolving Role of Novel Biomarkers in Glomerular Disease: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2021, 77, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, Y.; Kiryluk, K. Novel biomarkers in glomerular disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014, 21, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.A.; Powell, T.B.; Budisavljevic, M.N.; Oates, J.C.; Raymond, J.R.; Almeida, J.S.; Arthur, J.M. Urine biomarkers predict the cause of glomerular disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.D.; Cavallo, T.; Bonsib, S.M.; on behalf of The Ad Hoc Committee on Renal Biopsy. Practice guidelines for the renal biopsy. Mod. Pathol. 2004, 17, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Haas, M.; Markowitz, G.S.; D’Agati, V.D.; Rennke, H.G.; Jennette, J.C.; Bajema, I.M.; Alpers, C.E.; Chang, A.; Cornell, L.D.; et al. Mayo Clinic/Renal Pathology Society Consensus Report on Pathologic Classification, Diagnosis, and Reporting of GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Fervenza, F.C. Standardized classification and reporting of glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2019, 34, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bronstein, R.; Pace, J.; Gowthaman, Y.; Salant, D.J.; Mallipattu, S.K. Podocyte-Parietal Epithelial Cell Interdependence in Glomerular Development and Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 34, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicking, E.M.; Fuss, A.; Uhlig, S.; Jirak, P.; Dijkman, H.; Wetzels, J.; Engel, D.R.; Urzynicok, T.; Heidenreich, S.; Kriz, W.; et al. Subtotal ablation of parietal epithelial cells induces crescent formation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, K.H.; Jeong, H.J. Glomerular epithelial CD44 expression and segmental sclerosis in IgA nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2016, 20, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, H.; Moeller, M.J.; Smeets, B.; Yang, H.C.; D’Agati, V.D.; Alpers, C.E.; Fogo, A.B. Parietal epithelial cell activation marker in early recurrence of FSGS in the transplant. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppe, C.; Grone, H.J.; Ostendorf, T.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Boor, P.; Floege, J.; Smeets, B.; Moeller, M.J. Common histological patterns in glomerular epithelial cells in secondary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Guo, X.Y.; Quan, X.Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.J.; Su, H.Y.; An, N.; Liu, H.F. The Role of Parietal Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Podocytopathy. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 832772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariety, J.; Mandet, C.; Hill, G.S.; Bruneval, P. Parietal podocytes in normal human glomeruli. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2770–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, D.; Kershaw, D.B.; Smeets, B.; Yuan, G.; Fuss, A.; Frye, B.; Elger, M.; Kriz, W.; Floege, J.; Moeller, M.J. Recruitment of podocytes from glomerular parietal epithelial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, V.; Goike, H.; Panaretakis, K.W.; Einarsson, R. Clinical utility of cytokeratins as tumor markers. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, N.O.; Zhou, X.; Toivola, D.M.; Omary, M.B. The cytoskeleton of digestive epithelia in health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, G1108–G1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivola, D.M.; Strnad, P.; Habtezion, A.; Omary, M.B. Intermediate filaments take the heat as stress proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivola, D.M.; Boor, P.; Alam, C.; Strnad, P. Keratins in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 32, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guldiken, N.; Usachov, V.; Levada, K.; Trautwein, C.; Ziol, M.; Nahon, P.; Strnad, P. Keratins 8 and 18 are type II acute-phase responsive genes overexpressed in human liver disease. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djudjaj, S.; Papasotiriou, M.; Bulow, R.D.; Wagnerova, A.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Cohen, C.D.; Strnad, P.; Goumenos, D.S.; Floege, J.; Boor, P. Keratins are novel markers of renal epithelial cell injury. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulombe, P.A.; Omary, M.B. ‘Hard’ and ‘soft’ principles defining the structure, function and regulation of keratin intermediate filaments. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2002, 14, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, R.; Hage, C.; Thoenes, W. Expression of intermediate filament proteins in fetal and adult human kidney: Modulations of intermediate filament patterns during development and in damaged tissue. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 1991, 65, 74–86. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, R.; Divo, M.; Langbein, L. The human keratins: Biology and pathology. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 705–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarlos, D.P.; Peterfi, L.; Szanto, A.; Kovacs, G. Shift of Keratin Expression Profile in End-stage Kidney Increases the Risk of Tumor Development. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 5217–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berden, A.E.; Ferrario, F.; Hagen, E.C.; Jayne, D.R.; Jennette, J.C.; Joh, K.; Neumann, I.; Noel, L.H.; Pusey, C.D.; Waldherr, R.; et al. Histopathologic classification of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinde, K.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Huang, X.R.; Sakai, H.; Kurokawa, K.; Atkins, R.C.; Lan, H.Y. Tubular phenotypic change in progressive tubulointerstitial fibrosis in human glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 38, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastaldi, M.P.; Ferrario, F.; Giardino, L.; Dell’Antonio, G.; Grillo, C.; Grillo, P.; Strutz, F.; Muller, G.A.; Colasanti, G.; D’Amico, G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tubular epithelial cells in human renal biopsies. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Pollock, A.S.; Mahimkar, R.; Olson, J.L.; Lovett, D.H. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 and basement membrane integrity: A unifying mechanism for progressive renal injury. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1898–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; D’Agati, V.D.; Nast, C.C.; Fogo, A.B.; De Vriese, A.S.; Markowitz, G.S.; Glassock, R.J.; Fervenza, F.C.; Seshan, S.V.; Rule, A.; et al. A proposal for standardized grading of chronic changes in native kidney biopsy specimens. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boor, P.; Konieczny, A.; Villa, L.; Schult, A.L.; Bucher, E.; Rong, S.; Kunter, U.; van Roeyen, C.R.; Polakowski, T.; Hawlisch, H.; et al. Complement C5 mediates experimental tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djudjaj, S.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Raffetseder, U.; Guerrot, D.; Dussaule, J.C.; Boor, P.; Kerroch, M.; Hanssen, L.; Brandt, S.; Dittrich, A.; et al. Notch-3 receptor activation drives inflammation and fibrosis following tubulointerstitial kidney injury. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boor, P.; Celec, P.; Martin, I.V.; Villa, L.; Hodosy, J.; Klenovicsova, K.; Esposito, C.; Schafer, S.; Albrecht-Kupper, B.; Ostendorf, T.; et al. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonist, BAY PP1, attenuates renal fibrosis in rats. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1182–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No Significant Glomerular Sclerosis | Significant Glomerular Sclerosis | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tubular keratin expression (positive stained area ± SD) | |||
| K7 | 1.125 ± 0.73 | 2.31 ± 2.23 | 0.113 |
| K8 | 5.131 ± 2.89 | 9.57 ± 4.59 | 0.001 |
| K18 | 4.85 ± 4.29 | 12.6 ± 9.82 | 0.003 |
| K19 | 2.93 ± 1.5 | 4.32 ± 2.46 | 0.096 |
| Patients with Stable Kidney Function | Patients with Kidney Function Deterioration | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tubular keratin expression (positive stained area ± SD) | |||
| K7 | 1.144 ± 0.76 | 2.755 ± 2.31 | 0.034 |
| K8 | 6.489 ± 3.78 | 11.498 ± 4.11 | 0.006 |
| K18 | 9.409 ± 8.44 | 16.953 ± 11.75 | 0.081 |
| K19 | 3.092 ± 1.64 | 5.24 ± 2.55 | 0.024 |
| Glomerular keratin expression (positive stained area ± SD) | |||
| K7 | 1.059 ± 1.05 | 1.02 ± 1.15 | 0.945 |
| K8 | 1.846 ± 2.47 | 1.143 ± 1.41 | 0.502 |
| K18 | 0.899 ± 0.69 | 0.642 ± 0.37 | 0.415 |
| K19 | 0.93 ± 1.38 | 0.272 ± 0.21 | 0.171 |
| Patients with Stable Kidney Function (Positive Stained Area ± SD) | Patients with Kidney Function Deterioration (Positive Stained Area ± SD) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tubular keratin expression | |||
| K7 | 1.62 ± 0.41 | 3.137 ± 2.43 | 0.189 |
| K8 | 6.676 ± 3.58 | 12.819 ± 10.37 | 0.007 |
| K18 | 9.475 ± 4.66 | 19.067 ± 10.37 | 0.045 |
| K19 | 3.696 ± 1.26 | 6.275 ± 2.41 | 0.038 |
| Glomerular keratin expression | |||
| K7 | 1.754 ± 0.94 | 1.494 ± 1.14 | 0.704 |
| K8 | 3.113 ± 3.25 | 1.611 ± 1.8 | 0.438 |
| K18 | 1.333 ± 0.76 | 0.738 ± 0.37 | 0.198 |
| K19 | 1.625 ± 1.75 | 0.365 ± 0.37 | 0.191 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavlakou, P.; Gakiopoulou, H.; Djudjaj, S.; Palamaris, K.; Trivyza, M.S.; Stylianou, K.; Goumenos, D.S.; Papachristou, E.; Papasotiriou, M. Keratin Expression in Podocytopathies, ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031805
Pavlakou P, Gakiopoulou H, Djudjaj S, Palamaris K, Trivyza MS, Stylianou K, Goumenos DS, Papachristou E, Papasotiriou M. Keratin Expression in Podocytopathies, ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031805
Chicago/Turabian StylePavlakou, Paraskevi, Harikleia Gakiopoulou, Sonja Djudjaj, Kostas Palamaris, Maria Stella Trivyza, Kostas Stylianou, Dimitrios S. Goumenos, Evangelos Papachristou, and Marios Papasotiriou. 2024. "Keratin Expression in Podocytopathies, ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031805
APA StylePavlakou, P., Gakiopoulou, H., Djudjaj, S., Palamaris, K., Trivyza, M. S., Stylianou, K., Goumenos, D. S., Papachristou, E., & Papasotiriou, M. (2024). Keratin Expression in Podocytopathies, ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and IgA Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031805





