SERCA Modulators Reveal Distinct Signaling and Functional Roles of T Lymphocyte Ca2+ Stores
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
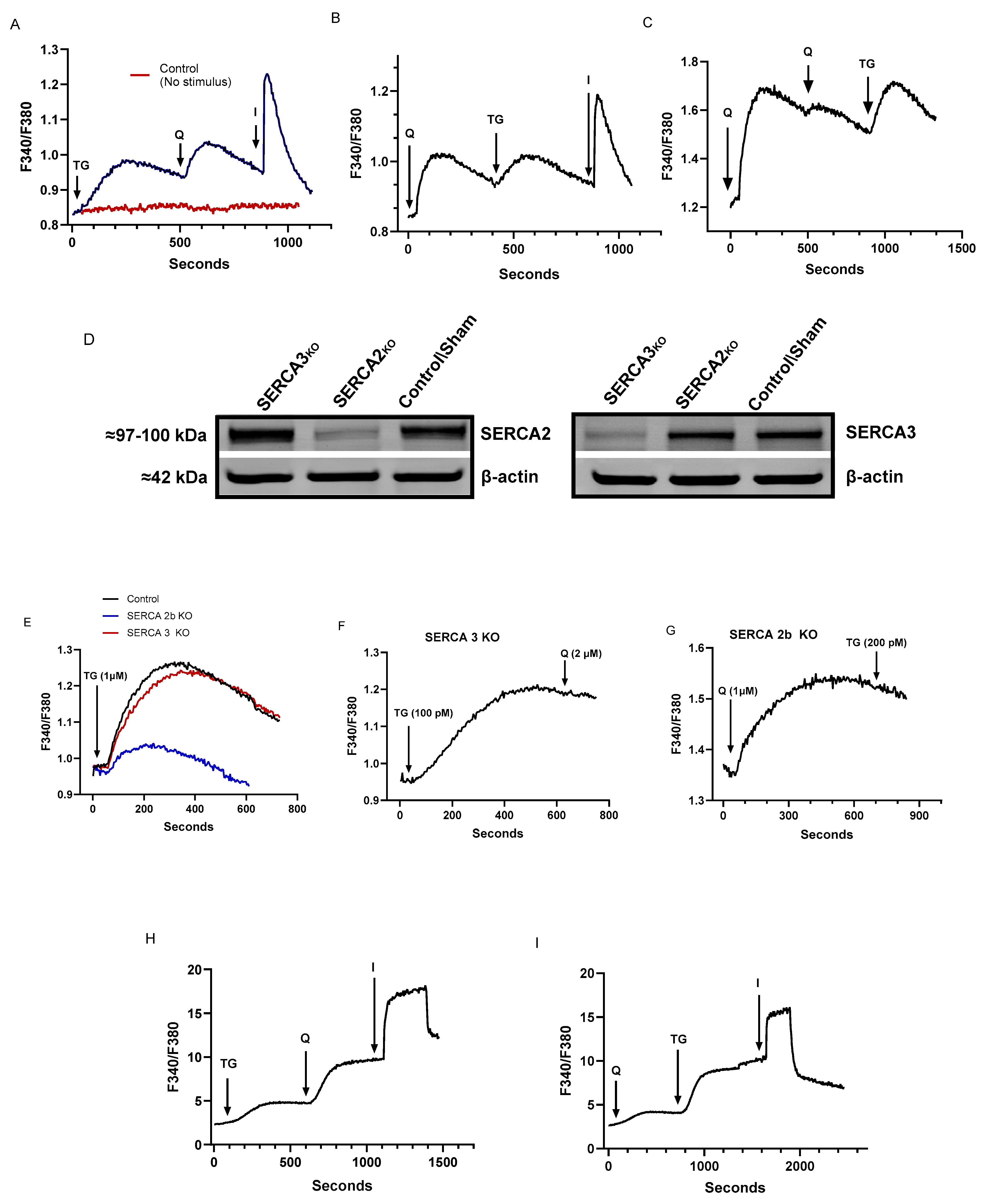
2.1. Low Concentrations of TG and tBHQ Induce Ca2+ Release in T Cells and Establish a Pharmacological Regimen for Specific Blockade of SERCA 2b and SERCA 3
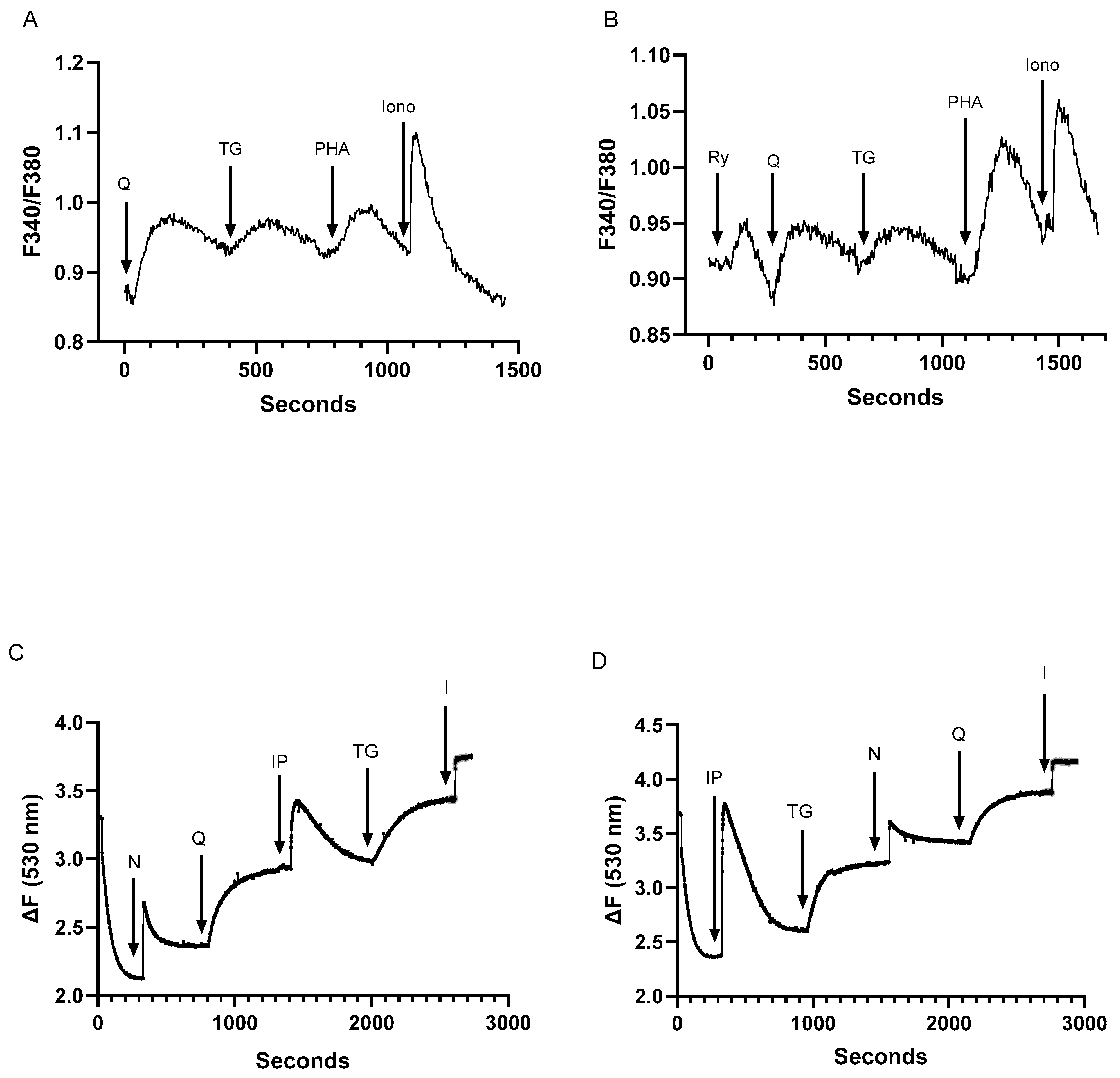
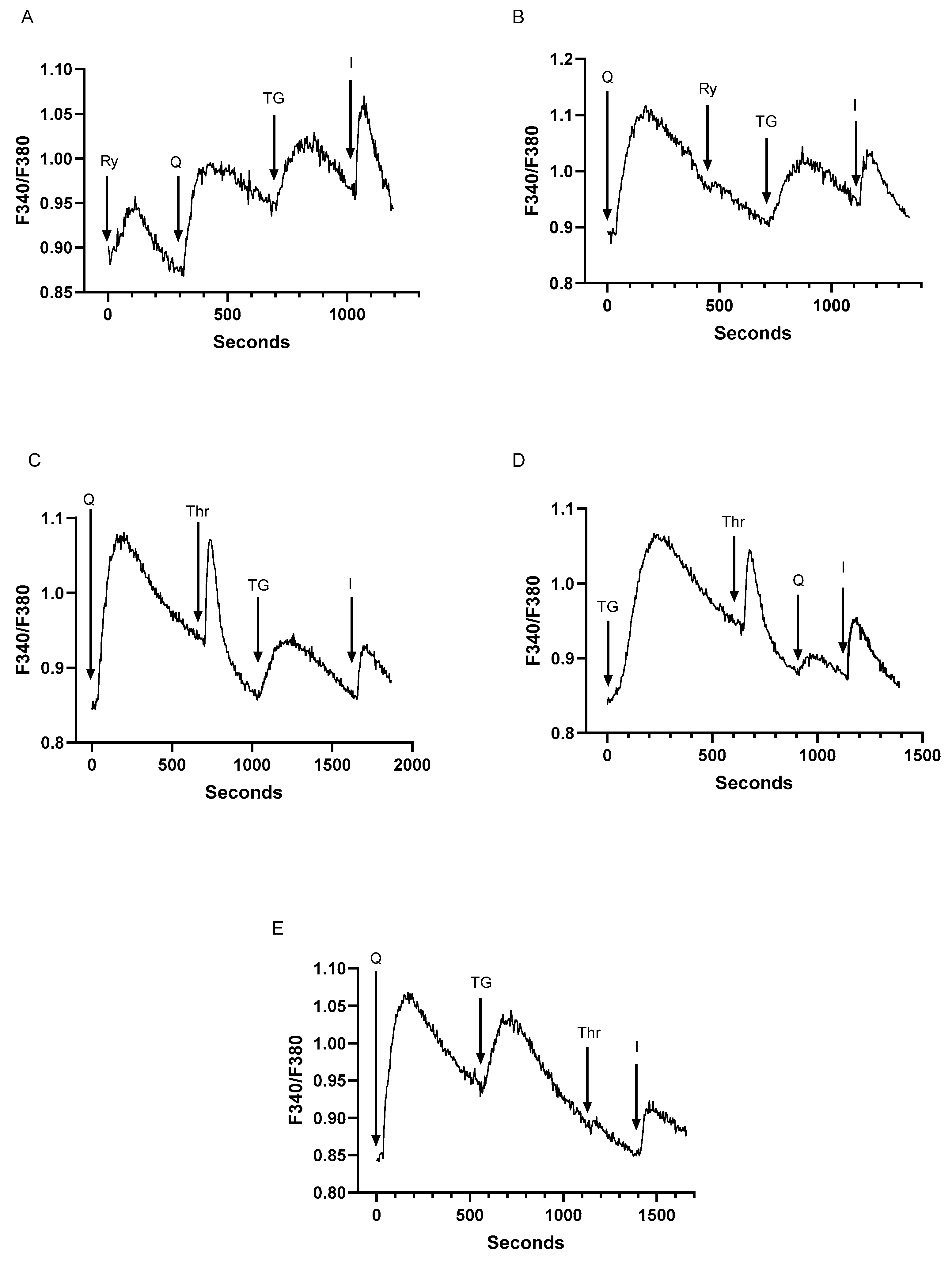
2.2. Low-Dose SERCA Blockers and Agonist-Induced Ca2+ Release Patterns Suggest a Complex T Cell Ca2+ Pool Profile with up to Five Distinct Ca2+ Store Compartments
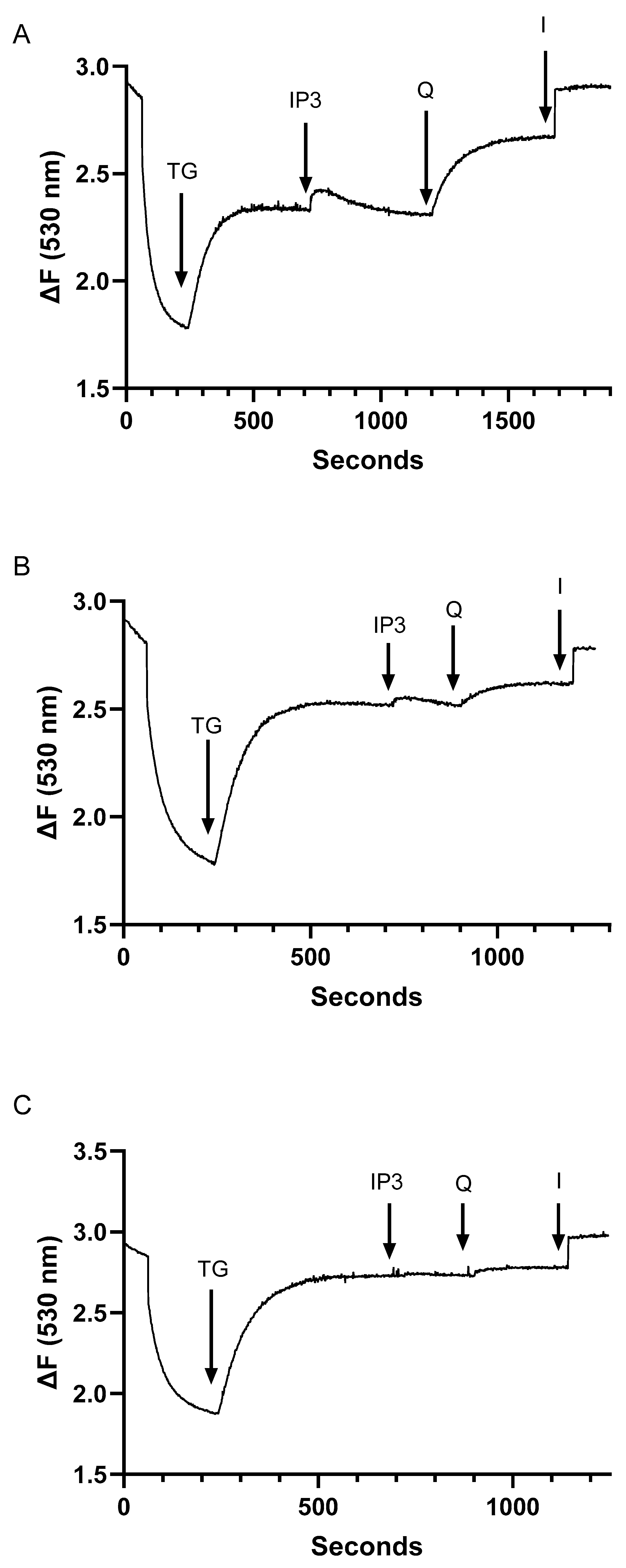
2.3. Assessment of Inter-Relationships of Agonist Releasable Ca2+ Pools in T Lymphocytes
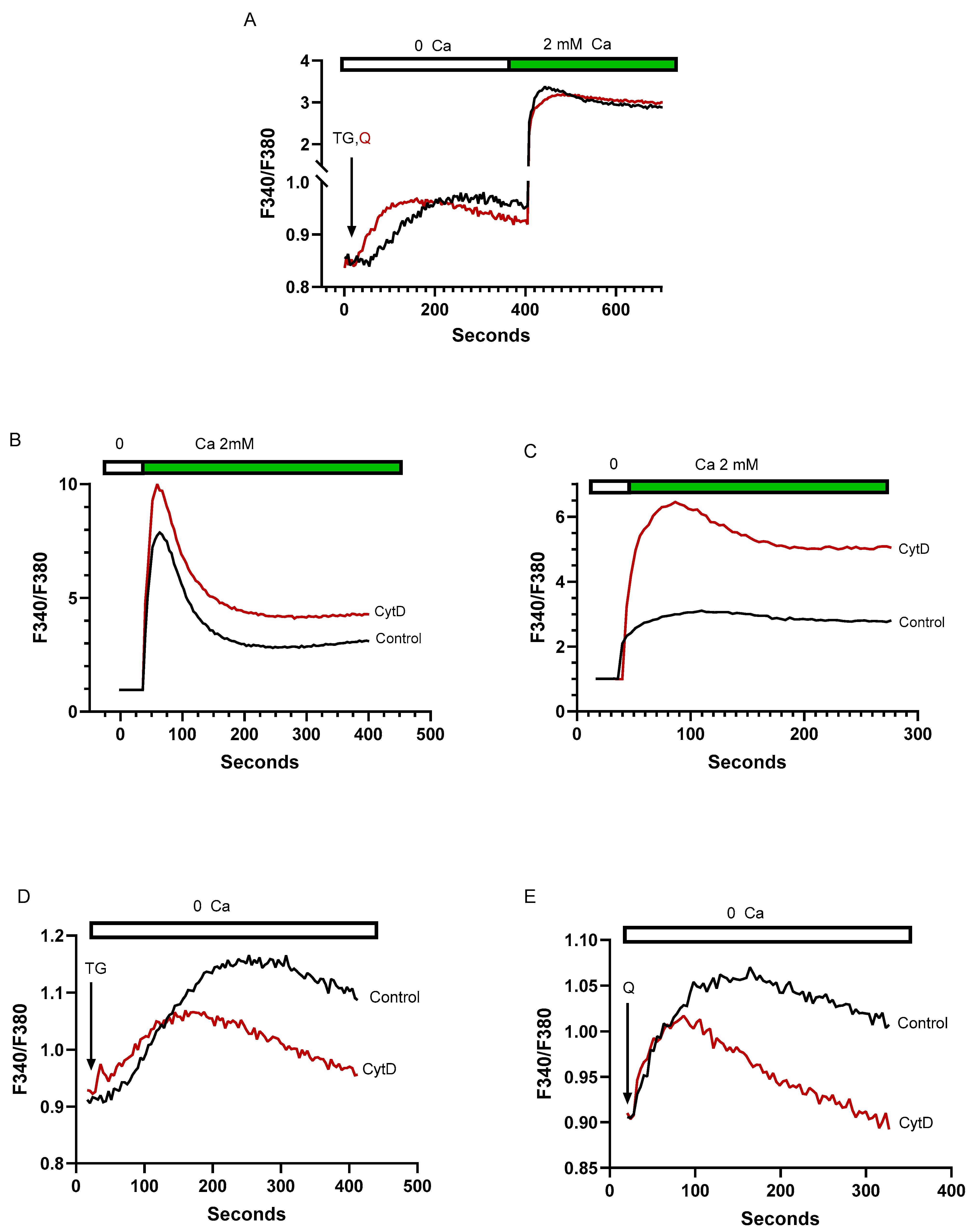
2.4. Despite Differences in SERCA Blocker Sensitivities and Agonist-Mobilizable Ca2+ Responses, the SERCA 2b and SERCA 3-Regulated Ca2+ Stores Exhibit Similar Ca2+ Influx Coupling Actions with Similar Sensitivity to Actin Cytoskeletal Disruption
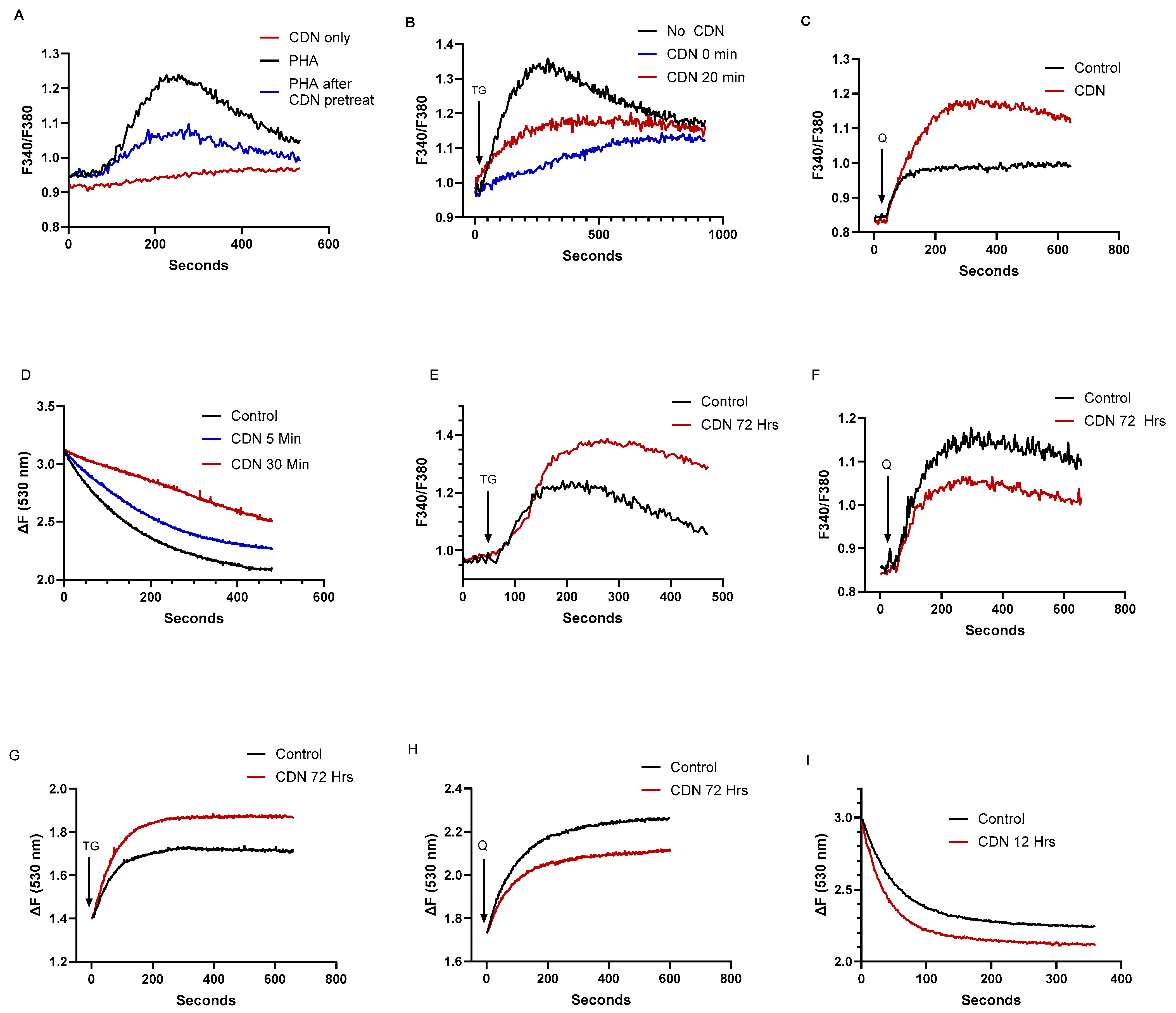
2.5. The SERCA Activator CDN1163 Exerts Complex Short- and Long-Term Effects on T Cell Ca2+ Stores, Revealing a Differential Regulatory Action on SERCA 2b Versus SERCA 3 Ca2+ Pools
2.6. The SERCA Activator CDN1163 Protects Against TG-Induced Cell Growth Suppression in Jurkat T Lymphocytes but Not Against tBHQ-Induced Growth Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Splenocyte Isolation
4.4. Cell Calcium Assays
4.5. Permeabilized Cell Assays
4.6. CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing of Jurkat T Lymphocytes
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Cell Viability Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janeway, C.A.; Bottomly, K. Signals and signs for lymphocyte responses. Cell 1994, 76, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.S.; Cahalan, M.D. Ion Channels and Signal Transduction in Lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1990, 52, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.S. Calcium Signaling Mechanisms in T Lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 497–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, D.; Diercks, B.-P.; Guse, A.H.; Dupont, G. Three-Dimensional Model of Sub-Plasmalemmal Ca2+ Microdomains Evoked by T Cell Receptor/CD3 Complex Stimulation. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 811145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M.J.; Lipp, P.; Bootman, M.D. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J. Lymphocyte Activation in Health and Disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 37, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebak, M.; Kinet, J.-P. Calcium signalling in T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornea, R.L.; Gruber, S.J.; Lockamy, E.L.; Muretta, J.M.; Jin, D.; Chen, J.; Dahl, R.; Bartfai, T.; Zsebo, K.M.; Gillispie, G.D.; et al. High-Throughput FRET Assay Yields Allosteric SERCA Activators. SLAS Discov. Adv. Sci. Drug Discov. 2013, 18, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidwell, P.A.; Yuen, S.L.; Li, J.; Berg, K.; Rebbeck, R.T.; Aldrich, C.C.; Roopnarine, O.; Cornea, R.L.; Thomas, D.D. A Large-Scale High-Throughput Screen for Modulators of SERCA Activity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bose, D.D.; Thomas, D.W. Paradoxical effects of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) activator gingerol on NG115-401L neuronal cells: Failure to augment ER Ca2+ uptake and protect against ER stress-induced cell death. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 762, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahate, K.; Bhatt, L.K.; Prabhavalkar, K.S. SERCA stimulation: A potential approach in therapeutics. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 95, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Dahl, R.; Hsieh, W.; Shin, A.; Zsebo, K.M.; Buettner, C.; Hajjar, R.J.; Lebeche, D. Small Molecular Allosteric Activator of the Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) Attenuates Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5185–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadini-Buoninsegni, F.; Smeazzetto, S.; Gualdani, R.; Moncelli, M.R. Drug Interactions with the Ca2+-ATPase From Sarco(Endo)Plasmic Reticulum (SERCA). Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakovskaya, A.; Erofeev, A.; Vinokurov, E.; Pchitskaya, E.; Dahl, R.; Bezprozvanny, I. Positive Allosteric Modulators of SERCA Pump Restore Dendritic Spines and Rescue Long-Term Potentiation Defects in Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajnak, K.; Dahl, R. A new target for Alzheimer’s disease: A small molecule SERCA activator is neuroprotective in vitro and improves memory and cognition in APP/PS1 mice. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1591–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordi, G.; Goti, A.; Young, H.S.; Palchetti, I.; Tadini-Buoninsegni, F. Stimulation of Ca2+-ATPase Transport Activity by a Small-Molecule Drug. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J. The endoplasmic reticulum: A multifunctional signaling organelle. Cell Calcium 2002, 32, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J.; Bootman, M.D.; Roderick, H.L. Calcium signalling: Dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemaly, E.R.; Troncone, L.; Lebeche, D. SERCA control of cell death and survival. Cell Calcium 2018, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inesi, G.; Sagara, Y. Specific inhibitors of intracellular Ca2+ transport ATPases. J. Membr. Biol. 1994, 141, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inesi, G.; Hua, S.; Xu, C.; Ma, H.; Seth, M.; Prasad, A.M.; Sumbilla, C. Studies of Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) Inhibition. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2005, 37, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytton, J.; Westlin, M.; Hanley, M.R. Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase family of calcium pumps. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17067–17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.; Hanley, M.R. Pharmacological tools for perturbing intracellular calcium storage. Methods Cell Biol. 1994, 40, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengeste, A.M.; Lund, J.; Katare, P.; Ghobadi, R.; Bakke, H.G.; Lunde, P.K.; Eide, L.; Mahony, G.O.; Göpel, S.; Peng, X.-R.; et al. The small molecule SERCA activator CDN1163 increases energy metabolism in human skeletal muscle cells. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2021, 2, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britzolaki, A.; Cronin, C.C.; Flaherty, P.R.; Rufo, R.L.; Pitychoutis, P.M. Chronic but not acute pharmacological activation of SERCA induces behavioral and neurochemical effects in male and female mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 399, 112984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Noriega Polo, C.; Wiederkehr, A.; Wollheim, C.B.; Park, K.S. CDN1163, an activator of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase, up-regulates mitochondrial functions and protects against lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta-cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 180, 2762–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guse, A.H.; Roth, E.; Emmrich, F. Intracellular Ca2+ pools in Jurkat T-lymphocytes. Biochem. J. 1993, 291, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadsetan, S.; Zakharova, L.; Molinski, T.F.; Fomina, A.F. Store-operated Ca2+ Influx Causes Ca2+ Release from the Intracellular Ca2+ Channels That Is Required for T Cell Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12512–12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astoul, E.; Edmunds, C.; Cantrell, D.A.; Ward, S.G. PI 3-K and T-cell activation: Limitations of T-leukemic cell lines as signaling models. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, J.C.; Romito, O.; Abdelnaby, A.E.; Xin, P.; Pathak, T.; Weir, S.E.; Kirk, V.; Castaneda, F.; Yoast, R.E.; Emrich, S.M.; et al. A multiple-oscillator mechanism underlies antigen-induced Ca2+ oscillations in Jurkat T-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, F.; Blagih, J.; Gruber, T.; Buck, M.D.; Jones, N.; Hennequart, M.; Newell, C.L.; Pilley, S.E.; Soro-Barrio, P.; Kelly, G.; et al. The dietary sweetener sucralose is a negative modulator of T cell-mediated responses. Nature 2023, 615, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuytack, F.; Papp, B.; Verboomen, H.; Raeymaekers, L.; Dode, L.; Bobe, R.; Enouf, J.; Bokkala, S.; Authi, K.; Casteels, R. A sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 3-type Ca2+ pump is expressed in platelets, in lymphoid cells, and in mast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.D.; Lee, W.S.; Wey, J.; Bungard, D.; Lytton, J. Localization and quantification of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase isoform transcripts. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1995, 269, C775–C784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poch, E.; Leach, S.; Snape, S.; Cacic, T.; MacLennan, D.H.; Lytton, J. Functional characterization of alternatively spliced human SERCA3 transcripts. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1998, 275, C1449–C1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, T.; Felfoldi, F.; Papp, B.; Paszty, K.; Bredoux, R.; Enyedi, A.; Enouf, J. All three splice variants of the human sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 3 gene are translated to proteins: A study of their co-expression in platelets and lymphoid cells. Biochem. J. 2001, 358, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallini, L.; Coassin, M.; Alexandre, A. Two classes of agonist-sensitive Ca2+ stores in platelets, as identified by their differential sensitivity to 2,5-di-(tert-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone and thapsigargin. Biochem. J. 1995, 310, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, B.; Enyedi, A.; Pászty, K.; Kovács, T.; Sarkadi, B.; Gárdos, G.; Magnier, C.; Wuytack, F.; Enouf, J. Simultaneous presence of two distinct endoplasmic-reticulum-type calcium-pump isoforms in human cells. Characterization by radio-immunoblotting and inhibition by 2,5-di-(t-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone. Biochem. J. 1992, 288, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.J.; Camello-Almaraz, C.; Pariente, J.A.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. Ca2+ accumulation into acidic organelles mediated by Ca2+- and vacuolar H+-ATPases in human platelets. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardín, I.; López, J.J.; Pariente, J.A.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. Intracellular Calcium Release from Human Platelets: Different Messengers for Multiple Stores. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2008, 18, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardin, I.; Ben Amor, N.; Bartegi, A.; Pariente, J.A.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. Differential involvement of thrombin receptors in Ca2+ release from two different intracellular stores in human platelets. Biochem. J. 2006, 401, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.J.; Redondo, P.C.; Salido, G.M.; Pariente, J.A.; Rosado, J.A. Two distinct Ca2+ compartments show differential sensitivity to thrombin, ADP and vasopressin in human platelets. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaïb, Z.; Adam, F.; Berrou, E.; Bordet, J.-C.; Prévost, N.; Bobe, R.; Bryckaert, M.; Rosa, J.-P. Full activation of mouse platelets requires ADP secretion regulated by SERCA3 ATPase–dependent calcium stores. Blood 2016, 128, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomina, A.F. Neglected wardens: T lymphocyte ryanodine receptors. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 4415–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Dadsetan, S.; Fomina, A.F. Bidirectional Coupling between Ryanodine Receptors and Ca2+ Release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) Channel Machinery Sustains Store-operated Ca2+ Entry in Human T Lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37233–37244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guse, A.H.; Diercks, B. Integration of nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP)-dependent calcium signalling. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 2735–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, I.M.A.; Guse, A.H. Ca2+ Microdomains in T-Lymphocytes. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzmann, N.; Kunerth, S.; Weber, K.; Mayr, G.W.; Guse, A.H. Knock-down of the Type 3 Ryanodine Receptor Impairs Sustained Ca2+ Signaling via the T Cell Receptor/CD3 Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 50636–50642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenegger, M.; Berg, I.; Weigl, L.; Mayr, G.W.; Potter, B.V.L.; Guse, A.H. Pharmacological activation of the ryanodine receptor in Jurkat T-lymphocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammermann, W.; Guse, A.H. Functional Ryanodine Receptor Expression Is Required for NAADP-mediated Local Ca2+ Signaling in T-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21394–21399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, M.; Kirchberger, T.; Guse, A.H. NAADP Mobilizes Calcium from the Endoplasmic Reticular Ca2+ Store in T-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18864–18871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, J. Acidic Ca2+ stores in platelets. Cell Calcium 2011, 50, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Elaïb, Z.; Borgel, D.; Denis, C.V.; Adam, F.; Bryckaert, M.; Rosa, J.-P.; Bobe, R. NAADP/SERCA3-Dependent Ca 2+ Stores Pathway Specifically Controls Early Autocrine ADP Secretion Potentiating Platelet Activation. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, E166–E183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, J.A.; López, J.J.; Harper, A.G.S.; Harper, M.T.; Redondo, P.C.; Pariente, J.A.; Sage, S.O.; Salido, G.M. Two Pathways for Store-mediated Calcium Entry Differentially Dependent on the Actin Cytoskeleton in Human Platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 29231–29235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-P.; Huang, W.-W.; Tsai, K.-F.; Shiao, L.-R.; Yang, Z.-H.; Tseng, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chan, P.; Leung, Y.-M. CDN1163, a SERCA activator, causes intracellular Ca2+ leak, mitochondrial hyperpolarization and cell cycle arrest in mouse neuronal N2A cells. NeuroToxicology 2023, 98, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chuang, C.-M.; Shiao, L.-R.; Chan, P.; Leung, Y.-M. Suppression of Ca2+ oscillations by SERCA inhibition in human alveolar type 2 A549 cells: Rescue by ochratoxin A but not CDN1163. Life Sci. 2022, 308, 120913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunerth, S.; Mayr, G.W.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Guse, A.H. Analysis of subcellular calcium signals in T-lymphocytes. Cell. Signal. 2003, 15, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, S.; Bobe, R.; Lacabaratz-Porret, C.; Bredoux, R.; Kovàcs, T.; Enouf, J.; Papp, B. Modulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Pump Expression during T Lymphocyte Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 10746–10750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobe, R.; Bredoux, R.; Corvazier, E.; Andersen, J.P.; Clausen, J.D.; Dode, L.; Kovács, T.; Enouf, J. Identification, Expression, Function, and Localization of a Novel (Sixth) Isoform of the Human Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ATPase 3 Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 24297–24306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbabian, A.; Brouland, J.-P.; Gélébart, P.; Kovàcs, T.; Bobe, R.; Enouf, J.; Papp, B. Endoplasmic reticulum calcium pumps and cancer. BioFactors 2011, 37, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, B.; Brouland, J.-P.; Arbabian, A.; Gélébart, P.; Kovács, T.; Bobe, R.; Enouf, J.; Varin-Blank, N.; Apáti, Á. Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Pumps and Cancer Cell Differentiation. Biomolecules 2012, 2, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.J.; Jardín, I.; Bobe, R.; Pariente, J.A.; Enouf, J.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. STIM1 regulates acidic Ca2+ store refilling by interaction with SERCA3 in human platelets. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uddin, M.N.; Thomas, D.W. SERCA Modulators Reveal Distinct Signaling and Functional Roles of T Lymphocyte Ca2+ Stores. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212095
Uddin MN, Thomas DW. SERCA Modulators Reveal Distinct Signaling and Functional Roles of T Lymphocyte Ca2+ Stores. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(22):12095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212095
Chicago/Turabian StyleUddin, Md Nasim, and David W. Thomas. 2024. "SERCA Modulators Reveal Distinct Signaling and Functional Roles of T Lymphocyte Ca2+ Stores" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 22: 12095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212095
APA StyleUddin, M. N., & Thomas, D. W. (2024). SERCA Modulators Reveal Distinct Signaling and Functional Roles of T Lymphocyte Ca2+ Stores. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(22), 12095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212095





