Assessing the Orthogonality of Phage-Encoded RNA Polymerases for Tailored Synthetic Biology Applications in Pseudomonas Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
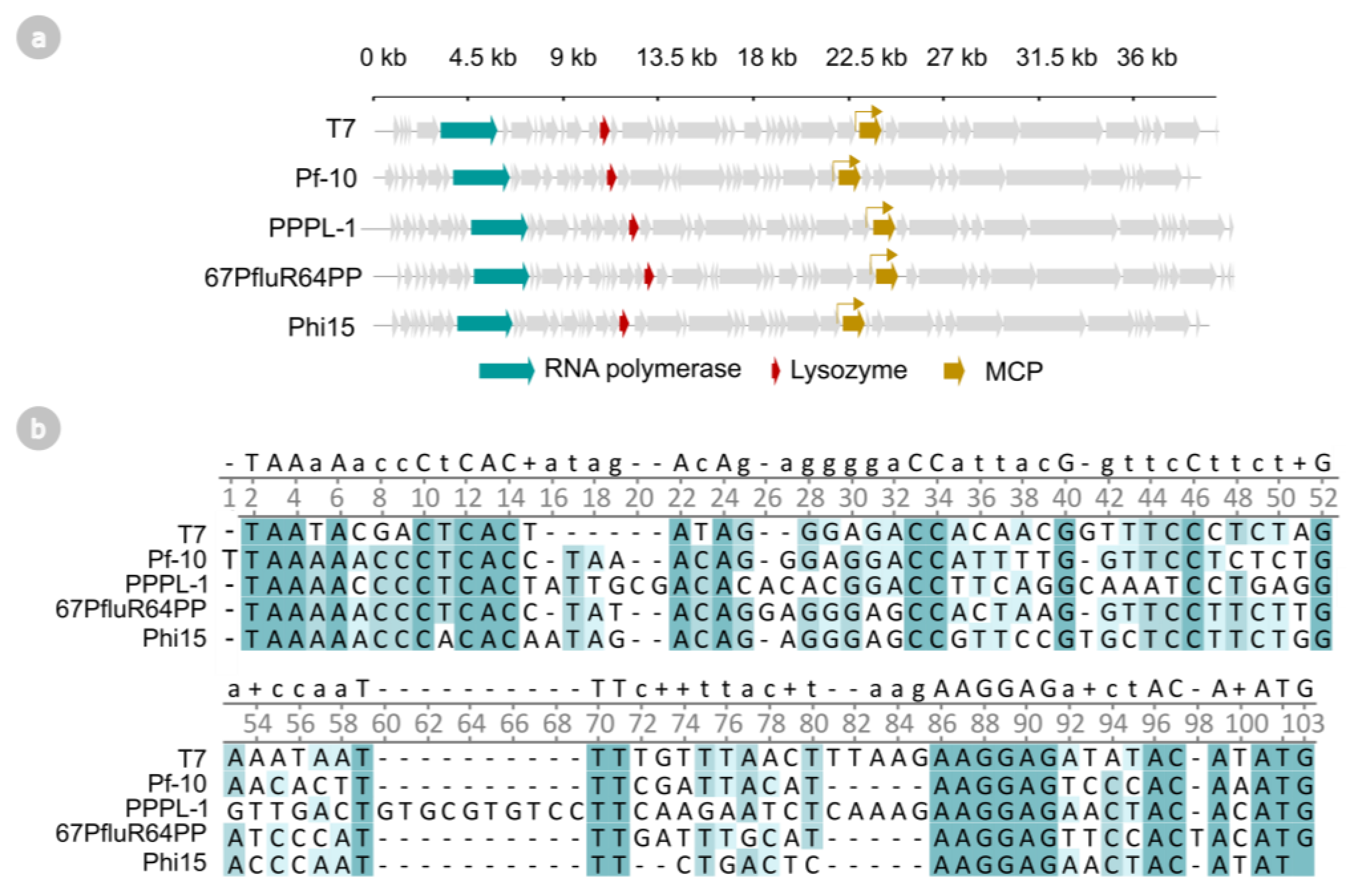
2.1. T7-like Pseudomonas Phage Genomes Encode Putative RNA Polymerases, Lysozymes, and Phage-Specific Promoters
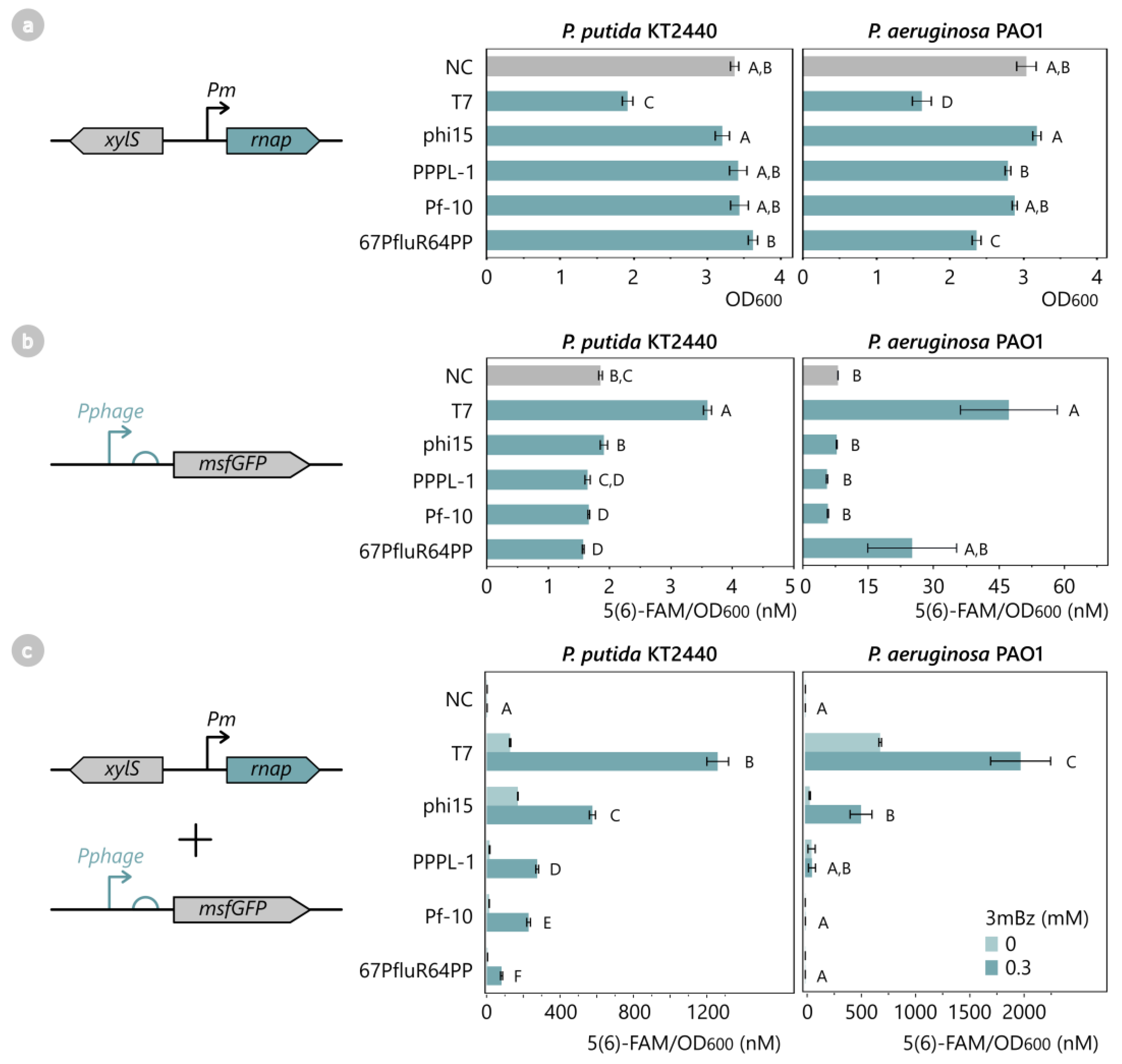
2.2. Screening Non-Toxic Phage RNA Polymerases and Their Transcriptional Activity
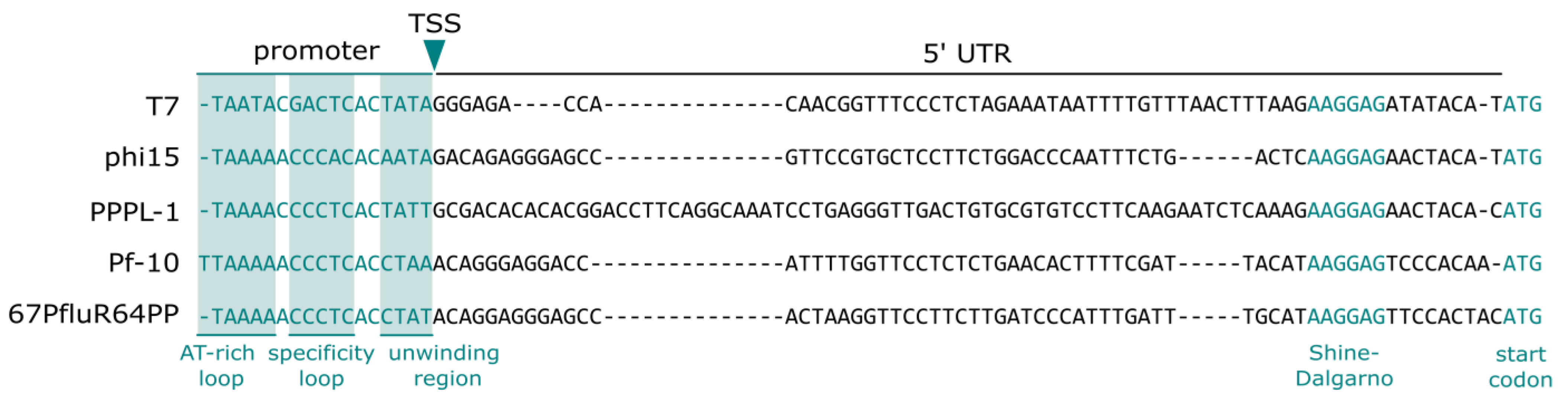
2.3. Phages phi15, PPPL-1, Pf-10, and 67PfluR64PP Encode Short, 17 bp Promoters
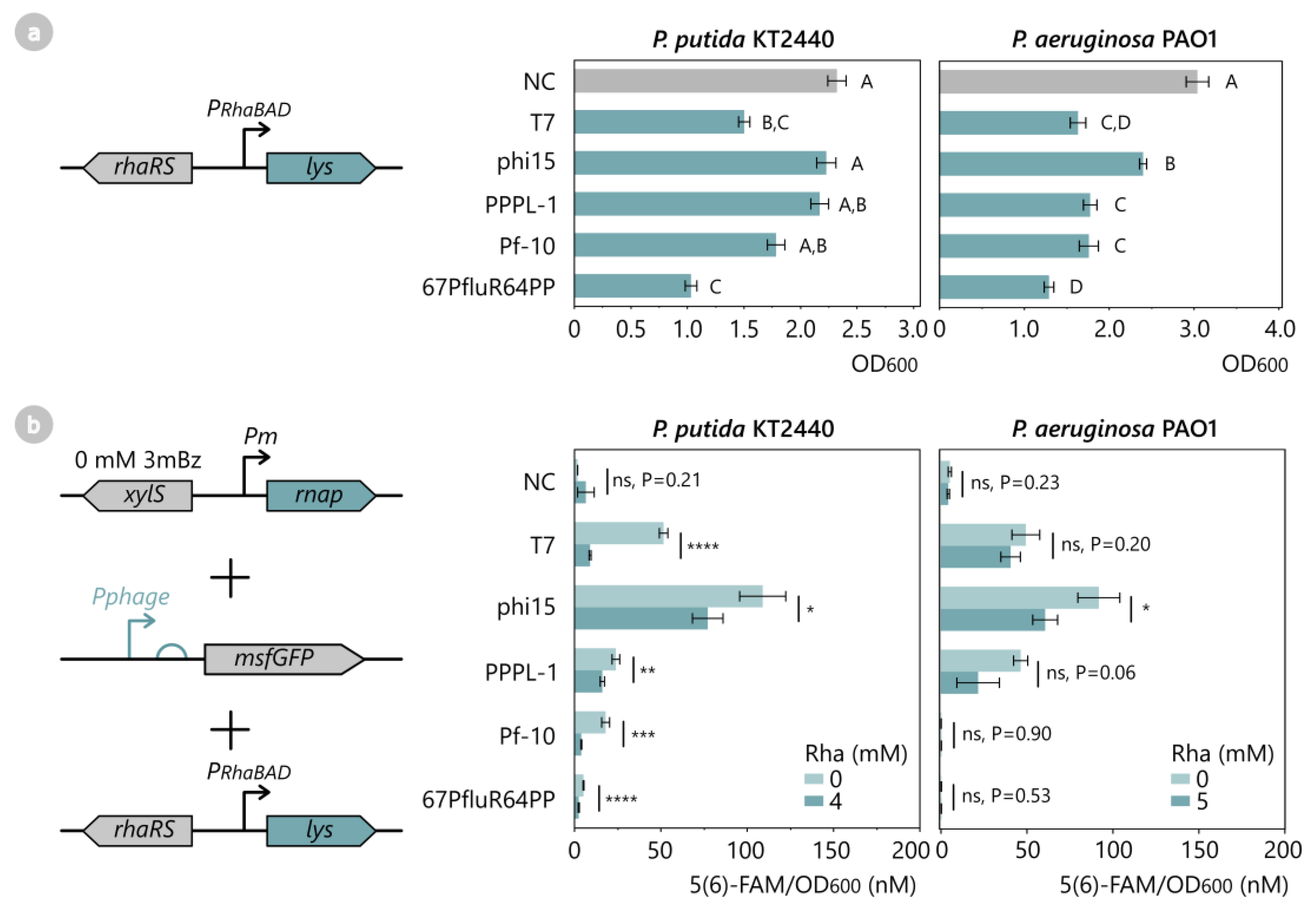
2.4. T7-like Phage Lysozymes Inhibit Transcriptional Activity of Their Corresponding Phage RNAP
2.5. T7-like Phage Lysozymes Efficiently Inhibit Phage RNAPs from Related T7-like Phages
2.6. Flow Cytometry-Based Quantitative Assessment of the phi15 Expression System
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacteriophage Genomes
4.2. Bacterial Manipulation
4.3. Vector Construction
4.4. Toxicity Evaluation by Growth Curve Monitoring
4.5. Fluorescence Intensity Assays
4.6. Transcription Start Site Determination with 5′-Capping-RACE
4.7. Flow Cytometry
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lammens, E.-M.; Nikel, P.I.; Lavigne, R. Exploring the Synthetic Biology Potential of Bacteriophages for Engineering Non-Model Bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davanloo, P.; Rosenberg, A.H.; Dunn, J.J.; Studier, F.W. Cloning and Expression of the Gene for Bacteriophage T7 RNA Polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 2035–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studier, F.W. Use of Bacteriophage T7 Lysozyme to Improve an Inducible T7 Expression System. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 219, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Lian, G.; Li, H.; Han, H.; Zhou, D.; Gong, X. Ultrasensitive Sensing of T4 PNK Phosphatase Activity through Establishing a Novel Transcription-Based Signal Amplification Platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 369, 132269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.; de Lorenzo, V.; Ensley, B.; Timmis, K.N. A T7 RNA polymerase-based system for the construction of Pseudomonas strains with phenotypes dependent on TOL-meta pathway effectors. Gene 1993, 134, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temme, K.; Hill, R.; Segall-Shapiro, T.H.; Moser, F.; Voigt, C.A. Modular control of multiple pathways using engineered orthogonal T7 polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 8773–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shis, D.L.; Bennett, M.R. Library of Synthetic Transcriptional AND Gates Built with Split T7 RNA Polymerase Mutants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5028–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall-Shapiro, T.H.; Meyer, A.J.; Ellington, A.D.; Sontag, E.D.; Voigt, C.A. A ‘Resource Allocator’ for Transcription Based on a Highly Fragmented T7 RNA Polymerase. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2014, 10, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumschlager, A.; Aoki, S.K.; Khammash, M. Dynamic Blue Light-Inducible T7 RNA Polymerases (Opto-T7RNAPs) for Precise Spatiotemporal Gene Expression Control. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milias-Argeitis, A.; Rullan, M.; Aoki, S.K.; Buchmann, P.; Khammash, M. Automated optogenetic feedback control for precise and robust regulation of gene expression and cell growth. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.; Ramirez, J.L.M.; Mahfouz, M. Synthetic evolution of herbicide resistance using a T7 RNAP–based random DNA base editor. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202201538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeschcke, A.; Thies, S. Pseudomonas putida—A Versatile Host for the Production of Natural Products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6197–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivisaar, M. Narrative of a Versatile and Adept Species Pseudomonas putida. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, M.; Salis, H.M. A portable expression resource for engineering cross-species genetic circuits and pathways. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Li, Q. Integrating T7 RNA Polymerase and Its Cognate Transcriptional Units for a Host-Independent and Stable Expression System in Single Plasmid. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihmann, R.; Domröse, A.; Drepper, T.; Jaeger, K.; Loeschcke, A. Protocols for yTREX /Tn5-based gene cluster expression in Pseudomonas putida. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 13, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beentjes, M.; Ortega-Arbulú, A.-S.; Löwe, H.; Pflüger-Grau, K.; Kremling, A. Targeting Transcriptional and Translational Hindrances in a Modular T7RNAP Expression System in Engineered Pseudomonas putida. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 3939–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, P.; Jensen, S.I.; Nielsen, A.T. Broad-Host-Range ProUSER Vectors Enable Fast Characterization of Inducible Promoters and Optimization of p-Coumaric Acid Production in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. ACS Synth. Biol. 2016, 5, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.B.; Rand, J.M.; Nurani, W.; Courtney, D.K.; Liu, S.A.; Pfleger, B.F. Genetic Tools for Reliable Gene Expression and Recombineering in Pseudomonas putida. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Pascual, M.; Batianis, C.; Bruinsma, L.; Asin-Garcia, E.; Garcia-Morales, L.; Weusthuis, R.A.; van Kranenburg, R.; dos Santos, V.A.M. A navigation guide of synthetic biology tools for Pseudomonas putida. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 49, 107732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Sun, J.; Ju, S.; Su, S.; Yang, L.; Wu, J. Construction of T7-Like Expression System in Pseudomonas putida KT2440 to Enhance the Heterologous Expression Level. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Újvári, A.; Martin, C.T. Identification of a minimal binding element within the T7 RNA polymerase promoter. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 273, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheetham, G.M.T.; Steitz, T.A. Structure of a Transcribing T7 RNA Polymerase Initiation Complex. Science 1999, 286, 2305–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Linhardt, R.J. Bacteriophage T7 transcription system: An enabling tool in synthetic biology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.D. DNA Sequence for the T7 RNA Polymerase Promoter for T7 RNA Species II. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 147, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Mukherjee, S. T7 RNA Polymerase. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2003, 73, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, K.; Chen, H.-C.; Liu, Z.-F. Capping-RACE: A simple, accurate, and sensitive 5′ RACE method for use in prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalik, V.K.; Guimaraes, J.C.; Cambray, G.; Lam, C.; Christoffersen, M.J.; Mai, Q.A.; Tran, A.B.; Paull, M.; Keasling, J.D.; Arkin, A.P.; et al. Precise and Reliable Gene Expression via Standard Transcription and Translation Initiation Elements. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobel, S.; Benedetti, I.; Eisenbach, L.; De Lorenzo, V.; Wierckx, N.; Blank, L.M. Tn7-Based Device for Calibrated Heterologous Gene Expression in Pseudomonas putida. ACS Synth. Biol. 2015, 4, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salis, H.M.; Mirsky, E.A.; Voigt, C.A. Automated Design of Synthetic Ribosome Binding Sites to Control Protein Expression. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, B.A.; Studier, F.W. T7 Lysozyme Inhibits Transcription by T7 RNA Polymerase. Cell 1987, 49, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Pflugrath, J.W.; Studier, F.W. The Structure of Bacteriophage T7 Lysozyme, a Zinc Amidase and an Inhibitor of T7 RNA Polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4034–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeruzalmi, D.; Steitz, T.A. Structure of T7 RNA Polymerase Complexed to the Transcriptional Inhibitor T7 Lysozyme. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4101–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammens, E.; Boon, M.; Grimon, D.; Briers, Y.; Lavigne, R. SEVAtile: A standardised DNA assembly method optimised for Pseudomonas. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 15, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemire, S.; Yehl, K.M.; Lu, T.K. Phage-Based Applications in Synthetic Biology. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, P.; Volke, D.C.; Lowe, P.T.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; O’Hagan, D.; Nikel, P.I. A Fluoride-Responsive Genetic Circuit Enables in Vivo Biofluorination in Engineered Pseudomonas Putida. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franden, M.A.; Jayakody, L.N.; Li, W.-J.; Wagner, N.J.; Cleveland, N.S.; Michener, W.E.; Hauer, B.; Blank, L.M.; Wierckx, N.; Klebensberger, J.; et al. Engineering Pseudomonas putida KT2440 for efficient ethylene glycol utilization. Metab. Eng. 2018, 48, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, V.; García, P.; García, J.L.; Prieto, M.A. Controlled autolysis facilitates the polyhydroxyalkanoate recovery in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyssens, P.-J.; De Smet, J.; Wagemans, J.; Akulenko, N.; Klimuk, E.; Hedge, S.; Voet, M.; Hendrix, H.; Paeshuyse, J.; Landuyt, B.; et al. The Phage-Encoded N-Acetyltransferase Rac Mediates Inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Transcription by Cleavage of the RNA Polymerase Alpha Subunit. Viruses 2020, 12, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Studier, F. Multiple Roles of T7 RNA Polymerase and T7 Lysozyme During Bacteriophage T7 Infection. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 707–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, A.; Ceyssens, P.-J.; T’Syen, J.; Van Praet, H.; Noben, J.-P.; Shaburova, O.V.; Krylov, V.N.; Volckaert, G.; Lavigne, R. The T7-Related Pseudomonas putida Phage φ15 Displays Virion-Associated Biofilm Degradation Properties. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lim, J.-A.; Yu, J.-G.; Oh, C.-S. Genomic Features and Lytic Activity of the Bacteriophage PPPL-1 Effective against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae, a Cause of Bacterial Canker in Kiwifruit. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierczak, J.; Wójcik, E.A.; Witaszewska, J.; Guziński, A.; Górecka, E.; Stańczyk, M.; Kaczorek, E.; Siwicki, A.K.; Dastych, J. Complete genome sequences of Aeromonas and Pseudomonas phages as a supportive tool for development of antibacterial treatment in aquaculture. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J. Mol. Biol. 1983, 166, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-H.; Kumar, A.; Schweizer, H.P. A 10-min method for preparation of highly electrocompetent Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells: Application for DNA fragment transfer between chromosomes and plasmid transformation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 64, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beal, J.; Haddock-Angelli, T.; Baldwin, G.; Gershater, M.; Dwijayanti, A.; Storch, M.; De Mora, K.; Lizarazo, M.; Rettberg, R.; with the iGEM Interlab Study Contributors. Quantification of bacterial fluorescence using independent calibrants. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.M.; Hoffmann, S.; Darfeuille, F.; Reignier, J.; Findeiß, S.; Sittka, A.; Chabas, S.; Reiche, K.; Hackermüller, J.; Reinhardt, R.; et al. The primary transcriptome of the major human pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 2010, 464, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| P. putida Wild-Type | P. putida phi15 | P. putida phi15 (G3RQ) | |||||
| FITC-A | Induced (%) | FITC-A | Induced (%) | FITC-A | Induced (%) | ||
| −RNAP | +lys | 44 | 0.16 | 17,803 | 80.00 | 12,730 | 66.66 |
| −RNAP | −lys | 70 | 0.12 | 15,270 | 74.74 | 32,128 | 78.50 |
| +RNAP | −lys | 99 | 0.30 | 72,956 | 95.40 | 122,739 | 92.82 |
| Fold induction * | 2.25 | 4.10 | 9.64 | ||||
| P. aeruginosa Wild-Type | P. aeruginosa phi15 | P. aeruginosa phi15 (G3RQ) | |||||
| FITC-A | Induced (%) | FITC-A | Induced (%) | FITC-A | Induced (%) | ||
| −RNAP | +lys | 647 | 3.22 | 33,429 | 77.52 | 527 | 5.94 |
| −RNAP | −lys | 692 | 6.18 | 7820 | 47.74 | 18,672 | 81.10 |
| +RNAP | −lys | 559 | 3.22 | 245,893 | 90.98 | 68,392 | 74.58 |
| Fold induction * | 0.86 | 7.36 | 129.78 | ||||
| Bacteriophage | Accession Number | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Phi15 | FR823298.1 | [41] |
| Pf-10 | NC_027292.1 | Unpublished |
| PPPL-1 | NC_028661.1 | [42] |
| 67PfluR64PP | MH179478.2 | [43] |
| Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| TSS_TSO | ACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTrGrGrG |
| TSS_outerprimer | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCT |
| TSS_innerprimer | ATAGCTCTTCTAGACTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCT |
| TSS_GSP1 | TCAGTTTACCGTTGGTTGCATCACCTTCACCTTCACCACGAACAGAGAATTTGTGGCC |
| TSS_GSP2 | TAGGCTCTTCTCTTCGAACAGAGAATTTGTGGCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lammens, E.-M.; Feyaerts, N.; Kerremans, A.; Boon, M.; Lavigne, R. Assessing the Orthogonality of Phage-Encoded RNA Polymerases for Tailored Synthetic Biology Applications in Pseudomonas Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087175
Lammens E-M, Feyaerts N, Kerremans A, Boon M, Lavigne R. Assessing the Orthogonality of Phage-Encoded RNA Polymerases for Tailored Synthetic Biology Applications in Pseudomonas Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087175
Chicago/Turabian StyleLammens, Eveline-Marie, Nathalie Feyaerts, Alison Kerremans, Maarten Boon, and Rob Lavigne. 2023. "Assessing the Orthogonality of Phage-Encoded RNA Polymerases for Tailored Synthetic Biology Applications in Pseudomonas Species" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087175
APA StyleLammens, E.-M., Feyaerts, N., Kerremans, A., Boon, M., & Lavigne, R. (2023). Assessing the Orthogonality of Phage-Encoded RNA Polymerases for Tailored Synthetic Biology Applications in Pseudomonas Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087175







