GSK2801 Reverses Paclitaxel Resistance in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines through MYCN Downregulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
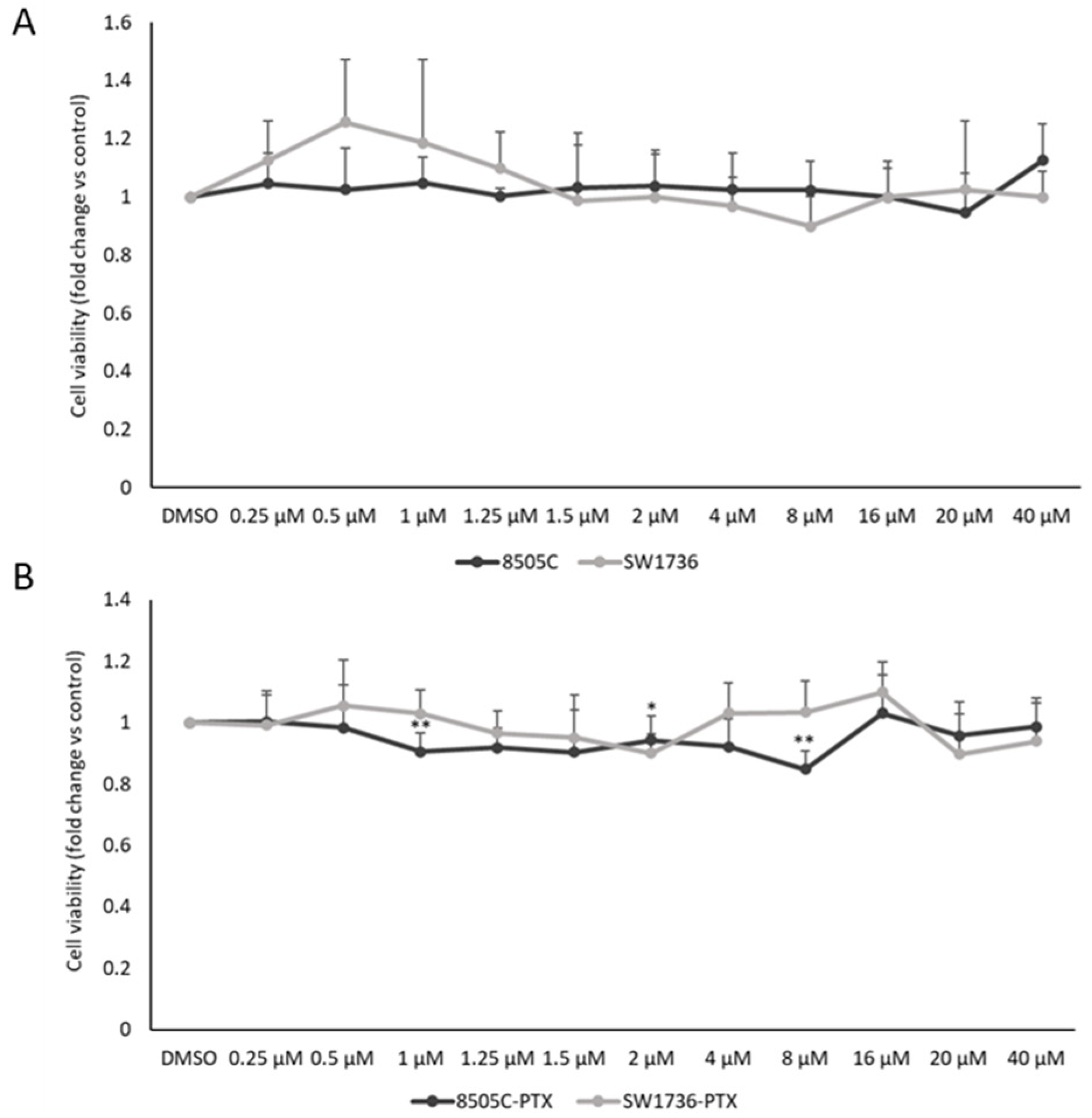
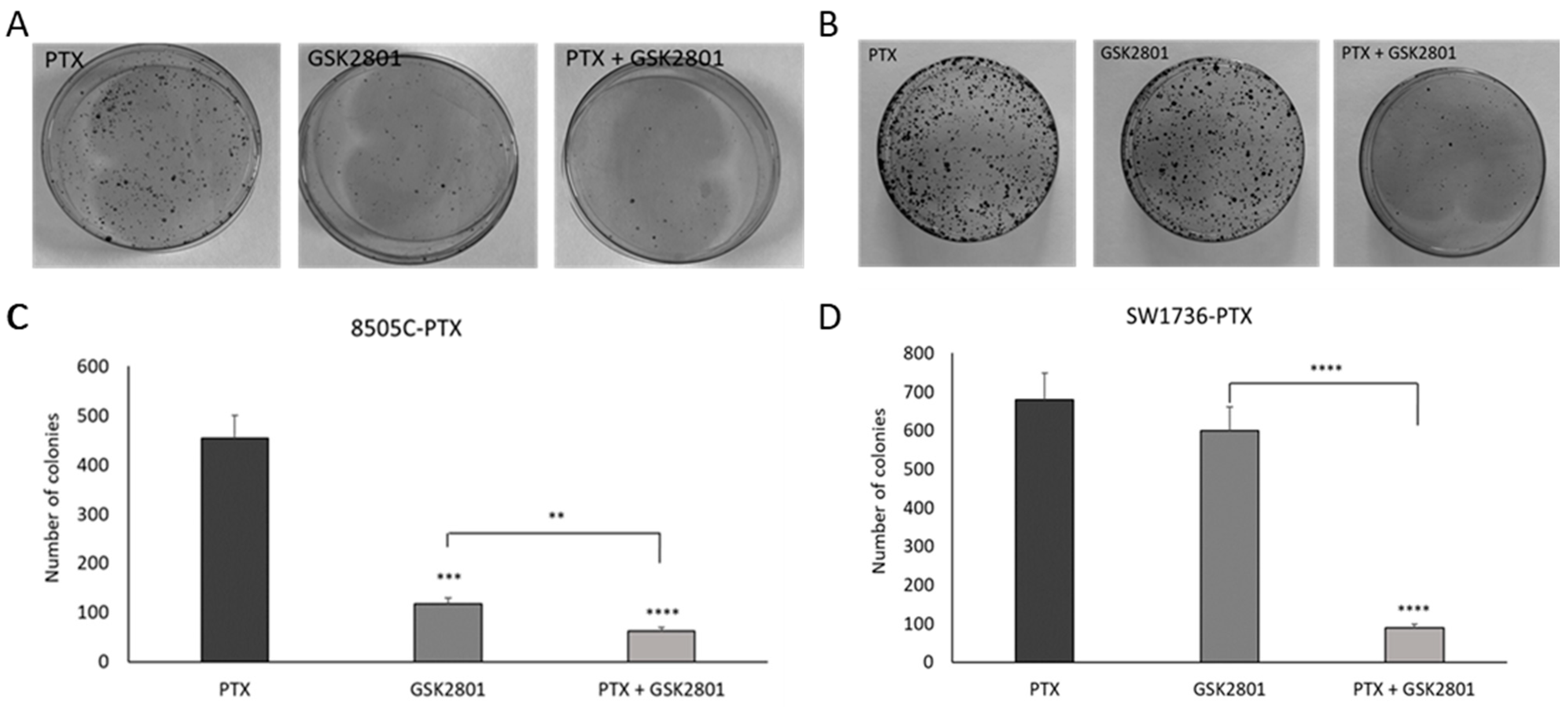
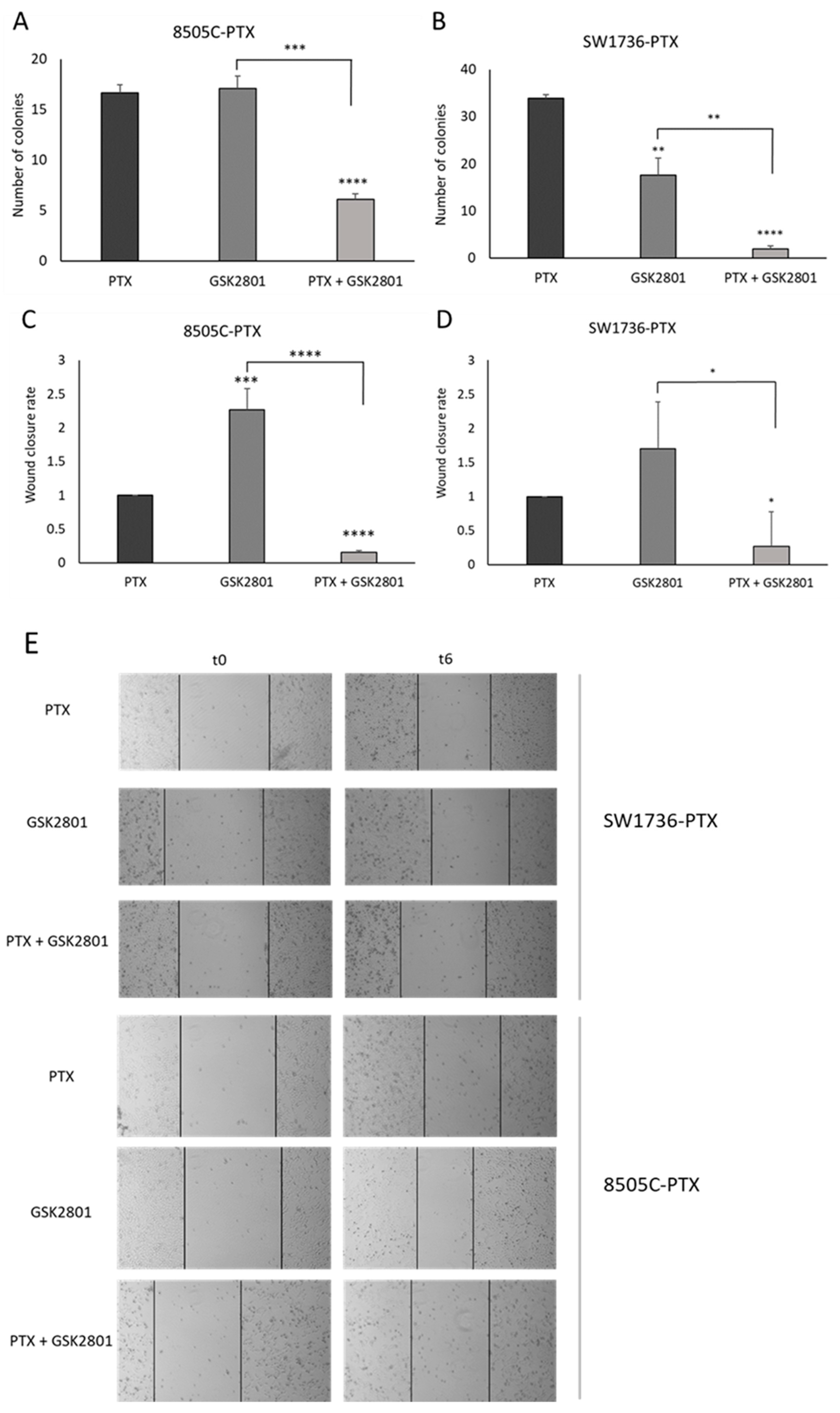
2.1. Effects of GSK2801 on ATC Cell Viability, Apoptosis, Colony Formation, and Cell Migration
2.2. Effects of GSK2801 on In Vitro Tumor Cell Aggressiveness
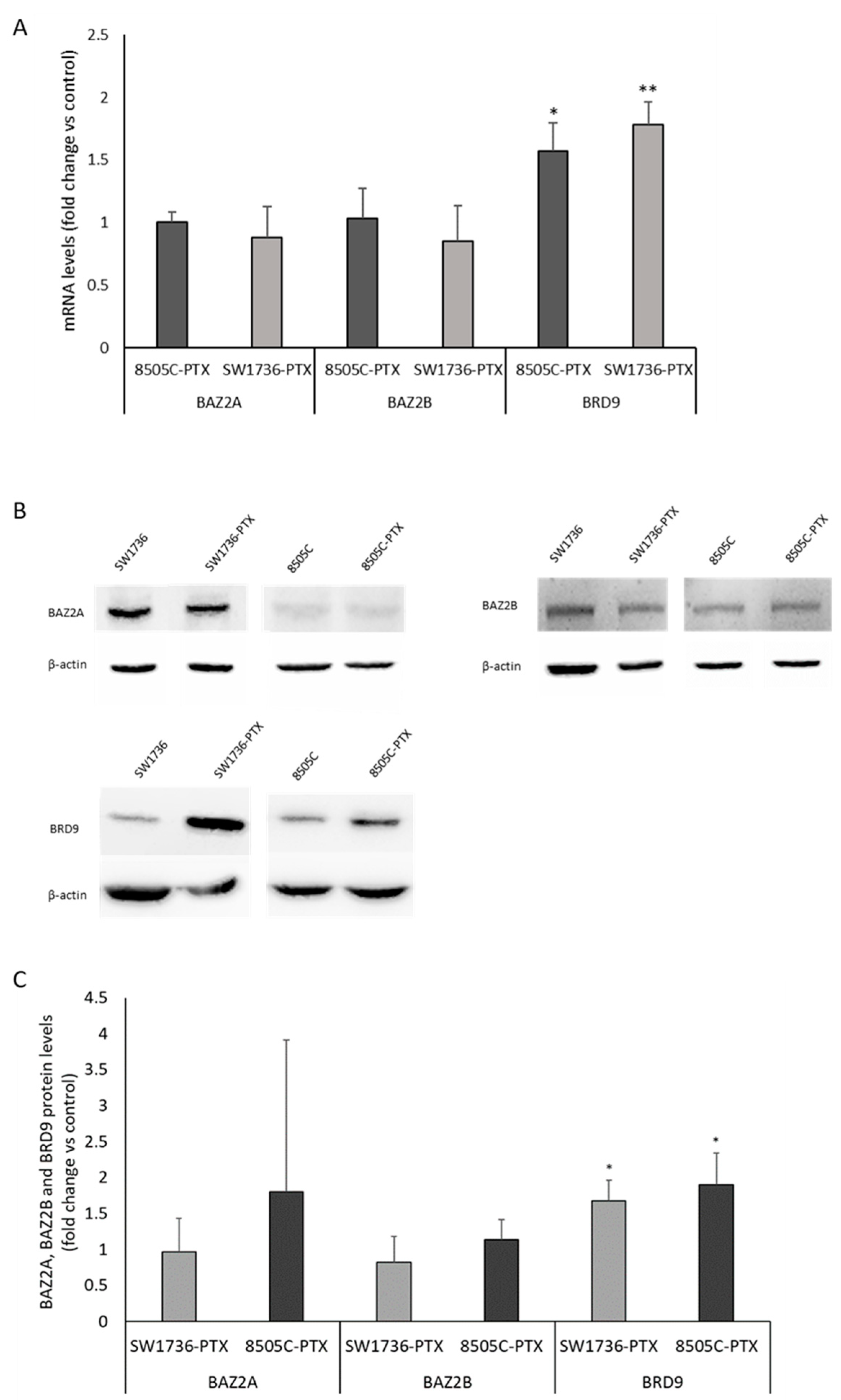
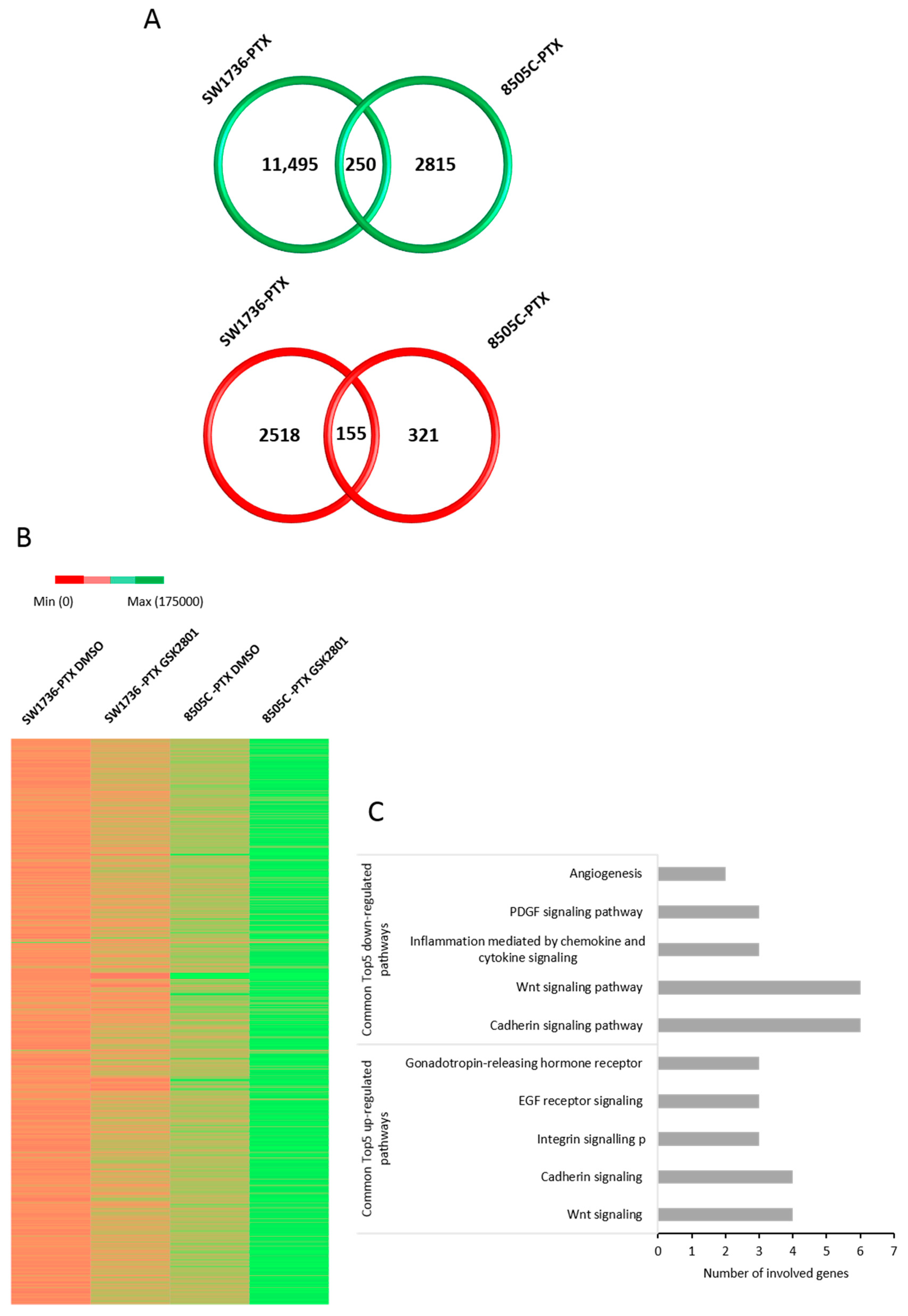
2.3. Effects of GSK2801 on Gene Expression in Paclitaxel-Resistant ATC Cells
2.4. ChIP Analysis of the Effects of GSK2801 on the Binding of BRD9 to Its Targets
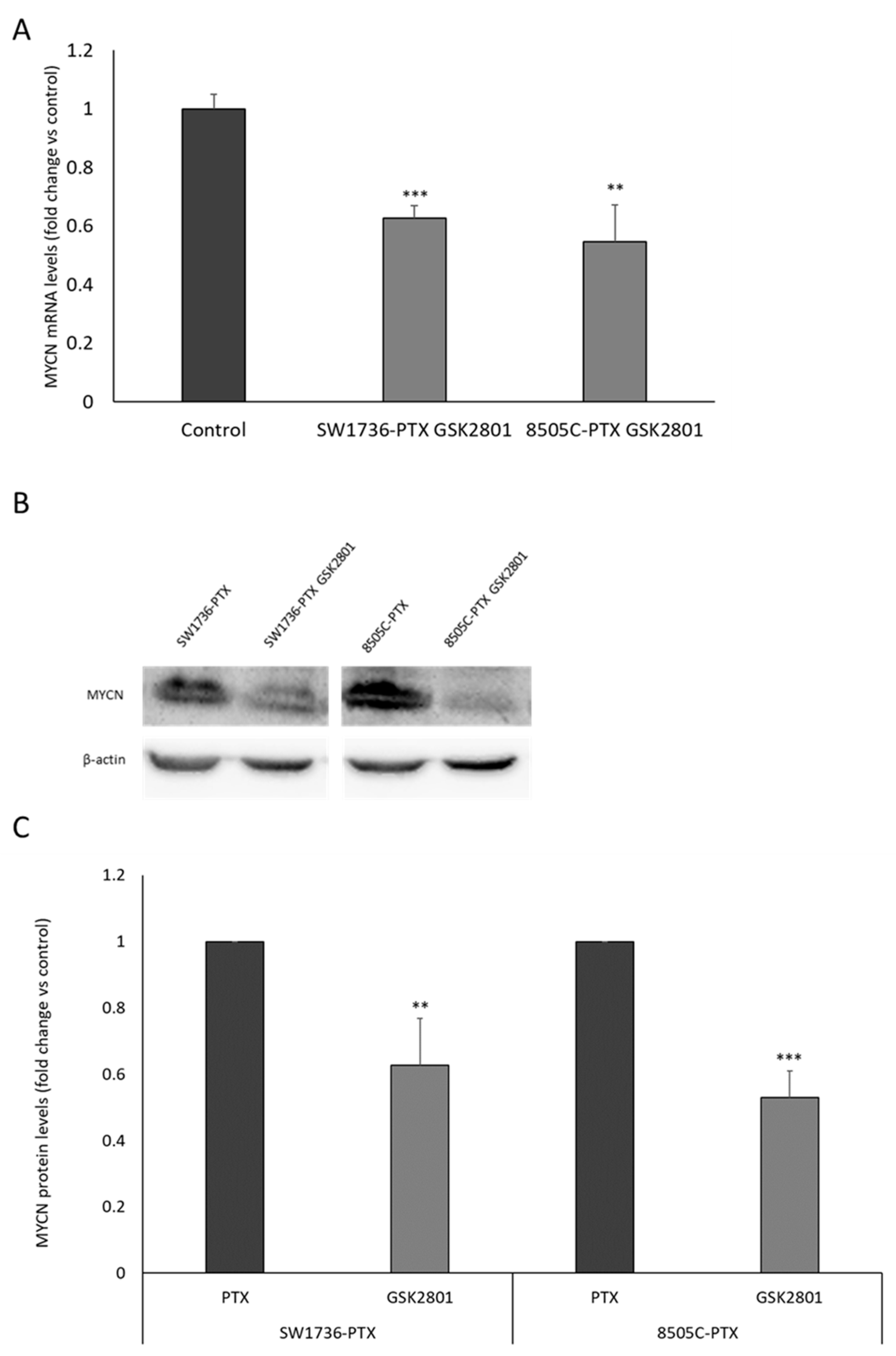
2.5. Effects of GSK2801 on MYCN RNA and Protein Levels in SW1736-PTX and 8050C-PTX Cell Lines
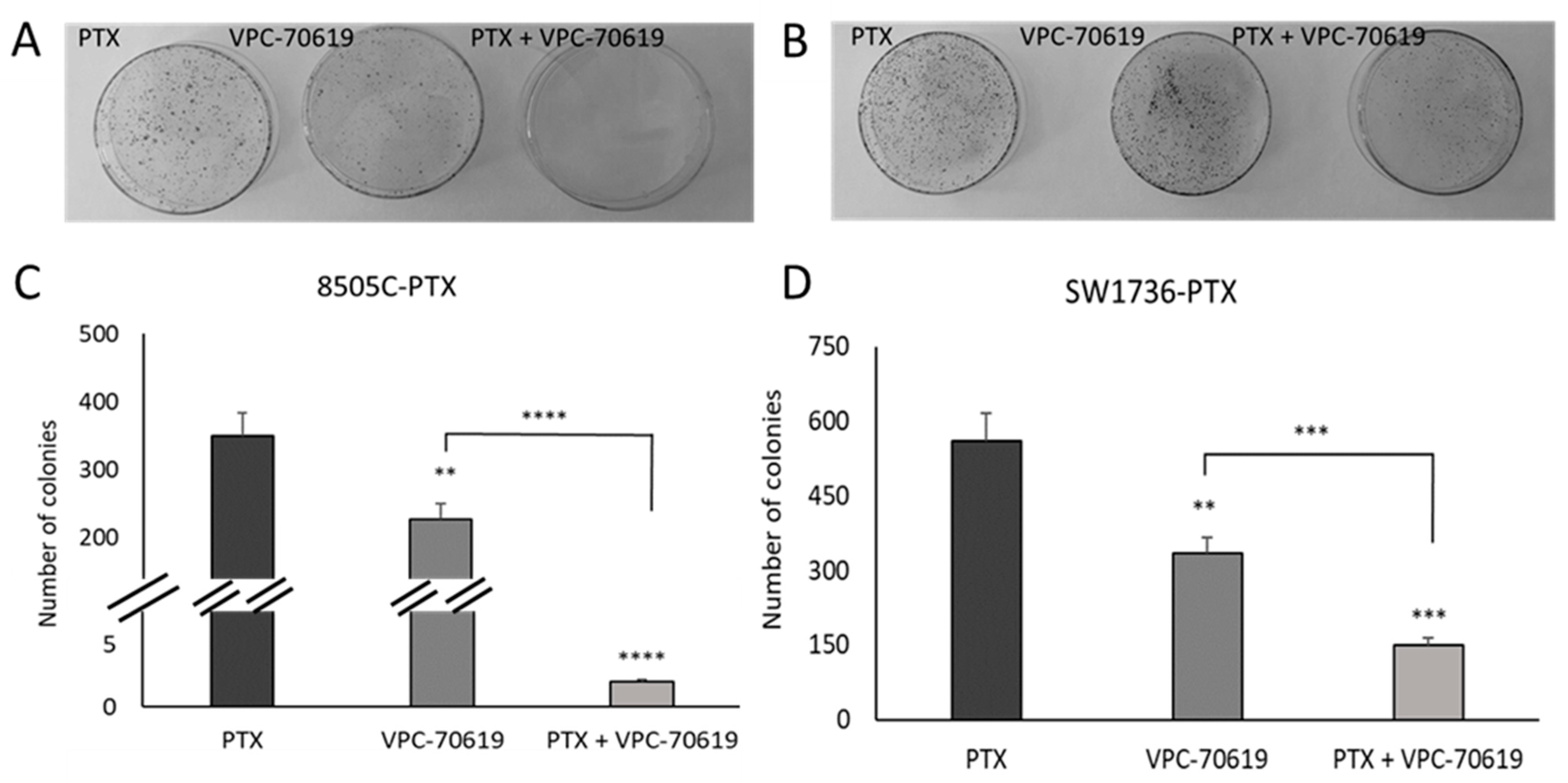
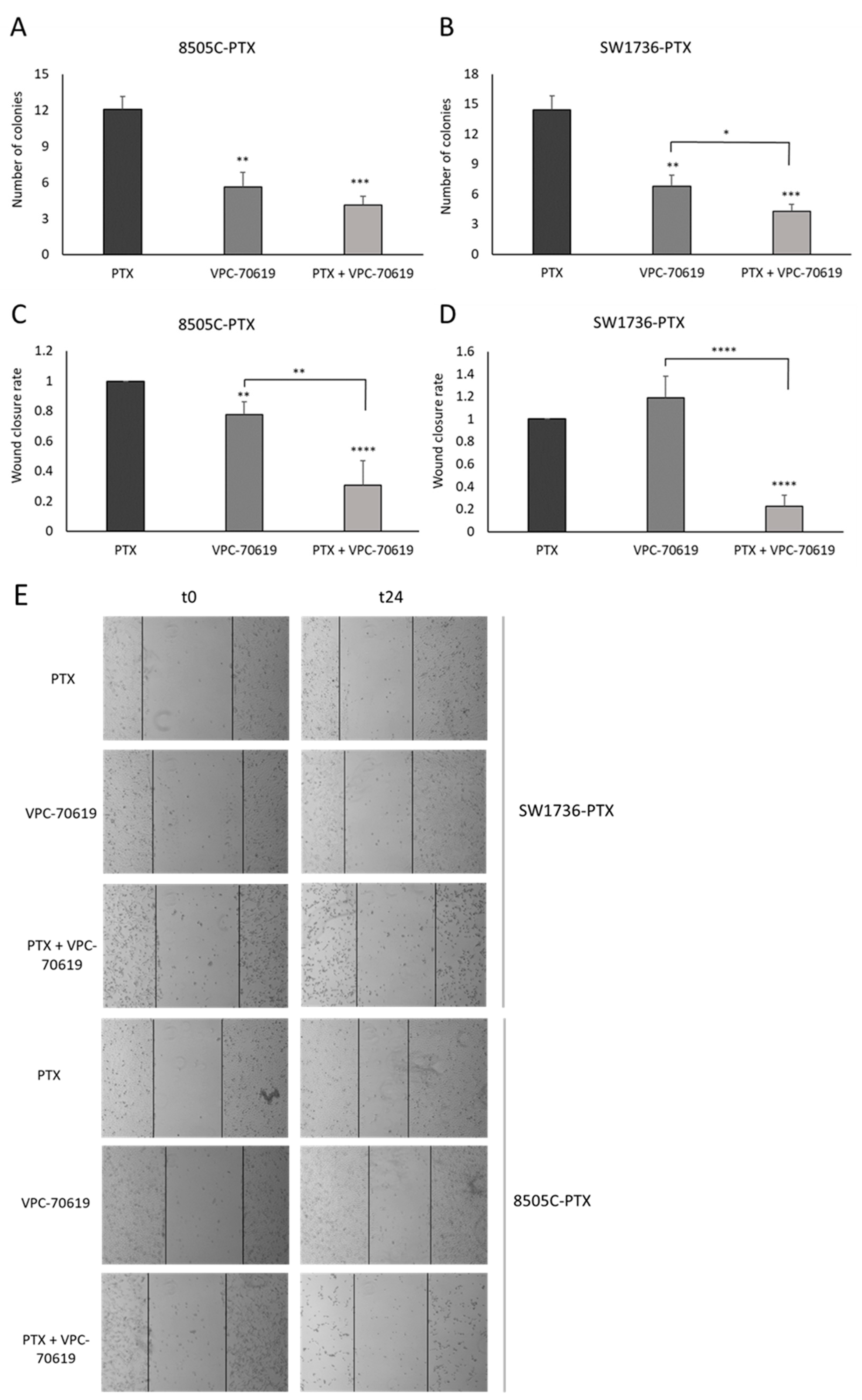
2.6. Effects of VPC-70619 on ATC Cell Viability and Colony Formation
2.7. Effects of VPC-70619 on In Vitro Tumor Cell Aggressiveness
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabanillas, M.E.; McFadden, D.G.; Durante, C. Thyroid cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, D.; Nilubol, N.; Boufraqech, M. New Therapies for Advanced Thyroid Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegri, L.; Capriglione, F.; Maggisano, V.; Damante, G.; Baldan, F. Effects of Dihydrotanshinone I on Proliferation and Invasiveness of Paclitaxel-Resistant Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bible, K.C.; Kebebew, E.; Brierley, J.; Brito, J.P.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Clark, T.J.; Di Cristofano, A.; Foote, R.; Giordano, T.; Kasperbauer, J.; et al. American Thyroid Association Guidelines for Management of Patients with Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2021, 31, 337–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobuia, W.; Gillis, A.; Kebebew, E. Contemporary Management of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2020, 21, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Elia, G.; Ragusa, F.; Paparo, S.R.; Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A. Molecular targets of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in thyroid cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 79, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thyroid Association Guidelines for Management of Patients with Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer—PMC. 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8349723/ (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, M.; Samadi, N.; Ghanbari, P.; Yousefi, B.; Tabasinezhad, M.; Sharifi, S.; Nazemiyeh, H. Co-treatment by docetaxel and vinblastine breaks down P-glycoprotein mediated chemo-resistance. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 19, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, L.; Barra, F.; Foreste, V.; Giampaolino, P.; Evangelisti, G.; Ferrero, S.; Bifulco, G. Advances in paclitaxel combinations for treating cervical cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding Selectivity of Inhibitors toward Bromodomains BAZ2A and BAZ2B Uncovered by Multiple Short Molecular Dynamics Simulations and MM-GBSA Calculations—PMC. 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8154142/ (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Arrowsmith, C.H.; Bountra, C.; Fish, P.V.; Lee, K.; Schapira, M. Epigenetic protein families: A new frontier for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 384–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, F.; Kim, W.; Tu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Nowsheen, S.; Zhu, Q.; Deng, M.; et al. The bromodomain containing protein BRD-9 orchestrates RAD51–RAD54 complex formation and regulates homologous recombination-mediated repair. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Enomoto, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Willingham, M.C.; Meltzer, P.; Qi, J.; Cheng, S.-Y. Bromodomain and Extraterminal Protein Inhibitor JQ1 Suppresses Thyroid Tumor Growth in a Mouse Model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chen, D.; Qian, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Ma, Z.; Wang, S. AZD5153, a novel BRD4 inhibitor, suppresses human thyroid carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, H. Bromodomain-containing protein 4 is critical for the antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of gambogic acid in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaware, N.; Zhou, M.-M. Chemical Modulators for Epigenome Reader Domains as Emerging Epigenetic Therapies for Cancer and Inflammation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 39, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yao, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, J. Targeting BRD9 by I-BRD9 efficiently inhibits growth of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3364–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, T.; Filippakopoulos, T.F.P. Functions of bromodomain-containing proteins and their roles in homeostasis and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greschik, H.; Schüle, R.; Günther, T. Selective targeting of epigenetic reader domains. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Hernández, R.; Aprigliano, R.; Frommel, S.C.; Pietrzak, K.; Steiger, S.; Roganowicz, M.; Lerra, L.; Bizzarro, J.; Santoro, R. BAZ2A-mediated repression via H3K14ac-marked enhancers promotes prostate cancer stem cells. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e53014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Cancer, I.P.O.E.O.P.; Frommel, S.C.; Oakes, C.C.; Simon, R.; Grupp, K.; Gerig, C.Y.; Bär, D.; Robinson, M.D.; Baer, C.; et al. BAZ2A (TIP5) is involved in epigenetic alterations in prostate cancer and its overexpression predicts disease recurrence. Nat. Genet. 2014, 47, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedove, A.D.; Spiliotopoulos, D.; D’Agostino, V.G.; Marchand, J.-R.; Unzue, A.; Nevado, C.; Lolli, G.; Caflisch, A. Structural Analysis of Small-Molecule Binding to the BAZ2A and BAZ2B Bromodomains. Chemmedchem 2018, 13, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellapu, N.K.; Ly, T.; Sardiu, M.E.; Pei, D.; Welch, D.R.; Thompson, J.A.; Koestler, D.C. Synergistic anti-proliferative activity of JQ1 and GSK2801 in triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chaikuad, A.; Bamborough, P.; Bantscheff, M.; Bountra, C.; Chung, C.-W.; Fedorov, O.; Grandi, P.; Jung, D.; Lesniak, R.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of GSK2801, a Selective Chemical Probe for the Bromodomains BAZ2A and BAZ2B. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 59, 1410–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevill, S.M.; Olivares-Quintero, J.F.; Sciaky, N.; Golitz, B.T.; Singh, D.; Beltran, A.S.; Rashid, N.U.; Stuhlmiller, T.J.; Hale, A.; Moorman, N.J.; et al. GSK2801, a BAZ2/BRD9 bromodomain inhibitor, synergizes with BET inhibitors to induce apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 1503–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Gopal, P.; Shen, S.; Zhou, K.; Yu, X.; Sharma, T.; Zhang, Y.; Siegwart, D.J.; et al. In vivo CRISPR screening identifies BAZ2 chromatin remodelers as druggable regulators of mammalian liver regeneration. Cell Stem Cell 2022, 29, 372–385.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowicz, S.; Van Scoyk, M.; Avasarala, S.; Karuppusamy Rathinam, M.K.; Tauler, J.; Bikkavilli, R.K.; Winn, R.A. The Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 92, e51998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinotti, S.; Ranzato, E. Scratch Wound Healing Assay. In Epidermal Cells: Methods and Protocols; Turksen, K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2109, pp. 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Gu, X.; Wei, W.; Wu, Z.; Gong, F.; Dong, X. BRD9 is an essential regulator of glycolysis that creates an epigenetic vulnerability in colon adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 2022, 12, 1572–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, A.-T.; Foo, J.; Singh, K.; Lee, J.; Kalyta, A.; Morin, H.; Perez, C.; Ban, F.; Leblanc, E.; Lallous, N.; et al. Development of VPC-70619, a Small-Molecule N-Myc Inhibitor as a Potential Therapy for Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.; Chen, L.; Liu, T.; Marshall, G.M.; Lunec, J.; Tweddle, D.A. MYCN oncoprotein targets and their therapeutic potential. Cancer Lett. 2010, 293, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filetti, S.; Durante, C.; Hartl, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Locati, L.; Newbold, K.; Papotti, M.; Berruti, A. Thyroid cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1856–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegri, L.; Baldan, F.; Mio, C.; Puppin, C.; Russo, D.; Kryštof, V.; Damante, G. Effects of BP-14, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, on anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2413–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulotta, S.; Celano, M.; Costante, G.; Russo, D. Novel therapeutic options for radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer: Redifferentiation and beyond. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2020, 32, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, A.; Wong, D.J. Perspectives on the Treatment of Advanced Thyroid Cancer: Approved Therapies, Resistance Mechanisms, and Future Directions. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 592202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegri, L.; Rosignolo, F.; Mio, C.; Filetti, S.; Baldan, F.; Damante, G. Effects of nutraceuticals on anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 144, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mio, C.; Conzatti, K.; Baldan, F.; Allegri, L.; Sponziello, M.; Rosignolo, F.; Russo, D.; Filetti, S.; Damante, G. BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 modulates microRNA expression in thyroid cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 39, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mio, C.; Lavarone, E.; Conzatti, K.; Baldan, F.; Toffoletto, B.; Puppin, C.; Filetti, S.; Durante, C.; Russo, D.; Orlacchio, A.; et al. MCM5 as a target of BET inhibitors in thyroid cancer cells. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardenne, E.; Beltran, H.; Benelli, M.; Gayvert, K.; Berger, A.; Puca, L.; Cyrta, J.; Sboner, A.; Noorzad, Z.; MacDonald, T.; et al. N-Myc Induces an EZH2-Mediated Transcriptional Program Driving Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, H. The N-myc Oncogene: Maximizing its Targets, Regulation, and Therapeutic Potential. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, D.A.; Bhakta, N.R.; Kessenbrock, K.; Prummel, K.D.; Yu, Y.; Takai, K.; Zhou, A.; Eyob, H.; Balakrishnan, S.; Wang, C.-Y.; et al. Single-cell analysis reveals a stem-cell program in human metastatic breast cancer cells. Nature 2015, 526, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henssen, A.G.; Althoff, K.; Odersky, A.; Beckers, A.; Koche, R.; Speleman, F.; Schäfers, S.; Bell, E.; Nortmeyer, M.; Westermann, F.; et al. Targeting MYCN-Driven Transcription by BET-Bromodomain Inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 22, 2470–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.M.; Lehmann, B.D.; Gonzalez-Ericsson, P.I.; Marshall, C.B.; Beeler, J.S.; Redman, L.N.; Jin, H.; Sanchez, V.; Stubbs, M.C.; Scherle, P.; et al. Targeting MYCN-expressing triple-negative breast cancer with BET and MEK inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegri, L.; Baldan, F.; Molteni, E.; Mio, C.; Damante, G. Role of m6A RNA Methylation in Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldan, F.; Mio, C.; Lavarone, E.; DI Loreto, C.; Puglisi, F.; Damante, G.; Puppin, C. Epigenetic bivalent marking is permissive to the synergy of HDAC and PARP inhibitors on TXNIP expression in breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| SW1736-PTX and 8505C-PTX Common Altered Genes | WNT Signaling Only | WNT_Cadherin Signaling Common | Cadherin Signaling Only |
|---|---|---|---|
| Downregulated | MYCN | PCDHGA5, PCDHB4, PCDHGB6, PCDHGC4 | ACTBL2 |
| Upregulated | DCHS1 | DCHS1, PCDHGA8, PCDHB12 | ERBB4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molteni, E.; Baldan, F.; Damante, G.; Allegri, L. GSK2801 Reverses Paclitaxel Resistance in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines through MYCN Downregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065993
Molteni E, Baldan F, Damante G, Allegri L. GSK2801 Reverses Paclitaxel Resistance in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines through MYCN Downregulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065993
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolteni, Elisabetta, Federica Baldan, Giuseppe Damante, and Lorenzo Allegri. 2023. "GSK2801 Reverses Paclitaxel Resistance in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines through MYCN Downregulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065993
APA StyleMolteni, E., Baldan, F., Damante, G., & Allegri, L. (2023). GSK2801 Reverses Paclitaxel Resistance in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines through MYCN Downregulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065993





