Generation and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Characterization of a Large Human Combinatorial Antibody Library
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
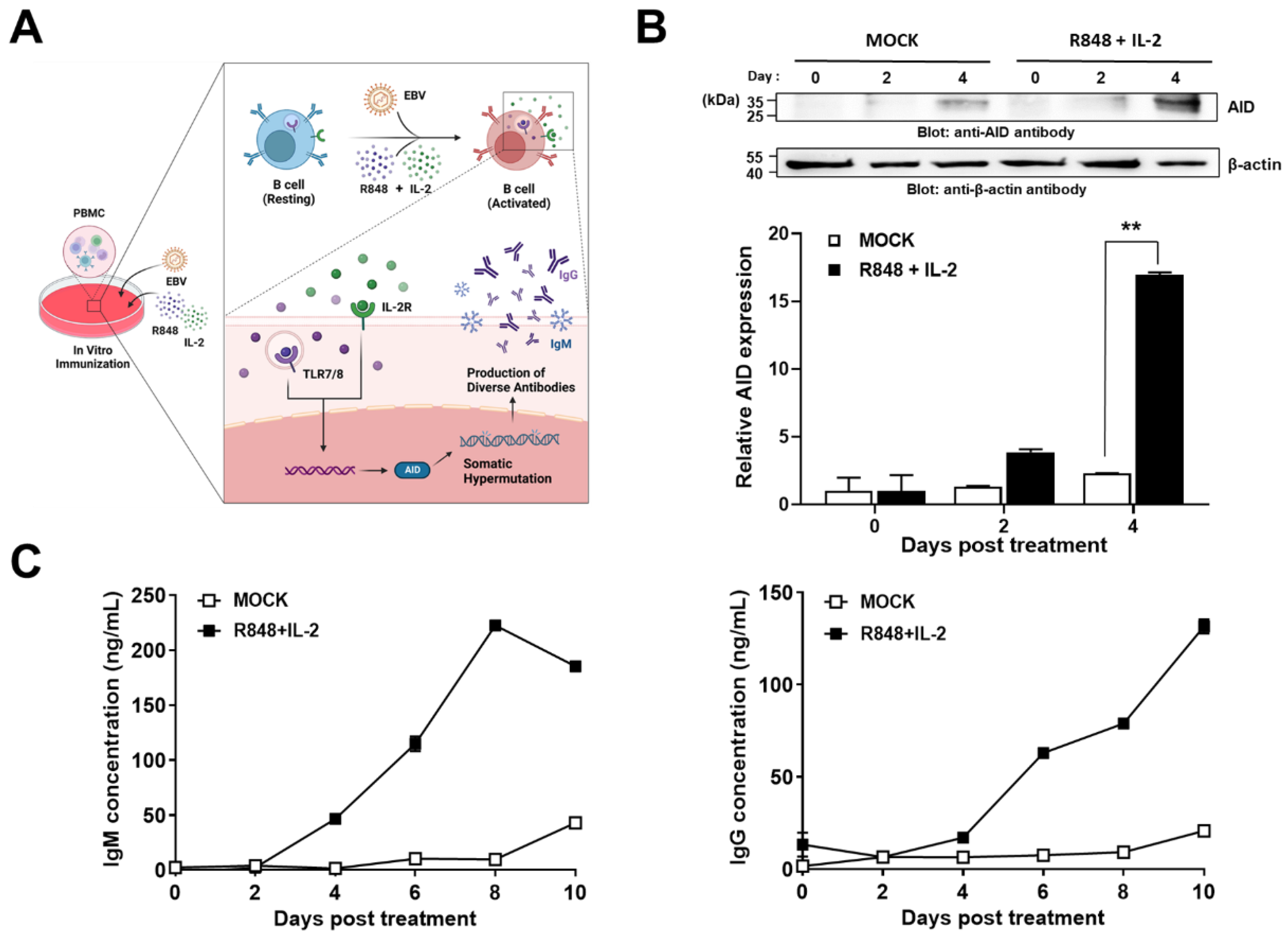
2.1. Construction of a Novel Human Combinatorial Antibody Library from Activated B-Cells
2.2. NGS of the Constructed Human scFv Antibody Library
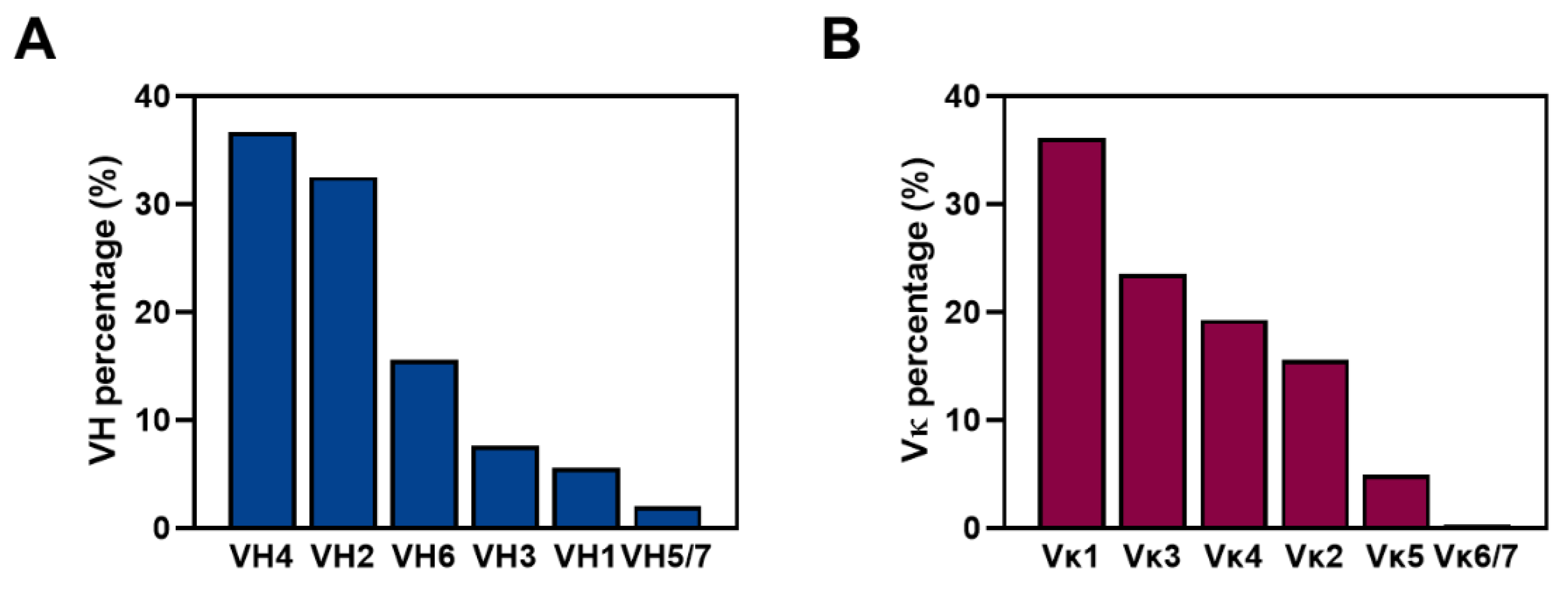
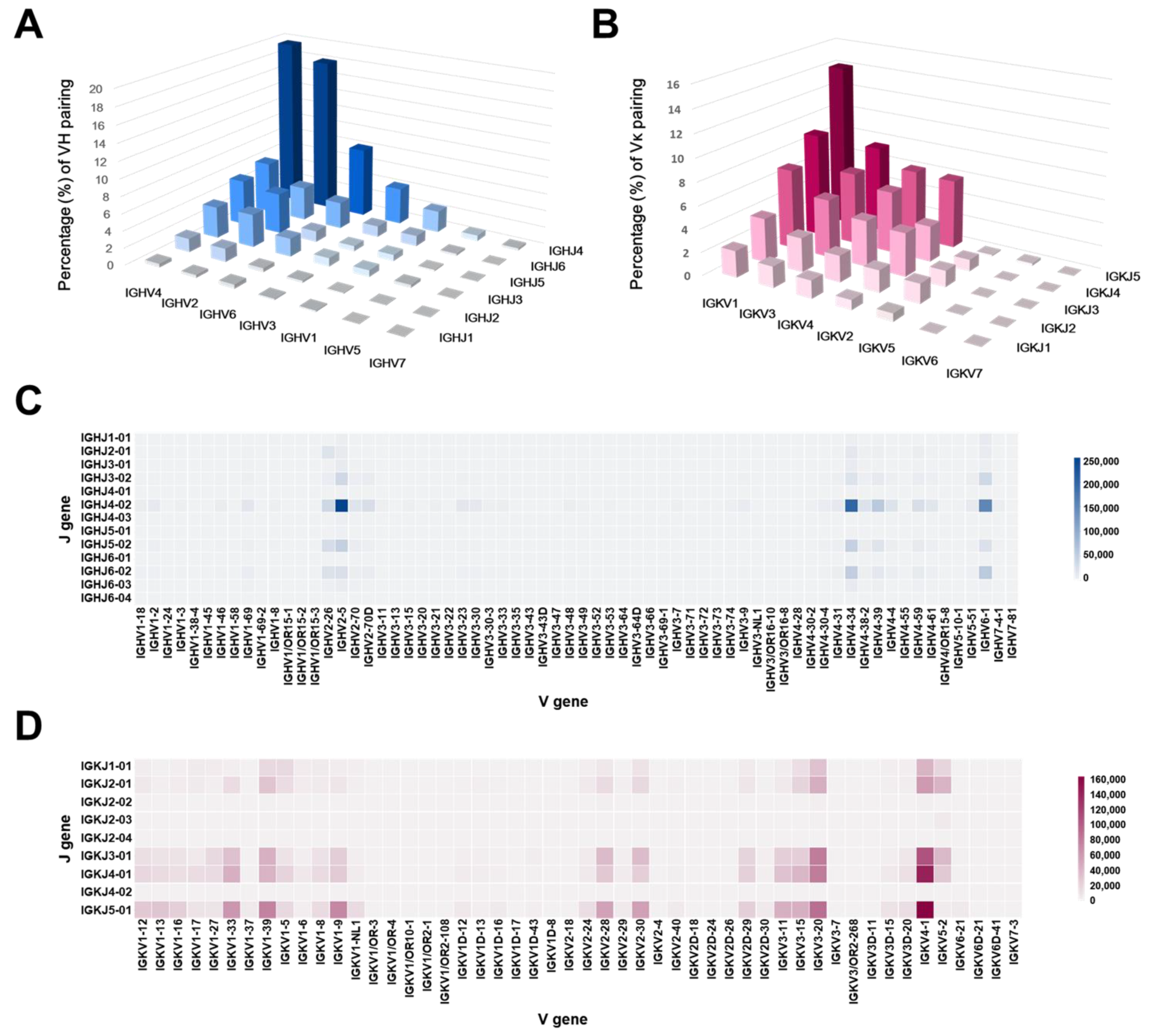
2.3. Germline Distribution Analysis of the Antibody Library Clones
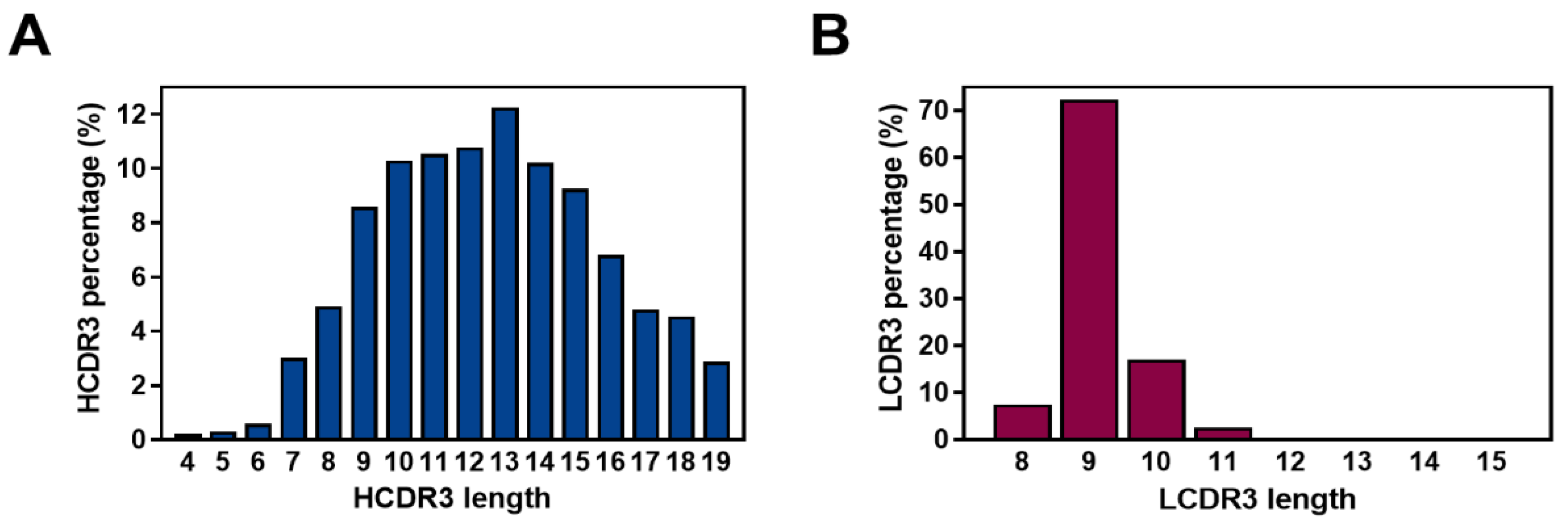
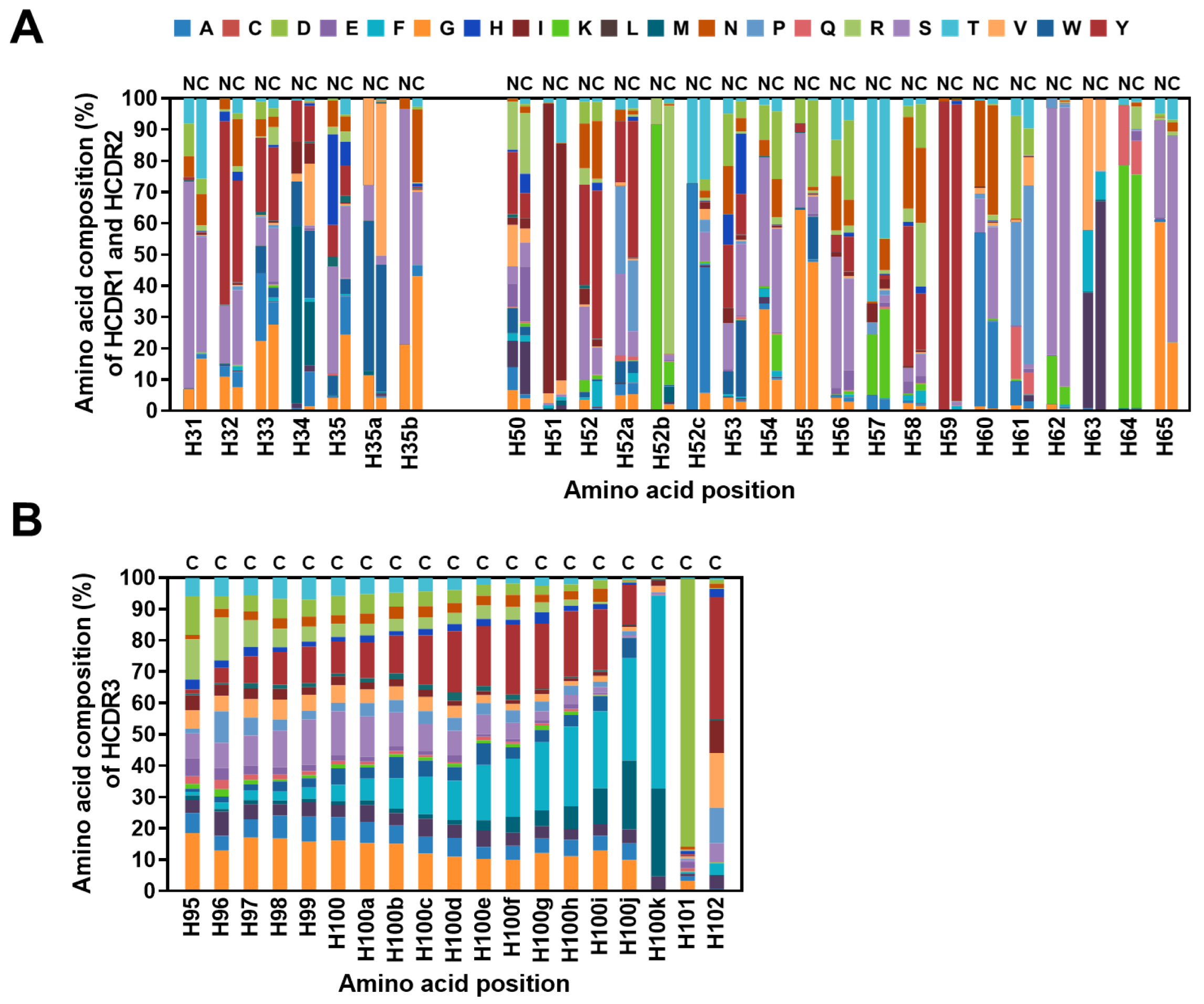
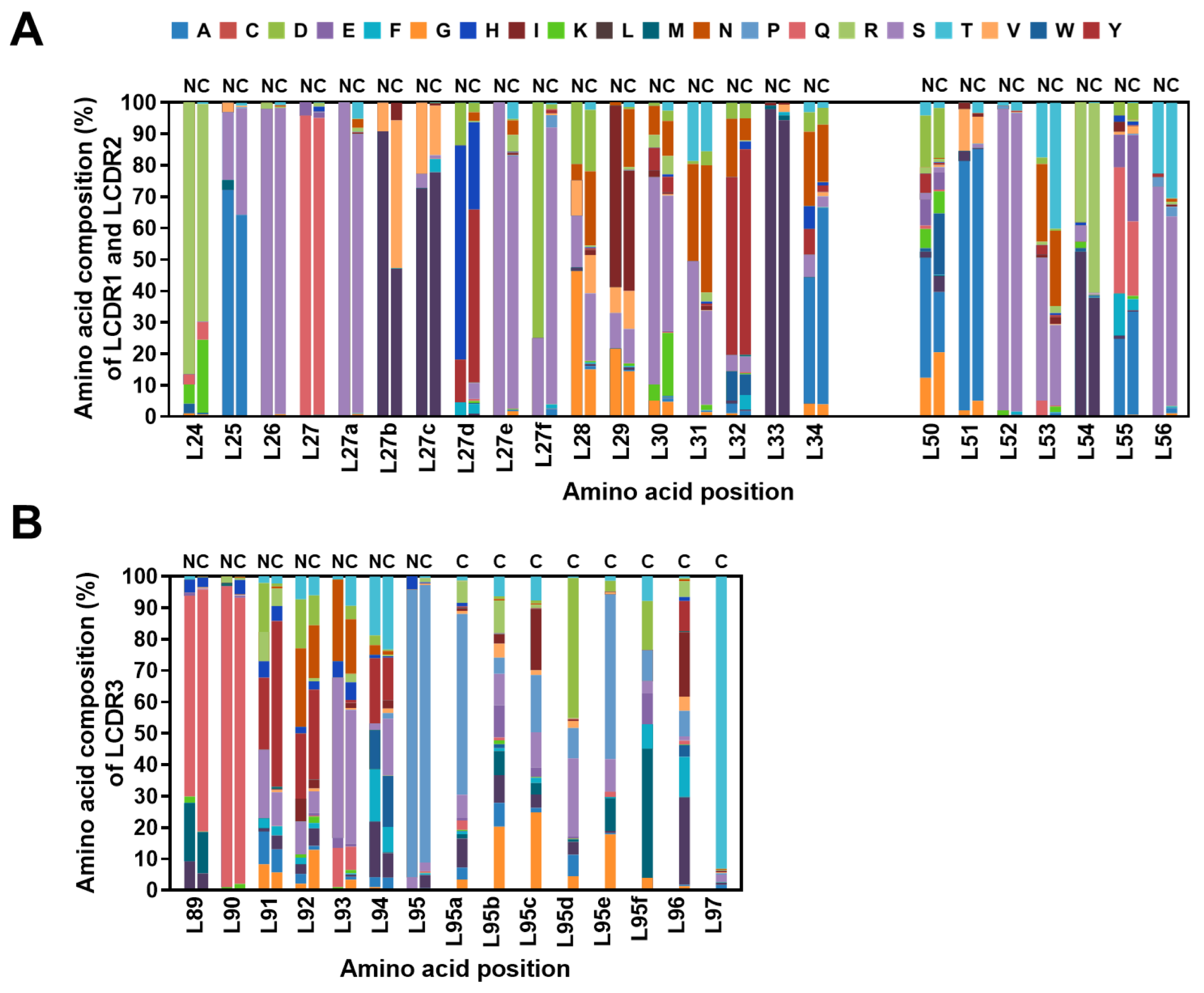
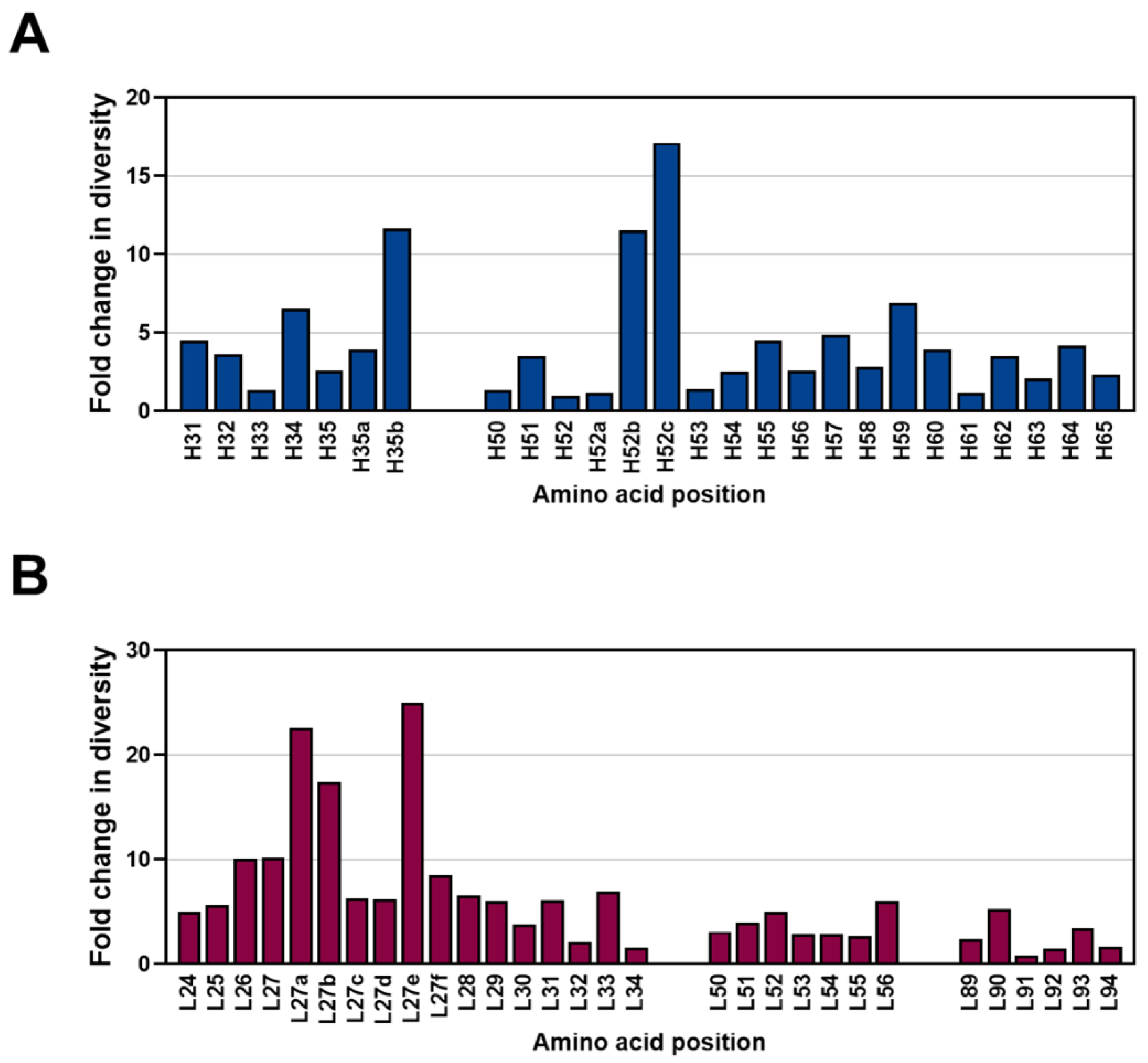
2.4. Diversity Assessment of the Length and Amino Acid Composition of CDRs
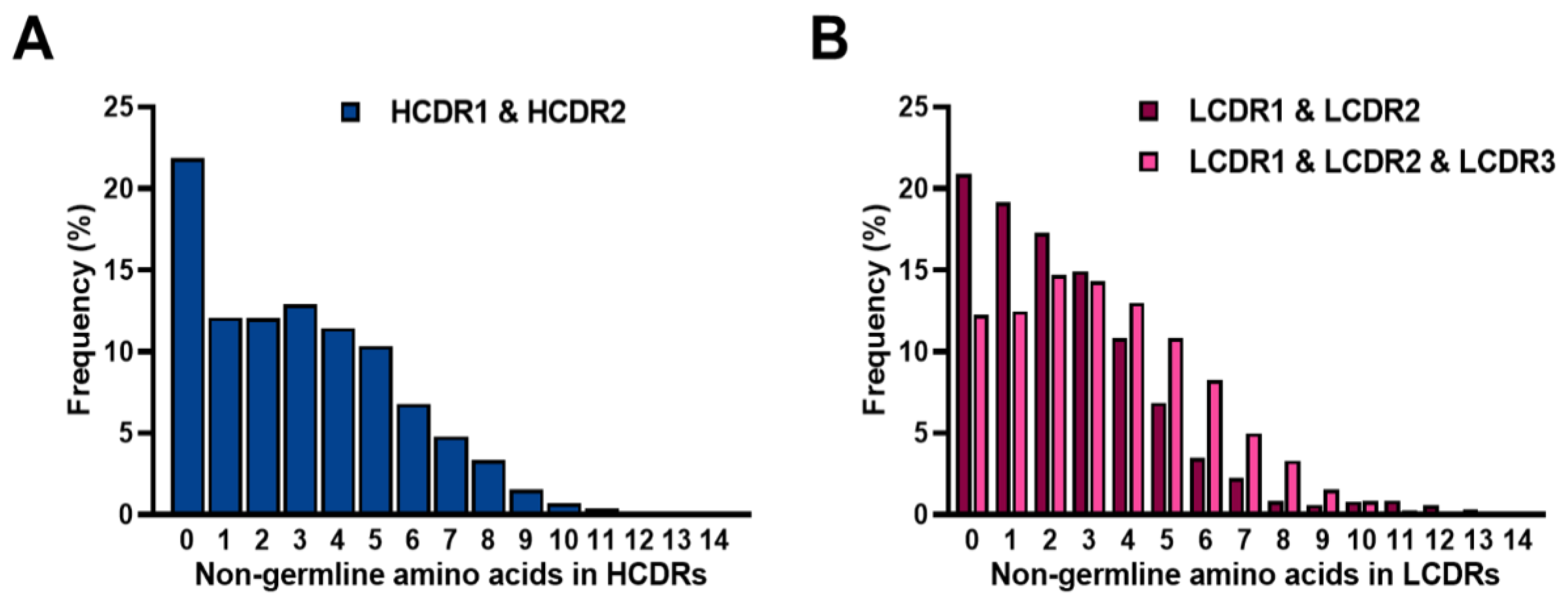
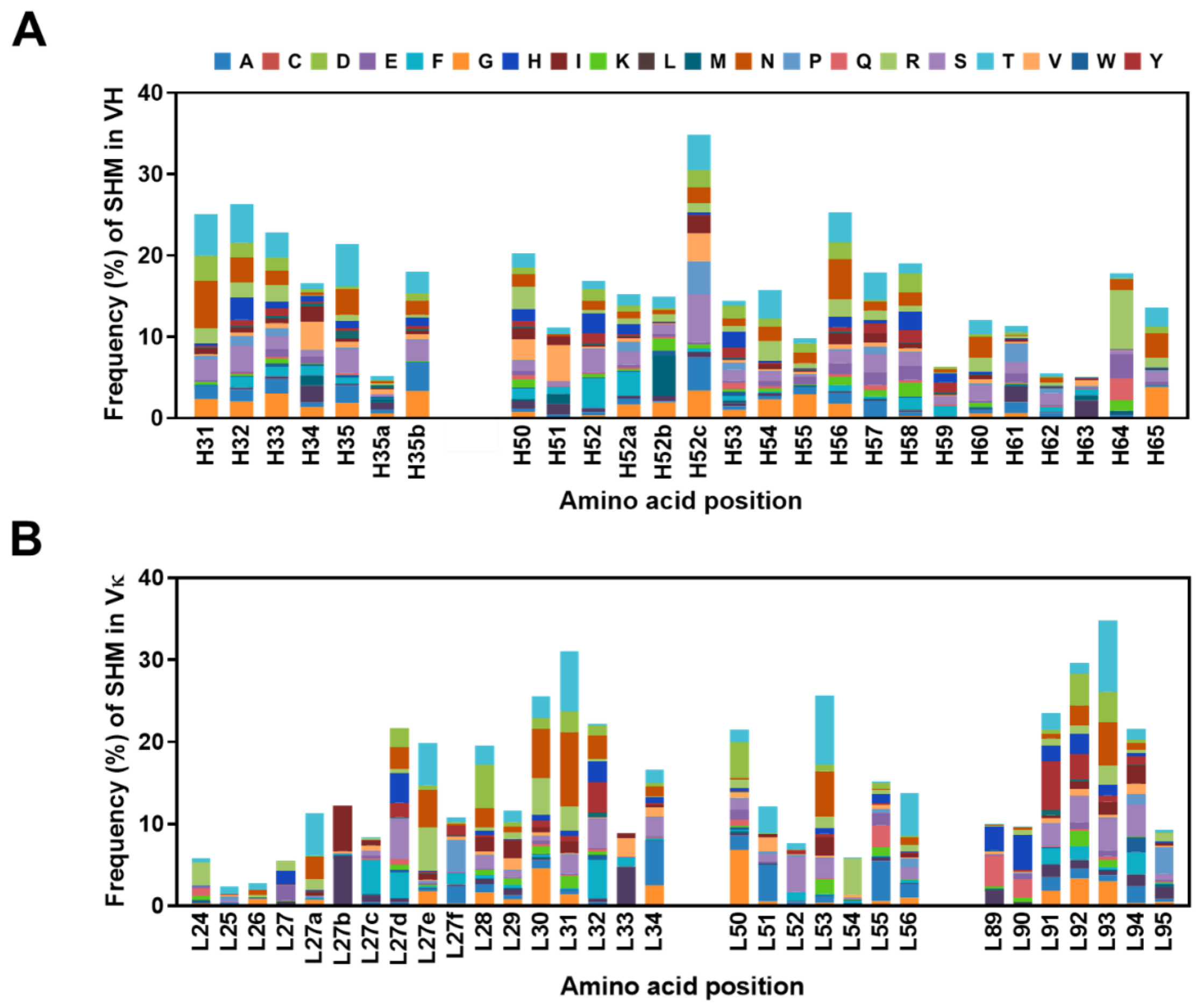
2.5. Frequencies of SHMs in CDRs
2.6. Selection of Antigen-Specific Antibodies from the Constructed Library
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. ELISA
4.3. Immunoblot Analysis
4.4. Construction of Human Combinatorial Antibody Library
4.5. NGS of the Antibody Library
4.6. Sequence Analysis of the Antibody Library
4.7. Selection of Human scFvs from a Phage-Displayed Antibody Library
4.8. Phage ELISA
4.9. Production and Purification of Selected Human scFvs
4.10. Determination of Binding Kinetics of Selected Target-Specific scFvs
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, R.-M.; Hwang, Y.-C.; Liu, I.J.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, H.-Z.; Li, H.-J.; Wu, H.-C. Development of therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, N.K.; Dwiwedi, P.; Charan, J.; Kaur, R.; Sidhu, P.; Chugh, V.K. Monoclonal Antibodies: A Review. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parray, H.A.; Shukla, S.; Samal, S.; Shrivastava, T.; Ahmed, S.; Sharma, C.; Kumar, R. Hybridoma technology a versatile method for isolation of monoclonal antibodies, its applicability across species, limitations, advancement and future perspectives. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Tomar, P.C. Hybridoma technology; advancements, clinical significance, and future aspects. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, D.J.; Shield Iii, C.F.; Barry, J.M.; Henell, K.; Funnell, B.; Lemon, J. Therapeutic use of OKT3 monoclonal antibody for acute renal allograft rejection. Nephron 1987, 46, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanack, K.; Messerschmidt, K.; Listek, M. Antibodies and selection of monoclonal antibodies. Protein Target. Compd. Predict. Sel. Act. Specif. Inhib. 2016, 917, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, H.R. Selecting and screening recombinant antibody libraries. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Min, S.W.; Lee, J.; Shin, H.G.; Choi, H.L.; Yang, H.R.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, Y.B.; Shim, H.; Lee, S. Development and Characterization of Phage-Display-Derived Novel Human Monoclonal Antibodies against the Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, A.; Schirrmann, T.; Hust, M. Phage display-derived human antibodies in clinical development and therapy. MAbs 2016, 8, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledsgaard, L.; Ljungars, A.; Rimbault, C.; Sørensen, C.V.; Tulika, T.; Wade, J.; Wouters, Y.; McCafferty, J.; Laustsen, A.H. Advances in antibody phage display technology. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 2151–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säll, A.; Walle, M.; Wingren, C.; Müller, S.; Nyman, T.; Vala, A.; Ohlin, M.; Borrebaeck, C.A.K.; Persson, H. Generation and analyses of human synthetic antibody libraries and their application for protein microarrays. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2016, 29, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.; Ferrara, F.; Naranjo, L.; Erasmus, M.F.; Hraber, P.; Bradbury, A.R.M. Many routes to an antibody heavy-chain CDR3: Necessary, yet insufficient, for specific binding. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briney, B.S.; Jr, J.E.C. Secondary mechanisms of diversification in the human antibody repertoire. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.W.; Orban, N.; Riches, J.C.; Clear, A.J.; Warnes, G.; Teichmann, S.A.; James, L.K. Antibody repertoire and gene expression dynamics of diverse human B cell states during affinity maturation. BioRxiv 2020, 2020–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Pone, E.J.; Al-Qahtani, A.; Park, S.-R.; Zan, H.; Casali, P. Regulation of aicda expression and AID activity: Relevance to somatic hypermutation and class switch DNA recombination. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 27, 367–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GÜNaydin, G. Activation induced cytidine deaminase: An old friend with new faces. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 965312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, B.Q.; Chaudhuri, J. Combinatorial mechanisms regulating AID-dependent DNA deamination: Interacting proteins and post-translational modifications. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishana, M.; Raghavan, S.C. Role of recombination activating genes in the generation of antigen receptor diversity and beyond. Immunology 2012, 137, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, L.M.; Fugmann, S.D.; Schatz, D.G. Collaboration of RAG2 with RAG1-like proteins during the evolution of V (D) J recombination. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Greiff, V.; Karatt-Vellatt, A.; Muyldermans, S.; Jenkins, T.P. Animal Immunization, in Vitro Display Technologies, and Machine Learning for Antibody Discovery. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelchen, S.; Micheel, B.; Hanack, K. In vitro immunization approach to generate specific murine monoclonal IgG antibodies. BioRxiv 2020, 499, 113149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, S.-E.; Yamashita, M.; Katakura, Y.; Noguchi, E.; Aiba, Y.; Ichikawa, A.; Teruya, K.; Shirahata, S. In vitro immunization can elicit the expansion of diverse repertoire of B cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cytotechnology 2006, 52, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, A.; Katakura, Y.; Teruya, K.; Hashizume, S.; Shirahata, S. In vitro immunization of human peripheral blood lymphocytes: Establishment of B cell lines secreting IgM specific for cholera toxin B subunit from lymphocytes stimulated with IL-2 and IL-4. Cytotechnology 1999, 31, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijkhuisen, A.; Savatier, A.; Cordeiro, N.; Léonetti, M. Production of antigen-specific human IgGs by in vitro immunization. BMC Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaum, M.C.; Narula, S.; Song, D.; Zheng, Y.; Anderson, A.L.; Pletcher, C.H.; Levinson, A.I. Toll-like receptor 7-induced naive human B-cell differentiation and immunoglobulin production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 224–230.e224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnmatz, M.; Kesa, G.; Netterlid, E.; Buisman, A.-M.; Thorstensson, R.; Ahlborg, N. Optimization of a human IgG B-cell ELISpot assay for the analysis of vaccine-induced B-cell responses. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 391, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simchoni, N.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. TLR7- and TLR9-Responsive Human B Cells Share Phenotypic and Genetic Characteristics. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3035–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettengill, M.A.; van Haren, S.D.; Li, N.; Dowling, D.J.; Bergelson, I.; Jans, J.; Ferwerda, G.; Levy, O. Distinct TLR-mediated cytokine production and immunoglobulin secretion in human newborn naïve B cells. Innate Immun. 2016, 22, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, D.; Corti, D.; Jarrossay, D.; Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A. Clonal dissection of the human memory B-cell repertoire following infection and vaccination. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behjati, S.; Tarpey, P.S. What is next generation sequencing? Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. 2013, 98, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day-Williams, A.G.; Zeggini, E. The effect of next-generation sequencing technology on complex trait research. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranneheim, H.; Lundeberg, J. Stepping stones in DNA sequencing. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadt, E.E.; Turner, S.; Kasarskis, A. A window into third-generation sequencing. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, R227–R240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, B.; Yan, J. Application of Next-generation Sequencing Technology in Forensic Science. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2014, 12, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouet, R.; Jackson, K.J.L.; Langley, D.B.; Christ, D. Next-generation sequencing of antibody display repertoires. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellouse, F.A.; Esaki, K.; Birtalan, S.; Raptis, D.; Cancasci, V.J.; Koide, A.; Jhurani, P.; Vasser, M.; Wiesmann, C.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; et al. High-throughput generation of synthetic antibodies from highly functional minimalist phage-displayed libraries. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 373, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, A.E.; Sexton, D.J.; Ladner, R.C. Drugs derived from phage display: From candidate identification to clinical practice. MAbs 2014, 6, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelson, A.S.; Oster, G.F. Theoretical studies of clonal selection: Minimal antibody repertoire size and reliability of self-non-self discrimination. J. Theor. Biol. 1979, 81, 645–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelson, A.S. Immune network theory. Immunol. Rev. 1989, 110, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, A.D.; Williams, S.C.; Hartley, O.; Tomlinson, I.M.; Waterhouse, P.; Crosby, W.L.; Kontermann, R.E.; Jones, P.T.; Low, N.M.; Allison, T.J.A. Isolation of high affinity human antibodies directly from large synthetic repertoires. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 3245–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.A.; Yeap, S.K.; Ali, A.M.; Ho, W.Y.; Alitheen, N.B.M.; Hamid, M. scFv Antibody: Principles and Clinical Application. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 980250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechaly, A.; Diamant, E.; Alcalay, R.; Ben David, A.; Dor, E.; Torgeman, A.; Barnea, A.; Girshengorn, M.; Levin, L.; Epstein, E.; et al. Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibody Targeting the Botulinum Neurotoxin Type E Exposed SNAP-25 Neoepitope. Antibodies 2022, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, F.; Erasmus, M.F.; D’Angelo, S.; Leal-Lopes, C.; Teixeira, A.A.; Choudhary, A.; Honnen, W.; Calianese, D.; Huang, D.; Peng, L.; et al. A pandemic-enabled comparison of discovery platforms demonstrates a naïve antibody library can match the best immune-sourced antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.E.Z.; Lim, A.P.C.; MacAry, P.A.; Hanson, B.J. The role of phage display in therapeutic antibody discovery. Int. Immunol. 2014, 26, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, A.S.; Moutinho, I.; Dias, J.N.R.; Aires-da-Silva, F. In vivo Phage Display: A promising selection strategy for the improvement of antibody targeting and drug delivery properties. Phage Disp. Tech. Appl. 2023, 13, 962124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.E.Z.; Chan, A.H.Y.; Lim, A.P.C.; Hanson, B.J. Comparison of the efficiency of antibody selection from semi-synthetic scFv and non-immune Fab phage display libraries against protein targets for rapid development of diagnostic immunoassays. J. Immunol. Methods 2011, 373, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garet, E.; Cabado, A.G.; Vieites, J.M.; González-Fernández, Á. Rapid isolation of single-chain antibodies by phage display technology directed against one of the most potent marine toxins: Palytoxin. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.K.; Rahumatullah, A.; Lai, J.Y.; Lim, T.S. Naive human antibody libraries for infectious diseases. Recomb. Antibodies Infect. Dis. 2017, 1053, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.C.; Choong, Y.S.; Lim, T.S. High Affinity Maturated Human Antibodies from Naïve and Synthetic Antibody Repertoires. In Antibody Engineering; Böldicke, T., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Keck, Z.-y.; Saha, A.; Xia, J.; Conrad, F.; Lou, J.; Eckart, M.; Marks, J.D.; Foung, S.K.H. Affinity Maturation to Improve Human Monoclonal Antibody Neutralization Potency and Breadth against Hepatitis C Virus*. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44218–44233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtalan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fellouse, F.A.; Shao, L.; Schaefer, G.; Sidhu, S.S. The intrinsic contributions of tyrosine, serine, glycine and arginine to the affinity and specificity of antibodies. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hust, M.; Meyer, T.; Voedisch, B.; Rülker, T.; Thie, H.; El-Ghezal, A.; Kirsch, M.I.; Schütte, M.; Helmsing, S.; Meier, D. A human scFv antibody generation pipeline for proteome research. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 152, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, I.; Park, S.G.; Cho, S.; Kim, J.H.; Ipper, N.S.; Choi, S.S.; Lee, E.S.; Hong, H.J. Generation, diversity determination, and application to antibody selection of a human naive Fab library. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, L.; Maurer, D.P.; Wec, A.Z.; Lilov, A.; Champney, E.; Sun, T.; Archambault, K.; Burnina, I.; Lynaugh, H.; Zhi, X.; et al. Affinity Maturation Enhances Antibody Specificity but Compromises Conformational Stability. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 3300–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.; Hiniker, A.; Collet, J.-F.; Bardwell, J.C.A. Isolation of Bacteria Envelope Proteins. In Bacterial Cell Surfaces: Methods and Protocols; Delcour, A.H., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antigen | Antibody (scFv) | Ka (1/Ms) | Kd (1/s) | KD (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 BA.2 RBD | K105.1 | 3.30 × 105 | 1.05 × 10−3 | 3.18 × 10−9 |
| K105.2 | 1.83 × 104 | 1.35 × 10−3 | 7.40 × 10−8 | |
| K105.3 | 7.03 × 104 | 1.54 × 10−3 | 2.19 × 10−8 | |
| K105.4 | 2.78 × 104 | 1.79 × 10−4 | 6.44 × 10−9 | |
| Human CD155 | K106.1 | 2.59 × 105 | 1.46 × 10−2 | 5.66 × 10−8 |
| K106.2 | 1.22 × 106 | 7.27 × 10−2 | 5.95 × 10−8 | |
| K106.3 | 1.86 × 106 | 8.91 × 10−2 | 4.79 × 10−8 | |
| K106.4 | 1.53 × 104 | 2.32 × 10−3 | 1.52 × 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.L.; Yang, H.R.; Shin, H.G.; Hwang, K.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, T.; Jung, Y.; Lee, S. Generation and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Characterization of a Large Human Combinatorial Antibody Library. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24066011
Choi HL, Yang HR, Shin HG, Hwang K, Kim JW, Lee JH, Ryu T, Jung Y, Lee S. Generation and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Characterization of a Large Human Combinatorial Antibody Library. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):6011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24066011
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hye Lim, Ha Rim Yang, Ha Gyeong Shin, Kyusang Hwang, Ji Woong Kim, Ji Hyun Lee, Taehoon Ryu, Yushin Jung, and Sukmook Lee. 2023. "Generation and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Characterization of a Large Human Combinatorial Antibody Library" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 6011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24066011
APA StyleChoi, H. L., Yang, H. R., Shin, H. G., Hwang, K., Kim, J. W., Lee, J. H., Ryu, T., Jung, Y., & Lee, S. (2023). Generation and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Characterization of a Large Human Combinatorial Antibody Library. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 6011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24066011








